
Effectiveness of Draw Cards for Language Development
of Dislexia Children
Maria Ulfa
Faculty of Psychology, Muhammadyah University, Aceh, Indonesia
Student at Universitas Pendidikan Sultan Idris, Perak, Malaysia
Keywords: Dyslexia, Language development, Picture Cards.
Abstract: A common problem experienced by children with dyslexia is difficulty in the ability to read and write. The
lack of vocabulary mastered by dyslexic children is due to neurological factors, namely in the left
hemisphere of the brain that is related to the sequence, linear thinking, and language skills have a small size
than normal humans. Good and appropriate treatment will make the child more able to overcome this
problem. The purpose of the study is to test a simple card-shaped technique and learning tool that is
attractive for dyslexic children to stimulate language development (eg vocabulary). This study uses
experimental techniques the one group pre-test post-test, which is an approach that gives treatment to one
group then the results will be calculated the difference. The treatment used is giving a picture card. The
subjects in this study were 4 people. This research is expected to make a new paradigm for the world of
education especially for dyslexic children.
1 PRELIMINARY
Child development is a process of increasing ability
in a child with information obtained from the family
environment and social environment progressively.
Some child development factors are strongly
influenced by several factors, including gene factors,
parenting and nutrition that children get from birth.
In addition, a very important factor that considered
in the child's growth and development are
environmental factors in which children live, go to
school, and socialize.
Talking is one of the children's developments
that must be got through properly, because the
development of language is an amazing
development process. Children will go through this
process not only demanded by their abilities, but
also greatly influenced by environmental factors.
Because children will learn to speak well if they hear
appropriate language. Usually children will know a
lot of vocabulary from the age of 3-4 years, when
the language used is not limited to as a
communication tool, but also as information to
stimulate cognitive development.
Dyslexic children who have difficulty in the
ability to read and write, even talk and listen to other
people's voices and translate them into words,
analyze the meaning of words and mix sounds in
words. Researchers from Yale University, Dr. Sally
Sahywittz, argue that to learn languages, dyslexics
use other parts of the brain, which are used by
people in general in processing language. Some
studies from a neurology Harvad Medical School
mention that the hemisphere of the human brain has
two asymmetrical hemispheres of the brain, while in
symmetrical dyslexics. This means that the right
hemisphere of people with dyslexia is greater than
the human right brain in general. This is what makes
dyslexics have strength in the right brain. The right
brain has abilities related to intuition, creativity, and
visual abilities. These are the strengths and
advantages of dyslexics. Meanwhile, the left
hemisphere associated with linear thinking and
children's language skills in dyslexic children tend to
be smaller than normal humans. This is what makes
language skills and processing linguistic information
different.
In connection with the foregoing, it is necessary
to have the right methods to stimulate the
development of the language of dyslexic children in
order to develop optimally so that cognitive
development can be maximized. The phenomenon
that often occurs is that dyslexic children who learn
in a school only get the same learning material and
284
Ulfa, M.
Effectiveness of Draw Cards for Language Development of Dislexia Children.
DOI: 10.5220/0009447902840290
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Psychology (ICPsy 2019), pages 284-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-448-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

repeat it, so that when the material is delivered, the
child will have difficulty remembering and must
repeat again.
Researchers as practitioners of child
development, encounter cases of children who
experience some characteristics of learning
difficulties such as not being able to understand
reading and having a limited vocabulary even
though they are 7 years old, having difficulty
concentrating, avoiding academic tasks, and
experiencing social-emotional problems. However,
when measuring its intellectual potential, the
cognitive abilities of these children in the above-
average category were measured.
Of course this learning difficulty is not due to
limited cognitive abilities, but there is a disruption of
learning difficulties. Researchers want to try to use a
simple and fun method to stimulate the development
of children's language to be more fully developed so
that children will have more vocabulary that affects
the ability to read and understand the contents of the
reading.
