
Analysis of Data Anonymization Techniques
Joana Ferreira Marques
1a
and Jorge Bernardino
1,2 b
1
Polytechnic Institute of Coimbra, Coimbra Institute of Engineering, Rua Pedro Nunes, 3030-199 Coimbra, Portugal
2
CISUC - Centre of Informatics and Systems of University of Coimbra, Pinhal de Marrocos, 3030-290 Coimbra, Portugal
Keywords: GDPR, Personal Data, Anonymization, Pseudonymization, Re-identification, Anonymization Techniques,
Suppression, Noise Addition, K-Anonymity, L-Diversity, Re-identification Risks, Anonymization Tools.
Abstract: The privacy of personal data is a very important issue these days. How to process the data and use it for
analysis without compromising the individual’s identity is a critical task and must be done in order to ensure
the anonymity of this data. To try to unanimously unify this anonymity, laws and regulations such as GDPR
were created. In this paper, GDPR will be described and the concepts of anonymization and pseudonymization
will be explained. We present some of the main anonymization techniques and efficient software to support
the application of these techniques. The main objective is to understand which techniques offer a higher level
of anonymization, the strengths and weakness of each one and the advantages in its use.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the exponential growth of digital
information has increased more than expected with
technological development. Nowadays, about 53%
(ONU News, 2019) of the world population has
access to Internet and, for this reason, their personal
data is spread out and accessible. Now, a
technological area in great expansion, precisely due
to the large volume of data available, is the area of
data analysis.
What happens in large organizations and which
has also been growing in smaller ones is that they
carry out analyzes on their data in order to find
patterns, trends and customer profiles. This would not
be a problem if these data were processed internally
within the organization. But what is happening is that
a lot of data is sold to other organizations or made
available to the public for research purposes as a
consultation service. These personal data may contain
information that allows to identify the individual and
being made public may violate privacy. With this, a
very debated question has been how to maintain the
privacy of this data without rendering it useless for
analysis.
To answer this question, data protection laws and
regulations have emerged around the world, such as
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9175-4320
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9660-2011
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation , s.d.),
and with them the concept of data anonymization that
allows the removal of personal identity from data
through anonymization techniques. But can these
techniques be reversible? Will it be possible to
identify the individual again after its application?
What data should or should not be anonymized?
These are some of the questions that arise in this
research topic.
In this paper, the concepts involved in data
anonymization will be addressed, some of the
techniques used for this anonymization will be
studied, which are the risks of re-identification
associated and the analysys of some software tools
that allows to perform these techniques.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the concepts of GDPR,
anonymization and pseudonymization. In Section 3,
the main techniques used for anonymizing data are
presented. Section 4 report the risks associated with
the re-identification of each technique. Then, in
Section 5, some software is presented that allows
applying the techniques described in section 3.
Finally, section presents the conclusions of the study
and future work.
Marques, J. and Bernardino, J.
Analysis of Data Anonymization Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0010142302350241
In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2020) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 235-241
ISBN: 978-989-758-474-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
235
2 DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS
To better understand the framing of this topic, it is
necessary to clarify some of the concepts. In this
section, we give an understanding what the GDPR
consists of and what it means to anonymize data.
2.1 GDPR
The GDPR – General Data Protection Regulation – is
an official European regulation that aims to
harmonize privacy and data protection laws in all
member states. It has been applied since May 25th,
2018 (General Data Protection Regulation , s.d.). In
general, this regulation contains clauses and
requirements on how personal data and information
are treated and is applicable to all companies
operating in the European Economic Area, regardless
of their country of origin. It is also required that the
stored data must be anonymized or pseudonymised in
such a way that they do not allow to identify any
individual again.
2.2 Pseudonymization vs.
Anonymization
The GDPR has many requirements about how data is
treated and differentiates personal data from
anonymized and pseudonymised data.
