
A Distributed Approach for Parsing Large-scale OWL Datasets
Heba Mohamed
1,2 a
, Said Fathalla
1,2 b
, Jens Lehmann
1,3 c
and Hajira Jabeen
4 d
1
Smart Data Analytics (SDA), University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany
2
Faculty of Science, University of Alexandria, Alexandria, Egypt
3
Fraunhofer IAIS, Dresden, Germany
4
Cluster of Excellence on Plant Sciences (CEPLAS), University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
Keywords:
In-memory Computing, Distributed Processing, Hadoop Streaming, Ontology Parsing, SANSA Framework,
Large-scale Datasets.
Abstract:
Ontologies are widely used in many diverse disciplines, including but not limited to biology, geology,
medicine, geography and scholarly communications. In order to understand the axiomatic structure of the
ontologies in OWL/XML syntax, an OWL/XML parser is needed. Several research efforts offer such parsers;
however, these parsers usually show severe limitations as the dataset size increases beyond a single machine’s
capabilities. To meet increasing data requirements, we present a novel approach, i.e., DistOWL, for parsing
large-scale OWL/XML datasets in a cost-effective and scalable manner. DistOWL is implemented using an in-
memory and distributed framework, i.e., Apache Spark. While the application of the parser is rather generic,
two use cases are presented for the usage of DistOWL. The Lehigh University Benchmark (LUBM) has been
used for the evaluation of DistOWL. The preliminary results show that DistOWL provides a linear scale-up
compared to prior centralized approaches.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the increasing interest in the semantic web and
knowledge graphs as well as the explosion of data
in almost all digital fields, the size and number on-
tologies are also increasing substantially. Ontolo-
gies enable the sharing and consensus of information
within a particular domain. Ontologies are being de-
veloped and used in many various domains such as bi-
ology (Smith et al., 2007), scholarly communication
(Fathalla et al., 2018; Fathalla et al., 2019), medicine
(Schriml et al., 2012), and geography (El Houby,
2015). Numerous machine learning algorithms deal
with the axiomatic structure of the ontology, such as
terminological decision trees (Fanizzi et al., 2010),
axiom-based inference (Lee and Shin, 1988), ontol-
ogy matching (F
¨
urst and Trichet, 2009), and many
others. In order to efficiently use these algorithms
over large scale ontologies at the axiom level, a dis-
tributed parser is required. Axioms are one of the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3146-1937
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2818-5890
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9108-4278
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1476-2121
main building blocks of an ontology that comprise
the overall theory that the ontology describes. Ax-
ioms are used for fixing the semantic interpretation of
the concepts and the relations of the ontology (F
¨
urst
and Trichet, 2005). The axiom-based representation
is more compact, efficient, and less error-prone. Be-
sides, the OWL 2 specification itself is defined at the
level of axioms (Horridge and Bechhofer, 2011), with
a mapping to triples specified separately.
Currently, a variety of tools (Bechhofer et al.,
2003; Knublauch et al., 2004) are designed to parse
OWL/XML ontologies . However, these tools lack the
ability to parse large-scale OWL/XML datasets. Such
tools have shown serious performance deficiencies
when the dataset size grows beyond the memory size
of a single machine; thus, this narrows down the us-
age of such tools to small- or medium-sized datasets
only. To the best of our knowledge, no existing tool
can parse axiom-based representation of large-scale
ontologies. To parse large-scale OWL/XML datasets,
distributed in-memory computing frameworks, e.g.,
Apache Spark
1
or Flink
2
can be used. These frame-
1
https://spark.apache.org/
2
https://flink.apache.org/
Mohamed, H., Fathalla, S., Lehmann, J. and Jabeen, H.
A Distributed Approach for Parsing Large-scale OWL Datasets.
DOI: 10.5220/0010138602270234
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2020) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 227-234
ISBN: 978-989-758-474-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
227

works are scalable and can run on a cluster of several
machines, i.e., the workload is spread across multi-
ple machines. Apache Spark has gained much at-
tention due to its efficiency in handling large-scale
datasets and scalability. The key abstraction offered
by Spark is the Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD),
which is a collection of elements partitioned across
the cluster nodes that can be executed in a paral-
lel and fault-tolerant manner (Zaharia et al., 2012).
There are many advantages of using RDDs, including
in-memory computation, fault tolerance, partitioning,
and persistence. In this paper, we introduce DistOWL
Parser, an OWL/XML parser for parsing large-scale
OWL/XML datasets that can be scaled out to a clus-
ter of multiple machines. The main contributions of
this work is summarized as follows:
• A novel approach for parsing large-scale
OWL/XML datasets,
• DistOWL - as an open-source implementation
using an in-memory and distributed framework,
Apache Spark,
• DistOWL is scalable in terms of data,
• DistOWL has been integrated into the SANSA
3
framework, and SANSA is being constantly main-
tained and uses the infrastructure of the commu-
nity, e.g., mailing list, website, etc.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: Section 2 describes the proposed approach.
Section 3 describes the implementation of DistOWL
parser. The experimental setup and discussion of
the results are presented in Section 4. Two use
cases are presented in Section 5. Section 6 gives
a brief overview of the related work on the existing
OWL/XML parsing systems. Finally, we conclude in
Section 7.
2 APPROACH
This section describes the strategies used and details
the tasks for parsing large-scale OWL/XML datasets.