Dyslexia is a form of specific learning
difficulties that is most often among the two other
specific forms of learning difficulties, namely
dysgraphia and dyscalculia. Dyslexia. Dyslexia
comes from Greek, "dys" which means difficulty
and "lexis" which means letters or lexical. So
dyslexia means a person's difficulties in carrying out
activities related to letters, especially reading and
writing activities, as well as language skills.
Dyslexia is one type of learning difficulty,
especially the difficulty in reading and writing which
is usually experienced by some children in this
world. According to the Child Development
Institute, (2008) (Martini Jamaris, 2014) that cases
of dyslexia are found in 3-6% of the population.
However, cases related to reading difficulties that
were not classified as dyslexia were found in more
than 50% of the population. Individuals with
dyslexia have a normal level of intelligence, even
above average, so that dyslexic sufferers are not
classified as mentally retarded children. Mulyadi,
(2010) explains in more detail that the notion of
dyslexia is difficulty reading, spelling, writing, and
in interpreting or recognizing the structure of words
that affects on the learning process or learning
disruption. Nini Subini, (2012) provides an
understanding of dyslexia based on internal causes
in the individual concerned, dyslexia is one of the
disorders of the development of brain function that
occurs throughout the life span. Dyslexia is
considered an effect caused by a disorder in memory
and central processing associations called primary
reading difficulties. To be able to read automatically
the child must go through education and normal
intelligence without any sensory interference.
Usually this difficulty is only detected after the child
enters the school world for some time.
Olivia (2016) Mentioning, there are five broad
areas of problems in dyslexic sufferers, namely: (1).
Mix letters or words that are the same pronunciation,
like B and D, P and Q, as well as words like; b with
d, was and saw, left with right, west with east. (2).
Problems with linear sequences such as alphabets,
schedules, sentences, list of instructions. (3).
Problems with short-term memory, (4). Coordination
problems, related to motion coordination with the
pronunciation of sentences, (5) problems in reading
and writing. Every dyslexic child certainly has
unique characteristics, so that not all of these
problems are shared by dyslexics. However,
generally sufferers have more than one category of
problems.
DSM V mentions dyslexia is an alternative term
used to refer to the type of learning difficulties
categories characterized by problems with word
recognition, poor coding, and poor spelling skills.
So, dyslexia is used to determine the pattern of
learning difficulties in the field of reading and
numeracy in mathematics.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Grouping of Dyslexia
2.1.1 Learning Method for Dyslexia
According to Mulyono Abdurrahman, (2012) there
are several methods of teaching reading for children
with learning difficulties, namely (a) Fernald (b)
Gillingham and (c) Glass Analysis. Here is a brief
explanation:
(a) Fernald Method. Fernald's method has developed
a multisensory reading teaching method that is
often known as the VAKT method (Visual,
auditory, kinesthetic, and tactile). This method
uses reading material selected from the words
spoken by the child, and each word is taught in
full. This method has four stages. In the first
stage, the teacher writes the words to be learned
on paper with crayons. Next the child traces the
writing with his finger (tactile and kinesthetic).
When tracing the writing, the child sees the
writing (visual), and pronounces it loudly
(auditory). This kind of process is repeated so
that the child can write the word correctly
without seeing an example. If the child has been
Effectiveness of Draw Cards for Language Development of Dislexia Children
285
able to write and read correctly, the reading
material is stored. In the second stage, the child
is not too long to trace the writings with a finger,
but learn the teacher's writing by watching the
teacher write, while saying it. Children learn new
words in the third stage, by looking at the writing
on the chalkboard or printed writing, and saying
the word before writing. At this stage the child
begins to read the writing from the book. In the
fourth stage, the child is able to remember the
words printed or the parts of the word that have
been learned.
(b) Gillingham Method. The Gillingham method is
a high-level structured approach that requires
five years of study time. The first activity is
directed at learning various letter sounds and the
combination of these letters. Children use tracing
techniques to learn various letters. The single
sound of the letters is then combined into larger
groups and then the phonics program is
completed.
