
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly
Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision
with Public Accountability and Organization
Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on
Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
Nila Aprila, Fenny Marietza, Madani Hatta, and Ripi Martalia
Faculty of Economy and Business, University of Bengkulu, Bengkulu, Indonesia
Abstract. This research aims to examine the influence of legislative assembly
knowledge about budget towards APBD supervision with public accountability
and organization commitment moderating variables. The data collection uses
primary data obtained from questionnaire distribution to the respondents, who
are legislative assembly in Bengkulu Province. The totals of sample used in this
research are 45 respondents. The data collection technique is done by using
survey through questionnaire give to legislative assembly of Bengkulu Province
by cencus method. The analysis used is Statistical Package for the Social
Sciences (SPSS). The result of hyphotheses test showed that the legislative
assembly knowledge about budget has positive effect towards APBD
supervision, and legislative assembly knowledge about budget has positive effect
towards APBD supervision moderated by public accountability, while
organization commitment do not moderate relationship between legislative
assembly knowledge about budget and APBD supervision.
Keywords: Legislative assembly knowledge about budget · APBD supervision
Public accountability · Organization commitment
1 Introduction
In this era of reformation, it appears many complicated problems. These problems have
encompassed many aspects, from economics, social, cultures, politics, and security
defense. After the falling of new order in this reformation era, the agenda that becomes
government main highlight was the problem of eradicating the cases of corruption. This
problem was one of main causes of the falling of new order government. Even in
election, the agenda of eradicating corruption was an issue that becomes main topic and
becomes worth selling for candidates to attract the masses (Halim and Kusufi, 2012).
Law No. 17 of 2014 about People’s Consulative Assembly, House of
Representatives, Regional Representative Board, and Regional House of
Representatives mentioned that Regional House of Representatives have three
functions, they are legislation function, budget function and supervision function. This
is in line with Law article 96 paragraph 2 No. 23 of 2014 about local government that
is about budget and supervision function. Commonly, budget was a statement on the
Aprila, N., Marietza, F., Hatta, M. and Martalia, R.
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and Organization Commitment Moderating Variables:
Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0009870200002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 339-352
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
339

estimation of performance that will be achieved during certain period of time which is
stated in financial measurement. While budget in the public sector was a document
which describes financial condition of an organization which covers information about
income, expenditure, and activity (Mardiasmo, 2009).
Supervision refers to an action done by the party outside of executive (society and
Legislative Assembly) to join in supervising government performance. The function of
Legislative Assembly related to supervision in Law No. 23 of 2014 was the board
authority to implement the supervision towards implementation of local and other
regulations, implementation of the State Budget Revenue, supervising local
government performance and policy in implementing local development, and
international cooperation in the region. According to Wasistiono and Wiyoso (2009)
supervision was an activity implemented to achieve vision, mission, and organization
goals smoothly without any deviation or every effort and activity to know and assess
the real facts regarding the implementation of tasks and activities whether it is as
appropriate or not. The members of Legislative Assembly actively involve in arranging
local regulation (not only approving the draft prepared by government) and play an
important role in the process of regional budgeting.
There are some phenomena in Bengkulu Province. First, regarding to budget abuse
about package arrears of construction of public works roads worth of Rp 5.64 billion,
when it is followed up is worth of Rp 5.01 billion, so there is still some that did not
followed up yet worth of Rp 629.27 billion. The result of checking over the capital
expenditure realization of irrigation road and network showed that from 29 road work
packages which are tested in quotes, there are 27 road work packages were not
appropriate to specification set in contract worth of Rp 5.64 billion. This has an impact
on the equity of capital expenditures presentation of irrigation road and network which
are presented in Budget Realization Report (MROL News Agency Bengkulu, June 10
th
,
2016). Second, Priority of the Provisional Budget Ceiling was stopped because of slow
RAPBD-P legalization. Third, the corruption allegation of road construction budget in
Enggano Island in 2016 done by PT. Gamely Alam Sari. Loss of state estimated up to
Rp 7.1 billion was mentioned when plenary in Legislative Assembly of Bengkulu
Province (Harian Rakyat Bengkulu, Tuesday, June 13
th
, 2017). Fourth, on August 25
th
,
2016 Regional Government Budget (APBD) of Bengkulu Province worth of Rp 1.9
trillion substracted by Rp 197 billion by the Ministry of Finance. This withdrawing
funds are caused by budget stacking in regional cash that has not been spent
(Liputan6.com August 25
th
, 2016). In August 2017, the budget absorption was still
29.76 percent until the end of December 2017 the budget absorption increases up to
72.33 percent (Ministry of Home Affairs December 28
th
, 2017).
