
Integrated E-Learning Implementation at University Learning Process
Sri Yuliani
1
and Dicki Hartanto
2
1
Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia
2
Universitas Islam Negeri Sultan Syarif Kasim, Riau, Indonesia
Keywords:
Integrated E-Learning, University Learning Process.
Abstract:
Even e-Learning application in some universities in Riau has began in 2010, but in learning practice, the
eLearning has not been done with integration with other methods. Therefore, the study was interested to be
done. The study was conducted at 2 universities in Riau in 2018. The sample of study was the students
followed e-Learning. The sampling technique was purposive sampling. From the findings, it is seen that the
application of distance education or e-learning during the processes of learning in both universities were still
limited. From the interviews, the students’ opinions were summarized as follows: 1) To provide appropriate
materials in the e-learning, 2) To offer more variations in e-learning, 3) To add more attractive images, 4) To
integrate the e-learning in learning processes 5) To announce information about activities in the university, 6)
To add words and video of motivation, 7) Each material should be attributed to applied context. The integrated
design of e-learning in the university is proposed to be implemented in both university with the steps of
integrated e-learning that can be divided into 3 steps as below: 1) Preliminary 2) Progress and 3) Evaluation.
In supporting the e-learning integration, the facilities and methods required were identified.
1 INTRODUCTION
The implementation of ICT (Information and
Communication Technology) recently grows so
rapidly. Even, the current ICT utilization has
developed to various areas such as economic, social,
trade, agriculture, education and other areas. This
phenomenon is increasingly recognized inseparable
from the belief in the benefits perceived by the public
in assisting the tasks and activities undertaken. When
the use of ICT in the 2000s was considered a new and
luxurious, but currently, ICT is no longer like that
happened 10-15 years ago. From the people in the
village to the city, from lower education to university
is very dependent and really need this ICT utilization.
From various usage of ICT, browsing activity may
be one of the most common Internet activities
performed. By browsing, an internet user will obtain
the desired text. Off course, an administrator (usually
abbreviated admin) of e-learning course can see the
potential of research in e-learning. But they are not
alone. People who have used the Internet also (or
using e-learning) can see the potential of the research.
The emergence of e-learning research is still virtually
new, because it is the advent of e-learning is also
crowded not until a dozen of years.
Presently, the number of universities that have
implemented Distance Education or e-learning is
still very minimal. From total 4,741 universities
in Indonesia, only 15-20 campuses of them have
already applied the online lectures. ”How many of
the 4,741 tertiary institutions, about 15-20 universities
have already implemented e-learning,” said Minister
of Research, Technology and Higher Education,
Mohamad Nasir after the ceremony commemorating
the 2019 National Education Day, on University of
Indonesia (UI) campus, Depok, Thursday, May 2,
2019.
The lecturers preparation is not only done through
training, but also grouping or clustering. From the
results of FGD, the next stage is training the campus
to prepare studio infrastructure. ”The next is the
online lecture system, later the lecturers and later
we will coordinate the chancellors in universities
in Indonesia,” Nasir concluded. The Ministry of
Research, Technology and Higher Education targets
an increase in the higher education gross enrollment
rate (APK) of 50 percent in the next five years. In
addition to continuing to run lectures on conventional
(face-to-face) courses, the target will also be boosted
by increasing the application of Distance Education
or e-learning in universities.
458
Yuliani, S. and Hartanto, D.
Integrated E-Learning Implementation at University Learning Process.
DOI: 10.5220/0009390604580464
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education and Humanity (ICoSEEH 2019) - Sustainable Development in Developing Country for Facing Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 458-464
ISBN: 978-989-758-464-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In general, we should understand on what the e-
Learning is in fact. e-Learning is a distance learning
which use technology, network of computer and or
Internet. e-Learning makes possible the learners to
learn through computers in their respective places
without having to physically go to follow lessons /
lectures in class. e-Learning often understood as a
form of web-based learning that can be accessed from
the intranet on a local network or the Internet.
