
A Winning Score-based Evolutionary Process for
Multi-and Many-objective Peptide Optimization
Susanne Rosenthal
1,3
and Markus Borschbach
2,3
1
Rheinische Fachhochschule K
¨
oln, University of Applied Sciences, Cologne, Germany
2
FHDW, University of Applied Sciences, Competence Center Optimized Systems, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany
3
Steinbeis Innovation Center ”Intelligent and Self-Optimizing Software Assistance Systems”, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany
Keywords:
Winning-score based Selection, Multi- and Many-objective Optimization, Biochemical Optimization,
Evolutionary Algorithm.
Abstract:
Target identification as part of drug design is a long process with high laboratory evaluation costs since optimal
candidate leads have to be identified in an iterative process including the determination of diverse physiochem-
ical properties, which have to be optimized simultaneously. MOEAs have become an established optimiza-
tion method in in silico-aided drug design processes. Since target identification becomes more complex, the
dimension of molecular optimization problems increases. Less work has been done so far to evolve an evo-
lutionary process efficiently solving both, multi- and many-objective molecular optimization problems while
considering application-specific conditions of molecule optimization. This work presents the enhancement of
a MOEA especially evolved for molecular optimization. The proposed algorithm is applicable to multi- and
many-objective molecular optimization problems identifying a selected number of qualified candidate pep-
tides within a very low number of iterations. It has a simple framework structure and optionally uses two
types of winning-score ranking method as survival selection. Default parameters are provided in the compo-
nents to enable a non-expert use. This algorithm is benchmarked to the recently proposed and promising AnD
(ANgle-based selection and shift-based Density estimation strategy) on molecular optimization problems up
to 6 objectives. Furthermore, the selection principles are exemplarily compared and discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Computer-assisted techniques gain importance in the
area of drug discovery and development. The suc-
cess of molecule design depends on simultaneous op-
timization on often conflicting biological and phys-
iochemical properties. Multi-objective Evolutionary
Algorithms (MOEAs) have proven to enhance the po-
tential of improving promising drug candidates (Ni-
colotti et al., 2011). The increase of complexity in
pharmaceutical research results in the challenge of
the design of a Many-objective Evolutionary Algo-
rithm (MaOEA) especially for molecular optimiza-
tion. To the best of our knowledge, less work has
been done so far regarding this issue. The design of
a MOEA as well as MaOEA for molecular optimiza-
tion has to take account of several application-specific
conditions: the objective of target identification usu-
ally requires expensive and time-consuming labora-
tory work since the numerical approximation of pep-
tide properties is challenging. Therefore, the objec-
tive function evaluations have to be limited to save re-
sources. Furthermore, the algorithm provides default
parameter settings to enable the non-expert use and
does not utilize weight vectors or reference points,
which are commonly unknown in real-world appli-
cations but have an impact on the algorithm perfor-
mance.
In addressing these issues, a single-objective evo-
lutionary algorithm especially evolved for molecu-
lar optimization has been introduced in (R
¨
ockendorf
and Borschbach, 2012), (Krause et al., 2018) pro-
viding an exponential fitness improvement within the
very low number of 10 iterations and a standard
population size. This approach has been enhanced
to a MOEA with similar properties. This MOEA
is termed COmponent-Specific Evolutionary Algo-
rithm for Molecular Optimization (COSEA-MO) and
is presented in (Rosenthal and Borschbach, 2017b).
COSEA-MO identifies a selected number of highly
qualified candidate peptides with a wide range of
genetic diversity within 10 iterations. Nevertheless,
Rosenthal, S. and Borschbach, M.
A Winning Score-based Evolutionary Process for Multi-and Many-objective Peptide Optimization.
DOI: 10.5220/0008065800490058
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2019), pages 49-58
ISBN: 978-989-758-384-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
49

the increase of the problem dimension reveals well-
known challenges of Pareto definition-based MOEAs
in solving Many-objective Optimization Problems
(MaOPs) comprising more than three objectives: the
inability of adequately differentiate higher dimen-
sional solutions and the loss of selection pressure.
This work presents an enhancement of COSEA-
MO to solve multi- and many-objective molecular op-
timization problems by the traditional Winning Score
(WS) technique (Maneeratano et al., 2006) or op-
tionally a new difference-based WS selection strat-
egy. Furthermore, the selection principles of these
WS techniques are exemplarily analyzed and dis-
cussed. The performance of the enhanced versions
of COSEA-MO are compared to a recently proposed
and promising MaOEA termed AnD (ANgle-based
selection and shift-based Density estimation strategy)
(Lee et al., 2018) on a three-dimensional up to a six-
dimensional molecular optimization problem.
The outline of this work is as follows: Section 2
gives an overview of the related work, the proposed
approach with WS-based selection strategies is intro-
duced in section 3 with the discussion of the selection
principles. Section 4 presents the experiments, sec-
tion 5 concludes this work and gives an outlook on
future work.
2 RELATED WORK
MOEAs are classifiable into three categories ac-
cording to their selection strategies: Pareto-based,
decomposition- based and indicator-based algo-
rithms. The effectiveness of MOEAs on Many-
objective Optimization Problems (MaOPs) is signif-
icantly decreased with the problem dimension (Ishi-
huchi et al., 2011). In the case of Pareto-based
MOEAs such as NSGA-II (Deb et al., 2002) and
SPEA2 (Zitzler et al., 2002), the number of non-
dominated solutions increases significantly with the
problem dimension since the Pareto dominance prin-
ciple as elitism strategy for survival selection is not
capable to adequately differentiate candidate solu-
tions. In the case of decomposition-based MOEAs
such as MOEA/D (Zhang and Li, 2007), it is chal-
lenging to define weight vectors or reference points
in higher dimensions. A rising dimension size leads
to a challenging consumption of computational time
in the case of indicator-based MOEAs such as SMS-
EMOA (Beume et al., 2007) and IBEA (Zitzler and
K
¨
unzli, 2004).
Several enhancements have been published to im-
prove the performance of Pareto-, decomposition-
and indicator-based MOEAs on MaOPs: The intu-
itive way of improving Pareto-based MOEAs is to
find alternative Pareto dominance definitions. The ε-
dominance principle uses a factor ε to compare the
dominance principle of individuals (Laumanns et al.,
2002). L-dominance is introduced selecting individ-
uals with objectives of similar importance regarding
the objective value improvement (Zou et al., 2008).