The cases which were occured also caused because of less board knowledge about
budget in doing supervision towards Regional Government Budget. Boards were not
only having enough knowledge about budget in supervising Regional Government
Budget, but Purnomo (2016) & Ramdhani (2014) stated that board’s knowledge also
moderated by public accountability and organization commitment. By the boards are
having knowledge about budget moderated by public accountability and organization
commitment, it can influence board’s performance in detecting abuse and violation of
budget which is occured during the implementation of Regional Government Budget.
Besides, it also helps a person in solving every problems occured as appropriate with
the position of the member of Legislative Assembly.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
340

This research refers to the research by Patiar et al (2014). The difference between
this research and the previous one is in the moderation variables, which are organization
commitment and public accountability, also, this research was done in Bengkulu
Province. The reasons of the researcher chooses those moderation variables were
because the interaction between board’s knowledge with organization commitment and
public accountability moderation variables are very important for the board to supervise
regional finance (APBD). Therefore, this research aimed to examine from those
moderation variables whether it has positive influence towards the interaction of
board’s knowledge in supervising regional finance (APBD). The reasons of this
research chooses the Secretariat Office of Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
was because there are some phenomena and problems occured in Bengkulu Province
as have been stated.
The purpose of this research was to demonstrate empirically that Legislative
Assembly knowledge about budget has influence towards APBD supervision. To
demonstrate that Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget has influence towards
APBD supervision moderated by public accountability. And to demonstrate that
Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget has influence towards APBD
supervision moderated by organization commitment.
2 Literature Review
There are any agency relation when one of the parties (principal) hires other parties
(agent) to do a service and, in doing it, by delegating authority to make decision for the
agent (Anthony and Govindarajan, 2005). Ikhsan and Ishak (2005), stated that this
theory is based on economic theory. The agency problems at least involve two parties,
the principal who has authority to do an action, and the agent who receives principal
and authority delegation. In the context of making policy by the legislative, the
legislature is a principal who delegates authority to the agent such as government or
committee at legislative to make a new policy. This agency relation occurs after the
agent make a policy proposal and ends after the proposal is accepted or rejected (Halim
and Abdullah, 2006).
According to Assagaf (2015), the board’s knowledge about budget can be
interpreted as board’s knowledge on the mechanism of arranging the budget starting
from planning stage until accountability stage also board’s knowledge about regulations
that organize the regional financial management/APBD. One of knowledges which is
needed in supervising the regional financial supervision is the knowledge about budget.
If the board’s knowledge about budget is good, it is expected that the board’s member
can detect an abuse and a waste or a failure in implementing the budget. The high
board’s experience and knowledge will be helpful for a person in solving a problem
that he faced which is appropriate with the position of Legislative Assembly as people’s
representative.
Halim and Kusufi (2007) defined that the regional financial supervision is APBD
supervision, mainly if seen from the main component, so that APBD supervision can
be defined as all activities to ensure that in collecting the regional income, and
expendituring the regional outcome can run as accordance with the plans, rules and
purposes that have been set. Basically, the main purpose of supervision is to compare
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and
Organization Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
341

between what must be occured and what is occured in order to achieve a certain
purpose.
Public accountability is an obligation of trust holders party (agent) to give
responsibility, present, report, and express all activities that become their
responsibilities to the trust givers party (principal) that have right and authority to ask
for the responsibilities (Mardiasmo, 2009). According to Arianti (2017) public
accountabililty is defined as public responsibility principles which mean that the
process of budgeting from planning, arranging and implementing must be truly reported
and be accounted to Legislative Assembly and society. Accountability requires that the
decision maker behaves consistent with the received mandate.
According to Lubis (2010) organization commitment is a level of how far an
employee takes side on a particular organization and the purposes, and intended to keep
his membership in that organization. Organizational commitment is often defined
individually and related to the involvement of the person on the involved organization.
Employee’s commitment to the organization is one of attitudes that reflect feeling of
like or not of the employee towards the organization he works.