Although the appplication of e-learning systems
that exist today are very varied, but all of it is based
on a principle or concept that e-learning is intended
as a distribution of learning materials through media
of electronic or the Internet, so that students are able
to access them anytime from around the world. The
characteristic of learning with e-learning is to create a
learning environment that is flexible and distributed.
The flexibility became the key word in the e-learning
system. Students become very flexible in choosing
the time and place to study because they do not have
to come in somewhere at a certain time. On the other
hand, the lecturer can renew its learning materials
anytime and from anywhere. In terms of content, the
learning material can be made very flexible ranging
from text-based lecture material to material that is
loaded with multimedia components.
The quality of learning with e-learning was also
very flexible or varied, which could be worse or better
than face-to-face learning system (conventional). To
get a good e-learning system is needed a good
design as well. The distributed learning refers to
learning in which teachers, students, and teaching
materials situated in different locations, so that
students can learn anytime and from anywhere they
are. In designing e-Learning systems, we need
to consider two things, namely the participants
or students who become targets and the expected
learning achievements. An understanding of the
learners is very important, namely, among others, the
expectations and their goals in a follow e- learning,
the speed in accessing the Internet or a network,
bandwidth limitations, the cost for Internet access,
as well as background knowledge concerning the
readiness of the following study. To understand
the outcomes of learning required to determine the
material scope, learning achievement assessment
framework, as well as prior knowledge.
From the research of the KTP students, the
readiness of PSB course participants in e-Learning
are as below : 1). Quite adequate utilization of
IT experience to follow e-Learning, but there was
still 7% who did not have sufficient experience,
2). Accessibility of technology usage has a great
achievement of 70%, but the rest of 30% is still
limited in accessibility, 3). IT-based learning
habits of students were adequate, but there were
14% of students that were not used to learn by
utilizing IT, 4). Online learning preferences of
students shows that 19% of students prefered the
conventional way. From the results, it deserves to be
utilized as a communication option that complements
the traditional classroom, but still requires the
consistently development, where it is visible on the
side of the design that was quite feasible used but it
was only in the good criteria (75%). In the aspect
of media display, it’s categorized as good (74%).
Specifically from the aspect of media, the usage
of images and videos that were relevant to support
the presentation improved the quality of the web
significantly (Pujiriyanto, 2010).
E-Learning application in the universities in Riau,
Indonesia varied based on facility and supported
policy in each university. In UIN Sultan Syarif
Kasim Riau as a state university in Riau, e- learning
had initiated with workshop and training provided
to lecturers from 2010 to 2014, while in Universitas
Islam Riau had started e-learning from 2015. In
fact, there are still small number of lecturers that
apply it in the process of learning. To encourage the
achievement of the vision and mission of university
and study programs, they should be formulated in the
Strategic Plan of each university, therefore e-Learning
and its implementation for the lecturers and students
to face 4.0 Industrial Era are very urgent to be applied.
Therefore this study is very interested to be done by
the universities in Indonesia, especially in Riau.
2 LITERATURE REVIEWS
Yusuf (2005) explained that the education has been
influenced by ICTs, that have undoubtedly given
the effects on the teaching, learning, and research.
Then Al-Ansari (2006) had the opinion which a
lot of researches have proven the benefits to the
education quality. ICTs provide the potential to
innovate, accelerate, enrich, and deepen the skills, to
motivate and engage the students, to help experiences
of the schools to work practices, create economic
viability for tomorrow’s workers, as well as to
strengthen teaching and helping schools change
(Davis and Tearle, 1999; Lemke and Coughlin,
1998; cited by Yusuf, 2005). Then Jhurreev
(2005) declared that so many has been declared
and reported about the technology effects, especially
computers, in education. In the first, the computers
were used to teach computer programming but the
development of the microprocessor in the early 1970s
Integrated E-Learning Implementation at University Learning Process
459

saw the introduction of affordable microcomputers
into schools at a rapid rate. The computers and
applications of technology became more pervasive in
society which led to a concern about the need for
computing skills in everyday life.