DistOWL parser consists of three main phases: Pre-
processing, Schema parsing, and Instance parsing.
The preprocessing step is an optional step that can be
used to obtain the correct set of OWL axioms. A com-
prehensive discussion of each phase follows.
2.1 Pre-processing
In the beginning, while trying to directly parse the
ontology without preprocessing, dereferenceable URI
issues were observed (i.e., some of the resources’
3
http://sansa-stack.net/
URIs were not dereferenceable). This issue is han-
dled in the preprocessing step of the DistOWL parser.
Dereferenceable URIs. Considerable attention
must be paid to check the dereferenceability of the
URIs found in the ontology. To comply with the
Linked Data principles (Berners-Lee, 2006), and to
be able to provide further information about a re-
source via HTTP, the prefixes URIs should be valid
and dereferenceable. Therefore, in the preprocessing
step, we first check if the used prefixes are derefer-
enceable or not using VAPOUR
4
validator before ini-
tiating the parsing process.
2.2 Schema Parsing
In the second phase of DistOWL, the schema
records are parsed, i.e., the records start with
one of owl:Class, owl:ObjectProperty,
owl:DataTypeProperty, ... etc. Figure 1 il-
lustrates the main steps of schema parsing phase.
Schema parsing phase is made up of six steps as
explained below:
Step 1: OWL/XML Data Loading. Spark needs
OWL/XML data to be stored in a large-scale storage
system in order to read it efficiently. Hadoop Dis-
tributed File-System (HDFS) (Shvachko et al., 2010)
is used for data storage. The Hadoop Distributed File
System was designed to store and stream large-scale
data sets to user applications efficiently. HDFS splits
the data into separate blocks when the data is loaded
into HDFS. Then, it replicates and distributes the
blocks to various nodes in a cluster, allowing highly
efficient parallel processing and fault-tolerance.
Step 2: OWL/XML Data Splitting. First, we create
a Map to define each opening and closing tags of the
schema elements. The Map structure is Map[String
S1, Map[String S2, String S3]]. The first ele-
ment of the Map, i.e. S1, defines the type of the pattern
used, such as "versionPattern" which defines the
version of XML file, or "owlClassPattern" which
defines the OWL Class records, ... etc. The second
element of the Map, i.e., Map[String S2, String
S3], defines the opening and closing tags of each
schema record. For example, the opening tag of OWL
Class is "<owl:Class" and the closing tags can be
"</owl:Class>" or "/>". For instance, the Map rows
for OWL Class pattern are:
Map("owlClassPattern1"-> Map("beginTag"
->"<owl:Class","endTag"->"</owl:Class>"))
Map("owlClassPattern2"-> Map("beginTag"->
"<owl:Class","endTag"->"/>"))
Second, based on the created Map, Hadoop
4
http://linkeddata.uriburner.com:8000/vapour
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
228
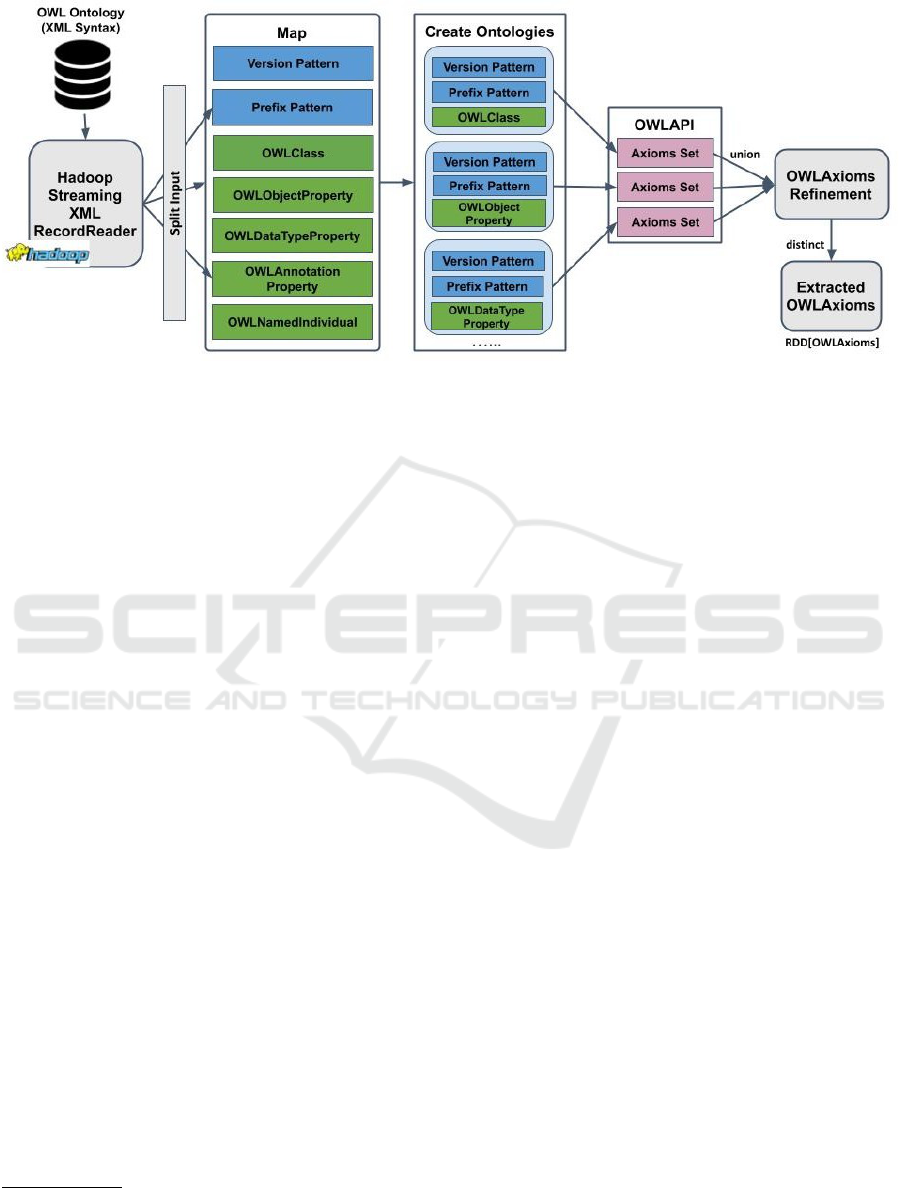
Figure 1: DistOWL Schema Parser Approach.