The agency relations between executive and legislative parties also occure in the
process of regional budgeting. The process of budgeting involves two parties, they are
executive and legislative. One of knowledges needed to do APBD supervision is the
knowledge about budget. By knowing about budget, the board’s member is expected to
be able to detect any abuse and waste or failure in implementing the budget. The high
board’s experience and knowledge will be very helpful for a person to solve problems
that he faced as appropriate with the position of Legislative Assembly as people’s
representative.
Widiyahningsih and Pujirahayu (2012), Utami and Syofyan (2013), Ramdhani
(2014), Rosita (2014), Zainal et al (2015), and Purnomo (2016) proved that board’s
knowledge about budget towards board’s supervision on regional finance (APBD)
indicated significant influence. From the above explanation, it can be formulated the
following hyphotheses:
H1: Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget has Positive Influence
towards APBD Supervision
2.1 Public Accountability and Legislative Assembly Supervision on
APBD
In the public sector organization, certainly the local government, the agency
relationship appears between the local government as agent and Legislative Assembly
as principal and public/citizen acts as principal who gives authority to the Legislative
Assembly (agent) to supervise the performance of local government. Ramdhani (2014)
stated that accountability becomes a logical consequence of the existing of relationship
between the agent and the principal. Board as a legislative member has to know and
understand the accountability guidance of government agencies in order to be able to
run the function in supervising the stages of arranging until APBD accountability
report. The failure in applying the operational standard of accountability procedures
causes time wasting, fund sources and other souces wasting, deviation of authority, and
decreased public trust towards government agencies.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
342

Sudiarta et al (2014), Purnomo (2016), and Arianti (2017) have proven that interaction
between board’s knowledge about budget has influence towards supervision over
APBD moderated by public accountability. The same thing also found in the research
by Ramdhani (2014), which stated that board’s knowledge about budget with public
accountability moderating variable has positive influence towards Legislative
Assembly supervision on APBD. Therefore, besides the knowledge about budget which
influences supervision done by the boards, the public accountability is expected to
increase the function of supervising. Then, it can be formulated the following
hyphotheses:
H2: Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget has Positive Influence
towards APBD Supervision Moderated by Public Accountability
2.2 Organization Commitment and Legislative Assembly Supervision
on APBD
Board’s psychology can be reflected from organization commitment that is really done
by the board as people’s representative. The board’s organization commitment is very
important remembering that the board’s member commonly came from politics (party).
It may strengthen or weaken the relation between board’s knowledge about budget and
APBD supervision. In the board’s performance context in Legislative Assembly,
organization commitment in the era of reformation and democration nowadays is
needed to be owned (Ramdhani, 2014).
Purnomo (2016) has proven that interaction between board’s knowledge about
budget has influence towards supervision over APBD moderated by organization
commitment. The same result also found in Ramdhani (2014), who stated that board’s
knowledge about budget moderated by organization commitment variable has positive
influence towards board’s supervision on APBD. From the above explanation, it can be
formulated the following hyphotheses:
H3: Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget has Positive Influence
towards APBD Supervision Moderated by Organization Commitment
3 Research Method
3.1 Data and Sample of the Research
This research was kind of research using quantitative approach that gives priority of
research towards data and empirical fact by using primary data sources (questionnaire).
The population in this research is Legislative Assembly of Bengkulu Province. The
sample in this research is all members of population. The method of taking this sample
is using cencus method. The reason of selecting the sample is by consideration that all
board’s members are joining in evaluating accountability report from local government
and approve the budget submitted by local government also supervise the
implementation of APBD. Besides, it is intended to obtain research findings which are
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and
Organization Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
343

more valid and unusual, so all members of Legislative Assembly became the
respondents.
3.2 Research Variables, Operational Definition and Variables
Measurement
1. Board’s Knowledge about Budget
According to Law No. 23 of 2014 about local government explained, Regional
Government Budget (APBD) is local annual financial planning assigned with local
regulation. According to Corynata (2007) the indicator used in measuring budget
knowledge variable is the perception of board’s member about budget
(RAPBD/APBD), procedures of implementing APBD, has understanding about
arranging the APBD based on related regulation, and detecting and identifying towards
wasting, failure or budget leak. This questionnaire referred to Corynata (2007) and
Robinson (2006). Variable measurement is using Likert-scale, with the scale from 1-5,
which means 1=Extremely Disagree, Disagree, Less Agree, Agree, and Extremely
Agree.
