
Tacit Knowledge Transfer: Information Technology Usage in
Universities
Ritesh Chugh
School of Engineering and Technology, Central Queensland University, Melbourne, Australia
Keywords: Tacit Knowledge, Tacit Knowledge Transfer, Information Technology, Technology, IT, Knowledge
Management, Universities.
Abstract: The importance of transferring tacit knowledge transfer is acknowledged in the literature, but the usage of
information technology for tacit knowledge transfer is not well researched. Through a mixed methods
approach, employing an online questionnaire and interviews, this study explored the perceptions of university
academic staff with regards to information technology usage, specifically relating to the transfer of tacit
knowledge. The study found a lack of specific tacit knowledge transfer technologies but relatively high use
of communication tools, a need for training on the use of new information technology was identified and
academic staff are generally quick to adapt to information technology. However, there appeared to be a lack
of confidence in information technology for the transfer of tacit knowledge and staff willingness to use
technology for sharing tacit knowledge was not high, exhibiting uncertainty. This study contributes to a better
understanding of the usage of information technology for tacit knowledge transfer and its adaptability by
university academics. The results of this study may stimulate future research by addressing sample size
limitation and replication in a different organisational setting.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tacit knowledge is an essential resource for
organisations. Tacit knowledge transfer can be
facilitated through the use of information technology
(Pant et al., 2018). In the current digital environment,
it is difficult to separate knowledge transfer from
technology. Information technology (IT) can be used
to capture, store and share knowledge, also making
knowledge access easier for users (O'Leary, 1998).
IT plays a vital role in supporting knowledge transfer.
The use of IT for tacit knowledge transfer
processes has shown to improve work-related tacit
knowledge flows among employees (Sarkiûnaitë &
Krikðèiûnienë, 2005) and can also be effectively used
for tacit knowledge transfer in geographically
dispersed teams (Jones, 2016). Technology that can
help in tacit knowledge transfer includes groupware,
social media, skills directory, intranets, blogs, wikis,
discussion forums and electronic rooms.
Organisational knowledge is embedded in its tools,
technology and processes, and people play an
important role in the success of its knowledge transfer
efforts (Argote & Ingram, 2000).
It is relatively easier to transfer tangible explicit
knowledge into databases, but the transfer of
intangible tacit knowledge is difficult (Brown &
Duguid, 2000). However, knowledge transfer
ultimately depends on the knowledge transferrer and
their traits (Albino, Garavelli & Gorgoglione, 2004),
especially for the transfer of tacit knowledge. It is
acknowledged that the key to success in knowledge
management lies in individual and organisational
factors (Margilaj & Bello, 2015; Saini, Arif &
Kulonda, 2018), and in technology that facilitates the
creation/acquisition, packaging/embodiment,
transfer, sharing and use of knowledge. However, it
is vital to understand how knowledge workers engage
in tacit knowledge transfer. To understand the
individualistic or human factors, it is important to
investigate the perceptions of knowledge workers.
The question that emerges from this background
information is if technology is provided to knowledge
workers, will they necessarily use it? This requires an
investigation of users, who possess tacit knowledge
and use IT for tacit knowledge transfer. Most prior
studies have highlighted the importance of IT for the
transfer of explicit knowledge only (Pant et al., 2018).
There is an apparent scarcity of literature that looks at
technology usage perspective for the transfer of tacit
Chugh, R.
Tacit Knowledge Transfer: Information Technology Usage in Universities.
DOI: 10.5220/0008355603490355
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2019), pages 349-355
ISBN: 978-989-758-382-7
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
349

knowledge, particularly in universities. This paper
explores the perceptions of university academic staff
with regards to IT usage, specifically relating to the
transfer of tacit knowledge. It also looks at issues
pertaining to academics’ adaptability to IT.