New Media Consortium (2007) states that ICT
gives an entirely new learning environment for
students, thus requiring a different skill set to be
the successfulness of critical thinking, research,
and evaluation skills are growing in importance as
students have increasing volumes of information from
a variety of sources to sort through. ICT is changing
teaching and learning processes by adding elements
of vitality to learning environments including virtual
environments for the 6 purposes. ICT is a potentially
powerful tool for offering educational opportunities.
It is difficult and maybe even impossible to imagine
future learning environments that are not supported,
in one way or another by ICT.
E-learning is learning that is structured with the
aim of using electronic or computer system that
can support the process of learning (Michael, 2013),
while according Chandrawati (2010) e-Learning is a
distance learning process by combining the principles
of the learning process technology. Ardiansyah
(2013) defines e-Learning as a learning system
that is used as a tool for teaching and learning
process is carried out without having to come
face to face directly between teachers and students.
According (Heinich et al., 2005), e- learning can
often be done in a live, face-to-face teaching and
learning is called blended or mixed (hybryd learning).
Likewise, e-Learning is intended to complement
online learning, not for conventional learning.
The characteristics of E-learning based on the
opinion of Nursalam (2008: 135) are described as
follows:
• To utilize the electronic technology service.
• To utilize the computer advantages (digital media
and networks of computer)
• To use the teaching materials which is
independent (self-learning materials) and then
stored in the computer, so it can be accessed by
the lecturers and students anytime and anywhere.
• To use the schedule of learning, curriculum,
learning progress results, and all matters related to
the education administration can be checked any
time on the computer.
E-Learning in a broad sense can include the
learning that are available in electronic media
(internet) either formally or informally. E-Learning
formally, for example learning with the curriculum,
syllabus, subjects and tests that have been organized
and prepared on a schedule agreed upon relevant
parties (manager of e-Learning and learners
themselves). The learning like these are usually
high level interaction and required by the company
to its employees or distance learning managed
by universities and companies (usually consulting
firms) which are usually engaged in the e-Learning
provision to the public (Rahmasari and Rismiati,
2013).
According to Pranoto et al (2009: 309) that some
of the benefits of learning E-learning can be described
as follows:
• The e-learning utilization to support the
implementation of the learning process can
improve the students absorption on the material
being taught.
• Increasing the active participation of students.
• Improving the self-learning ability of students.
• Improving the quality of teachers and training
materials.
• To improve the ability to display information
with information technology devices, where the
devices are very difficult to implement.
While related to integrated e-learning, the study
of Geoffrey Kituyi and Irene Tusubira (2013)
concluded that the requirements for the integration
of e-learning and other learning methods were
identified as the use of projectors, mixing face-to-
face and e-learning, harmonizing course content
for elearning and face-to-face during design phase
and incorporation of 3D pictures in face-to-face.
In addition, the use of videos, audio tapes, guest
lecturers, textbooks and other reading materials and
training were also suggested as requirements for
successful integration of e-learning. These findings
agree with Kanovsky and Or-Bach (2001); Raja
(2004; O’Neill et al, (2004).
3 METHODS
3.1 Location, Sample, Sampling
Technique and Instruments
Research was done at the State Islamic University
(UIN) of Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau and Universitas
Islam Riau in 2018, Pekanbaru.
Data was collected with purposive sampling in
both university. population was restricted to students
who had been studying in this college at least for 2
year, so that they can provide objective opinions and
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
460

judgments and unreliable about the implementation of
e-learning in learning processes.
The research instruments used in this study were
Interviews, observations and documentations from
the universities in Riau.
