
Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and
Liquidity to Profitability: Company Listed in the Jakarta
Islamic Index
Muhammad Nashikh, Puji Sucia Sukmaningrum, Ririn Tri Ratnasari, and
Achsania Hendratmi
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Airlangga, Campus B,
Jl. Airlangga No.4, 60286, Surabaya, Indonesia
Abstract. The aims of this study is to investigate the influence of Capital
Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity to company
profitability. Profitability is one of the important elements for the existence of a
company because it can be used as an indicator of the return on funds they invest.
The data used are companies listed in Jakarta Islamic Index period 2012-2016.
This study used a panel data and a multiple linear regression method. Based on
Random Effect Model shows that the variable of Capital Structure,
Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity are influence simultaneously and
significant to Profitability. The variable of Capital Structure, Macroeconomics,
Business Risk are influence and significant to Profitability partially.
Keywords: Company ꞏ Profitability ꞏ Capital structure ꞏ Macroeconomics ꞏ
Business risk ꞏ Liquidity
1 Introduction
The rapid development of economic condition and sharp competition in the global
market will become a new challenge and also opportunity for the company to develop
its business. As an effort to develop, the company requires a proper funding policy to
fulfill the company's operational and expansion activities. The decision on the
fulfillment of funds in the company includes a variety of considerations, whether the
company will use internal sources as well as external sources, which come from liability
including emission sukuk or issue new shares.
(Munawir, 2014) argues that "debt is all the financial liabilities of the company to
other parties that have not been met, which this debt is a source of funds or capital of
companies coming from creditors". Liabilities are divided into long-term liabilities and
short-term liabilities (current liabilities). Long-term liability is "the financial obligation
whose term of payment is still long term", while short-term liability (current liability)
is the financial obligation of the company that the repayment or payment will be made
in the short term by using current assets owned by the company.
The influence of the company's financial performance on capital structure has been
a long debate in various literatures. There are many theories that explain the effect of
the company's financial performance on capital structure. A number of studies that
Nashikh, M., Sukmaningrum, P., Ratnasari, R. and Hendratmi, A.
Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity to Profitability: Company Listed in the Jakarta Islamic Index.
DOI: 10.5220/0009854700002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 251-259
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
251

examine the effect of the company's financial performance on capital structure have
been done, whether it is viewed from the side of profitability, liquidity, leverage, level
of sales of companies and so on that show different results. The capital structure is also
considered the most important because the quality of capital structure owned by a
company will have an impact on its financial position
The role of financial management is needed in financing activities, because
financial management is the activities of companies that are related to how to get
working capital funding, allocate funds, and manage assets owned to achieve corporate
goals in which every good company should pay attention to the use of funds in operating
the company. The relationship between capital structure, macroeconomics, business
risk and liquidity to profitability cannot be ignored because increased profitability is
necessary for long-term survival. According to (Sartono, 2014) Profitability shows the
company's ability to earn profit in relation to sales, total assets, and own capital.
Financial performance is a description of the company's financial condition at a
certain period involving funding aspect and measured by using capital adequacy,
activity, liquidity, and profitability. Sources of information that can be used to
determine the level of financial performance of the company is the financial statements.
According to (Moeljadi, 2006) the analysis on the company performance is generally
done by analyzing the financial statements, which include benchmarking the
performance of a company with other companies in the same industry and evaluate the
trend of the company's financial position over time.
The capital market has an important role in bridging the relationship between the
owner of the fund (investor) and the user of the fund (issuer) in which the transaction
is conducted on the Stock Exchange. The rapid development of capital market made
PT Bursa Efek Jakarta together with PT Danareksa Investment Management (DIM)
launched a stock index based on Islamic Sharia, the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII)
consisting of 30 types of shares selected from Sharia compliant stocks. Jakarta Islamic
Index (JII) is a capital market formed to invest in sharia-based stocks and provide
benefits for investors in running Islamic sharia to invest in the stock exchange. JII is
also expected to support the process of transparency and accountability of sharia-based
stocks in Indonesia.
Based on the above description, the research is conducted to answer the research
question: Does Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity
influence Profitability of company registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) Period
2012-2016?
