
Application of Lateral Thinking Methods in Creative Process of
Gestalt Images as a Plagiarism Prevention Efforts
Tiyas Maheni D. K.
1
, Dwi Agnes Natalia Bangun
1
, Anggi Anggarini
1
1
Politeknik Negeri Jakarta, Jalan. Pr. Dr. G. A. Siwabessy, Depok, Indonesia
Department of Printing Technique and Publishing
Keywords: Plagiarism, Graphic Design, Lateral Thinking
Abstract: This article explains the application of lateral thinking methods in the graphic design process, especially in
the creative process of gestalt images by students of Graphic Design Study Program to prevent acts of
plagiarism. Time constraints, lack of ideas, and laziness are the three main factors causing plagiarism in the
gestalt design process, supported by the ease of internet access where gestalt image references can be obtained
from various sources. In an effort to prevent the occurrence of plagiarism due to the imitation of concepts,
shapes, compositions, and superficiality in modifying the elements of the image at the process stage of gestalt
design, students are provided with visual exploration exercises by applying lateral thinking methods. This
method is applied by making alternative images that use stylation, distortion, and deformation of objects.
Lateral thinking methods can reduce forms of plagiarism in the making process of gestalt images. Before the
application of lateral thinking methods, the number of plagiarism-indicated works amounted to 68%. After
applying the lateral thinking method, only 13% of the works indicated plagiarism and the remaining 87%
were not indicated as plagiarism. Through lateral thinking methods, students make visual alternatives in the
design sketching process. This exercise provides opportunities and space for students to create creative
concepts, forms, and new compositions so that plagiarism in gestalt tasks can be prevented.
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on the survey conducted by the Alumni
Reference Group (ARG) Team in 72 Universities in
Indonesia, it was stated that there were still many who
did not know and were aware of plagiarism so that
they often did not realize that they had committed
plagiarism. Besides, there is still wrong mindset and
misperception stated that the taking of ideas,
copyright and intellectual property rights is not a
problem or may be already prevalent (Mochtar,
2014).
Maheni (2017) found that forms of plagiarism
carried out by students in gestalt image making
process by imitating the concepts, shapes and image
composition, and superficiality in modifying image
elements. Based on this, it is necessary to make
strategic efforts in the learning process so that these
actions can be prevented as early as possible so that
acts of plagiarism can be avoided.
According to De Bono, the purpose of lateral
thinking is to view problems in different ways, to
rearrange patterns, and to generate alternatives.
Lateral thinking is related to the generation of new
ideas and is also related to the prison breakdown of
old concepts. Liberation from old ideas and
stimulation of new ideas is a twin aspect of lateral
thinking. Lateral thinking is very different from
vertical thinking that moves forward with sequential
steps. Lateral thinking opens alternative approaches
in each stage or process of thinking. Lateral thinking
is not a substitute for vertical thinking. Both are
needed and complementary. Lateral thinking is
generative, vertical thinking is selective (Kusumarini,
2004).
Lateral thinking ability has impact to the learning
achievement, which means that the better the lateral
thinking skills of students, the better the learning
achievement of the evaluation. There is a positive
learning ability towards learning achievement, which
means that the better the students' positive thinking
skills, the better their learning achievement
evaluation. This means that the lateral abilities and
positive thinking skills together influence on learning
performance evaluation, which means that the better
the lateral thinking skills and the ability to think
74
D. K., T., Bangun, D. and Anggar ini, A.
Application of Lateral Thinking Methods in Creative Process of Gestalt Images as a Plagiarism Prevention Efforts.
DOI: 10.5220/0009874800002905
In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar (ASAIS 2019), pages 74-77
ISBN: 978-989-758-468-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
positively of students together, the better the learning
achievement of the evaluation (Leonardt, 2015).
2 METHODOLOGY
The method used in this study is to use a descriptive
hypothetical approach, which uses qualitative
analysis efficiently as a supporter. This method is
used to determine the actions needed in making
gestalt works. The qualitative approach results will be
strengthened by quantitative (comparing the images
before and after applying the application of lateral
thinking methods and matched with the reference
images used). If the percentage numbers show that the
images produced are different from the reference
images is higher than the similar one, then the
application of lateral thinking methods is said to be
successful in reducing plagiarism.
