
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge
Management Ecosystem
Christian Nawroth
1
, Felix Engel
1
and Matthias Hemmje
2
1
Lehrgebiet Multimedia- und Internetanwendungen, FernUniversit
¨
at in Hagen, Germany
2
Research Institute for Communciation and Cooperation, FTK, Dortmund, Germany
Keywords:
Emerging Named Entity Recognition, Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem, Natural Language
Processing, Machine Learning.
Abstract:
In this paper, we present a knowledge engineering project in the medical domain. The objective of the project
is to identify recent medical knowledge represented by emerging Named Entities. Hence, we introduce the
concept of emerging Named Entities and present our studies on their occurrence and use in medical document
corpora. We derive an approach for the emerging Named Entity Recognition utilizing textual and temporal
features through Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning and present detailed evaluation results.
Furthermore, we present a complementary system design that utilizes emerging Named Entity Recognition
support several KE use cases in the medical domain.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recommendation Rationalisation (RecomRatio
(of Bielefeld, 2017)), is a DFG funded research
project that aims to support expert health profes-
sionals during informed decision-making processes
(e.g., for or against a certain diagnosis/therapy)
through providing evidence that is based on textual
arguments found in the medical literature. Within
RecomRatio, we intend to make emerging Named
Entities (eNEs) (Nawroth et al., 2019) available
for Information Retrieval supporting medical ar-
gumentation, e.g., by recognizing and visualizing
them in IR dialogues related to Controlled Clinical
Trials (CCTs) literature. Another use case is the
utilization of eNEs as a ranking/filtering criterion
for retrieving arguments to provide the most recent
medical knowledge supporting argumentation in
informed medical diagnostic and treatment decisions.
To express an information need, medical expert users
usually apply a professional terminology, that is
quite often formalized in taxonomies or vocabularies
like Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
1
(Lipscomb,
2000). Query log analysis (Herskovic et al., 2007)
indicates that on PubMed
2
more than 50 percent
of the users’ queries contain terms that contain
1
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/
2
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed
Named Entities (NEs), which are represented by a
domain-specific vocabulary like MeSH. Therefore,
the medical domain is predestined for Entity Re-
trieval (ER) (Balog et al., 2011; Balog, 2017). In the
remainder of this paper, first, we introduce definitions
for the concepts emerging Entities leading to the
task of emerging Entity Recognition used in this
paper, followed by a state-of-the-art overview. We
derive use cases and design a system for recognizing
emerging knowledge in medical use cases and
explain feature-engineering and feature selection
for our approach. With relative temporal features,
we introduce and evaluate a new feature set for our
approach to increase its generalization. This paper’s
main contribution is a detailed quantitative evaluation
of our approach of combining textual and temporal
features. This evaluation also addresses challenges
posed by label imbalance in our real-world scenario.
2 DEFINITIONS
ER aims to fulfill medical users’ information needs on
domain-specific entities like, e.g., diagnostic methods
and results or treatment methods. However, ER in
medical domain contexts faces the major challenges
of Information Explosion (Huth, 1989) and Overload
(Bawden and Robinson, 2009). These effects are re-
Nawroth, C., Engel, F. and Hemmje, M.
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem.
DOI: 10.5220/0010061200290041
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2020) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 29-41
ISBN: 978-989-758-474-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
29

flected in the two medical document corpora that we
use for this work: PubMed MEDLINE Baseline 2020
3
(MEDLINE) and PubMed Open Access (PMC OA)
Subset
4
. While the first one generally only consists
of the title and abstract, the second one also contains
the full texts, so we decided to use both in parallel
for our project. Between 1970 and 2019, the number
of citations added to MEDLINE grew from 219.337
entries per year to 1.406.789, based on our corpus in-
dex statistic derived from our experimental corpora.
This essentially means that the yearly growth rate in-
creased by a factor of 6.4 within 50 years. Also, the
medical expert terminology and its use is changing
over time ((Nawroth et al., 2020)). To identify new
and emerging elements of terminology is a challeng-
ing task. Each of these new entries typically is a name
for a new medical entity. They could also represent
at least a new name for an existing entity. In gen-
eral, new entities that arise in a domain are known as
Emerging Entities (EEs): Hoffart et al. define EEs as
entities that have been out-of-knowledge-base before
(Hoffart et al., 2014). (Brambilla et al., 2017) define
EEs as entities that are not included in a knowledge
graph of a domain but are present in social media.
(Derczynski et al., 2018) define the task of EE recog-
nition in a generic setup and report a max. F
1
5
of 0.42.
Our initial approach for addressing EEs (Nawroth
et al., 2019) is different. It focuses on the textual
representation (the name/the label) and temporal rep-
resentation (the initial appearance and the acknowl-
edgment by the community) of an entity instead of
the knowledge object. Therefore, we refer to it as an
emerging Named Entity (eNE). In several preparatory
studies (Nawroth et al., 2020), we showed that eNEs
are used in medical document corpora before their ac-
knowledgment. Furthermore, the preparatory studies
revealed that eNEs represent more recent knowledge
compared to non-emerging NEs. Hence, emerging
Named Entity Recognition (eNER) aims to recognize
eNEs as early as possible in the document corpus and
make the represented emerging knowledge available
for medical Information Retrieval use cases. Based on
our statistical observations, we have developed a tem-
poral definition of eNEs that we initially introduced
in (Nawroth et al., 2018) and (Nawroth et al., 2019)
and that we are now refining here:
3
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/databases/download/
pubmed medline.html
4
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/tools/openftlist/
5
Precision, Recall and F
1
are commonly used to eval-
uate classification systems, using True Positives (TP),
False Positives (FP) and False Negatives (FN) (Manning
et al., 2008): Precision =
T P
T P+FP
,Recall =
T P
T P+FN
,F
1
=
2
Precision·Recall
Precision+Recall
Definition 1 (Emerging Named Entity (eNE)). A term
or a noun phrase that is in use in domain-specific lit-
erature since the time t
USE
and which is afterward ac-
knowledged at the time t
ACK
is defined as an emerging
Named Entity (eNE) for the time interval [t
USE
,t
ACK
].
After t
ACK
the eNE becomes an Named Entity (NE)
with the features t
USE
and t
ACK
.
Definition 2 (Emerging Named Entity Acknowledge-
ment through Vocabulary Acceptance (eNEAVA)).
An eNE is acknowledged as a NE through acknowl-
edgment for a common domain-specific vocabulary
by an expert community at the time t
ACK
. A single
domain expert also acknowledges an eNE through ac-
knowledgment for the expert’s own personal vocabu-
lary.
3 STATE OF THE ART AND
RELATED WORK
Based on the insights of the preparatory studies and
our motivation for this contribution, our state of the
art review covers selected publications from the fields
NER, IR, and ER. Furthermore, we illustrate ML ap-
proaches and related work from the field of emerging
topic detection and for using IR as a NER method.
Named Entity Recognition (NER) is a sub-task of
Natural Language Processing (NLP) (Nadeau and
Sekine, 2007). Traditional approaches are based on
local textual features (e.g. Part of Speech, charac-
ters) and use regular expressions (Nadeau and Sekine,
2007) or sequenced based learning models such as
Hidden Markov Model (HMM) (Zhou and Su, 2002)
or Conditional Random Fields CRF (Lafferty et al.,
2001; Andrew McCallum and Wei Li, 2003). More
recent NER approaches utilize Recurrent Neural Net-
works for language understanding tasks (Yao et al.,
2013). Recent Unsupervised methods as Bidirec-
tional Encoder Representations from Transformers
(BERT) (Devlin et al., 2019) for general tasks and
BioBERT (Lee et al., 2019) for medical language
tasks have led to impressive performance results. A
recent state-of-the-art NLP-library that utilizes some
of these techniques is SpaCy (Honnibal and Montani,
2017). The NER methods above use local textual
features and require an expert tagged training cor-
pus, large amounts of text, or use external knowl-
edge sources. In all these approaches, no appro-
priate training data for medical eNEs is available
at present. To the best of our knowledge, no such
training data exists in any other approach. In con-
trast, our approach uses existing temporal features
derived through semi-automatic retrieval from MED-
LINE. It works without explicit and manually expert
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
30

annotated training material. Instead, it uses training
material gained through community expert feedback
(eNEAVA). Combining IR and NER has been intro-
duced as Named Entity Retrieval, among others, by
Petcova and Croft (Petkova and Croft, 2007). They
propose an IR approach based on the proximity be-
tween the text of a document and the entities. Fur-
thermore, another common use case for NER in IR is
the task of entity linking and retrieval, which aims at
satisfying users’ information needs by providing ac-
tual entities instead of documents that mention them
(Meij et al., 2013; Balog et al., 2011; Balog, 2017).
