
Stock Performance before & after Stock Split on IDX
Ghazali Syamni
1
, Frisca Damayanti
1
, Wahyuddin Albra
1
, Mahdawi Mahdawi
2
,
and Nasir
3
1
Faculty of Economic and Business, Universitas Malikussaleh, Aceh, Indonesia
2
Magister of Economic, Faculty of Economic and Business, Universitas Trisakti,
Jakarta, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Economic and Business, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Aceh, Indonesia
mahdawi1601@gmail.com,nasiraziz@yahoo.com
Abstract. Stock split is one of the company's actions aimed at making investors
and potential investors more interested in a stock issuer. This research is
conducted to examine differences in stock performance in companies before and
after the stock split. This study uses data of companies registered in IDX for the
2015, 2016 and 2017. During this period, there are different company‘s data in
which there were 8 companies in 2015, 17 companies in 2016 and as many as 21
companies in 2017. The model of data analysis used in this study is a different
test model, particularly paired sample test. This study finds a difference in terms
of price and liquidity before and after the stock split. In addition, a different
performance is not found in term of return.
Keywords: Corporate ꞏ Action ꞏ Stock Split ꞏ Stock ꞏ IDX
1 Introduction
Changes in stock prices from year to year always occur either increase or decrease from
the value of the initial offering to the public. In certain conditions, it is likely that a
good share price will show a continually increase in certain issuers even it becomes
greater. Of course, this condition makes certain share prices more expensive to
investors. This condition requires the company’s management to implement a policy.
A common policy done is called breaking down stock prices into some parts. Then, this
policy is known as stock split.
Stock split is a stock split activity in certain parts and aims to make stock prices a
little cheaper and increase trading liquidity [1]. [2] explains that a stock split is called a
procedure of share distribution with the aim of increasing or decreasing the number of
shares outstanding without declining the value of the company. [3] who states a stock
split is as an action carried out by company’s management in order to make the stock
price lower and affordable for retail investors. Although some say stock split is only as
a sweetener besides it provides an effect on stock performance [4]. [5] mentions the
important reason for a stock split because high stock prices lead to be less excited about
the high stocks. Therefore, the stock split policy is enacted by the issuers.
Some previous studies had been conducted regarding to the stock split policy. [6]
explained how companies do stock split as a bell to remind investors that certain
Syamni, G., Damayanti, F., Albra, W., Mahdawi, M. and Nasir, .
Stock Performance before after Stock Split on IDX.
DOI: 10.5220/0009574600002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 33-38
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
33

companies have good prospects. [7] stated policy of doing a company's action provides
good news for owners of the company, but each company that carries out company
actions does not always provide the same results.
[8] concluded the stock split policy makes the company more liquid when the
announcement of the stock split, then it goes back to a decrease. [9] stated the stock
split policy on liquidity due to changes in high asset prices becomes lower and this
makes the uninformed investors more interested in participating in the transaction.
[10] and [11] explained there is a significant difference in positive abnormal returns
after the stock split policy is announced. On the other hand, [12] said it is not only stock
split which causes an improvement in stock performance. Even on the contrary, the
reverse stock split also provides better stock performance, especially institutional
investors. [13] stated a company which only conducts stock split in the short term gives
a positive return. Thus, investors do not be complacent with the policy.
[14] said the performance of shares before and after the stock split does not highlight
the different results. This is base on the value of EPS/PER which is not statistically
significant. [1] who stated there is no significant difference in stock performance before
and after a stock split and it is appeared in abnormal returns and market liquidity. [15]
and [16] who revealed there is a significant difference before and after a stock split, this
is reflected in abnormal returns and market liquidity. [4] who discovered stock split
increases the stock performance, although sometimes it can be seen there are no
differences in trading volume and return.
Based on the literature reviews aforementioned above, it can be concluded the stock
split policy in the capital market is still different. Even stock split as "cotton candy"
only provides signals in both the short term and not the long term. Therefore, the
purpose of this study is to examine the differences in stock split before and after the
stock split policy which has been carried out by the company.