This study uses a filling system technique, namely
by making data categories classification based on the
equation of visual concepts, changes in shape,
changes in composition and elements combinations
of gestalt images. After that the data is interpreted by
the researcher, combined with concepts or theories
that support understanding of the phenomenon under
study. From data collection, data is processed through
observation, recording, in accordance with
predetermined categories.
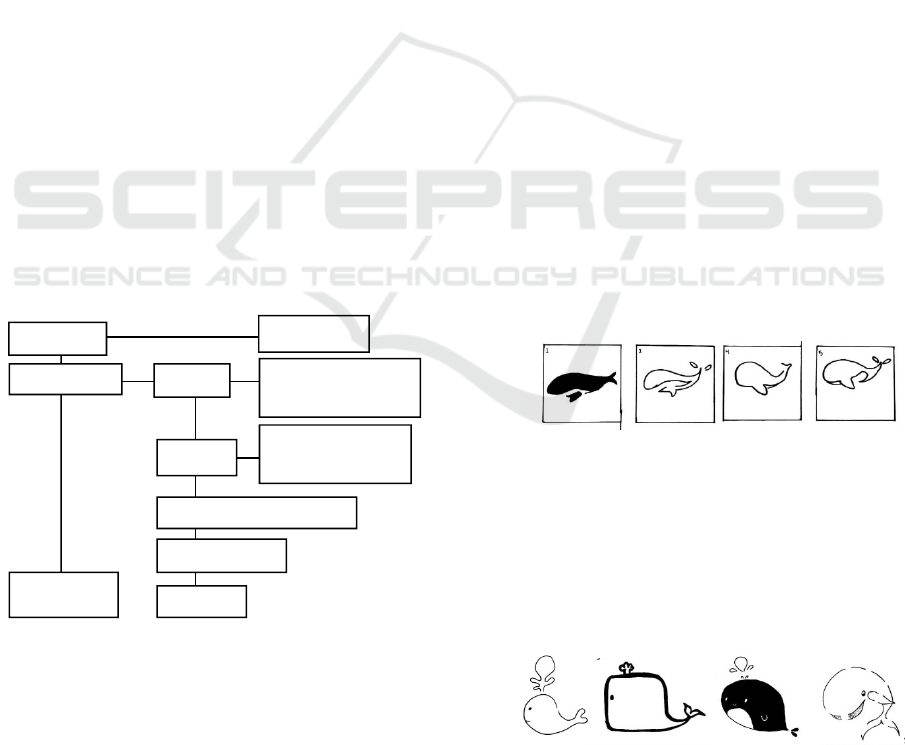
The research was carried out with the flow
chart as follows:
Figure 1. Research Flow Chart
In this study, 40 respondents were given specific
and detail brief about the gestalt task. The task was to
create a whale and giraffe using gestalt principle
closure and create an apple and tree using gestalt
principle (figure ground). The lecturer has determined
the image of the whale, giraffe, apple and tree as a
reference, which will be compared or matched with
the results of the images produced by the students.
a. Phase 1
In the first phase, respondents were given the task
of creating gestalt images by applying the
predetermined gestalt principles (closures and
figure grounds). In this stage, the construction of
gestalt images has not been directed towards
applying lateral thinking methods. The resulting
image is matched with the reference image to be
analyzed by looking at the equation of the concept,
shape, composition and modification of the
resulting image.
b. Phase 2
The lecturer gives guidance on the process of
making gestalt images by applying the lateral
thinking method, namely by making several
alternative images in gestalt image assignments.
