
Mobile Subject: M-Learning Student Profile
Laura Krimberg
a
, Anna Helena Silveira Sonego
b
, Leticia Rocha Machado
c
,
Ketia Kellen Araújo da Silva
1
d
and Patricia Alejandra Behar
1
e
Núcleo de Tecnologias Digitais Aplicadas à Educação (NUTED), Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul,
Avenida Paulo Gama 110, Porto Alegre, Brazil
Keywords: M-Learning, Mobile Subject, Mobile Devices, Education, Student, Technology, Social Media.
Abstract: This article aims to present the profile of M-Learning students, called Mobile Subject. For this, a mapping of
their characteristics related to mobile learning was carried out. The study establishes a relationship between
students engaged in educational activities through their mobile devices. For this purpose, questionnaires were
applied to students from two undergraduate and two extension courses, characterizing research as a case study,
with a qualitative-quantitative approach. The analysis consisted in the evaluation of the data, outlining the
profile of the Mobile Subject by identifying four main characteristics: Speed, Connectivity, Immersion in
Social Media and Multitasking and their respective elements. It is hoped that this research may contribute to
new discussions about the profile of the Mobile Subject student, proposing parameters and new strategies
focused on mobile learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, the use of mobile devices (smartphones
and tablets) has grown considerably and, due to its
democratization, M-Learning has become more
important in a wide range of fields (Bates, 2017).
However, the accentuated use of these devices in the
pedagogical process demands from the subjects
continuous learning in relation to the multiple
resources employed in such devices.
In this context, it becomes significant to
investigate the students profile, analyzing their
characteristics and their relation with mobile devices.
In addition, the integration of mobile technology,
such as smartphones and tablets, collaborates with the
motivation of the students through the interactions
and explorations made possible by the apps.
Thus, the article initially has a section that
presents "M-Learning and the new challenges". It
then identifies "the subjects and mobile digital
technologies”. Next, the methodology of this
research, the collected data, the discussion of the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9127-5223
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9238-1327
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4102-2225
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4722-8072
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6939-5678
results and, finally, the final considerations and
references used are presented.
2 M-LEARNING CHALLENGES
M-Learning emerges as a new educational possibility
for the use of mobile devices. Its concept, according
to UNESCO (2014, p. 8), "involves the use of mobile
technologies, alone or in combination with other
information and communication technologies (ICT),
to enable learning anytime, anywhere "Including
smartphones and tablets. Thus, it is observed that a
distinct concept of learning has emerged and is now a
reality. These technologies are characterized by the
possibility of spontaneity and customization, due to
their portability and lightness, being an informal
digital environment that complements the new profile
of the students of society (Behar, 2013).
According to the ICT Education research on the
Use of Information and Communication
Technologies in Brazilian private and public middle
236
Krimberg, L., Sonego, A., Machado, L., Araújo da Silva, K. and Behar, P.
Mobile Subject: M-Learning Student Profile.
DOI: 10.5220/0008344502360242
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2019), pages 236-242
ISBN: 978-989-758-382-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
and high Schools, 97% of students accessed the
Internet by cell phone in 2017, highlighting their
growth for educational purposes (CGIBR, 2018). In
addition, the data points to an increase in teachers'
access to the Internet through mobile devices, from
38% in 2013 to 97% in 2017. Therefore, a wide
dissemination of the Internet through these devices is
observed both in the use of resources by teachers in
the classroom and by students in different school
activities.
However, it is not possible to state that only the
use of mobile devices in the performance of
classroom activities enhances learning situations
(Sonego and Behar, 2015). It is observed that
“Resistance to mobile learning implementation and
adoption can be minimised by providing training to
the users (Chugh & Grandhi, 2012), i.e. students in
this case”. In this sense, the planning of the teacher,
involving the curricular content, didactic materials,
the use of the applications and the way that the mobile
devices are used become fundamental. Therefore,
exploiting the features of these devices, such as
shooting, recording and playing videos and audios,
downloading and annotating, editing texts,
transferring data, accessing Internet pages and
sending e-mail, can help in the learning process.
M-Learning can become a viable reality in the
teaching process, inside and outside the educational
environments (UNESCO, 2014). The profile of the
student inserted in the context of M-Learning is
presented below.
