
User Experience-based Information Retrieval from Semistar Data
Ontologies
Edgars Rencis
a
Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Latvia, 29 Raina blvd., Riga, LV-1459, Latvia
Keywords: Semistar Ontologies, Query Language, Information Retrieval, Query Translation.
Abstract: The time necessary for the doubling of medical knowledge is rapidly decreasing. In such circumstances, it is
of utmost importance for the information retrieval process to be rapid, convenient and straightforward.
However, it often lacks at least one of these properties. Several obstacles prohibit domain experts extracting
knowledge from their databases without involving the third party in the form of IT professionals. The main
limitation is usually the complexity of querying languages and tools. This paper proposes the approach of
using a keywords-containing natural language for querying the database and exploiting the system that could
automatically translate such queries to already existing target language that has an efficient implementation
upon the database. The querying process is based on data conforming to a Semistar data ontology that has
proven to be a very easily perceptible data structure for domain experts. Over time, the system can learn from
the user actions, thus making the translation more accurate and the querying – more straightforward.
1 INTRODUCTION
The time necessary for the doubling of medical
knowledge has been rapidly decreasing in the last
decades. While in the 1950s the doubling time of
medical knowledge was about 50 years, it has shrunk
to 3.5 years in 2010, and it is estimated to be only
about 73 days in 2020 (Densen, 2011).
The amount of gathered information rapidly
increases. Nowadays, even the smallest organizations
acquire vast amounts of data. Nobody complains
about the lack of information. However, a question
arises – is there a benefit from all this information?
Can we extract some knowledge from it?
What is knowledge, after all? It is the information
that one can apply to make decisions. There is no use
of the information in the database if nobody knows
that it is there and thus cannot extract any valuable
knowledge from it. To extract knowledge from the
information, we usually hire system analytics to do
the job. They acquire the IT skills necessary for
inspecting the database, understanding its structure,
retrieving the information and discovering the needed
knowledge by using the SQL or another querying
language.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1606-4944
However, it is not always the best option to hire a
system analyst. The real users in need of the
knowledge are those who make the decisions in the
organization. If we take a hospital as an example
organization, those end-users would be physicians,
ward managers, hospital managers. To make a
decision, such an end-user would need to receive
answers to his/her questions. To get those answers,
they need to consult the system analyst and ask
him/her to find the necessary information in the
database for them.
Several problems may arise here. Firstly, the
domain experts often lack any idea about what kind
of data are gathered and are available in the database
to start with, what kind of information can they ask
from the database and what kind of knowledge can be
extracted. To clarify these questions, they have to
interview the system analyst. It can be a one-time
engagement, but it is nevertheless time-consuming,
and it does not necessarily cover every aspect of what
domain experts want to know, because the system
analytic will only provide answers to the questions
asked, and the domain expert can miss some vital
question that could be beneficial for the next time.
Besides, the process would have to be repeated for
Rencis, E.
User Experience-based Information Retrieval from Semistar Data Ontologies.
DOI: 10.5220/0008345004190426
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2019), pages 419-426
ISBN: 978-989-758-382-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
419

every new domain expert who starts to work in the
organisation.
Secondly, even if one has understood the structure
of the database and the types of questions he/she may
ask, it takes some time for receiving the answers to
particular questions. The system analytic can be
overloaded with work, and answering all the
questions from the domain experts can take hours or
even days in some cases.
Thirdly, not every domain expert even has access
to such a resource as the system analytic. The hospital
manager more likely has an authority to give
commands to the system analytic, but not every
physician has such a privilege. Therefore, this process
may be even more time-consuming if at all possible
for them.
Finally, hiring a system analytic also costs a lot,
and exploiting this resource just for answering those
types of questions might not be the best way of
spending the money.
Taking into account all of the abovementioned
observations it is clear that it would be much better if
the domain expert could access the database and
query it him/herself – to understand its structure, to
form questions and to understand the answers to those
questions. This ability could undeniably accelerate
the information retrieval process, which in turn would
speed up the decision-making process that is one of
the most critical aspects of the operation of any
organisation.
