
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to
Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh
with Organizational Commitment as a Mediation
Variable
Em Yusuf Iis
1
, Sulaiman
2
, Muhammad Roni
1
, A. Hadi Arifin
1
, and Marbawi Adamy
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Malikussaleh, Aceh, Indonesia
2
Business Administration Study Program, Social and Political Sciences Faculty,
Universitas Al-Muslim, Aceh, Indonesia
ahadiarifin88@gmail.com,marbawi@unimal.ac.id
Abstract. This study aims to analyze the effect of compensation and career
development on organizational commitment and employee job satisfaction, to
know the effect of organizational commitment on employee job satisfaction, and
to examine the mediation effect of organizational commitment between
compensation and career development on employee job satisfaction at the Aceh
Government Public Works Service. The samples of this study are 133
respondents taken using the Census sampling technique. The analytical tool used
is path analysis with SEM (structural equation modeling) using Amos. The
results show that compensation and career development have a positive and
significant effect on job satisfaction, while organizational commitment
influences job satisfaction. Based on the mediation analysis, organizational
commitment partially mediates the effect of compensation on job satisfaction,
and organizational commitment mediates in full mediation the effect of career
development on job satisfaction.
Keywords: Compensation · Career Development · Organizational Commitment ·
Job Satisfaction
1 Introduction
Job satisfaction is felt by employees because of the underlying things. A person will
feel comfortable, and the level of loyalty at his job will be high if the person gets job
satisfaction at work (Nasution et al. 2018). Job satisfaction is a reflection of workers'
feelings towards their work. Luthans (2011) states that job satisfaction is the fulfillment
of all the needs of workers in carrying out their duties at a certain time. Job satisfaction
has a dynamic nature, which means that satisfaction is not a permanent condition
because it can be influenced and changed by forces both inside and outside the work
environment. Job satisfaction can decrease as fast as job satisfaction arises, so this
requires leaders to pay more attention. Unanue et al., (2017) Employees will be able
and want to work well and have high job satisfaction if they are placed in a position
under their interests and abilities and can meet various needs by doing work. Employees
must be placed in positions by their interests and abilities by considering efforts to meet
Iis, E., Sulaiman, ., Roni, M., Arifin, A. and Adamy, M.
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh with Organizational Commitment as a Mediation Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0009574400002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 21-32
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
21

the needs of human resources.
Organizational commitment is a strong desire to remain as a member of a particular
organization, a desire to strive based on the wishes of the organization, and confidence
in accepting the values and goals of the organization, Karim & Sciences,(2012).
Commitment is a person's ability to carry out obligations and responsibilities. An
organization member must commit himself. (Armstrong, 2009) The response system
provided by the organization sometimes receives less attention from employees to
foster a more loyal attitude towards the organization. This causes the employees to
worry about sanctions if they submit their complaints. The concept of commitment in
the workplace or organization becomes an interesting research topic Setyowati, (2017).
Ghosh & Swamy, (2014) and challenges that can be investigated in the area of
management and organizational behavior Robert L. Mathis, (2008) Steyrer,
Schiffinger, & Lang, (2008). Dixit & Bhati, (2012). If an employee already has a high
level of commitment to the organization where he works, good work motivation will
appear in him. People who are already happy and suitable for the workplace will surely
dismiss any negative assumptions about the organization, and he will always defend
the organization. Employees will work better and continue to try to improve all their
abilities for excellent job satisfaction.
Hong, et al (2012) claims that compensation is remuneration given by the company
to the employees financially and non-financially. Nowadays, the most important
problem with compensation is the compensation received by employees of the Public
Work Office of Aceh Government is not optimal compared to the workload carried out
by each employee. In the new organizational structures and work procedures,
employees are required to work more professionally, disciplined, and able to complete
existing work programs appropriately and with good work results, but the compensation
received by employees is not optimal.