Streaming
5
is used for splitting the input ontology.
Hadoop streaming is a Hadoop distribution tool that
enables creating and running Map/Reduce jobs as a
mapper and/or reducer with any executable or script.
Step 3: Creating Ontologies using OWL API. Af-
ter splitting the schema records using the previ-
ous Map, OWL API
6
is used to construct short
ontologies and generate the corresponding OWL
Axioms
7
. The constructed ontologies comprise
version pattern (<?xml version= ...?>), prefix
pattern (<rdf:RDF xmlns= ...>) and one of the
OWL/XML records.
Step 4: Extracting OWL Axioms. In this step, OWL
API interfaces are used to get OWL Axioms cor-
responding to the created ontology from the previ-
ous step. Afterwards, the generated set of axioms
from each small ontology are combined together us-
ing union operation, to form the list of generated ax-
ioms.
Step 5: Refinement of incorrect Axioms. The
objective of the refinement process is to fix the
incorrect axioms generated. In this step, in-
correct axioms created from OWL API, such
as incorrect OWLDataPropertyDomainAxiom,
OWLSubDataPropertyAxiom, OWLAnnotation-
AssertionAxiom, are fixed. In the refinement
step, we observed that the axioms corresponding to,
for example, owl:Class, owl:equivalentClass
are correctly generated, but the axioms related to
OWLObjectProperty, OWLDataTypeProperty,
and OWLAnnotationProperty are occa-
sionally incorrectly generated. For exam-
ple, OWLSubObjectProperty is generated as
5
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/streaming
6
http://owlapi.sourceforge.net/
7
https://www.w3.org/TR/owl2-syntax/#Axioms
OWLSubAnnotationProperty.
In order to check if the incorrect parsed ax-
ioms contain one of the three aforementioned prop-
erties, join operation is invoked. To check if the
OWLAnnotation axiom contains one of the mentioned
properties, join operation will be used. However, Join
operation performs data shuffling, which produces
high data communication overhead. To avoid such
overhead, we broadcast the entire schema elements,
since the amount of schema data is rather small and
almost remains constant (Gu et al., 2015). Broadcast-
ing the schema elements avoids data shuffle over the
network and executes all the join operations locally.
This step returns the refined axioms RDD.
Step 6: Eliminating Duplicate Axioms. In this step,
we remove the duplicate axioms using distinct op-
eration over the resultant Spark RDD. These dupli-
cate axioms come from parsing the header of each
record with each line inside the OWL/XML opening
and ending tags.
2.3 Instance Parsing
After completing the schema parsing phase, the third
phase starts, in which the instance records are parsed.
We encountered the following two cases when parsing
instance records: Case 1: If the instance records are
declared inside one of the schema records, then they
will be parsed directly, and Case 2: If they are de-
clared outside the schema records, then all the steps
from phase two are executed to parse the instance
records with some changes. The change will be in
step 2 from phase 2 (i.e., schema parsing phase). The
Map is created from the parsed schema records, all
classes are extracted from which the instance map is
created along with the used prefixes. For example, the
map row for the University OWL Class from LUBM
A Distributed Approach for Parsing Large-scale OWL Datasets
229

benchmark
8
is
Map("instancePattern1"->
Map("beginTag"-> "<ub:University",
"endTag"->"</ub:University>"))
Next, we carry out all the steps (i.e., Step 3 to 6)
from schema parsing phase to complete instance pars-
ing.
3 IMPLEMENTATION
This section explains the implementation of the pro-
posed DistOWL framework. All phases of DistOWL
parser have been implemented using Apache Spark.
Scala
9
programming language API has been used to
provide a distributed implementation of the proposed
approach.
In algorithm 1, the DistOWL parses the schema
records (as constructed from Step 2 in section 2),
which is in tuple form. Lines (2-4) select the XML
version, prefixes list, and the OWL schema records
from the input tuple, respectively. OWL schema
records are transformed by mapping from OWL/XML
record to its corresponding set of OWL Axioms using
makeAxiom method. Afterward, empty axioms are
removed using RDD filter transformation (lines 5-6).