2 Data and Method
This research is conducted on the Indonesia Stock Exchange and takes samples of the
issuers who carried out a stock split for periods of 2015 to 2017. The measurement of
issuer's stock performance is measured on the price, return and liquidity variables both
before and after the stock split activity. All data are collected through the site
http://www.idx.co.id quarterly, in addition to data on closing prices of shares and
trading volume on the website https://finance.yahoo.com. The sampling method in this
study uses a purposive sampling technique since not all samples have criteria in
accordance with those that have been determined.
The sample criteria desired in this study is as follows: The company conducted a
stock split on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in the periods of 2015 to 2017. The
company does a stock split once for the research period of 2015 to 2017. The company
carries out a stock split policy and does not undertake other corporate action policies
affecting the market; rights issue, distribution of bonus shares and others. The data are
completed to use in this study. Thus, the qualifying samples of this study are:
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
34
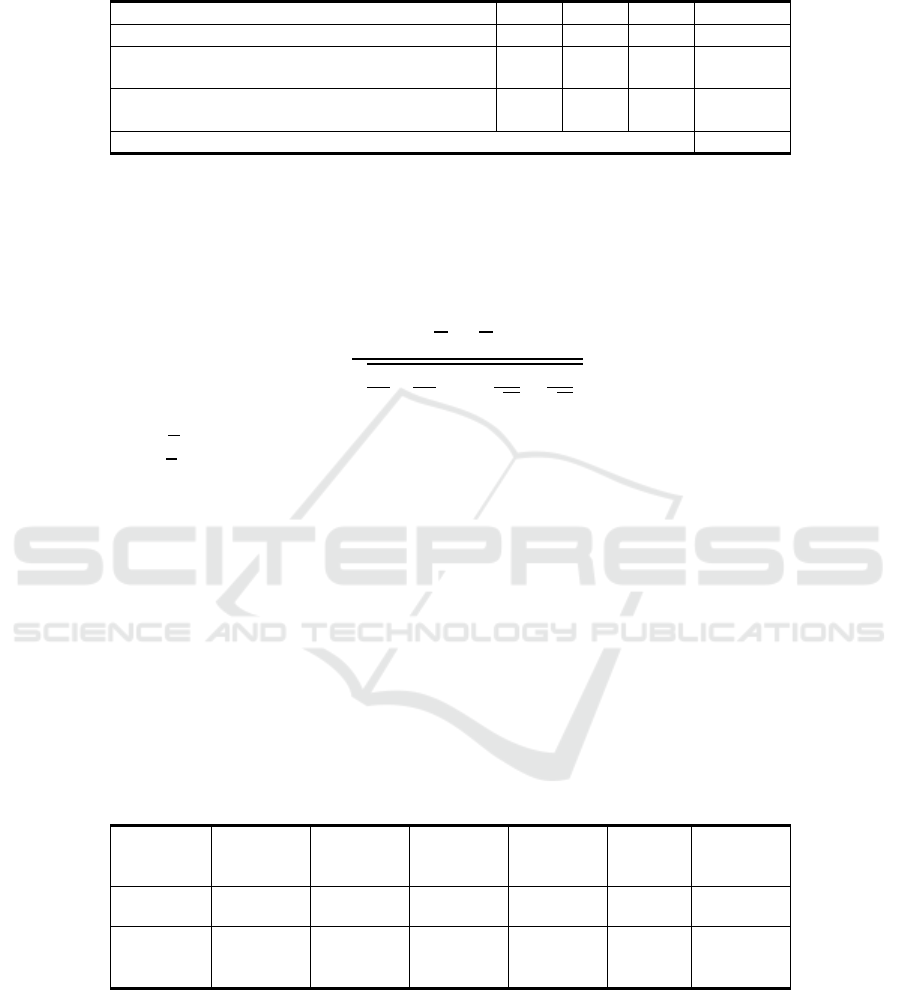
Table 1. Qualifying Samples.