Providing compensation is very important for organizational and employees
commitment so that organizational commitment gets employees who are willing to
work by carrying out their duties properly, and employees feel that compensation is
given as an appreciation for the work done. Bao, & Wu, (2017). Ivancevich et al, (2012)
Compensation is a function of human resource management related to all forms of
awards promised to be received by employees in return for carrying out tasks to achieve
organizational goals. This relationship will determine the survival and success of the
organization. Ulrich (2012) Career development has the role of Administrative,
Strategic Champion, Change Agent, and Champion employee. Employee Champion
explains the responsibilities of HR, Line Managers and employees themselves in terms
of increasing competence and employee involvement, while career development is a
personal improvement by someone to achieve a career plan and improvement by the
personnel department to achieve a work plan based on the path or level of the
organization, (Andana et al. 2012).
The phenomenon related to employee job satisfaction at the Public Works Service
show that many employees still do not want to be involved in work that involves
directly with the leaders because many employees feel that the leaders are very difficult
to accept ideas, so employees are more passive, and only accept ideas of leaders.
Besides, regarding promotion opportunities, it still does not look optimal because most
employees who are promoted are those closest to their superiors.
Another phenomenon related to organizational commitment is reluctance and lack
of willingness to help colleagues complete organizational tasks
. Besides, it is difficult
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
22

to unite perceptions and unite activities and priorities owned to achieve greater
organizational goals, even more so if the project being processed is a project that is
controlled by people closest to the boss. Also, there is a lack of employees in
understanding the needs of the organization to achieve greater organizational goals so
that more priority work is short-term needs.
The phenomenon of employee career development at the Aceh Government Public
Works Service reflects that the low level of employee education activities to continue
education, especially regarding study permits that require approval from superiors.
Besides, the lack of training provided that many jobs require the involvement of outside
experts such as consultants because employees are still not skilled in handling certain
projects. Another most difficult problem is regarding mutations or job placements that
are inappropriate with the expertise of employees that causes job dissatisfaction.
Besides, the phenomenon of compensation is also a problem for employees at the
Public Works Service of Aceh Government where the determination of individual
employee payments is considered unfair or uneven. The income of passive employees
is better because they are closer to superiors while employees who have no influence
only get their rights which are considered insufficient. Another problem also arises
when the method of payment of income is more to the percentage of position and not
on the performance and professionalism that causes many employees to complain about
the injustice of compensation distribution. For this reason, the researchers are
interested in conducting in-depth research with the title "The Effect of Compensation
and Career Development on Employee Job Satisfaction at the Public Works Service of
Aceh Government with Organizational Commitment as the Mediation Variable".
2 Literature Review
2.1 Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction is the fulfillment of all the needs of workers in carrying out their duties
at a certain time, (Usman, 2011). Job satisfaction theory is part of motivation theory
and tries to answer the question of what needs are satisfying and encourages the spirit
of work for the needs and satisfaction of non-material and material obtained from the
work. If needs and satisfaction are increasingly met, the spirit of work will get better.
Herzberg (1959), Job satisfaction is a reflection of the feeling of work towards the work
of an employee. The impact on the positive attitude of employees towards his work is
related to the output produced. So, the job satisfaction of employees depends on
expectations, which are obtained through work. If there is no difference between what
is desired has been fulfilled, it will be satisfying. The job satisfaction has a general
dimension to the job itself, through salary, promotion opportunities, supervision,
coworkers Luthans, (2012). Job satisfaction refers to several indicators of Ward and
Sloane (1999) in Koesmono (2005), namely the existence of colleague relationships,
relations with leaders, promotion opportunities, salary, and work comfort.
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh with Organizational
Commitment as a Mediation Variable
23

2.2 Organizational Commitment
Commitment is a psychological condition that characterizes the relationship between
employees and the organization and has implications for the individual's decision to
stay or leave the organization. Tobing, Armstrong (2009), commitment represents the
level or strength of the individual and is collected in an organization. Luthans (2011),
organizational commitment is a reflection of employee loyalty and the conservation
process in which members of the organization agree to pay attention to the organization
and trust to accept the values and goals of the organization. Robert Kreitner (2011),
organizational commitment is a reflection of where the employees in the organization
and help to achieve goals. This is an important work decision because people have
commitments that are expected to be able to predict better work outcomes to achieve
organizational goals and have a greater desire to work in an organization.