Line 7 converts the list of parsed axioms to RDD of
OWL axioms. At line 8, the data is persisted in mem-
ory. This operation speeds up further computation
by ten times. After that, we perform the refinement
phase in which we check if the axioms are parsed cor-
rectly (line 9). Algorithm 2 describes the main steps
of the refinement algorithm. Finally, before returning
the parsed axioms, we apply distinct() transformation
to eliminate duplicated axioms (line 10), in which the
degree of parallelism is passed. If the degree of paral-
lelism is not set to be highly enough for any process,
clusters would not be completely available. The de-
gree of parallelism is specified based on the number
of the cores in the cluster.
The refinement algorithm (i.e., Algorithm 2)
takes the initially parsed axioms RDD (schema
or instances RDD). Lines (2–4) extract the data,
object, and annotation properties from the input
RDD, respectively. Subsequently, broadcast the
aforementioned properties (lines 5–7). To refine the
input RDD, refineAxiom function is called using the
broadcasted properties. In the refineAxiom function,
the axiom type is obtained using getAxiomType
method (line 11). Afterwards, based on the type
of the axiom (OWLAnnotationPropertyDomain,
8
http://swat.cse.lehigh.edu/projects/lubm/
9
https://www.scala-lang.org/
Algorithm 1: DistOWL Schema Parsing.
Input : spark: Spark Session,
filePath: Path to OWL dataset,
recordsRDD: tuple of (RDD[String],
RDD[String], RDD[String])
Output: rdd: RDD[OWLAxiom]
1 begin
2 val xmlVersion = recordsRDD. 1.first()
3 val prefix = recordsRDD. 2.first()
4 val exprRDD = recordsRDD. 3
5 val ex2Axiom =
exprRDD.map(exprRecord⇒ makeAxiom
(xmlVersion, prefix, exprRecord))
6 .filter( != NULL)
7 val schemaRDD = ex2Axiom.flatMap(ex
⇒ ex.toList)
8 schemaRDD.persist()
9 val rdd = refineAxioms(schemaRDD)
10 rdd.distinct(parallelism)
11 return rdd
12 end
OWLSubAnnotationPropertyOf, or OWLAnnota-
tionAssertion), the suitable function is selected to
refine the incorrect axiom (lines 12-17). Finally, the
refined RDD is returned (Line 18).
4 EVALUATION
In this section, we describe the evaluation of the pro-
posed DistOWL parser. The evaluation procedure
consists of two tasks:
1. Data Scalability: In this part, we address
two scalability questions (SQ); SQ1) How does
the proposed DistOWL parser scale to larger
datasets? and SQ2) What is the speedup factor
with respect to the number of workers in the clus-
ter mode? and
2. Flexibility: In this part, we address the follow-
ing flexibility question (FQ); How does DistOWL
process different datasets?
First, we start with the experimental setup, in
which we explain in details the system configuration,
and the used benchmark. Afterwards, the results and
discussion are presented in detail.
4.1 Experimental Setup
System Configuration. All distributed experiments
ran on a cluster with four nodes. Among these nodes,
one is reserved to act as the master, and three nodes
used as computing workers. Each node has AMD
Opteron 2.3 GHz processors (64 Cores), 250.9 GB
memory, and the configured capacity is 1.7 TB. The
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
230
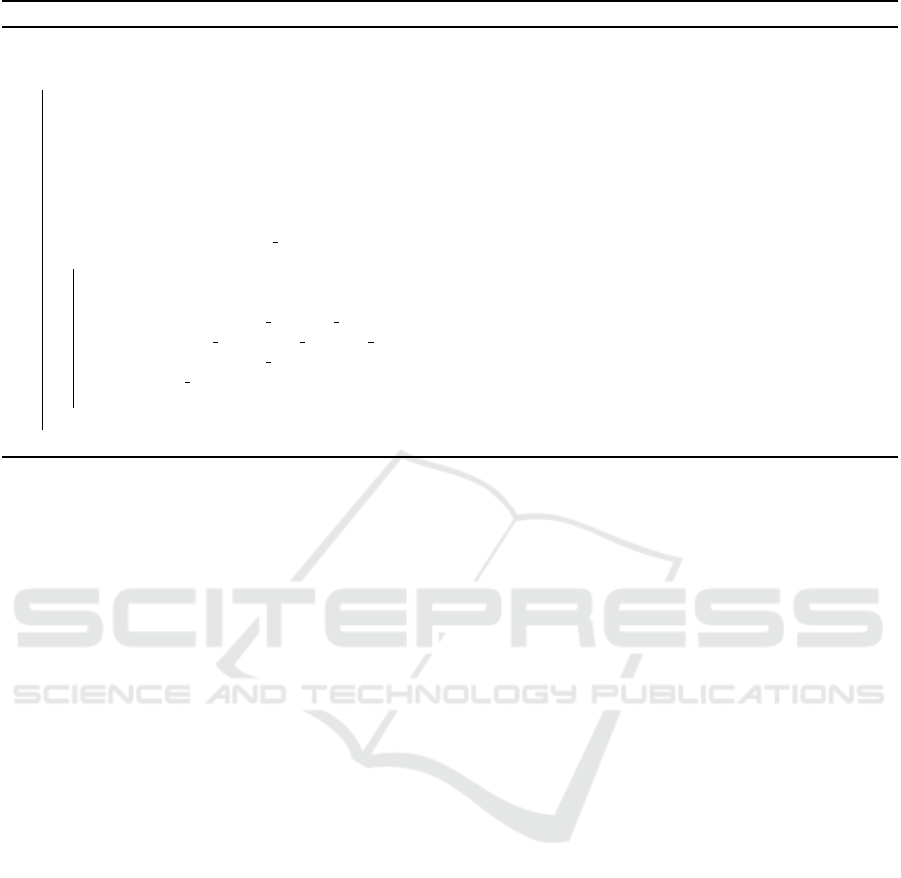
Algorithm 2: Axioms Refinement Algorithm.
