
Extended Knowledge Graphs: A Conceptual Study
∗
Weronika T. Adrian
a
, Marek Adrian
b
, Krzysztof Kluza
c
,
Bernadetta Stachura-Terlecka
d
and Antoni Lig˛eza
e
AGH University of Science and Technology, al. A.Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Krakow, Poland
Keywords:
Knowledge Graphs, Semantic Networks, Knowledge Representation, KRR, Rules, Ontologies, Reasoning,
Logic Programming, Answer Set Programming, Prolog.
Abstract:
The amount and variety of data that we produce every day pose a constant challenge for meaningful informa-
tion processing. While knowledge graphs have gained a considerable attention in the recent years, due to their
flexible and universal knowledge representation, they lack the mechanisms facilitating knowledge processing.
In this paper, we propose an information system called extended knowledge graphs (EKG) that augments the
concept of knowledge graphs with procedural attachments. We put forward the requirements and assumption
of the EKG structure and present a categorisation of supported reasoning tasks.
1 INTRODUCTION
The amount of data produced and stored every day
may be daunting for who wants to process it effi-
ciently. The variety of data adds an additional diffi-
culty layer for a meaningful analysis of the informa-
tion encoded within. In fact, it seems that knowledge
representation methods do not keep up with the ever-
growing mass of data to process, leaving us with sub-
optimal solutions, either in terms of possible tasks to
perform or the amount of data that can be processed.
In the recent years, a considerable attention has
been gained by so-called knowledge graphs (Hogan
et al., 2020; Fensel et al., 2020; Ji et al., 2020) –
graph-based knowledge representation systems that
can organize information in a flexible and intuitive
way. Although they are used in both academic (Paul-
heim, 2017) and business (Noy et al., 2019) commu-
nications, there is no commonly agreed upon defi-
nition of them (Ehrlinger and Wöß, 2016). In fact,
some parties see them as an reincarnation of on-
tologies (Uschold et al., 1996; Staab and Studer,
2010; Ławrynowicz, 2017), other define them as
knowledge-based systems (KBS) (Akerkar and Sajja,
2009; Ahmed et al., 2019) that consist of a knowledge
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1860-6989
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0435-0994
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1876-9603
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2887-5936
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6573-4246
∗
This Paper Is Supported by AGH UST Grant.
base and a reasoner, or finally — a KBS with a knowl-
edge integration component. In this last definition, a
knowledge graph should integrate information from
different sources into an ontology and provide means
to reason over the integrated knowledge.
Regardless of the adopted definition, knowledge
graphs still deal with only static knowledge represen-
tation, i.e., describing the properties of objects and
classes (sets of objects) and relations between them.
In practical use cases, one often is interested in associ-
ating also some dynamic procedures to static objects
or classes. For instance, an editor in a journal would
like to “process” a submitted paper which requiress,
i.a., finding a suitable person to review the article. To
this end, a candidate reviewer should be familiar with
the topics considered in the paper, he or she should
not have a conflict of interests with the paper’s author
(that e.g. may mean they should not be co-authors or
work in the same department) etc. While theoretically
we already have access to all the needed information
e.g., in the ORCID and DBLP databases or Microsoft
Academic Graph that describe the scientists and their
work in a graph-like structure, it is not easy to solve
such a problem automatically. To address such prob-
lems, we propose to extend the knowledge graph rep-
resentation with procedural attachments, such that a
procedure (understood as a process that contains some
decisions) can be associated with a specific type of
objects defined in the graph.
In the following sections, we present extended
knowledge graphs (EKG) to encode both structural
Adrian, W., Adrian, M., Kluza, K., Stachura-Terlecka, B. and Lig˛eza, A.
Extended Knowledge Graphs: A Conceptual Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0010111601730180
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2020) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 173-180
ISBN: 978-989-758-474-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
173

(static) and procedural (dynamic) knowledge. We
outline its rationale and main objectives, discuss main
features and components and illustrate its use with ex-
emplary use cases. We argue that a procedural exten-
sion to KG representation can be both beneficial for
practical use cases and plausible to implement using
existing logical reasoners.
The contributions of the paper are threefold:
• Knowledge Representation: we discuss a new lan-
guage for representing both static graph-based
knowledge and dynamic procedures;
• Typology of Operations: we consider differ-
ent types of problems that extended knowledge
graphs should address and organize them into
groups
• Applications: we illustrate the use of our sys-
tem on practical examples that describe academic
community in terms of publications and collabo-
ration.
2 BACKGROUND AND
MOTIVATION
Knowledge Representation (KR) methods can be di-
vided into descriptive (or declarative) and procedu-
ral (or imperative) ones (Torsun, 1995). The descrip-
tive methods include tables, formulas or graphs and
they are characterised by storing information explic-
itly. On the contrary, knowledge expressed in proce-
dural manner is manifested in the actual execution of
the program and is therefore stored implicitly. The
declarative methods are easier to expand and modify.
