
Translation Technique Analysis of the Root Word and Derivative of
Emotional Intelligence Term
Nur Hasyim, M. Nababan, Djatmika and Tri Wiratno
Pascasarjana UNS, Jalan Ir. Sutami, No. 36A, Jebres, Surakarta, Jawa Tengah, 57126
djatmika@uns.ac.id
Keyword: Term, Emotional, Intelligence, Translation, Technique.
Abstract: Problems related to lack of skill in translating must find solutions, by conducting research on the analysis of
translation techniques about the roots of words and derivatives about the terms about emotional intelligence,
from English to Indonesian in a case study on the translation book Working with Emotional Intelligent by
Daniel Goleman. Based on the results of a literature study, there were also no studies that have investigated
the term translation techniques that focus on root words and derivative forms. Then, research is carried out
with a qualitative research approach. The result is the word class of the term emotional intelligence generally
is a noun, adjective, and verb; translation technique is established equivalence, transposition, discursive
creation, both for root word and derivative.
1 INTRODUCTION
Translating a text from English into Indonesian
rightly is still a problem.(Nababan et al., 2012) As a
result, public knowledge about various things,
including the term knowledge of emotional
intelligence is limited. As an effort to overcome the
translation problems, it is necessary to research the
analysis of the term translation that focuses on
translating root words and derivative forms. The
research problem is significant to investigate because
these two things are the most basic form of a language
unit, so the translation techniques need to be known.
Understanding the methods of translating root words
and derivative forms is expected to be a skillful way
to bring other language units, such as translation of
phrases and clauses.
The root of the word in English is called root; root
is a morpheme in the core of a word that can be added
to the 'morpheme at the core of word to which affixes
are added', while invented words or derivative words
in English called derivative or derivation; derivatives
are formed from the results of affixation so as to
produce a word of impact or are formed from the
incorporation of words so as to produce compound
words or are formed from the repetition of
words/reduplication so as to produce repeated
words(Katamba, 2005).
The location of research on translation analysis
about the root words and derivative forms of technical
terms is in a book with the title Working with
Emotional Intelligent by Daniel Goleman(Goleman,
1998) and Kecerdasan Emosi untuk Mencapai
Puncak Prestasi (its translation book, by Alex Tri
Kantjono Widodo), and the technical term used as the
focus of the study is the term about emotional
intelligence
The focus of the research, which is also the focus
of the study in this article, is the technique of
translating root words and derivative forms against
the term emotional intelligence in a book entitled
Working with Emotional Intelligence.
The translation is a process of transferring
messages, the message transferred is written, and the
news is disclosed by the rules that apply in the target
language.
On the other side, translation techniques theory
can be used to translate the unit of language and
several translation techniques proposed by Molina
and Albir, as follows.(Khoirunnisa, 2015)
Adaptation is a translation technique that
replaces the cultural elements of the source text with
aspects of culture in the target. Amplification is a
translation technique that introduces in detail because
of the limited formulation of the source text.
Borrowing is a translation technique that takes words
or expressions that are appropriate to the source
10
Hasyim, N., Nababan, M., Djatmika, . and Wiratno, T.
Translation Technique Analysis of the Root Word and Derivative of Emotional Intelligence Term.
DOI: 10.5220/0009869600002905
In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar (ASAIS 2019), pages 10-13
ISBN: 978-989-758-468-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

language. Calce is a literal translation of foreign
words or phrases; conversion can be lexical
(according to the dictionary) or structural (paying
attention to structure). Compensation is a translation
technique in which the translator introduces elements
of information or the stylistic influence of text
(including language style) source language elsewhere
in the target language text. The description is a
translation technique that is applied by replacing a
term or expression with a description of its form and
function. Discursive creation is a translation
technique used to display unexpected temporary
equivalence ("to establish a temporary equivalence
that is unpredictable out of context"). The established
equivalent is a technique for using familiar terms or
expressions (based on dictionaries or daily use.
Generalization is to use more general or neutral terms
("to use a more general or neutral term").(Ardi, 2018)
Linguistic amplification is commonly applied in
consecutive interpretations or dubbing. Linguistic
compression is a translation technique that can be
used by translators in simultaneous translation or in
the conversion of film texts, by synthesizing
linguistic elements in the target language text ("to add
linguistic elements; this is often used in consecutive
interpreting a dubbing"). Literal translation (literal
translation) is a translation technique by means of
translators translating word for word expressions ("to
translate a word or expression word to word").
