
Intellectual Execution Scheme of Iterative Computational Models based
on Symbiotic Interaction with Application for Urban Mobility Modelling
Mikhail Melnik
1
, Denis Nasonov
1
and Alexey Liniov
2
1
ITMO University, Saint-Petersburg, Russian Federation
2
Lobachevsky State University of Nizhni Novgorod, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
Keywords:
Parallel Computation, Co-design, Scheduling, Supercomputer, Multi-agent Model.
Abstract:
In the modern world, with the growth of the volume of processed data arrays, the logic of solving problems also
becomes more complex. This leads more and more often to the need to use high-performance computational
clusters, such as supercomputers. Created multi-agent simulation applications require not only significant
resources but often perform time-consuming complex scenarios, which significantly affects the efficiency
of the executed process. However, there are various mechanisms for optimizing application execution for
different needs. Unfortunately, the specificity of multi-agent simulation does not allow the use of traditional
and modern algorithms due to the iteratively variable workload and limitations of a system software installed
on the supercomputers. In this paper, we propose a four-level scheme for organizing the symbiotic execution
(co-design) of multi-agent applications on supercomputers, as well as an effective two-level algorithm for
optimizing the flow of the execution of an urban mobility simulation application. The algorithm is based on
evolutionary approach and machine learning techniques.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, computational modeling applications are
in demand in many areas of research, both science
and business. With the growth of the processed data
amount and the complexity of the solving tasks, there
is a need to use high-performance computing and one
of the most popular way is modern supercomputers
utilization. Among such tasks, multi-agent modeling
problems takes a separate place. Usually, simulated
agents cooperate in a commonly organized virtual en-
vironment, which can be divided into parts when the
executed scenario needs too many computational re-
sources and time. In this case, the computational pro-
cess is split between computational nodes into spatial
domains, and each region with its part of the agents is
processed independently, transferring changes at the
boundaries to other regions. In such a way of orga-
nization, there is a significant number of peculiari-
ties that must be taken into account when develop-
ing models and scenarios. These peculiarities include
overhead costs arising from the interchanges of spa-
tial domains; unbalanced loading of each computa-
tional resource; specifics of approaches that perform
division of virtual environment into zones; compet-
ing for execution of several models at once, etc. To
ensure successful overcoming of these problems, var-
ious approaches are applied: a) implementation of the
logic of sustainable scalability and application per-
formance within the application’s internal part - pro-
vides only conditional overcoming of effective exe-
cution problems, because the application usually rep-
resent some models in the certain domain, as a rule,
optimization is not a professional competence of the
application’s author; b) performing optimization by
an external service - this option is rarely available
in high-performance computing environments, espe-
cially in supercomputers, where the planning mecha-
nism is often used to meet the needs of a live queue,
based on the greedy rules with several parameters
such as priorities and amount of required resources;
c) symbiotic execution (co-design) - using the logic
of mutually beneficial cooperation of an application
package and infrastructure software, where the appli-
cation provides the infrastructure the ability to cus-
tomize and control the workload for each application
agents (region) during the calculation of a scenario.
The last approach is the most promising, especially
if the implementation is not a particular case for a
specific task, but a single generalized scheme appli-
cable for different areas with the minimum required
changes on the application side. In this article, we
Melnik, M., Nasonov, D. and Liniov, A.
Intellectual Execution Scheme of Iterative Computational Models based on Symbiotic Interaction with Application for Urban Mobility Modelling.
DOI: 10.5220/0008365602450251
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2019), pages 245-251
ISBN: 978-989-758-384-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
245

propose a solution that divides the interaction logic
into four levels: model, environment and two system
levels. The model hidden internal logic of the appli-
cation, system levels correspond for scheduling and
control of execution process as well as resources allo-
cation, while the environment is used for simulation
by model and optimization by the system. During in-
vestigations, the hierarchical optimization algorithm
was created and experimentally studied on the appli-
cation of population mobility simulation in the city of
St. Petersburg.