Fuzzy dominance methods are presented using rank-
ing schemes to select promising individuals (He et al.,
2014). Moreover, a grid-based method is published
adjusting the grid size to control the proportion of
Pareto-optimal solutions (Yang et al., 2013).
Several enhanced variants of MOEA/D for
MaOPs have been published in the past. Most re-
cent algorithms are MOEA/D-AM2M which adap-
tively allocates the search effort (Liu et al., 2017),
MOEA/D-DU which exploits the perpendicular dis-
tance from the individuals to the weight vectors (Yuan
et al., 2016) and MOEA/D-PaS which uses a Pareto
adaptive scalarization method (Wang et al., 2016).
The hypervolume is the mostly used indicator in
indicator-based MOEAs such as in IBEA and SMS-
EMOA. Its major disadvantage is the experimental in-
crease of the computational complexity with the di-
mension increase. To overcome this disadvantage,
other indicator-based methods have been introduced
recently. The Inverse Generational Distance Plus
(IGD
+
) indicator is used in IGD
+
-EMOA to address
MaOPs up to 8 objectives (Lopez and Coello, 2016).
Furthermore, the collaboration of different indicators
of low computational complexity has been proven to
be a promising solution for solving MaOPs (Lee et al.,
2018).
Beneath these approaches, the widely used
NSGA-II has been improved to NSGA-III (Deb and
Jain, 2014) for MaOPs by the use of a set of
predefined well-distributed reference points. Non-
dominated solutions close to this set are prioritized.
An appropriate design of this set is challenging, es-
pecially in the case of real-word applications. A re-
cent promising MaOEA has been proposed termed
AnD (Lee et al., 2018). It has a simple framework
structure and selects promising individuals from the
union of parent and child population for the next it-
eration with a diversity-first-and-convergence-second
principle. AnD combines the well-known vector an-
gle and shift-based density estimation in the selection
process. Angle-based selection is used to identify two
individuals with minimal angle. This is motived by
the idea that these individuals represent the search in
the same direction and waste computational resources
if both individuals survive. The individual with lower
shift-based density estimation is deleted in order to
ensure convergence. AnD is compared to seven state-
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
50

of-the-art MaOEA on a variety of benchmark prob-
lems with 5, 10 and 15 objectives and reveals highly
competitive performance (Lee et al., 2018). AnD
is chosen for experimental comparison in this work
as it is the only algorithm apart from COSEA-MO
that has a simple framework structure, provides op-
timized default parameters for the non-expert use and
is independent of weight vectors or reference points,
which usually have a strong impact on the perfor-
mance and are usually unknown in real-world appli-
cations. Moreover, the framework structure of AnD is
similar to those of COSEA-MO.
The traditional WS technique has been introduced
with the Compressed–objective Genetic Algorithm
(COGA) (Maneeratano et al., 2006). Two conflict-
ing preference objectives, WS and a vicinity method,
are used to assign different preference levels to non-
dominated solutions to bound the increasing set of
non-dominated solutions in MaOPs. A rank is as-
signed to each non-dominated solution according to
the preference objectives to select high preferred non-
dominated solutions in survival selection and the trun-
cation method to maintain the archive size. COGA
has been enhanced to the Improved Compressed–
objective Genetic Algorithm (COGA-II) (Boolong
et al., 2010). A WS-based ranking mechanism is
applied instead of the two preference objectives of
COGA. The WS value of a non-dominated solu-
tion is determined by the weighted sum of competi-
tive scores from all objectives to the remaining non-
dominated solutions.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
This section proposes an enhanced version of
COSEA-MO to solve MaMOPs. Its characteristics
are a simple framework structure, optimized default
parameter settings for the non-expert use, determinis-
tic dynamic variation operators and WS-based selec-
tion mechanism. Two alternative WS-based mecha-
nism rank the population and select individuals for the
next generation according to the scores. Score values
are assigned to each individual based on the number
of superior or inferior objectives in the case of the tra-
ditional WS and additionally based on the quantity
of superiority or inferiority in the case of Difference-
based Winning Score (dWS) to the remaining individ-
uals in the population. The framework of COSEA-
MO with WS-based selection is referred to as WS-
COSEA-MO, the version with dWS is termed dWS-
COSEA-MO. The framework of both is given in Al-
gorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: Framework of (d)WS-COSEA-MO.
Input: Population P
t
, population size N,
Archive A
t
= {}, number of optimal
solutions m, total number of
generations T
Output: Next generation P
t+1
and archive
update A
t+1
1: Random initialization of P
0
;
2: while t < T do
Q
t
← RandomMatingAndVariation(P
t
);
U
t
← P
t
∪ Q
t
;
P
t+1
← (d)WS-Selection(U
t
);
A
t+1
← add m fittest individuals of P
t+1
acc. to (d)W S;
t ← t + 1;
end
Firstly, the start population P
0
of size N is ran-
domly initialized. The individuals represent peptides
in form of character strings. During the evolution pro-
cess, an offspring generation Q
t
of size N is deter-
mined by randomly selecting three parents of P
t
for
variation. The specific number of parents is motived
to ensure a high genetic diversity of the genetic mate-
rial. The variation operators are motivated by a suit-
able balance of global and local search. Determin-
istic dynamic variation operators are suitable opera-
tors to achieve this purpose. A linear dynamic re-
combination operator and an adapted version of the
deterministic dynamic mutation operator of B
¨
ack and
Sch
¨
utz (B
¨
ack and Sch
¨
utz, 1996) is used to generate
offspring (RandomMatingAndVariation). The varia-
tion rates are adapted dynamically by predefined de-
creasing functions with the iteration progress: the re-
combination operator varies the number of recombi-
nation points by a linearly decreasing function
x
R
(t) =
l
4
−
l/4
T
·t,
where l is the peptide length, T the total number of
the generations and t the index of the current gener-
ation. The adapted mutation operator determines the
mutation probabilities via
p
BS
= (a +
l − 2
T − 1
t)
−1
with a = 5. The mutation rates of the traditional op-
erator are reduced by a higher value for a. After that,
P
t
and Q
t
are combined to a population U
t
of size 2N.