2 Literature and Hypothesis Development
According to (Munawir, 2014), the financial performance of the company is one of the
fundamentals of the assessment of the company's financial condition performed based
on the analysis of the company's financial ratios. Interested parties need the results of
the measurement of the company's financial performance to see the condition of the
company and the success rate of the company in carrying out its operational activities.
In general, the profit equated with profit, in other words the ratio which is
considered able to measure the company's performance is profitability ratios. (Brigham
and Houston, 2011) explain that profitability is the end result of a number of policies
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
252

and decisions made by the company. Profitability is also a group of ratios that show a
combination of liquidity influence, asset management, and debt on operating outcomes.
According (Husnan, 2000) capital structure theory explains the relationship
between the availability of sources of funds and the cost of different capital and the
effect of changes in capital structure on the value of the company and the cost of capital.
The flexibility value of a company depends essentially on the estimation of how much
future funding flows and the rate of recovery as a return (capitalization) of the flow of
funds. The level of capital costs incurred by the company reflects the level of recovery
for investors.
The capital structure policy involves choosing between the risk and expected return,
the addition of the debt raises the risk level of the firm's revenue stream, but higher debt
also means a greater rate of expected return. The high level of risk will lower the stock
price, but the high expected rate of return will raise the price of the stock.
Tax is a mandatory fee derived from a tax subject and addressed to the state.
Company is one of the tax subjects that contributes the most in state tax revenues. Tax
for companies is a burden that can reduce corporate profits, while tax for the state is the
income that will be used to fund the administration. Progressive tax rate leads to the
higher profit of a company, the higher the amount of taxes that must be paid. In Islam,
the tax is known as Al-Usyr or Al-Maks or it can also be called Adh-Dharibah, which
means "levy withdrawn from the people by tax collectors who is called Shahibul Maks
or Al-Asysyar”. Meanwhile, according to linguists, tax is a payment made to the
government to finance expenditures made in the case of providing services for the
public interests.
According to (Suseno and Astiyah, 2009) in the book Seri Kebanksentral Bank
Indonesia, Inflation is an economic phenomenon that becomes the interests of various
parties. Inflation is not only the concern of the general public, but also the concern of
the business world, the central bank, and the government. Inflation can affect the
community and economy of a country. According to Islamic economists, inflation
creates a disruption to the function of money, especially in the saving function, in
advance payments and unit calculations, undermining the spirit of saving in society,
and directing investments in non-productive things such as land and precious metal.
(Brigham and Houston, 2011) state that business risk is uncertainty about the
projected return on assets in the future. Business risk is a failure of internal control
resulting in unexpected losses and unsuccessful management to ensure return to the
company. Therefore, risk is important to manage. In Islamic perspective, risk
management is an effort to keep God's trust in wealth for the welfare of people.
The liquidity of a company is closely related to the ability of a company to meet its
financial obligations that must be fulfilled immediately. In a debt company can affect
the company's performance because the company will assess the ability or speed of the
company in paying its debt.
2.1 Previous Studies
Study conducted by (Ching et al., 2015), relationship between earnings management
and financial performance are significant linear and positively correlated. According to
(Shah and Ilyas, 2014) leverage ratios are regressed on profitability ratio have strong
support for pecking order theory.
Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity to Profitability: Company Listed in the Jakarta Islamic Index
253

Capital structure variables are significantly associated with ROA regarding the
study of (Mokhtar, 2006) .In a study conducted by (Widiyanti and Elfina, 2015), Long
Term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER) is a comparison between long-term liabilities and
the company's own total capital. The lower the ratio the higher the company's ability to
pay long-term liabilities and vice versa (Utari, Purwanti and Prawironegoro, 2014).
According to (Widiyanti and Elfina, 2015) companies with too many liabilities will find
it difficult to obtain additional funds from outside. Then the influence between LDER
and ROA is negative.
Debt to Total Fixed Asset Ratio (DTFAR) is the ratio of debt used to measure the
ratio of total liabilities to total fixed assets. How much fixed assets the company
financed by the obligation or how much the company's liabilities affect the management
of assets.
In (Taqi, Ajmal and Pervez, 2016) study using panel regression analysis with pooled
OLS method, fixed effects and random effects, DTFAR values showed negative
correlation with profitability.
Tax is a mandatory fee derived from a tax subject and addressed to the state. The
Company as one of the tax subjects who contributed the most in state tax revenues.