Therefore, according to article 4 of the GDPR:
Personal data is “any information relating to an
identified or identifiable natural person (‘data
subject’);
Pseudonymised data is processed personal data
that can no longer be attributed to a specific holder
without the use of additional information;
Anonymized data is personal data treated in such
a way that it is impossible to re-identify or deduce
information about a specific individual.
So, if there is any way to identify the individual
data subject, the data were not anonymous but
pseudonymized.
Anonymization is important because these data
can be used for analysis by companies and does not
offer great risks to the data subject because, according
to Recital 26, “the principles of data protection should
therefore not apply to anonymous information,
namely information which does not relate to an
identified or identifiable natural person or to personal
data rendered anonymous in such a manner that the
data subject is not or no longer identifiable.” That is,
when a dataset is correctly anonymized, GDPR is no
longer applicable.
Thus, it is important to know the data
anonymization techniques and how they can be
applied.
3 DATA ANONYMIZATION
TECNHIQUES
In order to correctly choose the anonymization
techniques to be applied, we must understand what is
the purpose of this anonymization because the
different techniques have different characteristics and
may be more or less suitable for certain purposes. The
three most used ways to change data are to replace,
modify or remove an attribute or a record.
Note that it is important to be able to maintain the
usefulness of the data and at the same time respect the
privacy terms.
In this section, we describe some of the data
anonymization techniques and in what situations they
should be applied.
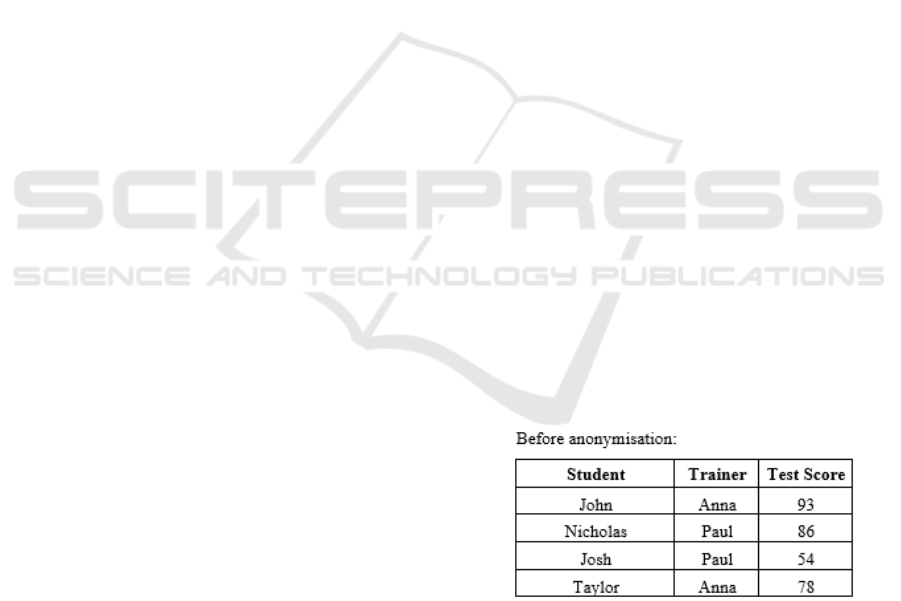
3.1 Remove Attributes (Suppression)
In this technique, an attribute is removed from the
dataset. This should happen whenever an attribute is
not relevant or necessary for analysis or whenever it
is impossible to anonymize it in any other way. In the
example given in the Guide to Basic Data
Anonymization Techniques (Personal Data
Protection Commission Singapore, 2018) for this
technique, in which it was intended to analyse
students’ grades in an assessment test, the dataset was
composed of three attributes: student name, trainer
and grade. Figure 1 shows an example of the original
dataset.
Figure 1: Suppression – Original dataset.
In order to anonymize the data, the attribute
“student name” was removed using the technique of
removing attributes, as we can see in the figure below.
