
The Development of Integration Technique Teaching Materials based on
Problem Based Learning in Integral Calculus Course
Zetriuslita and Rezi Ariawan
Mathematics Education Study Program, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
Keywords:
Integration Technique, Teaching Materials, Problem Based Learning.
Abstract:
This study aims to develop teaching materials of integration technique in Calculus course based on Problem
Based Learning approach that meet valid and practical criteria. The research method is development research
which consists of three stages: planning, development, and testing. The subjects of this study were the third
semester students of Mathematics Education involving 40 people. The data collection instrument consists
of validityand practicality sheets of teaching materials. The data collection technique was conducted with
non-test technique. The data analysis used descriptive quantitative technique. Based on the results of the
study, the teaching materials have met the valid criteria by 88.96% with Very Valid criteria. Furthermore, the
teaching materials also met practical criteria by 88.75%)with Very Practical criteria. Therefore, the findings
of this study indicate that the integration technique teaching materials based on Problem Based Learning in
Integral Calculus course meet very valid and very practical criteria.
1 INTRODUCTION
To improve the nation’s competitiveness in facing
the globalization era, higher education is needed to
develop science and technology. Higher education as
part of the National education system has a strategic
role in educating the nation’s life and advancing
science and technology. According to Law Number
12 of 2012 concerning Higher Education Article 4,
the functions of higher education are: (1) developing
capabilities and forming dignified national character
and civilization in order to educate the nation’s life;
(2) developing academicians who are innovative,
responsive, creative, skilled, competitive, and
cooperative through the implementation of Tridharma
Perguruan Tinggi (the University’s three main
purposes); (3) developing science and technology by
paying attention to and implementing the values of
humanities.
As one of the formal education institutions,
Universitas Islam Riau (UIR) is one of the institutions
which take part in realizing the function of higher
education that has been described above. In the field
of teacher training and education, FKIP (Fakultas
Keguruan dan Pendidikan—Faculty of Teaching
Training and Education) is a pioneer in producing
professional and reliable education personnel.
So far, the Mathematics Education, one of the
study programs in FKIP UIR, has tried to take
various actions in order to achieve the goals of higher
education, namely by trying to produce professional
and reliable education personnel. There are several
important elements, one of which is teaching staff or
lecturers. Law Number 12 of 2012 concerning Higher
Education Article 12 states that: (1) lecturers as
members of the academic community have the task of
transforming the knowledge and/or technology they
master to students by creating a learning atmosphere
so that active students develop their potential; (2)
lecturers as scientists have the task of developing
a branch of science and/or technology through
reasoning and scientific research and disseminating
it; (3) lecturers individually or in groups must
write academic textbooks, which are published by
universities and/or scientific publications as a source
of learning and for the development of academic
culture and civilization of writing activities.
The reality, however, contradicts the statement
above. Scientific writing in Indonesian universities
is unsatisfactory. The contribution of scientific
publications by Indonesian universities is only
0.0125% (Suroso, 2004; Mokhtar et al., 2010). He
supposes that Indonesia has 45 state universities and
1400 private universities with a total of 1,850,000
lecturers. If every lecturer in one year writes a book,
there will be 1,850,000 titles. But in reality, it is
Zetriuslita, . and Ariawan, R.
The Development of Integration Technique Teaching Materials based on Problem Based Learning in Integral Calculus Course.
DOI: 10.5220/0009094701230129
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education and Humanity (ICoSEEH 2019) - Sustainable Development in Developing Country for Facing Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 123-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-464-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
123

different. He added that the cause of lecturers’ weak
writing ability is the low activity of accessing the
internet. Lecturers do not have writing facilities such
as availability of collections, laziness in library visits
or downloading on the website. Furthermore, the
ability of lecturers to buy books, subscribe to journals,
and allocate a portion of their money to complete
their writing activities is also low, and include poor
translation skills. Besides, their weak writing ability
is also caused by people’s low interest in buying
books.
Meanwhile, according to Team Jago Nulis
Publisher Deepublish (2016), there are several
benefits from writing activities, including: (1)
obtaining passive income; (2) as a medium
for promotion / position; (3) self-promotion and
institution of work; (4) obtaining invaluable pride; (5)
getting credit points; (6) giving valuable contribution
to the people; (7) avoiding senility and improving
self-quality; (8) passing on the knowledge of future
civilizations.
