
On the Design of a Heuristic based on Artificial Neural Networks for the
Near Optimal Solving of the (N
2
–1)-puzzle
Vojt
ˇ
ech Cahl
´
ık and Pavel Surynek
a
Faculty of Information Technology, Czech Technical University in Prague, Th
´
akurova 9, 160 00 Praha 6, Czech Republic
Keywords:
(N
2
−1)-puzzle, Heuristic Design, Artificial Neural Networks, Deep Learning, Near Optimal Solutions.
Abstract:
This paper addresses optimal and near-optimal solving of the (N
2
–1)-puzzle using the A* search algorithm.
We develop a novel heuristic based on artificial neural networks (ANNs) called ANN-distance that attempts to
estimate the minimum number of moves necessary to reach the goal configuration of the puzzle. With a well
trained ANN-distance heuristic, whose inputs are just the positions of the pebbles, we are able to achieve better
accuracy of predictions than with conventional heuristics such as those derived from the Manhattan distance
or pattern database heuristics. Though we cannot guarantee admissibility of ANN-distance, an experimental
evaluation on random 15-puzzles shows that in most cases ANN-distance calculates the true minimum distance
from the goal, and furthermore, A* search with the ANN-distance heuristic usually finds an optimal solution
or a solution that is very close to the optimum. Moreover, the underlying neural network in ANN-distance
consumes much less memory than a comparable pattern database.
1 INTRODUCTION
The (N
2
–1)-puzzle (Wilson, 1974; Korf and Taylor,
1996; Slocum and Sonneveld, 2006) represents an im-
portant benchmark problem for a variety of heuris-
tic search algorithms (Culberson and Schaeffer, 1994;
Korf, 1999). The task in the (N
2
–1)-puzzle is to rear-
range N
2
−1 square tiles on a square board of size
N ×N into a configuration where tiles ore ordered
from 1 to N −1 (see Figure 1 for an illustration of
the 8-puzzle). One blank position on the board allows
tiles to move; that is, a tile can be moved to the blank
position in one step.
It is well known that finding an optimal solu-
tion of the (N
2
–1)-puzzle, that is, finding the shortest
possible sequence of moves that reach the goal con-
figuration, is an NP-hard problem (Ratner and War-
muth, 1986; Ratner and Warmuth, 1990; Demaine
and Rudoy, 2018). Hence the problem is considered
to be a challenging benchmark for a variety of search-
based solving algorithms.
Various approaches have been adopted to ad-
dress the problem using search-based and other tech-
niques. They include heuristics built on top of pat-
tern databases (Felner and Adler, 2005; Felner et al.,
2007) that are applicable inside A* to obtain optimal
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7200-0542
solutions. Another approach is represented by solving
the puzzle sub-optimally using rule-based algorithms
such as those of Parberry (Parberry, 1995). The ad-
vantage of these algorithms is that they are fast and
can be used in an online mode.
Various attempts have been also made to combine
good quality of solutions with fast solving. Improve-
ments of sub-optimal solutions by using macro op-
erations, where instead of moving single tile to its
goal position, multiple tiles form a snake and move
together, were introduced in (Surynek and Michal
´
ık,
2017). Moving tiles together consumes fewer moves
than if tiles are moved individually. Another approach
is to design better tile rearrangement rules that by
themselves lead to shorter solutions as suggested in
(Parberry, 2015a). In the average case, these rule-
based algorithms can generate solutions that are re-
liably effective (Parberry, 2015b).
In this short paper, we present an attempt to solve
the (N
2
–1)-puzzle near-optimally or optimally with
high probability using a heuristic based on artificial
neural networks (ANNs) (Haykin, 1999). Our heuris-
tic is intended to be integrated into the A* algorithm
(Hart et al., 1968).
We try to directly calculate the estimation of
the number of moves remaining to reach the goal
configuration using ANN. Our experimentation with
the 15-puzzle shows that our heuristic called ANN-
Cahlík, V. and Surynek, P.
On the Design of a Heuristic based on Artificial Neural Networks for the Near Optimal Solving of the (N2–1)-puzzle.
DOI: 10.5220/0008163104730478
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2019), pages 473-478
ISBN: 978-989-758-384-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
473

=3
={1,2,…,8}
Solution sequence:
Less efficient solution
sequence:
Figure 1: An illustration of an initial and a goal configura-
tion of the 8-puzzle.
distance yields better estimations than the compara-
ble 7/8 pattern database (Felner et al., 2004). More-
over, although the ANN-heuristic is inadmissible,
sub-optimal solutions are produced by A* with ANN-
heuristic only rarely.