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
236
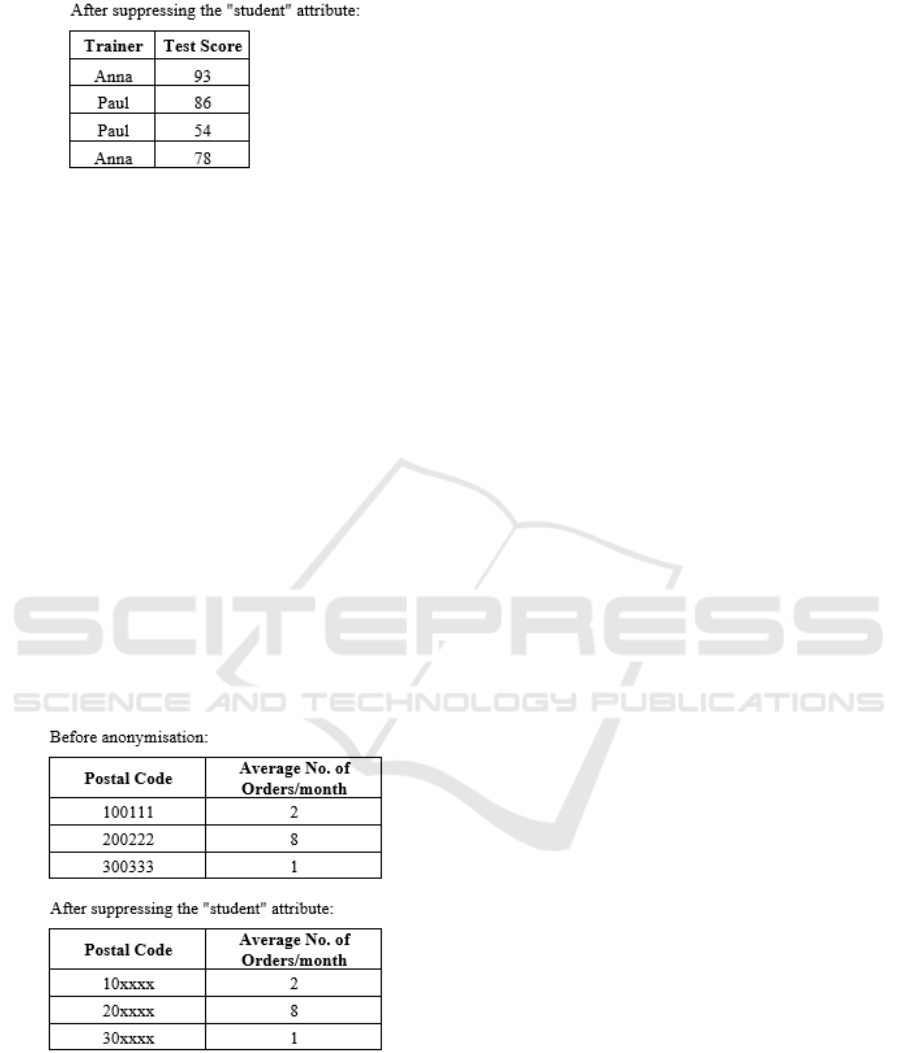
Figure 2: Suppression – Anonymized dataset.
Suppression can also occur for a complete dataset
record affecting several attributes.
The main advantage of this technique is that,
when permanently deleting an attribute or record, it
becomes impossible to retrieve the information.
3.2 Character Replacement
The substitution of characters consists of covering up
characters of an attribute or value of the data by
replacing those characters with a predefined symbol
(for example, by X or *). This substitution can be
partial, partially hiding a text or attribute, which may
be sufficient to anonymize its content.
Also, in the Guide to Basic Data Anonymization
Techniques (Personal Data Protection Commission
Singapore, 2018), an example can be found in which
to make an analysis of a dataset where the post code
was identified, the last 4 digits of the post code were
replaced by the character ‘X’. Figure 3 shows the
original dataset and the anonymized dataset.
Figure 3: Example of replacing characters.
3.3 Shuffling
In this technique, the data is randomly mixed or
reorganized and the values of the original attributes
remain in the dataset but can be associated with
another record. This technique can be used when it is
intended to analyse only one attribute and it is not
necessary to relate it to the others.