Due to the benefits and the effort to carry out
the Law on Higher Education, the researchers are
interested in developing teaching materials. In
addition, the development of teaching materials
is based on several observations, experiences and
interviews that the researchers have done as the
permanent lecturers in the Mathematics Education
Study Program. The researchers found that: (1) most
teaching materials are not available for each subject,
so that this can raise doubts about the professionalism
of the lecturers who teach the subject; (2) learning
resources available to students are very limited,
especially textbooks that are prepared exclusively for
certain subjects by lecturers; (3) the interaction of
students in the class when lecturing takes place is very
low because some students do not bring the learning
resources and some bring the intended learning
resources but they have difficulties in learning and
understanding the material.
In addition, based on an unstructured interview
with several students during the lecture process in the
second semester in the academic year of 2017/2018,
it was found that; (1) students are easy to find
book references related to the subjects, but find
difficulties in determining which material should be
studied in accordance with the competencies that
must be possessed while participating in the course.
Then, there are several materials in many different
books. Consequently, students must have many
books as learning resources, while they have financial
constraints to buy them. (2) students often find
learning resources that are invalid (incomplete); (3)
the authors of the books (articles) they find on the
internet are often ambiguous especially from blogs;
(4) if the lecturer assigns certain materials to the
students, then they only take what is relatively easy
to understand, while the relatively difficult one is
disposed because it is not understandable, so the
urgency or point of learning is not achieved; (5)
students are most happy during the group’s paper
presentations, because their presentations are clarified
by lecturers in the class.
The findings presented above also occur in the
subjects that the researchers have been able to teach so
far, namely Integral Calculus. Integral Calculus is one
of the compulsory courses in Mathematics Education
study program. With 3 credits, students are required
to pass this course, because this course is prerequisite
for advanced calculus courses, Differential Equations,
and Initial Value Problem and Boundary Condition
Problem. Therefore, it must be mastered by the
students.
It is considered important and urgent to do
a development research that can produce Integral
Calculus teaching material.In the teaching of science
and biology the didactic materials are fundamental
tools in the taeching-learning process, being an
important and variable alternative in schools of public
scholls system. Teh use of these materials can help
the student in the contextualization of knowledge,
filling many gaps felt during learning, facilitating the
students to build their own conceptions of scientific
knowledge in relation to common knowledge, and
the socialization to common knowladge and the use
the contruction of new designs more elaborate. The
availability of references for Integral Calculus is now
very large and accessible. However, the references
do not support the achievement of competency
standards. In addition, several references only teach
students to calculate. Even though the demands
of integral calculus courses do not only provide
skilled students in calculating integrals, but also
provide understanding about integrals and using them
in solving various problems associated with them.
Therefore, teaching materials must be created to
teach and encourage students to actively involve and
construct their own knowledge.
To be able to develop teaching materials, the
teaching materials can be arranged based on problem
based learning. Problem-based learning is an
alternative learning model that allows students to
develop thinking skills (reasoning, communication,
and connection) in solving mathematical problems
(Rusman, 2010). Ben Martz and Morgan Shepherd.
(2005: 1-2) states, ”PBL at its core is an interactive
tool that uses prolems as the context for students
to acquire knowledge. Problem Based Learning in
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
124

centered on providing the student with a problem
environment which that students can create and store
memories and meanings”.
Furthermore, Wina Sanjaya (2011) suggests that
there are 3 main characteristics in a problem-based
learning strategy, namely: (a) a problem-based
learning strategy is a series of learning activities,
meaning that in implementing a problem-based
learning strategy there are a number of activities
that students must do. The problem-based learning
strategy does not expect students to simply record,
listen, then memorize the subject matter, but through
problem-based learning strategies students actively
think, communicate, search and process data, and
finally conclude; (b) learning activities are directed
at solving problems, meaning that problem-based
learning strategies place problems as keywords of
the learning process, without problems there is no
possible learning process; (c) problem solving is done
by using a scientific thinking approach. This is similar
to what was conveyed by Savin-Baden in Wendy
Barber, et al (2015):
”There are significant characteristics of PBL that
include: (1) Complex real world situations that have
no one ‘right’ answer are the organizing focus for
learning; (2) Students work in teams to confornt the
problem, to identify gaps, and to develop variabel
solutions; (3) Students gain new information through
self-directed learning; (4) Staff act as facilitators;
(5) Problems lead to the development of clinical
problem-solving capabilites”.