The paper is organized as follows; We first intro-
duce the (N
2
–1)-puzzle formally and put it in the con-
text of related works. Then, we describe the design
of the ANN-distance and finally, we experimentally
evaluate the ANN-distance as part of the A* algo-
rithm and compare it with A* using the 7/8 pattern
database on random instances of the 15-puzzle.
2 BACKGROUND
The (N
2
–1)-puzzle consists of a set of tiles T =
{1,2,...,N −1} placed in a non-overlapping way on
a square board of the size N ×N where positions are
numbered from 1 to N. One position on the board
remains empty. Then a configuration (placement)
of tiles can be expressed as an assignment c : T →
{1,2,...,N}.
Definition 1. The (N
2
–1)-puzzle is a quadruple
P
N
2
−1
= [N,T,c
0
,c
g
], where c
0
: T → {1,2,..., N}
is an initial configuration of tiles and c
g
: T →
{1,2,...,N} is a goal configuration (usually an iden-
tity with c
g
(t) = t for t = 1,2, ...,N −1.
The movements of tiles are always possible into
blank neighboring positions; that is, one move at a
time. The task in the (N
2
–1)-puzzle is to rearrange
tiles into desired goal configuration c
g
using allowed
moves. The solution sequence can be expressed as
σ = [m
1
,m
2
,...,m
l
] where m
i
∈ {L,R,U, D} repre-
sents: Left, Right, Up, Down movements for i =
1,2,...,l and l is the length of solution. We call so-
lution σ optimal if l is as small as possible.
3 RELATED WORK
The (N
2
–1)-puzzle represents a special case of a prob-
lem known as multi-agent path finding (MAPF) on
graphs, where instead of the N × N-board we are
given a graph G = (V,E) with so called agents oc-
cupying its vertices. There is at most one agent per
vertex, and similarly to the N ×N-board we can move
an agent into the empty neighboring position (vertex).
The task is to move agents so that each agent reaches
its unique goal position (vertex). Hence in the terms
of MAPF, the (N
2
–1)-puzzle is a MAPF instance on
a 4-connected grid of size N ×N with one empty ver-
tex where goals of agents are set according to the goal
configuration of the puzzle.
There are currently many solving algorithms for
MAPF and consequently for the (N
2
–1)-puzzle. Op-
timal A*-based algorithms include independence de-
tection - operator decomposition ID-OD (Standley,
2010) that tries to make use of not fully occupied
graph by dividing the set of agents into multiple in-
dependent groups that are solved separately.
ICTS (Sharon et al., 2013; Sharon et al., 2011) and
CBS (Sharon et al., 2015; Boyarski et al., 2015) on the
other hand view the search space differently not as a
graph of states. ICTS searches through various dis-
tributions of costs among multiple individual agents.
CBS searches the tree of conflicts between agents and
resolutions of these conflicts.
Besides search-based algorithms there are also
polynomial-time rule-based algorithms like BIBOX
(Surynek, 2009) and Push-and-Swap (Luna and
Bekris, 2011). They use predefined macro-operations
to reach the goal configuration. Solutions generated
by rule-based algorithms are sub-optimal.
Generally all MAPF algorithms rely on the fact
that the environment is typically not fully occupied
by agents in MAPF. Hence these algorithms cannot
benefit from their advantages in case of the (N
2
–1)-
puzzle as their is only one empty position.
As for the state-space search approach,
(M. Samadi, 2008) successfully used an artifi-
cial neural network as a heuristic function to predict
the optimal solution costs of the 15-puzzle. They
used the estimates of several pattern database heuris-
tics as inputs to their neural network. They used a
custom error function in order to penalise overshot
predictions, biasing the heuristic’s estimates towards
admissibility.
(M. Ernandes, 2004) also used an artificial neural
network to predict the optimal solution costs of the
15-puzzle, using only pebble positions as the input
features. However, they used a very small network
with only a single hidden layer of neurons, which re-
sulted in optimal solutions being obtained by IDA* in
only about 50% of cases.
(S. Arfaee, 2011) used a bootstrapping procedure
which allowed them to eventually solve random 24-
puzzle instances even without starting with a suffi-
NCTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
474

ciently strong heuristic. They started with an un-
trained artificial neural network, which they used as
a heuristic to solve a number of 24-puzzle instances.
Even though this procedure failed to solve most of the
instances within time limit, they used the handful of
solved instances to train the neural heuristic. Repeat-
ing this procedure several times resulted in obtaining
a very powerful heuristic.