However, in various application, intelligent systems
may need both kinds of representation.
“A semantic network or net is a graphic nota-
tion for representing knowledge in patterns of inter-
connected nodes and arcs.” (Sowa, 1987). Semantic
nets have long been used in philosophy, psychology
and linguistic before the computer implementation of
them were developed. They have represented knowl-
edge or supported automated reasoning. A declar-
ative graphic representation characterizes semantic
networks. There exist various sorts of semantic net-
works, designed for different purposes and of differ-
ent levels of formalisation. In (Sowa, 1987), the fol-
lowing classification of semantic nets was introduced:
1. Definitional Networks. In these networks the sub-
type or is-a relation between a concept type and a
newly defined subtype is emphasised. Their basic
mechanisms are ”as old as Aristotle”, who worked
on a classification of nature. Definitorial networks
support the rule of inheritance and, usually, mono-
tonic reasoning, in which inferred knowledge is
added, but what is once known does not change.
2. Assertional Networks are designed to assert
propositions. Some of the assertional (proposi-
tional) networks have been used to graphically
represent structures underlying natural language
semantics. C. S. Peirce introduced relational
graphs and existential graphs, by means of which
he intended to show ”the atoms and molecules of
logic”. Propositional networks include also Tes-
nière’s dependency graphs used to represent nat-
ural language sentences. A variety of semantic
propositional networks called Conceptual Graphs
have been developed by J. F. Sowa. Core con-
ceptual graphs are successors of Peirce’s exis-
tential graphs while extended and research con-
ceptual graphs explored novel techniques for rea-
soning, knowledge representation and natural lan-
guage semantics. For core and extended CG the
semantics is defined by a mapping to ISO Com-
mon Logic standard using subset of First Order
Logic.
3. Implicational Networks. These structures use im-
plication as the primary relation for connecting
nodes. They may be used to represent patterns
of beliefs (belief networks, Bayesian networks),
causality (causal networks), or inferences (truth-
maintenance systems). To one graph different in-
terpretations and reasoning may apply. Both log-
ical, forward- and backward-chaining, as well as
probabilistic reasoning may be used.
4. Executable Networks. These networks contain
mechanisms which can perform inferences, pass
messages, or search for patterns and associations
and cause some changes to the network itself.
These mechanisms, which distinguish the net-
works from other, static ones include marker pass-
ing, attached procedures and graph transforma-
tions. Dataflow graphs and Petri Nets, although
rarely classified as semantic networks, use similar
techniques as procedural semantic networks.
5. Learning networks build or extend their repre-
sentations by acquiring knowledge from exam-
ples. The new knowledge may change the old
network by adding and deleting nodes and arcs
(rote memory) or by modifying numerical values,
called weights, associated with the nodes and arcs.
Rote memory techniques find an application in
case-base reasoning systems, whereas changing
weights is often used in artificial neural nets.
6. Hybrid networks combine two or more of the pre-
vious techniques, either in a single network or in
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
174

separate, but closely interacting networks.
The approach to knowledge representation based
on describing the world of interest in terms of ob-
jects enables to introduce hierarchy and structure into
a knowledge base. Sentences or rules can be grouped
by the concepts (objects) they refer to. One of the pro-
cedural knowledge representation formalism which is
object-oriented is the one of frames, first proposed by
Marvin Minsky in 1975. In a basic version of the
formalism, there are two types of frames: individ-
ual frames or instance-frames for representing single
objects and general frames or class-frames for repre-
senting classes or categories of objects. Frames have
attributes or slots, which are filled by fillers. Two
special distinguished slots were defined, INSTANCE-
OF for individual frames and IS-A for general frames.
By means of them one could specify that given ob-
ject is an instance of a class or introduce hierarchy
between two generic classes. The relations these
slots specify are called generalisation. Other relations
between frames include aggregation, in which sev-
eral frames representing components are associated
with another one, which represents a whole and as-
sociation, which denotes other semantic relationship.
Frame slots could also have attached procedures.
Two basic sorts of such procedures are IF-ADDED
and IF-NEEDED (Brachman et al., 2004) (or accord-
ing to (Negnevitsky, 2005): WHEN-CHANGED and
WHEN-NEEDED). The procedures are executed if a
frame is added or a new value is placed in a slot or
if some computation is needed to determine a slot
value. In (Negnevitsky, 2005), a distinction is drawn
between methods and demons which were both types
of attached procedures. Demons usually are in a form
of an IF-THEN rule and when the attribute specified
in IF statement changes its value, then the consequent
of the rule is fired. The term method is sometimes
used as a synonym, but it usually denotes more com-
plex procedure consisting of several actions.
