
Design of Waste Water Treatment Plant for Hospital
Nizar Kamil Perwira
1
, Kris Tri Basuki
1
, Nofriady Aziz
2
and Nuradam Effendy
3
1
Teknokimia Nuklir, Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi Nuklir STTN BATAN, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Pusat Teknologi Bahan Bakar Nuklir, Serpong, Indonesia
3
Pusat Reaktor Serba Guna, Serpong, Indonesia
Keywords: WWTP, Chlorination, Quality Standards.
Abstract: Many methods have been done to treat hospital waste water before it’s disposed into the environment because
it's containing high organic matters and chemical compounds so it's harmful for environment. In this research,
we designed Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) so the output will fulfil environmental quality standard
and can be disposed into the environment. The design of WWTP uses chemical and physical process to reduce
high chemical compounds and organic matters in hospital waste water. The purpose of this research is to
design WWTP in hospital, determine the output waste from WWTP and can be used as a basis in the
calculation of WWTP. The research method is to design WWTP and calculation result output of design
WWTP (Waste Water Treatment Plant). The WWTP design is consist of equalization bath, bath coagulation,
chlorination and sump. Based on the result, one of waste water of hospital in Indonesia with discharge is 60
m3/day, the result BOD is 44.87 mg/L, COD is 19.24 mg/L, and TSS is 56.68 mg/L. Waste water of hospital
processed from this WWTP can to be disposed into environment based on Minister of Health decree.
1 INTRODUCTION
Source of water pollution can be come from the
hospital. Sources of hospital wastewater can be
derived from bathrooms, kitchen rooms, the
examination rooms, laboratories, operating rooms
and other rooms containing hazardous materials and
germs. Various kinds of toxicities such as
pharmaceutical waste, radio-nuclides, solvents and
disinfectants for medical purposes with a high
concentration for laboratory activities. Hospital waste
as well as other waste containing organic and
inorganic materials, which the containing level can be
determined by testing waste water such as BOD,
COD, pH, microbiological, TSS and others. Water
waste from hospitals is one source of water pollution
potential because the hospital waste water is
containing organic compounds, chemical compounds
and pathogenic microorganisms that can cause
disease to the surrounding community. Pursuant to
Law No. 32 of 2009 in Indonesia about Protection and
Management of the Environment, an activity is
required to process and manage wastes produced by
its activities, in order to conserve the environmental
functions so the waste must be processed and managed
with the applicable quality standards. Kep-
MENLH/12/1995 concerning effluent quality
standards for hospital activities that requires every
hospital must treat wastewater to a permitted standard.
From the explanation above, those can be used as
a guide for the hospital to process and manage the
waste till get the environmental quality standards that
applicable. Hospitals need to build Wastewater
Treatment Plant to produce safe effluent which can be
disposed to the environment that passed the quality
standards. In this research, we make the WWTP so
that the result processed can be disposed into
environment. The main characteristics of the
hospital’s waste water is the content of coliform
bacteria, because it has very high value. In addition to
the high content of coliform bacteria, the
characteristics that is high of the waste water are
BOD, COD, and TSS. The objectives of this research
are to are to design WWTP in hospital, determine the
output waste from WWTP and can be used as a basis
in the calculation of WWTP.
2 BASIC THEORY
Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) is a structure
that is designed to dispose of biological and chemical
102
Perwira, N., Basuki, K., Aziz, N. and Effendy, N.
Design of Waste Water Treatment Plant for Hospital.
DOI: 10.5220/0010541700003108
In Proceedings of the 6th Food Ingredient Asia Conference (6th FiAC 2020) - Food Science, Nutrition and Health, pages 102-106
ISBN: 978-989-758-540-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

waste from the water thus allowing the water to be
reused at other activities. The main purpose of
wastewater treatment is to decompose the content of
pollutants in the water, especially organic
compounds, suspended solids, pathogens and organic
compounds that cannot be decomposed by
microorganisms found in nature. For treating
wastewater parameters, processing units that will be
applied consists of several treatment plant. Based on
the selection it has been done, then in WWTP will be
used unit - of processing unit as follows:
a. Equalisation
The use of equalization tank aims to generate a
uniform flow so that the processing units in the
installations be able to avoid shock loading. Form of
equalization tank that will be used are rectangular.