2 RELATED WORKS
Many researchers developed algorithms and ap-
proaches to solve problems related to the organi-
zation of computations in supercomputing environ-
ments. These works aimed at various aspects of com-
putation processes. This includes methods for manag-
ing memory, storage, resource managers and sched-
ulers. Moreover, there are works aimed at studying
the effective use of specific hardware (GPU), ensur-
ing high reliability or scalability of computations and
improving the energy consumption.
For example, an algorithm for scheduling of het-
erogeneous GPU resources was developed in (Zim-
mer et al., 2018) in order to provide enhanced reli-
ability of execution. The main idea was to assign
more reliable and modern GPU for large tasks. Ex-
periments were carried out on Titan supercomputer,
where the number of GPU-oriented tasks has been in-
creased significantly over the past 4 years.
For the qualitative reproduction of computation
process on supercomputers, (Martinasso et al., 2018)
developed a RM-Player. The difference to already ex-
isting models and simulators lies in the usage of the
same stack of technologies and resource managers.
This player allows user to configure system’s parame-
ters to adapt and improve computation processes. Ex-
periments were conducted on Piz Daint supercom-
puter. Another approaches to building a supercom-
puter simulator based on the Maui scheduler are being
studied in (Zitzlsberger et al., 2018).
Authors of (Malakar et al., 2018) explore ways
to efficiently organize parallel computations based on
partition of modelling domain according to architec-
ture of CPU. This study does not examine the internal
workload of partitions and their balancing.
An important criterion for effective computations
is the consideration of network structure and its band-
width. Authors of (Pollard et al., 2018) consider the
study of approaches to the organization of balancing
tasks in fat-tree networks. In (Smith et al., 2018) a
problem of analyzing forecasting tasks is studied, de-
pending on the network structure. This study also in-
cludes a routing scheme, allowing the user to reassign
tasks in order to avoid emergencies of overloaded hot-
spots.
An abstract infrastructure of a data center, which
implies scheduling and optimization mechanisms is
presented in (Andreadis et al., 2018). The abstract
infrastructure considers the complete workflow of
tasks’ computation process, painted in stages. Con-
ducted experiments used existing scheduling algo-
rithms associated with the developed structure.
Many works are focused on the problem of scal-
ing and problems related with that. In (Liu et al.,
2018) a scaling problem is solved by integration of
resources from external cloud clusters and by algo-
rithms for the transfer of data and computations be-
tween clusters. A model for estimating a bandwidth
of master nodes and corresponding tools for estimat-
ing the required amount of resources are presented in
(Kremer-Herman et al., 2018).
Authors of (Subedi et al., 2018) propose frame-
work Stacker for efficient data transfer inside mul-
tiscale composite applications running in supercom-
puter environments. In particular, the work is aimed
at optimizing operations with RAM during the execu-
tion process of distributed applications at its various
stages.
Despite the wide range of researches related to
multiscale modeling and optimization of supercom-
puters, there is a lack of works related to the anal-
ysis and monitoring of internal logic of applications
to be taken into account in the optimization mecha-
nisms. Therefore, a development of methods that can
not only take into account specifics of applications,
but also influence the computation process is an ac-
tual direction for research.
3 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The main idea of this work is to effectively parti-
tion the modeling domain based on load prediction
in these areas and transferring data between them.
3.1 Problem Statement
A computational model has its execution environment
that is organized as a spatial or temporal computa-
tional grid G =< V, E >, where V = v
j
is a set of ver-
texes and E = e
j1, j2
is a set of edges between them.
Let W = w
j
be a workload for a current iteration,
where w
j
represents computational intensity on a ver-
tex v
j
. R = r
m
is a set of computational resources.