3 STUDENTS AND DIGITAL
TECHNOLOGIES: OUTLINING
A PROFILE
A systematic review was carried out with the authors
who investigate students and digital technologies. It
is verified that the characteristics of this profile have
been developed over the years and different
generations, together with the evolution of digital
technologies. It was possible to observe that several
characteristics of these subjects are related to the use
of mobile devices and the relation of this profile with
them. Table 1 highlights the evolution of these
concepts according to 14 authors, used as a basis for
the definition of Mobile Subject:
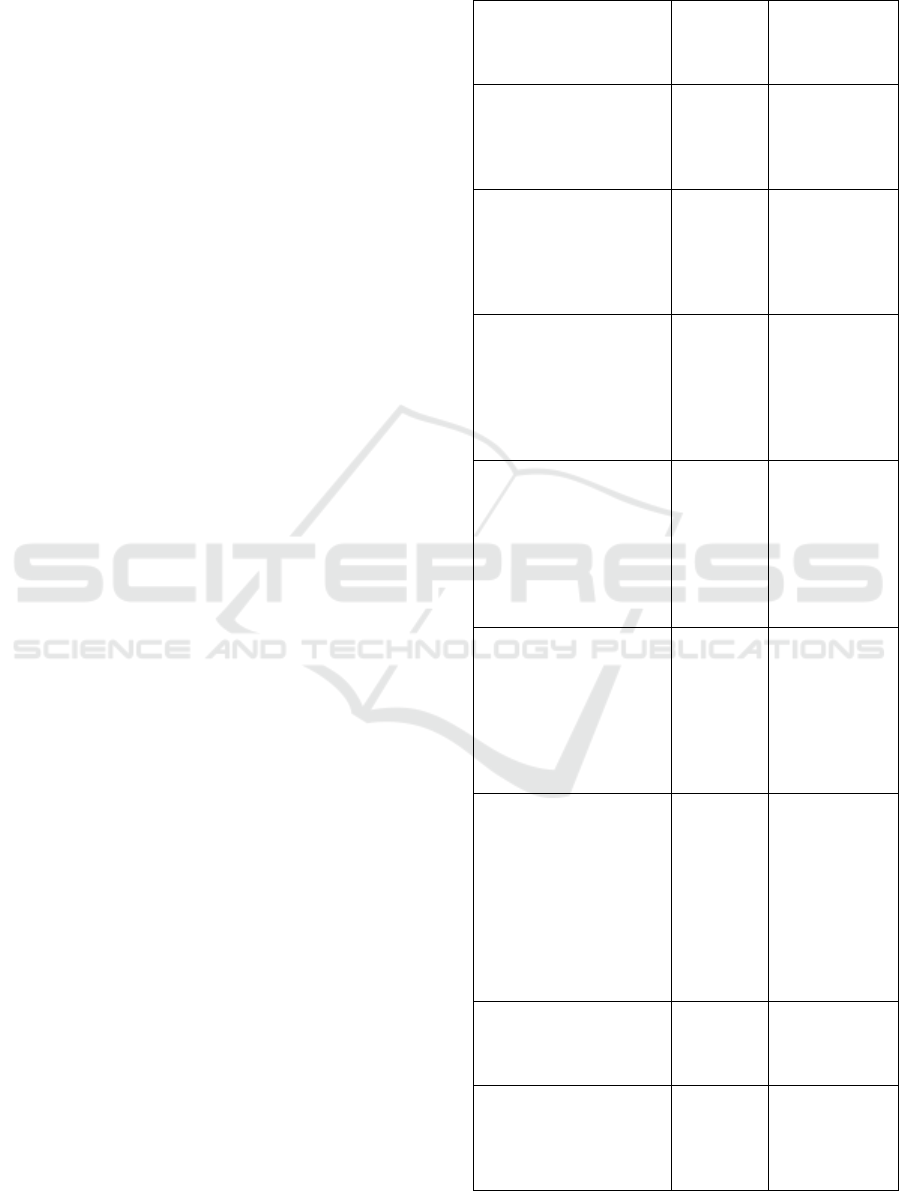
Table 1: Chronological evolution of different generations
and their relationship with technologies.
Characteristics of the
generation and its
relation with
technologies.
Author
Year of
publication
Speed in Internet
searches; multitasking;
linked to digital social
networks; need for
constant recognition.