This paper is organised as follows. First, in the
literature review section, prior research is
contextualised. This is followed by the research
method section, which provides a rationale for the
experimental design. The fourth section reports and
discusses the findings. Conclusion and direction for
future work are presented in the final section.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Information communication technology encompasses
digital technology, communication tools, and/or
networks for accessing, managing, integrating,
evaluating and creating information and it can be
viewed as an amalgamation of IT and
telecommunications (ICT Literacy Panel, 2002). In
line with this definition of information
communication technology, knowledge management
tools can support knowledge creation, storage and
retrieval, transfer and application (Alavi & Leidner,
2001).
While the transfer of explicit knowledge is
relatively easier over tacit knowledge (Smith, 2001),
it is typical to expect that IT will contribute to the
transfer of both explicit and tacit knowledge. The use
of IT can assist in easily sharing information, making
information exchange faster by increasing the speed
of communication, reducing physical distances,
enabling the minimisation of misinterpretation and
avoid divergence (Albino et al., 2004). It is expected
that IT can endow these key benefits on tacit
knowledge transfer, especially when technology is
used to facilitate the knowledge transfer, in the form
of web portals, video-conferencing tools, expertise
finder directories, blogs, newsletters, discussion
groups, email and group decision support systems.
Contrary to expectations, technology is an important
enabler of tacit knowledge sharing and can assist in
capturing, sharing and applying tacit knowledge
(Chugh, 2017).
Information technology, systems, policies and
procedures, and organisational culture are factors that
potentially affect knowledge transfer. A study by
Karlsen and Gottschalk (2004) found that IT and
systems and processes do not solely contribute to
project success until there is an organisational culture
for knowledge transfer. A Bahraini study of public
and private sector organisations found that there is a
positive relationship between IT and knowledge
sharing (Ismail Al-Alawi, Yousif Al-Marzooqi &
Fraidoon Mohammed, 2007).
A study found that organisations used a variety of
systems, such as database applications, CRM
systems, ERP systems, CAD tools, intranets and
business portals, to support knowledge-intensive
activities but there was no explicit focus on assessing
the use of technology for tacit knowledge transfer
(Nevo & Chan, 2007). It called for studying
knowledge management technologies that support
tacit knowledge.
Tacit knowledge, in the minds of employees, is
vital for the success of an organisation (Nonaka &
Takeuchi, 1995) and it can be captured, stored and
transferred using technology (Al-Qdah & Salim,
2013). However, there is an argument around the use
of traditional technologies for tacit knowledge
transfer but contemporary technologies such as social
networks, blogs and wikis have found support for the
sharing of tacit knowledge (Panahi, Watson &
Partridge, 2016).
Perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use
are important influencing factors that users consider
for the usage of any technology (Davis, 1989). On the
other hand, adaptability implies the modification of
behaviour in response to environmental and system
changes and changing requirements (Patten et al.,
2005). People are important elements for the use (and
success) of technology. Understanding their belief
about IT usage can provide better insights. As newer
technology is introduced, the ability to adapt to
technological changes becomes crucial (Keillor,
Pettijohn & d'Amico, 2001).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
Tashakkori and Creswell (2007) have defined the
mixed methods approach as ‘research in which the
investigator collects and analyses data, integrates the
findings, and draws inferences using both qualitative
and quantitative approaches or methods in a single
study or program of inquiry’ (pg. 4). In almost every
applied social research project, there is value in
consciously combining both qualitative and
quantitative methods in what is referred to as a mixed
methods approach (Trochim & Donnelly, 2007).
When addressing exploratory questions, mixed
methods research is considered better than a single
approach (Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2009). Adopting a
mixed method approach would allow mixing and
matching components that would offer the best
chance of answering the questions raised by this
KMIS 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
350
paper. Furthermore, Onwuegbuzie and Leech (2004)
stated that ‘in many cases the goal of mixing is not to
search for corroboration but rather to expand on our
understanding’ (pg.19). Hence, a mixed methods
research approach was adopted.