4 DESIGNING A NEW
HEURISTIC
The heuristic search algorithm A* maintains the
OPEN list in which it stores candidate configura-
tions for further exploration. The algorithm always
chooses configuration c from OPEN with the mini-
mum g(c) + h(c) for the next expansion, where g(c)
is the number of steps taken to reach c from c
0
and
h(c) is the (lower) estimate of the number of remain-
ing steps from c to c
g
. In general, the closer h (from
below) is to the true number of steps remaining the
fewer total number of nodes the algorithm expands.
4.1 Artificial Neural Networks
In our attempt to design a heuristic that gives very
precise estimations we made use of a feed-forward
artificial neural network (ANN). The ANN consists
of multiple computational units called artificial neu-
rons that perform simple computations on their input
vectors~x ∈R
n
as follows: y(~x) = ξ(
∑
n
i=0
w
i
x
i
) where
~w ∈ R
n
is vector of weights, w
0
∈ R is a bias and
ξ is an activation function, for example a sigmoid
ξ(z) =
1
1+e
−λz
, where λ determines the shape of the
sigmoid.
Neurons in ANN are arranged in layers. Neurons
in the first layer represent the input vector. Neurons
in the second layer get the outputs of neurons in the
first layer as their input, and so on. So at every layer
neurons are fully interconnected with neurons from
the previous layer. Outputs of neurons in the last layer
form the output vector.
Usually we want an ANN to respond to given in-
puts in a particular way. This is achieved through the
process of learning (Rumelhart et al., 1986; Schmid-
huber, 2014) that sets the weight vectors ~w and biases
w
0
in individual neurons so that for a given input~x
i
the
network responds with an output ~y
i
in the last layer.
The network is trained for a data-set which contains
pairs of input ~x
i
and desired output ~y
i
. If the ANN
is designed well, that is if it has the proper number
of neurons in layers and if the data-set is representa-
tive enough, then the ANN can appropriately respond
even to inputs that are outside the training data-set.
We then say that the ANN generalizes well: this is
the goal in our design as it is unrealistic to train the
network for all possible configurations c of the (N
2
–
1)-puzzle that are as many as N! (N!/2 solvable ones).
4.2 Our Design
We tried various designs of ANNs for estimating the
number of remaining steps and eventually ended up
with the following topology. The underlying ANN for
the ANN-distance is a deep and fully-connected feed-
forward network composed of an input layer with 256
neurons, five hidden layers with 1024, 1024, 512, 128
and 64 neurons, and an output layer composed of a
single neuron.
The input layer corresponds to encoding of a puz-
zle configuration, that is we have 16 indexes of tiles
(one for the empty pebble), with each index one-hot
encoded resulting in a 256-dimensional input vector.
The output value is the estimate for the number of
steps required to reach the goal configuration in an op-
timal manner. The loss function we used is the mean
squared error of this estimate.
We used several state-of-the-art techniques to en-
hance the performance of the neural network. These
techniques include the Adam optimizer, ELU activa-
tion function, dropout regularization, and batch nor-
malization (Geron, 2017). Layer weights were ini-
tialized by He initialization (Geron, 2017).
4.3 Training Data and Training
Training was performed by Gradient Descent using
reverse-mode autodiff, a process also known as back-
propagation (E. Rumelhart, 1985). The neural net-
work was trained on a dataset of roughly 6 million
configurations and respective optimal solutions, with
the distribution corresponding to randomly permuting
the tiles on the board (unsolvable configurations were
discarded). The training data were obtained by the A*
algorithm with the 7/8 pattern database heuristic. All
algorithms and tests were implemented in Python
1
.
It is known that configurations corresponding to
odd permutations of tiles are unsolvable (Wilson,
1974). Therefore, half out of 15! configurations are
unsolvable. That is, the training configurations cov-
ers approximately
1
100000
of solvable configurations -
a very sparse covering yet leading to satisfactory re-
sults. The distribution of length of solutions in the
dataset used for training is shown in Figure 2 - it can
1
All experiments were run on an i7 CPU with 30 GB
of RAM and a NVIDIA Quadro P4000 graphics card under
Debian Linux.