Prensky
2001
Flexibility; individuality;
critical relationship with
the information found;
integrity; collaborative;
speed; creativity; need
for entertainment.
Tapscott
2010
Connected for most of
their lives; development
of social relationships
through mobile devices;
interact with information
from the Internet;
multitasking.
Palfrey and
Gasser
2011
Multitasking; speed, both
in handling of the devices
and in access to
information; need to feel
challenged or stimulated;
blind trust in digital tools;
smartphone addiction;
technological tutors.
Bortolazzo
2015
Familiar with new
technologies;
smartphones as additional
members of the bodies;
difficulty in solving
problems without the
technologies; need to be
connected all the time.
Vidal and
Dantas
2016
Difficulty in
systematizing
information; questioners;
anxious; constant need
for recognition;
impatient; individuality;
range of online
relationships; they can
not conceive of a world
without the devices.
Oliveira
2016
Invest in your own image
on the internet; need for
speed; competes with
others; impatient
Citelli
2016
Need to always be online;
difficulties in
communicating face to
face; user of online
information.
Patrão
2016
Mobile Subject: M-Learning Student Profile
237
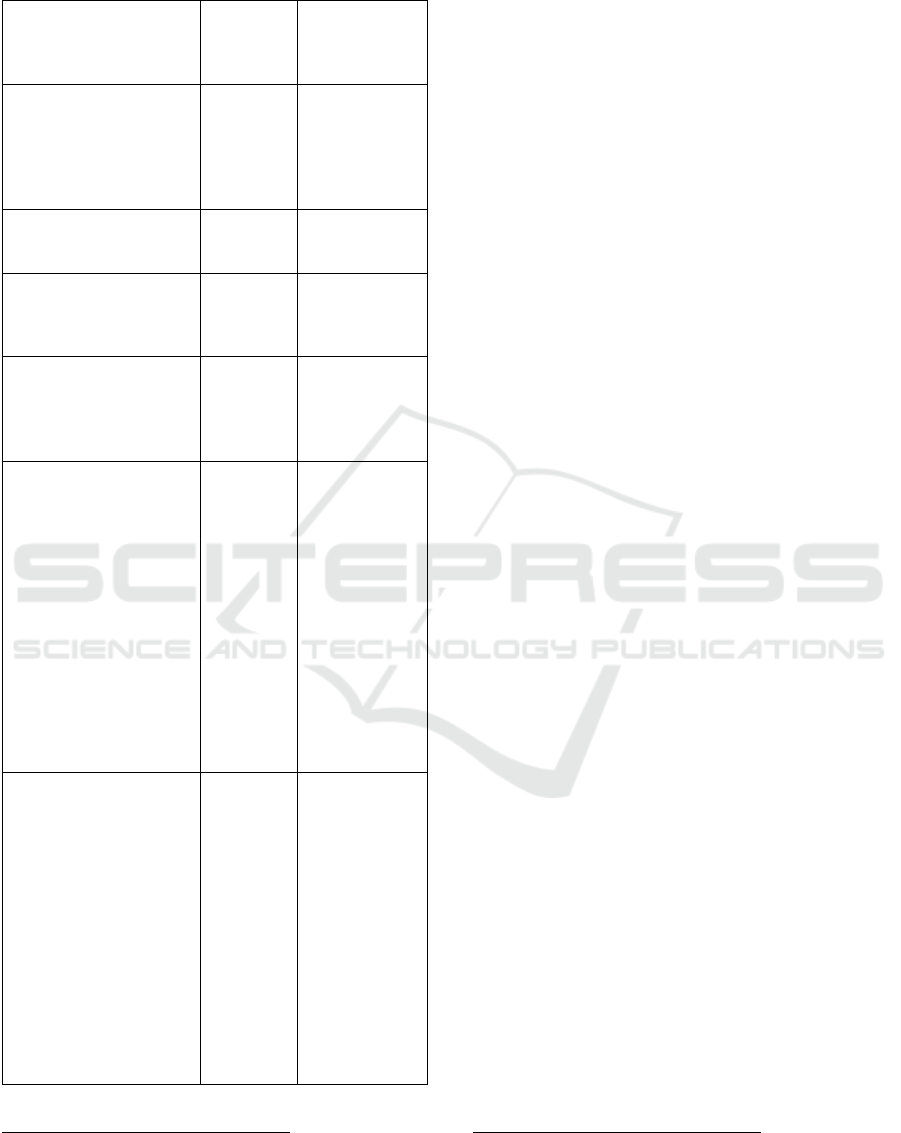
Table 1: Chronological evolution of different generations
and their relationship with technologies (cont.).