Modulation is a translation technique in which the
translator changes the point of view, focus, or
cognitive category about the source text; this change
of viewpoint can be lexical or structural ("to change
the point of view, focus, or cognitive category in
relation to the ST. Reduction: to suppress an ST
information item in the TT. Substitution (linguistic,
paralinguistic): to change linguistic elements for
paralinguistic elements (intonation, gestures) or vice
versa; transposition: to change a grammatical
category. Variation: to change linguistic or
paralinguistic elements (intonation, gestures) that
affect aspects of linguistic variation: changes of
textual tone, style, social dialect, geographical
dialect, etc.
Based on the results of the preliminary study of
the study, it has not been known that there has never
been a study investigating the translation techniques
of root word and derivation of the term emotional
intelligence. However, translation research was
found, which has investigated the translation
technique about technical terms other than the term
emotional intelligence, as follows.
Previous research on the translation of technical
terms has been carried out by researchers on the
translation of economic terms, about the translation
of the term financial management, about the
translation of research terms, about the translation of
machine technique terms, about the translation of
economic lexicon, about the translation specific
cultural terms, about the translation specific cultural
terms, and about the translation of terms on Quran.
Based on the eight studies, it is known that translation
techniques that are often used to translate technical
terms are established equivalent, borrowing,
transposition, addition, and reduction.
The results of the literature study also found that
there were studies that investigated the translation
model. The translation model of a sentence has
developed by doing (i) splitting/spelling complex
sentences), (ii) dropping and reordering/removing
certain words and rearranging them with certain
structures), or (iii) substitution/replacing certain
words with other relevant words . The translation
model of the cultural term has developed with
foreignization and domestication strategies .
Foreignization is a translation strategy using
translation techniques: repetition, orthographic
adaptation, translation or non-cultural translation
linguistics, extra-textual gloss, while domestication is
a translation strategy using synonymy, limited
universalization, absolute universalization,
naturalization, and compensation.
2 METHODOLOGY
This research is used; a qualitative research approach
is used. Namely, a research approach that is
descriptive, inductive, intuitive, and the instrument is
the researcher itself.
The data of this study is the technique of
translating the root words and derivative forms of the
terms of emotional intelligence in the sourcebook and
the translation book. Data was collected by (i) content
analysis, namely reading, observing, organizing,
interpreting, then retrieving data according to criteria,
(ii) focus group discussions (FGD). At the same time,
data analysis techniques were (i ) domain analysis, (ii)
taxonomic analysis, (iii) compound analysis, and (iv)
analysis of cultural themes .
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This study found that there were 761 terms of
emotional intelligence in the sourcebook, which were
then translated into the target book. The 761 data
Translation Technique Analysis of the Root Word and Derivative of Emotional Intelligence Term
11
conditions, 231 data (30%) in the form of root words
and 530 (70%) data in the form of derivatives. Thus,
it can be informed that the term emotional
intelligence is more in the way of a derivative form
than the root word.
From 231 data in the form of root words, the
distribution of word root types used to represent terms
of emotional intelligence: nouns 159 data (69%),
adjectives, and 51 data (22%), and verbs 21 data
(9%), while from 530 data in the form of derivatives,
it’s distribution: nouns 292 data (55%), adjectives,
and 158 data (30%), adverbial 41 (8%), and verb 39
data (7%). Based on the word class of the term
emotional intelligence, it can be seen that the terms
with the noun and adjective word classes are
dominant, both in the form of the root word and
derivative.