For example, if we want to analyse the amount of
sales in a given region, it is only necessary to use the
attribute ‘region’ and the permutation does not
influence the results because a certain region will
occur the same number of times before and after the
permutation.
However, this technique does not always provide
anonymization of the data and it may be possible to
reorganize it to its original form. Therefore, it must be
used in conjunction with other techniques.
3.4 Noise Addition
The addition of noise is one of the most used data
anonymization techniques, being applied by several
technological “giants” such as Google (Google, s.d.).
The technique is to slightly modify the attributes of
the dataset making them less accurate. An application
of this technique would be, for example, to add or
subtract days or months to a date.
Although this technique allows to hide the real
values, it is necessary to understand the level of noise
that must be applied in order to have little impact on
data analysis and individuals’ privacy.
3.5 Generalization
Generalization is another approach used by Google
(Google, s.d.) and consists of generalizing the
attributes in order to change the respective scale or
order of magnitude.
An example of this is to replace the “date”
attribute (day/month/year) with the “year” attribute,
removing the day and month.
Like the addition of noise, this approach may
prevent the individual from being identified, but it
may not result in effective anonymization.
There are two techniques that can be considered
generalization: K-Anonymity and L-Diversity,
described in the following subsections.
3.5.1 K-Anonymity
This technique consists of grouping the records of K
individuals into categories making them fall under the
same combinations. Thus, each record in the dataset “is
similar to at least K-1 other records” (El Emam, 2008).
For example, if the identifying attributes are age
and disease and K=3, the dataset anonymized by this
method will have at least 3 records for each
combination of the identifying attributes. Considering
the two individuals in the example illustrated in
Analysis of Data Anonymization Techniques
237
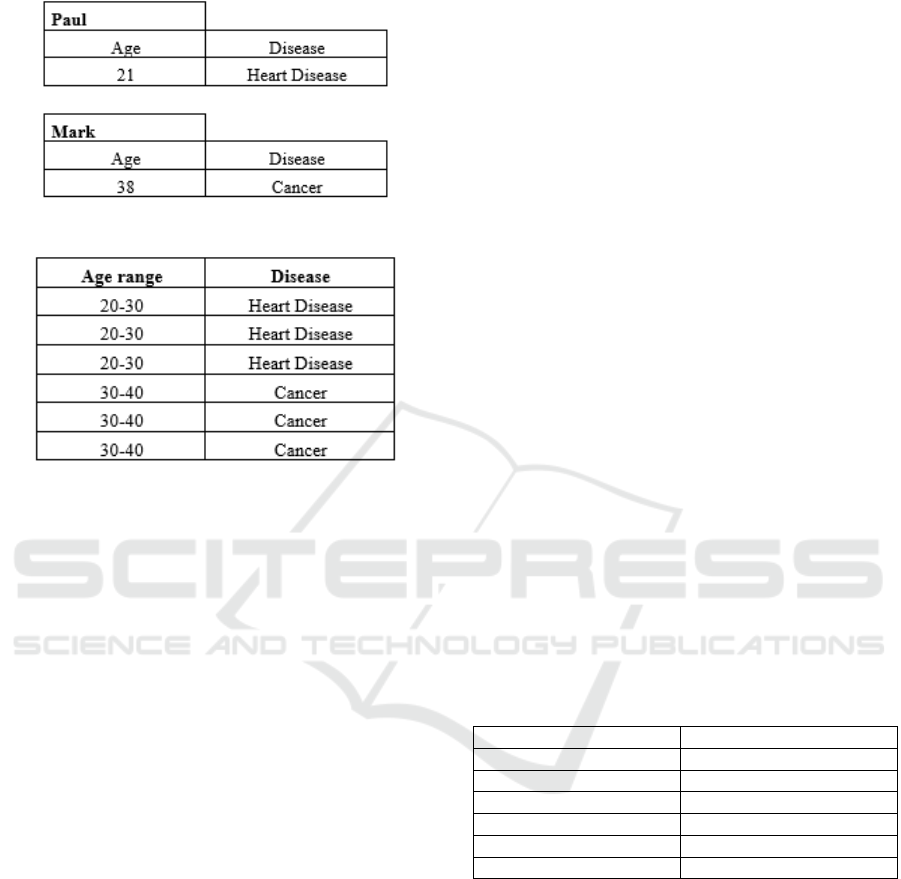
Figure 4, the result of k-anonymity with K=3 would
be the one illustrated in Figure 5.