There have been many attempts to solve the
abovementioned problem. The most popular of them
has been the introduction of the SQL in 1974
(Chamberlin, 1974). The original goal of this
language has been precisely the same – to make
querying possible for non-programmers. There was
the slogan that every housewife will now be able to
work with databases. However, the experience shows
that this goal has not been fulfilled – hardly any
domain expert that is not an IT specialist is able to use
the SQL nowadays because it is too technical and
complicated. It is so partly because it is based on the
relational database that is not a very easily-
perceptible data structure for end-users. Other related
work is inspected in Section 2.
In this paper, it is proposed to retreat from the
traditional approach of storing the data in the form of
the relations database and instead to use another data
format for storing the data – the Semistar data
ontology. This data structure is described in Section
3. Upon the Semistar data ontology, it is possible to
develop a simple querying language using the main
principle of the SQL – to create sentence templates
where the end-user would insert specific concepts of
the underlying data structure. The query language has
already been implemented, and Section 4 provides an
insight into it. It is also explained here what are the
most significant flaws of the language in terms of its
practical usage. To avoid these flaws, it is proposed
to write queries in the natural language. These queries
would then be translated automatically to the
abovementioned language. Section 5 describes the
main idea of the translation process. It is also
explained here how the user would be able to
ascertain that his/her query has been interpreted
correctly by the system and how the system could
learn from the user experience over time.
2 RELATED WORK
The first related work in the field is dated by the year
1974 when the SQL was created. It was the first
attempt to allow non-professionals to query their
databases. As already stated in Section 1, this attempt
has not been as successful as it could have been.
Much effort has been devoted to making the
querying easier so that it would become available to
end-users. There are several ways how this can be
done. One way is to use graphical query languages
that allow users to create queries by clicking the
mouse and entering only some specific concepts by
the keyboard. Such languages can be based either on
SQL or on its analogue for RDF data – the SPARQL.
Some examples of the graphical query languages
based on SQL or SPARQL are ViziQuer (Zviedris,
2011), Graphical Query Designer (Smart, 2008), SAP
Quick Viewer SQVI (Kaleske, 2011) and others.
Another way how to make querying easier is to
approach the natural language. There are many
solutions that are based on the idea that one can use
more or less strongly controlled natural language for
formulating queries. There have been attempts to
develop a Natural Language Interface to Databases
(NLIDB) which is to be used to querying relational
databases (Androutsopoulos, 1995; Li, 2014; Llopis,
2013; Papadakis, 2011; Popescu, 2004).
It is also possible to combine the two
abovementioned approaches allowing one to build a
part of the query graphically and a part of it textually.
It allows avoiding to some extent the biggest
drawback of fully graphical languages – their lack of
expressiveness – while at the same time the user can
create the largest and the most complicated part of the
query graphically. A couple of examples of this
approach are the NaLIR (Fei, 2014) and the DataTone
(Gao, 2015) tools.
KDIR 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
420

It must be noticed that most of the
abovementioned solutions are built exclusively for
the English language or in the best case – for some
other prominent languages. In this paper, the focus is
put on developing the tool for the needs of the
hospitals of Latvia, where the domain experts mostly
use the Latvian language, which is very different from
English. The English language belongs to the analytic
language family, while the Latvian language is highly
synthetic. It means that in English one primarily
conveys relationships between words in sentences by
way of helper words (such as particles or
prepositions) and word order. However, in Latvian,
this is done by changing the form of a word to convey
its role in the sentence. Therefore, it is not always
possible to exploit the principles that are valid for
analytic languages to synthetic languages.