3.2 Research Steps
The steps performed in this study are as follows:
• Preparation: theoretical frameworks and research
instruments
• Development: Design Development of integrated
e-Learning
• Application of e-Learning: integrated e-Learning
Application
• Model of integrated e-Learning based on
interviews and observations.
• Conclusion: Summing up the findings of research
3.3 Data Analysis
The data was analyzed descriptively after the
observations and interviews done. According to Agus
Irianto (2004) that even descriptive research results
are simple, but the user of this simplification can take
the meaning of the data. The assumption that this
would cast doubt not always true, because there is the
possibility of the nature of existing data can only be
analyzed descriptively.
Procedures of analysis began with the descriptions
of e-learning implementations in both universities
with their own characteristics. Then, the proposed
model of integrated e-learning is submitted as the
future model of integrated e-learning that can be
applied in each university.
4 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Research Findings
From all the descriptive statistical analysis obtained in
the study, then the researcher subsequently provided
conclusions and discussions related to the data that
was generated. Discussion and conclusions obtained
were followed or supported by the theories that have
been constructed by the researchers associated with
the discussion.
In addition to the existing theory, researcher also
included some information or additional information
obtained from the students or respondents’ opinions
about the role of higher education in general. The
application of ICT through e-Learning at UIN Sultan
Syarif Kasim Riau is done as follows:
• 1) E-learning UIN Suska Riau is implemented
with integrated online learning paradigm using
the LMS (Learning Management System) which
is very well known “Moodle”.
• The system of e-learning has been functioning as
being expected and can be accessed via the URL:
http://elearning.uin-suska.ac.id
• With e-learning system, the lecturers can manage
the learning material, namely: preparing a
syllabus for the course, uploading the learning
material, assigning tasks to the student, the
student receives a job, creating the tests / quizzes,
providing students’ scores, monitoring the activity
of students, interacting with students and other
lecturers through discussions in forums and chat
and others. In addition, students can access
information and learning materials, interact with
students and lecturers, conducting transactions of
lecturing assignments, taking tests / quizzes, and
so forth.
• E-learning at UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau is
implemented by using LMS Moodle. LMS is
a software for creating course materials on-line
(web based), managing learning activities and
results, facilitating interaction, communication,
cooperation between lecturers and students.
• e-Learning with Google Classroom also has been
developed by PTIPD UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim
Riau to support learning processes with online
base.
Moodle is an open source LMS which can be
got freely through http://moodle.org. Moodle can
easily be used to develop an e-learning system. The
e-learning portal with Moodle can be modified as
needed. Currently there are over 28 thousand e-
learning sites in more than 186 countries developed
with Moodle (http://moodle.org/sites/). Meanwhile,
in Indonesia there are more than 157 sites developed
with Moodle elearning included in UIN Sultan Syarif
Kasim Riau.
The designed e-Learning in UIN Sultan Syarif
Kasim Riau can be found as below :
Universitas Islam Riau (UIR) has been carrying
out an E-Learning program since 2015, but has
not been implemented effectively. E-Learning is a
computer electronics that gets learning materials that
are suitable for their needs and delivered teaching
materials to students using internet media, or other
computer network media.
Integrated E-Learning Implementation at University Learning Process
461
Figure 1: E-Learning with Moodle in UIN Sultan Syarif
Kasim Riau
Figure 2: Implementation of e-Learning for all faculties in
UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau
The purpose of UIR is to implement E-Learning
to improve the quality of lecturers in providing
learning, making it easier for students to understand
the material and assignments given by the lecturer
because they have been informed from the beginning.
So that the classroom atmosphere becomes more
active.
E-learning implemented in Universitas Islam Riau
with integrated online learning paradigm is described
as below :
• Implementation was done by each faculty with
various methods
• Lecturers and students must have an UIR email.