This initial stage is carried out so that students get a
general overview of the assignment and how to
solve it. Alternative image creation can be
generated by using several technics, which are
stylation, distortion, and deformation, described as
follows:
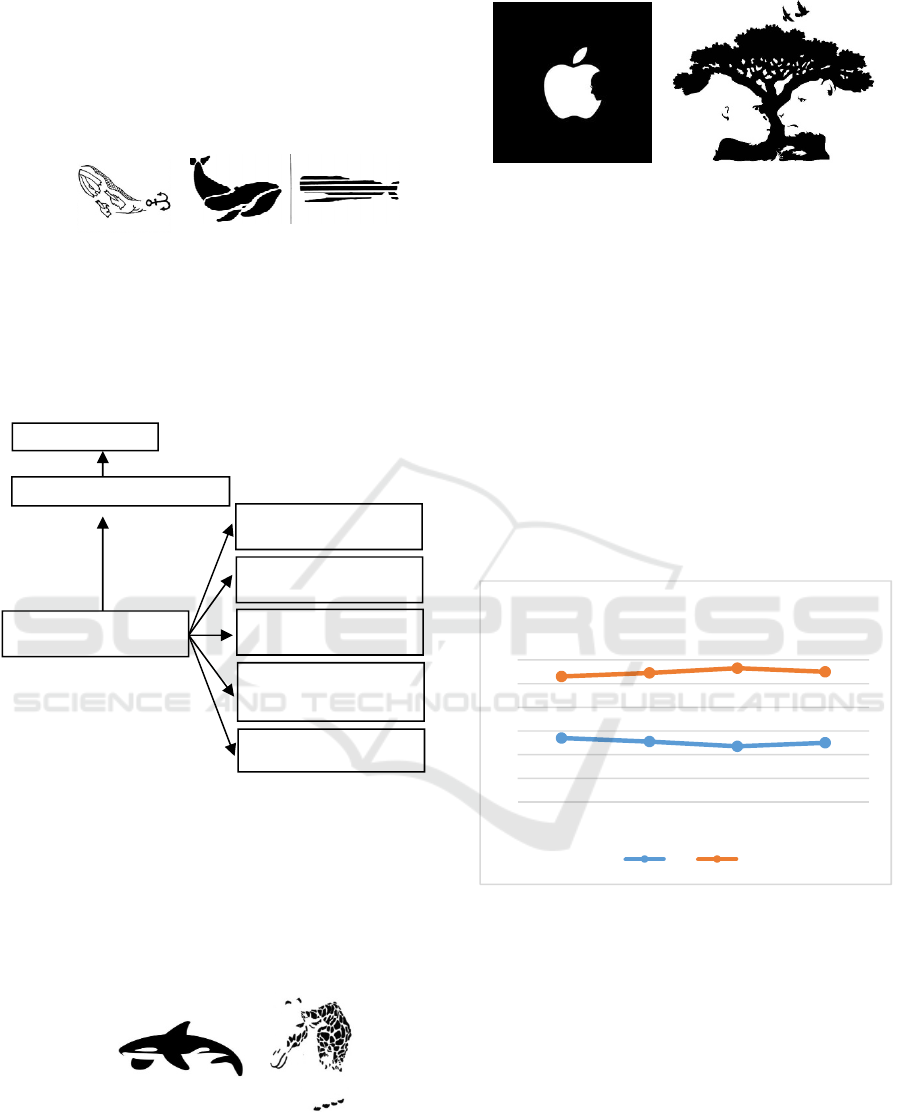
1. Stylation is simplifying or styling a form without
leaving its original form. In gestalt tasks,
stylation can be applied by simplifying the form,
becoming an iconic form that uses lines
(outlines), or reducing the details of the
anatomical structure of objects. The following is
the example of stylation drawing technic on
whale objects; The following is the example of
stylation drawing technic on whale objects;
Figure 2. Examples of picture using stylation technic
2. Distortion is distorting / exaggerating /
accentuating the shape of object. In gestalt tasks,
distortion can be applied by changing the shape
of the object of whales, giraffes, apples, and
trees so that the shape is no longer exactly the
same as the original shape, but objects can still
be identified. The following is the examples of
distortion drawing technic on whale objects;
Figure 3. Examples of picture using distortion technic
3. Deformation is rearanging the shape of the
object. In gestalt tasks, deformation can be
applied by rearranging the shape of objects of
Gestalt Image
Production by Using
Lateral Thinking Method
Implementation
Data and Information Analysis
Phase 2
Data Interpretation
Conclusion
Preliminary
Literature Study
Phase 1
Gestalt Image Production
Without Using Lateral
Thinking Method
Research Study
Report
Application of Lateral Thinking Methods in Creative Process of Gestalt Images as a Plagiarism Prevention Efforts
75
whales, giraffes, apples, and trees with other
forms, such as geometric shapes or abstract
shapes so that they eventually form objects of
whales, giraffes, apples, and trees. The
following is the examples of deformation
drawing technic on whale object ;
Figure 4. Examples of picture using deformation technic
In the sketching process, the lateral thinking methods
is applied by making 5 (five) alternative images for
each object and students are given the freedom to use
stylation, distortion, deformation, or a combination of
the three.