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
246

Performance of a resource is defined in r
m
. We de-
fine a schedule S = w
j,m
as an allocation of workload
elements w
j
across resources r
m
. Let define the cost
function for transfer from schedules S
1
and S
2
:
f (S
1
, S
2
) =
∑
c
j, j
0
b
j, j
0
δ
j
0
j
(1)
where:
δ
j
0
j
=
(
1, if j and j
0
are on different resources
0, otherwise
(2)
c
j, j
0
is a metadata that must be transferred from v
j
to v
j
0
, b
j, j
0
is a data transfer speed. The considered
function to estimate the modelling time during one
iteration:
T (S) = max
m
(
∑
j
w
j,m
r
m
+
∑
j
∑
j
0
c
j, j
0
b
j, j
0
δ
j
0
j
) (3)
Then, we can define a condition for transition be-
tween schedules:
f (S
prev
, S
new
) < (T (S
prev
− T (S
new
))θ (4)
where θ is a statistical depending value represents
the rate of changing of workload through vertexes of
computational grid.
3.2 Four-level Intellectual Execution
Scheme
An execution scheme for organizing computations is
developed based on the scheduling of partitions of a
modeling area. The scheme is based on a multi-agent
approach, where each intelligent agent is responsi-
ble for a specific area of modeling and provides its
own forecasts for the iteration time for its area. The
scheme is managed by a master agent. The master
agent performs scheduling by assign cells to intellec-
tual agents, and obtaining the developed performance
models from these agents. In the example of urban
modeling application, the master agent performs dy-
namic rescheduling to account changes in the dynam-
ics of population movement in the city.
The basis of developed scheme is a possibility of
integration into an application in order to obtain the
possibility of flexible partitioning of a modeling area,
which is impossible with the standard implementation
of the application, where the modeling area is divided
evenly into blocks. The scheme is shown in the Fig.
1.
The first level of the scheme is the composition
core of models that is responsible for managing the
launched models. The goal of this level is a seman-
tic analysis of the model to obtain the boundaries of
the modeling domain and define restrictions on how
the modeling domain can be divided into subregions
and thus form adapted distributed logic of application
models combined in a single workflow.
The result of the model analysis is a virtual mod-
elling environment for several competing or cooper-
ating models. Within the framework of the virtual en-
vironment, modeling areas are known, and tools for
profiling and monitoring of modeling process are pro-
vided. Also, at the level of the virtual modelling en-
vironment, the task of distributing application models
appears in the form necessary for the scheduler.
The third level is a distributed two-level intelli-
gent algorithm with a high-level central optimization
core and a multi-agent collaborative level of intellec-
tual agents. The optimization core performs the pro-
cess of optimizing the distribution of a simulation do-
main. Optimization is carried out on the basis of al-
location of regions of modeling domain to intellec-
tual agents. Intelligent agents build their performance
models on the designated areas of modeling and re-
turn their prediction results to the central core. The
forecast result included estimates of the simulation
time of the application being launched with the cur-
rent load and the amount of resources provided for the
calculations. The algorithm of optimization and dis-
tribution of modeling areas is based on a developed
genetic algorithm. The last level of the scheme is the
level of a computing environment.
For the execution scheme we can define a
partition-based model of computational process. Let
a
i
t
=< d
t
, x
t
> be an object from modelling logic
(for example, agent in term of multi-agent modelling
application) that should be processed at location x
t
,
p
k
t
=< S
p
, {a
i
t
} > is a partition of modelling area
which includes associated with it modelling objects.
A partition is a unit of scaling. e
r
t
is an envelope that
serves as data transferring between two connected
partitions and e
r
t+1
=< {a
i
t+1
}, p
a
t+1
>.
The computation of one iteration of modelling
process requires to set two user-define functions m
u
and g
u
.
p
k
t+1
= m
u
(p
k
t
, {e
r
t
}) (5)
p
a
t+1
= g
u
(x
t+1
) (6)
< p
k
t+1
, {e
r
t+1
} >= f (m, g, p
k
t
, {e
r
t
}) (7)
where m
u
- compute function that implements the
logic of modelling on the set of agents, g
u
- a func-
tion that determines a new partition for an agent after
its movement. Function f aggregates all this infor-
mation and performs all required operations to form
a new modelling state, including data exchange be-
tween processes of a computational application.