Criterion 2015 2016 2017 Quantities
Issuers carr
y
in
g
out stock s
p
lit 9 22 24 55
Issuers carrying out stock split more than once a
y
ear for the
p
eriod of stud
y
- 5 2 7
Issuers undertaking other corporate policies for the
p
eriod of stud
y
1 - 1 2
Total of Samples 46
The given Table 1 depicts the number of samples in this study are 46 qualifying
issuers. But companies that do stock splits are different each year. In analyzing the data
of differences before and after a stock split by a stock issuer listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange is performed using a different test. Moreover, the data is processed
using SPSS program. In this case, it is done by using paired sample t-test. This is due
to two measurements on the same object. Therefore, the difference test formula is:
𝑡
𝑋
𝑋
2𝑟
√
√
Where; 𝑥
1
= Average sample before treatment;
𝑥
2
= Average sample after treatment;
s
1
= Standard deviation before treatment;
s
2
= Standard deviation after treatment;
n
1
= Number of samples before treatment;
n
2
= Number of samples after treatment
3 Results and Discussion
3.1 Data Description
This section explains the description of research data before and after the stock split,
including: price, return, and liquidity in 2015-2017.
Table 2. Average values and standard deviations.
Statistics
Price
Before
Price
After
Return
Before
Return
After
TVA
Before
TVA
After
Mean 11.051 1.464 5,4200 0,4266 0,0004 0,0013
Std.
Deviation
71.606 2.741 22,8135 6,8152 0,0009 0,0055
The Table 2 depicts the state of the data of all variables used is not so good, this can
be interpreted that data in this study is still having a high difference except for the
trading volume activity variable. In addition, the data can also be explained the average
Stock Performance before after Stock Split on IDX
35
price before the stock split is of 11,051 with a standard deviation of 71,606. After the
stock split, the price is 1.464, which is lower with a standard deviation of 2.741.
Furthermore, the return variable before stock split, return is 5.4% and the standard
deviation of 22,813 and after the stockplit becomes 0.42% and the standard deviation
of 6,815. However, the different things do not happen in trading volume activity.
3.2 Correlation Analysis
The correlation analysis is performed to analyze the relationship of correlation levels
between variables before and after stock splits. The variables used in this study are
stock price, stock return and trading volume activity (TVA). The given table 3 below
describes the variable of prices before and after the stock split have respectively values
of 0.212 and 0.222 and significant as many as 1 percent.
Table 3. Correlation Analysis.
Pai
r
stock split variable N Cor
r
elation. Sig.
Pair 1 stock
p
rice before & stock
p
rice afte
r
460 0.212 0.000
Pair 2 stock return before & stock return afte
r
460 0.019 0.690
Pair 3 TVA
b
efore & TVA afte
r
460 0.222 0.000
In addition, the trading volume activity variable does not posses a significant
relationship before and after the stock split.
3.3 Analysis of Different Tests
After analyzing the descriptive and correlation, the different test is examined. The
testing of different tests is done in all and annually (Table 4).