The study was administered in two phases. The
first phase involved the administration of a custom-
designed online questionnaire to academics in four
Australian public universities. The questionnaire
comprised of close-ended Likert scale format
questions, which used a 6-point scale. The second
phase involved in-depth structured 30 to 40-minute
face-to-face interviews with academics. The first
phase gathered quantitative data, whereas the second
phase gathered qualitative data. One hundred forty-
one respondents responded to the online
questionnaire that was emailed to the universities’
academic mailing list. Eight interviews were
conducted, comprising of two academics (a lecturer
or senior lecturer and an associate professor or
professor) from each university.
The questions analysed in this paper have been
drawn from a larger study previously carried out by
the author, but the novelty lies in the focus of
assessing usage of technology for tacit knowledge
transfer, something which was not reported earlier
nor was this set of data used before. Presenting all the
findings of the large study was not possible without
breaking it down into meaningful portions to draw
relevant inferences.
Considering the nature of the data required and the
research questions, the survey amongst many other
aspects explored the technology dimension. In doing
so, it specifically focussed on exploring the use of
information and communication technologies and
academics’ adaptability to IT for tacit knowledge
transfer. The interview questions were designed to
assess whether there were any technologies in the
universities that aid tacit knowledge transfer and
identify academics’ adaptation to IT implemented by
the universities.
4 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
The analysis examines the use of technology for tacit
knowledge sharing, training on new technologies,
adaptation to IT, accessibility to documentation and
application software. Descriptive statistics of these
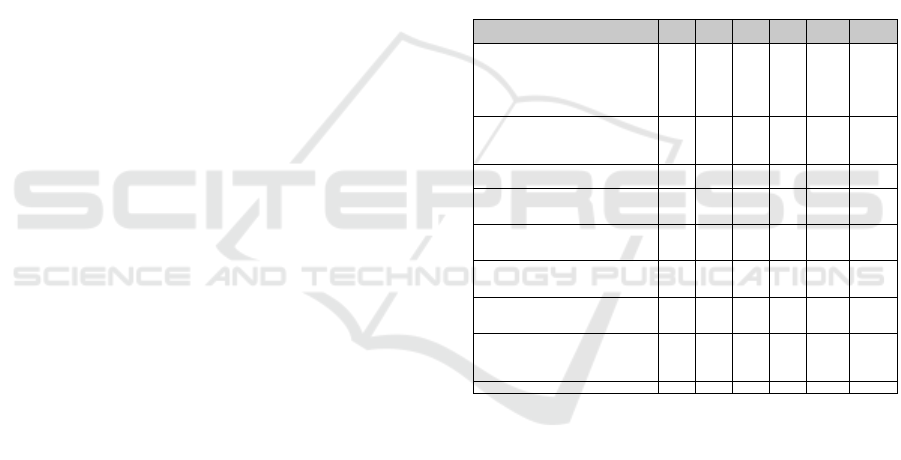
questions are outlined in table 1.
As shown in table 1, 61% of the surveyed
academics believe their universities make effective
use of various means of IT for developing better
communication between staff, students and
management with a mean response of 3.56. The
response is negatively skewed at skewness statistics
(-.554), showing most of the responses were on the
side of agreement. A previous study that found that
over three-quarters of the respondents showed
consensus that their workplace provided different
information technologies to share knowledge, thus
also demonstrating an awareness of the importance of
knowledge sharing (Ismail Al-Alawi et al., 2007). It
appears staff need to be made aware of the nexus
between communicative and tacit knowledge sharing
tools. Intranet, email service, bulletin boards, and
electronic forums are different technologies that
facilitate inter and intraorganisational knowledge
sharing (Song, 2002), and these are communication
tools too.
Table 1: Descriptive statistics of perceptions of technology
usage relating to the transfer of tacit knowledge.
Overall, 56% of the participants felt that training
and education are provided to help in the use of new
information technologies that universities introduce.
This is an area that requires consideration. Training
can assist in creating an awareness of knowledge
sharing mechanisms (Chugh, 2012). Adaptability to
new systems and processes can be seen as a global
trait in both personal and changing environments
(Keillor et al., 2001). Around three-quarters of the
academics are quick to adapt to information
technologies implemented by their university. The
mean response to this statement is 3.88 with a
skewness value of -.562 showing that a lot of
responses are towards an agreement with the
statement. Moreover, the functionality and features of
technology affect the success of knowledge transfer
efforts (Argote & Ingram, 2000).