Characteristics of the
generation and its
relation with
technologies.
Author
Year of
publication
Able to participate in
learning experiences in
which they act in an
active way; view M-
Learning as the successor
to DE.
Ligi e Raja
2017
Immersed in social
networks; want to use
technologies on anything.
Bates
2017
They reject the traditional
rules of society; insecure;
extension of childhood to
adolescence.
Twenge
2017
Personal
entrepreneurship;
building your own
knowledge; autonomous
access to technologies.
Loureiro
and Klein
2017
They have learned to use
privacy in technology;
Will to change the world;
Mentality centered on the
good of all; preference
for learning that they can
apply in their real lives;
observers; they learn by
visualizing examples;
autonomous; learning at
their own pace; see
educators as resources;
need for jobs that bring
personal fulfillment and
happiness.
Seemiler
and Grace
2017
Accustomed to the use of
digital media; need to
learn to use technology to
enrich education; open to
different teaching
methods and
technologies; use their
mobile devices both to
pursue knowledge and to
build virtual learning
environments; participate
actively and responsibly
on the Internet, reflecting
on their studies and
qualification.
Witt and
Gloerfield
2018
6
The extension courses were Mobile Learning: mobile
devices use possibilities in the classroom and
Construction of Educational Applications: a focus on
Different approaches to the definition of these
subjects can be observed in the Table 1, and
constituting attributes related to their relation with
digital technologies. It is verified that elements such
as impatience, ability to use mobile devices, use of
media and social networks and their connection to M-
Learning are presented by the great majority of
authors. The description of the profiles identified by
them can contribute as a basis for the mapping and
comparison of data of the characteristics of Mobile
Subject. The methodology of the study is presented
below.
4 METHOD
This section presents the methodology of this
research, characterized as a case study, with a
qualitative-quantitative approach, having as main
strategies: theoretical survey, questionnaire
application and content analysis. The case study was
set up in two unique cases, using replication, that is,
the use of the same pattern of classroom activities and
applied questionnaires. The analysis was performed
from the triangulation of data. The research involved
students as subjects from undergraduate courses of
universities of Porto Alegre, city located in the state
of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
In total, 92 students participated in the research,
among those enrolled in the subjects and courses
offered
6
. The students’ ages where between 18 and 49
years, being 78.1% female. During these classes,
several topics related to the use of digital technologies
in education were presented. The content of these
classes was mobile learning and the creation of
educational applications for mobile devices. Initially,
it was discussed the use of these technologies in
education and the relation of the students with them,
to later apply a questionnaire related to mapping the
characteristics of these individuals. The steps outlined
in this study are detailed below:
1. Development of the theoretical basis: includes a
review of the literature on the subject of students'
profile and their relationship with technologies,
mainly considering their performance in distance
education and mobile learning.
2. Multiple case study: application of four cases,
using, for data collection, a questionnaire with
open and closed questions. This step aimed to map
mobile learning, conducted from April to July 2018 and
from September to November 2018, respectively.
KMIS 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
238

characteristics related to the profile of the
students. The cases were as follows:
a. Case 1: Media, Technologies and Education
subject, held in 2018/1, of the pedagogy course of a
university from Porto Alegre, Brazil;
b. Case 2: Media, Technologies and Education
subject, held in 2018/2, of the pedagogy course of a
university from Porto Alegre, Brazil;
c. Case 3: Extension course open to the academic
community in 2018/1, at a university in Porto Alegre,
Brazil;
d. Case 4: Extension course open to the academic
community in 2018/2, at a university in Porto Alegre,
Brazil;
3. Construction of the Mobile Subject profile: from
the analysis of the data collected in the cases through
content analysis (Moraes, 1999), with the objective of
identifying characteristics of the Mobile Subject
profile.
The next section details the results of each step.
5 ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
OF RESULTS
As it was presented, the study was based on the
theoretical survey of 14 authors that point out the
characteristics of the generations with respect to the
evolution and use of mobile digital technologies.