2. APBD Supervision
APBD supervision in this research is a supervision done by board’s member starting
from arranging the budget, legalizing the budget, implementing the budget and budget
accountability. According to Government Regulation No. 16 of 2010 about the Guide
of Arranging Legislative Assembly Regulation, the indicator of supervising local
financial is Legislative Assembly supervision which is done from arranging, legalizing,
implementing until reporting through assessment towards Report of Accountability
Description (LKPJ) of local head and follow up if there is any misappropriation in
accordance with the law regulation and Legislative Assembly order. This variable is
measured by using questionnaire referred to Corynata (2007) and Robinson (2006) then
developed and adapted according to researcher needs. Variable measurement is using
Likert-scale, with the scale from 1-5 which means 1=Extremely Disagree, Disagree,
Less Agree, Agree, and Extremely Agree.
3. Public Accountability
Public accountability is an obligation of trust holder party to provide accountability,
present, report, and express all activities that become his responsibility to the trust giver
party who has right and authority to ask for the accountability (Mardiasmo, 2009). This
questionnaire referred to Corynata (2007) and Widiyahningsih & Pujirahayu (2012).
Variable measurement is using Likert-scale, with the scale from 1-5 which means
1=Extremely Disagree, Disagree, Less Agree, Agree, and Extremely Agree.
4. Organization Commitment
Organization commitment is the nature of relationship between an individual with the
work organization, where the individual has self confidence towards the values of work
organization goals and there is a willingness to use his effort seriously for the sake of
work organization and has the strength desires to still become a part of that work
organization (Paramita and Andriyani, 2010). Organization commitment is measured
by using an indicator developed by Wirawan (2014) who explained three components
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
344

of organization commitment, they are Affective Commitment, Continuous
Commitment, and Normative Commitment. This questionnaire referred to the
questionnaire by Paramita and Andriyani (2010) and Wirawan (2014), then developed
and adapted according to researcher needs. Variable measurement is using Likert-scale,
with the scale from 1-5 which means 1=Extremely Disagree, Disagree, Less Agree,
Agree, and Extremely Agree.
3.3 Analysis Method
Data analysis in this research was done using the assist of SPSS (Statistical Package for
Social Sciences) program version 16.0 for Windows. The analysis method done in this
research was statistical descriptive test, data qualidity test, and classical assumption
test.
3.4 Hyphotheses Test
The research hyphotheses is examined by using simple linear regression (single
regression) and interaction test or MRA (Moderated Regression Analysis). The test
towards hyphotheses 1 uses simple linear regression model that is examined on the
equation 1, hyphotheses 2 and 3 use MRA (Moderated Regression Analysis), with the
following equation models:
Y= α + β
1
x
1
+e........ (H1)
Y= α + β
1
x
1
+ β
2
x
2
+ β
3
x
1
x
2
+e....(H2)
Y= α + β
1
x
1
+ β
4
x
3
+ β
5
x
1
x
3
+ e....(H3)
Information:
Y = Regional Financial (APBD) Supervision
α = Constants
β1- β5 = Regression Coeffisient
X
1
= Board’s Knowledge about Budget
X
2
= Accountability
X
3
= Organization Commitment
X
1
X
2
= Interaction between the board’s knowledge about budget and public
accountability
X
1
X
3
= Interaction between the board’s knowledge about budget and organization
commitment
E = Error
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and
Organization Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
345

4 Research Finding and Discussion
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
Table 1. Descriptive Statistics.
Variables n Theoretical Range Actual Range Std.
Deviation
Min Max Mean Min Max Mean
APBD
Supervision
36 12 60 36 44 60 52.11 3.875
Budget
Knowled
g
e
36 6 30 18 22 30 25.89 2.227
Public
Accountabilit
y
36 6 30 18 20 30 26.14 2.295
Organization
Commitmen
t
36 9 45 27 27 40 33.19 3.454
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
4.2 Result of Data Quality
4.2.1 Result of Validity Test
Table 2. The Result of Data Validity Test.
No. Variables KMO Sig MSA
Values
Information
1 APBD Supervision 0.999 0.000 0.754 Vali
d
2 Bud
g
et Knowled
g
e 0.999 0.000 0.795 Vali
d
3 Public Accountabilit
y
0.999 0.001 0.649 Vali
d
4 Organization
Commitmen
t
0.998 0.004 0.642 Valid
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
4.2.2 Result of Reliability Test
Table 3. The Result of Data Reliability Test.