Q1. My university makes effective use of
information technology (e.g. e-mail,
groupware, Internet, Intranet, learning
management systems and videoconferencing)
for developing better communication between
staff, students and management.
141 3.5674 0.09459 1.12316 -0.554 61
Q2. My university provides training and
education on the use of new information
technologies that they introduce to make us
more adept at their usage.
140 3.4143 0.0967 1.14418 -0.459 56
Q3. I quickly adapt to information
technologies implemented by the university.
141 3.8865 0.07539 0.89516 -0.562 73
Q4. My university documents policies and
procedures and makes it available through the
staff Intranet.
139 4.1295 0.06445 0.75981 -1.127 86.5
Q5. I feel that electronic transmission leads to
an overload of information and encourages
frequent changes in policies.
141 3.1915 0.10601 1.25877 0.111 37.6
Q6. It is easy to access the documents that I
need within my university's databases i.e.
information is well organised.
141 2.9362 0.10275 1.22014 -0.044 37.6
Q7. The policies and procedures on the staff
Intranet at my university get rapidly and
continually updated.
141 3.5816 0.09767 1.15978 0.203 47.5
Q8. My university provides ready access to
application software (e.g. chatting, discussion
groups, bulletin boards) and hardware to help
me in sharing my personal experiences.
140 3.25 0.1059 1.25305 0.204 36.2
Valid N (list wise) 133
%
Agreement
Statement
Mean
Statistic
Std.
Error
Skewness
Statistic
N
Statistic
S.D.
Statistic
Tacit Knowledge Transfer: Information Technology Usage in Universities
351
At 86.5%, there is a high level of agreement with
universities’ tendency to document policies and
procedures and then make them available through the
staff Intranet with a mean response of 4.12. Table 1
shows that the average response is negatively skewed
and skewness coefficient being significant at -1.127,
demonstrating that most of the respondents have
indicated a high level of agreement to this statement.
Only 37.6% of participants feel that electronic
transmission leads to an overload of information and
encourages frequent changes in policies possibly due
to the ease with which changes can be implemented
electronically. The mean response of this statement is
3.19, which can be interpreted as overall
disagreement with the statement. This may also imply
that administrative goals are shifting. This contrasts
with Tang et al., (2008) who outlined that IT for
knowledge and information management can lead to
information overload.
37.6% of respondents agree that it is easy to
access the documents they need within the
university’s databases, i.e. information is well-
organised. The mean response to this perspective is
2.93, showing overall disagreement with the
statement. Access to the documents that academics
need within their university’s databases is not very
easy. In comparison, the situation is better regarding
the rapid and continuous upgrading of policies and
procedures on the staff Intranet in universities.
However, only 47.5 % of the respondents agree with
this viewpoint with a mean response of 3.58.
Furthermore, only 36.2% respondents agree that their
university provides ready access to application
software (e.g. chatting, discussion groups, bulletin
boards) and hardware to help them in sharing their
personal experiences with a mean response of 3.25.
Hence, a mix of technological and social methods are
required for successful knowledge transfer
(Lundberg, Lidelöw & Engström, 2017).