On the Design of a Heuristic based on Artificial Neural Networks for the Near Optimal Solving of the (N2–1)-puzzle
475
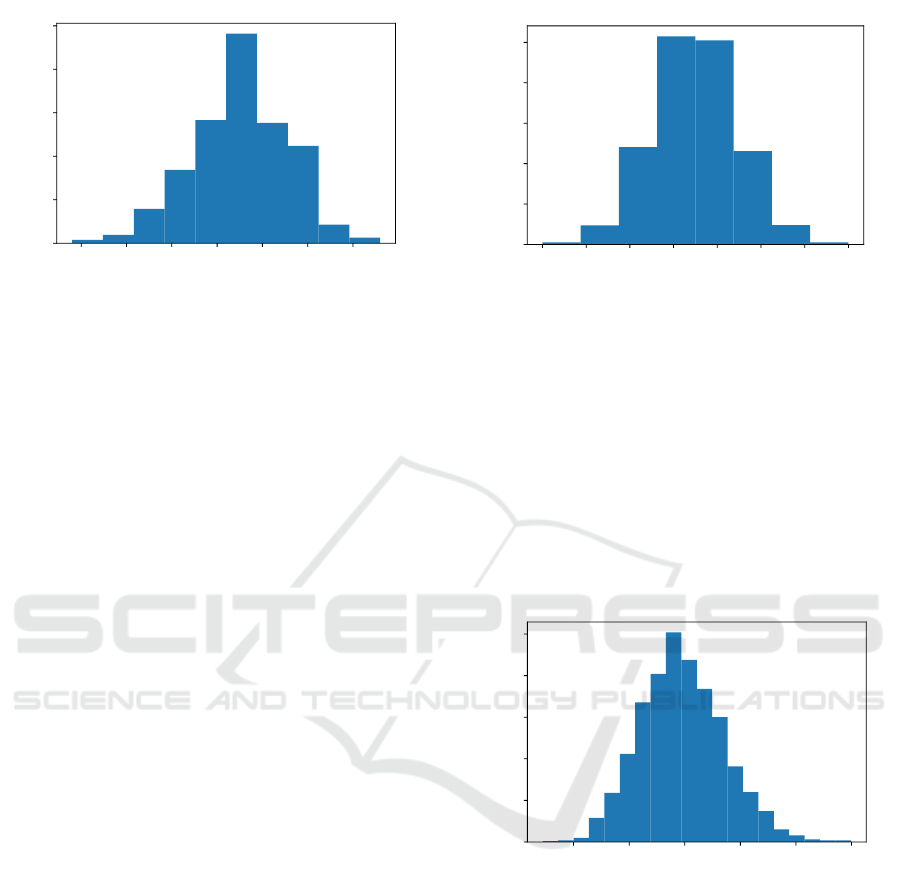
35 40 45 50 55 60 65
optimal solution length
0
100
200
300
400
500
Distribution of boards in dataset (histogram)
Figure 2: The distribution of lengths of solutions of in-
stances used for training.
be seen that the average length of a solution is roughly
about 52-53 moves.
The implementation of ANN and its training has
been carried out using the Keras library with Ten-
sorFlow backend (Chollet et al., 2015) and Numpy
(van der Walt et al., 2011) libraries.
5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
Our experimental evaluation was focused on competi-
tive comparison of ANN-distance against the 7/8 pat-
tern database. The 7/8 pattern database divides the
board into two disjoint parts: one consisting of 7 po-
sitions on the board and the other consisting of re-
maining 8 positions. For each configuration of 7 or 8
tiles we have a record in the database containing the
optimal solution length for a relaxed version of the
puzzle, where only 7 or 8 tiles respectively must be
placed in their goal positions. The relaxation ignores
the goal positions of the remaining tiles and hence
it is easier to solve. The value of the 7/8-heuristics
for a given configuration c is calculated as the sum of
lengths of optimal solutions for c|7 and c|8 from the
database (c|7 and c|8 denote c restricted on respective
disjoint part of the board). Such heuristic is admissi-
ble as shown in (Felner et al., 2004).
The tests were run on a test set of 1600 instances
obtained as random permutations. We focused on
measuring the performance of the heuristics sepa-
rately and when they are used as part of the A* al-
gorithm.
5.1 Competitive Comparison
The first series of tests show how closely the true dis-
tance from the goal configuration has been estimated
by the 7/8-heuristic and by the ANN-distance. Re-
−14 −12 −10 −8 −6 −4 −2 0
heuristic prediction error
0
100
200
300
400
500
PDB 7-8 Heuristic: distribution of errors on single predictions
Figure 3: The distribution of error of the 7/8-heuristic.
sults are shown in Figures 3 and 4 as the distributions
of errors with respect to the true minimal distances.