Input : rdd: schema or instance RDD
Output: refinedRDD: RDD[OWLAxiom]
1 begin
2 val dataProp = getDataProperties(rdd)
3 val objectProp = getObjectProperties(rdd)
4 val annotationProp = getAnnotationProperties(rdd)
5 val dataBC = sc.broadcast(dataProp.collect())
6 val objectBC = sc.broadcast(objectProp.collect())
7 val annotationBC = sc.broadcast(annotationProp.collect())
8 val refinedRDD = rdd.map(a ⇒ refineAxiom(a, dataBC, objBC, annBC)))
9 .filter( != null)
10 Function refineAxiom(axiom, dataBC, objectBC, annotationBC):OWLAxiom
11 val T = axiom.getAxiomType
12 val refinedAxiom = T match
13 case Annotation Property Domain ⇒ fixPropertyDomain(axiom, dataBC, objectBC)
14 case Sub Annotation Property Of ⇒ fixSubProperty(axiom, dataBC, objectBC)
15 case Annotation Assertion ⇒ fixPropertyAssertion(axiom, dataBC, objectBC, annotationBC)
16 case ⇒ axiom
17 return refinedAxiom
18 return refinedRDD
19 end
nodes are connected with 1 Gb/s Ethernet. Also,
Spark v2.4.4 and Hadoop v2.8.1 with Java 1.8.0 is in-
stalled on this cluster. Local-mode experiments are
all carried out on a single cluster instance. OWL API
version 5.1.12 is used for generating ontologies. All
distributed experiments run three times, and the aver-
age execution time is reported in the results.
Benchmark. Lehigh University (LUBM) (Guo
et al., 2005) synthetic benchmark has been used for
the experiment. For Semantic Web repositories eval-
uation, LUBM is a widely used benchmark to eval-
uate the performance of those repositories concern-
ing extensional queries over a large data set. LUBM
generator generates many A-Box axioms but no T-
Box axioms. We use the LUBM data generator in
our experiment to generate eight datasets of different
sizes: LUBM-5, LUBM-10, LUBM-20, LUBM-50,
LUBM-100, LUBM-150, LUBM-200, and LUBM-
500. The numbers attached to the benchmark name
is the number of generated universities.
4.2 Results and Discussion
We evaluate our approach using the previously men-
tioned datasets for analysing the performance as well
as the scalability of DistOWL against OWL API. Two
sets of experiments were performed. In Experiment
1, against the centralized OWL API, we measure the
loading and execution time of DistOWL, while in Ex-
periment 2, we evaluate the scalability performance
in the cluster.
Experiment 1: Performance Evaluation on Large-
scale OWL/XML Datasets. In the beginning, the
evaluation is built up by measuring the execution time
of the distributed implementation of DistOWL com-
pared to OWL API. Then, the evaluation was carried
out in a local environment (a single machine) and in
the cluster environment with tuning spark jobs. Ta-
ble 1 illustrates the performance of OWL API against
DistOWL on eight generated datasets (Fail indicates
out of memory exceptions). We observed that OWL
API was able only to load and parse datasets of size
less than 1 GB, i.e., it fails if the size exceeds this
limit. On the other hand, DistOWL can load and com-
pletely parse all datasets used in our evaluation in a
reasonable time (see Table 1). The size (in GB) and
the number of generated axioms of LUBM bench-
mark datasets are listed in Table 1. Figure 2 shows
the speedup performance of the proposed DistOWL
for local (i.e., only one machine with the same con-
figurations) and cluster environments, respectively.
The maximum speedup ratio is 9.2x, and the average
speedup ratio is 5.8x. For instance, the execution time
in local mode for LUBM-150 is 15.2 minutes, while
in cluster mode is 2.9 minutes, which speeds-up the
time by a factor of 5.3.
Experiment 2: Scalability Performance Analysis.
In this experiment, a data scalability experiment has
been carried out to evaluate the effectiveness of Dis-
tOWL. We evaluate the execution time of our dis-
tributed approach with different data sizes in local and
cluster modes. The results of the experiment are pre-
sented in, Figure 2 and Figure 3.