Afterwards, these concepts were compared to the
result of a characteristics' mapping of the Mobile
Subject profile with undergraduate students, based on
the methodology of Yin (2015) and Moraes (1999).
Four categories were defined, among them Speed,
Multitasking, Connectivity and Immersion in Social
Media. Figure 1 shows the description of each feature
and the complete profile of the Mobile Subject.
Thus, it was possible to observe different
characteristics of the Mobile Subject. Connectivity is
related to the difficulty in accomplishing problems
without access to the Internet and / or personal mobile
devices, depending on the task that the subjects
perform. Likewise, it is characterized by the ability to
know how to select information in a critical way,
mainly distrusting news spread by social networks
and registering on reliable news sites. As a result, they
become skilled in the search of sources cited in
portals of newspapers, magazines, academic articles,
etc. In addition, this element shows that the use of
smartphones and tablets in classrooms can contribute
to a greater attention and enthusiasm of this profile in
relation to the contents that are being presented.
However, it should be noted that educational
applications should be used as a complement to the
traditional classes for this profile, not neglecting the
importance of the teacher and his pedagogical
practices.
As for the Speed element, it is characterized by the
ease of this profile in operating his smartphone with
agile, performing functions quickly by the device. In
the same way, virtual search for educational activities
becomes much easier because of this feature,
available collection and the possibility of easily
finding keywords in a text. The learning of the Mobile
Subject is also influenced by this element, since it is
indicated a preference for activities and shorter
classes, that require less time. This demonstrates that
these individuals exhibit a need for minor activities
due to their lack of patience for very long tasks. Thus,
the use of technologies for learning is seen positively
for this type of student, since they show the need to
act with speed.
The concept of Multitasking, in this context, is
related to the subjects who can perform several
activities at the same time and / or alternate between
different functions. Related to this characteristic, it
was possible to observe that this profile, in addition
to being identified as multitasking, has the necessary
attributes to do multiple activities at the same time,
both virtually and in person. In addition, most
students visualize the potential of M-Learning
mobility because they can quickly switch between
different applications with different functions,
whether for study and research or for communication
and socialization.
Regarding the Immersion in Social Media
characteristic, this profile uses smartphones, mainly
to dialogue with others, either through e-mails or
social networks, reading class materials, access to
VLE, quick searches and entertainment. Moreover,
relationships built with other individuals through
these forms of conversation are not necessarily
superficial, and may be solid friendships, even with
the question of the time and space of the virtual world.
Regarding this element, it is also observed the use
of social networks to facilitate contact with people
closer to them and also individuals who live far from
their homes. In addition, it is verified the frequent
update of digital profiles through posting of different
media in these networks, with the objective of
contributing to the learning of other subjects. It stands
out mainly the possibility of developing collective
knowledge by conducting research, posting videos
and podcasts, exchanging ideas, reading and writing.
The final considerations are presented below.