No Variables Cronbach Alpha
Values
Information
1 APBD Supervision 0.794 Reliable
2 Bud
g
et Knowled
g
e 0.824 Reliable
3 Public Accountabilit
y
0.761 Reliable
4 Or
g
anization Commitmen
t
0.756 Reliable
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
346

4.3 Result of Classical Assumption Test
4.3.1 Result of Normality Test
Table 4. The Result of Data Normality Test.
Variables Asymp Sig. (2-tailed) Information
Bud
g
et Knowled
g
e 0.400
N
ormal
Public Accountabilit
y
0.200
N
ormal
Or
g
anization Commitmen
t
0.588
N
ormal
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
4.3.2 Result of Multicolonierity Test
Table 5. The Result of Multicolonierity Test.
Variables Tolerance VIF Information
Budget Knowledge 1.000 1.000
Free
Multicolonierity
Public Accountability 0.738 1.250
PAAP Moderation 0.845 1.184
Organization Commitment 0.874 1.144
PAKO Moderation 0.874 1.145
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
4.3.3 Result of Heteroscedasticity Test
Table 6. The Result of Heteroscedasticity Test.
Variables Sig Information
Budget Knowledge 0.293 Free Heteroscedasticit
y
Public Accountability 0.808 Free Heteroscedasticit
y
PAAP Moderation 0.485 Free Heteroscedasticit
y
Organization Commitment 0.686 Free Heteroscedasticit
y
PAKO Moderation 0.131 Free Heteroscedasticit
y
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
4.4 Regression Test
4.4.1 F Significant Test
Table 7. The Result of F Test.
Model F Sig. Information
Equation 1 16.247 0.000 Si
g
nifican
t
Equation 2 6.867 0.001 Si
g
nifican
t
Equation 3 5.528 0.004 Si
g
nifican
t
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and
Organization Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
347
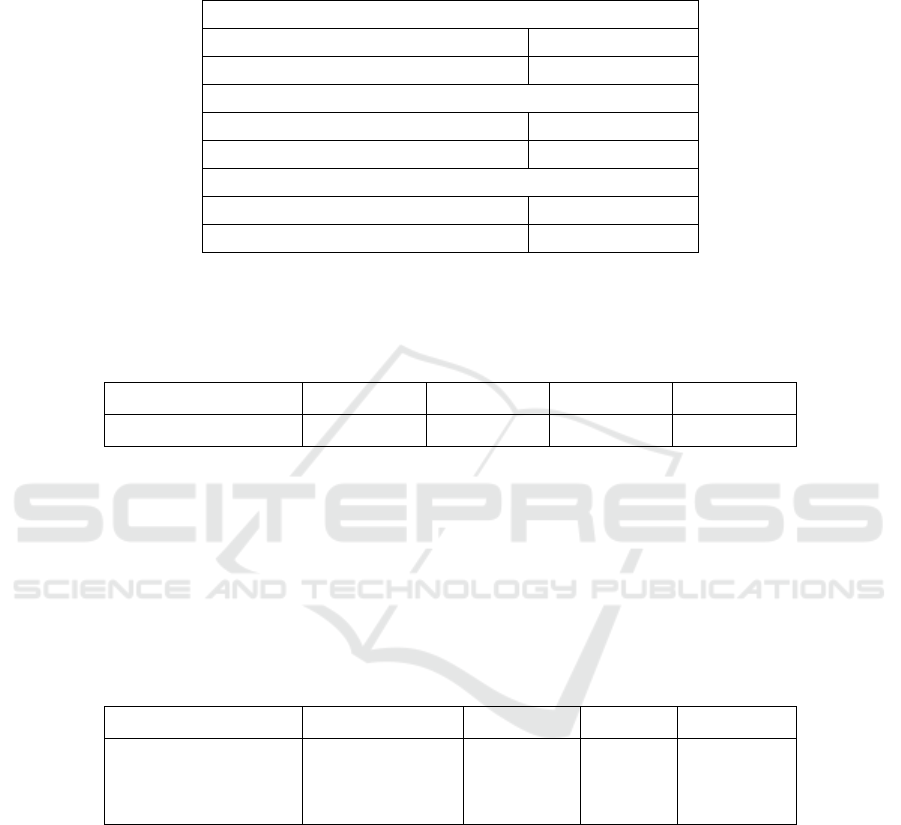
4.4.2 Determination Coefficient Test (R2)
Table 8. The Result of Determination Coefficient Test.
