
Ontological Integration of Semantics and Domain Knowledge in Energy
Scenario Co-simulation
Jan S
¨
oren Schwarz and Sebastian Lehnhoff
Department of Computer Science, University of Oldenburg, Oldenburg, Germany
Keywords:
Co-simulation, Data Management, Energy Scenarios, Information Model, Ontology, Sustainability.
Abstract:
The transition of the power system to more decentralized power plants and intelligent devices in a smart grid
leads to a significant rise in complexity. For testing new technologies before their implementation in the
field co-simulation is an important approach, which allows to couple diverse simulation models from different
domains. In the planning and evaluation of co-simulation scenarios experts from different domains have to
collaborate. To assist the stakeholder in this process, we propose to integrate on the one hand semantics of sim-
ulation models and exchanged data and on the other hand domain knowledge in the planning, execution, and
evaluation of interdisciplinary co-simulation based on ontologies. This approach aims to allow the high-level
planning of simulation and the seamless integration of its information to simulation scenario specification,
execution and evaluation. Thus, our approach intents to improve the usability of large-scale interdisciplinary
co-simulation scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
The intended transition from fossil to renewable ener-
gies in the power system poses many new challenges.
New technologies have to be developed to deal with
fluctuating energy resources and available flexibili-
ties. Additionally, the dependencies between differ-
ent domains become more and more important and
the power system can be considered neither detached
from the ICT system nor ecological, economic, or so-
ciotechnical systems. To handle this complexity in
the development of new technologies simulation is an
important approach. Especially, co-simulation is used
to couple diverse simulation models, which is ben-
eficial because in different domains usually specific
software, programming languages, and paradigms are
used. The coupling allows to reuse existing simula-
tion models without the need for reimplementation
and allows to use sophisticated models of the different
domains.
Commonly, a simulation expert works together
with the experts of the different simulation models in
the planning of a co-simulation. This collaboration
of simulation and domain experts can be a complex
task, because they have to understand at least partly
the other domains. For example, in the discussion the
used terminology can be unclear, because the same
terms may be used for different concepts. Therefore,
it would be beneficial for the development of energy
scenarios to directly integrate or reference external
domain knowledge.
Co-simulation scenarios, which describe an exe-
cutable co-simulation, are typically developed manu-
ally by the simulation expert. Central elements of this
process are the parameters, dependencies, and data
flows of simulation models. An increasing number of
simulation models makes the planning more complex
and error-prone, when done manually. Therefore, it
is essential for the planning of complex co-simulation
scenarios to get assistance in this process, e.g. in get-
ting recommendations of suitable simulation models.
Often co-simulation is not used as standalone tool,
but is integrated in energy scenarios adding even
more complexity. Energy scenarios are used to de-
scribe possible future developments of the energy sys-
tem (Grunwald et al., 2016). Typically, the future
states are defined, tested with simulation and eval-
uated afterwards. For this, a clear definition of the
parametrization, data flows, and results is crucial.
Our approach introduces ontological representa-
tions of domain knowledge in co-simulation of energy
scenarios to address the described problems. Addi-
tionally, it uses Semantic Web technologies to struc-
ture the process of planning, execution, and evalua-
tion of co-simulation. It has been developed in the
project NEDS, which consists of an interdisciplinary
Schwarz, J. and Lehnhoff, S.
Ontological Integration of Semantics and Domain Knowledge in Energy Scenario Co-simulation.
DOI: 10.5220/0008069801270136
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2019), pages 127-136
ISBN: 978-989-758-382-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
127

consortium from the domains of business adminis-
tration, computer science, economics, electrical engi-
neering, and psychology. In the project a process for
the integrated development of energy scenarios, their
simulation, and the evaluation of their sustainability
has been developed (Schwarz et al., 2019b) and ex-
ecuted for a future scenario for the German federal
state Lower Saxony. In this context, our proposed
ontology-based approach offers the following bene-
fits:
Firstly, it enables the integration of knowledge
from external ontologies. This allows to reuse ex-
isting ontologies from different domains and inte-
grate definitions of used terms. Thus, the terminology
used in a co-simulation project can be made clear and
transparent.
Secondly, it allows to describe the semantics
of data in several steps of co-simulation: The
parametrization of simulation models, the exchange
of data between simulation models, and the results of
simulation. All of these different kinds of data can be
semantically annotated to make the interpretation less
error-prone.
Thirdly, Semantic Web technologies like RDF,
OWL, and SPARQL offer a well-known and
widespread structure for knowledge representation
and querying. Their usage permits the utilization of
manifold available tools and techniques. Especially,
the querying based on the ontological description of
dependencies and data flows assists the planning of
simulation scenarios and enables the simulation ex-
pert on the one hand to check high-level scenarios for
completeness and missing models or evaluation func-
tions and on the other hand to verify simulation sce-
narios.
