
Analysis of Macroeconomics Factor Affecting Jakarta Islamic Index
Tri Wijayanti Septiarini
1
, Muhamad Rifki Taufik
2
, Mufti Afif
1
and Atika Rukminastiti Masrifah
1
1
Department of Islamic Economics, University of Darussalam Gontor, Indonesia
2
Department of Occupational, Safety and Health, University of Darussalam Gontor, Indonesia
atikamasrifah@ unida.gontor.ac.id
Keywords: Jakarta Islamic Index, Macroeconomics, Multiple Linear Regression.
Abstract: The goal of this study was to propose analyzing the influence of macroeconomics factor to Jakarta Islamic
Index. The macroeconomics factors consist of inflation, BI rate, exchange rate IDR/USD, and Gross Domestic
Product (GDP). The observation data concerned were obtained during April, 2016 to June, 2019 (in total 39
monthly observation data). The multiple linear regression model is applied to analyze the relation between
independent variable (inflation, BI rate, exchange rate IDR/USD, and Gross Domestic Product) and dependent
variable which is Jakarta Islamic Index (JII). The results explained that the independent variables are
significant except inflation.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Background
According to (Huang et al., 2008), there are two groups
in economic theory which are microeconomics and
macroeconomics. Macroeconomics focuses on wide
combination of actions (population agents), instead of
personal behaviour (a single agent). A macroeconomic
variable is a guiding monetary, natural, or geopolitical
event that give large impact in local or national
economy. Macroeconomic factors give effect broadly
to windrows of groups, rather than selected persons.
The examples of macroeconomic factors are economic
outputs, unemployment rates, and inflation. The
governments, businesses and consumers attentively
controlled the barometer of economic
accomplishment. A macroeconomic factor contain the
trend of a particular large-scale market. For example,
fiscal policy and numerous regulations influence state
and national economies, while powerful bring about
broader international implications.
Based on (Masrizal, Mustofa and Herianingrum,
2019), Indonesia is the largest Muslim countries
which represents prospect market for expanding
sharia financial industry. Further, sharia investment
has an crucial task to enhance the Islamic finance
industry in Indonesia. Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) is
the measuring instruments of performance for Sharia
capital market in Indonesia which was established in
July 2000. According to (Sakti and Yousuf, 2013),
Jakarta Stock Exchange Islamic Index (JII) is sharia
stock market index which has companies members in
the under provisions of Islamic stocks regulated by
National Sharia Board. One of the most favored
sectors of sharia investment is to invest in stocks
belonging to the JII. The issue listed in JII conducts
its business activities that are not contrary to the
principles of sharia. Shares listed in the JII consist of
30 most liquid stocks selected from Islamic
compliance shares. According to (Sakti and Yousuf,
2013), the dynamic linkage between macroeconomic
factors and stock returns is well proposed theory in
financial economics literature. As stated in the stock
evaluation model, macroeconomic factors might have
organized relationship on stock prices especially in
influence on discounted future cash flows.
The aim of this paper is to analyse the influence
further to the Jakarta Islamic Index and
macroeconomic linkages for developing economies.
The variables included are exchange rate, inflation,
gross domestic product, and BI rate as being
important in explaining Jakarta Islamic Index. Our
analysis, hence, might be further collecting our
understanding of the Indonesian Islamic equity
market behavior and its relations with various
components of macroeconomic variables. Therefore,
this research attend to complete this gap by analyzing
the influence of macroeconomic factors toward
Islamic stock prices in Indonesia.
Septiarini, T., Taufik, M., Afif, M. and Masrifah, A.
Analysis of Macroeconomics Factor Affecting Jakarta Islamic Index.
DOI: 10.5220/0009864700002898
In Proceedings of the 7th ASEAN Universities International Conference on Islamic Finance (7th AICIF 2019) - Revival of Islamic Social Finance to Strengthen Economic Development Towards
a Global Industrial Revolution, pages 19-22
ISBN: 978-989-758-473-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
19
1.2 Objectives
The study aims at analyzing how macroeconomic
variables influence the stock markets index by using
Jakarta Islamic Index as a case study.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
There are many methods that have been applied in
examining macroeconomic indicators to stock market
index. This section brings us to the adaptable
literature for this study which were reviewed and
based on the relevance of using any methods to
examine macroeconomic indicators to stock market
index.