(c) Glass Analysis Method. Glass Analysis Method
is a method of teaching through letter group
password breaking in words. This method
departs from the underlying assumptions of
reading as decoding or writing code. There are
two assumptions underlying this method. First,
decoding and reading processes are different
activities. Second, password breaking precedes
reading. Password solving is defined as
determining the sound that corresponds to a
written word correctly. Reading is defined as
decreasing the meaning of words in the form of
writing. If children cannot do writing passwords
efficiently, they will not learn to read. Through
the Glass Analysis method, children are guided
to get to know groups of letters while looking at
the word as a whole. This method emphasizes
auditory and visual training that is centered on
the word being studied. The material needed to
teach recognizes groups of letters can be made
by the teacher. Essentially, groups of letters can
be made on cards measuring 3 × 15 cm. On each
card, the teacher writes well the selected words
that have become the child's vocabulary. Word
groups are defined as two or more letters which
are one complete word, describing a relatively
fixed sound. In Indonesian, a group of letters
which is a single word consisting of only one
syllable is very rare. The word "no" for example,
actually stands for the word "tidak"; and the
word "pak" or "bu" is actually the approach of
the words "bapak" and "ibu". Thus, the
application of Glass analysis methods in
Indonesian will be in the form of syllables, for
example the word "bapak" consists of two
groups of letters "ba" and "pak".
From several methods or approaches available,
this study provides alternative interventions that
consider the needs of children with dyslexia in
improving language skills. Based on the exposure,
the hypothesis of this study is that there are
differences in the number of vocabulary mastered by
children before and after the card being given.
Children have more vocabulary after given the
picture card game.
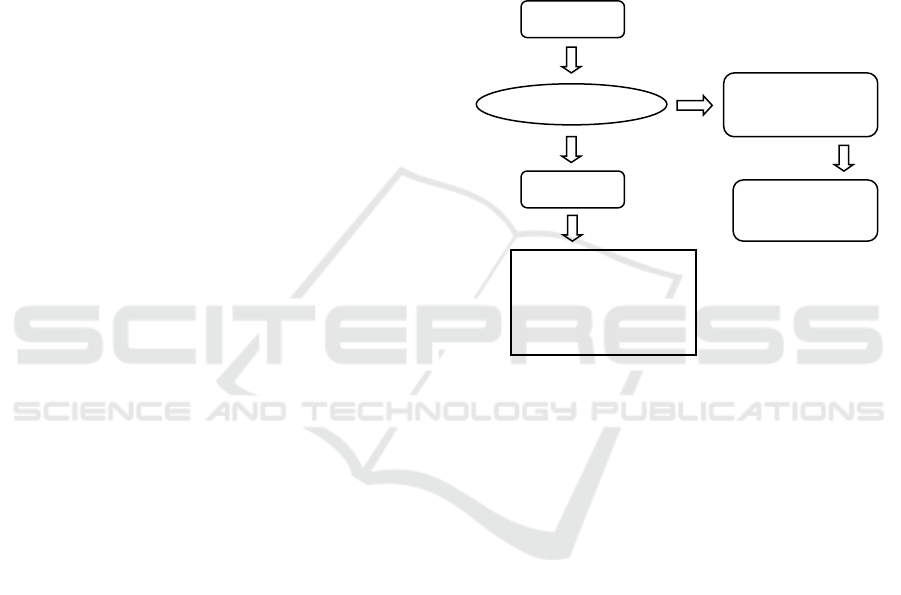
Figure 1. Research Framework.
3 METHODS
This research will be conducted using Quantitative
methods with the experimental approach. This
method was chosen because the researchers wanted
to see the results of the form of treatment in dyslexic
children who are the object of research on giving
picture cards.
Giving a picture card is one form of intervention
given to people with dyslexia which is a
combination of the Fernald method (VAKT), where
in the visual aspect given is the use of picture cards.
Furthermore, children do touching / tactile when the
child plays the picture card while voicing or
mentioning the type of picture card that is being
played. The picture card played by the child is
shaped like a piece of picture (puzzle), so that the
child is always learning while playing.