The remainder of this article is structured as fol-
lows: Section 2 gives an overview of the foundations
and related work. Section 3 describes the proposed
approach, gives some examples, and describes the
evaluation of the approach in a field study. A con-
clusion is given in section 4.
2 FOUNDATIONS AND RELATED
WORK
In this section, we will give an overview of related
work using co-simulation and ontologies in the en-
ergy domain (see section 2.1) and introduce our previ-
ous work of a process for the planning and evaluation
of energy scenarios with an information model and a
catalog of components for co-simulation (see section
2.2).
2.1 Co-simulation and Ontologies in
Energy Domain
As stated in the introduction, the power system be-
comes more and more complex, because multiple do-
mains have to be considered. An approach for hand-
ling this issue is co-simulation, which is defined as
“an approach for the joint simulation of models devel-
oped with different tools (tool coupling) where each
tool treats one part of a modular coupled problem”
(Bastian et al., 2011, p.1).
In energy domain, many different smart grid co-
simulation frameworks exist, which are developed
for different use cases. For example, the usage of
real-time and co-simulators for the development of
power system monitoring control and protection ap-
plications (Rehtanz and Guillaud, 2016), the coupling
with power flow simulators (Lehnhoff et al., 2015),
the integration of power system and communication
networks (Mets et al., 2014), or a holistic view on
the power system (Schwarz et al., 2019b). Schl
¨
ogl
et al. (2015) suggest a typification for the available
co-simulation frameworks and Vogt et al. (2018) com-
pare many of them. However, Palensky et al. (2017)
state that challenges in co-simulation are still massive,
which is caused among other things by often missing
software interoperability in the modeling.
Although ontologies would offer many benefits
for interoperability, the utilization in co-simulation
approaches is not common with two exceptions:
Teixeira et al. (2018) describe an approach for co-
simulation with integration of ontologies for the inter-
operability between different electricity market multi-
agent simulation platforms, which is called TOOCC
(Tools Configuration Center). But the focus of this
approach seems to be mainly on energy markets and
building energy management and the data structure of
messages between simulation models. Another ap-
proach is CODES (Composable Discrete-Event scal-
able Simulation), described by Teo and Szabo (2008).
It contains the COSMO ontology, which supports the
classification of components to allow component dis-
covery and reuse with a model repository, but it is lim-
ited to discrete-event simulation. As our focus is more
on the high-level scenario planning, the integration of
external domain knowledge, and the usability, our ap-
proach aims to be integrated in the established open-
source co-simulation framework mosaik
1
(Steinbrink
et al., 2019). It is focused on providing high usabil-
ity and flexibility to enable interdisciplinary teams to
develop co-simulation scenarios. For the coupling of
simulation models mosaik provides an API, which is
1
https://mosaik.offis.de
KEOD 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
128

Figure 1: Structure of the SEP information model (Schwarz et al., 2019b).
available in several programming languages and can
also be accessed via network packages.
2.2 Process for Assisted Simulation
Planning for Co-simulation
In previous work we have introduced the Sustain-
ability Evaluation Process (SEP) and an information
model for the high-level planning of co-simulation
in the context of energy scenarios (Schwarz et al.,
2019b). The SEP describes an integrated process for
the sustainability evaluation of future scenarios based
on literature review and co-simulation. The first step
of the SEP is the development of qualitative future
scenarios, which describe thinkable future states of
the power system – the energy scenarios. Afterwards,
these qualitative assumptions are quantified and used
as input for simulation. The last step is the evalua-
tion of the simulation results based on multi-criteria
decision making. The evaluation function for the SEP
is sustainability, but also other evaluation functions
could be defined in the information model. The infor-
mation model links future scenarios and simulation
scenarios to the sustainability evaluation as shown in
figure 1. On the left-hand side the domains of interest
are modeled and described by attributes, which can
be defined based on either future scenarios or sim-
ulation. On the right-hand side sustainability is de-
fined as evaluation function and subdivided in facets
and criteria. The connection between the two sides
is established through transformation functions from
attributes to the sustainability criteria. The informa-
tion model aims to support the information exchange
in the SEP. It describes a structure for modeling sce-
narios and assists the users in the process.
Based on the information model, a process for the
planning of co-simulation was developed, which is
shown in figure 2 (Schwarz et al., 2019a). In this plan-
ning of a co-simulation, simulation models have to be
found, which can provide the results defined in the in-
formation model. For this, a catalog of co-simulation
components was developed to give an overview of the
available components. The interfaces of the simula-
tion models are described in the catalog based on the
Functional Mockup Interface (FMI) standard, which
has been developed to allow the coupling of different
simulation models in industrial and scientific projects
(Blochwitz et al., 2009). A substantial part of FMI is
the definition of variables, which define the inputs and
outputs of simulation models (Modelica Association
Project FMI, 2013). Each variable can be described
by seven attributes in FMI. For example, the attribute
causality can have values like input, output, parame-
ter, or calculatedParameter or the attribute variabil-
ity characterizes time instants when a variable can
change its value and can have values like constant,
fixed, discrete, or continuous.