Reasoning with frames mainly consists in discov-
ering the relations between frames and creating indi-
vidual instances of generic frames. It involves fill-
ing some slots with values and inferring other val-
ues. Of a particular significance are INSTANCE-OF
and IS-A slots. They enable for instantiating indi-
viduals and triggering procedures, which were not
stated explicitly in an individual frame. The pro-
cess of ”passing information from generic frames
down through their specializations and eventually to
their instances” (Brachman et al., 2004) is called in-
heritance and it is present both in frame formalism
and in object-oriented programming. In fact, inheri-
tance is an essential feature of frame-based systems.
Frames were developed concurrently with object-
oriented programming languages and share some of
their intuition. According to (Negnevitsky, 2005),
”frames are an application of object-oriented pro-
gramming for expert systems”. Although frames were
applied in several fields (Brachman et al., 2004), they
lack the reasoning support and are too inexpressive
for many problems.
More advanced formalisms based on an idea to
represent knowledge in terms of concepts and object
are Description Logics (DL) (Baader et al., 2003).
They enable for constructing complex descriptions
which denote the classes of individuals. As opposed
to the frame languages, Description Logics have for-
mal, First Order Logic semantics. Therefore, they
extend frames’ capabilities and provide intrinsic rea-
soning support. Description Logics became the log-
ical foundations of the Semantic Web ontology lan-
guages, and respective OWL subsets have their log-
ical counterparts in DL languages. It is noteworthy
that the catalogue of reasoning tasks in Description
Logics is limited to several problems, such as classifi-
cation, consistency checking, realization or retrieval.
3 RELATED WORK
Graph-based knowledge representation has been suc-
cessfully used in almost every branch of Artificial In-
telligence (Sowa, 1992). The newest incarnation of it
are knowledge graphs. As a term, Knowledge Graph
was “re-discovered” and popularized by Google in
their communication about search based on objects,
not words (Singhal, 2012). Since then, the term has
been widely adopted in the Semantic Web community
and beyond.
Basic notions of the knowledge graphs have been
further extended in several directions. Yahya et
al. considers extended knowledge graphs as graphs
that combine relational facts with textual web con-
tents (Yahya et al., 2016a; Yahya et al., 2016b).
Zhang et al. (Zhang et al., 2020) extend knowledge
graphs in order to integrate heterogeneous data re-
sources and enhance knowledge-based services for
health care systems. Thus, their Health Knowledge
Graph Builder may be used to construct disease-
specific and extensible health knowledge graphs from
multiple sources. Another interpretation of extending
knowledge graphs has been put forward in (Yoo and
Jeong, 2020) in which the authors proposed a method
for auto-extending knowledge graphs.
Combining static graph-based knowledge with a
description of dynamics of a system is a recurring
challenge. Depending on the domain and application,
it appeared thorough years in a form of simple as-
Extended Knowledge Graphs: A Conceptual Study
175

sert/retract operations on conceptual graphs (Mineau,
1998), a range of proposals for integrating rules
and ontologies (Eiter et al., 2008), associative graph
data structures (Horzyk, 2013), and recently in com-
plex processes integrated with “full-fledged data mod-
els” (van der Aalst, 2019). Specific ways to model the
dynamics are processes and rules.
Business Process Model and Notation
(BPMN) (OMG, 2011) is a notation created by
OMG (Object Management Group) to graphically
represent business processes using diagrams. It
is now a well established standard not only for
modeling, but also for managing process knowledge
of organizations. Recently, the Decision Model
and Notation (DMN) standard (OMG, 2014), also
created by OMG, has been proposed. It works
as a complementary notation for describing rules
and decisions in organizations. DMN is especially
useful for modeling decision logic for processes. As
both processes and decisions constitute executable
specifications (Janssens et al., 2016), it is possible to
use process and decision engine for deployment and
enactment of such models.
Integrating logic based on rules with static se-
mantic representation of objects is another way to in-
tegrate declarative and procedural knowledge, both
on the theoretical (Eiter et al., 2008; Nalepa and
Furma
´
nska, 2010a) and practical (Nalepa and Fur-
ma
´
nska, 2010b) level. Embedding a rule engine into a
semantic system (Adrian et al., 2011) allows to prac-
tically model and test such an integration.
This paper is a communication of a work-in-
progress research on defining yet another knowledge
representation system that would meet the challenges
of processing large graph-based datasets with differ-
ent types of data transformations, outlined and cate-
gorized in the following sections.
4 EXTENDED KNOWLEDGE
GRAPHS
In this section, we put forward our rationale and main
assumptions of extended knowledge graphs (EKG).
We introduce the language syntax and semantics and
outline the architecture of the systems adopting the
language.
4.1 Main Assumptions
In the era of interconnected information systems, we
recognize the value of graph-based knowledge rep-
resentation and its visualization (Dudycz, 2017). It
is both flexible and universal and so we assume that
the data model rely on graphs. Moreover, we assume
that it is convenient to distinguish different levels of
abstraction in a knowledge based system. Thus, we
assume that the following layers should be supported:
1. graph-based knowledge representation,
2. logic layer that allows for different kinds of data
transformations,
3. visualization layer for clear knowledge summary.