Data Scalability. In this experiment, we measure
the performance of DistOWL with the growing size
of the datasets. We keep the number of nodes con-
A Distributed Approach for Parsing Large-scale OWL Datasets
231
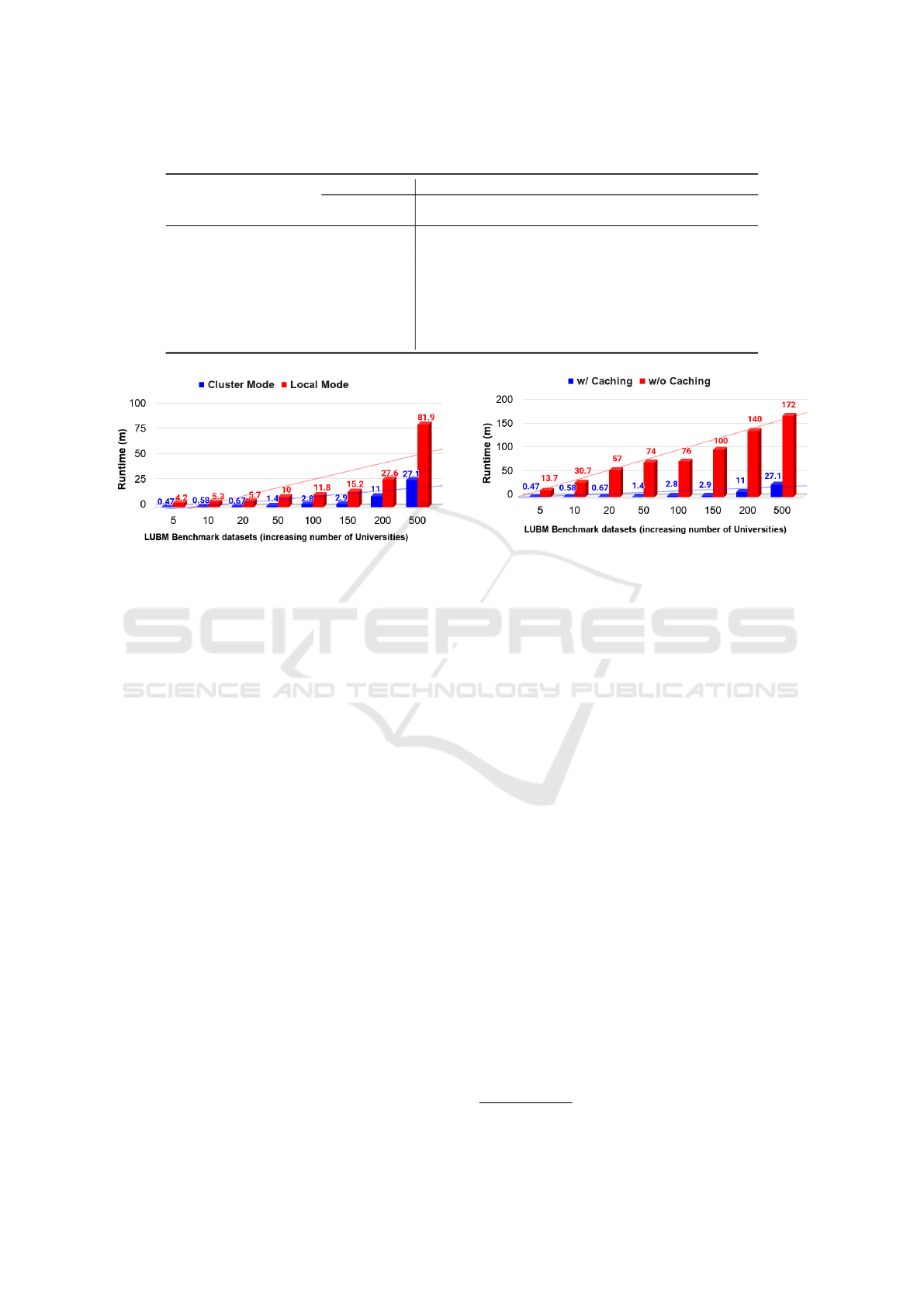
Table 1: Performance evaluation for LUBM benchmark datasets for both OWL API and DistOWL parser (OWL/XML format).
OWL API DistOWL
Dataset Size
(GB)
Execution
Time(s)
Load
Time(s)
Execution
Time(s)
#Axioms Speedup
LUBM-5 0.05 42 2 28.2 624,771 8.9x
LUBM-10 0.11 49 9 35.3 1,272,809 9.2x
LUBM-20 0.25 88 10 39.6 2,688,270 8.5x
LUBM-50 0.56 217 17 82 6,654,756 7.2x
LUBM-100 1.1 Fail 39 172 13,405,526 4.2x
LUBM-150 1.7 Fail 67 175.3 19,946,220 5.3x
LUBM-200 2.2 Fail 88 538 26,921,986 2.5x
LUBM-500 5.6 Fail 244 1625 54,468,672 3.2x
Figure 2: Speedup performance evaluation of DistOWL
parser in cluster and local environments.
stant at four and increase the size of datasets to mea-
sure whether the proposed approach can accommo-
date larger datasets. To measure data scalability for
DistOWL parser, we run the experiments on eight dif-
ferent sizes of the LUBM benchmark. We start by
generating a dataset of 5 universities (LUBM-5), then
we double the number of universities iteratively. Fig-
ure 2 illustrates the performance gained from execut-
ing DistOWL in a cluster environment with multiple
machines (four machines). The x-axis represents the
generated LUBM datasets with doubling the number
of universities (i.e., scaling up the size), while the y-
axis represents the execution time in minutes. For
example, consider the LUBM-500 dataset, the exe-
cution time decreased from 81.9 minutes in a sin-
gle machine environment (local) down to 27.1 min-
utes in multiple machines environment (cluster). The
observed decrease in time can be interpreted as a re-
sult of distributing the computation between multiple
machines. Using cluster mode speeds up the perfor-
mance by three times for LUBM-500, which answers
SQ2.