Intellectual Execution Scheme of Iterative Computational Models based on Symbiotic Interaction with Application for Urban Mobility
Modelling
247

Figure 1: Four-level intellectual execution scheme.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
4.1 Urban Mobility Simulation
In this paper, we experimented on the task of or-
ganizing efficient calculations for an application on
multiscale modeling of urban mobility of population.
The application is called City-Simulator and it im-
plements the Extreme Scaling computational pattern
(Alowayyed et al., 2019). The application is a multi-
agent model, where agents move along a modelling
area that corresponds to a city. The simulation area
is divided by a uniform grid into cells. Applications
running in distributed mode based on MPI and can
be launched on a supercomputer. Parallelization of
the application occurs due to the distribution of cells
in the simulation area across computing nodes. The
modelling time of one iteration is summed up from
agents modelling time and data transfer time between
computational nodes in cases when an agent moves
between cells assigned to different nodes. Agents
modelling time is defined as the maximum modelling
time among all computing nodes and it depends on
the number of agents in this cell. Data transfer time is
determined by the maximum data exchange time be-
tween nodes. Profiling of this application with various
parameters was performed in (Nasonov et al., 2018)
The simulation scenario sets routes for all agents.
Due to the dynamics of their movement and possibly
clusters in certain areas (for example, in the center),
the problem of load balancing arises. To maintain the
efficiency of computations, it is necessary to reallo-
cate areas of modeling by resources as changes in the
load of cells. To estimate the computational load, it
is necessary to carry out modeling and forecasting of
this workload. For forecasting, it is necessary to take
into account both the rise and fall intervals of the cur-
rent load, and the characteristics of a specific mod-
eling area. Certain areas of the simulation area may
have features that affect the simulation time. Thus,
the prediction of the density of the load must be car-
ried out for each region separately.
In this work, we developed a wrapper for this
application, that allows arbitrary partitioning of the
modeling area and distributes the modeling process
among the supercomputer nodes. This wrapper is de-
veloped according to presented intellectual execution
scheme and was integrated with Lomonosov (Lom,
2019) and Lobachevskiy (Lob, 2019) supercomput-