Figure 5. Lateral thinking method in gestalt images
making process
From several alternative images, one gestalt image is
selected and then be finalized. At the gestalt image
selection stage, there is a lecturer intervention on the
alternative image made by the respondent, which is
controlled through the assistance sheet.
Figure 6.Reference image of whale and giraffe using
closure principle of gestalt
Source : Google and Pinterest
Figure 7. Reference image of apple and tree using
figure ground principle of gestalt
Source : Google and Pinterest
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The application of lateral thinking methods as a
prevention strategy for plagiarism in the making of
gestalt images, is achieved by comparing the results
of gestalt images produced without applying lateral
thinking and those produced by applying lateral
thinking. The comparation between those phases is
whether the respondent has changed the concept,
changed the form, changed the composition and
modified the reference / reference image used.
The comparation result is as follows :
Figure 8. Comparison result of gestalt images without
applying lateral thinking
Based on the table above, data shows that the gestalt images
made by respondents without applying the literal thinking
method are still indicated by plagiarism (having similarities
with the reference image used) more than 60%. Only 33.8%
made changes to the concept, 31.9% made changes in form,
29.4% made changes in composition and 31.3% modified
the reference image.
While the results of the comparison of gestalt images
produced by respondents after applying lateral thinking
methods are as follows:
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
changeinvisual
consep
changeinshape Changesin
Composition
Modification
Comparisonresultofgestalt imageswithout
applyinglateralthinking
yes no
Gestalt Ima
g
es Alternative Selection
Gestalt Ima
g
e Final
Gestalt Image Production by
Using Lateral Thinking Method
Gestalt Image Alternative 1
(Stylation)
Gestalt Image Alternative 2
(Distortion)
Gestalt Image Alternative 3
(Deformation)
Gestalt Image Alternative 4
(Combination between drawing
technic)
Gestalt Image Alternative 5
(
etc
)
ASAIS 2019 - Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar
76
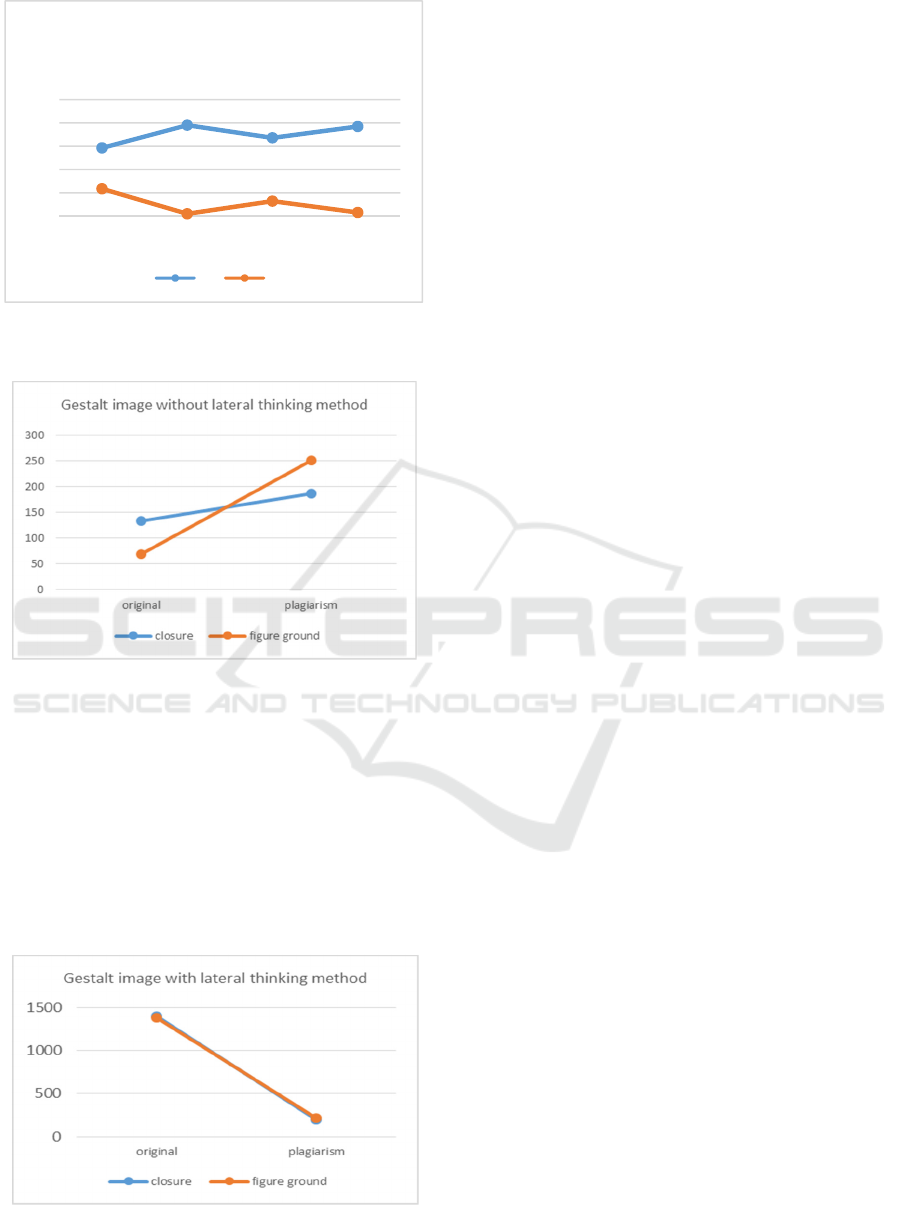
Figure 9. Comparison result of gestalt images alternatives
after applying lateral thinking methods
Figure 10. Result of gestalt images alternatives before
applying lateral thinking methods