Regression of Equation 1
R Square 0.323
Adjusted R
2
0.303
Regression of Equation 2
R Square 0.433
Adjusted R
2
0.370
Regression of Equation 3
R Square 0.381
Adjusted R
2
0.312
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
4.4.3 Test of Hyphotheses 1
Table 9. The Result of Hyphotheses 1 Test.
Variable Coefficient t-count Sig. Result
Budget Knowledge 0.569 4.031 0.000 Accepted
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
The significant value was 0.000 < 0.05, so the first hyphotheses is accepted. It
means that the better Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget which is owned,
it will increase the role of Legislative Assembly in APBD supervision, or the higher
knowledge about budget owned by Legislative Assembly members, so the better the
role of Legislative Assembly in APBD supervision.
4.4.4 Test of Hyphotheses 2
Table 10. The Result of Hyphotheses 2 Test.
Variables Coefficient t-count Sig. Result
Budget Knowledge
Public Accountability
Moderation
0.206
0.538
0.329
1.273
3.188
2.087
0.214
0.004
0.046
Accepted
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
The result of regression from this second hyphotheses states that Legislative
Assembly knowledge about budget has positive influence towards APBD supervision
moderated by public accountability is accepted. The higher interaction of Legislative
Assembly knowledge about budget with the public accountability, so the local finance
supervision done by the board will be more increased.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
348

4.4.5 Test of Hyphotheses 3
Table 11. The Result of Hyphotheses 3 Test.
Variables Coefficient t-count Sig. Result
Budget Knowledge
Organization
Commitment
Moderation
0.414
0.360
-0.166
2.399
2.222
-0.717
0.024
0.035
0.480
Rejected
Source: Processed Primary Data, 2018
The result of regression from the third hyphotheses for organization commitment
stated that Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget has positive influence
towards APBD supervision moderated by organization commitment can not be
accepted (rejected) because organization commitment moderating variable that
influence interaction between budget knowledge with APBD supervision is not
significant, so it can be concluded that organization commitment variable is not a
moderating variable, which indicated that the third hyphotheses is rejected.
5 Conclusion
Based on the result of this research, it can be concluded that:
1. Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget has positive influence towards
APBD supervision. It indicates that the higher level of budget knowledge, so the
better APBD supervision done by Legislative Assembly.
2. Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget is proven that it has positive
influence towards APBD supervision moderated by public accountability. The
higher interaction between Legislative Assembly knowledge and public
accountability, so APBD supervision done by Legislative Assembly will be better
and increase.
3. Legislative Assembly knowledge about budget is not proven that it has positive
influence towards APBD supervision moderated by organization commitment. It
indicates that organization commitment variable is not a moderating variable
because it is not strengthen or weaken the relations between Legislative Assembly
knowledge about budget towards APBD supervision, because from the result of
absolute difference value test is not proven as moderating.
5.1 Suggestion
Based on the research finding, discussion and conclusion above, also consideration of
any limitation in this research, so it suggested for the further researcher to consider the
following things:
1. For the further research, it is expected to add independent variable or moderating
variable to know other variables which can influence and strengthen/weaken the
dependent variable, such as leadership style and political background.
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and
Organization Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
349

2. For the further research, it is expected to add or change questionnaire instrument
which is easier to be understood by respondents so that the variable can be measured
perfectly.
References
A.A, Zainal, Ahmad Sayudi., dan Sarwani. 2015. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang
Anggaran dan Partisipasi Masyarakat Terhadap Penyusunan APBD. JSAI: Vol.2, No.1,Hal
37-49.
Anthony, Robert N. dan Govindarajan Vijay. 2005. Management Control System. Buku 2.
Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Ariati, Elsi. 2017. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran Terhadap pengawasan
Keuangan Daerah (APBD) dengan Political Backround, Akuntabilitas Publik dan
Transparansi Kebijakan Publik Sebagai Variabel Pemoderasi. JOM Fekon. Vol.4 No 1,
Februari.