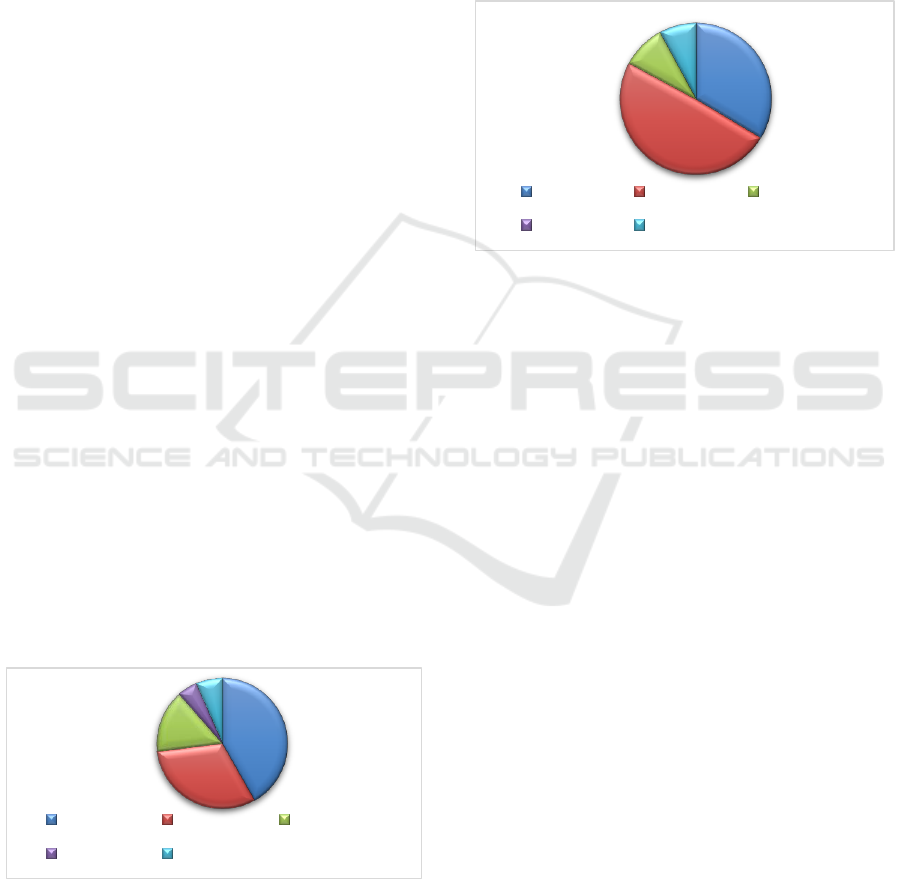
Figure 1: Can technology help in tacit knowledge transfer.
As shown in figure 1, 42% of respondents feel that
technology can assist in the transfer of tacit
knowledge. However, this presents a lack of overall
confidence. This is in contrast to Sarkiûnaitë &
Krikðèiûnienë (2005), who posited that the usage of
information technologies causes significant work-
related tacit knowledge flows. This may perhaps also
reflect a preference for face-to-face contact where
tacit knowledge transfer can take place more
effectively. Despite advances in technology,
preference for face-to-face contact for tacit
knowledge sharing was outlined by Panahi et al.,
(2016).
Figure 2: Academics willingness to use technology for
sharing tacit knowledge.
Figure 2 indicates that 34% of the academics are
willing to use technology to share their knowledge,
skills and ideas with others. Universities are
implementing different technologies to enhance tacit
knowledge transfer (such as video conferencing,
online meetings, online chat rooms, discussion
forums, intranet, portals) but 49% of the participants
feel that with technology they ‘may be’ in a position
to share their knowledge, skills and ideas. This
uncertainty is of concern and requires further
investigation of the causes. Other participants are
either not sure or probably do not believe in improved
knowledge sharing with enhanced technology.
However, IT is an important enabler of knowledge
sharing efforts (Mitchell, 2003). Subramaniam and
Venkatraman (2001) found that effective transferral
and sharing of tacit knowledge involved face-to-face
interaction, often complemented and enhanced with
the use of IT. The use of IT to convert tacit to explicit
will be a positive way of moving forward in
knowledge management efforts.
Majority of the interviewees were not aware of
any specific IT used by their universities to aid tacit
knowledge transfer. This was also highlighted in
response to question eight of the survey. The
interviewees even commented about the lack of any
such technology in their workplace. Some verbatim
excerpts from the interviews have been reproduced
below to illustrate these facts:
42%
31%
16%
5%
6%
Yes Cannot know Probably not
No Do not know
34%
49%
9%
0%
8%
Definitely Probably Probably not
No Do not know
KMIS 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
352

‘I don’t see any systems or technology actually
specifically for knowledge management.’