UIR email can be registered at sikad.uir.ac.id
on the email registration menu provided like
edu.uir.ac.id for the lecturers and student.uir.ac.id
for the students
E-Learning application is intended for all lecturers
and all fields of study. For this reason, UIR needs
to make various efforts so that this system can be
implemented such as making internet shops so that
students who do not have laptops can also take part
in this program. ”By implementing this system,
the lecturers in the class are only facilitators both
theoretically and pragmatically. ”Field issues and
empirical data can enrich students and lecturers
in conducting discussions and there are still many
obstacles faced such as lecturers who are still
stuttering technology and students who do not have
facilities such as laptops and UIRs themselves do
not have large capacity servers to accommodate this
system so that communication is smooth and not
slow,” said Deputy Rector I UIR, Dr. Nurman, S.Sos,
M.S (AKLaMASI on Friday 24/2/2017).
Figure 3: E-learning in FKIP UIR
Figure 4: E-learning in Psychology UIR
When interviewed about E-learning there
were students who disagreed like Putri Royantika
(Teaching and Education Faculty) and Nartiyani
(Faculty of Economics) on the basic reason
that the e-Learning system was complicated and
difficult, while Desti Nur Anisa Sundari (Faculty
of Communication Sciences) if e-learning is
implemented it will make it easier to follow the fields
of study provided by lecturers and more closely
follow technological developments.
In recent years, UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau
has continued to promote the development of ICT
in order to support the development of the quality
of teaching, administration and finance in supporting
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
462
the effectiveness and efficiency of higher education
in order to support the achievement of the vision and
mission of UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau, one of
which is related to the development of technology.
As for efforts in improving the quality and
academic services, UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim
Riau issued several strategic policies such as the
implementation of SIMAK (Academic Management
Information System), KRS Online and Free Wifi
for the academic community. Even in 2015, it was
developed further of Integrated Systems of Iraise
through the innovation conducted by Computer
Center at UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau. This was
done in addition to the use of technology in support
of academic and simplify the process of academic
services, as well as to amend paradigna from a
manual system to a digital system.
While in the field of teaching education, UIN
develops special blog for lecturers and students,