Finally, the WS- or dWS-based selection mechanism
is performed to select N individuals of U
t
for the next
generation P
t+1
((d)WS-Selection) and the archive is
updated by adding the m-optimal individuals of P
t+1
according to the scoring points. Optimal solutions de-
tected in previous generations are not added twice into
the archive.
A Winning Score-based Evolutionary Process for Multi-and Many-objective Peptide Optimization
51

The motivation and the decisive characteristics of
WS- and dWS-based selection are described and dis-
cussed in the sequel.
3.1 WS-based Selection Mechanisms
In (Benedetti et al., 2006), three reasons are summa-
rized about the unsatisfactory of Pareto dominance
definition in the case of a large number of objectives:
• The number of improved objective function val-
ues are not taken into account.
• The (normalized) relevance of improvement is not
taken into account.
• No preference among the objectives is considered.
In the present biochemical optimization problems, all
objectives are equally important and therefore, the last
issue is negligible. The traditional WS method meets
the first issue in an intuitive way, it describes the dif-
ference between the number of superior and inferior
objectives between two individuals: let sup
i j
be the
number of objectives in a solution i that is superior
to the corresponding objectives in a solution j while
in f
i j
is the number of objectives in i that is inferior to
j. The WS-values of the i-th solution in a population
of size N is given by (Maneeratano et al., 2006):
W S(i) =
N
∑
j=1
w
i j
with w
i j
= sup
i j
− in f
i j
Obviously, it is w
i j
= −w j i and w
ii
= 0. This assign-
ment ensures that solutions with high WS-values are
close to the true Pareto front.
We assume the following expression of a MaOP:
minimize F(x) = ( f
1
(x), f
2
(x),..., f
K
(x)) with x ∈ Ω,
where x is the decision variable in the search space
of all feasible peptides (Ω), F(x) the objective vector
and K the number of objectives. To address the sec-
ond issue additionally to the first one, dW S is used:
dW S(x
i
) =
N
∑
j=1
K
∑
k=1
dw
i jk
with
dw
i jk
=
( f
k
(x
i
) − f
k
(x
j
))
2
, if f
k
(x
i
) ≺ f
k
(x
j
),
0, if f
k
(x
i
) = f
k
(x
j
),
−( f
k
(x
i
) − f
k
(x
j
))
2
, if f
k
(x
i
) f
k
(x
j
),
where x
i
and x
j
are two individuals of the population,
N is the population size and K the number of objec-
tives. dWS has especially been evolved to rank the
solutions according to their exact objective value dif-
ferences. With this approach, the amount of objective
improvement and worsening is considered, not only
the number of superior and inferior objectives. The
quadrate of the differences ensures that higher differ-
ences have a stronger impact on the scores.
The aim of WS- or dWS-based selection is to
find N approximately optimal individuals from U
t
for
the next generation. Furthermore, the update of the
archive with the m fittest individuals is also based
on the ranking according to the scores. Therefore,
a score is assigned to each individual x
i
of the cur-
rent population relative to the remaining population
members x
j
. W S
i
or respectively dW S(x
i
) of an in-
dividual x
i
reflect the quality of x
i
relative to the re-
maining members of the current population. A high
positive score value indicates superior quality of this
individual compared to the others, whereas high neg-
ative values indicates a low qualified solution. In con-
trast to COGA and COGA2, the scores are standalone
selection criteria and are assigned to every member of
the population with the aim of ranking, they are not
only used to differentiate a pair of non-dominated so-
lutions.
After this scoring point assignment to each indivi-
dual, the population is ranked according to the scores.
The selection process of the N individuals from
U
t
performs as described in Algorithm 2. R
t
is the
ranked set of U
t
and R
t
(i) is the i-th front set of R
t
.
Algorithm 2: Selection process.
Input: Ranked population R
t
with |R
t
| = 2N,
population size N
Output: Next generation P
t+1
1: while |P
t+1
| + |R
t
(i)| ≤ N do
P
t+1
← P
t+1
∪ R
t
(i);
i++;
end
2: while |P
t+1
| < N do
binary tournament selection
{x
i
,x
j
} ∈ R
t
\ P
t+1
;
if VolumeDominance(x
i
) <
VolumeDominance(x
j
) then
P
t+1
← P
t+1
∪ {x
i
};
end
else
P
t+1
← P
t+1
∪ {x
j
};
end
end
The population of the next iteration is filled by each
rank subsequently until the population size exceeds
N. In the case that adding the individual set of rank
R
t
(i) exceeds N, the remaining individuals for P
t+1
are selected by binary tournament selection of two in-
dividuals from the remaining ranks R
t
\ P
t+1
accord-
ing to the better Volume Dominance (VD) value. VD
is simply the spanned space of an individual to the
zero point (VolumeDominance). In the case of a min-
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
52
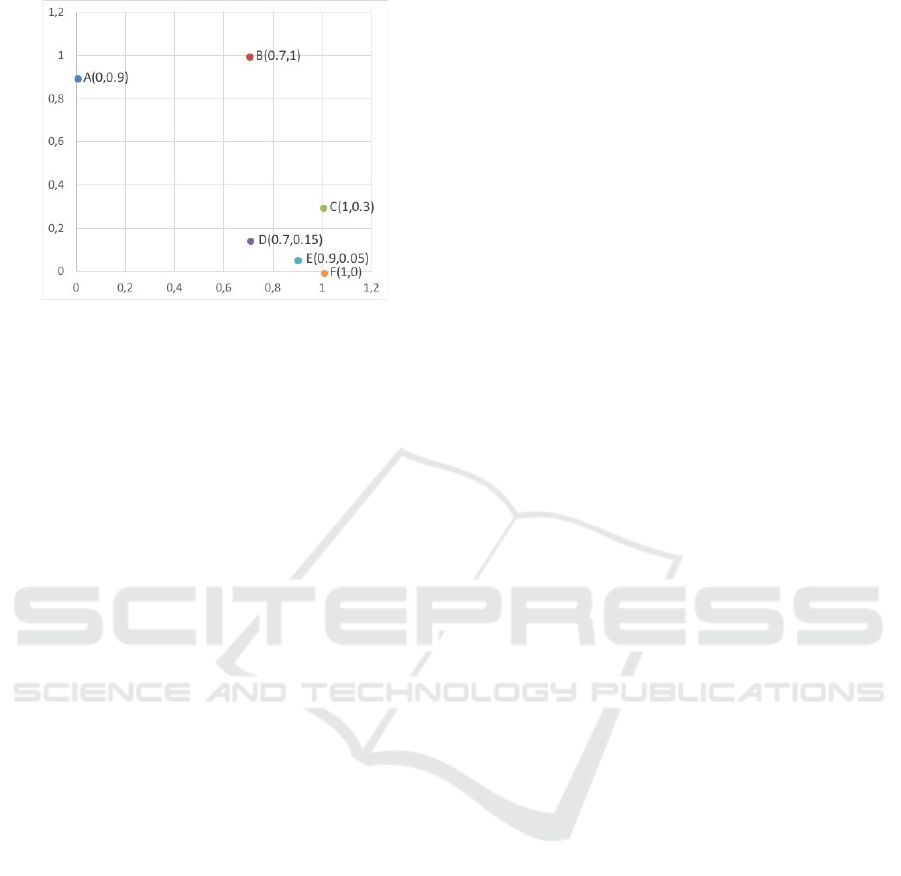
Figure 1: Selection principle of AnD, NSGA-II and (d)WS-
COSEA-MO.