According to (Ibrahim and Agbaje, 2018), it had
been examined the relationships between stock
returns (monthly data of the Nigerian Stock Exchange
and Nigerian Consumers Price Index ) and Nigeria
inflation. According to (Alam and Uddin, 2009), due
to monthly data during January 1988 to March 2003,
the study had conducted to explore the entity
efficiency of share market efficiency and represent
the relationship between stock index and interest rate
for fifteen developed and developing countries.
According to (Galí and Gambetti, 2015), VAR is
being as tool to predict the response of stock prices to
monetary policy shocks. According to (Zhao, 2010),
likelihood ratio statistic is used as tool to observe the
cross-volatility effects between foreign exchange and
stock markets. According to (Kurihara, 2006), this
paper investigates the effect macroeconomic factors
of stock prices. According to (Rjoub, Tu¨rsoy and
Gu¨nsel, 2009), the six pre-specified macroeconomic
variables which are the term structure of interest rate,
unanticipated inflation, risk premium, exchange rate
and money supply had been analyzed in this study.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data
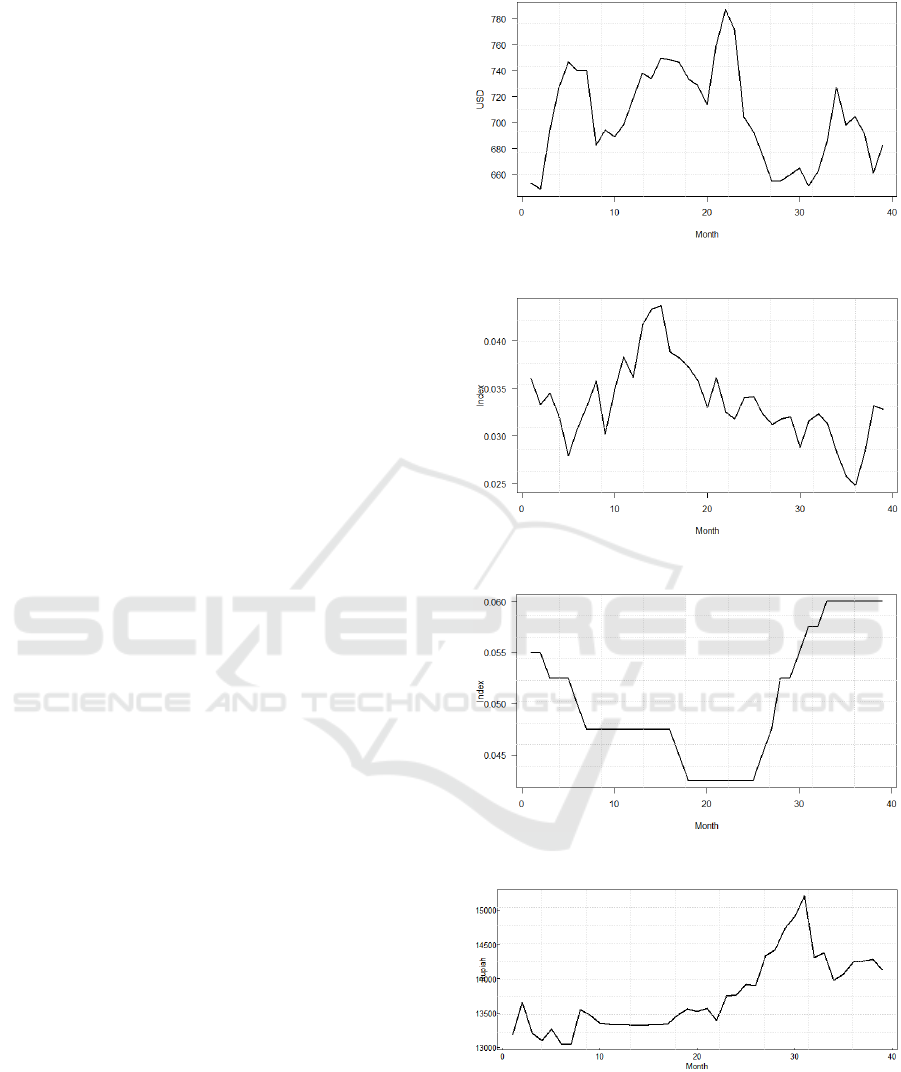
The observations data considered in this study is
contained of Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) as showed in
Figure 1, inflation as showed in Figure 2, BI rate as
showed in Figure 3, exchange rate IDR/USD as
showed in Figure 4, and Gross Domestic Product
(GDP) as showed in Figure 5. All of data are collected
during April, 2016 to June, 2019 (in total 39 monthly
observation data).