To support ER, several approaches aim at detecting
NEs in queries, which are referred to as Named En-
tity Recognition in Query (NERQ) (Guo et al., 2009;
Du et al., 2010). In (Piccinno and Ferragina, 2014;
Cornolti et al., 2014; Cucerzan, 2014) multiple ap-
proaches for entity recognition and disambiguation
have been presented that utilize external knowledge
sources (e.g. Wikipedia, Freebase). In the medical
sector, the Mesh on Demand tool (Dan Cho, 2014)
represents a practical implementation of a system that
combines IR and NER for medical Entity Retrieval
use cases. Coming to the ML part of our approach, the
following methods provided by scikit-learn (G
´
eron,
2017) are compared for the task of eNER on temporal
features: AdaBoost (AB), Decision Tree (DT), Gradi-
ent Boosting Classifier (GBC), K Nearest Neighbour
(KNN), Naive Bayes (NB), Linear Support Vector
Machine (LSV), Multi-Layer Perceptron (Neural Net-
work, NN), Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA),
Random Forest (RF) and Stochastic Gradient De-
scent (SGD). As scikit-learn (G
´
eron, 2017) integrates
seamlessly with SpaCy, both are our frameworks of
choice for our initial prototypical work. A major chal-
lenge for several ML applications is class imbalance,
i.e., scenarios in which the distribution of the posi-
tive and negative classes is highly imbalanced (Ling
Charles X. et al., 2010). To handle challenges com-
ing from the class imbalance between eNEs and NEs,
we use the library imbalanced-learn (Lema
ˆ
ıtre et al.,
2017), which integrates with the other frameworks
as well. Imbalanced-learn provides amongst others
the following recent imbalance handling strategies,
SMOTE (Chawla et al., 2002), SMOTEEN (Batista
et al., 2004) and Random Under Sampling (RUS).
4 DISCUSSION AND APPROACH
Our approach follows (Chang and Manning, 2014),
who propose to complement statistical or learning-
based methods with rule-based approaches, especially
if there is no appropriate training data available. Our
work is related to the task of realtime Emerging Topic
Detection in Microblogs as presented by (Chen et al.,
2013), which also utilizes ML techniques on non-
textual features to detect emerging topics within mi-
croblogs. Our approach differs as it does not focus
on realtime detection but long-term eNEs in a scien-
tific text corpus, and therefore, it uses different non-
textual temporal features compared to (Chen et al.,
2013). Furthermore, our approach for eNER aims
at recognizing eNE in scientific corpora and hence
combines techniques from traditional NER and ML.
Compared to Chen et al.(Chen et al., 2013) we in-
vestigate more ML approaches. In their work, (Chen
et al., 2013) also address the topic of class imbalance,
which we investigate in this paper in more detail con-
cerning imbalance handling strategies. The max. re-
ported F
1
from Chen et al.(Chen et al., 2013) in a bal-
anced setup is 0.90. The definition of an emerging
topic by (Chen et al., 2013) is similar to our definition
of eNEs. In a recent work of Wang et al. (Wang et al.,
2019), apply hot topic detection to the field of aca-
demic big data, which they call Academic Hot Topic
Detection. Like our approach, they combine a textual
NER approach in the first stage with a feature learn-
ing approach. Their main features are a co-occurrence
graph and word embeddings amongst additional doc-
ument related features. In contrast, we focus on eNEs
in a solely temporal way, not yet analyzing whether
these topics are “hot”, which means setting a trend
of popular information need/interest. Similar to our
approach (Foley et al., 2018) propose to understand
NER as an IR/search task that addresses the challenge
of missing training material. They present a study,
how to transform textual features derived from CRF-
based NER and handcrafted rules into search queries.
In their approach, the search engine returns tokens in-
stead of documents that belong to a NE class, and they
collect users’ feedback on the result sets. In contrast,
in our approach, the search engine does not directly
return eNE candidates but provides temporal features
of the eNE candidate for further use in an eNER clas-
sifier. To implement this approach, we now give an
overview of our emerging Named Entity Recognition
Information Retrieval System (eNER-IRS) architec-
ture design that addresses the challenges outlined in
the previous sections.
5 SYSTEM DESIGN
To design the eNER-IRS, we will apply a user-
centered design approach (Norman and Draper,
1986). Therefore, we introduce the relevant use cases
first and derive an overview of the system’s general
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem
31
architecture.
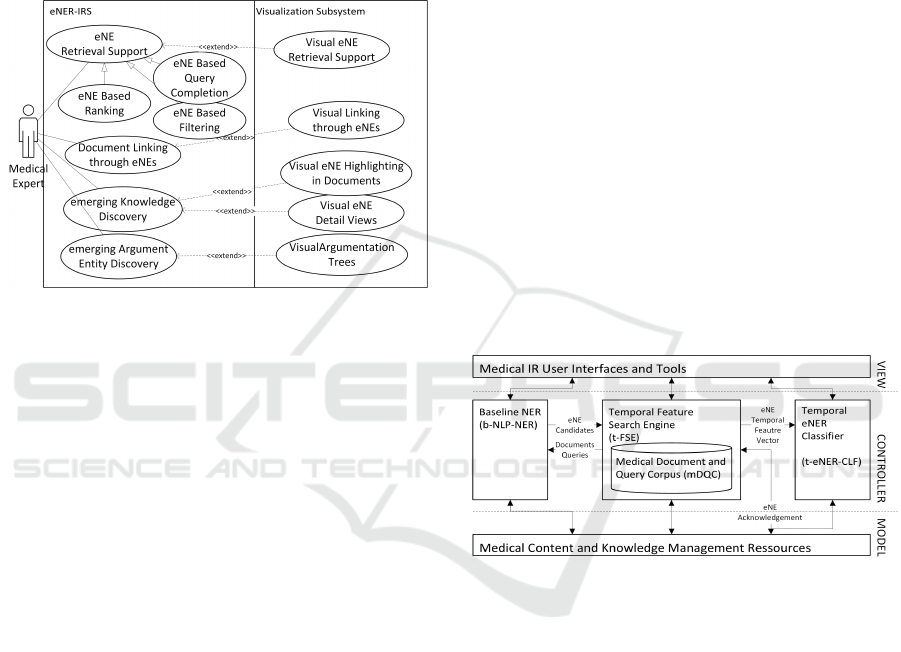
5.1 eNER-IRS Use Cases
The eNER-IRS is intended to support four differ-
ent information retrieval use cases. These are eNE
retrieval support, document linking through NEs,
emerging Knowledge Discovery, and emerging Argu-
ment Entity discovery as displayed in Figure 1. All
Figure 1: UML Use Case Model.
of these four use cases are supported by one or two
visualization use cases provided through the visual-
ization subsystem. In the following, we briefly in-
troduce the four general use cases. The first gen-
eral use case ENE Retrieval Support (see Figure 1),
aims at providing functionality that utilizes eNEs to
enhance and support several standard retrieval meth-
ods, like query completion, filtering, faceted search,
and boosting of ranking results depending on eNEs.