ers.
4.2 Genetic Algorithm
A genetic algorithm was developed to distribute the
application modeling domain. The algorithm is in-
tegrated in our execution scheme and wrapper for su-
percomputers. The optimization problem corresponds
to the formulated partition model in 3.2, which is
presented in the form of the distribution of cells in
the simulation domain by computational resources,
which are supported by intelligent agents within the
scheme. The modeling area is defined by a NxN grid,
and there are M intelligent agents. Each agent has a
set of computing resources.
The genotype of the developed algorithm is an ar-
ray of dimensions (m, c, d), where m is the number
of agents, c is a parameter - the number of centers
for each agent, and d is the dimension of the simu-
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
248
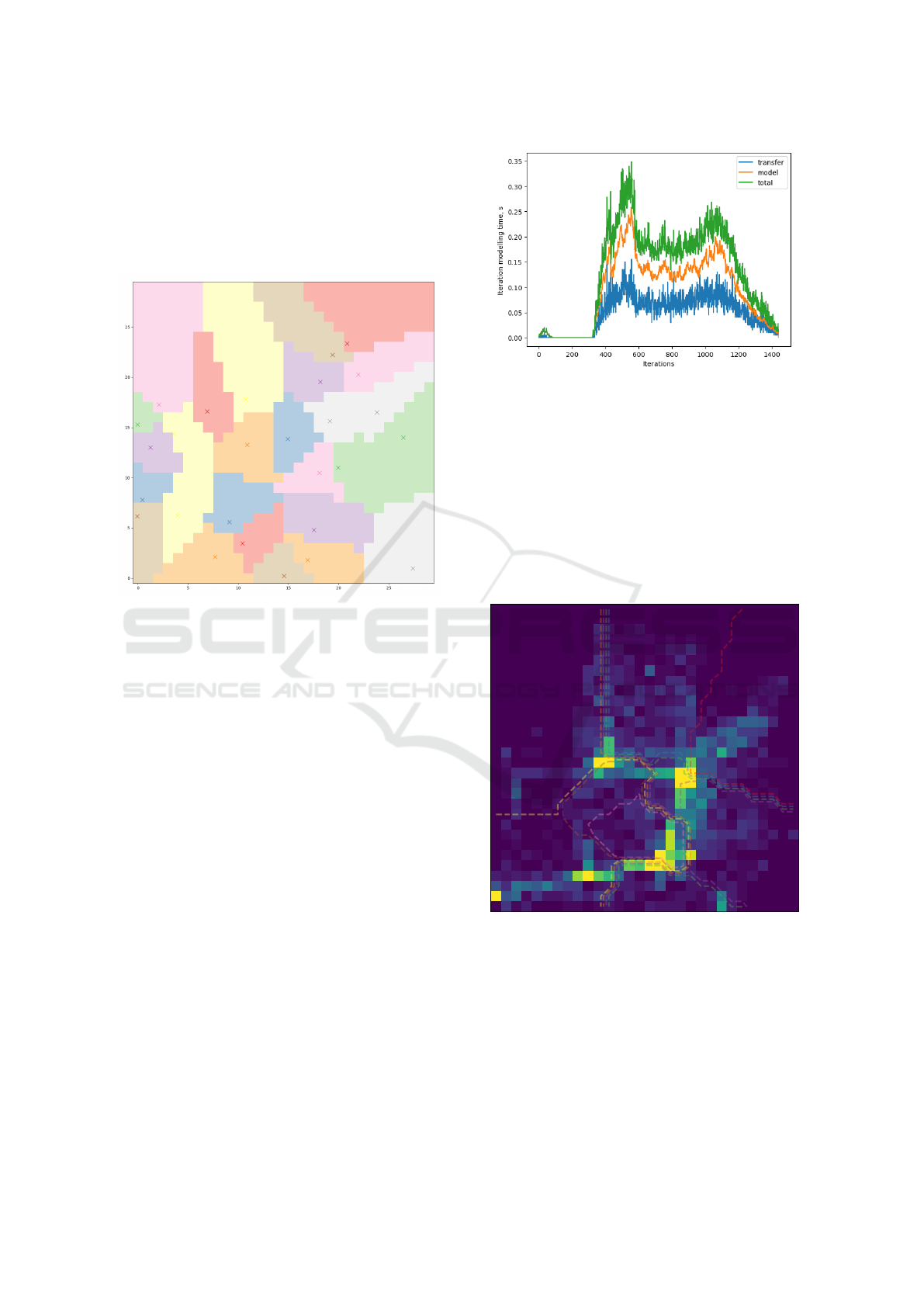
lation domain. The meaning of such a genotype is
the spread of a given number of centers in the mod-
elling area and assignment of cells to nearby centers
of corresponding intelligent agents. An example of a
genotype and its corresponding distribution is shown
in Fig. 2. Each color represents an allocated area for
specific agent.
Figure 2: Example of genotype with marked centers.
The mutation operator moves randomly selected
centers by adding a normally distributed values. The
crossover is a two-pointed crossover, which selects
centers for agents from two parents. The selection is
performed by tournament with 3 participants. Each
individual presents a schedule. To estimate fitness
function we launch a model that estimates modelling
time of application for specified period of time under
constructed schedules from individuals. It allows user
to perform forecast of the workload on a future itera-
tions for each intellectual agent. The fitness function
summarizes the modelling times of all iterations in
accordance with the modelling time on each of the in-
telligent agents. Aggregated estimation of modelling
time is presented in Fig. 3.
5 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
To conduct experimental studies, the scenario
with simulation of daily dynamics of people in
St.Petersburg was used. The specifics of this scenario
is that people move from sleeping area to center in the
morning and return to sleeping areas in the evening.
The length of one day modelling is 1440 iterations
(minutes). The goal of experiments is to optimize the
execution time of modelling process. This is achieved
Figure 3: Estimation of modelling time at each iteration.
by workload forecasting and scheduling by developed
GA.