imization problem, a lower VD value reveals a higher
solution quality than a lower one. Since all individ-
uals from the previous ranks are selected, elitism is
ensured.
3.2 Discussion of the Selection
Principles
WS and dWS as selection criteria have been chosen
under the subsequent considerations:
• the individuals are ranked according to their qual-
ity relative to each other,
• the ranking process is also applicable in higher
problem dimensions without loss of effectiveness,
• Solutions with lower function values in one ob-
jective but highly qualified function values in the
other objectives are termed boundary solutions
and are of importance for the spread of the true
Pareto front, they receive an evolutionary advan-
tage,
• individuals positioned in a crowded area achieve
similar ranks.
The potential of these targeted characteristics is
demonstrated in the following examples:
Firstly, a two-dimensional example is used to il-
lustrate the selection principle of WS-COSEA-MO,
dWS-COSEA-MO, AnD as well as NSGA-III. This
example is taken from (Lee et al., 2018). Six in-
dividuals are given, A(0,0.9), B(0.7,1), C(1,0.3),
D(0.7,0.15), E(0.9, 0.05) and F(0, 1). Four promis-
ing individuals haven to be selected into the next
generation. Figure 1 illustrates the selection princi-
ples: Since NSGA-III prefers non-dominated solu-
tions, therefore A, D, E and F are selected. In the case
of AnD, C and E are removed as C and D as well as
E and F provide minimal vector angles, but the shift-
based density estimation of C and E are worse. In
the case of WS-COSEA-MO and dWS-COSEA-MO,
A, D, E and F are selected into the next generation.
The difference between WS-COSEA-MO and dWS-
COSEA-MO is the ranking of the solutions A and D.
In the case of WS-COSEA-MO, D has a higher win-
ning score than A, this is vice versa in the case of
dWS-COSEA-MO. Summarizing, the selection prin-
ciples of the winnings score–based algorithms are
comparable to the one of NSGA-III. Point B is only
selected by AnD. This point is potentially important
to maintain the diversity in the population, but the ex-
periments in this work show that this selection mech-
anism lacks of a suitable convergence within a very
low number of generations.
Furthermore, a three-dimensional example is used
to illustrate the characteristics of WS- and dWS-based
selection according to the characteristics mentioned
above: Eleven points are given, A(0.15,0.1, 0.08),
B(0.2,0.3,0.15), C (0.02, 0.3,0.7),
D(0.25,0.75,0.32), E(0.32, 0.27,0.81),
F(0.3,0.4, 0.25), G(0.28,0.35,0.31),
H(0.32,0.43,0.28), I(0.15,0.1,0.78),
K(0.17, 0.68,0.15) and L(0.18, 0.17,0.73). The win-
ning scores as well as the difference-based winnings
scores are determined and given in Table 1. Point A
has the highest score value in both cases followed by
point B. Points C, I, K and L are boundary points and
achieve an evolutionary advantage by good score val-
ues in the case of WS. In the case of dWS, the scores
of these points are positioned in the lower half of the
ranking. F an G are positioned very close to each
other and achieve very similar scores in both cases.
D and E are worse individuals and have the lowest
scores in both cases. Summarizing, the evolutionary
advantage of the boundary points in the case of WS is
the main difference between the winning score alter-
natives.
4 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
The performance of the proposed WS-COSEA-MO
and dWS-COSEA-MO are compared to the re-
cently published AnD on four differently dimensional
molecular optimization problems according to the
convergence behavior and diversity. All experiments
are implemented in the open source jMetal library 4.5.
(Nebro and Durillo, 2018) and uses the open source
BioJava framework 4.2.0 (Prlic et al., 2018). Each
experiment is run 20 times on each molecular opti-
mization problem with 10 iterations and a population
size of 100. The individuals are 20-mer peptides com-
posed of the 20 canonical amino acids. Short peptides
of length 20 are of specific interest because of their fa-
A Winning Score-based Evolutionary Process for Multi-and Many-objective Peptide Optimization
53

Table 1: Winning Score values of WS-COSEA-MO and dWS-COSEA-MO.
A B C D E F G H I K L
WS 26 8 7 -14 -15 -6 -6 -13 8 2 2
dWS 3.3 1.8 -0.9 -1.7 -2.3 0.6 0.8 0.4 -1.0 -0.03 -0.9
vorable properties as drugs.
4.1 Molecular Optimization Problems
Four molecular optimization problems with 3 to 6 ob-
jective functions predicting physiochemical proper-
ties are used as experimental studies. Table 2 presents
the composed physiochemical optimization problems
with the used abbreviations: Needleman Wunsch Al-
gorithm (NMW), Molecular Weight (MW), Average
Hydrophilicity (Hydro), Instability Index (InstInd),
Isoelectric Point (pI) and Aliphatic Index (aI). These
molecular functions are provided by the BioJava li-
brary (Prlic et al., 2018). The physiochemical func-
tions are shortly described in the following, a de-
scription of the functions is given here (Prlic et al.,
2018): NMW is a well known and used method for
the global sequence alignment of a solution to a pre-
defined reference individual. This algorithm refers to
the common hypothesis that a high similarity between
molecules refers to similar molecular properties.