While the layered architecture can be already ob-
served in the Semantic Web in the form of the famous
semantic stack, the intention of extended knowledge
graphs is to encode also dynamic knowledge in the
“logic layer” that could be related to Semantic Web’s
ontologies and rules. With use of rules and proce-
dures, we would like to be able to design and imple-
ment a dynamic knowledge based system, that should
be able to modify the knowledge if needed, rather than
only query the static part of it.
Another important assumption is that we would
like to be able to define different kinds of objects in
EKG. The objects’ classes (or categories) would de-
termine what is possible to do upon the considered
object.
Finally, we intend to express a range of tasks and
problems to solve with our system. In particular, we
would like to allow for tasks beyond simple query-
ing (SELECT-like operations), such as information
retrieval, path-finding, forward-chain and backward-
chain reasoning, hard and weak constraints (optimiza-
tion). To this end, we consider appropriate operators
and envision the transformations they would induce.
4.2 Knowledge Representation in EKG
In principle, we propose to identify three main types
of objects:
1. Agents: “active objects” that represent persons in
the system that can initiate some actions or oper-
ations over the static objects, and who can have
particular permissions over certain classes of ob-
jects and roles in the system, defined by these per-
missions;
2. Objects: “passive objects” that can be acted upon
– they have methods, as in object-oriented pro-
gramming, that define the operations in which
they can participate
3. Transformations: “functional objects” that de-
fine the operations to be performed with active
and passive objects; they are defined by the re-
quired input and expected output, a trigger that
initiates them and the task definition that can be
expressed in multiple forms such as a process, a
set of rules and constraints or a process.
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
176

The transformations can be triggered by events. It is
possible to distinguish different types and subtypes of
them (the following specification of events is inspired
by BPMN event types (OMG, 2011)):
• a message event indicates that a message is re-
ceived,
• a timer event (Rademakers and van Liempd, 2012)
usually provides some time specification which
may denote:
– a specific time and date, e.g in the format ISO
8601, when to trigger the event,
– a time duration which sets some period of time
that must elapse before the event is triggered,
e.g. ”for 3 days”,
– a time cycle which sets time intervals to trigger
an event periodically, e.g. 5 repetitions, each
for an hour,
• a conditional event which checks if a certain con-
dition is true,
• a signal event which catches a global signal deliv-
ered to the process,
• an exception event, which in some cases may be
realized by the abovementioned events, but usu-
ally is implemented as:
– an error event in the case of occurring of a po-
tential error,
– an escalation event to escalate an exception
from the sub-processes to the parent process,
– a cancel event, used in the context of the trans-
actions and invokes compensation events to
compensate the specific tasks.
Agents, Objects and Transformations can be con-
nected with each other with links that represent rela-
tions between them.
To put it into a slightly more formal perspective,
we define an agent as:
A = hid, AT T, ROL, PRCi
where:
• id is a string identifier
• AT T is a set of attributes such as for example a
name, a surname, age, nationality etc.
• ROL is a set of permissions over the Objects
• PRC is a set of procedures the agent can initiate
We define a (passive) object as:
O = hid, ATT, PRCi
where:
• id is a string identifier
• AT T is a set of attributes
• PRC is a set of procedures that can be performed
over (using) the object
and a Transformation objects as:
T = hid, tr, ts, OBJi
where:
• id is a string identifier
• trg is a type of trigger that initiate the transforma-
tion
• tsk is a definition of the “task” to be executed
• OBJ is a set of objects that are transformed
The EKG structure is partially based on the entity
network introduced in (Adrian and Manna, 2018) and
is a tuple
Y = hC, I, P, R, rel, proci
where:
• C is a set of concept names, denoting both agents’
and objects’ classes
• I is a set of object instances
• P is a set of procedures (transformations)
• R is a set of relation names
• rel : (I ∪C ∪ P) × (I ∪C) → 2
R
is a function that
associated the relation names to pairs of entities in
the network
• proc : C → 2
P
is a function that associate proce-
dures with classes of objects
5 REASONING WITH EKG
The language of the logic layer should cover differ-
ent forms of rules, processes as well as hard and weak
constraints. In fact, we envision that several differ-
ent “levels” of tasks could be considered, from simple
database-like operations, through more sophisticated
logical reasoning up to full-fledged data analysis. To
systematically analyze and define these operations in
EKG, we propose the following categories of prob-
lems:
Level 0: CRUD (Create / Read / Update / Delete) op-
erations – these are basic transformations of the
underlying graph database
Level 1: SELECT operations, aggregation, creating
views – these are the transformations available in
classical relational databases. They “return” por-
tions of data present in the knowledge graph or the
results of simple operations such as sum or aver-
age of data.