Based on the table above, data shows that after applying the
lateral thinking method, there is a change in the results of
the drawing made by the respondent. The majority (more
than 70%) are not indicated as plagiarism. The resulting
image has a difference with the reference image. 70.6% of
the concept changes have been made, 97.5% of the images
have been deformed, 83.9% of the images have been
changed in composition and 96.1% of the images have
modified the reference image into a new or different image.
Figure 11. Result of gestalt images alternatives after
applying lateral thinking methods
Based on the table above, there is a significant
difference in the number of plagiarism-indicated
works between the gestalt images made without
applying lateral thinking methods and alternative
gestalt image results are made by applying lateral
thinking methods. On images that do not apply lateral
thinking methods, 68% of the images indicated
plagiarism. Whereas in the results of the drawings
made by applying the lateral thinking method, 13% of
the images indicated plagiarism thus the majority
(87%) of the work of the respondents did not commit
plagiarism.
4 CONCLUSION
The application of lateral thinking methods in making
gestalt images can or successfully reduce the number
of works indicated by plagiarism. The better the
lateral thinking abilities possessed by students, the
more original work can be produced in the making of
gestalt images. The lateral thinking method in making
gestalt images is applied by making alternative
images using stylation, distortion, deformation, or a
combination of the three.
REFERENCES
Kusumarini, Yusita, 2004, Berpikir Lateral Dalam
Prespektif Pembelajaran Desain, Jurnal Dimensi
Interior. Vol. 2. No.1 Juni 2004 : 80-96.
Leonardt. 2015, Peran Kemampuan Berpikir Lateral Dan
Positif Terhadap Prestasi Belajar Evaluasi Pendidikan,
Cakrawala pendidikan, Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan, on
line ISSN 2442- 8620
Maheni, Tiyas dkk, 2017, Plagiarisme dalam Pembuatan
Karya Gestalt oleh Mahasiswa Program Studi Desain
Grafis Jurusan Teknik Grafika dan Penerbitan
Politeknik Negeri Jakarta”
Mochtar, Marhum. 2014. Kasus Plagiarisme Dan Upaya
Penanganannya. Jikti. Bakti.or.id
0
200
400
600
800
1000
changeinvisual
consep
changeinshape Changesin
Composition
Modification
Comparisonresultofgestalt imagesalternatives
afterapplyinglateralthinkingmethods
yes no
Application of Lateral Thinking Methods in Creative Process of Gestalt Images as a Plagiarism Prevention Efforts
77