Figure 4: K-Anonymity: original dataset.
Figure 5: K-Anonymity: original dataset.
After the application of K-Anonymity, the
probability of identifying an individual is equal to or
less than 1/K. Therefore, the higher the K, the lower
the probability of identification.
3.5.2 L-Diversity
Based on Machanavajjhala et al. (2007), L-Diversity
is an evolution of K-Anonymity in which at least L
distinct values must exist for each equivalent group
and sensitive attribute (identifier). That is, it is
guaranteed that in each equivalent group each
attribute has at least L different values.
The objective of this technique is to limit the
occurrence of equivalence classes with low
variability of the attribute. Thus, an intruder who has
access to data for specific individual always remains
with a degree of uncertainty.
However, this technique is susceptible to attacks
of probabilistic inference.
4 RE-IDENTIFICATION RISKS
In anonymization processes where it is crucial to
maintain data privacy, there is always a need to assess
the risks of re-identification.
There are three types of risks that should be
managed (CHEO Research Institute, s.d.):
Prosecutor Risk: re-identifying a record knowing
that the individual exists in the dataset;
Journalist Risk: re-identifying a record without
being sure that the individual exists in the dataset;
Marketer Risk: re-identifying large volumes of
records.
When the risk of re-identification is measured, the
following conditions are valid (CHEO Research
Institute, s.d.):
The prosecutor risk will be equal to or larger than
journalist risk;
Journalist risk will be equal to or larger than
marketer risk;
Prosecutor risk will be equal to or larger than
marketer risk.
Risk estimates are calculated assuming that a
potential attacker has access to only the dataset
available. These results are usually presented for each
type of risk using indicators that show the percentage
of records at risk, highest risk and success rate. In the
case of marketer risk, only the success rate is
calculated.
Each company is responsible for establishing the
risk limit for re-identification that it is willing to
accept and is responsible for assessing the risk
associated with the processing of personal data.
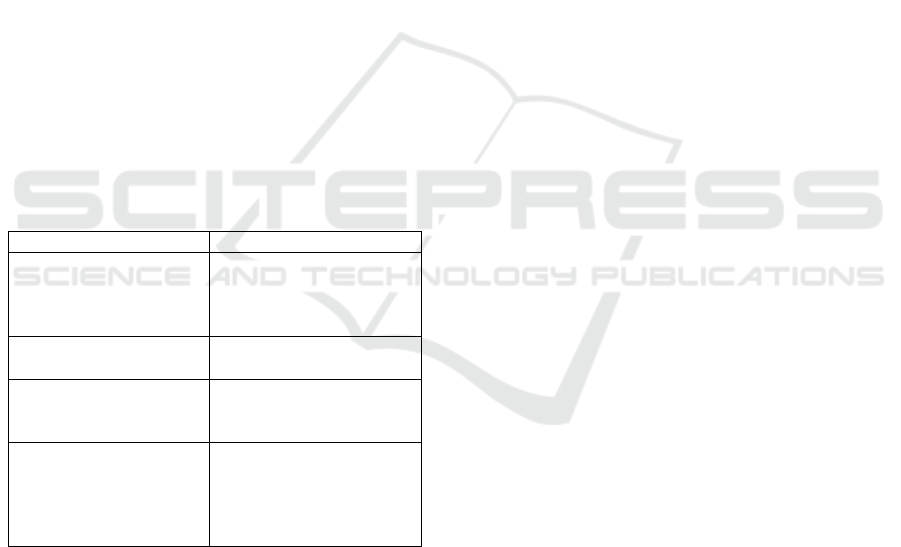
In the Table 1, the anonymization techniques
presented above are identified and those that allow or
can easily allow re-identifying an individual through
the dataset.