3 APPROACH
Our approach for the ontological integration of do-
main knowledge in co-simulation is based on the in-
formation model and component catalog summarized
in the previous section. In previous papers, first ideas
of this approach were described (Schwarz and Lehn-
hoff, 2018; Schwarz et al., 2019a,b), which will be
detailed in the following regarding the ontological in-
tegration.
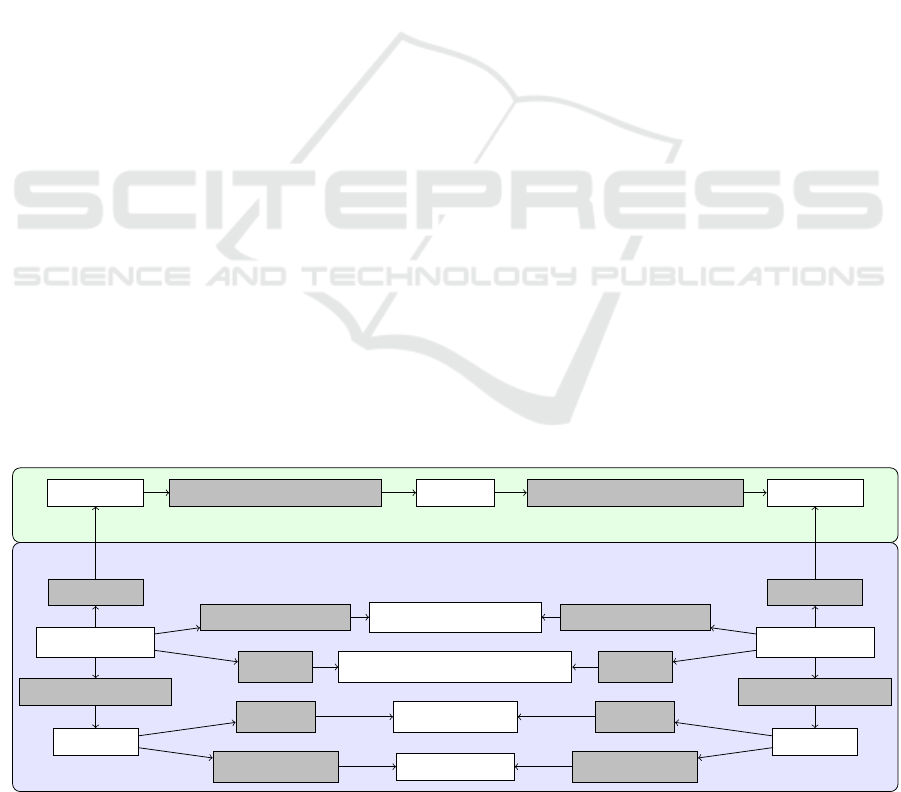
The information model of the SEP aims to assists
the collaboration of a simulation expert and domain
experts, which provide the simulation models. It can
Ontological Integration of Semantics and Domain Knowledge in Energy Scenario Co-simulation
129

High Level Scenario
Definition
Instantiated
Information Model
Information Model
Base Ontology
Co-Simulation
Component Catalog
Simulation
Scenarios
SPARQL Queries
External Domain
Knowledge
Figure 2: Overview of the approach for ontological integration of domain knowledge in energy scenario simulation (Schwarz
et al., 2019a).
be assumed that the simulation expert is a software
expert familiar with the co-simulation framework and
several programming languages and simulation tools,
but has only limited knowledge about all domains in-
cluded in simulation. The domain experts may also be
software experts, especially, if they provide simula-
tion models. But they could also have no background
in computer science or software development. There-
fore, an important requirement for our approach is to
facilitate the participation of domain experts in the
modeling without previous knowledge of Semantic
Web technologies. Thus, a semantic diagram in form
of a mind map is used for modeling the SEP informa-
tion model (see high level scenario definition in figure
2). This allows to start the planning of scenarios with
brainstorming in the project team and bringing the in-
formation step by step in the correct structure. Ob-
jects in the mind map can also be annotated directly
with additional information. For example, references
to external ontologies (see section 3.1), or the context
of the future scenarios can be annotated.
The map has to comply to the structure of the in-
formation model shown in figure 1 in the end. Other
methods for knowledge modeling with the graph-
based structure of concept maps also exist, as Simon-
Cuevas et al. (2009) describe it for example. We ar-
gue that a tree-based mind map is sufficient for the
described use case and the superior flexibility of a
graph-based concept map would distract the users.