The associated visual use case is visual eNE Retrieval
Support. Within this visual use case, it is intended
to highlight eNEs during several steps of the user in-
teraction with the retrieval system. The second gen-
eral use case supported by one visual use case is
document-linking through eNEs. In this use case,
eNEs are utilized to provide a link between docu-
ments from different corpora. E.g., a user finds a clin-
ical trial in the ClinicalTrials (CT) Corpus that con-
tains eNEs that represent new medical knowledge in
the respective clinical trial. Then these eNEs can be
used to search for documents in another text corpus,
e.g., MEDLINE, to retrieve new and emerging knowl-
edge from that text corpus too. The associated visual-
ization is intended to provide an interactive graphical
representation of that use case, i.e., a network graph
showing links between documents from different cor-
pora based on eNEs. The third general use case is
emerging Knowledge Discovery. This use case has an
exploratory characteristic and allows the user to ex-
plore new knowledge on the document level and the
single emerging entity level. The associated visual
use cases provide views for both exploratory aspects,
which means visual highlighting of eNEs in selected
documents and providing detailed information on se-
lected eNEs based on the textual and temporal analy-
sis from the ML-eNER components of the eNER-IRS.
The fourth use case is emerging Argument Entity Dis-
covery. Based on emerging Argument Entities (e.g.,
from a survey article) in arguments’ premises or con-
clusions, the expert medical users can retrieve argu-
ments that cover the most recent medical knowledge.
Based on the emerging Argument Entities, an argu-
mentation tree is visualized. This use case and the
visualization is published in (Nawroth et al., 2020).
5.2 eNER-IRS System Architecture
Following the motivation and the four initial use
cases, our architectural modeling approach (see Fig-
ure 2) for recognizing eNEs in medical a document
and query corpus (mDQC) combines methods from
NLP, NER, IR, and ML (Nawroth et al., 2019). Our
approach follows the Model View Controller (MVC)
paradigm (Krasner et al., 1988). The focus of this
Figure 2: Conceptual System Architecture.
section is the conceptual design of the controller layer
that contains the core components of the eNER-IRS.
The overall design objective is to implement a three-
phased pipeline for eNER. As a first baseline step,
eNE candidates are automatically extracted from doc-
uments of the mDQC based on their textual features
using NLP-baseline NER methods (b-NLP-NER, see
Figure 2). The eNE candidates are then passed to a
temporal-feature search engine (t-FSE) that has in-
dexed the mDQC. The temporal IR-result set of the t-
FSE is then transformed into an eNE temporal-feature
result vector to obtain the temporal features for each
baseline eNE candidate in addition to the textual fea-
tures. The feature vector is then passed to a temporal
eNER classifier (t-eNER-CLF) model that needs to
be trained on temporal IR-feature vectors of already
acknowledged eNEs beforehand. The eNER t-eNER-
CLF provides a classification result, whether the eNE
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
32

candidate is likely an eNE or not. If the classifier out-
come is positive, the recognized eNE is passed to the
IR system users of the IR-supported argumentation
use case. Afterward, the users can finally acknowl-
edge the eNE as a NE for their vocabulary (eNEAVA)
or reject it. In both cases, users’ feedback is used to
update the ML training material for future learning.
Furthermore, in the case of acknowledgment, the term
or noun phrase is indexed as a NE for further utiliza-
tion for supporting the argumentation use case. The
temporal properties (i.e., t
USE
,t
ACK
) of it are prop-
erly recorded. For the integration of eNER-IRS with
the view and controller layers within the medical use
cases (e.g., medical argumentation), we use a REST-
Ful API to allow a lightweight and flexible interface
that may also be used in cross-organizational con-
texts (Kleppmann, 2017). Our conceptual architec-
tural modeling approach is based on an application of
machine learning and, thereby, data-driven. Hence for
our conceptual system modeling approach, besides
the use case and the conceptual architecture model-
ing also the underlying textual and temporal test and
training data resource play a significant role. There-
fore, we will introduce the resource design in the next
chapter.
6 DATA MODELLING
In this section, we introduce the relevant data model-
ing and analysis aspects leading to our machine learn-
ing feature modeling that will interact with the system
design. Furthermore, along with the test and training
data resource modeling, we introduce our evaluation
approach.
6.1 Test and Training Data Resources
The structure of the test and training data is derived
from our retrospective evaluation approach (see sec-
tion 8). We go back to the year 2012 and evaluate how
far our approach is capable of recognizing eNEs from
the perspective of 2012, which are acknowledged in
the meantime (2020). Furthermore, as a text cor-
pus, we use MEDLINE Baseline 2020
6
, and PMC
OA 2020, both with a limited year range from 1969
to 2012 to avoid temporal artifacts resulting from his-
torical documents. The limit in 2012 is necessary for
the evaluation from the 2012 perspective. The MED-
LINE corpus’s overall document count in that time
range is 19,139,708, and the SOLR index size is ap-
prox. 28.2 GB. For PMC OA, the count is 2.739.074,
6
https://mbr.nlm.nih.gov/
and the index size is 85.9 GB. This shows that the in-
dexed text per document is approx 21.28 times higher
for PMC OA compared to MEDLINE. For the task
of eNERD, we created smaller MEDLINE and PMC
OA subsets that follow the design of the CONLL 2003
corpus for NER evaluation (Sang, Erik F. Tjong Kim
and de Meulder, 2003) (due to performance scaling
reasons for the training and testing the b-NLP-NER
model). The size of the MEDLINE subset is 1.443
documents and for PMC OA, 2.154 documents. Each
of the subsets consists of training and test sets (ra-
tio 1:1). To prepare a gold-standard of the test and
training documents, we retrospectively automatically
tagged all eNEs (noun chunks) within the subsets us-
ing the MeSH 2020 vocabulary. All documents are
taken randomly from MEDLINE / PMC OA in 2012,
and each contains at least one eNE from the perspec-
tive of 2012. For our prototypical implementation, we
prefer MeSH over other (meta) thesauri like UMLS as
it provides a widely-used vocabulary that is domain-
specific for the medical domain. At the same time, it
is somehow generic to ensure that it represents topics
that are widely-used during medical discourse and re-
search. For the task of eNERQ, we randomly chose a
portion from the eNEs acknowledged between 2012
and 2020 from MeSH 2020 to create ML training
queries (the positive class ’eNE’). The remaining part
of the acknowledged eNEs are test queries that should
be correctly classified as eNEs through the t-eNER-
CLF and which we use for evaluation. They are un-
known to the t-eNER-CLF model during training. To
create training and test queries for the negative class
’non-eNE,’ we used randomly chosen arbitrary medi-
cal queries from a public log file of PUBMED (Mosa
and Yoo, 2013).
6.2 Absolute Temporal Feature Models
To identify, calculate, and select relevant temporal IR-
features that can be used for the t-eNER-CLF, we ap-
plied Feature Engineering (FE)(Zheng and Casari, )
and Feature Selection (G
´
eron, 2017) methods. As in-
troduced above for eNERD and eNERQ, candidates
for eNEs are passed to t-FSE as a query q. The search
engine returns a result set of the length n. For each
document in the result set returned for q, the publi-
cation year (DOC YEAR) is used as a temporal fea-
ture. This leads to an initial result vector ~r
q
for each
query q. First of all, we identified six relevant tempo-
ral IR-features that are calculated from ~r
q
: the number
of documents (n) per result vector, minimum, max-
imum, mean, and median of DOC Y EAR per result
vector, and the DOC Y EAR
0
, which is the year of
the first ranked document of the result set. Through
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem
33

Figure 3: Feature Correlation.
the last-mentioned feature (besides the temporal and
corpus features), we also utilize ranking information
(i.e., the year of the first ranked document) from the
underlying IR algorithm. In this way, FE leads to the
following feature vector
~
f
q
for a result vector ~r
q
:
~r
q
=
DOC Y EAR
0
.
.
.