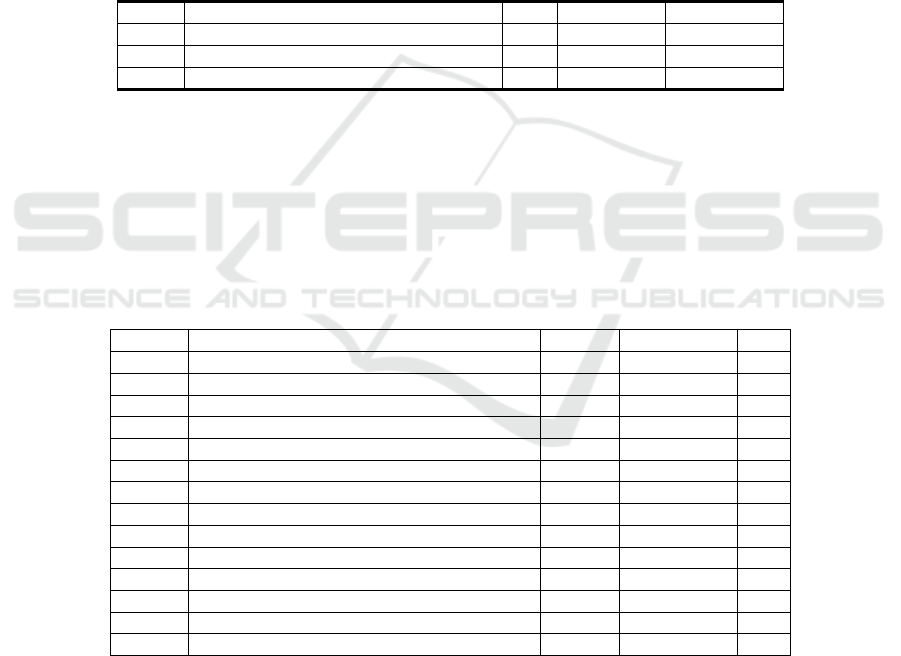
Table 4. Results of different test using paired test.
PAIR Stock S
p
lit Variable: Price N Correlation. Si
g
.
Pair 1 stock price before & stock price after (all) 460 .212 .000
Pair 2 stock price
b
efore & stock price after _2015 80 .961 .000
Pair 3 stock price before & stock price after_2016 180 .402 .000
Pair 4 stock
p
rice before & stock
p
rice after
_
2017 200 .071 .321
PAIR Stock S
p
lit Variable: Return N Correlation. Si
g
.
Pair 1 Return
_
before & Return
_
after
(
all
)
460 .244 .102
Pair 2 Return_before & Return_after _2015 80 -.025 .826
Pair 3 Return_before & Return_after _2016 180 -.063 .398
Pair 4 Return
_
Before & Return
_
After _2017 200 -.027 .699
PAIR Stock S
p
lit Variable: TVA n Correlation. Si
g
.
Pair 1 TVA
_
before & TVA
_
after
(
all
)
460 .599 .000
Pair 2 TVA_before & TVA_after _2015 80 .465 .000
Pair 3 TVA_before & TVA_after _2016 180 .046 .543
Pair 4 TVA_before & TVA_after _2017 200 .400 .000
The Table 4 shows there are 460 observations as a whole, but if it is seen annually,
there are different things. In 2015, there were 80 observations, 180 observations in 2016
and 200 observations in 2017.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
36

Moreover, the paired t test is tested. The test results show that after the stock split
policy is carried out, overall the price and trading volume prove that there is a difference
and the relationship between before and after the stock split. Furthermore, if it is looked
at the testing per year proves that there is year with no difference in performance before
and after the stock split policy is performed. This occurred in 2017 for prices and 2016
for trading volume activity, in which there was no significant value for those years. On
the other hand, returns happening on companies that carry out stock split show no
difference either before and after the policy is done. This can be seen statistically in
both overall and yearly statistics such as 2015, 2016 and 2017.
The results of the study indicate that the company's policy of taking stock split
action only provides a little prospect for investors. This can be seen in terms of prices
and trading volumes, that there are differences before and after the stock split policy.
Instead, it is not with the desired return for investors.
This finding is in accordance with the research conducted by [14]; [1]; [4] [9] and
[6]. They stated the stock split policy is only a sweetener in the company and on the
performance side there is no difference. This stock split policy is only used by the
issuers as an effort of company to attract small investors or retails to transact at the
issuer.
4 Conclusion
This research examines differences in stock performance after stock split. Stock split is
one of the ways carried out by companies to attract investors. Because if a stock split is
done, as if the performance will be better and cheaper price in the sides of investors.
The analyzed performance includes: stock prices, stock returns and trading volume
activity (TVA).
This study finds that price side highlights a significant price defference before and
after the stock split. However, if it was seen per year for the study period of 2015, 2016
and 2017, only in 2017 did not have price differences after a stock split. The stock
returns show that there is no difference in returns either overall or annually. There is no
significant difference in stock returns since the investors are less interested in terms of
stock split conducted by stock issuers. Yet the trading volume activity was only in 2016,
in which there is no difference in company‘s performance before and after a stock split.