For the ontological representation of the modeled
information, a base ontology representing the infor-
mation model structure has been developed (see sec-
tion 3.2). The mind map tool XMind
2
was used and
extended with a plug-in to instantiate the information
model ontology. Therefore, the scenario can be mod-
eled inside the mind map and be transformed to RDF
(see instantiated information model in figure 2).
To build an executable co-simulation based on
this, a co-simulation component catalog was imple-
2
https://www.xmind.net/
mented (Schwarz et al., 2019a). For this, a Semantic
MediaWiki (SMW) (Kr
¨
otzsch et al., 2007) was used
to collect available simulation models. It is used to fa-
cilitate the participation of users without experiences
in Semantic Web technologies. With the page forms
extension
3
it offers intuitive usable forms to add new
models to the catalog. The SMW allows to import
vocabularies from external ontologies and to export
the content to RDF or to use directly a triplet store
as database. Thus, the catalog can directly be inte-
grated in the instantiated ontology of the information
model and the user can be assisted in finding the suit-
able simulation models for his purpose. Some ex-
ample queries showing this assistance are shown in
section 3.3. For the integration of the approach in
co-simulation a prototype for the framework mosaik
has been developed. It allows to use the information
from the information model and the component cata-
log to assist the simulation expert in the development
and validation of executable simulation scenarios. Fi-
nally, the integration in data management is shortly
described in section 3.4 and the evaluation of the ap-
proach in section 3.5.
3.1 Referencing External Ontologies
The ontological modeling allows to reference exist-
ing external ontologies in different manners. Exem-
plary ontologies for the following relevant use cases
are described in this section. On the one hand, the
objects of interest for the simulation (domain objects)
and objects of evaluation (sustainability criteria) in
the information model can be mapped to external on-
tologies to define their meaning. On the other hand,
external ontologies can be used for the definition of
units of measurement for different kinds of attributes
in the information model.
3
https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Extension:Page Forms
KEOD 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
130

Figure 3: Mapping of individuals of the instantiated information model from project NEDS to external ontologies.
3.1.1 Definition of Terms
In the energy domain the Common Information
Model (CIM) is widespread to facilitate interoperabil-
ity in the power system. It contains a data model in
form of a domain ontology, various interface speci-
fications, and mappings between technologies. Thus,
it enables automated communication between compo-
nents of smart grids. For our approach mainly the first
use case for CIM described by Uslar et al. (2012) is
of interest, which is CIM as a large domain ontology
providing a vocabulary. This vocabulary can be used
to map objects to definitions in the CIM. The CIM is
defined as an UML model, but the complete model or
subsets (so-called profiles) can be transformed to Web
Ontology Language (OWL) with the CIMTool
4
.
As in the SEP sustainability is evaluated, it is
examined here as example as well. The United
Nations defined Sustainable Development Goals
(SDGs), which should be fulfilled until the year 2030
(UN General Assembly, 2015). To reference these
goals and their indicators the SDG Interface Ontol-
ogy
5
(SDGIO) based on the Environment Ontology
(ENVO) (Buttigieg et al., 2016) is under develop-
ment. It contains definitions of indicators for the mea-
surement of the SDGs defined by the United Nations.
The mapping to external ontologies allows inte-
grating definitions of terms to make clear their mean-
ing in an interdisciplinary simulation or to relate in-
ternal evaluation criteria to external criteria. Exam-
ples of mapping to the external ontologies CIM and
SDGIO are described as follows (see also figure 3).
The CIM ontology contains definitions for objects of
the power system like CIM-generic#EnergyMarket,
CIM-generic#HydroPowerPlant, and CIM-generic#
GasPrice, which are mapped to domain objects and
attributes of the information model in the project
NEDS. Additionally, the domain object attribute foot-
print in NEDS is mapped to the class material foot-
4
http://wiki.cimtool.org
5
https://github.com/SDG-InterfaceOntology/sdgio
print (sdg/SDGIO 00010057) and its definition in the
SDGIO. Another example is the sustainability crite-
rion Percentage of income used for energy in NEDS,
which addresses the SDG 7: “Ensure access to afford-
able, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all”
(UN General Assembly, 2015, p. 21), which is repre-
sented by the individual sdg/ SDGIO 00000041 in the
SDGIO.
3.1.2 Units of Measure
The Ontology of units of Measure (OM) is an OWL
ontology of the domain of quantities and units of mea-
sure described by Rijgersberg et al. (2013). It aims to
“support making quantitative research data more ex-
plicit, so that the data can be integrated, verified and
reproduced” (Rijgersberg et al., 2013, p. 1). In the
OM every measure is defined by a unit of measure,
which can have a prefix. These units of measure are
defined by a quantity and each quantity has a dimen-
sion. For example, the measure “3 meters” would be
defined by the unit “meter”, which could be defined
by the quantity “length” or “height”, which both are
in the “length dimension”. Additionally, a java library
for conversion of units based on the ontology is avail-
able
6
.