Based on research conducted (Vătavu, 2015) showed that taxes have a significant
positive effect on ROA. When taxes are high, companies tend to invest less to keep
their income.
Inflation is an increase in the price of daily necessities of life from time to time on
an ongoing basis. Based on research conducted (Vătavu, 2015), it shows that inflation
has a positive impact on ROA.
The business risk of the company can be illustrated by measuring the fluctuations
of the firm's earnings. Companies experiencing profit fluctuations face uncertainty in
terms of ability to raise funds to pay off their loans to creditors. Research conducted by
Saraswathi (Saraswati, Wiksuana and Rahyuda, 2016) shows that business risk has a
significant positive effect on profitability.
Current Ratio is a ratio that indicates a company's ability to pay its short-term
liabilities using its current assets. Based on research (Mahardhika and Aisjah, 2014), it
shows that the Current Ratio (CR) has a significant positive effect on Return on Assets
(ROA).
2.2 Hypothesis
Based on the background, problem formulation, research objectives, and the literature
review, the hypothesis proposed in this research are:
H1: There is influence of Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER), Debt to Total
Fixed Assets Ratio (DTFAR), Taxes, Inflation, Business Risk and Current Ratio
(CR) to Return on Assets (ROA) of the companies listed in Jakarta Islamic Index
(JII) simultaneously
H2: There is influence of Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER), Debt to Total
Fixed Assets Ratio (DTFAR), Taxes, Inflation, Business Risk and Current Ratio
(CR) to Return on Assets (ROA) Index (JII) partially.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
254
3 Methodology
Panel data used to combine information from time series data and cross section can
overcome the problems that arise when there are problems omitted variable (omitted
variables) (Widarjono, 2007). To overcome the intercorrelation between independent
variables resulting in misinterpretation of regression, panel data methods are more
appropriate to use (Hill, Griffiths and Judge, 2001). The population in this study is all
companies registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) Year 2012-2016. Sample
determination was done by a purposive sampling method. The number of samples in
this research were 70. This research used multiple linear regression to find the
correlation between independent variable and dependent variable. Equation model
used in this research is as follows:
ROA = a + β LDER + β DTFAR + βTAX+ βINF + βBUSRISK + βCR + e
Variables
A total of 6 variables were used to determine factors affecting the profitability of
companies listed in Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) Year 2012-2016. These variables were
divided into 4 groups: Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and
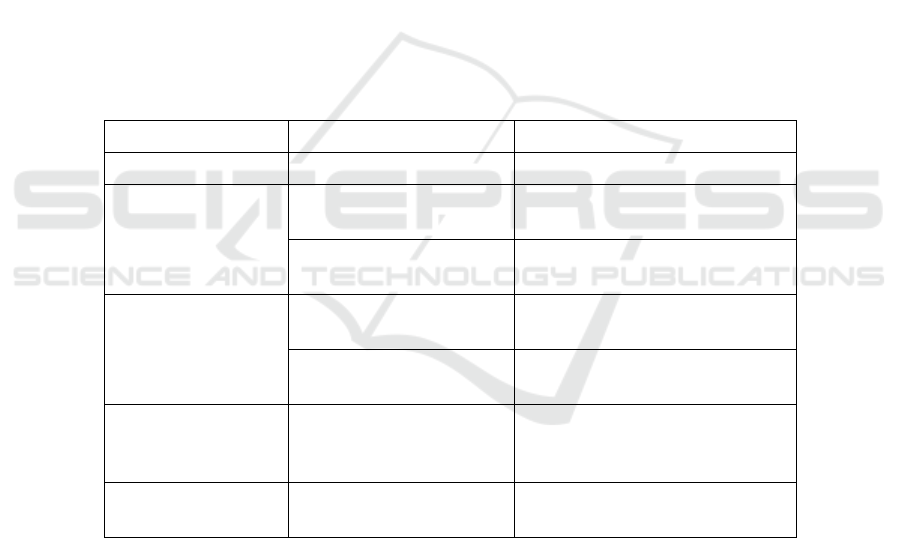
Liquidity. Table 1 represents the variables and how to calculate these variables:
Table 1. Variables and Measurement Tools.