Clearly the ANN-distance is an inadmissible
heuristic according to the test. However the vari-
ance is greater in case of 7/8-heuristic. In other
words, the ANN-heuristic gives more precise estima-
tions of the true distance to the goal, yet it sometimes
overestimates. The question hence is whether over-
estimations of ANN-distance lead to significant devi-
ations from the optimal solutions when ANN-distance
is used as part of A*.
−4 −2 0 2 4 6
heuristic prediction error
0
50
100
150
200
250
ANN Heuristic: distribution of errors on single predictions
Figure 4: The distribution of error of the ANN-distance.
The positive result is that A* with ANN-distance
usually returns an optimal solution as shown in Fig-
ure 5. Only in a minority of cases it happens that the
solution length is slightly higher than the optimum.
Moreover the most important benefit of using
ANN-distance is that A* expands significantly fewer
nodes with this heuristic. The number of expanded
nodes as shown in Figure 6 and Table 1 is significantly
lower in case of A* with the ANN-distance heuristic
compared to A* with 7/8-heuristic.
Another important advantage of the ANN-
distance is the fact that it consumes much less space
than comparable pattern databases. A relatively good
performance can be achieved with just a small ANN,
NCTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
476

0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
solution length difference from optimal solution length
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
ANN Heuristic: distribution of solution length errors (A*)
Figure 5: The distribution of differences of lengths of so-
lutions returned by A* with ANN-distance from their true
optimas.
Table 1: The number of expanded nodes.
Instance A*(ANN) A*(PDB 7-8)
Easy 2517 4791
Medium 6392 15645
Hard 15756 45135
Extreme 384139 3367519
which consumes very little memory. On the other
hand, the pattern database must store all relevant
instances, which consumes a significant amount of
memory.
Altogether A* with the ANN-distance heuristic
represents a promising alternative to common admis-
sible heuristics.
0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000
expanded nodes
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
A*: Distribution of number of expanded nodes
ANN
PDB 7-8
Figure 6: The distribution of the number of expanded nodes
in A* with ANN-distance and A* with the 7/8-heuristic.
In addition to above experiments, we made mea-
surements of runtime, which is still higher for A* with
ANN-distance than in A* with 7/8-heuristic despite
the fact that ANN-distance is consulted much fewer
times than the 7/8-heuristic. There is however still
great room for improvement of the computation of the
output of ANN as it can be strongly paralleled or im-
plemented on a faster GPU.
6 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSION
This paper highly recommends the use of artificial
neural networks as the underlying paradigm for the
design of heuristics for the (N
2
–1)-puzzle. We de-
signed a heuristic called ANN-distance that estimates
for a given configuration the distance from the goal
configuration (the number of steps). Although the
heuristic is not admissible, it is relatively accurate and
does not significantly overestimate the true distance.
As a result, the ANN-distance usually yields an opti-
mal solution when used as a part of A*. Moreover,
since ANN-distance is relatively precise in its esti-
mations, the A* with ANN-distance expands much
fewer nodes than with other heuristics like 7/8 pattern
database. Another advantage of the ANN-distance is
that it consumes much less space than a comparable
pattern database.
We also considered the heuristic design that does
not compute exact distance towards the goal config-
uration but rather orders configurations in the OPEN
list relatively. That is, the ANN will only compare
two configurations and say which one out of the two
is better. Preliminary tests revealed that determining
the best node for further expansion is quite expensive
as it requires to evaluate the ANN’s output multiple
times.
As we continue our work, we plan to improve the
implementation of ANN-distance so that it will be
able to respond faster than pattern database heuris-
tics. We also plan to implement the bootstrapping
algorithm (S. Arfaee, 2011) and use it to solve 24-
puzzle instances.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported by GA
ˇ
CR - the
Czech Science Foundation, grant registration number
19-17966S. We would like to thank anonymous re-
viewers for their valuable comments.
REFERENCES
Boyarski, E., Felner, A., Stern, R., Sharon, G., Tolpin,
D., Betzalel, O., and Shimony, S. (2015). ICBS:
improved conflict-based search algorithm for multi-
agent pathfinding. In IJCAI, pages 740–746.
Chollet, F. et al. (2015). Keras. https://keras.io.
Culberson, J. C. and Schaeffer, J. (1994). Efficiently search-
ing the 15-puzzle. Technical report, Department of
Computer Science, University of Alberta.
On the Design of a Heuristic based on Artificial Neural Networks for the Near Optimal Solving of the (N2–1)-puzzle
477

Demaine, E. D. and Rudoy, M. (2018). A simple proof
that the (n2-1)-puzzle is hard. Theor. Comput. Sci.,
732:80–84.