Table 1: Risk of re-identification for each technique.
Technique Allows re-identification?
Suppression No
Character replacement Yes
Shuffling Yes
Noise Addition Yes
K-Anonymity No (minimum)
L-Diversity No
In the next section, some software is presented for
the application of anonymization techniques and that
perform the risk analysis.
5 DATA ANONYMIZATION
TOOLS
As mentioned earlier, there is anonymization
software that allows to systematically apply the
techniques described.
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
238
Based on the work developed in 2014 by Bergeat
et al. (Maxime Bergeat, 2014) and in 2017 by Pinho
(Pinho, 2017), software for these purposes are
presented below.
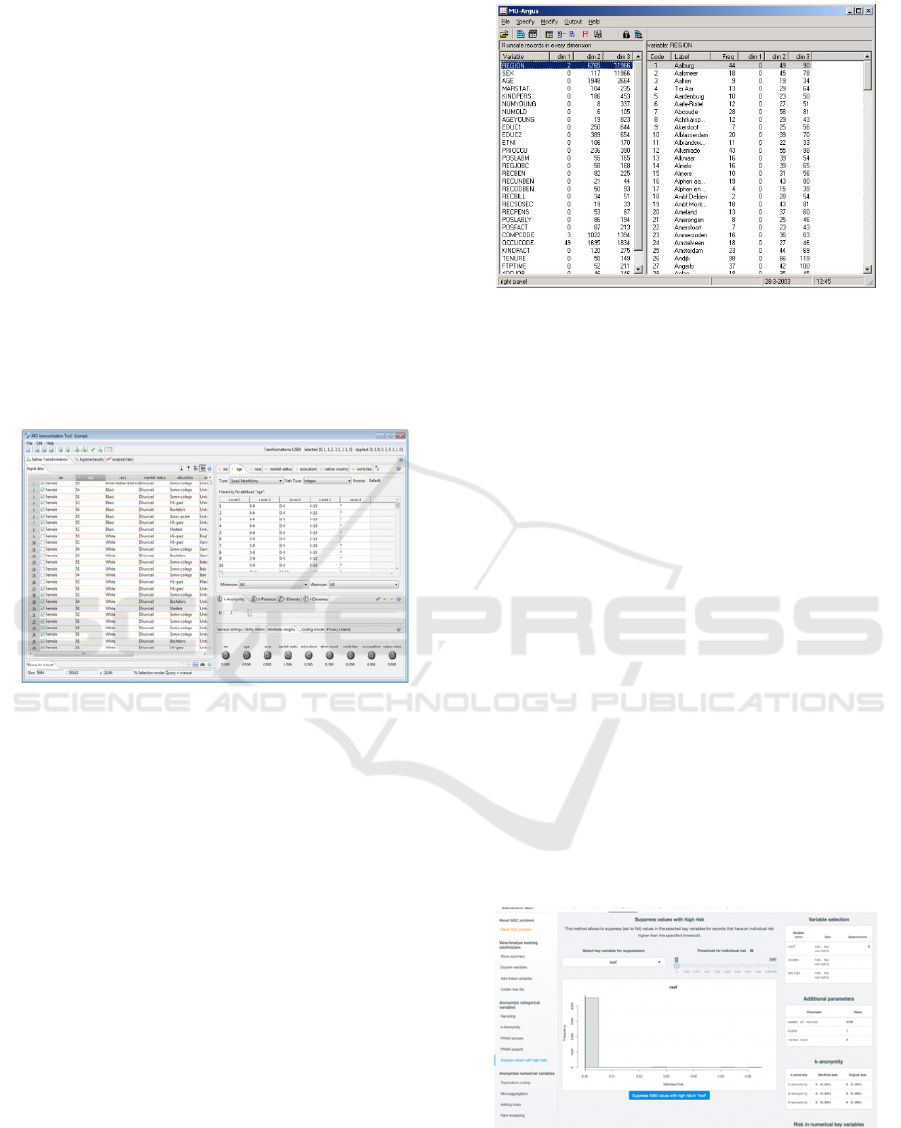
5.1 ARX
ARX is an open source framework developed in Java
(ARX, s.d.). It allows to implement several of the
techniques described, such as K-Anonymity and L-
Diversity, and also to implement a set of metrics to
assess the loss of information.