Extended Knowledge Graphs: A Conceptual Study
177
Level 2: Deduction – these are operations that return
data inferred from those present in the knowledge
base via logical rules, possibly with use of recur-
sion, chaining, transitive closure etc.
Level 3: Finding similar objects to the ones given –
these are even higher level tasks that include an
analysis of the given examples (with use of se-
lected metrics of similarity), followed by search
mechanisms to discover relevant objects in the
knowledge base
Level 4: Induction – these are the operations that
perform generalizations from given examples to
more general assumptions about classes of ob-
jects; this level encompasses optimization prob-
lems based on data analysis, clustering and com-
parison.
Level 5: Merge – integration of knowledge from sev-
eral graphs, understood not as a simple sum, but
taking into consideration consistency analysis, in-
duction and concept alignment
When it comes to the implementation perspec-
tives, an EKG system is intended to work as a frame-
work, with configurable elements: reasoners, knowl-
edge graph databases and visualization component(s).
As for the database layer, we consider both RDF stan-
dard based on triple representation and URIs for data
identification, and labeled property graph paradigm
in which both edges and vertices are represented with
key-value structures. While the former is the base of
Semantic Web standards and supported with differ-
ent triple stores, the latter has been adopted in widely
used graph databases such as Neo4j.
As far as reasoning layer is concerned, there are
many reasoners that could realize particular tasks out-
lined above, such as Prolog implementations for de-
duction, constraint satisfaction problems and goal-
driven inference, ASP engines (Adrian et al., 2018)
for various graph problems, data-driven reasoning as
well as constraint and optimization problems, ontol-
ogy reasoners, process mining tools etc.
6 APPLICATIONS
The extended knowledge graphs could be used in var-
ious scenarios that include processes operating over
a networked knowledge. In this section, we demon-
strate an exemplary application of EKG over knowl-
edge about researchers and their works. Let us con-
sider a part of an extended knowledge graph de-
signed for a simplified science database 1. We have
three researchers R1, R2, R3, five topics/keywords
T 1, T 2, T 3, T 4, T 5 and seven papers (P1 − P7). In
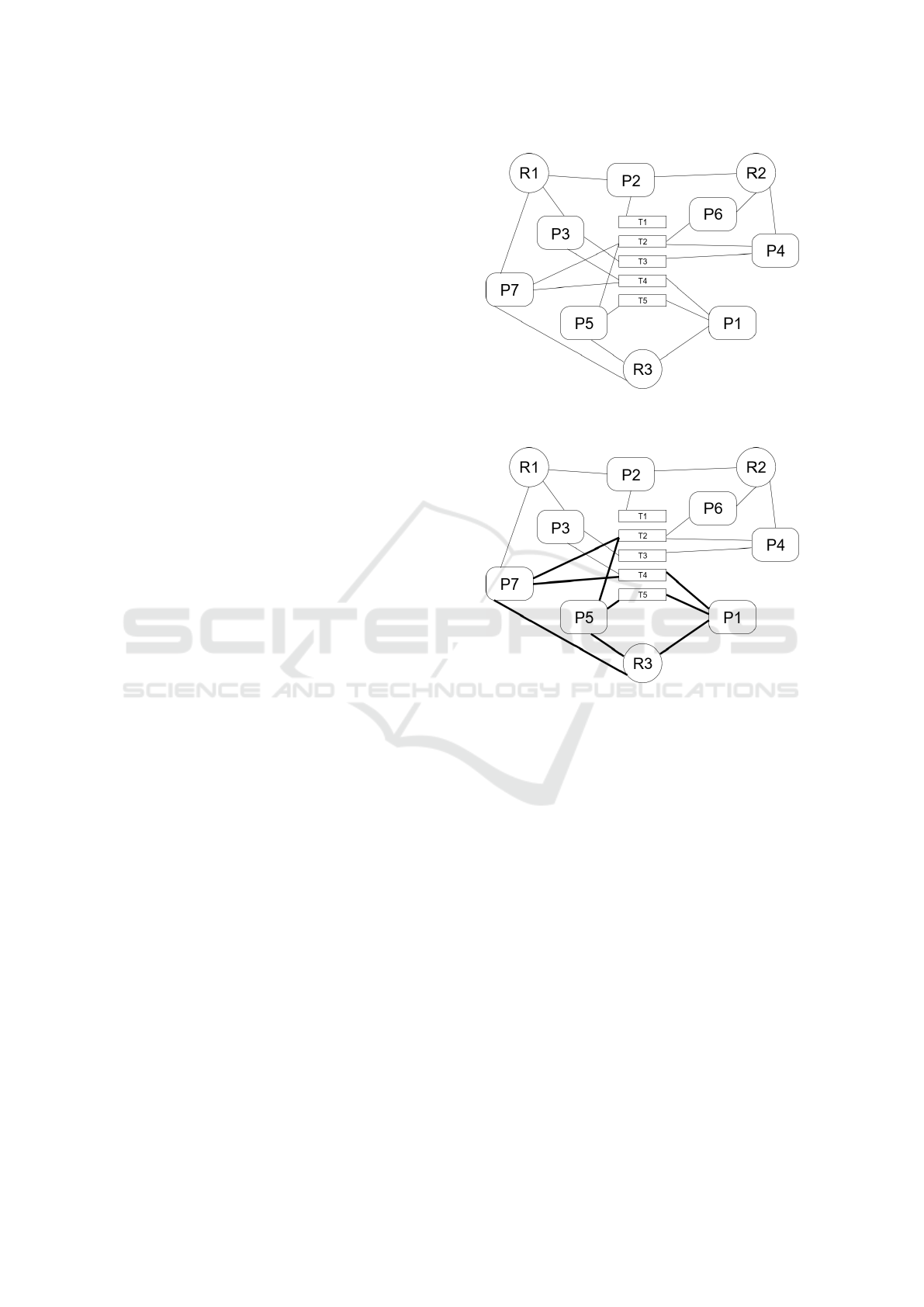
Figure 1: Exemplary extended knowledge graph about re-
searchers and their work.