Based on the problems above and due to
time constraints, the researchers are interested in
conducting this research entitled ”The Development
of Integration Technique Teaching Materials in
Integral Calculus Courses Based on Problem
Based Learning”. The textbook is systematically
organized as follows: Cover, chapter titles,
material concepts, competency standards, basic
competencies, indicators, sub-chapter headings,
material presentation that directs students to do
activities with the following steps entitled: (1) let’s
focus on the problem; (2) let’s collaborate with your
group members; (3) let’s start working; (4) let’s
innovate and understand the results; (5) let’s analyze
and evaluate, examples of exercises, summaries,
exercises.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
Research that produces a product is known as
development research. According to Sugiyono
(2010), research and development is a research
method used to produce certain products and test the
effectiveness of these products.
Nana Syaodi Sukmadinata (2008) (Sukmadinata,
2011) stated that the steps of research and
development broadly consist of: (1) a preliminary
study consisting of literature review. In the literature
review, find and read articles in international journals
and national journals as well as source books related
to the textbook material that you want to develop;
(2) product development; activities carried out from
drafting instruments, validating instruments and
revising instruments, lastly (3) product testing. The
activity is to test the testing instruments that have
been valid and revised by the validators, and carry
out the analysis. Thus, in general the research design
consists of three stages including: development stage
(conducting observations and interviews, conducting
material analysis, analysis of competency standards
and learning indicators), planning stage (compiling
teaching materials according to material that has been
analyzed at the planning stage, compiling the validity
sheet and practicality sheet of teaching materials,
validating teaching materials to 3 experts, conducting
an analysis of the validity result, revising the teaching
materials that have been validatedby the experts,
and the testing stage (conducting trials and revise
teaching materials based on the result of the tests).
This research was conducted in the Mathematics
Education Program FKIP UIR in the odd semester
of 2018/2019. The subjects in this study were the
third semester students of the FKIP UIR Mathematics
Education study program who had taken part in
Integral Calculus course. The location, research time
and the subject of this study were selected on certain
considerations, namely:
• Ease of communication between researchers and
students because researchers are lecturers from
the students concerned.
• A research on the development of teaching
materials for integration techniques based on
Problem Based Learning in integral calculus
course has never been conducted in Mathematics
education study program.
The research instrument used to collect data in
this study is the validity sheet of teaching materials
compiled using several aspects: presentation, content,
compatibility with the principles of problem based
learning and mathematical critical thinking skills, and
language. Then, the practicality sheet of teaching
materials is compiled using the following indicators:
Interest in mathematics teaching materials based on
Problem Based Learning, Effect of Problem Based
Learning teaching materials on student learning
activities and motivation, Use of sentences in teaching
The Development of Integration Technique Teaching Materials based on Problem Based Learning in Integral Calculus Course
125
materials based on Problem Based Learning, Ease of
understanding material in teaching materials based
on Problem Based Learning, teaching materials
support mastery of material, teaching materials based
on Problem Based Learning in accordance with
students’ thinking background, Teaching materials
help construct understanding of a material, Delivery
of the material is associated with daily life, Teaching
materials help facilitate the students’ mathematical
critical thinkingability, Questions based on Problem
Based Learning are straightforward and challenging,
and It is good or not to be used in Mathematics
learning.
Data collection technique is carried out with
non-test technique. To get the data about the validity
of teaching materials, the researcher requested
validity from the experts by using the validity sheet
that had been designed. Lastly, to obtain the
data about the practicality of teaching materials, the
researchers used a practicality sheet given to students
during the testing process.The result of validity test
was analyzed in the following stages:
• Add the values of each indicator of the validity
sheet.
• Find the average value of each indicator given by
the validator with the following formula:
• Determine the combined validity with the
following formula:
• Determine the average value category based on
the Likert scale and determine the textbook
validity category. The following are the validity
categories of teaching materials.
Table 1: Interpretation Criteria for Teaching Material
Validity
Mean Score Category
85,01% ≤ V ≤ 100%
Very practical, or can be used
without revision
70,01% ≤ V < 85,01%
Quite practical, or can be used with
minor revisions
50,01% ≤ V < 70,01%
Less practical, it is recommended not
to use because it requires major revisions
V < 50,01% Not practical, or may not be used.