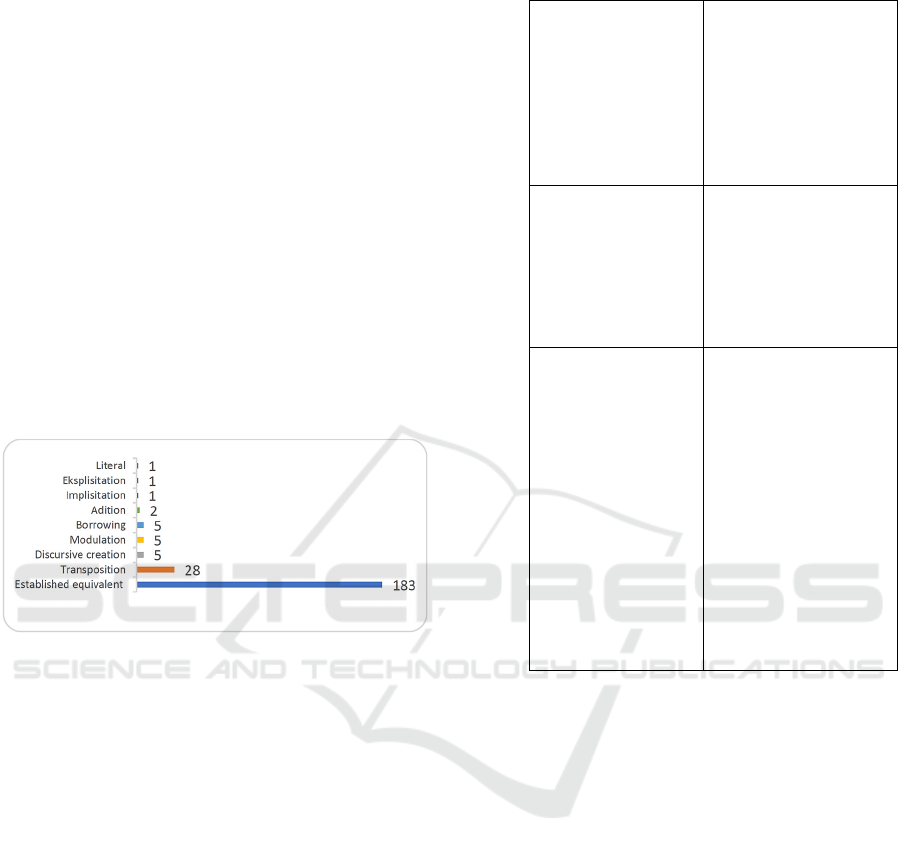
The following is a table of translation techniques
used to translate the term emotional intelligence in
the form of root words (Chart 1).
Chart: Types of Translation Techniques Used for
Translating The term Emotional Intelligence in the Form of
Word Root.
From Chart 1 and Chart 2, it is known that the
translation techniques that are widely used to translate
the term emotional intelligence are established
equivalent, transposition, discursive creation,
modulation, and borrowing.
Examples of using translation technique from
established equivalent (example 1), transposition
(example 2), and discursive creation (example 3) in
the translation of the term emotional intelligence in
the form of a root word, as follows.
Table 1.
1. In jobs like these,
where stress is
high and
frustrations
common, a rosy
outlook may get
better result.
Dalam pekerjaan-
pekerjaan seperti ini,
dengan tingkat stress
tinggi dan frustasi
dianggap lazim, sikap
ceria dapat
memberikan hasil
lebih baik.
2. Deep change
requires the
retooling of
ingrained habits of
thought, feeling,
and behavior
Perubahan yang
mendalam menuntut
perombakan yang
mengakar dalam hal
kebiasaan berpikir,
perasaan, dan
perilaku.
3. Interpersonal
ineptitude in
leaders lowers
everyone’s
performance: it
wastes time,
creates acrimony,
corrodes
motivation and
commitment,
builds hostility,
and apathy.
Ketidakmampuan
pemimpin menjalin
hubungan
antarpribadi bisa
membuat kinerja
semua orang rendah:
membuang-buang
waktu, menyulut
ketegangan,
mengikis motivasi,
serta komitmen,
membangun rasa
permusuhan dan
apatisme.
The term emotional intelligence, rosy (example 1)
is translated ceria (Indonesian); this is a translation
with established equivalence technique because most
people know that the translation of rossy is ceria.
The term thought (example 2) is translated
berpikir (Indonesian); this is a translation with
transposition technique because the translator
provides translation with the term that has different
word classes with the source language. In English,
though is a noun, while thinking is a verb.
The translation of apathy with apatisme in
Indonesian (example 3) is inappropriate translation
because, in Indonesian, there is an apati that is more
appropriate and accurate to be used as a translation of
apathy. The incorrect translation in that case by
Molina and Albir is called discursive creation.
Examples of using translation technique from
modulation (example 4) and borrowing (example 5),
in the translation of the term emotional intelligence in
the form of a derivative, as follows.
ASAIS 2019 - Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar
12

Table 2.
4. Spell out specifics
of the competence
and offer workable
plan to get there.
(D: 0661)
Uraikan kekhasan
suatu kecakapan dan
tawarkan rencana
yang tidak muluk-
muluk untuk
meraihnya.