Figure 2: Research interests of R3.
this knowledge graph, topics/keywords can only be
connected to papers and so are the researchers, but
researchers are also agents so they can initiate proce-
dures. In the following sections, we present possible
operations over this piece of knowledge.
6.1 Exemplary Use Cases
The most basic procedure would be recognizing in
what topic a given researcher has a strong interest. In
our case, we would define a strong interest as having
written at least 2 papers related to a topic/keyword.
So, R3 has a strong interest in T 2, T 4, T 5 (see Fig. 2),
R1 in T 4, but has also written papers on T 1, T 2 and
T 3 (see Fig. 3(a)) and R2 has a strong interest in T 2,
but has also written on T1 and T 3 (see Fig. 3(b)).
Another obvious procedure would be finding col-
laborators of a given researcher, namely researchers
that have at least one co-authored paper with a given
researcher. For instance, R1 is a collaborator of R3,
but R2 is not.
We can broaden this operation to an “Erdös
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
178
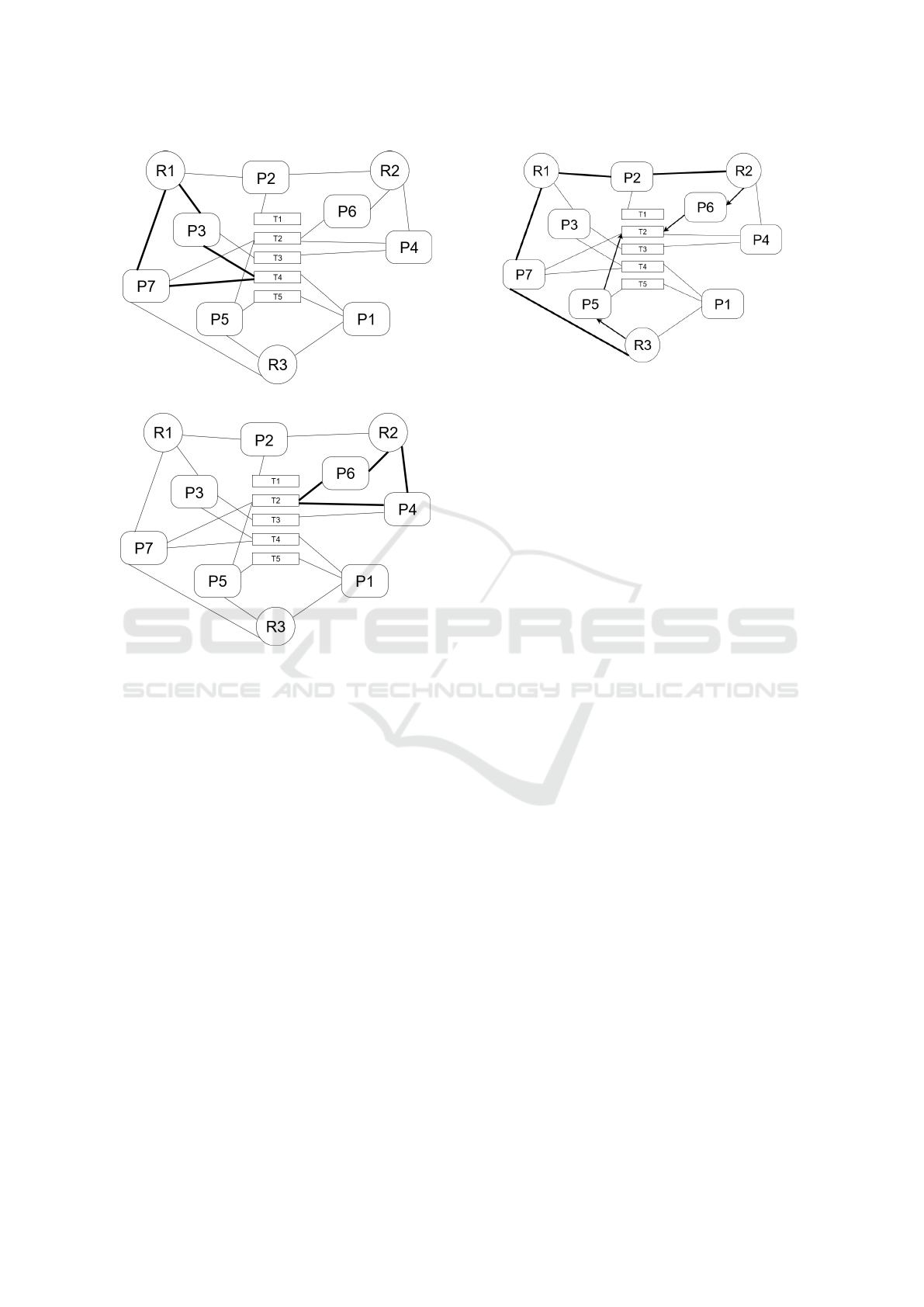
(a) Research interests of R1.
