
The Effect of Red Fragon Fruit toward Blood Glucose Levels
Decreased
Rostiodertina Girsang, Dewi Tiansa Barus, Rentawati Purba, Nur Mala Sari, Tetty Junita Purba
Health Institute of DELI HUSADA,Jl.Besar Delitua No 77,Medan
Keywords: Diabetes Melitus, Fasting Blood Glucose Level, Dragon Fruit
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus prevalence continues to increase every year, World Health Organization data says about
346 million people suffer from diabetes and Indonesia is ranked fourth in the number of people with
diabetes in the world. Diets management of DM patients needs to be modified, especially fibre and
antioxidants intake. Dragon fruit can control blood glucose levels so as to prevent complications. The
numbers of respondents were 30 people, the sampling technique with purposive sampling. This research
was quasi-experimental study with non equivalent control group design. From the study results, average
blood glucose levels before treatment 349.73 mg / dl and after 323.27 mg / dl. There is decrease in
glucose levels after consuming dragon fruit juice for 14 days because of its fibre and vitamin C content so
that DM sufferers have decreased glucose levels up to 29 mg / dl.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease whose
prevalence is increasing rapidly every year
throughout the world. DM sufferers in the world in
2000 totalled 171 million people, in 2011 totalled
346 million and it is expected to double in 2030
(Glauber, 2016; WHO, 2015). Indonesia is fourth
ranked that has most DM sufferers in the world.
Sedentary diet and lifestyle are risk factors that
influence the increased prevalence of DM, the shift
in eating patterns towards high-energy, fat and low-
fibre diets trigger an imbalance in nutritional intake
that leads to the development of degenerative
diseases such as DM which is as serious health
problem and difficult to overcome until now
(Widya, et al, 2016). An increasing sufferer’s
number of non-communicable diseases occurs
consistently, it shows that diabetes mellitus is health
problem that needs special attention from various
parties including the government. The health
policies that have been made by Indonesia
Government are listed in the Regulation of Health
Minister of Indonesia Republic Number: 1144 /
Menkes / per / VIII / 2010 concern the Organization
and Administration of Health Ministry, the
government has established Sub-Directorate for
controlling diabetes mellitus and metabolic diseases.
In Indonesia, DM is the main cause of
death which is 2.1% of all deaths (MOH, 2016). One
feature of DM is blood glucose levels that rise above
normal called hyperglycaemia. Uncontrolled glucose
levels cause various complications, including
cardiovascular disease such as coronary heart
disease which is characterized by high levels of
cholesterol and blood lipids (Shrivastava et all,
2016; Farnz et al, 2016: bernaurd, 2016).
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that is mostly
suffered by most Indonesian people. However,
people still perceive diabetes mellitus as elderly
disease or disease that only arises because of
heredity. In fact, anyone can have diabetes mellitus
both young and old because the main factors causing
diabetes mellitus are diet and sedentary lifestyle.
Diabetes mellitus is disorder that occurs
due to the body's lack of the hormone insulin, as a
result glucose continues to circulate in the
bloodstream and it is difficult to penetrate the cell
wall. The absence of glucose entering the cell causes
the cell experience less energy for cellular metabolic
processes.
The reported incidence of pre diabetes
continues to increase. 4-9% of pre diabetes sufferers
will become diabetic every year (PERKENI, 2011).
Based on DM prevalence illustrates the importance
of early prevention for the disease. DM management
is very effective in the early stages before the
66
Girsang, R., Purba, R., Barus, D., Sari, N. and Purba, T.
The Effect of Red Fragon Fruit toward Blood Glucose Levels Decreased.
DOI: 10.5220/0009463600660073
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 66-73
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

symptoms of pre diabetes (Sizer, 2008). In
accordance with the criteria of American Diabetic
Association (ADA), pre diabetes is characterized by
fasting blood glucose (FBG) between 100-125 mg /
dL (ADA, 2012). Various efforts to overcome this
disease have been carried out, including by
regulating diet, regular exercise (Malawiq 2012),
oral anti diabetic drugs usage and insulin injections
(Levich 2011). Intensive administration of insulin
requires relatively expensive cost. The synthetic
drugs usage such as sulfonyl and biguanide groups
also cannot reduce glucose concentrations to normal
and restore the normal pattern of glucose
homeostasis permanently.