Mobile Subject: M-Learning Student Profile
239
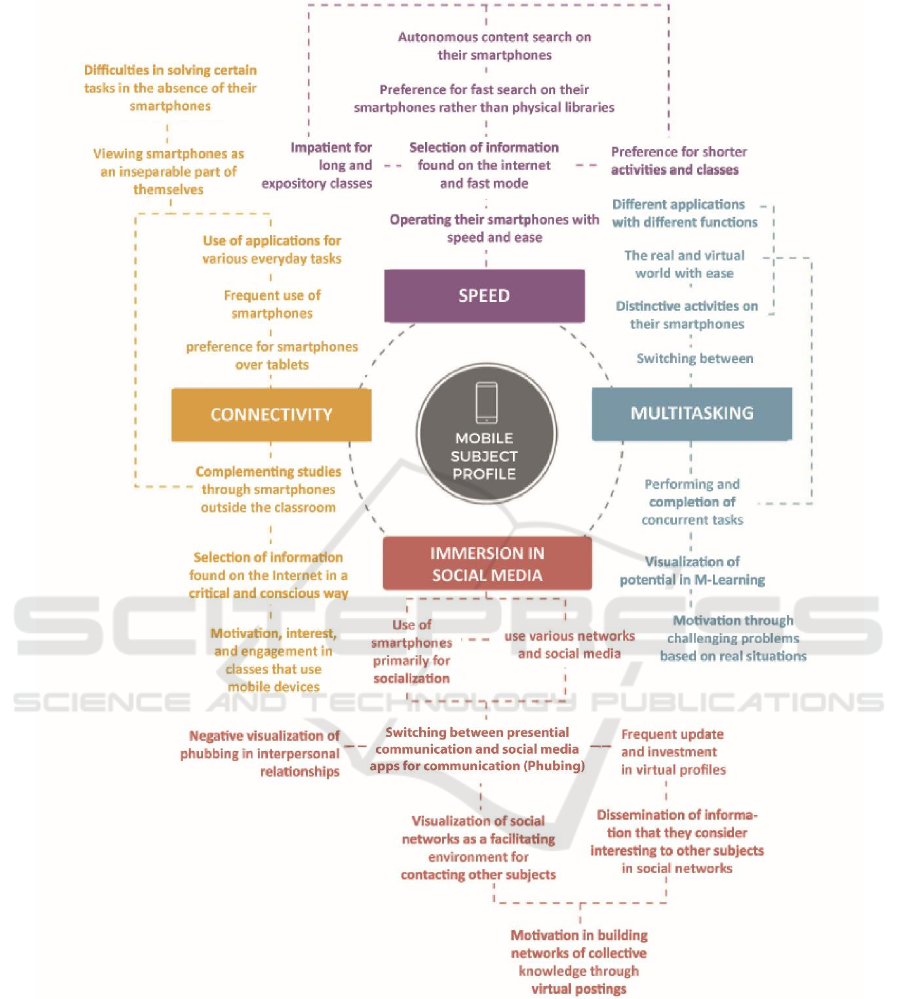
Figure 1: Profile of the Mobile Subject.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The main objective of this article was to define the
profile of the Mobile Subject, defining the
characteristics of these students. The data showed that
the students demonstrate attributes in common with
the theoretical reference, related to the profile of the
Mobile Subject and M-Learning. It is observed that
the demand for the development of knowledge for the
accomplishment of educational tasks through mobile
devices increases more and more, for the different
scopes of life. However, in M-Learning it is necessary
to develop didactic-pedagogical activities together
with the constant updating of the new applications
KMIS 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
240

and resources of mobile devices, in order to build
meaningful teaching-learning processes.
Based on these perspectives, Mobile Subject is
understood as a connected individual, fast, immersed
in social media and multitasking. In addition, it is a
profile that uses the mobile devices in their teaching
and learning process and that knows and relates to M-
Learning in a natural way.
It is understood that the knowledge of the Mobile
Subject's profile characteristics can contribute mainly
on the planning by teachers, identifying the behavior
of their students and enabling the development of
activities that use mobile devices focused on them. In
addition, it's noted the importance of this type of
study in the academic world, especially in what
concerns the Brazilian society, since several
international works related to the subject were
identified, but a small amount of national research in
this area.
In the same way, this study can help in the
qualification of professionals from different areas,
from the use of this profile as a basis for the creation
of educational applications for this public, identifying
parameters for the construction of these technologies.
These can include pedagogical aspects, such as the
division of content into modules and the availability
of videos, texts and animations of short duration, to
meet the difficulty of the profile in focusing on very
long activities. This way, it can be seen that the
teaching planning aligned to the use of the
applications, focusing on this profile, can contribute
to an engaging learning.
It is understood that motivation, interest, and
engagement in classes that use mobile devices, for
example, may be related to learning objectives, target
audience, and activities related to students' personal
interests.
This article noted the need for an investigation
about the relationship between students and M-
Learning, especially regarding the importance of
identifying the characteristics of this profile. It is
verified that observing their preferences and needs in
the use of educational applications for mobile
devices, such as smartphones and tablets, enables
teachers to develop motivational activities through
the construction of this type of technology. It should
be highlighted that the mapped indicators, in their
majority, have similarity to those that were pointed
out by several authors. However, those validated in
this research prioritized the importance of meeting the
specificities of the contemporary student profile.
The main result of this mapping was to investigate
the profile of the Mobile Subject and to understand
their needs regarding M-Learning. It is assumed that
this research can contribute to teaching practices in
relation to the development of students involved in
mobile learning. Finally, it is intended to conduct
future studies based on the profile of the Mobile
Subject in order to build pedagogical strategies for the
use of educational applications.