Organizational commitment refers to several indicators of Spencer and Spencer (1993)
in Kaswan (2015) namely that there is a willingness to help colleagues complete
organizational tasks, uniting their activities and priorities to achieve the goals of a larger
organization, understanding the organization's needs to achieve greater organizational
goals and choose appropriate organizational needs rather than following some
professional interests.
2.2.1 Career Development
Career development is a personal improvement done by someone to achieve a career
plan and improvement by the personnel department to achieve a work plan based on
the path or level of the organization (Andana et al. 2012). Judging from HR Champion
Ulrich (2012), there are roles of Administrative, Strategic Champion, Change Agent,
and employee Champion. Employee Champion explains the responsibilities of HR,
Line Managers and employees themselves in terms of increasing competence and
employee involvement. The role of building a career path by building employee
champions, and is the responsibility of human resources, superiors, and employees
themselves must be responsible for the aspirations and interests in career. Hartigh et al,
(2018), career development refers to several indicators according to Donnelly, et al
(2012) consist of education, training, mutation, and promotion of position and tenure.
2.2.2 Compensation
Compensation is a remuneration provided by the company to employees, both financial
and non-financial, Robbins, (2013), employee compensation is all forms of payment as
gifts given to employees from their work. Compensation is all income consisting of
money or goods, directly or indirectly received by employees as the rewards for
services given to the organization. Raithatha et al, (2016), compensation of employees
in the form of balance given to employees in return for their work. Ivancevich et al,
(2012), Compensation is a function of the rewards promised to be received by
employees as a reward for carrying out tasks to achieve organizational goals.
Compensation refers to several indicators. According to Huffman, et al, (2015),
Mangkunegara (2010), the indicators of compensation consist of the High level of
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
24

Compensation
Career
Development
Organizational
Commitments
Job
Satisfaction
payment given, Payment Structure, Determination of Individual Payments, Payment
Methods, and Payment Control.
2.2.3 Conceptual Framework
The conceptual framework in this study was built on the theoretical view of experts,
and empirical research results on the relationship between compensation and
organizational commitment, the relationship between career development and
organizational commitment, and the relationship between organizational commitment
and job satisfaction.
For the progress of an organization, it does not only lie on high organizational
commitment and optimal employee performance but also job satisfaction as a driving
force to achieve organizational goals in doing work to be productive. According to
Markoulli et al., (2017). Unanue et al, (2017), job satisfaction is one of the
psychological aspects that reflects a person's feelings towards their work.
Previous research on compensation and its effects on organizational commitment as
conducted by Arta and Huczynski & Buchanan (2008), compensation has a positive
effect on organizational commitment. Then, the relationship between career
development and organizational commitment as stated by Robert L. Mathis, (2008),
there is an influence of career development on organizational commitment positively
and significantly.
Another research by Robbins, (2013) about the effect of compensation on job
satisfaction indicate that there is a positive and significant effect between compensation
and employee job satisfaction. Then, research on the relationship between career
development and job satisfaction stated by Vogel, (2016) shows that career
development has a significant effect on employee job satisfaction. Furthermore,
previous research examining organizational commitment and its effect on job
satisfaction conducted by David P. MacKinnon, (2012) show that organizational
commitment has a positive and significant effect on employee job satisfaction.
Based on the description above, the conceptual framework in this study is illustrated
in Figure 3.1 below:
H6
H1 H3
H5
H2
H4
H7
Fig. 1. Conceptual Framework.
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh with Organizational
Commitment as a Mediation Variable
25

2.3 Hypotheses
There are 7 (seven) hypothetical statements based on the research framework as
appeared below:
H1: Compensation has a significant effect on Organization Commitment of
Employee at the Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
H2: Career development has a significant effect on work commitment at the Public
Works Office of Aceh Government.