People/patinets with diabetes mellitus in the long
term will experience complications that can cause
organ damage such as decreased vision, weak heart,
kidney failure, liver damage, and others. Treatment
is usually done by people with diabetes mellitus is
by injection or anti-diabetic chemical drugs, such as
glibenclamide which is a derivative of sulfonylurea.
Glibenclamide works by stimulating insulin
secretion by pancreatic beta cells (Handoko and
Suharto, 2005). However, these methods of
treatment can cause side effects such as nausea,
abdominal discomfort and anorexia (Puspati et al.,
2013) and maintenance of diabetes, taking up huge
funds each year (Sovia et al., 2011).
In dietary settings, DM sufferers are advised
to pay attention to carbohydrate and fibre intake
because it is important in controlling blood glucose
levels. In fact, DM sufferers who have already run
diet program have not been able to control blood
glucose properly so that their daily levels remain
high. The reason is the lack of fruit and vegetable
intake as source of fibre and antioxidants. The
research result in United States showed that fibre
intake of DM sufferers <15 g / day, it is lower than
recommendation of 25 g / day. Based on the
research result that conducted at General Hospital,
Sanglah Denpasar reported their average fibre intake
was only 8.9g / day and according to Malaysian
Medical Faculty division said that dragon fruit
administration as much as 200-300 g / day was able
to reduce blood sugar levels and choleterol type 2 of
DM patients (Wiardiani, 2013; Khalili, 2016).
Increased blood glucose levels can be
controlled with chemical drugs besides food
regulation which also provides an effective effect on
reducing blood glucose levels that are relatively
inexpensive. Red dragon fruit (Hylocereus
Polyrhizus) is one of the best fruits in the functional
food category (Norhayati, 2006), which contains
water-soluble fibre (19 gr) and archaic acid (vitamin
c - 540.27 mg) which plays a role in the human body
to neutralize free radicals. Vitamin C which acts as
an antioxidant can reduce insulin resistance by
increasing endothelial function and reducing
oxidative stress. Based on study proving that
supplementation of vitamin C 1000 mg / day
significantly reduces fasting blood glucose levels
(Afkhami, 2007).
To overcome the above problem, previous
research has been done with the respondent method
divided into two treatments with intervention for 21
days by giving 70 ml of juice, and also with three
treatments for 10 days by giving 250 ml of juice and
two treatments for 11 days by giving juice as much
as 200 ml (Widyastuti, 2015; Wiardiani, 2013,
Roiffatul, 2017). In this study, researchers
collaborated with Karo District Health Office and
researchers proposed management dragon fruit juice
usage with the method of juice administering for 14
days at dose of 200 mg / 250 cc. Dragon fruit can be
blood sugar levels balancer because this fruit
contains variety of antioxidants namely flavonoids,
vitamin E, vitamin C, and beta-carotene which have
the ability to reduce oxidative stress and Reactive
Oxygen Species so that they can cause protective
effects on pancreatic β cells and increase sensitivity
insulin (Lianiwati, 2011).
2 METHOD
This research conducted at Barusjahe Public Health
Center, Barusjahe District, Karo District with
sample of 30 people with fasting blood glucose level
criteria ≥ 126 mg / dl, age> 30 years, did not use
insulin injection and herbal supplements, with
sampling technique used purposive sampling
technique. The research type carried out quasi-
experimental study by using non-equivalent control
group design.
In the dependent variable, blood glucose
levels measured by GCU Easy Touch tool. Diabetes
Mellitus patients are given education about the
benefits of dragon fruit firstly. After being given
education, approval is sought for action to be taken.
Before the patient is checked for blood glucose
levels, the patient advised to fast for 10 hours.