provides special e-mail for university such as:
dicki.hartanto@uin-suska.ac.id, continues to develop
e-learning, e-journal that can be accessed directly
online, the alumni- online based tracking system, the
manufacture of correspondence and other online. In
2015, LPPM is also as one of the institutions at UIN
Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau that applied the registration
process for research and community services with
online system. From the use of ICT, it is expected
in the next few years, both academic, financial and
teaching began gradually shifting from the traditional
one into the multimedia system.
4.2 Discussion
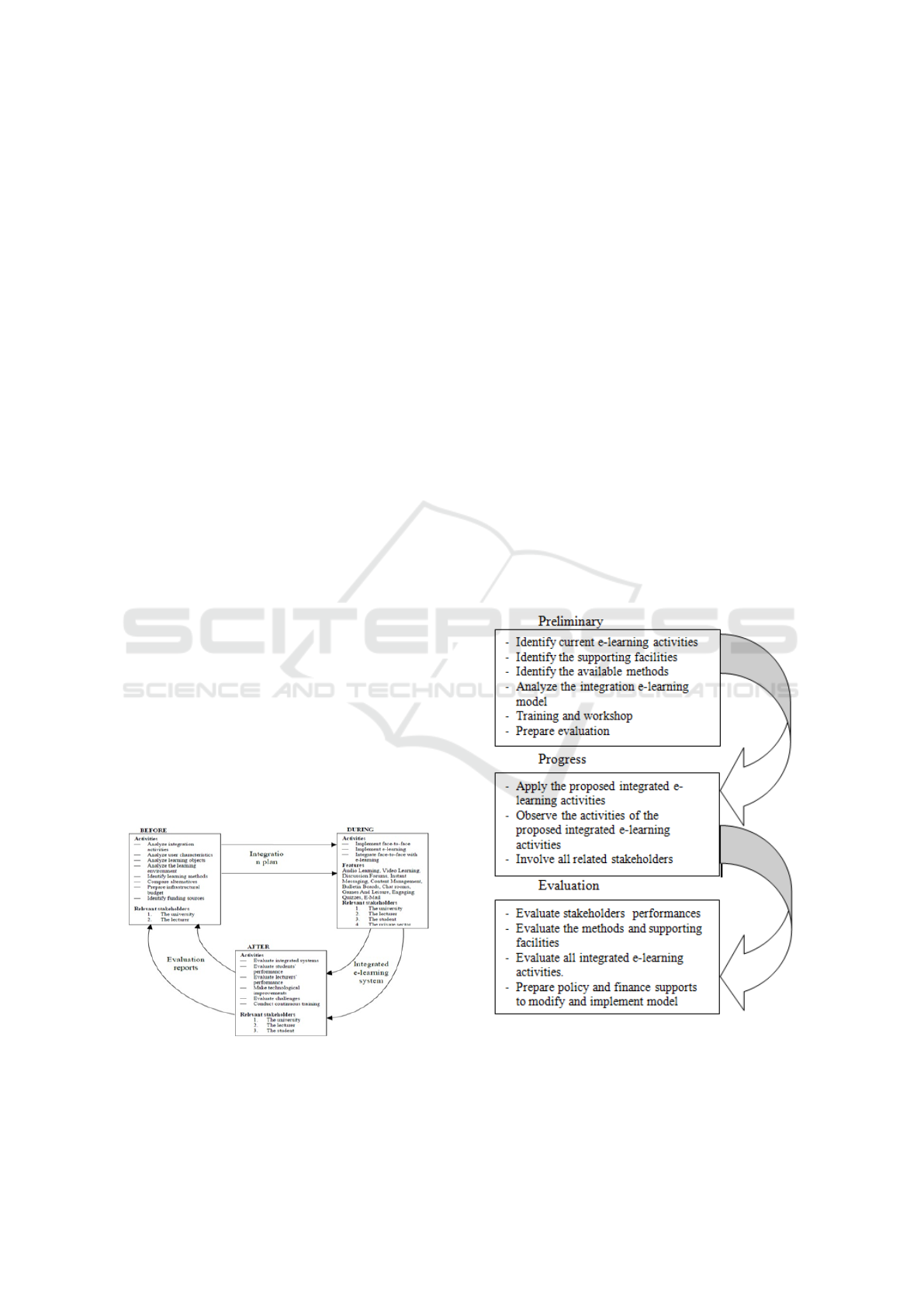
The below model is one integrated model that was
proposed by Geoffrey Kituyi and Irene Tusubira
(2013) that was divided into 3 phases as below :
Figure 5: Integrated E-learning Framework by (Kituyi and
Tusubira, 2013)
The application of e-learning in both university in
Riau still varied and have different design, although
they have some similarities like the implementation of
e-mail for lectureres, stass and students. In learning
process, UIN Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau has used
e-learning with moodle, while in UIR has applied
e-learning by using blogspot or any designed web
in each faculty. In general, the implementation of
e-learning in the universities in Riau is still very
limited and not grow quickly.
The current implementations of e-learning can be
explained as below :
• E-learning is applied in moodle and blogspot or
paid web design.
• E-learning is not managed properly by both
universities
• Methods of e-learning implementation in both
universities are not clear.
• There are no particular policies from universities
to implement e-learning.
• Limited training and workshops are done to
support e-learning application in the university.
Therefore, the integrated design in e-learning in
the university is proposed to be implemented in both
university that become the sample of this study.
Figure 6: Proposed Integrated E-learning Model (Yuliani
and Hartanto, 2019)
To support the e-learning integration, the facilities
and methods required were identified like projection
equipment as infocus; implementation of e-learning
Integrated E-Learning Implementation at University Learning Process
463

methods to teach online and direct learning method
to administer the tests and exams; course content
harmonization for e-learning and direct learning
method during design phase; incorporation of 3D
pictures, audio and videos in classrooms among
others, integration traditional methods with update
social media implementation like Whatssup, Line,
Facebook, Instagram and others online methods like
website or blogs that can be freely done.