3 STAR AND SEMISTAR DATA
ONTOLOGIES
As was already mentioned in Section 1 there is not
much hope to find a solution to the problem of natural
language-based querying for relational databases if
this has not been done for the last 40 years since the
emergence of the SQL. Therefore, it is worth
considering other data formats in the search for one
that would satisfy the following two conditions
simultaneously:
1) It is not so trivial as to be of no use in practical,
real-world applications;
2) It is simple enough so that there could be a hope
of solving the abovementioned problem of natural
language-based querying.
3.1 Star Data Ontology
One example of such data structure that satisfies the
two abovementioned conditions is the Star data
ontology. It has been introduced in (Barzdins, 2014-
1; Barzdins, 2014-2) and later refined in (Barzdins,
2016-3). The main idea of the Star ontology is that it
always contains one so-called central class which
serves as the starting point for “reading” the ontology.
From the central class, there are outgoing associations
to other classes, but only one type of associations is
allowed – the “consists of” association. The same
type of associations can be formed also further on
from those classes to other classes and so on, as long
as the associations do not form loops. All the classes
of a Star ontology together form a tree- or a star-like
structure with one class being the centre of the star.
Finally, there is also a specific condition put on the
cardinalities of the associations – the cardinality of
the proximal end of the association (the end that is
nearer to the centre of the star) is exactly one while
the cardinality of its distal end is *.
It can seem at first that such a data structure is very
limiting and that it does not have much practical use.
However, the reality is just the opposite. This
phenomenon has been observed in (Barzdins, 2016-
1; Barzdins, 2016-2) where the authors admit that
“even in more general cases when some ontology is
not a semistar ontology, one can usually find an
important subset of it to comply to principles of
semistar ontology. We can always think of a semistar
ontology as a subject-oriented ontology where the
role of the subject can be performed by a patient (in
case of the medical management domain), a customer
(in case of some service domain), etc.” It is admitted
that the practice shows that the Star data ontology (or
more precisely – the Semistar data ontology which is
explained in Section 3.2) is very suitable for such
subject-oriented domains, i.e. the domains where
there is always one central subject around which
everything else is sorted out. The hospital
management domain is an excellent example of a
subject-oriented domain because everything is sorted
around the patient being its central subject. Therefore,
the hospital management domain serves very well as
the base for developing the natural language-based
query language.
3.2 Semistar Data Ontology
The Semistar data ontology is a data structure that
allows a small derogation from the standard definition
of the Star ontology (Barzdins, 2016-1). In the
Semistar data ontology, some additional classes
(called classifications and registers) are allowed
besides the basic classes that form the basic star-like
structure. Those classes are, in fact, nothing more
than enumerations that can serve as the data types for
attributes of the basic classes. An example of a
Semistar data ontology of the medical management
domain is seen in Figure 1.
Practice shows that the Semistar data ontology is a
data structure that is very easily-perceptible by end-
users (Rencis, 2018-3). It contains concepts that are
well known to the domain expert, and it allows
avoiding the usage of technical details such as the
names of associations because there can only be one
association between any two classes of the ontology.
Therefore, the Semistar data ontology serves as an
appropriate basic data structure upon which one can
build a more straightforward query language.