H3: Compensation has a positive and significant effect on job satisfaction of
employees at the Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
H4: Career development has a positive and significant impact on job satisfaction of
employees at the Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
H5: Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on Job
Satisfaction of employees at the Public Works Office of Aceh Government..
H6: Organizational commitment provides a mediating effect on the relationship
between compensation and job satisfaction of employees at the Public Works
Office of Aceh Government.
H7: Organizational Commitment mediates the Job Satisfaction of employees at the
Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
2.4 Research Methodology
This study uses a statement using a questionnaire as a tool to retrieve data using a
modified Linkert scale 1-5. The population in this study are 133 employees of the Public
Works Office of Aceh Government selected using a Census sampling. Baron & Kenny,
(1986) The analysis technique used is the Structural Equation Model (SEM) using SPSS
16.0 and Amos. The validity test of the instrument is conducted using the Confirmatory
Factor Analysis (CFA) of each construct by looking at the Loading Factor value of each
indicator and the results of each statement that has a value of > 0.6. The reliability test
uses the following formula:
Construct Reliability =
∑
.
∑
.
∑
While the variant extract can be calculated with the following formula:
Variance Extracted =
∑
.
∑
.
∑
2.5 Results and Discussions
The results of the full model 1 analysis (initial model) using SEM analysis are shown
in figure 2.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
26

Fig. 2. CFA Full Model Constructs before Modification.
Furthermore, the suitability test of the model is in the following Table 1:
Table 1. Structural Equation Model Full Model Conformity Index Test before Modification.
Goodness o
f
Fit Index Cut-o
ff
Value Anal
y
sis Results Evaluation Models
χ
2
Chi-S
q
uare Statistics Ex
p
ected to be low 165,954
Goo
d
Probabilit
y
>0,05
0.016
Mar
g
inal
CMIN/DF <2.00 129
Goo
d
GFI >0.90
0.881
Marginal
AGFI >0.90
0.842
Mar
g
inal
TLI >0.95
0.958 Goo
d
CFI >0.95
0.965
Bai
k
RMSEA <0.08
0,047
Bai
k
Based on table 1 above, in general, all the constructs used in forming this research
model, both in the confirmatory analysis (CFA), the value of the regression between
constructs and the goodness of fit test consisting of CDMIN/DF already meet the
required criteria except Probability, GFI, and AGFI have values that are not good and
needs modification.
Fig. 3. CFA Full Model Constructs before Modification.
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh with Organizational
Commitment as a Mediation Variable
27

CE JS
OC
A=0,382
P=0,001
B=0,350
P=0,001
C=0,400
P=0,001
C’=0,134
P= 0,011
Furthermore, the suitability test of the model is in the Table 2 below:
Table 2. Structural Equation Model Full Model Conformity Index Test After Modification.
Goodness o
f
Fit Index Cut-o
ff
Value Anal
y
sis Results Evaluation Models
χ
2
Chi-S
q
uare Statistics Ex
p
ected to be low 165,954
Goo
d
Probabilit
y
>0,05
0.016
Mar
g
inal
CMIN/DF <2.00 129 Goo
d
GFI >0.90
0.881
Mar
g
inal
AGFI >0.90
0.842
Mar
g
inal
TLI >0.95
0.958 Goo
d
CFI >0.95
0.965 Goo
d
RMSEA <0.08
0,047 Goo
d
Figure 3 and table 2 above show the final results of the full model confirmatory
factor analysis. In general, all the constructs used in forming this research model, both
in the confirmatory analysis (CFA), the value of the regression between constructs and
the goodness of fit test consisting of CDMIN / DF, probability, TLI, CFI GFI and
RMSEA, have met the required criteria except AGFI which is at almost good value,
and the model can be concluded to be fit and support the data, but there is a marginal
value of AGFI but it is acceptable because the probability value is above 0.05. So, the
model is acceptable and feasible to be used in this study. To see how much direct,
indirect, and total influence is shown in Table 3:
Table 3. Tests of direct, indirect, and total influence.