Patients advised to fast starting from 22:00 until
08:00. After fasting, blood glucose levels are
checked firstly, after checking the initial blood
glucose level within 15 minutes given 250 mL of
dragon fruit juice. After giving the intervention, the
blood glucose level is checked again 20 minutes
later. After completing the intervention, the patient
The Effect of Red Fragon Fruit toward Blood Glucose Levels Decreased
67
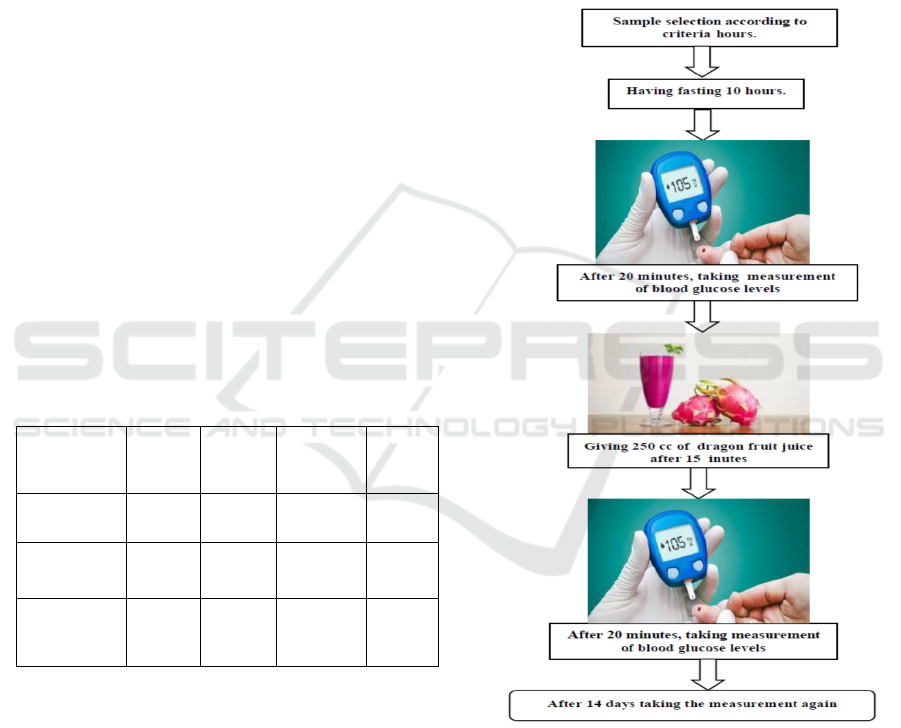
is not recommended to eat or drink sweet or high fat
foods because these foods and drinks can increase
blood glucose levels even if it is given the
intervention. So that patients can control their food
patterns, each patient is given a food recall sheet
whose purpose is to find out what foods and drinks
are consumed by the patient during the intervention.
The act of giving this intervention carried out for 14
days. During these 14 days blood glucose level is
controlled before and after the administration of the
intervention, it is expected that during the
intervention the patient does not violate the food
rules recommended by the researcher, if any patient
eats sweet or fatty foods, then the expected results is
not optimal because it cause an increase in blood
glucose levels and the administration of the
intervention considered a failure. After 14 days of
the intervention is checked again and the results
obtained from the first day until the fourteenth day
seen in comparison that the administration of the
dragon fruit has an effect on reducing blood glucose
levels or not.
During the treatment, the portion of juice
consumed was monitored and all complaints
experienced by the sample were recorded. The data
obtained was processed on a computer for univariate
and bivariate analysis. This research used paired-T
test.
Table 1: Concentration of blood sugar at time and fasting
Blood Glucose
Level (mg/dL)
Blood Not
DM
Uncertain
DM
DM
In the time
that (mg/dL)
Plasma
Vena
<110
mg/dL
110-199
mg/dl
>200
mg/Dl
Fasting
(mg/dL)
Plasma
Vena
<100
mg/dL
110-125
mg/dL
>126
mg/dL
Darah
Kapiler
<90
mg/dL
90-99
mg/dL
>110
mg/dL
The intervention was by administering 250 ml
of dragon fruit juice derived from 200 grams of red
dragon that was rendered without sugar with
frequency of 1x / day for 14 days. Dragon fruit juice
is administered directly by the researcher and each
respondent must drink it in front of the researcher
until it runs out. Blood glucose levels are measured
with glucose meter. Before intervene the subject, it
is recommended fasting for 10 hours and then
measuring blood glucose levels and after 15 minutes
checking, it is given dragon fruit juice, after 20
minutes of giving dragon fruit juice is done again
checking blood glucose levels and this intervention
is carried out every day for 14 days.