From the observations and interviews, some
respondents’ opinions of students about e-Learning-
based are summarized as follows: 1) To provide
appropriate materials with integration, 2) To offer
more various learning, 4) To announce information
about activities in university, 5) To integrate e-
learning in learning processes 6) To add words and
video of motivation, 7) Each material should be
attributed to applied context.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study concluded that the e-Learning
implementation in both universities seems limited
and need to develop the alternative model by the
supports of university management. Some efforts
to improve the e-learning as below: 1) To provide
appropriate materials in the e- learning, 2) To offer
more variations in e-learning, 3) To add more
attractive images, 4) To integrate the e-learning
in learning processes 5) To announce information
about activities in the university, 6) To add words
and video of motivation, 7) Each material should
be attributed to applied context. The integrated
design of e-learning in the university is proposed
to be implemented in both university with the steps
of integrated e-learning that can be divided into 3
steps as below: 1) Preliminary 2) Progress and 3)
Evaluation. In supporting the e- learning integration,
the facilities and methods required were identified.
Then, it is recommended to conduct next study on
the e-Learning implementation based on integration
by each university and lecturers. Then, the design of
e-Learning should be updated frequently to improve
the learning processes.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We need to express our appreciation and
thanks to all parties that contributed to this study,
especially lecturers and students who participated in
e-learning and the observations and interviews in both
universities : Universitas Islam Negeri Sultan Syarif
Kasim Riau and Universitas Islam Riau.
REFERENCES
Al-Ansari, H. (2006). Internet use by the faculty
members of kuwait university. The electronic library,
24(6):791–803.
Ardiansyah, I. (2013). Eksplorasi Pola Komunikasi dalam
Diskusi Menggunakan Moddle pada Perkuliahan
Simulasi Pembelajaran Kimia. Universitas
Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung-Indonesia.
Chandrawati, S. R. (2010). Pemamfaatan e-learning dalam
pembelajaran. Jurnal Cakrawala Kependidikan, 8(2).
Heinich, R., Molenda, M., Russell, J. D., and Smaldino,
S. E. (2005). Instructional technology and media for
learning ( 8ed). Merrill prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Jhurree, V. (2005). Technology integration in education
in developing countries: Guidelines to policy makers.
International Education Journal, 6(4):467–483.
Kituyi, G. and Tusubira, I. (2013). A framework for
the integration of e-learning in higher education
institutions in developing countries. International
Journal of Education and Development using ICT,
9(2).
Michael, A. (2013). Michael allen’s guide to e-learning.
Canada: John Wiley & Sons.
New Media Consortium, . (2007). Horizon
Report. retrieved July 1 2007 from
www.nmc.org/pdf/2007 Horizon Report.pdf.
Nursalam and Efendi, F. (2008). Pendidikan dalam
Keperawatan. Salemba Medika, Jakarta.
Pranoto, Alvini, d. (2009). Sains dan Teknologi. PT
Gramedia Pustaka Utama, Jakarta.
Pujiriyanto (2010). Pengembangan E-Learning Berbasis
Learning Management System Pada Mata Kuliah
Pengelolaan Sumber Belajar E-learning berbasis
LMS. Laporan Penelitian.
Rahmasari, G. and Rismiati, R. (2013). E-Learning
Pembelajaran Jarak Jauh. Penerbit Yrama Yudha,
Bandung, volume 103. Yrama Yudha, Bandung.
Yusuf, M. O. (2005). Information and communication
technology and education: Analysing the nigerian
national policy for information technology.
International education journal, 6(3):316–321.
ICoSEEH 2019 - The Second International Conference on Social, Economy, Education, and Humanity
464