‘There isn’t any technology or computerised systems
at this place that can assist tacit knowledge transfer.’
‘Technology used in the university-None come to
mind.’
‘Only in the extent of the expertise guide. The
expertise guide simply tells people which people have
this knowledge.’
‘No, there are no technologies or systems in this
University that aid in knowledge transfer.’
‘Technology should be used, yes. That’s right. We
are living in the IT world. Why don’t we capture this
potential? I am not aware of any IT usage not that I’m
aware of.’
Lack of IT has been identified as a barrier to the
successful sharing and transfer of knowledge (Asrar-
ul-Haq & Anwar, 2016). Since information
technologies can be used to improve tacit knowledge
transfer, it was imperative to assess how academics
adapted to any IT implemented by their university.
Universities are implementing different technologies
to enhance learning and teaching activities although,
there is a lack of technology in the area of tacit
knowledge transfer. An interviewee commented that
‘there’s a lot of technology floating around and I
think that’s happening in all universities’.
In the arena of adaptability to IT, academics are
not laggards that also resonated in response to
question three of the survey. However, putting a
different perspective on adapting to technology, an
interviewee remarked that ‘informally is the way I’m
thinking of it.’ This interviewee also highlighted that
‘I find it very slow and time-consuming and I’ve
talked to people at other universities about it, too, and
they’ve said the same thing.’ On the other hand, an
interviewee felt that he was ‘a quick learner, but a
lonely learner.’ The lonely learner adage was used
because this interviewee was able to access IT
support through phone only and hence felt that
geographical distance was a limitation. Not forgetting
the human element, adaptability, user-friendliness
and easy access were some desired capabilities users
expected from a knowledge management system
(Nevo & Chan, 2007).
Although 56% of respondents agreed that training
is provided for new IT, it is an area that can benefit
from increased training. Lack of training of
academics in IT was a problem that came out in the
interviews. One interviewee exemplified that ‘I did
figure it out by trial and error, trial and error. But I
wouldn’t claim that I’m on top of things, but I can get
by with the changes in technology.’ Another
interviewee echoed similar thoughts on the adoption
of IT by saying that ‘I'm certainly not the first out
there, I can tell you. I'm the third, probably – the
third or fourth – and I need to find out its social
benefit before I leap into it.’ Lack of individual staff
capacity to use the available IT was identified as a
barrier to tacit knowledge sharing (Olaniran, 2017).
However, an interviewee who was more confident in
the use of technology commented that ‘I can’t
consider myself a digital native but, certainly, I feel
comfortable with any IT systems.’ Action-oriented
user training can contribute to improved technology
implementation (Sokol, 1994).
As evident from the interviewees’ comments,
there is currently a dearth of systems in universities
that support tacit knowledge transfer however in
anticipation that such technology will be made
available in the future, academics have to adapt to it
rapidly. In summary, it is important to highlight that
IT for knowledge transfer is here to stay and
academics will have to use it in the near future (if they
have not already begun). There will be a learning
curve for every new technology. This interviewee’s
comment helps to conclude this section- ‘We have to
do it - no choice. Being a slow learner, medium
learner, quick learner depends on your operational
use of that technology.’
5 CONCLUSIONS
Transfer of tacit knowledge is vital for all
organisations, especially universities who create and
utilise knowledge for its diverse activities. Tacit
knowledge, in the form of skills and experience, is
embedded in university academics. Information
technology plays an important role in the facilitation
of knowledge transfer, particularly that of tacit
knowledge. Hence, this mixed-method study
explored the perceptions of university academic staff
with regards to IT usage.
Although this was an exploratory study, insights
from this study provide important contributions to
understanding staff perceptions about IT usage,
specifically relating to the transfer of tacit knowledge
and academics’ issues in adapting to IT. The findings
of this study have implications for researchers,
practitioners and managers alike.