DOC Y EAR
n−1
FE
−−→
~
f
q
=
max(~r
q
)
min(~r
q
)
mean(~r
q
)
median(~r
q
)
n
DOC Y EAR
0
(1)
For feature selection we use a correlation matrix
(e.g., see Figure 3), based on Pearsons Correlation
Coefficient
7
ρ. The correlation matrix displays the
correlation of the calculated features f
i
and the clas-
sification outcome (class), which may be an eNE
or non-eNE. Figure 3 displays that for the eNERQ
task, there is a medium negative correlation from fea-
tures COU NT with the class labels of the queries for
both subtasks and corpora. On the other hand, for
the feature min, the correlation is with exception to
NERQ and MEDLINE medium positive (approx 0.27
- 0.37). For NERQ on MEDLINE, there are no fea-
tures prominent positive features visible. However,
we decided to use the same features for both tasks
and corpora to ensure comparability between the sub-
tasks eNERD and eNERQ. As we will show in the
evaluation section, absolute temporal features lead
to the best classification results in our experiments.
However, they lack generalization as they have to be
retrained each year to be up to date regarding absolute
years. Furthermore, they require extensive user ac-
knowledgment to provide sufficient training data. So,
a challenge is bootstrapping an empty eNER model
with them.
7
https://libguides.library.kent.edu/SPSS/PearsonCorr
6.3 Relative Temporal Feature Models
In addition to the feature set above, we developed an
alternative feature set that uses relative temporal fea-
tures instead of absolute features. This feature set can
be automatically constructed completely from already
known emerging Named Entities from the past. As
they use relevant temporal features calculated in past
years, we argue that these features generalize better
and are suitable for bootstrapping new eNER models.
To implement relative temporal features, we introduce
the PIV OT Y EAR. In training, the PIV OT Y EAR is
a year in the past that is within the training year range
(e.g., last ten years). For each PIVOT Y EAR during
training, eNEs / NEs are identified, and for each, a
relative feature vector ~r
qr
is calculated as follows:
~r
qr
=
PIVOT Y EAR − DOC Y EAR
0
.
.
.
PIVOT Y EAR − DOC Y EAR
n−1
(2)
On ~r
qr
, the same feature engineering is applied as
introduced for the absolute features. In the following
section, we introduce an exemplary proof-of-concept
implementation of our approach to combine the con-
ceptual architecture and the data model in a real-world
scenario.
7 PROOF-OF-CONCEPT
The focus of this section is on the prototypical proof-
of-concept implementation controller layer, which
comprises the core components of our project, which
are the t-eNER-CLF pipeline, b-NLP-NER, and t-
FSE. Furthermore, we explain the implementation of
the model and view layers through a knowledge man-
agement ecosystem.
7.1 Temporal eNER Classification
Pipeline (Controller Layer)
The t-eNER-CLF component is prototypically imple-
mented through a scikit-learn (G
´
eron, 2017) pipeline
(see Figure 4). This initial proof-of-concept pipeline
implementation consists of one of the scikit-learn
Standard Scaler (G
´
eron, 2017). The scaler is followed
by the imbalance handling method, which is SMOTE,
RS, or SMOTEEN. This way, we consider each gen-
eral imbalance handling strategy, namely oversam-
pling, undersampling, and a combination of both. The
final step is one of the following classifiers, as intro-
duced in section 3: AB, DT, GBC, LSV, KERAS-
MLP, QDA, RF, or SGD. The choice of these ML
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
34
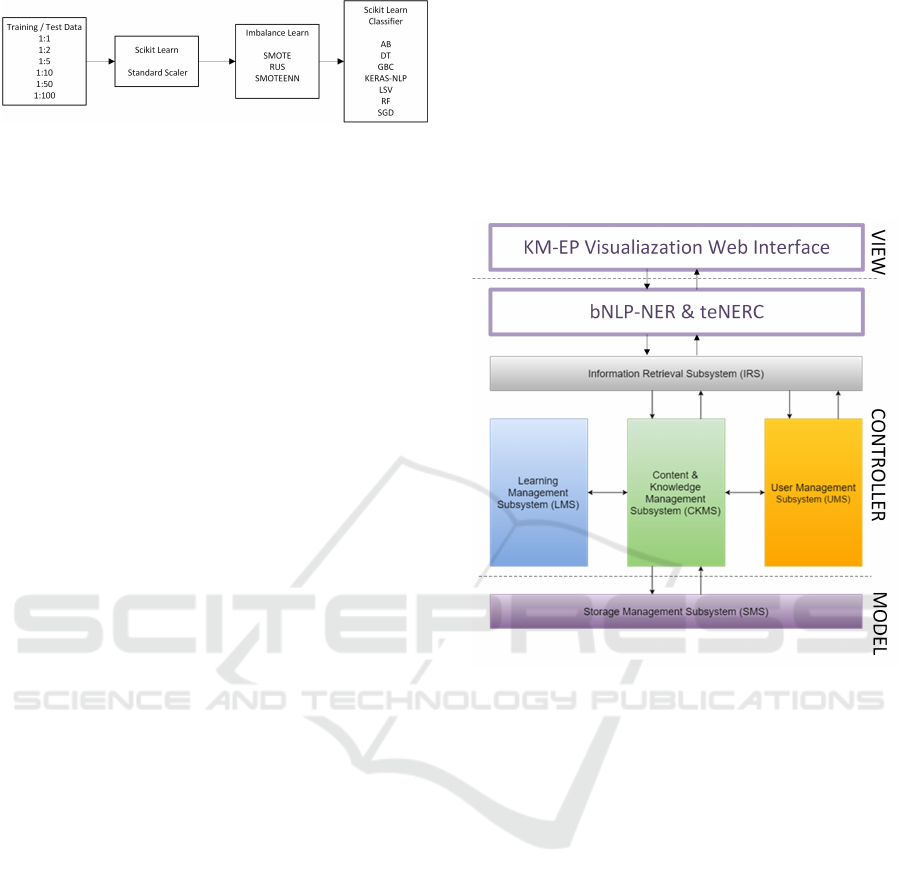
Figure 4: scikit-learn (G
´
eron, 2017) t-eNER-CLF Pipeline.
techniques is based on the insight that machine learn-
ing strategies often have to be investigated empirically
(Chollet, 2018). So, the choice comprises different
ML models that have proven to be sufficient for sev-
eral ML problems (G
´
eron, 2017) and that utilize dif-
ferent basic ML approaches (e.g., Vector Machines,
Trees, Neural Networks). To investigate class im-
balance between eNE and non-eNE, the training and
test input data is split in the following ratios between
eNE and non-eNE class: 1:1, 1:2, 1:5, 1:10, 1:50,
and 1:100. For the evaluation, we tested all possible
pipeline combinations and ratios.
7.2 Baseline NLP NER (Controller
Layer)
For b-NLP-NER, as a technical baseline for the tex-
tual recognition of eNEs and as a benchmark for our
approach, we implement two b-NLP-NER models
based on SpaCy that use only textual features. First
of all, we implemented an (initially naive) rule-based
system for b-NLP-NER that utilizes regular expres-
sions for the task of eNERD. The main textual fea-
tures for the rule-based approach are noun chunks
provided through SpaCy’s Dependency parser. For
the task eNERD, we applied our rule-based approach
to the evaluation subset documents as introduced
above. As shown by (Guo et al., 2009), traditional
NER approaches on textual features fail for the use
in queries. Therefore, we do not consider the rule-
based or training based textual approach for the task
of eNERQ. In addition to the rule-based approach for
eNERD, we trained two own SpaCy models, each one
for MEDLINE and PMC OA. The model for eNERD
was trained on the training subset and evaluated on
the test split of the respective subsets as introduced
above.
7.3 Temporal Feature Search Engine
(Controller Layer)
The t-FSE is implemented through SOLR with a stan-
dard configuration that indexed the MEDLINE 2020
Baseline and PMC OA 2020 corpora in two distinct
indexes as introduced above.