MW is an important peptide property as a min-
imized MW ensures a good cell permeability. MW
of a peptide sequence a of length l is calculated
summarizing the mass of each amino acid (a
i
) plus a
water molecule:
MW (a) =
∑
l
i=1
mass(a
i
) + 17.0073(OH) +
1.0079(H), where O (oxygen) and H (hydrogen) are
the elements of the periodic system.
A common challenge of drug peptides is the sol-
ubility in aqueous solutions, especially peptides with
stretches of hydrophobic amino acids. Therefore, Hy-
dro is calculated by the hydrophilicity scale of Hopp
and Woods (Hopp and Woods, 1983) with a window
size equal to the peptide length l. An average hy-
drophilicity value is assigned to each candidate pep-
tide a using the scales for each amino acid a
i
:
Hydro(a) =
1
l
· (
l
∑
i=1
hydro(a
i
)).
The use of molecules as therapeutic agents is po-
tentially restricted by their instability and their poten-
tial degradation by enzymes in systemic application.
The stability is addressed by the InstInd as stability is
a very important feature of drug components. InstInd
is determined by the Dipeptide Instability Weight Val-
ues (DIWV) of each two consecutive amino acids in
the peptide sequence. DIWV are provided by the
GRP-Matrix (Guruprasad et al., 1990). These values
are summarized and the final sum is normalized by
the peptide length l:
InstInd(a) =
10
l
l−1
∑
i=1
DIWV (a
i
,a
i+1
).
pI of a peptide is characterized as the pH-value at
which a peptide has a net charge of zero. A peptide
has its lowest solubility at its pI. Therefore, the charge
of a peptide influence the solubility in aqueous solu-
tions. The pI value is calculated as follows: Firstly,
the net charge for pH = 7.0 is determined. If this
charge is positive, the pH at 7 +3.5 is calculated; oth-
erwise the pH at 7 − 3.5 is determined. This process
is repeated until the modules of the charge is less or
equal 0.0001.
aI of a peptide is characterized as the relative vol-
ume occupied by aliphatic side chains consisting of
the amino acids alanine (Ala), valine (Val), isoleucine
(Ile) and leucine (Leu). aI is regarded as a positive
factor for the increase of thermostability. aI is calcu-
lated according to the formula:
aI = X(Ala) + d · X (Val) + e · (X(Ile) + X(Leu)),
where X(Ala), X(Val), X (Ile) und X (Leu) are mole
percent of the amino acids. The coefficients d and
e are the relative volume at the valine side chain
(d = 2.9) and Lei, Ile side chains (e = 3.9) to the side
chain Ala.
These six objective functions comparatively act
to reflect the similarity of a particular peptide and a
pre-defined reference peptide: f (CandidatePept.) :=
| f (CandidatePept.) − f (ReferencePept.)|. Therefore,
the four objective functions have to be minimized
and the optimization problems are minimization prob-
lems. Furthermore, the objective values are normal-
ized by the theoretical maximal value of each objec-
tive:
¯
f
k
(x
i
) =
f
k
(x
i
)
Max
k
for the k-objectives.
4.2 Performance Metrics
Two statistical metrics are chosen to evaluate the con-
vergence and diversity performance. These metrics
are applied on 10% approximately optimal individ-
uals in each iteration for all algorithms. These op-
timal individuals are determined by WS in all test
cases. The value of 10% optimized individuals is a pa-
rameter motivated by the number of peptides selected
for subsequent laboratory analysis and therefore mo-
tivated by the practical application. Furthermore, the
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
54
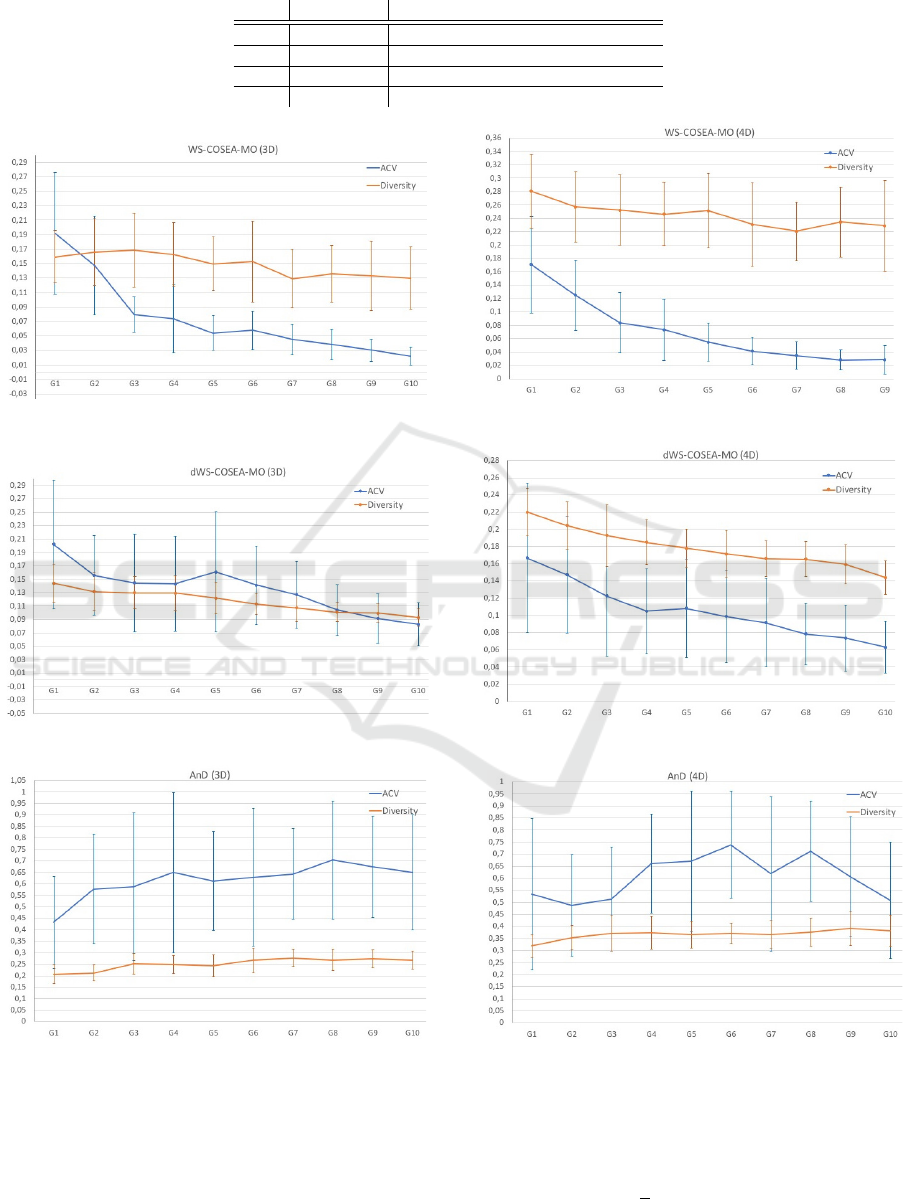
Table 2: Physiochemical functions of the different optimization problems.