Carreer
Development
Compensation of
Employees
Organizational
Commitment
Job Satisfaction
Direct Effects
Organizational
Commitment 0,186 0,382 0 0
Job Satisfaction 0,213 0,400 0,350 0
Indirect Effects
Organizational
Commitment 0 0 0 0
Job Satisfaction 0,065 0,134 0 0
Total Effects
Organizational
Commitment 0,186 0,382 0 0
Job Satisfaction 0,278 0,534 0,350 0
The results of testing the effect of mediating (intervening) on the relationship
between the compensation and job satisfaction mediated by the organizational
commitment are in Figure 4:
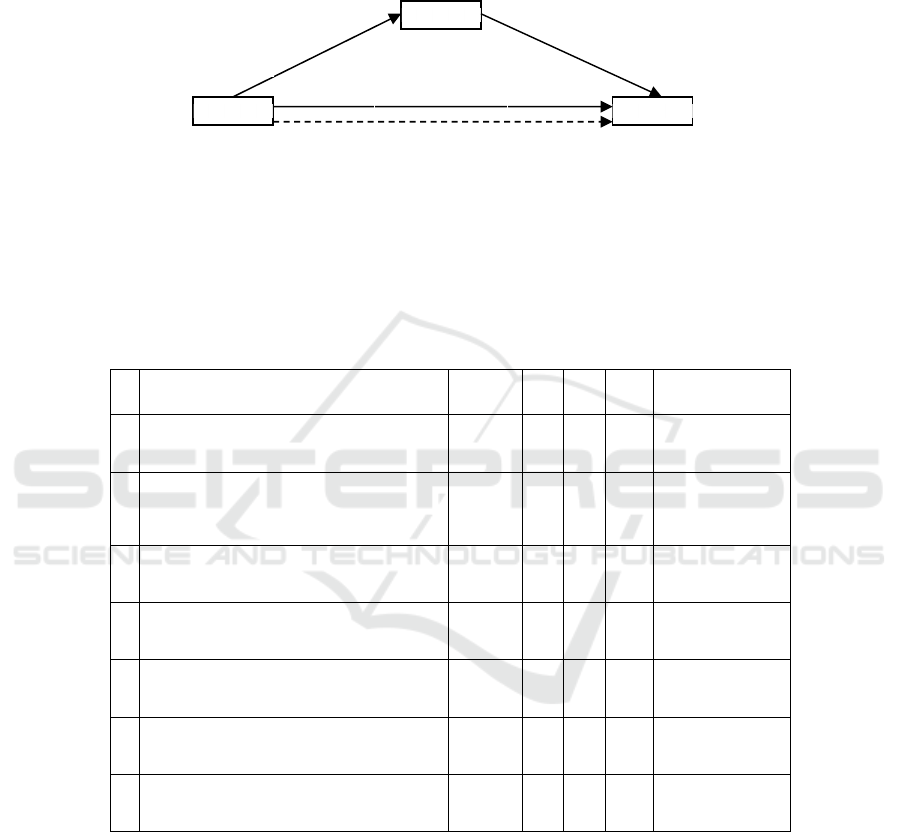
Fig. 4.
Figure 4 explains that the coefficients of path A, path B, and path C are significant,
and the significance value of path C is not significant. Because the probability of path
C 'is significant, a partial mediation relationship can be concluded. In other words,
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
28
CD JS
OC
A=0,186
P=0,042
B=0,350
P=0,001
C=0,213
P=0,001
C’=0,065
P= 0,101
organizational commitment mediates in full mediation between compensation and job
satisfaction at the Public Works Office of Government of Aceh.
The results of testing the mediation effect of organizational commitment between
career development and job satisfaction shown in the form of Figure 5:
Fig. 5.
Figure 5 explains that the path coefficients of path A, path B, and path C are
significant, and the significance value of path C 'is not significant. Since the probability
of path C 'is insignificant, it concludes that there is a full mediation relationship or
organizational commitment fully mediates between career development and employee
job satisfaction at the Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
Table 4. Hypothesis Test Results.