After completing the intervention, it is
recommended for the patient do not to eat or drink
sweet or high fat foods because these foods and
drinks can increase blood glucose levels even if it is
given the intervention. So that patients can control
their food patterns, each patient is given a food
recall sheet whose purpose is to find out what foods
and drinks are consumed by the patient during the
intervention.
Figure 1: Research conceptual framework
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
DM is a metabolic disorder characterized by blood
glucose levels increased due to insulin insufficiency
or resistance. Control of blood glucose levels is very
important to prevent further complications. Giving
therapy that contains fibre, antioxidants and has low
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
68

glycaemia value is one of the main pillars of DM
control especially DM type 2. One of the fruits that
can be utilized is red dragon fruit. Provision of red
dragon fruit juice in the sample shows good
acceptance. All samples finished the juice according
to the portion which is given because basically they
like the colour and taste of fresh juice of red dragon
fruit.
The amount of 1 gram of dragon fruit contains
50 calories which is the same as one exchange unit
on the exchange list. Dragon fruit consumption is
recommended at least one exchange unit (100 gr) to
two exchange units (200 gr) in one serving that can
be consumed with the lunch menu or as a snack
(Wiardiani, 2014). Juice therapy is given every day
with dose of 250 ml of juice for 14 consecutive days.
The samples number used by researchers were
30 people and they were given the action of
consuming 200 grams of red dragon fruit (250 ml)
for 14 days and the process of consuming the dragon
fruit was carried out for 20 minutes after breakfast
and dinner. Presentation of data includes a
description of the respondent's characteristics, blood
glucose levels before consuming red dragon fruit
(pre-test) and after consuming red dragon fruit (post-
test).
Based on study results, it is noted that the
sample of DM sufferer diagnosed between 4 months
to 2 years. The average age of the sample are 63
years, the majority are male, with an average
educational background of completing elementary
school, with agricultural work.
The analysis results of the average level from
blood glucose levels before consuming red dragon
fruit was 349.73, the median was 359.00 with a
standard deviation of 51.579 and standard error of
9.417, minimum value of 219 and maximum of 420
and the results of an average analysis of blood
glucose levels after consuming the red dragon fruit
was 323.27, the median was 339.00 with standard
deviation of 61.476 and standard error of 11.224,
minimum value of 170 and maximum value of 410.
It can be seen in Table 2 below.
There was a difference between all respondents
after being given red dragon fruit juice therapy, the
highest difference was 49 mg / dl and the lowest
difference was 10 mg / dl.
The most difference is 20 mg / dl that is equal
to 20 mg / dl; this is because each respondent has
different value of glucose levels and activity, some
of the respondents who do regular exercise so that it
looks very significant glucose levels decrease. In
addition, it also because the average respondents
were elderly and local village health center is very
encouraging for elderly gymnastics, thus making the
activities of the elderly with DM more directed and
controlled.
Table 2. Frequency of blood glucose level in diabetes
mellitus patients before and after consuming red dragon
fruit (n = 30).
No Before
Emergency
Nursing
After
Emergency
Nursing
Differe
nce
1 219 170 49
2 225 189 36
3 229 190 39
4 310 269 41
5 315 275 40
6 317 276 41
7 319 276 43
8 328 284 44
9 332 289 43
10 336 290 46
11 342 320 22
12 347 325 22
13 350 330 20
14 354 335 19
15 358 338 20
16 360 340 20
17 369 348 21
18 375 354 21
19 379 355 24
20 385 360 25
21 385 364 21
22 387 367 20
23 388 369 19
24 390 370 20
25 390 375 15
26 391 378 21
27 396 379 17
28 398 385 13
29 398 388 10
30 420 410 10
The average analysis results of blood glucose
levels in diabetes mellitus patients before consuming
red dragon fruit is mean value of 349.73 with
standard deviation of 51.579. The blood glucose
levels of diabetes mellitus patients after consuming
red dragon fruit is mean value of 323.27 with
standard deviation of 61.476.
The value of difference between blood glucose
levels before and after consuming red dragon fruit is
26.467 with standard deviation of 12.019. From the
statistical tests results, the p value = 0,000 was
obtained. Based on the provisions of hypothesis test
that if p (0,000) <α (0.05) then the decision Ho is
The Effect of Red Fragon Fruit toward Blood Glucose Levels Decreased
69

rejected and Ha is accepted, then it is concluded that
there is significant influence between glucose levels
of diabetes mellitus patients before and after
consuming red dragon fruit.