The findings generally indicate a positive
predisposition towards IT usage, but a greater focus
on introducing specific technologies that assist tacit
knowledge transfer is required. A lack of tacit
knowledge transfer technologies in universities was
evident in the responses. Furthermore, to facilitate the
transfer of tacit knowledge, training on the use of new
Tacit Knowledge Transfer: Information Technology Usage in Universities
353

information technologies is needed. There appears to
be a lack of confidence in the role of technologies for
the transfer of tacit knowledge. Electronic
transmission of information does not lead to an
overload of information. The nexus between
communicative and tacit knowledge sharing tools
needs to be clarified. Academics are generally quick
to adapt to information technologies implemented by
their university. However, the uncertainty exhibited
by academic staff in their willingness to use
technology for sharing tacit knowledge requires
further exploration.
Like any study, this one is also not free of
limitations. Firstly, the qualitative sample was not
sufficiently large. Secondly, the sample consisted
only of academics from four Australian universities.
The explorative nature of the study can also be
viewed as a limitation. Hence, generalisability should
be avoided. Further studies can overcome these
limitations, replicate this study in a dissimilar
organisational setting and explore the different IT that
academics use in the knowledge management
lifecycle.
REFERENCES
Al-Qdah, M. S., & Salim, J. (2013). A conceptual
framework for managing tacit knowledge through ICT
perspective. Procedia Technology, 11, 1188-1194.
Alavi, M., & Leidner, D. E. (2001). Knowledge
management and knowledge management systems:
Conceptual foundations and research issues. MIS
Quarterly, 25(1), 107-136.
Albino, V., Garavelli, A., & Gorgoglione, M. (2004).
Organization and technology in knowledge transfer.
Benchmarking: An International Journal, 11(6), 584-
600.
Argote, L., & Ingram, P. (2000). Knowledge transfer: A
basis for competitive advantage in firms.
Organizational Behavior and Human Decision
Processes, 82(1), 150-169.
Asrar-ul-Haq, M., & Anwar, S. (2016). A systematic review
of knowledge management and knowledge sharing:
Trends, issues, and challenges. Cogent Business &
Management, 3(1), 1-17.
Brown, J. S., & Duguid, P. (2000). Balancing act: How to
capture knowledge without killing it. Harvard Business
Review, 78(3), 73-80.
Chugh, R. (2012). Knowledge sharing with enhanced
learning and development opportunities. Paper
presented at the IEEE International Conference on
Information Retrieval & Knowledge Management, 100-
104, 13-15 March, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Chugh, R. (2017). Barriers and Enablers of Tacit
Knowledge Transfer in Australian Higher Education
Institutions. International Journal of Education and
Learning Systems, 2, 272-276.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease
of use, and user acceptance of information technology.
MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319-340.
ICT Literacy Panel. (2002). Digital transformation: A
framework for ICT literacy. Retrieved from Princeton,
NJ.: http://oei.org.ar/ibertic/evaluacion/sites/default
/files/biblioteca/32_digitaltransformation.pdf
Ismail Al-Alawi, A., Yousif Al-Marzooqi, N., & Fraidoon
Mohammed, Y. (2007). Organizational culture and
knowledge sharing: critical success factors. Journal of
Knowledge Management, 11(2), 22-42.
Jones, N. B. (2016). Knowledge transfer and knowledge
creation in virtual teams. In Strategic management and
leadership for systems development in virtual spaces
(pp. 110-122). Hershey: IGI Global.
Karlsen, J. T., & Gottschalk, P. (2004). Factors affecting
knowledge transfer in IT projects. Engineering
Management Journal, 16(1), 3-11.
Keillor, B. D., Pettijohn, C. E., & d'Amico, M. (2001). The
relationship between attitudes toward technology,
adaptability, and customer orientation among
professional salespeople. Journal of Applied Business
Research, 17(4), 31-40.
Lundberg, M., Lidelöw, H., & Engström, S. (2017).
Methods used in the everyday practice of construction
projects for knowledge sharing and knowledge transfer.