Figure 1: The Jakarta Islamic Index time series plot.
Figure 2: The inflation rate time series plot.
Figure 3: The BI rate time series plot.
Figure 4: The exchange rate IDR/USD time series plot.
7th AICIF 2019 - ASEAN Universities Conference on Islamic Finance
20
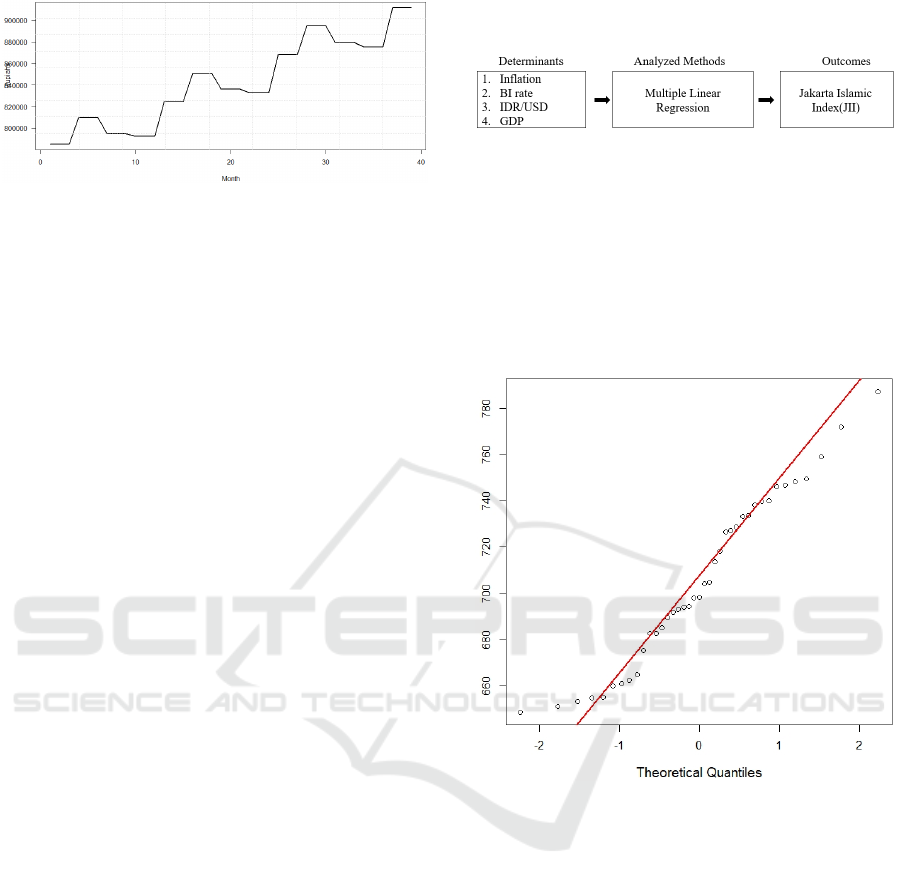
Figure 5: The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) time series
plot.
3.2 Method of Estimation Technique
There are various research hypotheses considered in
conditional relationship which is the effect between
single predictor with other factors. Such relations are
commonly evaluated as multiplicative interactions
and can be tested in both fixed- and random-effects
regression. The most common method for probing
interactions is to test simple slopes at specific levels
of the predictors for example multiple linear
regression.
The purpose of multiple regression is to construct
the relationship of the outcome with all of
determinants. The multiple regression equation is
constructed in equation (1) as follows
=
+
+
+⋯+
+
(1)
where,
is the outcome variable,
is the intercept,
,
,…,
are the regression coefficient in each
independent variable,
,
,…,
are independent variables
is error term.
After fitting the linear model, the normality
assumption of residuals is required for evaluating the
goodness of fit the model.
4 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The stepwise procedure of multiple linear regression
to analyze macroeconomics factor affecting Jakarta
Islamic Index (JII) is presented as:
1. Defining the dependent and independent
variables
The path diagram is represented in Figure 6
which show the outcome and determinants. The
outcome is Jakarta Islamic Index (JII) and and
multiple linear regression will be used to analyze
the correlation of all determinants with Jakarta
Islamic Index (JII).
Figure 6: The study path diagram.