The results showed that most respondents did
not follow dietary rules because they were not
accustomed to and were not ready to go on a diet in
accordance with the guidelines that had been
prepared previously. Apart from dietary factors, the
average respondent also only did light activities even
though the average job was farming. Approximately
43% of respondents never did physical training due
to busy work, most also have obesity status where
the condition has an impact on inhibiting the work of
insulin so that it can cause many complications.
Giving red dragon fruit juice aims to reduce blood
glucose levels in DM sufferers.
An increase of emergency nursing in patient
can be caused due to mental factors, eating foods
that contain fat, drinks that contain excessive alcohol
and soda, and the age factor that is no longer
productive, including the elderly. DM disease will
not only attack the elderly, in adulthood can also
occur in DM disease, especially patients who are
obese and lack of activities such as sports (Perkeni,
2011).
The results showed that blood glucose level of
the sample was relatively high with an average of
349.73 mg / dl and thereafter 323.27 mg / dl. High
blood glucose indicates a disturbance in
carbohydrate metabolism, where insulin is no longer
able to transport blood glucose to cells due to
interference with the sensitivity of cells to insulin
(Nelms, 2011).
Dragon fruit, especially red dragon fruit,
contains fibre and antioxidants that are beneficial for
diabetics and cardiovascular patients. The content of
dragon fruit fibre especially in the form of pectin has
the ability to slow the absorption of glucose by
increasing the thickness of the intestinal volume
which has the potential to reduce the speed of
diffusion so that glucose levels decrease. Dragon
fruit also contains phytochemicals that function as
antioxidants that can maintain the elasticity of blood
vessels and cell permibiality which will increase
insulin sensitivity so that more blood glucose is
carried by insulin into cells to be metabolized. It has
an impact on reducing blood glucose levels (Nelms,
2011).
The content of vitamin C can also affect blood
sugar levels. Red dragon fruit contains 540.27 mg /
100 g of vitamin C or reaches 6 times from the
requirement. Vitamin C which is very rich in red
dragon fruit functions as an antioxidant can reduce
insulin resistance by increasing endothelial function
and reducing oxidative stress (Chen. Et al, 2016).
Antioxidants are useful in maintaining the elasticity
and permibiality of blood vessels. To increase fibre
intake and antioxidants of DM sufferers, dietary
improvement is needed by adding a formula in the
form of juice therapy whose source of fruits as a
source of fibre-rich foods, especially soluble fibre
can improve blood glucose control (Raihana, 2016).
In addition to vitamin C, dragon fruit also
contains flavonoids which also function to reduce
blood glucose levels. Flavonoid compounds such as
isoflavones can prevent the efficacy of prostate
cancer; reduce the risk of heart disease, diabetes,
kidney and osteoporosis. Decreased blood sugar
levels occur because flavonoids which are
antioxidants can reduce the tension of the mind
which can have an impact on the inhibition of
pancreatic beta cells to increase insulin sensitivity
(Asih, 2012).
The type of antioxidant that plays the most
roles in reducing blood glucose levels namely
flavonoids. The flavonoids content of red dragon
fruit meat is 7.21 ± 0.02 mg CE / 100 gram. The
ability of flavonoids, especially quercetin, is to
inhibit Glucose Transporters 2 (GLUT 2) intestinal
mucosa so that it can reduce glucose absorption. It
causes decrease in absorption of glucose and
fructose from the intestine so that blood glucose
levels fall. Glucose Transporters 2 (GLUT 2) is
thought to be a major glucose transporter in the
intestine under normal conditions (Song 2014 in
Roiffatul, 2017).
The fibre found in red dragon fruit is water
soluble fibre that can be used as hypoglycaemic
therapy. The role of water soluble fibre as
hypoglycaemic therapy is to improve insulin
sensitivity and reduce insulin requirements.
Consumption of fibre in sufficient quantities can
provide metabolic benefits in blood glucose control.
Water-soluble fibre increases food transit time in the
intestine, delays gastric emptying and slows glucose
absorption. If glucose absorption is slow, insulin
secretion will not be excessive so that it will reduce
insulin requirements and insulin sensitivity
increases. Fibre also has the ability to slow the
absorption of glucose and fat by increasing the
viscosity of stool which indirectly decreases the
speed of diffusion so that blood glucose levels, lipid
profiles and cholesterol decrease (Sulstyani, 2012).