Units play an important role in the attributes,
transformation functions, and sustainability criteria in
the information model as well as in simulation models
and co-simulation. All connections have to be vali-
dated in consideration of their unit to ensure the func-
tionality. Therefore, the OM is used to add references
to the units of attributes and criteria annotated in the
information model. Additionally, the OM is used to
assist the user in annotating directly in the mind map,
comparable to the assistance with an Excel add-in de-
scribed by Rijgersberg et al. (2013). With this infor-
mation the OM allows to validate the connections. In
the case of problems, a conversion can be added or
the user be warned. The information can also be used
6
https://github.com/dieudonne-willems/om-java-libs
Ontological Integration of Semantics and Domain Knowledge in Energy Scenario Co-simulation
131

within the co-simulation scenarios to check for cor-
rectness of connections between simulation models.
3.2 Ontological Representation
Three base ontologies have been developed and are
imported in an additional ontology for integration.
This modularity enables the reuse of the ontologies.
The first ontology represents the structure of the in-
formation model for the high-level scenario planning.
The second ontology represents the structure of the
component catalog and the FMI-based specification
of variables. The third ontology represents the struc-
ture of a simulation scenario modeled in mosaik.
Such a scenario consists of multiple simulation com-
ponent with their parametrization and the connections
between simulation component and the exchanged at-
tributes between them. Based on these three ontolo-
gies the available data is described and can be used
for queries.
3.3 Example Queries
The usage of ontologies provides a structure for
querying the data of the planning in the information
model, the component catalog, and the mosaik sce-
nario with SPARQL to assist the development of sim-
ulation scenarios. In the following, two examples are
given, which show the opportunities of the ontolog-
ical representation in the planning of executable co-
simulation scenarios. For both examples the SPARQL
code and a visualization of the query are shown. The
following prefixes are used: The prefixes wiki and fmi
are referencing the component catalog in the SMW.
The prefixes imDB, imDom, and im are referencing
the information model base ontology. The prefix om
is referencing the OM. In the visualization (see fig-
ures 4(b), and 5(b)) the data source is indicated by the
background color and label.
SELECT DISTINCT ? d e r A t t r ? u n i t ? omUnit ? di m e n s i o n ? comp o nent ? f miV ar
? f m i U n i t
WHERE {
? d e r A t t r r d f : t y p e imDom: D e r i v e d D o m a i nO b j ec t A tt r i b u t e ; imDB : u n i t ? u n i t
? omUnit r df : t y p e om: U n i t ; om: s y mbol ? symb o l
FILTER( ? symbo l = ? u n i t )
? omUnit om: h as Di me n s i on ? d i m e n s i o n
? co mpon e nt r d f : t y p e w i k i C a te go ry : Component ; wi ki : f m i V a r i a b l e s ? fmi V ar
? fmiV ar r df : t y p e w i k i C at eg or y : F MI Va r i a bl e
? fmiV ar fmi : u n i t ? fm i U n i t ; fmi : c a u s a l i t y ? f m i C a u s a l i t y
FILTER( ? f m i C a u s a l i t y = ’ o u t p u t ’ )
? omUnit2 r d f : t y p e om: U n i t ; om : s ymbol ? sy m bol2
FILTER( ? symb o l2 = ? fm i U n i t )
? omUnit2 om: h a s D i m en si on ? d i m e n s i o n }
(a) SPARQL code
information model
ontology of units of measure
wiki
?derAttr
rdf:type
imDom:DerivedDomainObjectAttribute
imDB:unit ?unit
om:symbol
?omUnit
rdf:type
om:Unit
om:hasDimension ?dimension
om:hasDimension
?omUnit2
rdf:type
om:unit
om:symbol
?fmiUnit
fmi:unit?fmiVar
rdf:type
wikiCategory:FMIVariable
fmi:causality
FILTER(’output’)
wiki:fmiVariables
?component
rdf:type
wikiCategory:Component
(b) Visualization
Figure 4: Query 1 – Simulation models from wiki providing output for derived attributes of information model.
KEOD 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
132
3.3.1 Query 1
This query (see figure 4) assist the user in common
use cases for the development of a co-simulation sce-
nario. If the simulation models are not predefined,
the simulation expert has to find simulation models
matching the goal of the simulation. This can be a
complex task, because there can be a vast amount of
available simulation models, which were usually not
developed by the simulation expert. Therefore, the
simulation expert does not know all details about the
simulation models and is assisted by querying the in-
formation model and the specification of the simula-
tion models in the component catalog.