dim. abbr. objective functions
3D 3D-MOP NMW, MW, Hydro
4D 4D-MaOP NMW, MW, Hydro, InstInd
5D 5D-MaOP NMW, MW, Hydro, InstInd, pI
6D 6D-MaOP NMW, MW, Hydro, InstInd, pI, aI
Figure 2: 3D-MOP: WS-COSEA-MO. Figure 3: 4D-MaOP: WS-COSEA-MO.
Figure 4: 3D-MOP: dWS-COSEA-MO. Figure 5: 4D-MaOP: dWS-COSEA-MO.
Figure 6: 3D-MOP: AnD. Figure 7: 4D-MaOP: AnD.
metrics are applied on the archives of dWS-COSEA-
MO and WS-COSEA-MO.
The Average Cuboid Volume (ACV) is used to
measure the convergence behavior (Rosenthal and
Borschbach, 2017a). ACV calculates the averaged
spanned space of each solution to an ideal reference
point, which is usually known in real-world applica-
tions. The ACV indicator is given by
ACV =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
(
k
∏
j=1
(x
i j
− r
j
)), (1)
A Winning Score-based Evolutionary Process for Multi-and Many-objective Peptide Optimization
55
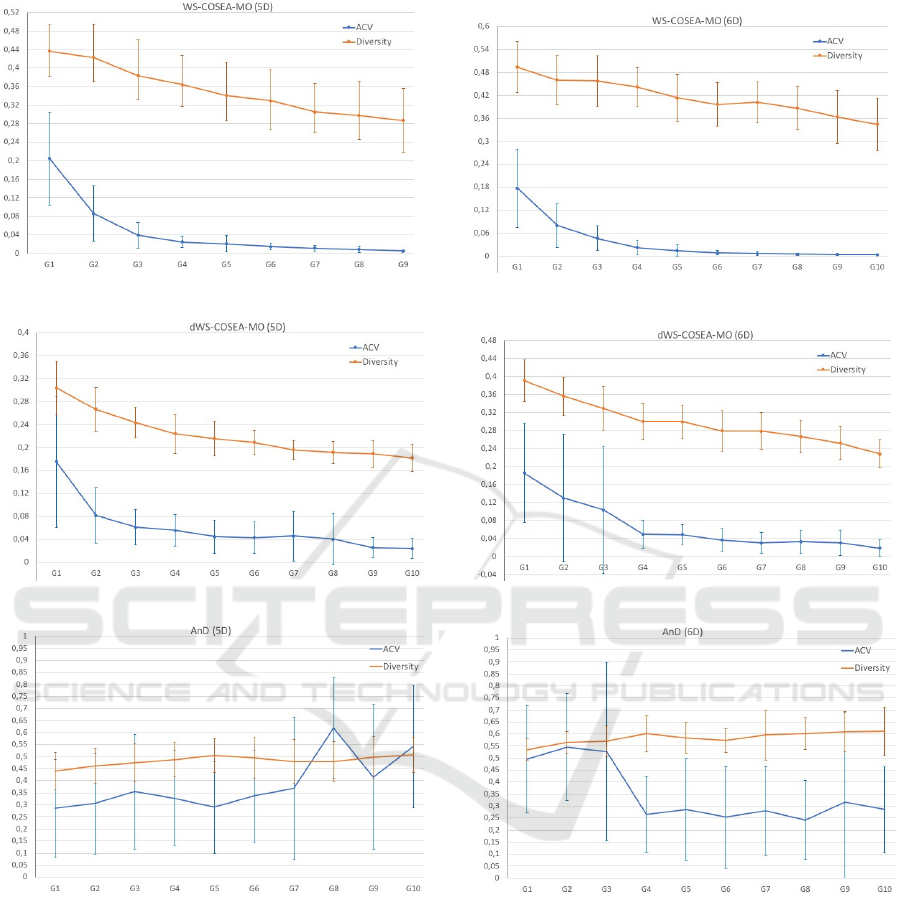
Figure 8: 5D-MaOP: WD-COSEA-MO. Figure 9: 6D-MaOP: WS-COSEA-MO.
Figure 10: 5D-MaOP: dWS-COSEA-MO. Figure 11: 6D-MaOP: dWS-COSEA-MO.
Figure 12: 5D-MaOP: AnD. Figure 13: 6D-MaOP: AnD.
where n is the number of individuals that are evalu-
ated, k the number of objectives and r
j
the ideal point.
The lower the ACV values, the better the convergence
behavior since the molecular optimization problems
have to be minimized. ACV as a simple statisti-
cal measure is preferred over traditional convergence
metrics since it is independent of Pareto optimal so-
lution sets which are usually unknown in real-world
applications, of low computation cost, independent of
the problem dimension and relative to the number of
solutions allowing a comparison of differently sized
archive sets.
A simple statistical evaluation method is used to
compare the diversity performance. The diversity is
determined by the standard deviation of the solution
set to the gravity point of this set.
4.3 Experimental Results
The performance results of WS-COSEA-MO, dWS-
COSEA-MO and AnD on 3D-MOP are depicted in
Figure 2, 4 and 6, the results of 4D-MaOP are shown
in Figure 3, 5 and 7, the results of 5D-MaOP are pre-
sented in Figure 8, 10 and 12 and those of 6D-MaOP
in Figure 9, 11 and 13. Generally, WS-COSEA-MO
and dWS-COSEA-MO provide a continuous con-
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
56
vergence improvement within 10 iterations, whereas
AnD does not provide any convergence behavior in
this low number of iterations in these molecular op-
timization problems except for a slight improvement
in 6D-MaOP, though these ACV values are worse
compared to those of the winning score-based algo-
rithms. Especially in the case of WS-COSEA-MO,
an exponential convergence improvement is observ-
able. As a consequence of the missing convergence,
AnD provides the highest diversity values in all test
cases. Moreover, AnD has the highest standard devia-
tion values of ACV and diversity indicating an highly
varying performance. Comparing dWS-COSEA-MO
and WS-COSEA-MO, it is observable that the tradi-
tional winning score-based algorithm provides a bet-
ter convergence behavior and the diversity is of a
higher level as well in all test cases.