The study results are in line with Hadi, et al
research (2016) who examined the effect of
consumption of red dragon fruit on glucose levels in
type 2 DM, showing a decrease in all groups and an
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
70

amount of 600 g most effective in reducing blood
glucose levels with decrease up to 34, 7% (Hadi. Et
al, 2016).
The same thing was stated by Raihana (2017)
that of dragon fruit pollen administration > 100 g for
1 month did not cause a negative impact on the liver
and kidneys as indicated by normal liver and kidney
function values (Raihana, 2016).
According to Englyst and Englyst (2016), one
determinant of carbohydrates absorption rate is the
degree of polymerization, where only
monosaccharides are absorbed by the small intestine
and circulated through the blood. Therefore, fruit
sugar in the form of glucose and fructose determines
the glycemic response. Raihana et al (2015) and
Khalili (2014) research stated red dragon fruit
contains fibre and antioxidants that are beneficial for
diabetics and cardiovascular patients. Dragon fruit
also contains phytochemicals that function as
antioxidants. Antioxidants can maintain blood vessel
elasticity and cell permiability. Giving red dragon
fruit therapy for 14 days with maximum amount of
200gr can be said to be relatively safe for
consumption. It is evident that during the
administration monitoring every day there were no
complaints, both physical and clinical. The same
thing was stated by Hadi et al (2016) that the red
dragon fruit pollen administration > 100gr for 1
month did not cause a negative impact on the liver
and kidneys.
Giving red dragon fruit juice therapy for 14
days with an amount of 250 ml can be said to be
relatively safe to consume, it can be proven that
during the administration or treatment there were no
physical and clinical complaints found.
The same was stated by Raihana (2016) that
the dragon fruit pollen administration > 100g for 1
month did not cause negative effects on the liver and
kidneys as indicated by the value of liver and kidney
function is still normal.
It shows that diet plays an important role in
maintaining glucose control. Diets should be varied
and integrated with other pillars of DM management
such as regular exercise, health education and drug
administration.
The study results are also in line with
Wiardani's research, 2014 which examined Red
Dragon Fruit Juice Reduce Blood Glucose Levels in
DM Patients who showed that administration of
dragon fruit juice with 200gr of dragon fruit was
more effective in reducing compared with 100 gr
therapies.
4 CONCLUSION
Dragon fruit juice therapy can significantly reduce
blood glucose and cholesterol levels. Decreased
blood glucose levels ranged from 9.1% - 29.1%.
There is a significant difference in the effectiveness
of dragon fruit juice therapy in reducing blood
glucose levels. Dragon fruit juice therapy with 200 g
of dragon fruit is more effective in reducing blood
glucose levels with the highest reduction of 29.1%.
There needs to be consistency in carrying out a
modified diet in DM patients so that blood glucose
levels are controlled.
It needs to be consistency in carrying out a
modified diet in DM patients so that blood glucose
levels are well controlled and there is further
research on red dragon fruit juice administration that
can be modified with fruits or vegetables that are
high in fibre and antioxidants so that respondents are
not saturated in running therapy.
5 SUGGESTIONS
a. For people/patients with diabetes mellitus, the
results of this study are expected to be a media of
information to increase their knowledge and
motivate them to be positive in choosing foods
that are in accordance with the recommended
diabetes mellitus diet and can use red dragon
fruit as one of the accompanying fruits of the
diabetes mellitus diet and the fruit can help to
reduce blood glucose levels.
b. For the community, the results of this study are
expected to make people more able to utilize red
dragon fruit as a natural alternative in reducing
blood glucose levels
c. For further researchers, the results of this study
are expected to be used as a reference for further
research, and it can be used to develop research
related to this research by controlling for factors
that might influence blood glucose levels such as
physical activity, stress, diet, and consumption of
anti-hyperglycemia drugs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Health Institute of
Deli Husada, Health Institute of Medistra Lubuk
Pakam, Sembiring General Hospital Foundation, and
Medistra Foundation, Indonesia.