Source: Sa’dun Akbar, 2013
Next, the data from the practicality questionnaire
was analyzed by calculating the percentage of
practical teaching materials. According to Sudijono
(2008), the percentage of a value can be calculated
using the following formula:
P =
f
N
× 100% (1)
Description:
P: Percentage of assessment
f: Score obtained
N: Total Score
The category of mean score and textbook validity
is determined based on the Likert scale. The
following table describes the categories of teaching
material validity.
Table 2: Interpretation Criteria of Teaching Material
Practicality
Mean Score Category
85,01% ≤ ∨ ≤ 100% Very valid, or can be used without revision
70,01% ≤ ∨ < 85,01% Quite valid, or can be used with minor revisions
50,01% ≤ ∨ < 70,01%
Less valid, it is recommended not to use because it
requires major revisions
V¡ 50,01% Not valid, or may not be used.
Source: Modified from Sa’dun Akbar, 2013
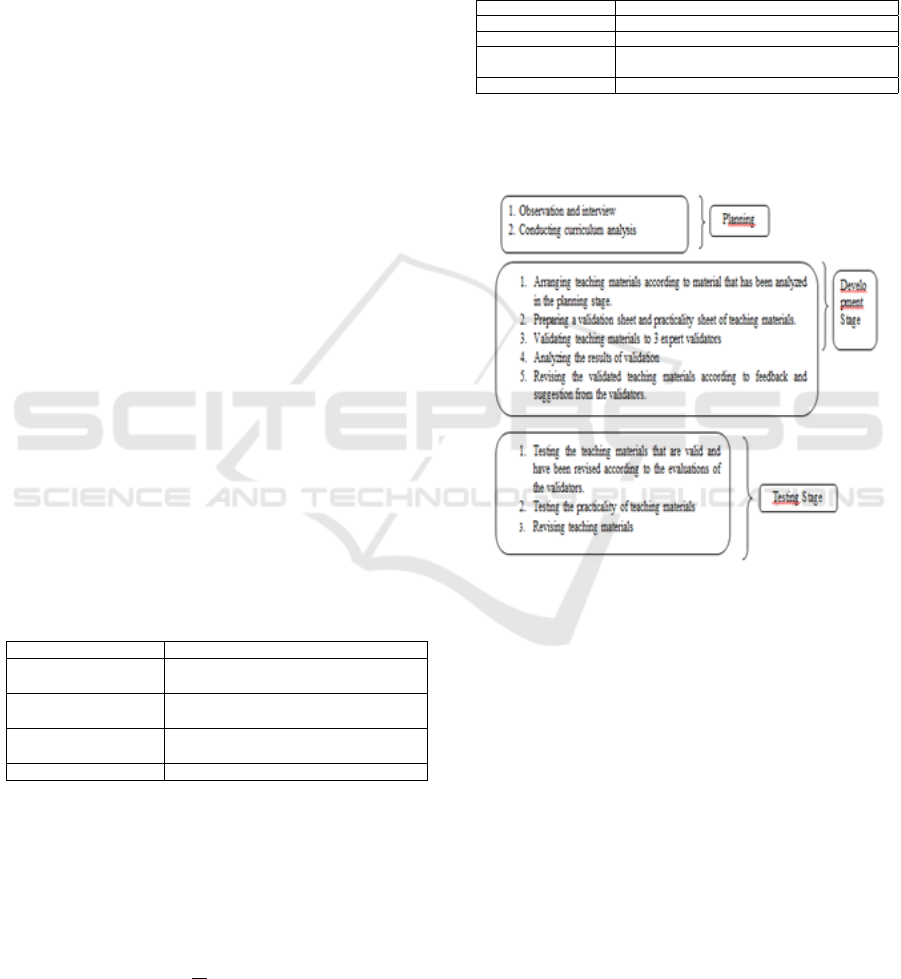
Figure 1 describes the procedures of this research.
Figure 1: Procedures of the Research
3 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Findings
Based on the development procedure in the planning
stage, the researcher conducted several things,
including:
3.1.1 Planning
The planning phase gins by analyzing the curriculum.
Curriculum analysis is carried out by conducting
reviews and discussions. The results of curriculum
analysis of the teaching material to be examined are
presented in Figure 2.