The data for the scenario is a dataset with daily
logs of usage of public transport travel cards. Dataset
contains logs with 300,000 unique travel cards. The
workload of agents (heatmap from violet to yellow)
at one of iterations and divided areas (contour plots)
are presented in Fig. 4. From the Fig. 3 we can see
two peaks of workload. These peaks are related to
morning and evening rush-hours.
Figure 4: Agents workload and division of modelling area.
Five subsamples of 100,000 random cards were
sampled. One of the datasets was used for training
(for build schedules), and the others were used for
validation of received schedules. The simulated area
of the city was divided into a grid of 30x30 cells. In
relation to the scale of the city, the side of each cell
is approximately 0.7 km. With the developed scheme
and scenario of daily dynamic of city we conducted
several experiments for each sampled datasets:
Intellectual Execution Scheme of Iterative Computational Models based on Symbiotic Interaction with Application for Urban Mobility
Modelling
249
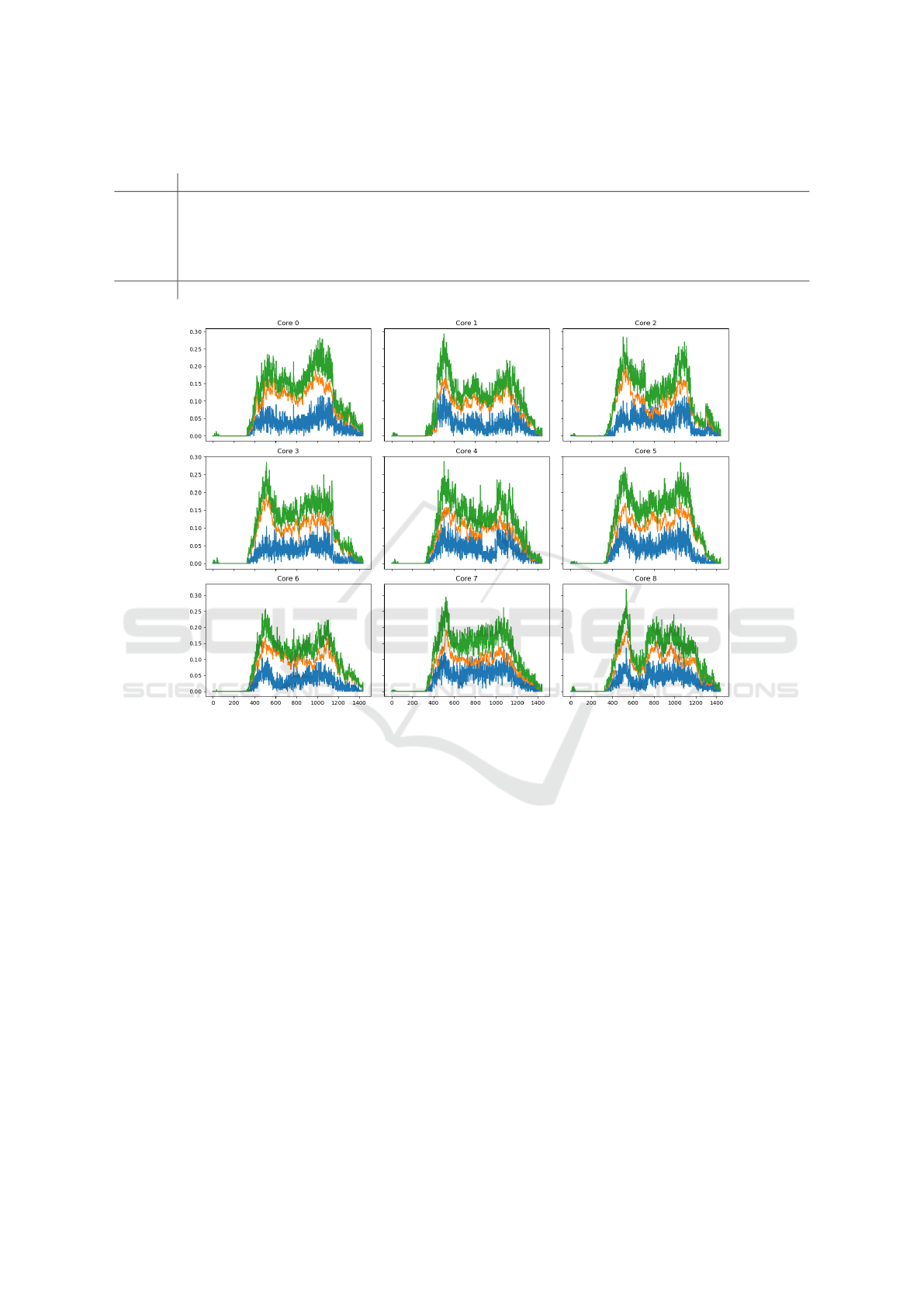
Table 1: Modelling time of urban mobility scenarios.