The Effect of Red Fragon Fruit toward Blood Glucose Levels Decreased
71

REFERENCES
American Diabetic Association. Standards of medical care
in diabetes. 2012. (cited 2014 March 19th).
Afkhami, Mohammad. 2007. Effect of Vitamin C on
blood glucose, serum lipids & serum insulin in type2
diabetes patient. Diabetes Research Center, Shahid
Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences & Health
Services, Yazd, Iran.
Asih, A.R, Ratnasaari K, Swardana B.I. (2012).Isolasi dan
identifikasi senyawa golonganflavonoid dari madu
kelengkeng (Nepheliumlongata L), (Skripsi)
Universitas Udayana.
Bernaud FS, Rodrigues TC. Dietary fiber-adequate intake
and effects on metabolism health. Arq Bras Endocrinol
Metabol. 2016;57:397–405
Bito H, Hamaguchi N, Hirai H, Ogawa K. Safety
evaluation of a newly-developed dietary fiber:
Resistant glucan mixture. J Toxicol Sci. 2016;41:33–
44
Breneman CB, Tucker L. Dietary fibre consumption and
insulin resistance-the role of body fat and physical
activity.Br J Nutr. 2017
Candalia, M., Lutjohan D, Brinkly L.J.. Beneficial Effect
of High Fiber Intake In Tipe 2 DM, New England
Journal Medicine, 2016. P. 1392 – 1398
Chen H, Karne RJ, Hall G, Campia U, Panza JA, Cannon
RO, et al. High-dose oral vitamin C partially
replenishes vitamin C levels in patients with type 2
diabetes and low vitamin C levels but does not
improve endothelial dysfunction or insulin resistance.
Am Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2016; 290: Hal 37-45.
Corwin Elozabeth J. Pankreas dan Diabetes Mellitus.
Dalam : Buku Saku Fisiologi, edisi 3. Jakarta: EGC;
2009. Hal 618-629.
Enes P, Martín-Frías M, Álvarez MÁ, Yelmo R, Alonso
M, Barrio R. Achievement of metabolic control goals
set by the American diabetes association and the
international society for pediatric and adolescent
diabetes in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes from
Spain. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;107:300–305
Englyst,KN, Potential of an in Vitro Digestion Method for
Predicting Glycemic Response of Foods and
Meals.Jounal List National Library of Medicine
National Institutes of Health. 2016
Franz MJ. Endocrine Disease. In: Hark L, Deen D,
Morrison G, editors. Medical Nutrition and Disease: a
case-based approach. 5th Ed. West Sussex: John
Wiley & Sons; 2016. p. 332–74.
Glauber H, Karnieli E. Preventing type 2 diabetes
mellitus: A call for personalized intervention. Perm J.
2016;17:74–79. doi: 10.7812/TPP/12-143.
Hadi, Abdul N. Marzhalina M., M. H. Khalili.. Effect Of
Red Pittaya Fruti Consumption in Blood Glucose
Level and Lipid Profile in Tipe 2 DM. Borneo Science.
Vl 31. 2016
Hartono A. Terapi Gizi dan Diet Rumah Sakit. Jakarta:
EGC; 2006. Hal 141.
Indonesia. Depkes..Profil Kesehatan Indonesia. Jakarta :
Badan Litbang Kesehatan,2006
Khalili, R., Norhayati, A.H, Rokiah, M.Y., Asmah,. 2016.
Hypocholesterolemic Effect of red. International Food
Research Journal 16 : 431-440 (2016)
Levich BR. 2011. Diabetes management : optimizing roles
for nurses in insulin initiation. J Multidiscip Healthc.
4:15-24.
Lianiwati, V. (2011). Pemberian Ekstrak Buah Naga
Merah Menurunkan Kadar F2 Isoprosta pada Tikus
Putih Jantan yang Diberi Aktivitas Berlebih, Jurnal
Kedokteran UNUD. 8 (17). 45-55.
Malkawi. 2012. Review Article: The effectiveness of
physical activity in preventing type 2 diabetes in high
risk individuals using well-structured interventions: a
systemic review. Journal of Diabetology. 2:1.