Category Variable Measurement Tools
Dependent Variable Profitability (ROA) Profit before tax on total assets
Capital Structure
Long-term Debt to Equity
Ratio (LDER)
Total long-term debt to total
equity
Debt to Total Fixed
Assets Ratio (DTFAR)
total debt to total fixed assets
Macroeconomic
TAX
ratio of tax on earnings before
interest and taxes
Inflation (INF)
The annual rate of inflation
provided by Bank Indonesia
Business Risk BUSRISK
standard deviation ratio of Profit
before interest and tax on total
assets
Liquidity Current Ratio (CR)
ratio of current assets to current
liabilities
4 Results and Discussion
Table 2 describes the results of descriptive analysis of each variable used to measure
the profitability level of companies listed in Jakarta Islamic Index (JII).
Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity to Profitability: Company Listed in the Jakarta Islamic Index
255
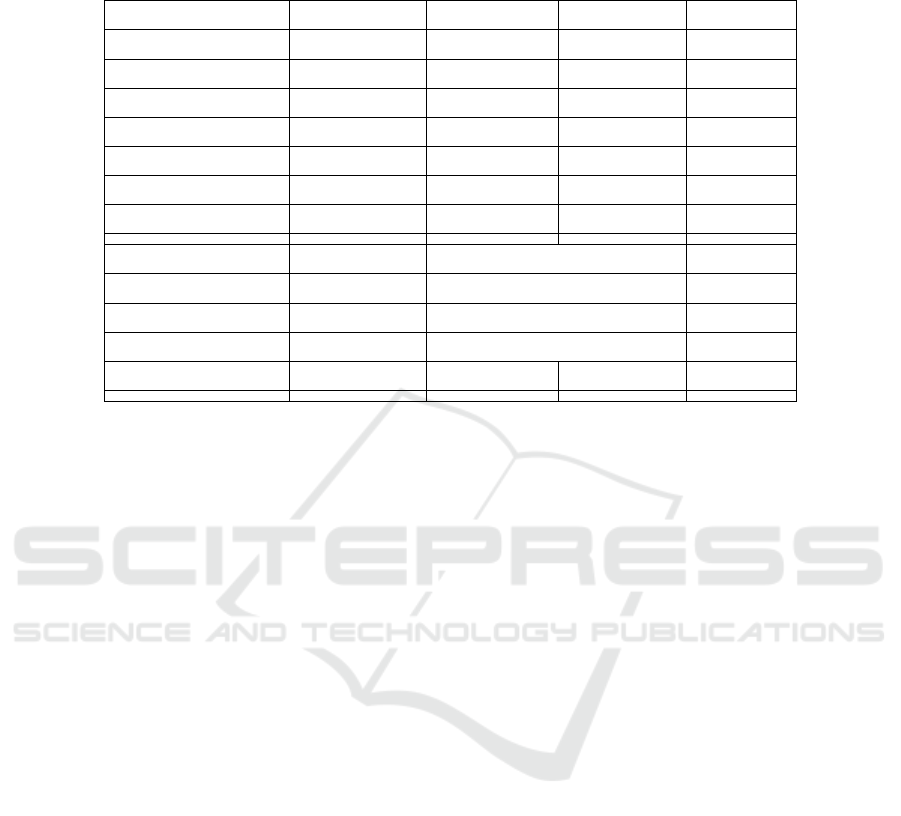
Table 2. Statistic Descriptive.
Variable Coefficient Std. Error t-Statistic Prob.
C 0.057179 0.023158 2.469119 0.0163
LDER? -0.082128 0.027815 -2.952660 0.0044
DTFAR? -0.010688 0.006607 -1.617745 0.1107
TAX? 0.018393 0.057412 0.320370 0.7497
INFLATION 0.265602 0.120564 2.202993 0.0313
BUSRISK? 1.809059 0.123493 14.64909 0.0000
CR? 0.007389 0.005553 1.330670 0.1881
R-square
d
0.833084 Mean dependent va
r
0.033666
Ad
j
usted R-square
d
0.817188 S.D. dependent va
r
0.053709
S.E. of re
g
ression 0.022964 Sum squared resi
d
0.033224
F-statistic 52.40607 Durbin-Watson sta
t
1.245625
Prob(F-statistic) 0.000000
Constant value of 0.057179 indicates if the variable LDER, DTFAR, Tax, Inflation,
business risk and CR is zero or constant, then the value of ROA is 0.057179.