User Experience-based Information Retrieval from Semistar Data Ontologies
421
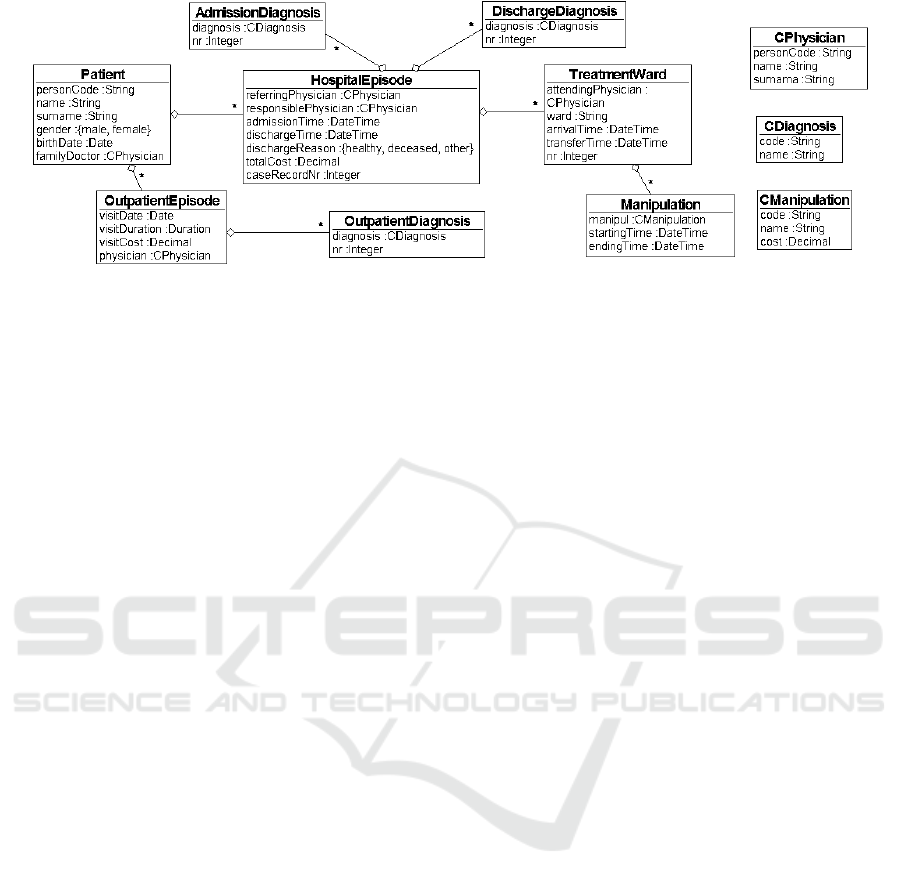
Figure 1: Semistar data ontology for the hospital management domain.
4 QUERY LANGUAGE FOR
SEMISTAR ONTOLOGIES
The first step in the way towards allowing the domain
experts to understand the data located in the database
of the organisation is to develop a data structure that
is easily perceptible to him/her. As was concluded in
Section 3, the Semistar data ontology can be exploited
for this purpose. If the domain expert now
understands what data are located in the database,
he/she is prepared for the next step – querying those
data.
To be able to query the database, one must use a
query language that is understandable by that
database. To fulfil the goal of simple querying, a
natural language-based query language (further in the
text – the Base Language) was implemented because
the natural language acquires all the required features
simultaneously – it is easily perceptible by the end-
user, it is convenient to use, and it is sufficiently
expressive. The approach of the SQL was used in
developing the query language, i.e. several sentence
templates were developed that define the level of
control of the natural language. The user would then
be able to fill in the missing parts in those templates
with particular concepts of the underlying Semistar
data ontology, thus formulating queries as sentences
in the controlled natural language. This approach,
although being very similar to SQL, is, however,
much easier for the end-user because the underlying
data structure (being the Semistar data ontology
instead of the relational database) is much more
intuitive and easily perceptible.
We will not go into more detail in this paper about
how these sentence templates look like. A full
description of the Base Language and the templates
can be found in our previous work (Rencis, 2018-3).
To gain some insight and to better understand the
query translation process described in Section 5,
below are some examples of valid queries in the Base
Language that are based on the Semistar data
ontology seen in Figure 1.
COUNT Patients WHERE EXISTS
HospitalEpisode WHERE
referringPhysician=familyDoctor.
SUM totalCost FROM
HospitalEpisodes WHERE
dischargeReason=healthy AND
birthDate.year()=2012.
SELECT FROM HospitalEpisodes
WHERE dischargeReason=deceased
ATTRIBUTE
responsiblePhysician.surname ALL
DISTINCT VALUES.
It can be noticed that these queries are indeed
quite readable by a domain expert, mainly thanks to
the fact that it lacks technical details like the
association and role names and the cardinalities.