Moreover, in the planning stage, researchers
have also done observations and interviews with the
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
126
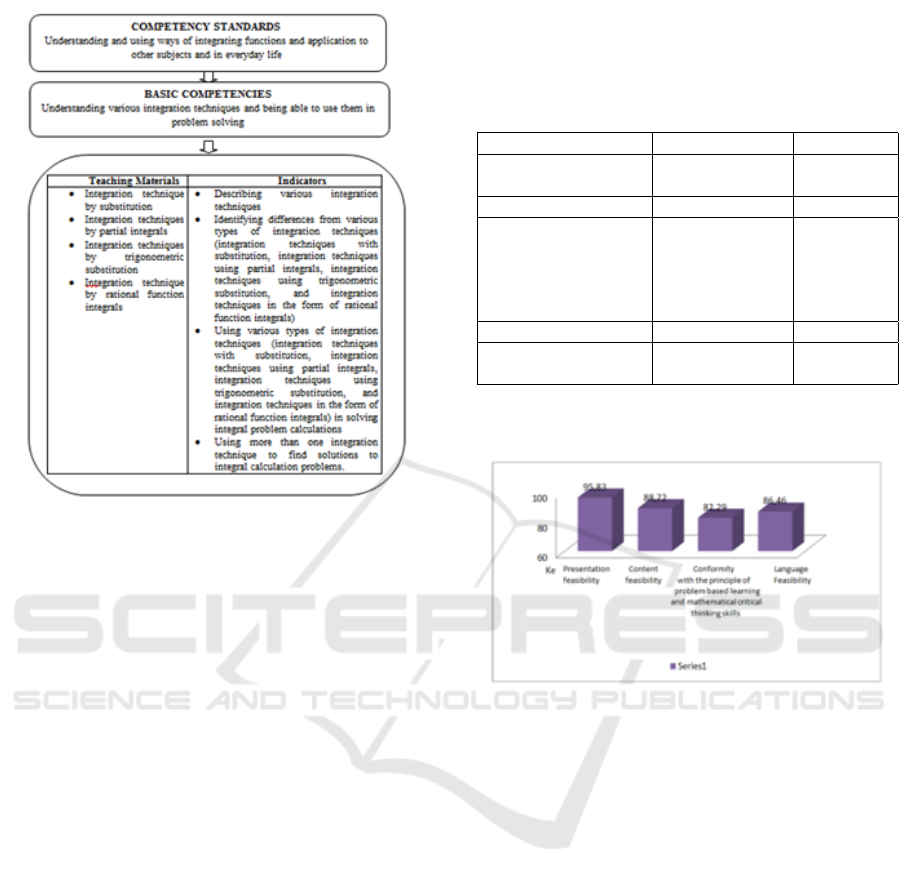
Figure 2: Curriculum analysis of the teaching material.
lecturers who teach integral calculus courses. The
information was obtained that innovation is needed
in conducting integral calculus learning. One of the
innovations is the development of teaching materials
that can involve students actively. In addition,
most students want integral calculus material to be
straightforward especially the material of integration
technique. Then, the learning process can involve
students and improve their mathematical thinking
ability.
3.1.2 Development
After the planning stage is carried out, the next
step that the researchers do is to develop teaching
materials. Teaching materials include: (1) cover; (2)
introduction; (3) table of contents; (4) Explanation
of basic learning competencies; (5) Explanation of
learning indicators; (6) A description of the focus of
teaching materials; (7) Instructions for using teaching
materials; (8) Exposure to teaching material presented
with the following activities namely let’s focus on
the problem, let’s have a discussion with your group
members, let’s start working, let’s innovate and
understand the results, let’s analyze and evaluate ; (9)
Sample Questions; (10) Summary; (11) Exercise.
The draft of teaching materials will be validated
by 3 experts. Experts will provide validity of teaching
materials with aspects of presentation feasibility,
content feasibility, conformity with the principles of
Problem Based Learning and mathematical critical
thinking skills and language feasibility. The results
of the validity can be seen in Table 3 and Figure 3
below.
Table 3: Teaching Material Validity Result by Experts
Aspects Assessed Percentage (%) Criteria
Presentation
Feasibility
95.83 Very Valid
Content Feasibility 88.72 Very Valid
Conformity with the
principle of problem
based learning and
mathematical critical
thinking skills
82.29 Quite Valid
Language Feasibility 86.46 Very Valid
Overall Percentage
(%)
88.96 Very Valid
tSource: Processed Data
Figure 3: Curriculum analysis of the teaching material.