Scenario Basic Expert Dynamic 5 Dynamic 10 Forecast 5 Forecast 10
Main 307.9 299.5 175.3 159.5 146.0 137.4
Valid 1 307.6 298.7 172.9 158.4 147.2 138.9
Valid 2 310.1 296.4 176.0 158.7 147.8 136.1
Valid 3 308.2 301.0 173.4 156.1 146.5 137.4
Valid 4 306.8 297.8 170.7 157.9 146.1 135.9
Average 308.1 298.7 173.7 158.1 146.7 137.1
Figure 5: Results of workload distribution across intellectual agents by GA in Forecast 10 scenario.
1. Static - modelling area is divided into 9 equal par-
titions.
2. Expert - there are 3 schedules, that were defined
by expert at iterations: 0, 550, 1050. These sched-
ules divide the modelling area according to daily
dynamic and rush-hours.
3. Dynam 5 - scheduling by GA every 288 iterations
(5 times) without forecasting.
4. Dynam 10 - scheduling by GA every 144 itera-
tions (10 times) without forecasting.
5. Forecast 5 - scheduling by GA every 288 itera-
tions with forecasting for the next scheduling in-
terval (developed execution scheme).
6. Forecast 10 - scheduling by GA every 144 itera-
tions with forecasting for the next scheduling in-
terval (developed execution scheme).
Schedules were build only in a case of Main sce-
nario. For experiments with validation scenario we
used according schedules. In all experiments we used
9 intellectual agents. This means that we can divide
our modelling area on 9 parts. Each part will be pro-
cessed on a specific computing resources according
to intellectual agents. These experiments were con-
ducted on Lomonosov supercomputer. Result of ex-
periments are shown in Table. 1. Values in the table
are presented in seconds and mean total modelling
time of scenario, which was scheduled by presented
scheduling approaches.
Results of experiments show that by using de-
fault uniform schedule, modelling time is 308.1s in
average. Schedules performed by expert reduce the
modelling time only on 9.4s. When we start to ap-
ply developed execution scheme and developed GA
but without a forecasting of future workload we re-
ceived average modelling times of 173.7s and 158.1s
for cases with 5 and 10 dynamic schedules accord-
ingly. The best results were obtained when we per-
formed a forecasting of workload for each intellec-
tual agent (Fig. 5). Experiments show that the more
often we perform rescheduling, the better our execu-
ECTA 2019 - 11th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
250

tion scheme adapts to changes in the model. The best
result 137.1s (10 times with forecasting) ) is 55.5%
faster than the one obtained with the basic scenario.
6 CONCLUSION
In this work, a symbiotic four-level scheme of the
organization of the computational process for multi-
agent simulation was proposed. The key feature of
interaction between the model and the system is con-
centrated in the virtual modeling environment, which
includes the application agents’ activities and opti-
mization results, formed by the planning and control
module. This module implements an algorithm with
the genetic optimization core and intelligent agents
for workload prediction. The obtained results show
the high efficiency of the proposed approach, as they
not only complete the set of test scenarios faster but
also increase the potential ability for scaling, by se-
lecting the right division areas of the space and reduc-
ing overhead costs. The results of experiments show
the efficiency of proposed execution scheme and GA
by the improvement of the modelling time in compar-
ison to the default schedule by 55%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is financially supported by The Russian
Foundation for Basic Research, Agreement #18-37-
00416.