5. This mimicry
involves a
biological
phenomenon
called entrainment,
a sort of intimate
emotional tango.
(D: 0335)
Reaksi peniruan
ini melibatkan
fenomena biologis
yang disebut
entrainment,
semacam esetalaan
derap emosi
The translation workable with yang tidak muluk-
muluk, in Indonesia (example 4) is an incorrect
translation. The translator might translate with a
different angle. That translation by Molina and Albid
is said modulation; that is a translation technique in
which the translator changes the point of view, focus,
or cognitive category in relation to the source text;
this change of viewpoint can be lexical or structural
("to change the point of view, focus, or cognitive
category in relation to the ST.
The translation entrainment with entrainment is
borrowing translation (example 5); that is a
translation technique that takes words or expressions
that are appropriate to the source language.
The results of this study inform that established
equivalence, transposition, discursive creation, both
for root word and derivative are the dominant
translation techniques used to translate the term
emotional intelligence almost the same as found in
the translation studies of terms conducted by
Handayani(Handayani, 2009), Sukaesih(Sukaesih,
2015), Hidayat,(Hidayat, 2018) and
Fachruddin(Fachrudin, 2017). In essence, the
translation of technical terms is appropriate when
used from one of several alternative translation
techniques.
That the results of this study strengthen previous
studies. This condition becomes interesting to be an
inspiration so that research can be conducted on the
term research model as research translation models
have been carried out by Mardiana(Mardiana, 2015).
4 CONCLUSION
This study informs that the translation techniques that
are widely used to translate the terms of emotional
intelligence are established equivalent, transposition,
discursive creation, modulation, and borrowing. The
tendency to use these translation techniques occurs
both in terms of emotional intelligence in the form of
root words and derivatives. Thus, the results of this
study open the opportunity to be able to do research
on other technical terms whether the terms root word
and derivative also have the tendency to use the same
translation techniques, such as the phenomenon in the
translation of the term emotional intelligence.
REFERENCES
Ardi, H. (2018). Model penerjemahan penanda strategi
kesantunan pada tindak tutur direktif dalam novel dari
bahasa inggris ke dalam bahasa indonesia. Universitas
Sebeals Maret.
Fachrudin. (2017). Analisis terjemahan istilah teknik dari
bahasa Inggris ke bahasa Indonesia: studi kasus buku
Fundamental of Engineering Thermodinamics
karangan Michael J. Moran. Universitas Sebelas
Maret.
Goleman, D. (1998). Working with emotional intelligence.
Bantam Books.
Handayani, A. (2009). Analisis ideologi penerjemahan dan
penilaian kualitas terjemahan istilah kedokteran dalam
buku ” lecture notes on clinical medicine ” ( Kajian
Terhadap Istilah Kedokteran Lecture Notes on Clinical
Medicine dan Istilah Kedokteran Lecture Note
Kedokteran Kl.
Hidayat, T. N. (2018). Translation Shift of a Transitivity
System in Obama and Trump’S Inauguration Speech.
LiNGUA: Jurnal Ilmu Bahasa Dan Sastra, 13(2), 91.
https://doi.org/10.18860/ling.v13i2.4990
Katamba, F. (2005). Should English be spelt as she is
spoke? In English Words: Structure, history, usage.
http://pasca.uns.ac.id/s3linguistik/wp-
content/uploads/sites/44/2016/10/Francis_Katamba_E
nglish_Words.pdf
Khoirunnisa, R. (2015). Kajian terjemahan istilah budaya
dalam novel “ The Bliss Bakery Trilogi # 1 ” ke dalam
ahasa Indonesia.
Mardiana, W. (2015). Teknik Transposisi Dan Modulasi:
Kesepadanan Dan Pergeseran Dalam Penerjemahan
Cerpen Berjudul “My Beloved Edith.” Parole: Journal
of Linguistics and Education, 4(2 Oct), 120–130.
https://doi.org/10.14710/parole.v4i2Oct.7889
Nababan, M., Nuraeni, A., & Sumardiono. (2012).
Pengembangan Model Penilaian Kualitas Terjemahan
(Mangatur Nababan, dkk. Kajian Linguistik Dan
Sastra, 24(1), 39–57.
Sukaesih, I. (2015). Analisis teknik dan kualitas terjemahan
istilah manajemen keuangan. UNS.
Translation Technique Analysis of the Root Word and Derivative of Emotional Intelligence Term
13