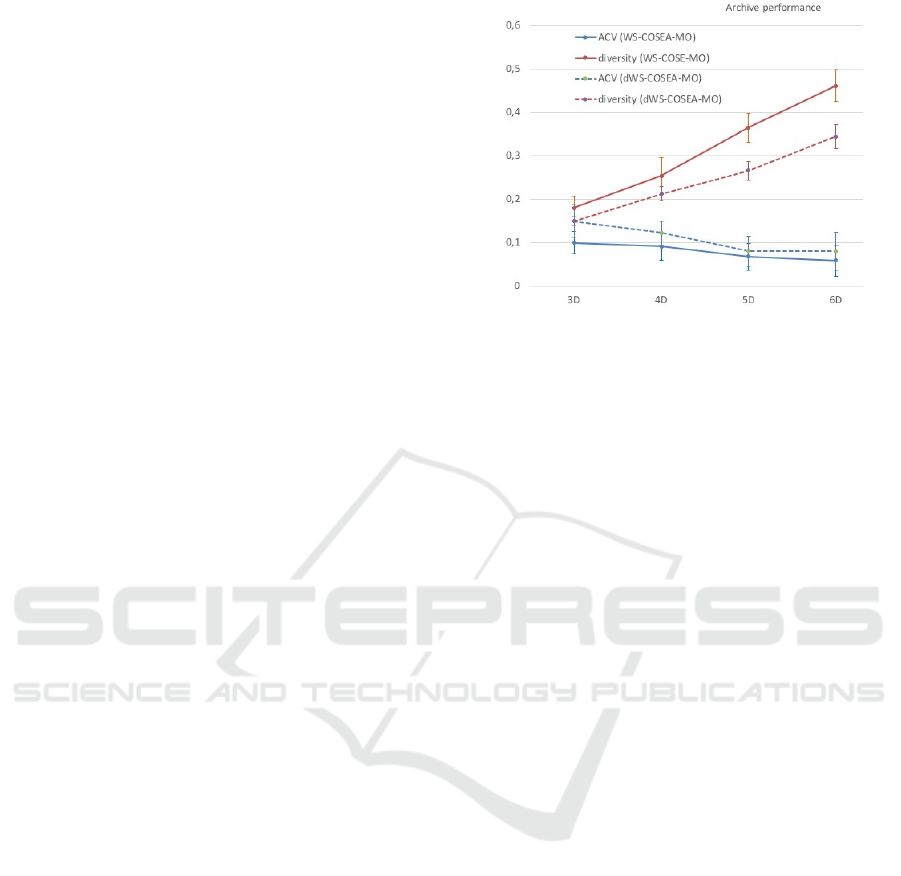
The archive sizes of WS-COSEA-MO and dWS-
COSEA-MO after 10 iterations in each test case have
also been examined. Generally, the archive sizes
of both algorithms are in the same range of a 95%
confidence interval between 32 and 47. The mean
of the archive sizes of both algorithms is the same,
avg = 39. Figure 14 depicts the archive performance
of WS-COSEA-MO and dWS-COSEA-MO after 10
iterations. As is has been expected from the previ-
ous results, WS-COSEA-MO provides higher quali-
fied solutions than dWS-COSEA-MO, whose diver-
sity is better compared to dWS-COSEA-MO as well.
Since AnD does not converge within this low
number of 10 iterations, further experiments have
been applied with a higher iteration number of 100. In
the case of 3D-MOP to 5D-MaOP, no convergence is
observable wihin the 100 iterations, whereas conver-
gence behavior is observable in the case of 6D-MaOP.
As AnD has not been applied to optimization prob-
lems with less than 5 objectives so far, this allows the
hypothesis that AnD is only suitable for optimization
problems with a higher dimension number.
5 CONCLUSION
This work presents an enhancement of COSEA-MO
that is especially evolved for multi-objective molec-
ular optimization addressing the application-specific
condition of identifying highly qualified candidate
peptides while limiting the number of objective func-
tion evaluations to save resources. COSEA-MO is
enhanced by WS-based selection mechanism. Two
types of winning scores are used to and differen-
tiate the individuals of a population effectively in
multi- and many-objective molecular optimization
problems. The performance of WS-COSEA-MO and
Figure 14: (d)WS-COSEA-MO: Performance of archives
after 10 iterations.
dWS-COSEA-MO is compared to the recently pro-
posed and promising AnD in terms of convergence,
diversity and exemplary analysis of the selection prin-
ciples. AnD is chosen for benchmarking as it has a
similar properties compared to COSEA-MO and is
the only MaOEA apart from COSEA-MO that has a
simple framework structure, provides optimized de-
fault parameters for the non-expert use and is inde-
pendent of weight vectors or reference points, which
usually have a strong impact on the performance and
are usually unknown in real-world applications. WS-
COSEA-MO reveals superior performance in terms
of convergence and diversity in all test cases. It
complies the problem-specific requirement of allocat-
ing an evolutionary advantage to boundary solutions.
WS-COSEA-MO provides exponential convergence
improvement within the very low number of 10 iter-
ations. Otherwise, AnD does not reveal any conver-
gence behavior within this low number of iterations,
since diversity is the preference objective of this evo-
lutionary process at the cost of convergence.
In future research, the selection process is ana-
lyzed regarding to the important biochemical objec-
tive of genetic dissimilarity among the candidate pep-
tides. The improvement of dWS as part of the selec-
tion mechanism is in the focus for the specification of
the search process. Furthermore, the prioritization of
different objectives in the evolutionary process is in
the focus and suitable method for this purpose will be
addressed. Moreover, since descriptor-based fitness
functions are missing for diverse but important molec-
ular properties and the evaluation time of these molec-
ular properties have to be reduced, the proposed ap-
proach will be revised by surrogate-assisted principles
(Diaz-Manriquez et al., 2016) as pre-screening tech-
niques in advance of the expensive laboratory analysis
for further improvement.