However, to justify our belief about the usability
of the language by the domain experts, we conducted
an experiment involving students of the Faculty of
Medicine, University of Latvia. Those students are
the future target group of our language and tool.
Firstly, we delivered a two-hour-long lecture to the
students about the general concepts like the concept
of the ontology, the Semistar data ontology and the
particular ontology of the hospital management
domain. Also, the Base Query Language was
explained, and the tool implementing the language
was demonstrated.
Afterwards, the students were asked to perform
two tasks – the reading task and the writing task. In
the reading task, they were given sentences in the
Base Language, and they had to answer in their own
words what is asked to the database in those queries.
In the writing task, they were given informal
descriptions about what information should they get
KDIR 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
422

from the database, and they had to write queries in the
Base Language within the provided tool to get
answers to those questions.
The results were ambiguous. One the one hand,
we got affirmation for the fact that the Base Language
is indeed very readable because almost all of the
students did excellently in the reading task. On the
other hand, we understood that the language is not yet
handy for creating queries because only three of 15
students had been able to do the writing task more or
less well. The results of the experiment are described
in more detail in our previous work (Rencis, 2018-1).
This experiment proved our hypothesis that the
Base Language is very well readable, but not so well
writable. That meant we had to go one step further in
the process of formulating queries, i.e. to approach
the natural language more closely. In other words, we
had to lessen the level of control of our query
language.
5 QUERY GENERATION FROM
KEYWORDS-CONTAINING
TEXT
The main idea how to lessen the level of control of
the query language thus making the language easier
to use by the domain experts is to allow end-users
writing queries in the natural language that contains
only specific keywords. A translator could then be
built that translates this keywords-containing text into
a valid query in the Base Language. For example, the
end-user could write such a query:
Can you, please, find for me those
patients who have been hospitalised
at least 2 times?
This sentence is completely normal in the English
language. Of course, it does not comply with any of
the sentences templates of the Base Language.
However, it contains keywords from which we can
guess what the user had meant by this query. For
example, the word “find” is probably a synonym to
the word “show” that is one of the keywords of the
Base Language. The word “patients” most certainly
means the class “Patient” of the underlying ontology
(by the way, as can be seen in the query examples
above, also in the Base Language it is allowed to
exploit different forms of keywords and concepts, as
well as it is allowed to have some typos which can be
corrected automatically). Next, the word “who” has
the same meaning as our keyword “where”. The
concept “hospitalised” is a bit more complicated, and
it could mean the phrase “exists HospitalEpisode”.
Finally, “at least” denotes the logical operator “>=”,
and the keyword “times” is perhaps a synonym of our
keyword “count”. Everything else can be regarded as
a noise which can thus be omitted.
As a result, the abovementioned query could be
translated automatically to the following query in the
Base Language:
SHOW Patients WHERE (COUNT
HospitalEpisodes) >= 2.
The translation process is described in more detail
in (Rencis, 2019).
5.1 The Concept of Entropy
The translation example described at the beginning of
Section 5 is, of course, very simplified. In the real
world, it is not always guaranteed that the system will
understand the query of the user unequivocally. For
example, the user might not have used the keywords
that the system understands. Moreover, he/she might
have used too many keywords so that the system can
understand the query in several different ways.
Finally, some keywords are even ambiguous
themselves – they can mean different things in
different contexts.
For example, one can perceive the keyword “is”
as a synonym of the keyword “exists” which might
not be so natural to the end-user. Thus, the user could
write a phrase “there is HospitalEpisode” instead of
the phrase “exists HospitalEpisode”. However, the
same keyword “is” can also be found in other
contexts, e.g. in the phrase “is greater than 2”. The
translation of the keyword “is” would be different in
those two cases. The conclusion here is that in most
cases, the query written in the natural language can be
translated to the Base Language in more than one
way.