The LDER variable has a probability value of 0.0044 significant at the 5%
significance level so that H0 is rejected and H1 is accepted. This shows that there is
significant influence between Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER) to ROA. While
the value of LDER variable coefficient is equal to - 0.082128, it shows that each
decrease of one unit LDER then ROA has increased by 0.082128 with the assumption
that the other variable is constant. So it can be concluded that LDER has a significant
negative effect on ROA. So the lower the Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER) the
higher the Return on Assets (ROA) of the company.
The DTFAR variable has a probability value of 0.1107 not significant at the 5%
significance level so that H0 is accepted and H2 is rejected. This shows that Debt to
Total Fixed Assets (DTFAR) has no significant effect on the ROA of companies
registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) period 2012-2016. If the debt ratio is higher
in the fear of the company is not able to cover its obligations with the assets it has.
Because of how much fixed assets the company is financed by the obligation or how
much the company's liabilities affect the management of assets will determine the
financial health of the company.
The Tax Variable has a probability value of 0.7497 not significant at the 5%
significance level so that H0 is accepted and H3 is rejected. This indicates that Tax has
an insignificant influence on the ROA of companies registered in the Jakarta Islamic
Index (JII) period 2012-2016.
Inflation variable has a probability value of 0.0313 smaller than the 5% significance
level (α = 0.05) so that H0 is rejected and H4 is accepted. This shows that there is a
significant influence between Inflation on ROA. While the value of the variable
coefficient of inflation is 0.265602 it shows that every increase of one unit of inflation,
then ROA also increased by 0.265602 with the assumption that the other variable is
constant. So it can be concluded that inflation has a significant positive effect on ROA.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
256

The higher the Inflation rate, the higher the Return on Assets (ROA) of the company.
If the price increase that can be enjoyed by the company is higher than the production
cost incurred, then the profitability of the company will rise because the increase of
inflation during a certain period of time followed by the average increase of ROA.
Business risk variable (BusRisk) has a probability value of 0.0000 is smaller than
the 5% significance level (α = 0.05) so that H0 is rejected and H5 is accepted. This
shows there is a significant influence between Busrisk on ROA. While the value of the
variable coefficient of BusRisk is 1.809059 it shows that every increase of one unit of
inflation, then ROA also increased by 0.265602 with the assumption that the other
variable is constant. Then it can be concluded that BusRisk has a significant positive
effect on ROA. The higher the level of business risk the higher the Return on Assets
(ROA) of the company. In the theory of high risk high return, to get a high return, the
risk is also high, and vice versa. If the risk of business in the company is high, then the
profitability of the company will increase. Described in QS. Luqman verse 34:
ِ
ّ
ﺰَﻨ
ُ
ﻳ
َ
ﻭ
ِ
ﺔ
َ
ﻋﺎ
ﱠ
ﺴﻟٱ
ُ
ﻢ
ۡ
ﻠ
ِ
ﻋ ۥ
ُ
ﻩ
َ
ﺪﻨ
ِ
ﻋ
َ
ﱠ
ٱ
ﱠ
ﻥ
ِ
ﺇ
ۢ
ُ
ﺲ
ۡ
ﻔَﻧ ﻱ
ِ
ﺭ
ۡ
ﺪ
َ
ﺗ ﺎ
َ
ﻣ
َ
ﻭ
ۖ
ﺍ
ٗ
ﺪَﻏ
ُ
ﺐ
ِ
ﺴ
ۡ
ﻜ
َ
ﺗ ﺍ
َ
ﺫﺎ
ﱠ
ﻣ
ٞ
ﺲ
ۡ
ﻔَﻧ ﻱ
ِ
ﺭ
ۡ
ﺪ
َ
ﺗ ﺎ
َ
ﻣ
َ
ﻭ
ۖ
ِ
ﻡﺎ
َ
ﺣ
ۡ
ﺭ
َ
ۡ
ﻷٱ ﻲ
ِ
ﻓ ﺎ
َ
ﻣ
ُ
ﻢ
َ
ﻠ
ۡ
ﻌ
َ
ﻳ
َ
ﻭ
َ
ﺚ
ۡ
ﻴَﻐ
ۡ
ﻟٱ
ُ
ﻝ
ۢ
ُ
ﺮﻴ
ِ
ﺒَﺧ
ٌ
ﻢﻴ
ِ
ﻠ
َ
ﻋ
َ
ﱠ
ٱ
ﱠ
ﻥ
ِ
ﺇ
ۚ
ُ
ﺕﻮ
ُ
ﻤ
َ
ﺗ
ٖ
ﺽ
ۡ
ﺭ
َ
ﺃ
ِ
ّ
ﻱ
َ
ﺄ
ِ
ﺑ٣٤
'Inna Allāha `Indahu `Ilmu As-Sā`ati Wa Yunazzilu Al-Ghaytha Wa Ya`lamu Mā