The language ability of the child intended in this
study is the ability of the child to master the number
of vocabulary words, both verbs, command words
Pre tes
t
Treatment
(
X
)
Method Fernal
treatment
Pos
t
tes
t
Through gifted
card giving can
add vocabulary of
dyslexic children
Visual (picture
car
d
)
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
286

and other types of vocabulary, such as vocabulary in
the form of types of transportation, verbs and so on.
The research design used was a Pre-experimental
case study through a case; pre-post test design:
Table 1: Pre-post test design.
Pre Test
Treatment (X)
Post test
(T1)
Picture cards
(T2)
Remarks T1 = observation & measurement before
treatment
T2 = observation & measurement after
treatment
This research is a quasi-experimental research
conducted by not exercising full control of
experimental scheduling stimulus which includes
time, subject, and random ability.
3.1 Procedure
• Researchers provide treatment to children. In this
case the treatment given is in the form of a picture
card, in forms illustrated cards, ranging from
transportation and picture cards telling stories of
children's daily activities.
• The treatment is independent variable and the
result is the dependent variable.
• The researcher conducted a post test by checking
how much mastery of the vocabulary number after
the subject received the treatment.
The focus of attention of this study is to study one
case in children who experience Specific Learning
Difficulties, especially in reading disorders
(dyslexia), where researchers try to analyze it from
language skills mastered by children. The main data
collectors are in-depth observations and interviews.
Observations carried out here are closed
observations, meaning observing without being
known by the subject with a natural setting
(Moleong, 2001) by using observation guides made
by researchers. Whereas to add qualitative data,
interviews were conducted with parents.
4 RESULT
The results in this study are presented in the
form of descriptive data obtained before the study
(pretest) and after research (posttest). Summary of
treatment for giving a picture card are shown on
Tabele 2.
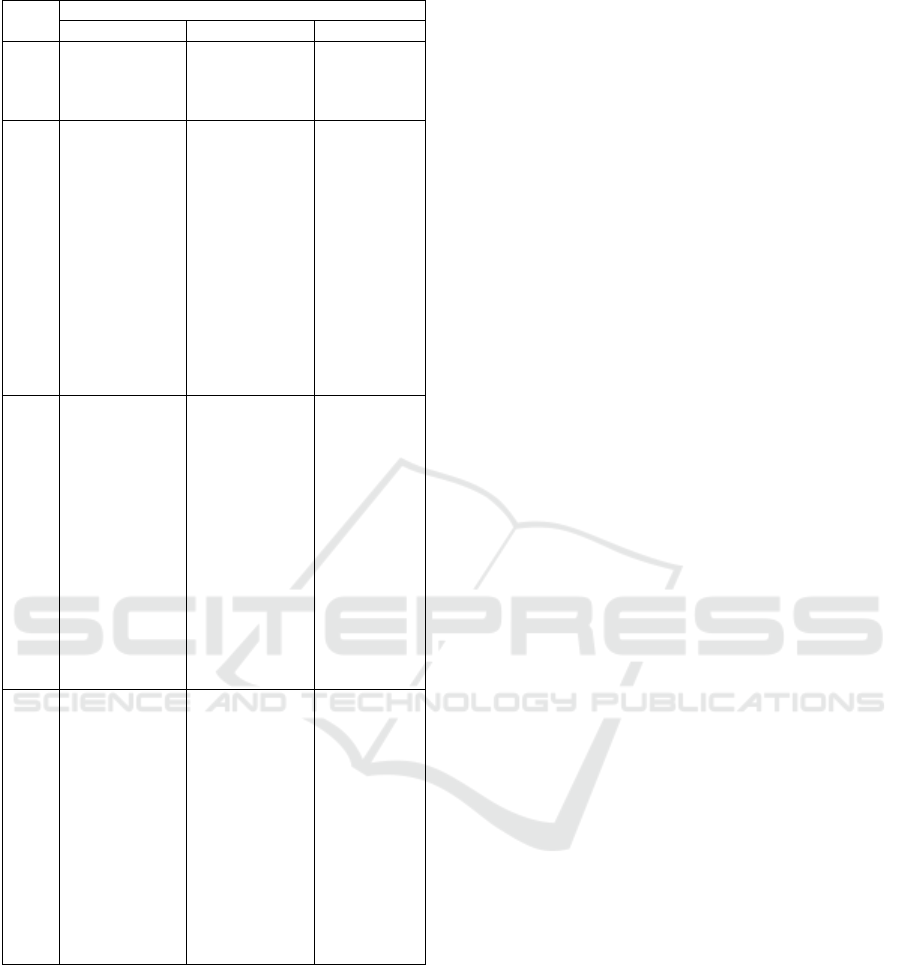
Table 2: Treatment for giving a picture card.