To cope with the several possible translation
results, we have introduced the concept of the entropy
being the opposite of the notion of the plausibility of
the query (or more precisely – of its translation
result). The entropy characterises the level of disorder
of the original query, i.e. the distance of the original
query to its translation into the Base Language. In
other words, the entropy indicates how many
corrections have to be made in the original query in
order to turn it into a valid query of the Base
Language. Let us call those corrections the primitive
operations. Some examples of such primitive
operations can be the correction of a typo in a
keyword, swapping words in the part of the sentence,
swapping parts of the sentence or adding missing
keywords. If the query written by the user is already
executable in the Base Language, its entropy is zero.
User Experience-based Information Retrieval from Semistar Data Ontologies
423

The greater the distance from the original query to the
executable query in the Base Language, the higher its
entropy.
The entropy is calculated for objects of various
granularities. Firstly, it is calculated for the keywords
found in the original query taking into account the
typos in them. Secondly, the entropy is calculated for
the parts of the sentence taking into account the
entropies of individual words of that part and the
mutual sequence of the words. Thirdly, the entropy is
calculated for the sentence taking into account the
entropy of its parts and the mutual sequence of those
parts, as well as the entropy of the sub-sentences of
the sentence if the sentence contains any sub-
sentences (e.g. the sentence example at the beginning
of Section 5 contained the sub-sentence “count
HospitalEpisodes”).
Finally, there is a list of primitive operations that
turns the original query into an executable query in
the Base Language. Every primitive operation has a
penalty that is added to the query translation result
when the operation is applied in the translation
process. If there is an ambiguity so that the original
query can be understood in several different ways
(which is the case in most situations), the translation
process branches, and the translation tree is made.
The leaves of the translation tree represent all
possible translation results for that particular original
query. Each of those results contains a valid query
that is executable in the Base Language and a list of
primitive operations (and their total entropy) that has
been applied to obtain the result.
5.2 Learning from User Experience
Every user is unique in his/her way of formulating
queries in the natural language. Every user exploits
different concepts, different forms of concepts and
different phrases, and every user builds sentences
differently. Some of those phrases can be closer to the
requirements of our existing strongly-controlled Base
Language, and others are not so close. The closer to
the Base Language is the particular sentence the user
has formulated, the lesser amount of corrections
needs to be performed in order to translate the
sentence into a valid query in the Base Language, and
the lesser is the entropy of the translation result (thus
the result is shown higher in the list of all the possible
translation results for that query). However, if a user,
when offered the list of the translation results,
regularly picks a result that is not the highest in the
list (i.e. that does not have the smallest entropy), it
would be beneficial to adapt to the specifics of the
user and to learn from his/her habits so that next time
the correct translation result is ranked higher in the
list of all the results.
The experiment described in Section 4 proved that
the Base Language is very well readable by the
domain experts. This knowledge has allowed us to
rank the translation results in cases of ambiguity
when there is more than one result and to offer the list
of those results back to the user so that he/she can
choose the one that represents the query he/she has
really intended to ask. The user is able to read the
provided translation results in the Base Language and
to pick the correct one from them. To implement the
facility of teaching to the system the specifics of the
user, the penalties of the primitive operations that
have been applied to obtain the correct translation
result (i.e. the one that the user has picked) are slightly
decreased. That way, the resulting entropy for such
type of queries will be slightly smaller next time when
the same user will formulate the sentence in the
natural language using the same specific habits.
A special case is the correction of typos. The
penalty of correcting a typo in a keyword is not
decreased in the abovementioned situation, but
instead, the word that is supposedly written with a
typo is added to the list of synonyms for the particular
keyword. The justification for this approach is the
specificity of the Latvian language. As was described
in Section 2, Latvian is a synthetic language, which
means there can be different endings of words
depending on the role the word takes in the sentence.