F
ī Al-'Arĥāmi Wa Mā Tadrī Nafsun Mādhā Taksibu Ghadāan Wa Mā Tadrī
Nafsun Bi'ayyi 'Arđin Tamūtu 'Inna Allāha `Alīmun Khabīrun
Meaning:
“Indeed, Allah [alone] has knowledge of the Hour and sends down the rain and
knows what is in the wombs. And no soul perceives what it will earn tomorrow,
and no soul perceives in what land it will die. Indeed, Allah is Knowing and
Acquainted”.
Variable Current Assets (CR) has a probability value of 0.1881 is not significant at
the 5% significance level so that H0 is accepted and H6 is rejected. This indicates that
Current Assets (CR) have an insignificant influence on the ROA of companies
registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) year 2012-2016.
Based on test result with best model that is Random Effect Model (REM), it can be
seen that F-statistic probability value is 0.0000000, this value is smaller than 0.05 and
significant at 95% confidence level (α=0,05), so H0 is rejected and H1 accepted. It can
be concluded that the independent variables, namely the Long-term Debt to Equity
Ratio (LDER), Debt to Total Fixed Assets Ratio (DTFAR), Tax, Inflation, Business
Risk, and Current Ratio (CR) simultaneously have significant effect to the dependent
variable, ie Return on Assets (ROA) of companies listed in Jakarta Islamic Index (JII)
year 2012-2016.
Based on the results of statistical tests with the best model of the Random Effect
Model (REM), R-Squared value of 0.833084 was obtained. So it can be concluded that
the independent variables of Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER), Debt to Total
Fixed Assets Ratio (DTFAR), Taxes, Inflation, Business Risk, and Current Ratio (CR)
can impact 83.30% to Return on Assets (ROA) of companies listed in the Jakarta
Islamic Index (JII) period 2012-2016 and the remaining 16.70% influenced by other
factors not used in regression model in this research.
Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity to Profitability: Company Listed in the Jakarta Islamic Index
257

5 Conclusion
Based on the results of research and discussion that has been done, the conclusions that
can be taken are:
1. Long-term Debt to Equity Ratio (LDER) partially has a negative and significant
effect on Return on Assets (ROA) of companies registered in the Jakarta Islamic
Index (JII) period 2012-2016 at 5% significance level (α = 0.05).
2. Debt to Total Fixed Assets Ratio (DTFAR) partially have no significant effect
on Return on Assets (ROA) of companies registered in Jakarta Islamic Index
(JII) period 2012-2016 at 5% significance level (α = 0,05).
3. Tax partially have no significant effect on Return on Assets (ROA) of companies
registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) period 2012-2016 at 5% significance
level (α = 0,05).
4. Inflation partially has a positive and significant impact on Return on Assets
(ROA) of companies registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) period 2012-
2016 at 5% significance level (α = 0,05).
5. The business risks partially have a positive and significant impact on the Return
on Assets (ROA) of companies registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII)
period 2012-2016 at the 5% significance level (α = 0,05).
6. Current ratio (CR) partially has no significant effect on Return on Assets (ROA)
of companies registered in the Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) period 2012-2016 at
5% significance level (α = 0,05).
7. Long-term debt to Equity Ratio (LDER), Debt to total Fixed Assets Ratio
(DTFAR), Tax, Inflation, Business Risk and Current Ratio (CR) simultaneously
have a significant effect on Return on Assets (ROA) Jakarta Islamic Index (JII)
period 2012-2016 at 95% confidence level (α = 0,05).