Treat
ment
Subjec
t
M
K
S
1 Picture card
pieces:
compile 7
transportation
illustrated
vocabulary
cards properly
The story
telling card
sequence:
Reverse order
on cards 2 and
3
Picture card
pieces:
compile 7
transportation
illustrated
vocabulary
cards properly
The story card
sequence :
Reverse order
on cards 2 and
3
Picture card
pieces:
compile 7
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Reverse
order on
cards 2 and
3
2 Picture card
pieces:
compile 7
transportation
illustrated
vocabulary
cards properly
The story card
sequence :
Reverse order
on card 2
Picture card
pieces:
compile 10
transportation
illustrated
vocabulary
cards properly
The story card
sequence :
Reverse order
on card 2
Picture card
pieces:
compile 7
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Good order
in story tell
3 Pieces of
picture cards:
arrange 9 cards
with fruit
vocabulary
images
properly
The story card
sequence:
Reverse the
order on cards
3 and 5
Pieces of
picture cards:
compile 10
cards with fruit
vocabulary
images well
The story card
sequence :
Reverse the
order on cards
3 and 5
Picture card
pieces:
compile 10
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Good story
orde
r
4 Pieces of
picture cards:
compile 10
cards with fruit
vocabulary
images well
The story card
sequence:
Good sequence
of stories
Pieces of
picture cards:
arrange 10 fruit
vocabulary
cards with fruit
well
The story card
sequence:
Good story
order
Picture card
pieces:
compile 10
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Effectiveness of Draw Cards for Language Development of Dislexia Children
287
Treat
ment
Subjec
t
M
K
S
Reverse the
order on
cards 3 and
5
5 Picture card
pieces:
compile 10
school
equipment
illustrated
vocabulary
cards properly
The story card
sequence:
Reverse order
story
Potongan kartu
bergambar:
menyusun 11
kartu kosakata
bergambar
perlengkapan
sekolah dengan
baik
The story card
sequence :
Reverse order
story
Picture card
pieces:
compile 12
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Good order
story
6 Picture card
pieces:
compile 10
school
equipment
illustrated
vocabulary
cards properly
The story card
sequence:
Reversed the
order on card
2, but the next
is goo
d
Potongan kartu
bergambar:
menyusun 11
kartu kosakata
bergambar
perlengkapan
sekolah dengan
baik
The story card
sequence :
Reversed the
order on card
2, but the next
is goo
d
Picture card
pieces:
compile 12
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Good order
story
7 Pieces of
picture cards:
compile 11
well-illustrated
clothing
vocabulary
cards
The story card
sequence:
Good order on
card story
Potongan kartu
bergambar:
menyusun 11
kartu kosakata
bergambar
pakaian
dengan baik
The story card
sequence :
Good order on
card story
Picture card
pieces:
compile 12
transportatio
n illustrated
vocabulary
cards
properly
The story
card
sequence :
Good order
on card story
From the results of the treatment carried out 7
times, it appears that the difficulty of the subject is
the task of sorting illustrated story cards. The subject
is still upside down in the sequence of stories,
especially those with similar stories. However, for
the activity of compiling images on vocabulary
cards, subjects can do well, even able to do more
than the number of cards expected. The subject was
very fond of the activity of compiling this picture
card, so the subjects did not feel bored and tired
when the researchers gave treatment to them.