Query 1 shows simulation models, whose output
can be used in the information model. These de-
rived attributes in the information model are by def-
inition the output of a simulation. In the query the
derived attributes (?derAttr) in the information model
are mapped to the variables (?fmiVar) of simulation
models (?component) in the component catalog. The
variables are filtered by their fmi:causality, which has
to be output. To find suitable combinations of de-
rived attributes and variables the units annotated in
the mind map are used. In this query the units are not
compared directly, but the OM is used to reference the
dimension (?dimension) of the unit, e.g., the unit “me-
ter” is in the length dimension. Hence, differences in
unit prefixes or the system of measurement (imperial
or metric system) are of no importance for mapping.
3.3.2 Query 2
This query searches for simulation models that use the
output of another simulation model as input(see figure
5). In the information model such kind of connection
is modeled via a derived attribute, but it is usually re-
alized by a direct coupling of the two simulation mod-
els in co-simulation. For these cases, the query checks
the technical interfaces and characteristics of the sim-
ulation models for compatibility based on the compo-
nent catalog. In the query, the first simulation model
(?simMod1) is mapped to the derived attributes (?de-
rAttr) and the second simulation model (?simMod2).
If two simulation models in the information model are
modeled this way, the technical characteristics of the
SELECT DISTINCT ? simMod1 ? fmiV ar1 ? f m i U n i t 1 ? d e r A t t r ? fmi V ar2 ? f mi U n i t 2
? simMod2
WHERE {
? simMod1 im : f e e d s D e r i v e d A t t r i b u t e ? d e r A t t r
? d e r A t t r im : f e e d s S i m u l a t i o n M o d e l ? simMod2
? co mpon e nt1 r df : t y p e w i k i C at eg or y : MosaikM odel
? co mpon e nt1 w ik i : name ? simMod1 ; w ik i : f m i V a r i a b l e s ? fmi V ar1
? fmiV ar1 r d f : t y p e w ik iC at eg or y : F M I V ar ia b l e
? co mpon e nt2 r df : t y p e w i k i C at eg or y : MosaikM odel
? co mpon e nt2 w ik i : name ? simMod2 ; w ik i : f m i V a r i a b l e s ? fmi V ar2
? fmiV ar2 r d f : t y p e w ik iC at eg or y : F M I V ar ia b l e
? fmiV ar1 fmi : t y p e ? fmi V ar1T y pe ; fmi : v a r i a b i l i t y ? fm i V a r 1 V a r i
? fmiV ar2 fmi : t y p e ? fmi V ar1T y pe ; fmi : v a r i a b i l i t y ? fm i V a r 1 V a r i
? co mpon e nt1 w ik i : ti m e Domain ? comp1time Domain
? co mpon e nt2 w ik i : ti m e Domain ? comp1time Domain
(a) SPARQL code
information model
wiki
?simMod1
wiki:name
?component1
wiki:fmiVariables
?fmiVar1
wiki:name
?component2
wiki:fmiVariables
?fmiVar2
im:feedsDerivedAttribute
?derAttr
im:feedsSimulationModel
?simMod2
wiki:timeDomain wiki:timeDomain
?comp1timeDomain
rdf:type rdf:typewikiCategory:MosaikModel
fmi:type fmi:type?fmiVar1Type
fmi:variability fmi:variability
?fmiVar1Vari
(b) Visualization
Figure 5: Query 2 – Finding suitable simulation models for coupling with another simulation model.
Ontological Integration of Semantics and Domain Knowledge in Energy Scenario Co-simulation
133

simulation models can be checked for compatibility
based on the component catalog.
In the example, the characteristics fmi:variability
and fmi:type of the FMI variables (?fmiVar1 and ?fmi-
Var2) are compared. Additionally, the characteristics
wiki:timeDomain of the simulation models (?compo-
nent1 and ?component2) are compared. This charac-
teristic can have values like “discrete”, “continuous”,
or “stationary” and addresses the common problem
of different timing in simulation models. This query
can also be adapted to find suitable simulation mod-
els based on these characteristics, if one of them is
missing in the information model.
3.4 Data Management
In the SEP, values from future scenarios, simulation
scenario parametrization, and simulation results have
to be managed and are directly integrated in the infor-
mation model. The information model provides one
central storage for the semantics of all relevant data
in the complete process. Thus, also the data manage-
ment is integrated with the information model.
As briefly mentioned in Schwarz et al. (2019b) the
information model was used to generate the schema
for a data store, which was implemented in a re-
lational database (RDB) in the NEDS project. To
facilitate the collaboration of different domain ex-
perts, different views were defined on the schema.
To integrate the data from a relational database again
Ontology-based Data Access (OBDA) could be used.
It is based on a three-level architecture containing
an ontology, data sources, and a mapping between
them Daraio et al. (2016). Thus, OBDA faces the
challenge of data heterogeneity by replacing a global
scheme in data management with the ontology de-
scribing the domains. It allows also to integrate data
from other sources like CSV, XML, and XLSX di-
rectly in SPARQL queries, which can be helpful in
the interdisciplinary environment of co-simulation.