(b) Research interests of R2.
Figure 3: Research interests recognition.
number”-style concept for any researcher. To recall,
we define Erdös number recursively: if a researcher
has a paper with Erdös, their Erdös number is 1; if
the researcher has a paper with someone whose Erdös
number is 1, but no paper with Erdös, their Erdös
number is 2, and so on. In our case, the R3 number
for R1 is 1 and is 2 for R2.
Finally, we can put some more sophisticated de-
duction using this knowledge representation. Con-
sider a researcher who looks for people with simi-
lar research interests, but not too far away form him
with respect to collaboration. To this end, we would
look for all the researchers with at least one common
strong interest and the “researcher number” within a
given small boundary (for example 2). In our case,
the potential collaborators of R3 are both R1 and R2.
What is interesting is that while connection with R1
could be returned via simple SELECT operation, the
connection between R2 and R3 is not that obvious,
seeing that R1 and R2 have no common strong inter-
est. However, R2 has a common strong interest with
R3 and the R3-number of 2 as seen in Figure 4 which
renders them a valid candidate.
Figure 4: Looking for potential collaborators.
7 CONCLUSION
We have presented a concept of extending knowledge
graphs with procedural attachments under a com-
mon knowledge representation. We have introduced
extended knowledge graphs — a knowledge repre-
sentation and reasoning system that integrates static
knowledge from existing knowledge sources and can
perform logical reasoning in forward and backward
chaining mode.
For future work, we plan to fully implement the
idea, define new use cases and problems over existing
knowledge graphs and evaluate empirically the effi-
ciency of the system. Moreover, we will continue to
add new tasks to be possible to define and execute
with the system.
REFERENCES
Adrian, W. T., Alviano, M., Calimeri, F., Cuteri, B., Do-
daro, C., Faber, W., Fuscà, D., Leone, N., Manna,
M., Perri, S., et al. (2018). The asp system dlv: ad-
vancements and applications. KI-Künstliche Intelli-
genz, 32(2-3):177–179.
Adrian, W. T., Bobek, S., Nalepa, G. J., Kaczor, K., and
Kluza, K. (2011). How to reason by heart in a se-
mantic knowledge-based wiki. In 2011 IEEE 23rd
International Conference on Tools with Artificial In-
telligence, pages 438–441. IEEE.
Adrian, W. T. and Manna, M. (2018). Navigating online
semantic resources for entity set expansion. In Proc.
of PADL’18, pages 170–185.
Ahmed, A., Al-Masri, N., Abu Sultan, Y. S., Akkila, A. N.,
Almasri, A., Mahmoud, A. Y., Zaqout, I. S., and Abu-
Naser, S. S. (2019). Knowledge-based systems survey.
Akerkar, R. and Sajja, P. (2009). Knowledge-based systems.
Jones & Bartlett Publishers.
Baader, F., Calvanese, D., McGuinness, D., Patel-
Schneider, P., Nardi, D., et al. (2003). The description
Extended Knowledge Graphs: A Conceptual Study
179

logic handbook: Theory, implementation and applica-
tions. Cambridge university press.
Brachman, R., Levesque, H., and Pagnucco, M. (2004).
Knowledge Representation and Reasoning. Morgan
Kaufmann.
Dudycz, H. (2017). Application of semantic network visu-
alization as a managerial support instrument in finan-
cial analyses. Online Journal of Applied Knowledge
Management A Publication of the International Insti-
tute for Applied Knowledge Management, 5(1).
Ehrlinger, L. and Wöß, W. (2016). Towards a definition
of knowledge graphs. SEMANTiCS (Posters, Demos,
SuCCESS), 48.
Eiter, T., Ianni, G., Krennwallner, T., and Polleres, A.