Assagaf, Abubakar. 2015. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Anggota DPRD Terhadap Pengawasan APBD
Dengan Partisipasi Masyarakat, dan Transparansi Kebijakan Publik Sebagai Variabel
Moderasi (Studi pada DPRD Kota Ternate dan DPRD Kota Tidore Kepulauan). Tesis
Program Pasca Sarjana Universitas Khairun Ternate. Dipublikasikan
Bastian, Indra. 2010. Akuntansi Sektor Publik-Suatu Pengantar. Edisi 3. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Coryanata, Isma. 2007. Akuntabilitas, Partisipasi Masyarakat, dan Transparansi Kebijakan
Publik sebagai pemoderating Hubungan pengetahuan Dewan tentang Anggaran dan
Pengawasan keuangan daerah (APBD). Simpsium Nasinal Akuntansi X. Makassar.
Ghozali, Imam. 2013. Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate Dengan Program SPSS, Edisi Keenam.
Jakarta: Universitas Diponegoro.
Halim, Abdul. 2007. Akuntansi Keuangan Daerah. Jakarta: Penerbit Salemba Empat.
Halim, Abdul & Muhammad Syam Kusufi. 2012. Akuntansi Sektor Publik. Jakarta: Penerbit
Salemba Empat.
Halim, Abdul & Muhammad Syam Kusufi. 2007. Seri Bunga Rampai Manajemen Keuangan
Daerah: Akuntansi dan Pengendalian Pengelolaan keuangan Daerah. Edisi Revisi
Yogyakarta:UPP STIM YKPN.
Halim, Abdul & syukriy Abdullah. 2006. Hubungan dan Masalah Keagenan di Pemerintahan
Daerah: Sebuah Peluang Penelitian Anggaran dan akuntansi. Jurnal Akuntansi Pemerintahan.
Vol 2, No 1, Hal: 53-64.
Harian Rakyat Bengkulu. 2016, 24 Oktober. Deal-Deal Ketok Palu APBD-P. Tersedia di
http://harianrakyatbengkulu.com/ver3/2016/10/24/deal-deal-ketok-palu-apbd-p/ (diakses
pada 24 Oktober 2016).
Harian Rakyat Bengkulu. 2016. Kejati Periksa Dua Pejabat Pemerintah Provinsi Sebagai Saksi
korupsi Jalan Pulau Enggano. Tersedia di http://harianrakyatbengkulu.com/ver3/2017/06/
13/kejati-periksa-dua-pejabat-pemprov-sebagai-saksi-korupsi-jalan-pulau-enggano/(diakses
pada 13 juni 2017).
Ikhsan, Arfan dan Ishak Muhammad. 2005. Akuntansi Keprilakuan. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Jensen, M.C, and Meckling W. 1976. Theory of the Firm : Manajerial Behavior, Agency Cost
and Ownership Structure. Journal of Financial Economics 3. Pp : 305-360.
Kementerian Dalam Negeri. 2017, 28 Desember. Jelang Akhir 2017, Serapan Anggaran Pemprov
Bengkulu 72,33 Persen. Tersedia di http://www.kemendagri.go.id/news/2017/12/28/jelang-
akhir-2017serapann anggaran-pemprov-bengkulu-7233-persen (Diakses pada 28 Desember
2017).
Kusumawati, Eny. 2014, Pengaruh Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran Terhadap
Pengawasan Keuangan Daerah (Studi Empiris Pada DPRD Provinsi Jawa Tengah Dan DPRD
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
350

Kabupaten Karanganyar).Seminar Nasional dan Call Of Paper, ISBN 978-602-70429-2-6
Juni.FEB UMS.
Liputan6.Com. 2016, 25 Agustus. Anggaran Bengkulu Dipotong Rp 197 Miliar. Tersedia di
http://regional.liputan6.com/read/2585820/anggaran-bengkulu-dipotong-rp-197-miliar
(diakses pada 25 Agustus 2016).
Lubis, Arfan Ikhsan. 2010. Akuntansi Keperilakuan. Jakarta: Penerbit Salemba Empat.
Mardiasmo. 2009. Akuntansi Sektor publik. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Andi.
Nordiawan, Deddy. 2009.Akuntansi Sektor Publik. Jakarta: Salemba empat.
Patiar., Sri Rustiyaningsih., dan Dwi Handayani. 2014. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Dewan tentang
Anggaran terhadap pengawasan Keuangan Daerah (APBD) dengan Variabel Moderating
Partisipasi Masyarakat dan Transparansi Kebijakan Publik. Jurnal Riset Manajemen dan
Akuntansi: Vol.02, No.01, Hal:14-24.
Pramita Devi Yulindan dan Lilik Andriyani. 2010. Determinasi Hubungan Pengetahuan Dewan
Tentang Anggaran dengan Pengawasan Dewan Pada Keuangan Daerah (APBD). SNA 13.