To reduce the complexity the direct usage of a
triple store would be preferable compared to a RDB
with ODBA, but is not always possible. However, the
usage of a triple store or OBDA would allow to access
data based on the information model ontology and to
integrate the data store directly in SPARQL queries.
3.5 Evaluation
The proposed approach aims to support users in the
modeling and management of information in the de-
velopment of co-simulation scenarios. For its evalua-
tion, the process was used in a field study in the inter-
disciplinary project team of the project NEDS. Alto-
gether, 28 scientific researchers participated and used
the information model to model a simulation scenario,
which integrated several simulation models from dif-
ferent domains and to evaluate the results of simula-
tion. The members of the project team came from the
domains energy, computer science, business admin-
istration, economics, electrical engineering, and psy-
chology. 29 domain objects, 231 attributes, and 19
sustainability criteria where modeled with their de-
pendencies and data flows in the information model
and transformed to RDF automatically for further us-
age. Based on the RDF representation of the informa-
tion model SPARQL queries where used to check for
completeness and correctness of the modeled infor-
mation. As the project partners were mostly not from
computer science, we defined the SPARQL queries to
get the needed information. The implementation of a
GUI to enable the users to do this themselves would
be interesting future work.
The field study showed that the process was help-
ful to include domain experts in the design of simula-
tion scenarios. The use of the information model al-
lowed easy participation and offered a central model.
Also, the semantic diagram was supportive as tool
for discussion in the project team. The field study
showed that not all participating domains have ontolo-
gies which could be referenced for definition of terms.
However, the modeling of the information model im-
proved the processes in the interdisciplinary project
team during the development of energy scenarios and
helped significantly making clear the terminology.
4 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we described an approach for the on-
tological integration of semantics and domain knowl-
edge in the process of planning, execution, and eval-
uation of interdisciplinary co-simulation of the en-
ergy system. Our approach incorporates the SEP and
its information model representing the process and
providing the ontological structures for the modeling
of energy scenarios using co-simulation. It can be
instantiated in collaboration of interdisciplinary do-
main experts and allows to integrate external ontolo-
gies for definition of terms and referencing external
works. The modeling of the scenarios in the informa-
tion model allows also the integration in data manage-
ment of scenario parametrization and results.
Also, a catalog of simulation components in a
SMW was integrated to assist the simulation expert
finding suitable simulation model during the planning
of co-simulation. The integration of the approach in
the co-simulation framework mosaik has been imple-
KEOD 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
134

mented prototypical. This prototype uses the informa-
tion model and simulation model specification from
the SMW to validate simulation scenarios. Based on
this validation, also wrong connections of simulation
components should be found in the future. These
could be corrected by automatically added conver-
sions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research project ’NEDS Nachhaltige Energiev-
ersorgung Niedersachsen’ acknowledges the support
of the Lower Saxony Ministry of Science and Culture
through the ’Nieders
¨
achsisches Vorab’ grant program
(grant ZN3043).
REFERENCES
Bastian, J., Clauß, C., Wolf, S., and Schneider, P. (2011).
Master for Co-Simulation Using FMI. Proceedings
of the 8th International Modelica Conference, pages
115–120.
Blochwitz, T., Otter, M., Arnold, M., Bausch, C., Clauß,
C., Elmqvist, H., Junghanns, a., Mauss, J., Monteiro,
M., Neidhold, T., Neumerkel, D., Olsson, H., Peetz,
J. V., and Wolf, S. (2009). The Functional Mockup
Interface for Tool independent Exchange of Simula-
tion Models. 8th International Modelica Conference
2011, pages 173–184.
Buttigieg, P. L., Pafilis, E., Lewis, S. E., Schildhauer, M. P.,
Walls, R. L., and Mungall, C. J. (2016). The envi-
ronment ontology in 2016: Bridging domains with in-
creased scope, semantic density, and interoperation.
Journal of Biomedical Semantics, 7(1):1–12.
Daraio, C., Lenzerini, M., Leporelli, C., Naggar, P., Bonac-
corsi, A., and Bartolucci, A. (2016). The advantages
of an Ontology-Based Data Management approach:
openness, interoperability and data quality. Sciento-
metrics, 108(1):441–455.
Grunwald, A., Dieckhoff, C., Fischedick, M., H
¨
offler, F.,
Mayer, C., and Weimer-Jehle, W. (2016). Consult-
ing with energy scenarios: Requirements for scientific
policy advice. Series on Science-Based Policy Ad-
vice. acatech/Leopoldina/Akademienunion (Eds.).
Kr
¨
otzsch, M., Vrandecic, D., V
¨
olkel, M., Haller, H., and
Studer, R. (2007). Semantic wikipedia. Web Seman-
tics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide
Web, 5(4):251 – 261. World Wide Web Conference
2006 Semantic Web Track.
Lehnhoff, S., Nannen, O., Rohjans, S., Schl
¨
ogl, F., Dal-
hues, S., Robitzky, L., Hager, U., and Rehtanz, C.