Paper presented at the 5th International Workshop
When Social Science Meets Lean and BIM, 26-27
January 2017, Aalborg, Denmark.
Margilaj, E., & Bello, K. (2015). Critical success factors of
knowledge management in Albania business
organizations. European Journal of Research and
Reflection in Management Sciences, 3(2), 15-24.
Mitchell, H. J. (2003). Technology and knowledge
management: Is technology just an enabler or does it
also add value? In Knowledge management: Current
issues and challenges (pp. 66-78): IGI Global.
Nevo, D., & Chan, Y. E. (2007). A Delphi study of
knowledge management systems: Scope and
requirements. Information & Management, 44(6), 583-
597.
Nonaka, I., & Takeuchi, H. (1995). The knowledge-creating
company: How Japanese companies create the
dynamics of innovation: Oxford university press.
O'Leary, D. E. (1998). Knowledge-management systems:
Converting and connecting. IEEE Intelligent Systems
and Their Applications, 13(3), 30-33.
Olaniran, O. J. (2017). Barriers to tacit knowledge sharing
in geographically dispersed project teams in oil and gas
projects. Project Management Journal, 48(3), 41-57.
Onwuegbuzie, A. J., & Leech, N. L. (2004). Enhancing the
interpretation of significant findings: The role of mixed
methods research. The Qualitative Report, 9(4), 770-
792.
Panahi, S., Watson, J., & Partridge, H. (2016).
Conceptualising social media support for tacit
knowledge sharing: physicians’ perspectives and
KMIS 2019 - 11th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
354

experiences. Journal of Knowledge Management,
20(2), 344-363.
Pant, A., Shrestha, A., Kong, E., & Ally, M. (2018). A
systematic literature mapping to investigate the role of
IT in knowledge stock and transfer. Paper presented at
the Proceedings of the 22nd Pacific Asia Conference on
Information Systems (PACIS 2018).
Patten, K., Whitworth, B., Fjermestad, J., & Mahindra, E.
(2005). Leading IT flexibility: anticipation, agility and
adaptability. Paper presented at the AMCIS 2005
Proceedings.
Saini, M., Arif, M., & Kulonda, D. J. (2018). Critical factors
for transferring and sharing tacit knowledge within lean
and agile construction processes. Construction
Innovation, 18(1), 64-89.
Sarkiûnaitë, I., & Krikðèiûnienë, D. (2005). Impacts of
information technologies to tacit knowledge sharing:
Empirical approach. Informacijos Mokslai, 35, 69-79.
Smith, E. A. (2001). The role of tacit and explicit
knowledge in the workplace. Journal of Knowledge
Management, 5(4), 311-321.
Sokol, M. B. (1994). Adaptation to difficult designs:
Facilitating use of new technology. Journal of Business
and Psychology, 8(3), 277-296.
Song, S. (2002). An internet knowledge sharing system.
Journal of Computer Information Systems, 42(3), 25-
30.
Subramaniam, M., & Venkatraman, N. (2001).
Determinants of transnational new product
development capability: Testing the influence of
transferring and deploying tacit overseas knowledge.
Strategic Management Journal, 22(4), 359-378.
Tang, L. C., Zhao, Y., Austin, S. A., Darlington, M., &
Culley, S. (2008). Overload of information or lack of
high value information: Lessons learnt from
construction. Paper presented at the 9th European
Conference on Knowledge Management and
Evaluation, Southampton, UK.
Tashakkori, A., & Creswell, J. W. (2007). The new era of
mixed methods. Journal of Mixed Methods Research,
1(1), 3-7.
Teddlie, C., & Tashakkori, A. (2009). Foundations of mixed
methods research: Integrating quantitative and
qualitative approaches in the social and behavioral
sciences: Sage Publishing.
Trochim, W., & Donnelly, J. (2007). The research methods
knowledge base 3rd Ed: Mason. OH: Thompson
Publishing Group.
Tacit Knowledge Transfer: Information Technology Usage in Universities
355