Therefore, it is not right to consider only one of those
different forms of the word the correct one and to
assume that all other forms are typos. Since all the
forms of the keyword that the user exploits are being
stored as the synonyms of that keyword, the system
learns those forms as valid keywords over time, and
not considering those forms as typos will again
decrease the entropy of the whole query.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Knowledge discovery and information retrieval are
becoming progressively more topical since the time
necessary for the doubling of medical knowledge is
rapidly decreasing and will presumably reach only 73
days in 2020 (Densen, 2011). In such conditions, it is
of utmost importance to ensure that the information
does not flow in only one direction – to the database
–, but that the information located in the database is
also accessible by domain experts who could exploit
it in their decision-making process. The information
retrieval process must be fast, convenient and
KDIR 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
424

straightforward, but it often lacks at least one of these
properties.
This paper proposes an approach where the
domain experts are able to formulate their queries in
the natural language sentences that contain particular
keywords. The system would then translate the query
into one or more valid queries in the Base Language
that is also based on the natural language and that
already has an efficient implementation. The Base
Language has proven to be very easily readable by
non-IT specialists (i.e. the domain experts of the
medical management domain). Thus the domain
expert would be able to understand the translation
results and to select the correct one, that is, the query
he/she had intended to formulate.
For it to be possible to implement such natural
language-based querying, this paper proposes a data
schema called the Semistar data ontology that
alleviates the process of formulating queries. The
practice has shown that such a data structure is
prevalent in subject-oriented domains such as
hospital management.
To test the base query language, a tool was
developed that allows users to create queries and to
receive answers to them. An experiment was
conducted where the tool was taught to a group of
students. After having worked with the tool and the
Base Language for some time, they acknowledged the
language as very well readable. Therefore, it justifies
the approach of showing the list of the query
translation results in the Base Language back to the
user so that he/she can point out to the correct one. As
a result, the system learns from the user experience so
that the correct query will have higher credibility (i.e.,
smaller entropy) next time.
This paper describes the work in progress that
continues the work described in (Rencis, 2018-2). A
prototype implementing the natural language-based
querying has been developed, as well as the
calculation of the entropy for the query translation
results has been implemented. The user experience-
based learning is a part of the future work that has yet
to be implemented.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the ERDF PostDoc Latvia
project Nr. 1.1.1.2/16/I/001 under agreement Nr.
1.1.1.2/VIAA/1/16/218 “User Experience-Based
Generation of Ad-hoc Queries From Arbitrary
Keywords-Containing Text”.
REFERENCES
Androutsopoulos, I., Ritchie, G. D., Thanisch, P. 1995.
Natural language interfaces to databases – an
introduction. In: Natural Language Engineering, 1(1),
29-81. DOI: 10.1017/S135132490000005X.
Barzdins, J., Rencis, E., and Sostaks, A. 2014. Data
Ontologies and Ad Hoc Queries: a Case Study. In: H.M.
Haav, A. Kalja, T. Robal (Eds.) Proc. of the 11th
International Baltic Conference, Baltic DB&IS, 55-66,
TUT Press.
Barzdins, J., Rencis, E., Sostaks, A. 2014. Fast Ad Hoc
Queries Based on Data Ontologies. In: H.M. Haav, A.
Kalja, T. Robal (Eds.), Frontiers of AI and
Applications, Vol. 270, Databases and Information
Systems VIII, 43-56, IOS Press.
Barzdins, J., Grasmanis, M., Rencis, E., Sostaks, A.,
Barzdins, J. 2016. Self-service Ad-hoc Querying Using
Controlled Natural Language. In: G. Arnicans et al.
(Eds.) Proc. of the 12th International Baltic
Conference, Baltic DB&IS, 18-34, CCIS 615.
Barzdins, J., Grasmanis, M., Rencis, E., Sostaks, A.,
Barzdins, J. 2016. Ad-hoc Querying of Semistar Data
Ontologies Using Controlled Natural Language. In:
Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications.
Databases and Information Systems IX, Vol. 291, IOS
Press, 3-16. DOI: 10.3233/978-1-61499-714-6-3.