Overall, there are differences in stock performance and it happened again in 2015 and
2017, however.
References
[1] Dewi, A. S., & Zulfiah, A. (2018). Comparative Analysis of Liquidity and Abnormal
Return Before and After Stock Split (Case Study on the Company Taking Sock Split Period
2013-2014). Sustainable Collaboration in Business, Technology, Information and
Innovation (SCBTII).
[2] Nadig, A. (2015). An empirical study of stock split announcements of select BSE sectors
using event study methodology. SDMIMD Journal of Management, 6(1), 1-12.
[3] Baker, H. K., & Powell, G. E. (1993). Further evidence on managerial motives for stock
splits. Quarterly Journal of Business and Economics, 20-31.
Stock Performance before after Stock Split on IDX
37

[4] Adisetiawan, R. (2018). Does Stock Split Influence to Liquidity and Stock
Return?(Empirical Evidence in The Indonesian Capital Market). Asian Economic and
Financial Review, 8(5), 682-690.
[5] Nagendra, M., & Babu, M. S. (2018, May). Impact of Corporate (Stock Split) Action on
Stock Price in India. In Presented paper in International Conference, Organised by St.
Joseph College, Bangalore.
[6] Smith, G. (2019). Stock Splits: <em>A Reevaluation</em>. The Journal of Investing,
28(4), 21-29. doi: 10.3905/joi.2019.1.085
[7] Pradhan, S. K., & Kasilingam, R. (2019). Impact of Corporate Actions on Shareholder
Wealth: <em>A Study on the Bombay Stock Exchange</em>. The Journal of Wealth
Management, 21(4), 85-97. doi: 10.3905/jwm.2019.21.4.085
[8] Huang, G.-C., Liano, K., & Pan, M.-S. (2015). The effects of stock splits on stock liquidity.
Journal of Economics and Finance, 39(1), 119-135. doi: 10.1007/s12197-013-9250-6
[9] Hu, M., Jain, A., & Zheng, X. (2018). Stock Splits and Liquidity Risk in the Chinese Stock
Market. Paper presented at the 9th Conference on Financial Markets and Corporate
Governance (FMCG).
[10] How, C. C., & Tsen, W. H. (2019). The Effects of Stock Split Announcements on the Stock
Returns in Bursa Malaysia (Kesan Pengumuman Pembahagian Saham terhadap Pulangan
Saham di Bursa Malaysia). Jurnal Ekonomi Malaysia, 53, 2.
[11] Gharghori, P., Maberly, E. D., & Nguyen, A. (2017). Informed Trading around Stock Split
Announcements: Evidence from the Option Market. Journal of Financial and quantitative
Analysis, 52(2), 705-735. doi: 10.1017/S0022109017000023
[12] Chung, K. H., & Yang, S. (2015). Reverse Stock Splits, Institutional Holdings, and Share
Value. Financial Management, 44(1), 177-216. doi: 10.1111/fima.12077
[13] Chan, K., Li, F., & Lin, T.-C. (2019). Earnings management and post-split drift. Journal of
Banking & Finance, 101, 136-146. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2019.02.004
[14] Saureka, N. S., & Tanti Irawati, M. (2012). Stock Performance Analysis Before and after
Stock Split on Basic Industry and Chemical in Indonesia. Academic Journal, 43, p175.
[15] Listarani, P. R., & Kesuma, I. K. W. (2014). Analisis perbandingan Abnormal Return dan
Likuiditas saham sebelum dan sesudah stock split. E-Jurnal Manajemen, 3(10).
[16] Munthe, K. (2016). Perbandingan Abnormal Return Dan Likuditas Saham Sebelum Dan
Sedudah Stock Split: Studi Pada Perusahaan Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia.
Jurnal Akuntansi, 20(2), 254-266.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
38