REFERENCES
(2019). Lobachevskiy supercomputer. http://www.itmm.
unn.ru/ob-institute/oborudovanie/. Accessed: 2019-
06-10.
(2019). Lomonosov supercomputer. https://parallel.ru/
cluster/about. Accessed: 2019-06-10.
Alowayyed, S., Piontek, T., Suter, J. L., Hoenen, O., Groen,
D., Luk, O., Bosak, B., Kopta, P., Kurowski, K.,
Perks, O., et al. (2019). Patterns for high performance
multiscale computing. Future Generation Computer
Systems, 91:335–346.
Andreadis, G., Versluis, L., Mastenbroek, F., and Iosup,
A. (2018). A reference architecture for datacenter
scheduling: design, validation, and experiments. In
Proceedings of the International Conference for High
Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and
Analysis, page 37. IEEE Press.
Kremer-Herman, N., Tovar, B., and Thain, D. (2018). A
lightweight model for right-sizing master-worker ap-
plications. In SC18: International Conference for
High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage
and Analysis, pages 504–516. IEEE.
Liu, F., Keahey, K., Riteau, P., and Weissman, J.
(2018). Dynamically negotiating capacity between
on-demand and batch clusters. In Proceedings of the
International Conference for High Performance Com-
puting, Networking, Storage, and Analysis, page 38.
IEEE Press.
Malakar, P., Munson, T., Knight, C., Vishwanath, V., and
Papka, M. E. (2018). Topology-aware space-shared
co-analysis of large-scale molecular dynamics simu-
lations. In SC18: International Conference for High
Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and
Analysis, pages 305–319. IEEE.
Martinasso, M., Gila, M., Bianco, M., Alam, S. R., McMur-
trie, C., and Schulthess, T. C. (2018). Rm-replay: a
high-fidelity tuning, optimization and exploration tool
for resource management. In Proceedings of the In-
ternational Conference for High Performance Com-
puting, Networking, Storage, and Analysis, page 25.
IEEE Press.
Nasonov, D., Butakov, N., Melnik, M., Visheratin, A.,
Linev, A., Shvets, P., Sobolev, S., and Mukhina, K.
(2018). The multi-level adaptive approach for efficient
execution of multi-scale distributed applications with
dynamic workload. In Russian Supercomputing Days,
pages 675–686. Springer.
Pollard, S. D., Jain, N., Herbein, S., and Bhatele, A. (2018).
Evaluation of an interference-free node allocation pol-
icy on fat-tree clusters. In Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Conference for High Performance Computing,
Networking, Storage, and Analysis, page 26. IEEE
Press.
Smith, S. A., Cromey, C. E., Lowenthal, D. K., Domke, J.,
Jain, N., Thiagarajan, J. J., and Bhatele, A. (2018).
Mitigating inter-job interference using adaptive flow-
aware routing. In Proceedings of the International
Conference for High Performance Computing, Net-
working, Storage, and Analysis, page 27. IEEE Press.
Subedi, P., Davis, P., Duan, S., Klasky, S., Kolla, H.,
and Parashar, M. (2018). Stacker: an autonomic
data movement engine for extreme-scale data staging-
based in-situ workflows. In Proceedings of the In-
ternational Conference for High Performance Com-
puting, Networking, Storage, and Analysis, page 73.
IEEE Press.
Zimmer, C., Maxwell, D., McNally, S., Atchley, S., and
Vazhkudai, S. S. (2018). Gpu age-aware scheduling
to improve the reliability of leadership jobs on titan.
In Proceedings of the International Conference for
High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage,
and Analysis, page 7. IEEE Press.
Zitzlsberger, G., Jans
´
ık, B., and Martinovi
ˇ
c, J. (2018). Fea-
sibility analysis of using the maui scheduler for job
simulation of large-scale pbs based clusters. IADIS
International Journal on Computer Science & Infor-
mation Systems, 13(2).
Intellectual Execution Scheme of Iterative Computational Models based on Symbiotic Interaction with Application for Urban Mobility
Modelling
251