7.4 Knowledge-Management Ecosystem
Portal (View and Model Layer)
In our contribution to the RecomRatio project
the MVC layers are already implemented through
an existing knowledge-management ecosystem, the
Knowledge-Management Ecosystem Portal (KM-EP)
(Vu and Hemmje, 2019). Therefore, the RecomRa-
Figure 5: eNER-IRS integration with KM-EP adapted from
(Vu and Hemmje, 2019).
tio KM-EP has been developed to provide powerful
web-based tools for managing knowledge resources
and content. The underlying KM-EP technology con-
sists of five subsystems as displayed in Figure 5 and
explained in (Vu and Hemmje, 2019) as follows:
• “Information Retrieval Subsystem (IRS) indexes
contents and lets the user search for them in a
quick manner.”
• “Learning Management Subsystem (LMS) helps,
e.g., a course creator, who is not an expert of
the KM-EP and the underlying Learning Man-
agement System - Moodle, to create and manage
courses.”
• “Content and Knowledge Management Subsys-
tem (CKMS) manages contents and knowledge
resources. It allows users to create, edit, remove,
and rate different types of contents in the ecosys-
tem.”
• “User Management Subsystem (UMS) manages
users, groups of users, authentication, and access
control for all subsystems.”
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem
35

Table 1: Baseline NER Performance.
Task NER Method Rec. Prec. F1
MEDLINE Spacy Training Model 0.50 0.04 0.07
MEDLINE Spacy Rule Based Model 1.00 0.02 0.04
PMC OA Spacy Training Model 0.55 0.03 0.06
PMC OA Spacy Rule Based Model 1.00 0.02 0.04
• “Storage Management Subsystem (SMS) pre-
serves the integrity of the digital file and its meta-
data for the lifetime of an asset.”
While the medical RecomRatio IR use cases pro-
vided by the RecomRatio KM-EP, the eNER-IRS in
the controller layer is a new and additional func-
tionality. As the eNER-IRS service is implemented
through a python server, it is provided through a rest-
ful API to the other controller layer components of
KM-EP. A more detailed description of this imple-
mentation will be detailed in another publication due
to page space limitation. Besides the components in-
troduced above, KM-EP contains an advanced visual
Web-interface that implements the view layer in the
MVC and provides the visual use cases. This section
has explained how a prototypical proof-of-concept
implementation and an integration into the RecomRa-
tio KM-EP looks like. From the proof-of-concept im-
plementation based on the conceptual design and the
data modeling in the following section, we will eval-
uate the b-NLP-NER and t-eNER-CLF components
that are the core components of our work.
8 EVALUATION
To evaluate the outcome of our eNER approach, we
use the standard measure F
1
on the class ’eNE’ for the
b-NLP-NER and the t-eNER-CLF. Due to its weak-
nesses with imbalanced datasets, we do not use ac-
curacy for evaluation. We evaluate the performance
of the b-NLP-NER, followed by a detailed evalua-
tion of t-eNER-CLF concerning balanced and imbal-
anced class ratios and evaluation of imbalance han-
dling strategies.
8.1 Baseline NLP NER Evaluation
The first evaluation phase addresses the b-NLP-NER
outcome for the eNERD sub task. Table 1 displays the
results for both corpora, MEDLINE and PMC OA.
For both corpora, it becomes clear that the training-
based approach delivers a medium recall (approx.
0.5) while maintaining a low precision leading to a
low F
1
in both corpora. In contrast, the rule-based ap-
proach is based on an (initially) naive rule set, which
explicitly aims at a high recall of 1.00 to identify all
relevant eNE candidates for further processing in the
t-eNER-CLF. So the low F
1
of 0.04 for both corpora
resulting from a low precision of only 0.02 at this
point is not surprising. The rule-based approach’s
outcome reveals that the “real world” ratio in the 2012
document selections between noun chunks contain-
ing eNEs and non-eNE noun chunks is 1:50. Due
to the limitations of textual NER approaches (Guo
et al., 2009) for NERQ, we resign from applying tex-
tual NER on queries. Hence we do not calculate a
b-NLP-NER baseline for the subtask of eNERQ.
8.2 Temporal eNER Classification
Evaluation (balanced class labels)
In the second evaluation phase, we evaluate the out-
come of the t-eNER-CLF. To avoid overfitting, for
evaluation of t-eNER-CLF, we apply stratified five-
fold cross-validation
8
. That means every pipeline
combination is tested five times with stratified test and
training data. Hence, for each of the prototypical clas-
sifier implementations, we identify the pipeline com-
bination that leads to the best max. and mean F
1
out of
five folds for a 1:1 class ratio between eNEs and non-
eNEs. To achieve the overall benchmarks, we calcu-
lated an F
1
for all eNEs from 2012 to 2020. These
benchmarks reflect the ability to recognize an arbi-
trary eNE from the time range 2012 to 2020 from the
perspective of the year 2012. For the described task
setting to the best of our knowledge, there exists no
baseline benchmark. Hence, for the 1:1 class ratio,
we choose a common-sense baseline as proposed by
(Chollet, 2018) in cases there is no “known solution
(yet)”. For F
1
, a common-sense baseline is 0.67. This
is the F
1
of the trivial combination from a Recall of
1 and a Precision of 0.5. In contrast, a trivial random
classifier achieves a F
1
of 0.5, which could also be
used for baseline. We decided to use the higher base-
line for benchmarking to ensure the robustness and
generability of our models. Figure 6 displays the re-
sulting max. and mean. F
1
results for absolute and
relative features for eNERD on both corpora.
For the sub-task of eNERD the max. values for F
1
8
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/
sklearn.model selection.StratifiedKFold.html
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
36
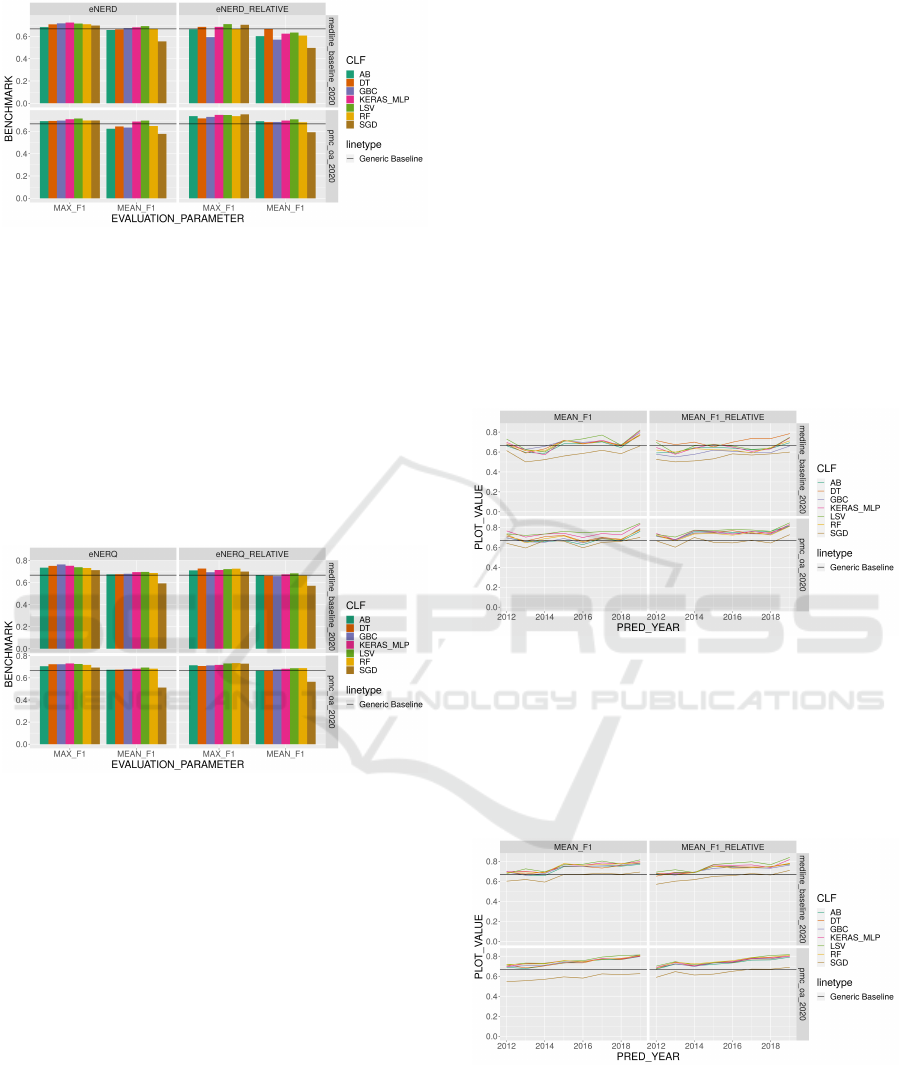
Figure 6: eNERD Benchmark 2012 - 2020 for Ratio 1:1.