Barzdins, J., Grasmanis, M., Rencis, E., Sostaks, A.,
Steinsbekk, A. 2016. Towards a more effective
hospital: helping health professionals to learn from their
own practice by developing an easy to use clinical
processes querying language. In: International
Conference on Health and Social Care Information
Systems and Technologies, Procedia Computer Science
Journal, 100, 498-506. DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.
09.188.
Chamberlin, D.D., Boyce, R.F. 1974. SEQUEL: A
structured English query language. In: Proc. ACM
SIGFIDET Workshop, Ann Arbor, Mich., 249-264.
Densen, P. 2011. Challenges and opportunities facing
medical education. In: Transactions of the American
Clinical and Climatological Association, 122, 48-58.
Fei, L., Jagadish, H.V. 2014. NaLIR: An interactive natural
language interface for querying relational databases. In:
Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD International
Conference on Management of Data. DOI:
10.1145/2588555.2594519.
Gao, T., Dontcheva, M., Adar, E., Liu, Z., Karahalios, K.G.
2015. DataTone: Managing Ambiguity in Natural
Language Interfaces for Data Visualization. In:
Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on
User Interface Software & Technology (UIST '15).
ACM, New York, NY, USA, 489-500. DOI:
10.1145/2807442.2807478.
Kaleske, S. 2011. SAP Query Reporting – Practical Guide,
Galileo Press.
Li, F., Jagadish, H. V. 2014. Constructing an interactive
natural language interface for relational databases. In:
Journal Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 8(1),
73-84.
User Experience-based Information Retrieval from Semistar Data Ontologies
425

Llopis, M., Ferrández, A. 2013. How to make a natural
language interface to query databases accessible to
everyone: An example. In: Computer Standards &
Interfaces, 35 (5), 470-481.
Papadakis, N., Kefalas, P., Stilianakakis, M. 2011. A tool
for access to relational databases in natural language.
In: Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 7894-7900.
Popescu, A. M., Armanasu, A., Etzioni, O., Ko, D., Yates,
A. 2004. Modern natural language interfaces to
databases: Composing statistical parsing with semantic
tractability. In: COLING '04 Proceedings of the 20th
international conference on Computational Linguistics,
article no. 141.
Rencis, E. 2018. Towards a Natural Language-Based
Interface for Querying Hospital Data. In: Proc. of 2018
International Conference on Big Data Technologies,
ICBDT’18, Hangzhou, China, 25-28. DOI:
10.1145/3226116.3226133.
Rencis, E. 2018. On Keyword-Based Ad-Hoc Querying of
Hospital Data Stored in Semistar Data Ontologies. In:
International Conference on Health and Social Care
Information Systems and Technologies, Procedia
Computer Science Journal, ISSN 1877-0509, Vol. 138,
27-32, DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.005.
Rencis, E., Barzdins, J., Grasmanis, M., Sostaks, A. 2018.
Facilitation of Health Professionals Responsible
Autonomy with Easy-To-Use Hospital Data Querying
Language. In: Audrone Lupeikiene et al. (Eds.): Proc.
of the 13th International Baltic Conference on
Databases and Information Systems, Baltic DB&IS,
CCIS 838, 1-14, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-97571-9_17.
Rencis, E. 2019. Natural Language-Based Knowledge
Extraction in Healthcare Domain. In: Proc. of the 3
rd
International Conference on Information System and
Data Mining, ICISDM, Houston, Texas, USA, 138-142,
DOI: 10.1145/3325917.3325948.
Smart, P.R., Russell, A., Braines, D., Kalfoglou, Y., Bao,
J., Shadbolt, N.R. 2008. A Visual Approach to
Semantic Query Design Using a Web-Based Graphical
Query Designer. In: Gangemi A., Euzenat J. (eds)
Knowledge Engineering: Practice and Patterns. EKAW
2008. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5268.
Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 275-291. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-540-87696-0_25.
Zviedris, M., Barzdins, G. 2011. ViziQuer: A Tool to
Explore and Query SPARQL Endpoints. In: The
Semantic Web: Research and Applications, 6644, 441-
445.
KDIR 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
426