Mayo Clinic. Metabolic Syndrome..tersedia dalam
http//www.mayocliic.com diakses tanggal 20 februari
2017
Menteri Kesehatan, RI. (2010). Peraturan Menteri
Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Nomor:
1144/menkes/per/VIII/2010 tentang Organiasi dan
Tata Kerja Kementrian Kesehatan dalam
http://www.ppl.depkes.go.id,
Nelms,M.,Kathryn S.,Karen L.,Sara L.R.. Nutrition
Therapy and Pathophysiology USA.Wadworth.2011
Norhayati, A. H. 2006. “Komposisi Kimia dan Aktivis
Antioksidan Buah Pitaya Merah (Hylocereus Sp.) dan
Kesan atas Paras Glukosa dan Profil Lipid Tikus yang
diaruh Hiperglisemia”. Thesis M. S. Universiti Putra
Malaysia, Serdang.
Nugroho SA. 2010. Hubungan Antara Tingkat Stress
Terhadap Kadar Glukosa Darah Penderita Diabetes
Mellitus di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Sukoharjo I
Kabupaten Sukoharjo. Tesis Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan,
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
Perkumpulan Endokrinologi Indonesia. Konsesus
pengelolaan dan pencegahan diabetes mellitus tipe 2 di
Indonesia. Jakarta: PB. PERKENI; 2011.
Puspati NKS., MS Anthara, AAGO Dharmayudha. 2013.
Pertambahan bobot badan tikus diabetes mellitus
dengan pemberian ekstrak etanol buah naga daging
putih. Indonesia Medicus Veterinus 2 (2): 225234.
Raihana, S M. Rokiah.. Hipercholesterolemic of Spray
Dried Pitaya Powder Among Normocholesterolemia
subject. International conference Nutrition and Food
Science. ICBEE 12 (30). 2016
Roiffatul, Ana H. Pengaruh Buah Naga Terhadap Kadar
Glukosa Darah Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe IIDi
Puskesmas Temon 1 Kulon Progo Yogyakarta.
Yogyakarta : Universitas ‘Aisyiyah, 2017
Sari, Dkk, 2017. Komposisi Kandungan Gula Buah Naga
Hylocereus Costaricensis. Borneo Journal
Pharmascientech, Vol 01, No. 02
Shrivastava S, Shrivastava P, Ramasamy J, Kinra S,
Bowen L, Lyngdoh T, et al. Role of self-care in
management of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab
Disord. 2016;12(1):14.
Sizer FS, Whitney E. The Carbohydrates: Sugar, Strach,
Glycogen and fibre. Dalam: Nutrition Concept and
Controversies 11th edition. Canada: Wadsworth;
2008.p.121-38.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
72

Sovia R., RR Tjandrawinata, E Setiawati, VA Gunawan, F
Ong, LW Susanto & D Nofiarny. 2011. Ekuivalensi
farmakokinetik dua sediaan kapsul pregabalin 150 mg.
Medicinus 28 (1): 15-23
Sulistyani. . Sehat deng Menu Berserat. Jakarta: Trubus
Agriwijaya. 2012
Suyono S dan Samsisalah Widya karya pangan dan Gizi.
Jakarta : LIPI, 1196
World Health Organization. (2013). Prevalensi Diabetes
Melitus di Indonesia dalam http://www.depkes.go.id,
WHO. (2015). Prevalensi Diabetes Mellitus di Indonesia
dalam http://www.depkes.go.id
Wiardani, Ni Komang. Pola Makan dan Obesitas Sebagai
Faktor Resiko Diabetes Mellitus di RSUP Sanglah
Denpasar (Tesis). Yogyakarta : UGM, 2013.
Widyastuti1, Amalia Nita. Pengaruh Pemberian Jus Buah
Naga Merah (Hylocereus polyrhizus) Terhadap Kadar
Glukosa Darah Puasa Pria Prediabetes. Semarang :
UNDIP, 2015
Wiardani, Ni Komang. Jus Buah Naga Merah
Menurunkan Kadar Glukosa Darah Penderita SMT2.
Yogyakarta : UGM, 2014, Jurnal Skala Husada Vol 11
: 59 – 66
Waspadji S.. Diabetes Melitus : Mekanisme Dasar dan
Pengelolaan yang Rasional dalam Penatalaksanaan
DM Terpadu. Cet 3. Jakarta : RSCM dan FKUI, 2008
The Effect of Red Fragon Fruit toward Blood Glucose Levels Decreased
73