However, for a series of illustrated story cards shows
the level of difficulty on the subject because the
subject must sort the card image and tell it into a
series of stories. Results show short Short-term
Memory (STM).
However, qualitatively some behaviors that can
lead to progress, although not significant, can be
reported. For example: 1) The subject has mastered a
lot of additional vocabulary in the sub-field of
transparency, whereas previously the mastery of this
vocabulary was only small. 2) The subject is more
interested in learning by using a card than before, it
can be seen from the subject's interest in being
present every day and asking to add hours to study.
3) The subject looks more telling stories using the
card as a media story to the researcher, where before
the subject was more silent and seemed confused
about what to say to the researcher.
5 DISCUSSION
Dyslexia is a disorder that occurs in the
neurobiological process in reading activities. To be
able to read a person must have mastery of verbal
language, short-term memory sequential memory,
adequate visual spatial functions, sufficient
attention, and can express it verbally. In the research
subjects there was no visual motor function found,
because the subjects were able to write and draw
well and had good verbal expressions. The problem
experienced by the subject lies in short-term
sequential memory and is confused to see /
determine direction. Subjects are still limited in
reading, so that they have difficulty understanding
the contents of the reading.
From the results of interviews with mothers,
there is indeed a history that his mother also
experienced a delay in reading even though he
finally got it. According to teacher information, the
subject is still often confused to determine the right
or left, also slow in reading. Based on the division of
dyslexia according to Sidiarto (1990), the subject
can be categorized as a type of visual dyslexia
because the subject does not experience sharpness or
visual impairment, the subject can see but is unable
to distinguish, interpret or remember the words he
sees.
This is probably due to a dysfunction in the
central nervous system. Visual dyslexia symptoms
are as follows: (1) Presence of reversal and inversion
tendencies (2) Difficulties in visual discrimination
and confusing letters or similar words, (3) Difficulty
following and remembering visual sequences. This
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
288

is seen when the subject sorts pictorial story cards,
where the subject is still often swapped by the order
of cards, the treatment of 1 subject 1 (1.1). (4)
Visually impaired memory; Subjects who forget to
mention the name of the tool / school kit, treatment 5
on subject 1 (5,1). (5) The speed of perception is
slow. Children are slow in scanning letters. (7)
Difficulties in visual analysis and synthesis (8) Poor
reading test results (9) Better in auditory activity
skills - more remembering teacher explanations (9)
Difficulties in playing sports (10) Ability to draw
inferiorly and lacking in detail.
The method of giving picture cards is an exercise
in remembering images and connecting in the
preparation of storytelling sentences. Storytelling
card images that are arranged sequentially are
intended to train subjects to be able to think of a
series. The combination of the use of picture cards
and illustrated story order cards is to train the
subject's memory. In addition to increasing the
vocabulary of the subject, so that the development of
the subject language becomes better.
From the post-test results, it can be seen that the
use of this picture card can improve children's
language development, where vocabulary increases
after the child has received treatment 7 times. The
subject tells more about using picture card media
and is more interested in learning to read than
before. However, the significance value is greater
than 0.05 (p> 0.05), which is equal to 0.95. This is
because theoretically the learning of individuals with
dyslexia takes a short time, is done repeatedly, and
continuously (continuous). While learning in this
study only lasts for ± 1 week (7 meetings).
In this study also, the learning process using
cards is not repeated at home because it considers
the saturation of the subject and also the lack of
assistance carried out by the mother, because
mothers who work fulltime in the office from
morning to evening are too exhausted to repeat the
material at home. From the results of this study, it
can be concluded that there is no addition of subject
vocabulary through images and subjects have no
difficulty in remembering vocabulary through
images, subjects can mention vocabulary in the card
well, although not all pictorial cards can be
remembered well by the subject. However, for
storytelling card images that are presented
sequentially the subject has difficulty in sorting the
story well, the difficulty in sequencing is probably
caused by a neurobiological disorder that occurs in
the brain, especially in the language area so the
subject often forgets and is confused in sorting
illustrated story cards that is.