A Winning Score-based Evolutionary Process for Multi-and Many-objective Peptide Optimization
57

REFERENCES
B
¨
ack, T. and Sch
¨
utz, M. (1996). Intelligent mutation rate
control in canonical genetic algorithm. Proc. of the
International Symposium on Methodology for Intelli-
gent systems, pages 158–167.
Benedetti, A., Farina, M., and Gobbi, M. (2006). Evolu-
tionary multiobjective industrial design: the case of a
racing care tire-suspension system. IEEE Transaction
on evolutionary Computation, 10(3):230–244.
Beume, N., Naujoks, B., and Emmerich, M. (2007). Mul-
tiobjective selection based on dominated hypervol-
ume. European Journal of Operational Research,
18(3):1653–1669.
Boolong, K., Chaiyaratana, N., and Maneeratana, K.
(2010). Improved compressed-objective genetic algo-
rithm: COGA-II. International Conference on Evolu-
tionary Computation (ICEC), 1:95–103.
Deb, K. and Jain, H. (2014). An evolutionary many-
objective optimization algorithm using reference-
point-based nondominated sorting approach, Part i:
Solving problems with box constraints. IEEE transac-
tions on Evolutionary Computation, 18(4):577–601.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., and Meyarivan, T. (2002).
A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:
NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Com-
putation, 6(2):182–197.
Diaz-Manriquez, A., Toscano, G., Barron-Zambrano, J.,
and et al. (2016). A review of surrogate assisted multi-
objective evolutionary algorithms. Computational In-
telligence and Neuroscience.
Guruprasad, K., Reddy, B., and Pandit, M. (1990). Corre-
lation between stability of a protein and its dipeptide
composition: A novel approach for predicting in vivo
stability of a protein from its primary structure. Pro-
tein Engineering, 4(2):155–161.
He, Z., Yen, G., and Zhang, J. (2014). Fuzzy-based
pareto optimality for many-objective evolutionary al-
gorithms. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Com-
putation, 18(2):269–285.
Hopp, T. and Woods, K. (1983). A computer program for
predicting protein antigenic determinants. Mol. Im-
munol., 20(4):483–489.
Ishihuchi, H., Akedo, N., and Ohyanagi, H. (2011). Be-
havior of emo algorithms on many-objective opti-
mization problems with correlated objectives. IEEE
Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2011),
pages 1465–1472.
Krause, T., R
¨
ockendorf, N., El-Sourani, N., and et al.
(2018). Breeding cell penetrating peptides: Optimiza-
tion of cellular uptake by a function-driven evolution-
ary process. Bioconjug Chem.
Laumanns, M., Thiele, L., Deb, K., and Zitzler, E. (2002).
Combining convergence and diversity in evolutionary
multiobjective optimization. Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 10(3):263–282.
Lee, Z.-Z., Wang, Y., and Huang, P.-Q. (2018). And:
A many-objective evolutionary algorithm with angle-
based selection and shift-based density estimation. In-
formation Sciences, Elsevier.
Liu, H., Chen, L., Zhang, Q., and Deb, K. (2017). Adap-
tively allocating search effort in challenging many-
objective optimization problems. IEEE Transactions
on Evolutionary Computation, 22(3):433–448.
Lopez, E. and Coello, C. (2016). idg
+
-EMOA: A multi-
objective evolutionary algorithm based on igd
+
. IEEE
Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), pages
996–1006.
Maneeratano, C., Boonlang, K., and Chaigaratana, N.
(2006). Compressed-objective genetic algorithm. Par-
allel Problem solving from Nature - PPSN IX, LNCS
4193:473–482.
Nebro, A. and Durillo, J. (2018). jmetal: Metaheuristic Al-
gorithms in Java.
Nicolotti, D., Giangreco, I., and Introcasa, A. (2011).
Strategies of multi-objective optimization in drug dis-
covery and development. Expert Opin Drug Discov.,
6(9).
Prlic, A., Yates, A., Spencer, E., and et al. (2018). BioJava:
an open-source framework for bioinformatics.
R
¨
ockendorf, N. and Borschbach, M. (2012). Molecular evo-
lution of peptide ligands with custom-tailored charac-
teristics. PLOS Computational Biology, 8(12).
Rosenthal, S. and Borschbach, M. (2017a). Average cuboid
volume as a convergence indicator and selection cri-
terion for multi-objective biochemical optimization.
EVOLVE - A Bridge between Probability, Set Oriented
Numerics and Evolutionary Computation VII.
Rosenthal, S. and Borschbach, M. (2017b). Design perspec-
tives of an evolutionary process for multi-objective
molecular optimization. Proc. of the 9th Interna-
tional Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion
Optimization (EMO 2017), LNCS 10173, pages 529–
544.
Wang, R., Zhang, Q., and Zhang, T. (2016).
Decomposition-based algorithms using pareto
adaptive scalarization methods. IEEE Transactions
on Evolutionary Computation, 20(6):821–837.
Yang, S., Li, M., Liu, X., and Zheng, J. (2013). A grid-
based evolutionary algorithm for many- objective op-
timization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Com-
putation, 17(5):721–736.
Yuan, Y., Xu, H., Wang, B., and Yao, X. (2016). Balanc-
ing convergence and diversity in decomposition-based
many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on
Evolutionary Computation, 20(2):180–198.
Zhang, Q. and Li, H. (2007). MOEA/D: A multi-objective
evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE
Trans. on Evolutionary Computation, 11(6):712–731.
Zitzler, E. and K
¨
unzli, S. (2004). Indicator-based selection
in multi-objective search. Parallel Problem Solving
from Nature - PPSN VIII, LNCS 3242:832–842.
Zitzler, E., Laumanns, M., and Thiele, L. (2002). SPEA2:
improving the strength pareto evolutionary algorithm
for multi-objective optimization. Evolutionary Meth-
ods for Design, Optimisations and Control, pages 19–
26.
Zou, X., Chen, Y., Liu, M., and Kang, L. (2008). A new
evolutionary algorithm for solving many-objective op-
timization problems. IEEE Transactions on Sys-
tems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics),
38(5):1402–1412.
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
58