No Hypothesis Statements
Estimate
Std.
S.E. CR P Conclusion
1 Compensation has a positive and significant effect
on the organizational commitment of employees at
the Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
0,408 0,110 3,714 0,001
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
2 Career development has a positive and significant
effect on the organizational commitment of
employees at the Public Works Office of Aceh
Government.
0,208 0,102 2,029 0,042
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
3 Compensation has a positive and significant effect
on job satisfaction of employees at the Public
Works Office of Aceh Government.
0,391 0,100 3,92 0,001
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
4 Career development has a positive and significant
effect on job satisfaction at the Public Works Office
of Aceh Government.
0,218 0,085 2,557 0,011
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
5 Career development has a positive and significant
effect on job satisfaction of employees at the Public
Works Office of Aceh Government.
0,320 0,094 3,415 0,001
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
6 Organizational commitment partially mediates
between compensation and job satisfaction in the
Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
0,134 0,052 2,539 0,011
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
7 Organizational commitment fully mediates between
career development and job satisfaction at the
Public Works Office of Aceh Government.
0,065 0,039 1,637 0,101
The hypothesis is
accepted and the data
supports the model
2.5.1 Research Implications
The research carried out must be able to contribute or theoretically implicate to the
development of science and make practical contributions to managerial policy. This
research has contributed theoretically and practically.
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh with Organizational
Commitment as a Mediation Variable
29

2.5.2 Theoretical Implications
This research has several theoretical implications, as follows:
1. Compensation and career development have a positive and significant effect on
organizational commitment and job satisfaction. This is in line with most previous
research findings that found a positive and significant effect on compensation and
career development on organizational commitment and job satisfaction. Thus, this
research has strengthened the theoretical framework related to the effect of
compensation and career development on organizational commitment and job
satisfaction.
2. Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on job satisfaction,
and this is in line with most previous research findings that found a positive and
significant effect on organizational commitment to job satisfaction.
3. Organizational commitment partial mediates the relationship between
compensation and job satisfaction. This is not in line with the results of previous
studies, which indicate that there is a significant partial mediation effect of job
satisfaction that mediates the relationship between compensation and job
satisfaction..
4. Organizational commitment fully mediates the relationship between career
development and job satisfaction. This is not in line with the results of previous
studies, which finds that there is a significant partial mediation effect of job
satisfaction that mediates the relationship between compensation and job
satisfaction
.
2.6 Practical Implications
1. Compensation and career development have a positive and significant effect on
organizational commitment. This means that the better the compensation and career
development, the more the organizational commitment increases. The consequences
of compensation and career development certainly increase organizational
commitment.
2. Compensation and career development have a positive and significant effect on job
satisfaction. It means that the better the compensation and career development, the
more job satisfaction increases. The consequence of compensation and career
development is certainly to increase job satisfaction.
3. Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on Job Satisfaction
of the Public Works Office of the Aceh Government. In other words, the higher the
job satisfaction, the higher the Job Satisfaction of the Public Works Office of the
Aceh Government. This finding suggests that organizational commitment is
something that must be considered by leaders to employees to increase employee
job satisfaction.
4. Organizational commitment can partially mediate the relationship between
compensation and work satisfaction. The implication for the Public Works Office
of Aceh Government who wants to improve job satisfaction can be achieved
through efforts to increase fair employee compensation under applicable regulations
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
30

in the Public Works Office of Aceh Government without having to be supported by
strengthening organizational commitment.
5. Organizational commitment can fully mediate the relationship between career
development and job satisfaction. The implication for the Office of Public Works
of the Government of Aceh who wants to improve Job Satisfaction can be achieved
by improving employee career development. This means that the Head of the Public
Works Office of the Aceh Government must focus attention on efforts that can
increase job satisfaction. Moreover, it will be stronger if strengthened by
organizational commitment
.