The language area in the brain is located in
Broca's area and Wernicke's area. Broca's area is a
speech production center located in a small area in
the inferior portion of the left prefrontal cortex in the
brain, while the Wernicke area is a cortical area of
language compatibility (language understanding)
located in the left temporal lobe right posterior to the
primary auditory cortex (Pinel, 2011). The
difficulties experienced by the subject related to
neurobiology certainly require continuous and
continuous handling, in addition to that, proper
accommodation is needed. Accommodation is the
availability of varied tools according to the needs of
the learning program for people with dyslexia,
picture cards are one of the innovative learning
media in helping learning dyslexic people.
6 CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATION
The pictorial card method has not been able to
improve the mastery of language skills in people
with dyslexia to the fullest. Based on the results of
statistical analysis with a significance value of 0.95,
it means there is no significant difference in the
value of the pre test and the value of the post test.
However, judging from the average value of the
subject there were differences in the value of the
pre-test and post-test, the subject experienced a
small increase in vocabulary. Observation,
interviews and continuous repetition of material are
important factors in the development of the language
of dyslexic children. Some suggestions that can be
submitted for further research include:
1. The target module needs to be adjusted to the
subject's condition and increase the number of
subjects.
2. The main focus is more on the repetition process,
preferably in the training process the provision of
pictorial cards must be repeated at home and
outside school hours.
3. Variations in the delivery of material and the use
of various props to increase children's
vocabulary can be done to motivate the subject,
so as not to get bored following training.
Effectiveness of Draw Cards for Language Development of Dislexia Children
289

REFERENCES
Abdurrahman, M. (2012). Anak berkesulitan belajar: teori,
diagnosis, dan remediasinya. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Aliah B., & Purwakanta H. Psikologi perkembangan
islami. Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada.
Direktorat Pendidikan Luar Biasa. (2004). Pedoman
penyelenggaraan pendidikan inklusi. (seri: 1-7)
Jakarta.
Fauzi, A. (2004). Psikologi umum. Bandung: Pustaka
Setia.
Hermijayanto, O., B. (2016). Disleksia bukan bodoh,
bukan malas, terapi berbakat. Jakarta: Gramedia.
Jamaris, M. (2014). Kesulitan belajar: perspektif, asesmen,
dan penanggulangannya. Bogor: Ghalia Indonesia.
Masyitah. (2018). Efektivitas stimulasi visual
menggunakan media gambar terhadap kemampuan
membaca pada siswa disleksia di sekolah dasar negeri
tlekung 02 kota batu. Tesis. Universitas Islam Negeri
Maulana Malik Ibrahim Malang.
Mulyadi. (2010). Diagnosis kesulitan belajar & bimbingan
terhadap kesulitan belajar. Yogyakarta: Nuha Litera.
Pinel, J. P. J. (2011). Biopsychology 8th edition. Boston:
Pearson Education, Inc.
Sidiarto, L. (1990). Berbagai gejala minimal otak yang
berujud kesulitan belajar spesifik dan
permasalahannya. Makalah Seminar. (Tidak
Diterbitkan). Surakarta: Program PLB FKIP/ UNS/
PSSR PUSLIT UNS bekerjasama dengan Dewan
Nasional Indonesia Untuk Kesejahteraan Sosial
(DNIKS) dan Badan Koordinasi Kesejahteraan Sosial
(BKKKBS) Propinsi Jawa Tengah.
Subini, N. (2012). Mengatasi kesulitan belajar pada anak.
Yogyakarta: Javalitera.
Woodevort, R.S. & Marquis. (1962). Psychology. New
York: Rinehart and Winston.
Zannah, M. (2018). Peningkatan kemampuan membaca
pada layanan remedial untuk anak disleksia melalui
penggunaan permainan kartu kata siswa kelas iii sdn
kelapa gading timur 03 jakarta utara. Jurnal Ilmiah
Wahana Pendidikan, 4(3), 51-61.
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
290