for the different pipeline combinations are in a span
of [0.68, 0.72] for absolute features and [0.59, 0.71]
for relative features for MEDLINE. For PMC OA
the range of max F
1
values for absolute features
is [0.69,0.71] and [0.72,0.75] for relative features.
Looking at the mean values for both tasks and cor-
pora indicates that the respective spans are broader,
due to a bad mean overall performance of SGD. Fig-
ure 7 displays the resulting max. and mean. F
1
results
for absolute and relative features for eNERQ on both
corpora. For the sub-task of eNERQ the max. val-
Figure 7: eNERQ Benchmark 2012 - 2020 for Ratio 1:1.
ues for F
1
for all pipeline combinations are in a span
of [0.71, 0.76] for absolute features and [0.69, 0.73]
for relative features for MEDLINE. For PMC OA
the range of max F
1
values for absolute features is
[0.69,0.73] and [0.71,0.73] for relative features. The
lowest F
1
for each measure again is provided by SGD
classifier pipeline. Comparing Figures 6 and 7 it be-
comes clear that the overall performance of the clas-
sification pipelines is slightly better for the subtask
of eNERQ. Furthermore, for eNERQ the variance of
the results is lower, again with exception of the SGD
result. Overall the evaluation of t-eNER-CLF in 1:1
class ratio showed satisfactory F
1
results with a max
of 0.76 for eNERQ that can keep up with generic
baselines. However, in real world scenarios label im-
balance plays a major role that we evaluate in subsec-
tion 8.4.
8.3 Temporal eNER Classification
Lookahead Evaluation
While evaluating the overall F
1
aims at all eNEs in
the full-time range between 2012 and 2020, the next
evaluation step is intended to achieve a year based
evaluation. Based on the absolute or relative train-
ing material of 2012, we evaluated the F
1
values per
year, concerning the T
ACK
years of the eNEs in the
range 2012 - 2020. Figure 8 displays the mean F
1
val-
ues per year for both corpora and absolute and rela-
tive feature sets for eNERD. It becomes clear that the
mean F
1
for MEDLINE in both features sets mostly
meanders above and below the baseline. In contrast,
for PMC OA, the mean F
1
values are predominantly
above the baseline for both feature sets.
Figure 8: eNERD Lookahead 2012 - 2020 for Ratio 1:1.
Figure 9 displays the mean F
1
values per year for
both corpora and absolute and relative feature sets for
eNERQ. Compared to eNERD, the lookahead perfor-
mance for eNERQ is higher. Except for SGD, the
mean F
1
of other classifier pipelines predominantly
remains above the baseline. For both tasks eNERD
Figure 9: eNERQ Lookahead for Ratio 1:1.
and eNERQ, it is visible that the F
1
rises with an
increasing T
ACK
year. We argue that the features of
eNEs with T
ACK
in the “remote future” are more dis-
criminable compared to eNEs that have a T
ACK
close
to the year of the analysis. The lookahead analysis
showed that the best t-eNER-CLF classifier pipelines
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem
37

can correctly recognize eNEs in a range of at least
eight years with approx. baseline or better perfor-
mance.
8.4 Temporal eNER Classification
Evaluation with Label Imbalance
While the subsection before was intended to eval-
uate the general appropriateness of our model, this
subsection is intended to evaluate our approach con-
cerning a real-world scenario. Hence, we evaluate
the t-eNER-CLF approach in a scenario with imbal-
anced class labels, i.e., the classes “eNE” and “non-
eNE” have a ratio of 1:50. This ratio is derived
from the naive rule-based approach of the b-NLP-
NER task that revealed approximately this ratio be-
tween eNE and non-eNE noun-chunks. In this sub-
section, we changed the scales of the plots to have a
better-detailed view. Hence, the plots are not visu-
ally comparable to those from the former subsection.
The common-sense baseline, as used in the balanced
ratio for the 1:50 ratio, is 0.04 for a trivial classifier
with recall one and precision 0.02. In addition, we
introduce a second baseline that comes from our real-
world b-NLP-NER setup: The spacy training model,
based only on textual features, achieves a F
1
value of
0.07 for MEDLINE and 0.06 for PMC OA (see Table
1).
Figure 10 displays the resulting max. and mean.
F
1
results for absolute and relative features for eN-
ERD on both corpora. For the sub-task of eNERD the
Figure 10: eNERD Overall Benchmark 2012 - 2020 for Ra-
tio 1:50.
max. values for F
1
for the different pipeline combina-
tions are in a span of [0.06, 0.18] for absolute features
and [0.10, 0.18] for relative features for MEDLINE.
For PMC OA the range of max F
1
values for absolute
features is [0.08,0.10] and [0.08, 0.17] for relative fea-
tures.
Figure 11 displays the resulting max. and mean.
F
1
results for absolute and relative features for eN-
ERQ on both corpora. For the sub-task of eNERQ the
Figure 11: eNERD Overall Benchmark 2012 - 2020 for Ra-
tio 1:50.
max. values for F
1
for the different pipeline combina-
tions are in a span of [0.08, 0.2] for absolute features
and [0.09,0.2] for relative features for MEDLINE.
For PMC OA the range of max F
1
values for abso-
lute features is [0.08,0.22] and [0.08, 0.23] for relative
features.
Overall, Figures 11 and 11 indicate that for all cor-
pora, subtasks and feature sets the mean and max F
1
values outperform the generic baseline. However, for
eNERD, the SpaCy baselines are only exceeded by
max. F
1
values of selected classifier pipelines. Only
for the eNERD task on absolute features with PMC
OA also the mean F
1
outperform the SpaCy base-
line. This indicates that our temporal approach in
principle is capable of keeping up with state of the art
learning-based NER, especially when there are only
small training sets available (see above). During our
experiments, we found out that for a 1:50 class ratio
pipeline without imbalance handling is not capable of
achieving an F
1
> 0, so for both evaluations above,
we did not consider them for the max. and mean F
1
values indicated in Figures 10 and 11. The follow-
ing Figures 12 and 13 display the impact of different
imbalance handling strategies on the F
1
values in de-
pendency on the class ratio. They show exemplarily
the F
1
performance of a GBC classifier pipeline. We
have chosen GBC as in the 1:50 class ratio as it has
shown good overall performance in all subtasks, cor-
pora, and feature sets, compared to other classifiers
(see above).
For all subtasks, corpora and feature sets it be-
comes clear, that with imbalanced class label ratios
of <
1
2
without imbalance handling for the respec-
tive F
1
is decreasing immediately towards 0. In all
these cases imbalance handling significantly increases
F
1
for smaller ratios. However, the plots indicate
that the choice of concrete imbalance handling strat-
egy (SMOTE, RUS, SMOTEENN) only influences
the outcome marginally.