References
Armstrong, Reilly, P, & Brown D, (2011), ”increasing the effectiveness of reward management,”
Employee Relations, Emerald Group, (33), 2, 106-120.
Kabak, E, K, Gocer, K, S, A, Kucuksoylemez, S, Tuncer, G, (2014) “strategies for employee job
satisfaction: a case of service sector,” Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 150 (2014)
1167 – 1176.
Farooqui, S, & Nagendra, A, (2014). “The Impact of Person organization Fit on Job Satisfaction
and Performance of the Employees,” Procedia Economics and Finance, 11, (2014) 122 – 129
Fareed E,abidan Z,shahzad F,ameen U, lodhi N R, 2013, “The Impact of Rewards on Employee’s
Job Performance and Job Satisfaction,” management and administrative science, (2), 5 ,431-
442.
Bao, J., Bao, J., & Wu, A. (2017). Equality and Equity in Compensation. Working Paper 17-093,
Harvard Business School Working, JEL Classi.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The Moderator-Mediator Variable Distinction in Social
Psychological Research: Conceptual, Strategic, and Statistical Considerations. Journal of
Pe~nality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173–1182.
David P. MacKinnon, and L. J. L. (2012). NIH Public Access. Statistical analysis for identifying
mediating variables in public health dentistry interventions, 71(Suppl 1), 1–15.
Huczynski, A. A., & Buchanan, D. A. (2008). Organizational Behaviour. Annual Review of
Psychology, 30, 980. http://doi.org/10.4324/9780203765326
Huffman, J. B., Powell, D., Otto, D., & Member, C. (2015). Organizational Behavior: Perceptions
Analysis of Micro and Macro Organizational Behavior in an Organizational Setting.
James L. Gibson John M. Ivancevich James H. Donnelly, J. R. K. (2012). Organizations
Behavior, Structure, Processes.
Karim, F., & Sciences, A. (2012). Impact of Job Satisfaction, Perceived Organizational Justice
and Employee Empowerment on Organizational Commitment in Semi- Government
Organizations of Pakistan, 3(4), 92–104.
Luthans, F. (2012). Organizational behavior an evidence-based approach 12th edition.
Organizational behavior: an edivence-based approach.
Markoulli, M., Lee, C. I. S. G., Byington, E., & Felps, W. A. (2017). Mapping Human Resource
Management: Reviewing the field and charting future directions. Human Resource
Management Review, 27(3), 367–396. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2016.10.001
Ng, E., Hong, C., & Ramendran, C. (2012). An Effectiveness of Human Resource Management
Practices on Employee Retention in Institute of Higher learning: - A Regression Analysis.
International Journal of Business Research and Management (IJBRM), 3(2), 60–79.
Robbins, S. (2013). Organizational Behavior. Zhurnal Eksperimental’noi i Teoreticheskoi Fiziki.
http://doi.org/10.12737/4477
Robert L. Mathis, J. H. J. (2008). Human Resource Management, Twelfth Edition.
The Effect of Career Compensation and Development to Employee Satisfaction of Public Works Office in Aceh with Organizational
Commitment as a Mediation Variable
31

Setyowati, R. (2017). Investigating Organizational Commitment among Medical Doctors,
Hospital Nurses and Two Other Professional Jobs : A Systematic Review, 9(12), 99–106.
http://doi.org/10.5539/gjhs.v9n12p99
Steyrer, J., Schiffinger, M., & Lang, R. (2008). Organizational commitment — A missing link
between leadership behavior and organizational performance ? Available at
www.sciencedirect.com, 24, 364–374. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.scaman.2008.04.002
Unanue, W., Gómez, M. E., Cortez, D., Oyanedel, J. C., Anthony, M., & Fabio, A. Di. (2017).
Revisiting the Link between Job Satisfaction and Life Satisfaction: The Role of Basic
Psychological Needs, 8(May). http://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00680
Vogel, F. H. R. (2016). Article information: Human resource management and public service
motivation : where are we , and where do we go from here ?
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
32