Based on the result of the validity from the
experts, it can be seen that overall the validator
assessed that the teaching material has been very
valid and feasible for testing with minor revisions.
At last, referring to the feedback from the experts,
the researchers revised the teaching material that had
been developed.
3.1.3 Testing
The product testing was conducted on 40 third
semester students of Mathematics Education who had
attended Calculus II course. The test was conducted
on October 18, 2018 in room 6.09 Building A,
2nd floor. The trial process started from 13.30
- 16.00 WIB. The test was carried out in several
stages, including: (1) Opening lessons by conveying
apperception, giving motivation, delivering learning
objectives, and explaining the steps of learning to be
carried out by students in the class; (2) instructing
students to study in groups that have been formed at
the beginning of the meeting; (3) Providing revised
teaching materials; (4) Instructing students to study
The Development of Integration Technique Teaching Materials based on Problem Based Learning in Integral Calculus Course
127
with other group members by following the learning
steps contained in the teaching material; (5) At
the end of the meeting, the researcher distributed
questionnaire to students which serves to provide
an assessment of the new instructional materials in
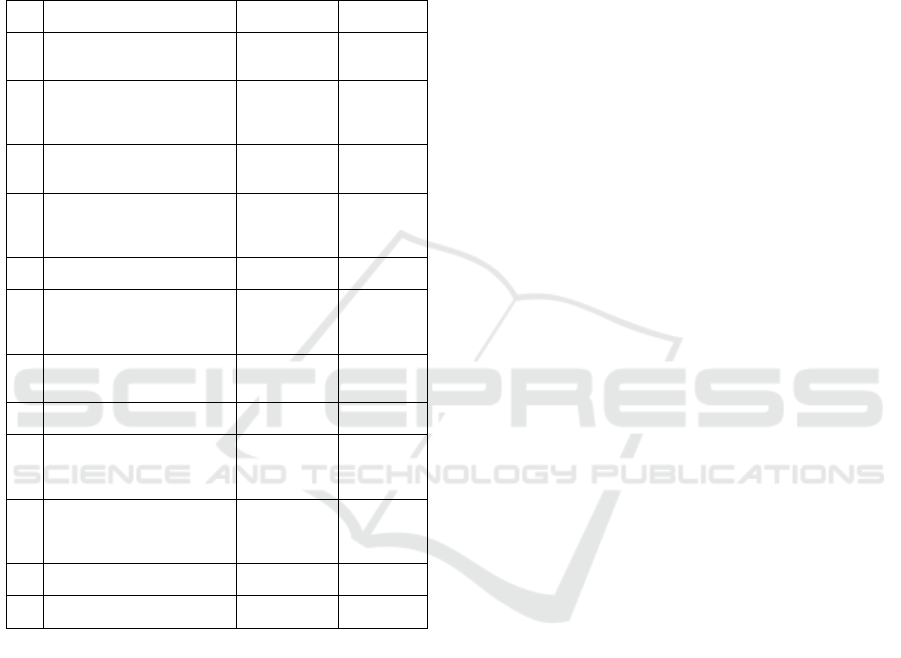
terms of practicality.Table 4 shows the result of
the practicality of teaching materials according to
students.
Table 4: Practicality Result of Teaching Materials
No. Indicators Percentage (%) Criteria
1
Interest in mathematics
teaching materials based
on Problem Based Learning
87.5 Very practical
2
Effect of Problem Based
Learning based learning
materials on student learning
activities and motivation
86.56 Very practical
3
Use of sentences in teaching
materials based on Problem
Based Learning
90 Very practical
4
Ease in understanding the
material in teaching materials
based on Problem Based
Learning
84.06 Quite practical
5
Teaching materials support
mastery of the material
86.88 Very practical
6
Teaching materials based on
Problem Based Learning are
in accordance with students’
thinking backgrounds
88.75 Very practical
7
Teaching materials help
construct understanding of the
subject
84.34 Quite practical
8
Submission of material is
associated with everyday life
88.13
Very
practical
9
Teaching materials
help facilitate students’
mathematical critical thinking
skills
79.69 Quite practical
10
The questions given in
teaching materials based
on Problem Based Learning are
straightforward and challenging
70 Quite practical
11
It is good or not to be used in
mathematics learning
88.75
Very
practical
Overall Percentage (%)
88.75
Very
practical
After testing and getting the students’ practicality
result of teaching materials with very practical
criteria, it can be stated that the final product of
teaching materials has been produced.