E. Rumelhart, G. Hinton, R. W. (1985). Learning internal
representations by error propagation.
Felner, A. and Adler, A. (2005). Solving the 24-puzzle with
instance dependent pattern databases. In SARA-05,
pages 248–260.
Felner, A., Korf, R. E., and Hanan, S. (2004). Additive
pattern database heuristics. Journal of Artificial Intel-
ligence Research, 22:279–318.
Felner, A., Korf, R. E., Meshulam, R., and Holte, R. C.
(2007). Compressed pattern databases. J. Artif. Intell.
Res., 30:213–247.
Geron, A. (2017). Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-
Learn and TensorFlow, pages 275–312. First edition.
Hart, P. E., Nilsson, N. J., and Raphael, B. (1968). A for-
mal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum
cost paths. IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and
Cybernetics, SSC-4(2):100–107.
Haykin, S. (1999). Neural Networks: A Comprehensive
Foundation. Prentice Hall.
Korf, R. E. (1999). Sliding-tile puzzles and Rubik’s Cube
in AI research. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 14:8–12.
Korf, R. E. and Taylor, L. A. (1996). Finding optimal solu-
tions to the twenty-four puzzle. In Proceedings of the
Thirteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence and Eighth Innovative Applications of Artificial
Intelligence Conference, AAAI 96, IAAI 96, Portland,
Oregon, USA, August 4-8, 1996, Volume 2., pages
1202–1207.
Luna, R. and Bekris, K. (2011). Efficient and complete
centralized multi-robot path planning. In IROS, pages
3268–3275.
M. Ernandes, M. G. (2004). Likely-admissible and sub-
symbolic heuristics.
M. Samadi, A. Felner, J. S. (2008). Learning from multiple
heuristics.
Parberry, I. (1995). A real-time algorithm for the (n
2
-1)-
puzzle. Inf. Process. Lett., 56(1):23–28.
Parberry, I. (2015a). Memory-efficient method for fast com-
putation of short 15-puzzle solutions. IEEE Trans.
Comput. Intellig. and AI in Games, 7(2):200–203.
Parberry, I. (2015b). Solving the (n2 - 1)-puzzle with 8/3 n3
expected moves. Algorithms, 8(3):459–465.
Ratner, D. and Warmuth, M. K. (1986). Finding a shortest
solution for the N x N extension of the 15-puzzle is
intractable. In AAAI, pages 168–172.
Ratner, D. and Warmuth, M. K. (1990). Nxn puzzle
and related relocation problem. J. Symb. Comput.,
10(2):111–138.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., and Williams, R. J. (1986).
Learning representations by back-propagating errors.
Nature, 323:533–.
S. Arfaee, S. Zilles, R. H. (2011). Learning heuristic func-
tions for large state spaces.
Schmidhuber, J. (2014). Deep learning in neural networks:
An overview. CoRR, abs/1404.7828.
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Felner, A., and Sturtevant, N. R.
(2015). Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent
pathfinding. Artif. Intell., 219:40–66.
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Goldenberg, M., and Felner, A.
(2011). Pruning techniques for the increasing cost tree
search for optimal multi-agent pathfinding. In Sympo-
sium on Combinatorial Search (SOCS).
Sharon, G., Stern, R., Goldenberg, M., and Felner, A.
(2013). The increasing cost tree search for optimal
multi-agent pathfinding. Artif. Intell., 195:470–495.
Slocum, J. and Sonneveld, D. (2006). The 15 Puzzle.
Slocum Puzzle Foundation.
Standley, T. (2010). Finding optimal solutions to coopera-
tive pathfinding problems. In AAAI, pages 173–178.
Surynek, P. (2009). A novel approach to path planning for
multiple robots in bi-connected graphs. In ICRA 2009,
pages 3613–3619.
Surynek, P. and Michal
´
ık, P. (2017). The joint movement
of pebbles in solving the ( n
2
- 1 )-puzzle subopti-
mally and its applications in rule-based cooperative
path-finding. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent
Systems, 31(3):715–763.
van der Walt, S., Colbert, S. C., and Varoquaux, G. (2011).
The numpy array: A structure for efficient numerical
computation. Computing in Science and Engineering,
13(2):22–30.
Wilson, R. M. (1974). Graph puzzles, homotopy, and the
alternating group. Journal of Combinatorial Theory,
Series B, 16(1):86 – 96.
NCTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
478