Purwokerto.
Purnomo, Debby. 2016. Determinasi Hubungan pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran dengan
Pengawasan Dewan Pada Keuangan daerah (APBD). JOM FEKON: Vol. 3. No. 1
Ramdhani, Dadan. 2014. Determinasi Hubungan pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran dengan
Pengawasan Dewan Pada Keuangan daerah. Jurnal Akuntansi.
Republik Indonesia. Undang-Undang Nomor 17 Tahun 2014 tentang Majelis Permusyawaratan
Rakyat, Dewan perwakilan Rakyat, Dewan Perwakilan Daerah, dan Dewan Perwakilan
Rakyat Daerah.
_______________. Undang-Undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 23 tahun 2014 tentang
Pemerintah Daerah.
_______________. Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 58 Tahun 2005 tentang Pengelolaan keuangan
Daerah.
_______________. Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 16 Tahun 2010 tentang Pedoman Penyusunan
Peraturan dewan perwakilan Rakyat Daerah tentang Tata Tertib Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat
Daerah.
Robins, Stephen P dan Jugde Timothy A. 2008. Prilaku Organisasi, Jilid 1, Edisi 12. Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
Robinson. 2006. Pengaruh Kualitas Anggaran Terhadap Efektifitas pengawasan Anggaran
:Pengetahuan Tentang Anggaran Sebagai Variabel Moderating (Studi Empiris Pada DPRD
Kabupaten Kota se-Provinsi Bengkulu). Tesis Program Pasca Sarjana Magister Sains
Akuntansi Universitas Diponegoro Semarang.
Rosita, Ni Made Ana., Nyoman Trisna H dan Ni Kadek Sinarwati. 2014. Pengaruh Latar
Belakang Anggota Dewan dan Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran Terhadap
Pengawasan Keuangan Daerah (APBD) Dengan Variabel Moderating Transparansi
Kebijakan Publik. E-Journal S1 Akuntansi Universitas Pendidikan Ganesha.
Sekaran, Uma. 2011. Metodologi Penelitian untuk bisnis, Edisi 4, Buku 1. Jakarta: Salemba
Empat.
Sugiyono. 2011. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan (Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R & D).
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sudiarta, Gede Dewa.,Ni Luh Gede Erni S, dan Edy Sujana. 2014. Analisis Pengaruh
Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran Terhadap Pengawasan Keuangan Daerah dengan
Akuntabilitas Publik, Partisipasi Masyarakat dan Transparansi Kebijakan Publik Sebagai
Variabel Moderating. e-journal S1 Akuntansi Universitas Pendidikan ganesha: Vol.2. No.1
Ulum, Ihyaul dan Ahmad Juanda. 2016. Metodologi Penelitian Akuntansi. Malang : Penerbit
Aditya Media Publishing.
Utami, Kurnia dan Efrizal Syofyan. 2013. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran
Terhadap Pengawasan Keuangan Daerah Dengan variabel Pemoderasi Partisipasi
Masyarakat dan Transparansi Kebijakan Publik. Jurnal WRA : Vol.1. No. 1
The Influence of Indonesian Legislative Assembly Knowledge about Budget towards APBD Supervision with Public Accountability and
Organization Commitment Moderating Variables: Empirical Study on Legislative Assembly in Bengkulu Province
351

Wasistiono, Sadu dan Yonatan Wiyoso. 2009. Meningkatkan Kinerja Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat
Daerah (DPRD). Bandung: Fokus Media
Widiyahningsih dan Pujirahayu. 2012. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Anggota Legislatif Daerah
Tentang Anggaran Terhadap Pengawasan Anggaran Pendapatan dan Belanja Daerah Dengan
Akuntabilitas Sebagai Variabel Moderating. Jurnal Akuntansi UPI. ISSN 2088-2106.
Wirawan. 2014. Kepemimpinan: Teori, Psikologi, Prilaku Organisasi, Aplikasi dan Penelitian.
Jakarta : Raja Grafindo Persada.
Wulandari, Trini dan Deviani. 2013. Pengaruh Pengetahuan Dewan Tentang Anggaran Terhadap
Pengawasan Keuangan Daerah Dengan variabel Pemoderasi Akuntabilitas Publik. Jurnal
WRA : Vol.1. No. 2.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
352