(2008). Rules and ontologies for the semantic web.
In Reasoning web, pages 1–53. Springer.
Fensel, D., ¸Sim¸sek, U., Angele, K., Huaman, E., Kärle, E.,
Panasiuk, O., Toma, I., Umbrich, J., and Wahler, A.
(2020). Knowledge Graphs. Springer.
Hogan, A., Blomqvist, E., Cochez, M., d’Amato, C.,
de Melo, G., Gutierrez, C., Gayo, J. E. L., Kirrane, S.,
Neumaier, S., Polleres, A., et al. (2020). Knowledge
graphs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.02320.
Horzyk, A. (2013). Artificial associative systems and as-
sociative artificial intelligence. EXIT, Warsaw, pages
1–276.
Janssens, L., De Smedt, J., and Vanthienen, J. (2016). Mod-
eling and enacting enterprise decisions. In Interna-
tional Conference on Advanced Information Systems
Engineering, pages 169–180. Springer.
Ji, S., Pan, S., Cambria, E., Marttinen, P., and Yu, P. S.
(2020). A survey on knowledge graphs: Represen-
tation, acquisition and applications. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2002.00388.
Ławrynowicz, A. (2017). Semantic data mining: an
ontology-based approach, volume 29. IOS Press.
Mineau, G. W. (1998). From actors to processes: The rep-
resentation of dynamic knowledge using conceptual
graphs. In International Conference on Conceptual
Structures, pages 65–79. Springer.
Nalepa, G. J. and Furma
´
nska, W. T. (2010a). Integration
proposal for description logic and attributive logic–
towards semantic web rules. In Transactions on
computational collective intelligence II, pages 1–23.
Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Nalepa, G. J. and Furma
´
nska, W. T. (2010b). Pellet-heart–
proposal of an architecture for ontology systems with
rules. In Annual Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
pages 143–150. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Negnevitsky, M. (2005). Artificial intelligence: a guide to
intelligent systems. Pearson education.
Noy, N., Gao, Y., Jain, A., Narayanan, A., Patterson, A., and
Taylor, J. (2019). Industry-scale knowledge graphs:
Lessons and challenges. Queue, 17(2):48–75.
OMG (2011). Business Process Model and Notation
(BPMN): Version 2.0 specification. Technical Report
formal/2011-01-03, Object Management Group.
OMG (2014). Decision model and notation. beta1. Tech-
nical Report dtc/2014-02-01, Object Management
Group.
Paulheim, H. (2017). Knowledge graph refinement: A sur-
vey of approaches and evaluation methods. Semantic
web, 8(3):489–508.
Rademakers, T. and van Liempd, R. (2012). Activiti in
Action: Executable business processes in BPMN 2.0.
Manning Publications.
Singhal, A. (2012). Introducing the knowledge graph:
things, not strings, may 2012. URL http://googleblog.
blogspot. ie/2012/05/introducing-knowledgegraph-
things-not. html.
Sowa, J. (1987). Encyclopedia of Artificial Intelligence,
chapter Semantic Networks. Wiley, New York. re-
vised and extended for the second edition, 1992.
Sowa, J. F. (1992). Conceptual graphs as a universal knowl-
edge representation. Computers & Mathematics with
Applications, 23(2-5):75–93.
Staab, S. and Studer, R. (2010). Handbook on ontologies.
Springer Science & Business Media.
Torsun, I. S. (1995). Foundations of intelligent knowledge-
based systems.
Uschold, M., Gruninger, M., et al. (1996). Ontologies: Prin-
ciples, methods and applications. Technical Report-
University of Edinburgh Artificial Intelligence Appli-
cations Institute AIAI TR.
van der Aalst, W. M. (2019). Modeling and reasoning over
declarative data-aware processes with object-centric
behavioral constraints. In Business Process Man-
agement: 17th International Conference, BPM 2019,
Vienna, Austria, September 1–6, 2019, Proceedings,
volume 11675, page 139. Springer.
Yahya, M., Barbosa, D., Berberich, K., Wang, Q., and
Weikum, G. (2016a). Relationship queries on ex-
tended knowledge graphs. In Proceedings of the Ninth
ACM International Conference on Web Search and
Data Mining, pages 605–614.
Yahya, M., Berberich, K., Ramanath, M., and Weikum, G.
(2016b). Exploratory querying of extended knowl-
edge graphs. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment,
9(13):1521–1524.
Yoo, S. and Jeong, O. (2020). Automating the expansion of
a knowledge graph. Expert Systems with Applications,
141:112965.
Zhang, Y., Sheng, M., Zhou, R., Wang, Y., Han, G., Zhang,
H., Xing, C., and Dong, J. (2020). Hkgb: An in-
clusive, extensible, intelligent, semi-auto-constructed
knowledge graph framework for healthcare with clini-
cians’ expertise incorporated. Information Processing
& Management, page 102324.
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
180