Figure 3 reports the run time of the proposed dis-
tributed algorithm on each dataset with and without
caching. Caching the data into memory accelerates
the computations. In Figure 3, there is a notice-
able decrease in the execution time between DistOWL
with caching (red columns) and without caching (blue
columns). Persisting the data in memory gain the ad-
Figure 3: Sizeup performance evaluation of DistOWL
parser.
vantage of in-memory computations. For more il-
lustration, DistOWL ran for 172 minutes with the
LUBM-500 dataset without caching, while the time
decreased to 27.1 minutes after the caching was trig-
gered. It is apparent that the execution time increases
linearly as the scale of the dataset expands. As pre-
dicted, as long as the data fits in memory, the execu-
tion time remains near-constant. Spark comes with
the performance advantage of using in-memory data
storage. Utilization of in-memory data storage leads
to a reduction of the overall time spent in network
communication and data read/write using disk-based
approaches. The results show that our algorithm is
scalable in terms of size, which answers SQ1 and FQ.
5 USE CASES
DistOWL parser is a generic framework for parsing
any OWL data presented in XML format. In this
section, we present two use cases for our parser.
SANSA-Stack: DistOWL has been successfully
integrated into Scalable Semantic Analytics Stack
(SANSA-Stack) framework (Lehmann et al., 2017).
SANSA is an open source
10
large-scale processing
engine for efficient processing of large-scale RDF
datasets. The need for utilizing fault-tolerant big
10
https://github.com/SANSA-Stack
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
232

data frameworks, such as Apache Spark and Flink,
is raised to process this massive amount of data ef-
ficiently. SANSA is built on top of Spark, offer-
ing a set of facilities for the representation (RDF
and OWL), querying, and inference of semantic data.
Currently, SANSA-OWL
11
layer can parse ontologies
only in Functional and Manchester Syntax to generate
OWL expressions (RDD[String]) and OWL axioms
(RDD[OWLAxiom]). Some of the machine learning al-
gorithms in the inference and machine learning layers
are built on top of axioms level. Therefore, we inte-
grated DistOWL into the SANSA framework in order
to support the SANSA-OWL layer, thus widening the
scope to parse more large-scale ontologies.
Bio2Vec
12
: Bio2Vec is a life science project
that extensively uses Gene Ontology (GO)
13
, that is
the largest source of information on gene functions
found in the literature. This ontology is both human-
readable and machine-readable and is a basis for the-
oretical analysis of studies in biomedical research in-
volving large-scale molecular biology and genetics.
We parsed both go
14
ontology, which contains the
core GO ontology in OWL format, and go-plus
15
on-
tology, which is the fully axiomatised version of the
GO. DistOWL has parsed the go-plus ontology within
765 seconds and generates 601,235 total axioms on a
cluster with four nodes.
Benchmarking: The University Ontology
Benchmark (UOBM)
16
extends LUBM (Guo et al.,
2005) with further OWL language constructs and can
generate more realistic datasets. UOBM includes
both OWL Lite and OWL DL ontologies covering
a complete set of OWL 2 constructs. UOBM gen-
erates three different data sets: one, five, and ten
universities. DistOWL has parsed UOBM benchmark
with ten universities within 13 seconds and generates
1,475,833 total axioms on a cluster with four nodes.
The combination of DistOWL and UOBM can be
used to validate the scalability of ontology analysis
approaches.
6 RELATED WORK
We provide a summary of the work related to OWL
dataset parsing. Despite this interest, no tool, to
the best of our knowledge, can parse such a massive
amount of OWL datasets. All the existing approaches
11
https://github.com/SANSA-Stack/SANSA-OWL
12
https://bio2vec.cbrc.kaust.edu.sa/
13
http://geneontology.org/
14
http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/go.owl
15
http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/go/extensions/go-plus.owl
16
https://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/isg/tools/UOBMGenerator/
use small to medium scale datasets and do not scale to
larger datasets. Prot
´
eg
´
e (Musen, 2015) is one of the
most well-known tools that help developers to con-
struct reusable ontologies and to build knowledge-
based systems. Prot
´
eg
´
e has become the most com-
monly used ontology construction and maintenance
technology. One of the biggest problems of Prot
´
eg
´
e
is its inability to load and parse large scale datasets.
The OWL API (Bechhofer et al., 2003) is a pro-
grammatic interface designed to access and manip-
ulate OWL ontologies it is available as open-source
(under LGPL license). The latest version of the API
is targeted at OWL 2 (Hitzler et al., 2009). OWL API
offers many features to handle different ontology syn-
tax. The API contains components for RDF/XML,
OWL/XML, Turtle, and OWL functional syntax pars-
ing and writing. Some services are implemented us-
ing the OWL API, such as syntax converter (Horridge
and Bechhofer, 2011), in which the loaded ontology
should be in one of the supported syntaxes. Subse-
quently, the ontology can be converted to a different
format, or directly getting the axioms presented in the
ontology. OWL API uses an in-memory representa-
tion; therefore, this limits the size of ontologies that
can be manipulated using the API.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presents a novel approach (DistOWL)
for parsing large-scale OWL datasets. DistOWL
is an open-source distributed framework for parsing
OWL/XML datasets in order to produce the corre-
sponding OWL axioms. The prominent feature of
DistOWL is the capability to parse large scale on-
tologies using an in-memory approach in a distributed
manner. The utilization of in-memory data stor-
age leads to a reduction of the overall time spent
in network communication and data read/write us-
ing disk-based approaches. Additionally, DistOWL
has been integrated into the SANSA framework for
wider reuse. We conducted two experiments for eval-
uating the performance as well as the data scalabil-
ity of DistOWL. The evaluation results show that the
proposed DistOWL can load and completely parse all
large datasets (up to 5.5GB) used in our evaluation
in a reasonable time, while OWL API fails when the
size exceeds 1 GB. Two use cases of DistOWL are
presented, i.e., SANSA and Bio2vec.