This research also cannot be separated from the limitations that include the variables
used suggestions that can be delivered from the above conclusions are:
1. For managers and owners of the company, should better optimize its debt, so the
company's profit will increase. The optimization of debt will have a positive
impact that will increase the value of the company.
2. For other stakeholders, should pay more attention to the company's financial
ratios, because the company's financial ratios can provide the information
needed as a decision-making material in projecting its investment.
3. For the next researcher
a. the need for further research where there are many other variables that can
also affect the profitability of the company.
b. preferably more advanced research using other issuers such as ISSI and also
should the study period of observation be extended so that will give more
different picture.
References
Brigham, E. F. and Houston, J. F. (2011) Dasar-dasar Manajemen Keuangan Buku 2. Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
258

Ching, C. P. et al. (2015) ‘The relationship among audit quality, earnings management, and
financial performance of Malaysian public listed companies’, International Journal of
Economics and Management, 9(1), pp. 211–229.
Hill, R. C., Griffiths, W. and Judge, G. (2001) Undergraduate econometrics, Volume 1.
University of California: Wiley.
Husnan, S. (2000) Manajemen Keuangan : Teori dan Penerapan (Keputusan Jangka Panjang).
Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Mahardhika, B. P. and Aisjah, S. (2014) ‘Pengujian Pecking Order Theory Dan Trade Off Theory
Pada Struktur Modal Perusahaan (Studi Pada Perusahaan Consumer Goods Di Bursa Efek
Indonesia)’, JIMFEB, Vol 2, No.
Moeljadi (2006) Manajemen keuangan 1: pendekatan kuantitatif dan kualitatif. Malang:
Bayumedia.
Mokhtar, M. Z. (2006) ‘An Evaluation of the factors affecting corporate performance of Malaysia
listed companies’, International Journal of Economics and Management, 1(1), pp. 91–116.
Munawir, S. (2014) Analisa Laporan Keuangan. 17th edn. Yogyakarta: Liberty.
Saraswati, I. A. A., Wiksuana, I. G. B. and Rahyuda, H. (2016) ‘Pengaruh Risiko Bisnis,
Pertumbuhan Perusahaan Dan Struktur Modal Terhadap Profitabilitas Serta Nilai Perusahaan
Manufaktur’, E-Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis Universitas Udayana, 6(5), pp. 1729–1756. doi:
10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Sartono, R. A. (2014) Manajemen Keuangan Teori dan Aplikasi. 4th edn. Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Shah, A. and Ilyas, J. (2014) ‘Is Negative Profitability-Leverage Relation the only Support for
the Pecking Order Theory in Case of Pakistani Firms ?’, Pakistan Development Review,
53(1), pp. 33–55.
Suseno and Astiyah, S. (2009) ‘Inflasi’, in, p. 55.
Taqi, M., Ajmal, M. and Pervez, A. (2016) ‘Impact Of Capital Structure On Profitability Of
Selected Trading Companies Of India’, Arabian Journal of Business and Management
Review (Oman Chapter), 6(3), pp. 1–16.
Utari, D., Purwanti, A. and Prawironegoro, darsono (2014) Manajemen Keuangan (Kajian
Praktik dan Teori dalam Mengelola Keuangan Organisasi Perusahaan). Revisi. Bogor:
Mitrawacanamedia.
Vătavu, S. (2015) ‘The Impact of Capital Structure on Financial Performance in Romanian Listed
Companies’, Procedia Economics and Finance, 32(15), pp. 1314–1322. doi: 10.1016/S2212-
5671(15)01508-7.
Widarjono, A. (2007) Ekonometrika : teori dan aplikasi untuk ekonomi dan bisnis. Yogyakarta:
Ekonisia.
Widiyanti, M. and Elfina, F. D. (2015) ‘Pengaruh Financial Leverage terhadap Profitabilitas pada
Perusahaan Sub Sektor Otomotif dan Komponen yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia’,
Jurnal Manajemen dan Bisnis Sriwijaya Bisnis, 13(1), pp. 117–136.
Capital Structure, Macroeconomics, Business Risk and Liquidity to Profitability: Company Listed in the Jakarta Islamic Index
259