2. Checking the normality distribution
Multiple linear regression has assumption that
the dependent variable satisfied the normality
distribution. Saphiro-Wilk normality test can be
a tool to check the normality distribution. Since
p-value 0.1577 > 0.05, it means that the
dependent variable fulfill the assumption of
multiple linear regression.
Figure 7: The Q-Q plot.
The Q-Q plot is being as a tool to check the normality
distribution by visual. And Figure 7 shows the Q-Q
plot, the dot group follow the red line so it indicate
that the dependent variable is acceptable in normally
distribution.
3. Building model
Multiple linear regression model of Jakarta
Islamic Index (JII) was identified using four
predictors where all were time series. The model
were able to estimate JII up to 57% with very
small p-value. Four time series data had vary
performances since three of four determinants
indicating high significances level precisely BI
rate, PDB and exchange rate. Exchange rate seem
negatively influenced JII more than others while
exchange rate increased then JII would decreased
where this effect was likely BI rate toward JII.
Contrary with PDB, it had positive impact to JII.
Analysis of Macroeconomics Factor Affecting Jakarta Islamic Index
21

Figure 8: The multiple linear regression results.
Based on model summary, the multiple linear
regression model well fitted to JII with three
significant predictors. Moreover, residual of
model was depicted in Figure 9, where residuals
fit to linear line depicted by Q-Q plot.
Figure 9: The model residuals plot.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATION
5.1 Conclusions
The aim of this study was to analyse the influence of
macroeconomics factor to Jakarta Islamic Index. The
multiple linear regression method is applied to
analyse the relation between independent variable
(inflation, BI rate, exchange rate IDR/USD, and
Gross Domestic Product) and dependent variable
which is Jakarta Islamic Index. The results explained
that the independent variables are all significant
except inflation. It means that BI rate, exchange rate
IDR/USD, and Gross Domestic Product has
possibility to give influence on Jakarta Islamic Index.
5.2 Recommendation
In this study, it may consider the independent
variables which are inflation, BI rate, exchange rate
IDR/USD, and Gross Domestic Product. It also can
be investigated to other macroeconomics factors, for
example economic growth (index of industrial
production), oil price, etc. Nowadays, there are
various statistical which can be as tool to analyze for
example Vector Auto Regression (VAR),
multivariate co-integration, Autoregressive
Distributed Lag (ARDL), etc.
REFERENCES
Alam, M. and Uddin, M. G. S. (2009) ‘Relationship
between Interest Rate and Stock Price : Empirical
Evidence from Developed and Developing Countries
Relationship between Interest Rate and Stock Price :
Empirical Evidence from Developed and Developing
Countries’, 4(3), pp. 43–51.
Galí, J. and Gambetti, L. (2015) ‘The Effects of Monetary
Policy † on Stock Market Bubbles: Some Evidence’,
7(1), pp. 233–257.
Huang, P. et al. (2008) ‘Macroeconomics based Grid
resource allocation’, 24, pp. 694–700. doi:
10.1016/j.future.2008.03.003.
Ibrahim, T. M. and Agbaje, O. M. (2018) ‘The Relationship
Between Stock Return and Inflation in Nigeria’,
(February 2013).
Kurihara, Y. (2006) ‘The Relationship between Exchange
Rate and Stock Prices during the Quantitative Easing
Policy in Japan’, 11(4).
Masrizal, Mustofa, M. U. Al and Herianingrum, S. (2019)
‘Macroeconomic Determinants of Jakarta Islamic
Index’, 2019(2016), pp. 510–524. doi: 10.18502/
kss.v3i13.4227.
Rjoub, H., Tu¨rsoy, T. and Gu¨nsel, N. (2009) ‘The effects
of macroeconomic factors on stock returns : Istanbul
Stock Market’. doi: 10.1108/10867370910946315.
Sakti, M. R. P. and Yousuf, M. (2013) ‘Relationship
between Islamic Stock Prices and Macroeconomic
Variables: Evidence from Jakarta Stock Exchange
Islamic Index’, 1(1), pp. 71–84.
Zhao, H. (2010) ‘Research in International Business and
Finance Dynamic relationship between exchange rate
and stock price : Evidence from China’, Research in
International Business and Finance. Elsevier B.V.,
24(2), pp. 103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.ribaf.2009.09.001.
7th AICIF 2019 - ASEAN Universities Conference on Islamic Finance
22