As with the balanced class ratio, the last evalua-
tion step again is the lookahead performance. Fig-
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
38
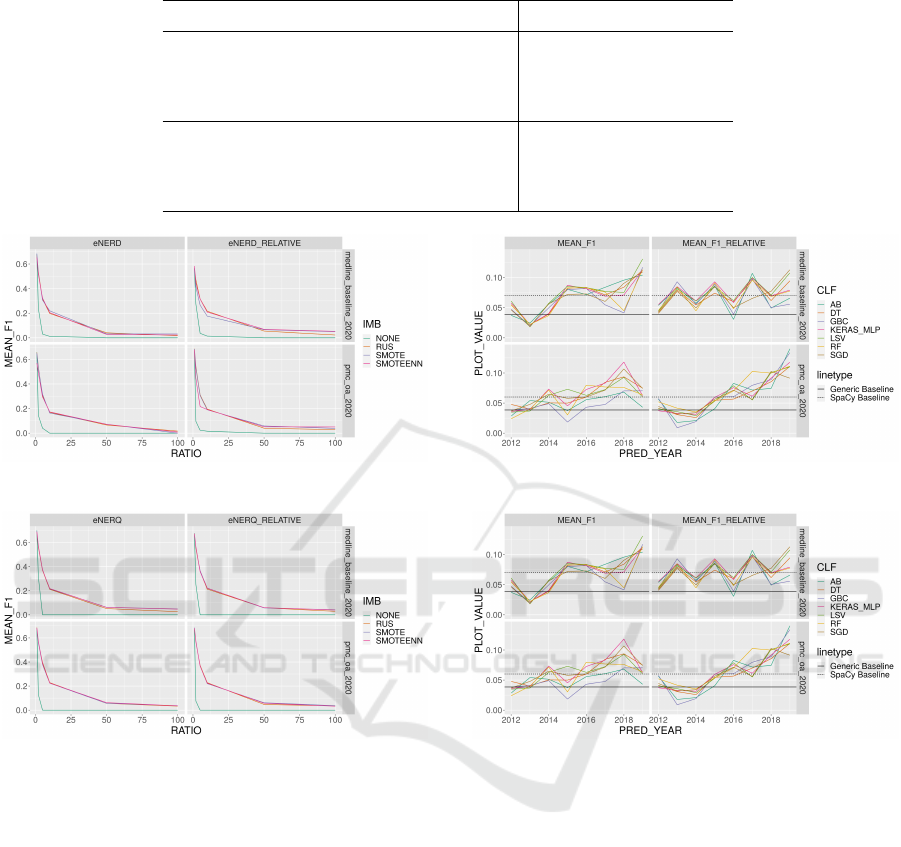
Table 2: Examples for correct classified eNEs.
Term / Query T
ACK
MeSH ID Task
neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists 2013 D064729 eNERD
atazanavir sulfate 2015 D000069446 eNERD
bortezomib treatment 2015 D000069286 eNERD
trali 2016 T000909011 eNERQ
lescol 2018 T209301 eNERQ
adalimumab 2015 D000068879 eNERQ
Figure 12: Imbalance Handling for GBC (F
1
, eNERD).
Figure 13: Imbalance Handling for GBC (F
1
, eNERQ).
ures 14 and 15 indicate that for all analyzed cases,
the lookahead performance over the whole time range
again oscillates around the baselines. Furthermore,
the figures reveal an overall increase towards the end
of the time range, similar to the 1:1 class ratio. For
eNERD towards the end of the time range, selected
classifiers outperform the SpaCy baseline. This leads
to the conclusion that in general, t-eNER-CLF is ca-
pable of early recognizing eNEs and can be used in
addition to a textual training based approach.
8.5 Outlook: Qualitative Evaluation
Finally, to have “hands-on” results, we also conducted
a qualitative evaluation and created an exemplar list of
recognized eNEs for both sub-tasks. Table 2 displays
an extract. Due to space limitation, the details of the
qualitative evaluation will be published elsewhere. In
Figure 14: eNERD Lookahead for Ratio 1:50.
Figure 15: eNERQ Lookahead for Ratio 1:50.
general, the evaluation showed that t-eNER-CLF is
capable of recognizing eNEs in a balanced label set
with F
1
values that are above generic baselines. The
max. observed F
1
is 0.76 for the task of eNERQ in a
balanced setup. Except for SGD for balanced class la-
bels, all evaluated classifier models mostly performed
on a similar level. This leads to the conclusion that
not the ML model, but the features have the main im-
pact on the t-eNER-CLF outcome.
9 CONCLUSION
In our real-world scenario, the evaluation showed that
t-eNER-CLF connected with a rule-based b-NLP-
NER can keep up with baselines achieved by our tex-
tual training SpaCy NER models. However, the ra-
tio between eNE and non-eNE (class imbalance) in
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem
39

particular use cases significantly influences the per-
formance, as also already reported by (Chen et al.,
2013) in their emerging Topic scenario. This requires
the use of an appropriate imbalance handling strategy.
Applying sufficient feature engineering and designing
an ML pipeline with a proper combination of an ML
and an imbalance handling strategy is the major chal-
lenge for future practical use of eNER on temporal IR
features, e.g., in medical argumentation support. The
difference between max. and mean evaluation results,
in particular, cases, indicates that the models in those
cases may be prone to overfitting. Overall the results
indicate that as future work, more non-local features
should be considered in the classification, as proposed
by (Chen et al., 2013). Feature candidates from MED-
LINE are, e.g., the number of non-emerging MeSH
concepts per document in the result set, or the pub-
lishing journals’ IDs in the result set. Parameter opti-
mization of the ML models is also advised.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been funded by the Deutsche
Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the project
Empfehlungsrationalisierung, Grant Number
376059226, as part of the Priority Program ”Robust
Argumentation Machines (RATIO)” (SPP-1999).
REFERENCES
Andrew McCallum and Wei Li (2003). Early results for
named entity recognition with conditional random
fields, feature induction and web-enhanced lexicons.
In Proceedings of the seventh conference on Natural
language learning at HLT-NAACL 2003 - Volume 4,
pages 188–191. Association for Computational Lin-
guistics, Edmonton, Canada.
Balog, K. (2017). Entity Retrieval. In Encyclopedia of
Database Systems, pages 1–6. Springer New York,
New York, NY.
Balog, K., Serdyukov, P., and De Vries, A. P. (2011).
Overview of the TREC 2011 entity track. NIST.
Batista, G. E., Prati, R. C., and Monard, M. C. (2004). A
study of the behavior of several methods for balancing
machine learning training data. ACM SIGKDD explo-
rations newsletter, 6(1):20–29. Publisher: ACM New
York, NY, USA.
Bawden, D. and Robinson, L. (2009). The dark side of
information: Overload, anxiety and other paradoxes
and pathologies. Journal of Information Science,
35(2):180–191.
Brambilla, M., Ceri, S., Della Valle, E., Volonterio, R.,
and Acero Salazar, F. X. (2017). Extracting Emerg-
ing Knowledge from Social Media. In Proceedings
of the 26th International Conference on World Wide
Web, WWW ’17, pages 795–804, Republic and Can-
ton of Geneva, Switzerland. International World Wide
Web Conferences Steering Committee.
Chang, A. X. and Manning, C. D. (2014). TokensRegex:
Defining cascaded regular expressions over tokens.
Number CSTR 2014-02. Department of Computer
Science, Stanford University.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., and Kegelmeyer,
W. P. (2002). SMOTE: synthetic minority over-
sampling technique. Journal of artificial intelligence
research, 16:321–357.
Chen, Y., Amiri, H., Li, Z., and Chua, T. S. (2013). Emerg-
ing topic detection for organizations from microblogs.
In SIGIR 2013 - Proceedings of the 36th International
ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Develop-
ment in Information Retrieval, pages 43–52.
Chollet, F. (2018). Deep learning with Python. Manning
Publications Co, Shelter Island, New York. OCLC:
ocn982650571.
Cornolti, M., Ferragina, P., Ciaramita, M., Sch
¨
utze, H., and
R
¨
ud, S. (2014). The SMAPH System for Query En-
tity Recognition and Disambiguation. In Proceedings
of the First International Workshop on Entity Recogni-
tion & Disambiguation, ERD ’14, pages 25–30, New
York, NY, USA. ACM.