In future work, we are planning to further improve
DistOWL regarding time efficiency by persisting the
data into different storage levels. Furthermore, we are
going to evaluate our approach using larger datasets
A Distributed Approach for Parsing Large-scale OWL Datasets
233

and study the node scalability. A significant limita-
tion to overcome in the future is to handle imported
ontologies, since, at the moment, DistOWL lacks the
ability to parse the imported ontologies. Another di-
rection to extend DistOWL is to develop an algorithm
to convert the generated axioms to a complete ontol-
ogy with a different syntax.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by the following EU
Horizon2020 projects: LAMBDA project (GA no.
809965) and PLATOON project (GA no. 872592).
REFERENCES
Bechhofer, S., Volz, R., and Lord, P. (2003). Cooking the
semantic web with the owl api. In International Se-
mantic Web Conference, pages 659–675. Springer.
Berners-Lee, T. (2006). Linked data. Available at https:
//www.w3.org/DesignIssues/LinkedData.html.
El Houby, E. (2015). World geographical ontology
model. International Journal of Computer Applica-
tions, 120:25–33.
Fanizzi, N., d’Amato, C., and Esposito, F. (2010). Induc-
tion of concepts in web ontologies through termino-
logical decision trees. In Joint European Conference
on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in
Databases, pages 442–457. Springer.
Fathalla, S., Vahdati, S., Auer, S., and Lange, C. (2018).
Semsur: a core ontology for the semantic representa-
tion of research findings. Procedia Computer Science,
137:151–162.
Fathalla, S., Vahdati, S., Auer, S., and Lange, C. (2019).
The scientific events ontology of the openresearch.
org curation platform. In Proceedings of the 34th
ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing,
pages 2311–2313.
F
¨
urst, F. and Trichet, F. (2005). Axiom-based ontology
matching. In Proceedings of the 3rd international con-
ference on Knowledge capture, pages 195–196.
F
¨
urst, F. and Trichet, F. (2009). Axiom-based ontology
matching. Expert Systems, 26(2):218–246.
Gu, R., Wang, S., Wang, F., Yuan, C., and Huang, Y.
(2015). Cichlid: efficient large scale rdfs/owl reason-
ing with spark. In 2015 IEEE International Parallel
and Distributed Processing Symposium, pages 700–
709. IEEE.
Guo, Y., Pan, Z., and Heflin, J. (2005). Lubm: A bench-
mark for owl knowledge base systems. Web Seman-
tics: Science, Services and Agents on the World Wide
Web, 3(2-3):158–182.
Hitzler, P., Kr
¨
otzsch, M., Parsia, B., Patel-Schneider, P. F.,
Rudolph, S., et al. (2009). Owl 2 web ontology lan-
guage primer. W3C recommendation, 27(1):123.
Horridge, M. and Bechhofer, S. (2011). The owl api: A java
api for owl ontologies. Semantic Web, 2(1):11–21.
Knublauch, H., Fergerson, R. W., Noy, N. F., and Musen,
M. A. (2004). The prot
´
eg
´
e owl plugin: An open
development environment for semantic web applica-
tions. In International Semantic Web Conference,
pages 229–243. Springer.
Lee, S. and Shin, Y. G. (1988). Multi-agent Coopera-
tive Problem Solving and Learning with Axiom-based
Reasoning. Computer Research Institute, Department
of Computer Science, Department of . . . .
Lehmann, J., Sejdiu, G., B
¨
uhmann, L., Westphal, P.,
Stadler, C., Ermilov, I., Bin, S., Chakraborty, N.,
Saleem, M., Ngomo, A.-C. N., et al. (2017). Dis-
tributed semantic analytics using the sansa stack. In
International Semantic Web Conference, pages 147–
155. Springer.
Musen, M. (2015). The prot
´
eg
´
e project: A look back and
a look forward. AI Matters.Association of Computing
Machinery Specific Interest Group in Artificial Intelli-
gence, 1(4).
Schriml, L. M., Arze, C., Nadendla, S., Chang, Y.-W. W.,
Mazaitis, M., Felix, V., Feng, G., and Kibbe, W. A.
(2012). Disease ontology: a backbone for dis-
ease semantic integration. Nucleic acids research,
40(D1):D940–D946.
Shvachko, K., Kuang, H., Radia, S., Chansler, R., et al.
(2010). The hadoop distributed file system. In MSST,
volume 10, pages 1–10.
Smith, B., Ashburner, M., Rosse, C., Bard, J., Bug, W.,
Ceusters, W., Goldberg, L. J., Eilbeck, K., Ireland, A.,
Mungall, C. J., et al. (2007). The obo foundry: coor-
dinated evolution of ontologies to support biomedical
data integration. Nature biotechnology, 25(11):1251–
1255.
Zaharia, M., Chowdhury, M., Das, T., Dave, A., Ma, J.,
McCauley, M., Franklin, M. J., Shenker, S., and Sto-
ica, I. (2012). Resilient distributed datasets: A fault-
tolerant abstraction for in-memory cluster computing.
In Proceedings of the 9th USENIX conference on Net-
worked Systems Design and Implementation, pages 2–
2. USENIX Association.
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
234