3.2 Discussion
In developing both the development of mathematical
critical thinking ability test instruments and teaching
materials, researchers have followed the stages and
procedures. Testing and processing of test result have
also been done by researchers with the procedures and
steps stated in chapter 3. The results of the validity
test showed that the teaching material falls into a very
valid category, can be used with a slight revision.
But there is avalidator who considers that the sample
questions and exercises presented in the teaching
material have not been able to stimulate students’
HOT skill. It is mentioned that the sample questions
and exercises are too easy for students, even though
they are based on indicators of mathematical critical
thinking. Meanwhile the other validators consider the
sample questions and exercises to be appropriate but
the variations are lacking, so it must be added. The
feedback is actually good, but the researchers have
other considerations, related to the difficulty level of
the sample questions and exercises. The researchers
consider that the sample questions that the researcher
presents with steps , but students also still have to
find it themselves, adjusted to the level of ability
and needs that researchers get based on research and
experience of researchers as the lecturer who teach
integral calculus course. It is assumed that such
teaching materials can help the students’ learning
process in integral calculus. We can compare this with
the results of the practicality questionnaire obtained
from the testing of the use of integral technique
teaching materials based on Problem Based Learning.
The result of the testing shows that that the
teaching materials are “very practical”. However,
there are Problem Based Learning indicators in
teaching materials that are straightforward and
challenging. Teaching materials that help facilitate
the students’ mathematical critical ability have
practical criteria and have the smallest percentage
score compared to other indicators. This was in
line with the statement that the sample questions
and exercises had not been able to stimulate HOT
students. But based on the interviews with the
students, the sample questions and exercises were
too difficult for them to complete. Based on these
statements, the researcher assumed that the statement
by the validators and the students had different
meanings. The former stated that the questions and
exercises must be changed and the level of difficulty
increased so as to stimulate students’ higher order
thinking skills, while the latter stated that the sample
questions and exercises were too difficult for them. In
conclusion, the teaching materials that the researchers
have developed are “very valid” and “very practical”.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
In conclusion, teaching materials of integration
technique based on Problem Based Learning are
considered very valid and very practical. The
researchers have developed valid and practical
materials to be used in teaching integration technique
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
128

in integral calculus course. The researchers suggest
that the practicality of students in using teaching
materials should not be used as a benchmark
in determining or seeing an increase in students’
abilities. The practicality does not describe their
abilities. Then, teaching materials must be presented
in steps with a variety of problems that are more
straightforward.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank the financial support
provided by University of Indonesia University
through the PITTA 2019 funding scheme managed
by Directorate for Research and Public Services
(DRPM) University of Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Akbar, S. (2013). Instrumen Perangkat Pembelajaran.
Rosda karya, Bandung.
Barber, W., King, S., and Buchanan, S. (2015). Problem
based learning and authentic assessment in digital
pedagogy: Embracing the role of collaborative
communities. Electronic Journal of E-Learning,
13(2):59–67.
Martz, B. and Shepherd, M. (2005). Problem Based
Learning and the business school environment.
Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences, 00(C):40.
Mokhtar, M., Tarmizi, R. A., Ayub, M., and Tarmizi,
M. A. A. (2010). Enhancing calculus learning
engineering students through problem-based learning.
WSEAS transactions on Advances in Engineering
Education, 7(8):255–264.
Rusman (2010). Model-model Pembelajaran
(Mengembangkan Profesionalisme Guru). Rajawali
Pers, Jakarta.
Sanjaya, W. (2011). Strategi Pembelajaran Berorientasi
Standar Proses Pendidikan.
Sudijono, A. (2008). Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan.
Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada.
Sugiyono (2010). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan
(Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D).
Alfabeta, Bandung.
Sukmadinata, N. S. (2011). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan.
Rosdakarya, Bandung.
Suroso (2004). Penulisan Buku ajar Perguruan Tinggi.
Makalah disampaikan Dalam Penulisan Buku Sekolah
Alkitab Baptis.
The Development of Integration Technique Teaching Materials based on Problem Based Learning in Integral Calculus Course
129