(2015). Exchangeability of power flow simulators in
smart grid co-simulations with mosaik. In Model-
ing and Simulation of Cyber-Physical Energy Systems
(MSCPES), 2015 Workshop on, pages 1–6.
Mets, K., Ojea, J. A., and Develder, C. (2014). Combin-
ing Power and Communication Network Simulation
for Cost-Effective Smart Grid Analysis. IEEE Com-
munications Surveys and Tutorials, pages 1–25.
Modelica Association Project FMI (2013). Functional
Mock-up Interface for Model Exchange and Co-
Simulation. Technical report, Modelica Association.
Palensky, P., Van Der Meer, A. A., Lopez, C. D., Joseph, A.,
and Pan, K. (2017). Cosimulation of Intelligent Power
Systems: Fundamentals, Software Architecture, Nu-
merics, and Coupling. IEEE Industrial Electronics
Magazine, 11(1):34–50.
Rehtanz, C. and Guillaud, X. (2016). Real-time and co-
simulations for the development of power system
monitoring, control and protection. In 2016 Power
Systems Computation Conference (PSCC), pages 1–
20.
Rijgersberg, H., Van Assem, M., and Top, J. (2013). Ontol-
ogy of units of measure and related concepts. Seman-
tic Web, 4(1):3–13.
Schl
¨
ogl, F., Rohjans, S., Lehnhoff, S., Velasquez, J.,
Steinbrink, C., and Palensky, P. (2015). Towards a
Classification Scheme for Co-Simulation Approaches
in Energy Systems. International Symposium on
Smart Electric Distribution Systems and Technolo-
gies. IEEE/IES, pages 2–7.
Schwarz, J. S. and Lehnhoff, S. (2018). Ontology-Based
Development of Smart Grid Co-Simulation Scenarios.
In Cimiano, P. and Corby, O., editors, Proceedings of
the EKAW 2018 Posters and Demonstrations Session
(EKAW-PD 2018), Nancy, France, November 12-16,
2018., number 2262 in CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
pages 21–24, Aachen.
Schwarz, J. S., Steinbrink, C., and Lehnhoff, S. (2019a).
Towards an Assisted Simulation Planning for Co-
Simulation of Cyber-Physical Energy Systems. In
7th Workshop on Modeling and Simulation of Cyber-
Physical Energy Systems (MSCPES), pages 1–6,
Montreal.
Schwarz, J. S., Witt, T., Nieße, A., Geldermann, J., Lehn-
hoff, S., and Sonnenschein, M. (2019b). Towards an
integrated development and sustainability evaluation
of energy scenarios assisted by automated information
exchange. In Donnellan, B., Klein, C., Helfert, M.,
Gusikhin, O., and Pascoal, A., editors, Smart Cities,
Green Technologies, and Intelligent Transport Sys-
tems, pages 3–26, Cham. Springer International Pub-
lishing.
Simon-Cuevas, A., Ceccaroni, L., Rosete-Suarez, A., and
Suarez-Rodriguez, A. (2009). A Formal Modeling
Method Applied to Environmental-Knowledge Engi-
neering. International Conference on Complex, Intel-
ligent and Software Intensive Systems.
Steinbrink, C., Blank-Babazadeh, M., El-Ama, A., Holly,
S., Lers, B., Nebel-Wenner, M., Ramrez Acosta, R. P.,
Raub, T., Schwarz, J. S., Stark, S., Niee, A., and
Lehnhoff, S. (2019). CPES testing with mosaik: Co-
simulation planning, execution and analysis. Applied
Sciences, 9(5).
Teixeira, B., Pinto, T., Silva, F., Santos, G., Prac¸a, I., and
Vale, Z. (2018). Multi-Agent Decision Support Tool
Ontological Integration of Semantics and Domain Knowledge in Energy Scenario Co-simulation
135

to Enable Interoperability among Heterogeneous En-
ergy Systems. Applied Sciences, 8(3):328.
Teo, Y. M. and Szabo, C. (2008). CODES: An integrated ap-
proach to composable modeling and simulation. Pro-
ceedings - Simulation Symposium, pages 103–110.
UN General Assembly (2015). Transforming our world:
The 2030 agenda for sustainable development.
https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/docum
ents/21252030%20Agenda%20for%20Sustainable%
20Development%20web.pdf (accessed March 9,
2018).
Uslar, M., Specht, M., Rohjans, S., Trefke, J., and Gonzalez
Vazquez, J. (2012). The IEC Common Information
Model. Springer, Berlin.
Vogt, M., Marten, F., and Braun, M. (2018). A survey and
statistical analysis of smart grid co-simulations. Ap-
plied Energy, 222(March):67–78.
KEOD 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
136