REFERENCES
Bates, T., 2017. Educar na Era Digital. Artesanato
Educacional. São Paulo. E-book. Viewed 20 November
2018,
http://abed.org.br/arquivos/Educar_na_Era_Digital.pdf
Behar, P. A., 2013. Competências em Educação a
Distância. Penso. Porto Alegre.
Bortolazzo, S. F., 2015. Narrativas acadêmicas e
midiáticas produzindo uma geração digital. Doctoral
thesis. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul.
Citelli, A. 2016. Educomunicação: Temporalidades e
Sujeitos. In: XXXIX Congresso Brasileiro de Ciências
da Comunicação, september. Intercom- Sociedade
Brasileira de Estudos Interdisciplinares da
Comunicação. São Paulo.
Comitê Gestor da Internet no Brasil (CGIBR), 2018. TIC
Educação: Pesquisa Sobre o Uso das Tecnologias de
Informação e Comunicação nas Escolas Brasileiras.
Núcleo de Informação e Coordenação do Ponto BR.
São Paulo. E-book. Viewed 27 december 2018,
https://www.cgi.br/media/docs/publicacoes/2/tic_edu_
2017_livro_eletronico.pdf
Grandhi, S., Chugh, R. 2012. Strategic Value of Mobile
CRM Applications: A Review of Mobile CRM at Dow
Corning and DirecTV. Artesanato Educacional. In:
International Conference on Innovation and
Information Management (ICIIM 2012), IPCSIT, v. 36,
LACSIT Press, Singapore.
Ligi, B., Raja, W. D. 2017. Mobile Learning in higher
education. In: International Journal of Research,
5(4)SE, 1-6, Granthaalayah, India.
Loureiro, C. B., Klein, R. R. 2017. Inclusão e
aprendizagem: contribuições para pensar práticas
pedagógicas. Appris. Curitiba.
Moraes, R, 1999. Análise de conteúdo. In: Revista
Educação, v. 22, n. 37, p. 7-32. Porto Alegre.
Oliveira, S. 2016. Gerações: encontros, desencontros e
novas perspectivas. Integrare. São Paulo.
Organização das Nações Unidas para a Educação
(UNESCO), 2014. Diretrizes políticas para a
aprendizagem móvel. Unesco. Brasília.
Palfrey, J. Gasser, U. 2011. Nascidos na Era Digital,
entendendo a primeira geração de nativos digitais.
Artmed. Porto Alegre.
Patrão, I. #Geração Cordão: A geração que não desliga!,
2016. Pactor. Lisboa.
Prensky, M. 2001. Digital natives, digital immigrants. In:
Lincoln, On The Horizon, v. 9, n. 5, oct. NCB
University Press.
Mobile Subject: M-Learning Student Profile
241

Seemiler, C., Grace, M. 2017. Generation Z: Educating and
Engaging the Next Generation of Students. In: About
Campus, InPractice, Wilet Library, p. 21-28, jul-aug.
American College Personnel Association and Wiley
Periodicals.
Sonego, A. H. S., Behar, P. A. 2015. M-Learning:
Reflexões e Perspectivas com o uso de aplicativos
educacionais. In: Anais do XX Congreso Internacional
de Informática Educativa (TISE), 2015, Santiago.
Nuevas Ideas en Informática Educativa TISE 2015.
Santiago, 2015. v. 11. p. 521-526.
Tapscott, D. 2010. A hora da geração digital: Como os
jovens que cresceram usando a internet estão mudando
tudo, das empresas aos governos. Agir Negócios. Rio
de Janeiro.
Twenge, J. M. 2017. Why Today’s Super-Connected Kids
Are Growing Up Less Rebellious, More Tolerant, Less
Happy--and Completely Unprepared for Adulthood--
and What That Means for the Rest of Us. Atria Books.
New York.
Vidal, P. V. C., Dantas, E. B. 2016. Dependência mobile: a
relação da nova geração com os gadgets móveis
digitais. In: Signos do consumo, v.8, n. 2, p. 67-84,
jul/dec. São Paulo.
Witt, C., Gloerfield, C. 2018. Mobile learning and Higher
education, In: Kergel, D. The Digital Turn in Higher
Education. Spring Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, p.
61-79.
Yin, R. K. 2015. Estudo de caso: planejamento e métodos.
Bookman. Porto Alegre.
KMIS 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
242