Cucerzan, S. (2014). Name Entities Made Obvious: The
Participation in the ERD 2014 Evaluation. In Pro-
ceedings of the First International Workshop on En-
tity Recognition & Disambiguation, ERD ’14, pages
95–100, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Dan Cho (2014). MeSH on Demand Tool: An Easy Way
to Identify Relevant MeSH Terms. Number 389:e2 in
NLM Technical Bullentin. U.S. National Library of
Medicine.
Derczynski, L., Nichols, E., van Erp, M., and Limsopatham,
N. (2018). Results of the WNUT2017 Shared Task on
Novel and Emerging Entity Recognition. pages 140–
147.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova,
K. (2019). BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirec-
tional Transformers for Language Understanding.
arXiv:1810.04805 [cs]. arXiv: 1810.04805.
Du, J., Zhang, Z., Yan, J., Cui, Y., and Chen, Z. (2010). Us-
ing Search Session Context for Named Entity Recog-
nition in Query. In Proceedings of the 33rd Interna-
tional ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and De-
velopment in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’10, pages
765–766, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Foley, J., Sarwar, S. M., and Allan, J. (2018). Named En-
tity Recognition with Extremely Limited Data. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1806.04411.
G
´
eron, A. (2017). Hands-on machine learning with Scikit-
Learn and TensorFlow: Concepts, tools, and tech-
niques to build intelligent systems. O’Reilly Media,
Sebastopol, CA, first edition edition.
Guo, J., Xu, G., Cheng, X., and Li, H. (2009). Named
Entity Recognition in Query. In Proceedings of the
32Nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Re-
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
40

search and Development in Information Retrieval, SI-
GIR ’09, pages 267–274, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Herskovic, J. R., Tanaka, L. Y., Hersh, W., and Bernstam,
E. V. (2007). A day in the life of PubMed: analysis
of a typical day’s query log. Journal of the American
Medical Informatics Association, 14(2):212–220.
Hoffart, J., Altun, Y., and Weikum, G. (2014). Discovering
emerging entities with ambiguous names. In WWW
2014 - Proceedings of the 23rd International Confer-
ence on World Wide Web, WWW ’14, pages 385–395,
New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Honnibal, M. and Montani, I. (2017). spaCy 2: Natural lan-
guage understanding with Bloom embeddings, convo-
lutional neural networks and incremental parsing.
Huth, E. J. (1989). The information explosion. Bulletin of
the New York Academy of Medicine, 65(6):647.
Kleppmann, M. (2017). Designing data-intensive appli-
cations: the big ideas behind reliable, scalable, and
maintainable systems. O’Reilly Media, Boston, first
edition edition. OCLC: ocn893895983.
Krasner, G. E., Pope, S. T., and others (1988). A description
of the model-view-controller user interface paradigm
in the smalltalk-80 system. Journal of object oriented
programming, 1(3):26–49.
Lafferty, J., McCallum, A., and Pereira, F. C. N. (2001).
Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for
segmenting and labeling sequence data.
Lee, J., Yoon, W., Kim, S., Kim, D., Kim, S., So, C. H.,
and Kang, J. (2019). BioBERT: a pre-trained biomed-
ical language representation model for biomedical text
mining. pages 1–8.
Lema
ˆ
ıtre, G., Nogueira, F., and Aridas, C. K. (2017).
Imbalanced-learn: A Python Toolbox to Tackle the
Curse of Imbalanced Datasets in Machine Learning.
Journal of Machine Learning Research, 18(17):1–5.
Ling Charles X., , and Sheng, V. S. (2010). Class Imbal-
ance Problem. In Sammut Claude, , and Webb, G. I.,
editors, Encyclopedia of Machine Learning, page 171.
Springer US, Boston, MA.
Lipscomb, C. E. (2000). Medical subject headings
(MeSH). Bulletin of the Medical Library Association,
88(3):265.
Manning, C. D., Raghavan, P., and Sch
¨
utze, H. (2008). In-
troduction to information retrieval. Cambridge Uni-
versity Press, New York.
Meij, E., Balog, K., and Odijk, D. (2013). Entity Link-
ing and Retrieval. In Proceedings of the 36th Interna-
tional ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and De-
velopment in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’13, page
1127, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Mosa, A. S. M. and Yoo, I. (2013). A study on pubmed
search tag usage pattern: Association rule mining of a
full-day pubmed query log. BMC Medical Informatics
and Decision Making, 13(1).
Nadeau, D. and Sekine, S. (2007). A survey of named entity
recognition and classification. Lingvisticae Investiga-
tiones, 30(1):3–26.
Nawroth, C., Duttenh
¨
ofer, A., and Hemmje, M. (2020). Ar-
gumentationsunterst
¨
utzung durch emergentes Wissen
in der Medizin. In to appear in: (Wilhelm Bauer,
Joachim Warschat, Innovation durch Natural Lan-
guage Processing - Mit K
¨
unstlicher Intelligenz die
Wettbewerbsf
¨
ahigkeit verbessern.
Nawroth, C., Engel, F., Eljasik-Swoboda, T., and Hemmje,
M. (2018). Towards enabling emerging named entity
recognition as a clinical information and argumenta-
tion support. In DATA 2018 - Proceedings of the 7th
International Conference on Data Science, Technol-
ogy and Applications.
Nawroth, C., Engel, F., Mc Kevitt, P., and Hemmje, M. L.
(2019). Emerging Named Entity Recognition on Re-
trieval Features in an Affective Computing Corpus. In
2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformat-
ics and Biomedicine (BIBM), pages 2860–2868.
Norman, D. A. and Draper, S. W. (1986). User centered
system design: New perspectives on human-computer
interaction. CRC Press.
of Bielefeld, U. (2017). Rationalizing Recommendations
(RecomRatio): Project-Homepage. Bielefeld.
Petkova, D. and Croft, W. B. (2007). Proximity-based doc-
ument representation for named entity retrieval. In
Proceedings of the sixteenth ACM conference on Con-
ference on information and knowledge management,
pages 731–740. ACM, Lisbon, Portugal.
Piccinno, F. and Ferragina, P. (2014). From TagME to WAT:
A New Entity Annotator. In Proceedings of the First
International Workshop on Entity Recognition & Dis-
ambiguation, ERD ’14, pages 55–62, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
Sang, Erik F. Tjong Kim and de Meulder, F. (2003). In-
troduction to the CoNLL-2003 shared task: language-
independent named entity recognition. In Proceed-
ings of the seventh conference on Natural language
learning at HLT-NAACL 2003 - Volume 4, pages 142–
147. Association for Computational Linguistics, Ed-
monton, Canada.
Vu, B. and Hemmje, M. (2019). Supporting Taxonomy De-
velopment and Evolution by Means of Crowdsourc-
ing:. In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint
Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge En-
gineering and Knowledge Management, pages 351–
358, Vienna, Austria. SCITEPRESS - Science and
Technology Publications.
Wang, B., Yang, B., Shan, S., and Chen, H. (2019). De-
tecting Hot Topics From Academic Big Data. IEEE
Access, 7:185916–185927. Publisher: IEEE.
Yao, K., Zweig, G., Hwang, M. Y., Shi, Y., and Yu, D.
(2013). Recurrent neural networks for language un-
derstanding. In Yao, K., Zweig, G., Hwang, M.-Y.,
Shi, Y., and Yu, D., editors, Proceedings of the Annual
Conference of the International Speech Communica-
tion Association, INTERSPEECH, pages 2524–2528.
Zheng, A. and Casari, A. Feature engineering for machine
learning : principles and techniques for data scien-
tists.
Zhou, G. and Su, J., editors (2002). Named entity recogni-
tion using an HMM-based chunk tagger. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Emerging Named Entity Recognition in a Medical Knowledge Management Ecosystem
41