This software has a graphical tool with a simple
and intuitive interface, shown in Figure 6, which
supports the import and cleaning of data, wizards for
creating transformation rules, intuitive ways to adapt
the anonymized dataset to the requirements and
visualizations of risks and re-identification.
Source: https://arx.deidentifier.org/overview/
Figure 6: ARX Interface.
ARX is also available as a library with an API that
provides data anonymization capabilities for any Java
program. ARX is compatible with SQL databases,
Microsoft Excel and CSV files.
Succinctly, to perform anonymization, we start by
importing the dataset, defining the indicators and
sensitive variables and defining the generalization
hierarchies. At the end, the transformations are
extracted.
5.2 µ-Argus
Argus stands for ‘Anti Re-identification General
Utility System’ and is a software developed to create
safe microdata files (MU-Argus, s.d.). It is based on
R programming language and uses different statistical
methods of anonymization such as noise addition and
suppression. It can also be used to generate synthetic
data.
Its interface can be seen in Figure 7.
Source: https://aircloak.com/top-5-free-data-anonymization-tools/
Figure 7: µ-Argus Interface.
Anonymization steps involve defining sensitive
indicators and variables, estimating the risk of
disclosure and re-identification, implementing
methods that reduce this risk and exporting
microdata.
5.3 SDCMicro
SDCMicro is a free open source package for
researchers and public use (International Household
Survey Network, s.d.). Can be used to generate
anonymous data by creating files that can be used by
the public and scientific researchers.
This tool allows to apply various anonymization
techniques such as suppression, adding noise and
shuffling and includes functions to measure the risk
throughout the process.
It is provided as a user-friendly GUI in which
users unfamiliar with R can implement
anonymization methods. Supports the import and
export of microdata in various formats such as
STATA, SAS, SPSS, CSV and R.
Figure 8 shows its interface.
Source:
https://ihsn.org/software/disclosure-control-toolbox
Figure 8: SDCMicro Interface.
One of the advantages of this tool is that it
includes functions to measure, visualize and compare
Analysis of Data Anonymization Techniques
239
risk and utility during the anonymization process,
helping organizations to prepare reports.
5.4 Privacy Analytics Eclipse
According to the website itself (Privacy Analytics,
s.d.), this tool anonymizes data allowing it to maintain
its quality and preserve compliance with many data
privacy regulations, including GDPR. It also allows
to adopt HIPPA’s Expert Determination Method that
classifies data attributes. It works with large volumes
of data and, like the previous ones, offers re-
identification risk assessment. Supports data export in
CSV and ODS formats.
This tool is widely used in the healthcare area. Its
main advantage is that it is a fast and very precise
anonymization tool that guarantees compliance with
legal regulations. Anonymization techniques are
optimized based on measures of risk to patient
privacy.
5.5 Software vs Techniques
Table 2 shows the software listed above and which is
usually used for the application of the studied
techniques.
Table 2: Software vs Techniques.
Software/Tool Techniques
ARX
Generalization
K-Anonymity
L-Diversity
Suppression
µ-Argus
Noise Addition;
Suppression
SDCMicro
Noise Addition
Suppression
Shuffling
Privacy Analytics
Eclipse
Generalization
K-Anonymity
L-Diversity
Noise Addition
Shuffling
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Anonymization is an important issue that has been
increasingly demanding the attention of the
community. With the large volume of personal data
available for analysis and treatment there is a need to
ensure the privacy of individuals.
If, on the one hand, GDPR harmonises the level
of data protection, on the other hand, the fact that
there are defined rules, allows companies to carry out
more actions with the information, allowing them to
analyse and adopt the information to assist business
decisions.
There are several anonymization techniques, the
main ones being presented in this paper. Each
technique has advantages and weaknesses; however,
it is necessary to choose the appropriate technique for
the dataset to be worked on at the moment. Therefore,
anonymization techniques guarantee data privacy
when properly applied. In some specific situations, it
may be advantageous to apply several combined
techniques. In many cases, after applying
anonymization techniques to the dataset, it may be
possible, in some way, to infer information about an
individual, even if is not very accurate.
The need to implement and comply with the
defined standards, as in the GDPR, means that there
are several tools and software capable of assisting the
anonymization of data, in addition to those presented
in this article. For example, in (Privacy Analytics
Eclipse Alternatives & Competitors, s.d.) is a list of
20 alternative tools to Privacy Analytics Eclipse. In
general, all of them allow to apply more than one
anonymization technique and include features of risk
assessment of re-identification. Note that some of
them are specific to a purpose or to work with a
certain type of data.
As future work, we intend to test each of these
tools with real datasets and evaluate the
anonymization performance of each one.
REFERENCES
ARX. (n.d.). ARX - Data Anonymization Tool. Retrieved
from ARX DEIDENTIFIER:
https://arx.deidentifier.org/
CHEO Research Institute. (n.d.). What is the relashionship
between prosecutor, journalist, and marketer risk?
Retrieved from Electronic Health Information
Laboratory:
http://www.ehealthinformation.ca/faq/relationship-
prosecutor-journalist-marketer-risk/
El Emam, K. &. (2008). Protecting Privacy Using K-
Anonymity. Journal of the American Medical
Informatics Association, pp. 627-637.
General Data Protection Regulation . (n.d.). Retrieved
from Intersoft Consulting: https://gdpr-info.eu/
Google. (n.d.). How Google Anonymises Data. Retrieved
from Google Privacy&Terms: https://policies.google.
com/technologies/anonymization
International Household Survey Network. (n.d.). Statistical
Disclosure Control (sdcMicro). Retrieved from
KEOD 2020 - 12th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
240

International Household Survey Network:
https://ihsn.org/software/disclosure-control-toolbox
Machanavajjhala, A., Kifer, D., Gehrke, J., &
Venkitasubramaniam, a. M. (2007). L-diversity:
Privacy beyond k-anonymity. ACM Transactions on
Knowledge Discovery from Data, 24-24.
Maxime Bergeat, N. C.-B. (2014). A French
Anonymization Experiment with Health Data. Privacy
in Statistical Databases. Eivissa, Spain.
MU-Argus. (n.d.). Retrieved from
http://neon.vb.cbs.nl/casc/mu.htm
Personal Data Protection Commission Singapore. (2018,
January 25). Guide to Basic Daa Anonymisation
Techniques. pp. 12, 13.
Pinho, F. A. (2017). Anonimização de bases de dados
empresariais de acordo com a nova Regulamentação
Europeia de Proteção de Dados. pp. 39-41. Retrieved
from http://cracs.fc.up.pt/sites/default/files/MSI_
Dissertacao_FINAL.pdf
Privacy Analytics Eclipse Alternatives & Competitors.
(n.d.). Retrieved from G2: https://www.g2.com/
products/privacy-analytics-eclipse/competitors/
alternatives
Privacy Analytics. (n.d.). Eclipse Risk is your enterprise
anonymization solution. Retrieved from Eclipse Risk:
https://privacy-analytics.com/health-data-
privacy/health-data-software/eclipse-risk/
UN study reveals world has gender digital divide. (2019,
November 9). Retrieved from ONU News:
https://news.un.org/pt/story/2019/11/1693711
Analysis of Data Anonymization Techniques
241