During the equalization stirring to prevent the
precipitation of solid and odor. Biological oxidation
due to the agitation in the tank, according to Metcalf
& Eddy (2004), can reduce the concentration of 10-
20% total COD, TDS and TSS by 15-20%.
b. Coagulation and Flocculation
In the process of coagulation and flocculation, the
water will be very role, because the chemical must be
mixed with water. Stirring / Agitation process will
very quickly and uniform dispersion of compounds in
water, the coagulation process occurs with rapid
stirring. In this case the process of coagulation and
flocculation chemical and physical reactions will
occur precipitation: Poly Aluminium Chloride. After
the formation of deposits caused by the large floc
settles, and this process occurs with slow stirring. A
fast stirrer is very important in the change of physical
factors as well as the efficiency of coagulant addition,
the flocculation is a method for taking particles and
highly dependent on particle size.
c. Sedimentation
Particles that are in the water may be eliminated in the
sedimentation vessel (Clarifier). In the sedimentation
tank types horizontal removed particles is dependent
upon over flow rate (Vo), in this type there are several
assumptions:
1. Particles and velocity vectors are distributed on a
cross-section of the tank, as a function of the inlet
zone.
2. Transfer the liquid will looking down on the length
of the tank.
3. Particles below will be removed from the tank.
d. Chlorination Tank
Chlorine is commonly used for disinfecting; the term
is usually used as a disinfectant is: Cl
2
; NaOCl or
CaOCl
2
. When chlorine is added to water, the mixture
Hipochlor (HOCl) and HCl will be formed by the
reaction:
Cl
2
(g) + H
2
O HOCl + H
+
+ Cl (1)
The above reaction depends on pH, when the pH ≈ 1
reaction will occur right and very sidikit Cl2 in a
solution. HOCl is a weak acid and dissociates at pH ≈
6, at a pH between 6 to 8.5 dissociation occurs to
HOCl.
HOCl =H
+
+ Cl pK = 7.537 at 25 ° C (2)
This chlorination with Cl2 generate HOCl at pH
between 4 - 6. Below pH = 1 then it will be left to
form Cl2 HOCl. While salt dissociates hypoklorida
such as:
NaOCl === Na
+
+ OCl
-
(3)
Ca(OCL)
2
=== Ca
2+
+ 2. OCl
-
(4)
The presence of chlorine will tend to lower the pH,
every mg / L of chlorine that is added will reduce
hardness of 1.4 mg / L (equivalent to the
concentration of CaCO3). Disinfectants will be well
on the pH interval 6.5 - 7.5. Chlorine reacts with
water to produce chlorine acts as an "oxidizing" very
destructive of the organism.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Study of Literature
Overview and Hospital Waste, Technique
Wastewater Treatment and Design Options WWTP.
3.2 Data Collection
Wastewater discharge and the characteristics of the
hospital.
3.3 Data Processing
The calculation of hospital waste, Determination of
the quality standard as the basis of design, and
Calculation of Dimension WWTP earned by each
process.
3.4 Data Processing and Conclusion
Calculation of Dimension WWTP, The calculation of
the final result output WWTP design results and
Conclusion.
Design of Waste Water Treatment Plant for Hospital
103

4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In this planning, hospital waste flow of water
obtained as follows: 28 m3 / day. It refers of literature,
including the text book Decentralised Wastewater
Treatment in Developing Countries and Treatment
and Reuse Fourth Edition by Metcalf and Eddy both
in obtaining design criteria of planning and
calculating the dimensions of the WWTP:
1. Equalization Tank.
The use of equalization tank aims to generate a
uniform flow so that the processing units in the
installations be able to avoid shock loading. Form of
equalization tank that will be used are rectangular.
During the equalization stirring to prevent the
precipitation of solid and odor. Biological oxidation
due to the agitation in the tank, according to Metcalf
& Eddy (2004). After doing calculation, it will be
shown at Table 1:
Table 1: Design Equalization from WWTP Hospital.
2. Coagulation and Flocculation.
In the process of coagulation and flocculation, the
water will be very role, because the chemical must be
mixed with water so that the process will very quickly
and uniform dispersion of compounds in water, the
coagulation process occurs with rapid stirring. In this
process of coagulation and flocculation, coagulant
Poly Aluminium Chloride will be used.
Concentration of PAC : 80 ppm
Diameter Stirrer : 0,26 m
Flow rate PAC : 0,2 kg/d
Solution PAC : 5%
Flow rate water : 3,8 kg/d
Total volume : 1,76 m
3
After doing calculation, it will be shown at Table 2:
Table 2: Design Coagulation and Floculation from WWTP
Hospital.
3. Sedimentation.
Over Flow Rate : 30 m
3
/hari.m
2
Number of Weir Loading : 1
Weir Loading : 150 m
3
/day.m
Scour Velocity :12,53cm/s
Horizontal Velocity : 0,83 cm/s
The slope of the Wall Channels : 0,00097
After doing calculation, it will b shown at Table 3:
Table 3: Design Sedimentation from WWTP Hospital.
4. Chlorination.
Debit (Q) = 0.138 L / dt
*The planned concentration = 4%
Chlorine that is used contains = 60% Chlorine
(Solution)
Chlorine density = 1.2 kg/L
Capacity affixing maximum = 600 cc / min
Chlorine binding force = 1.18 mg/L DPC
Residual chlorine planned = 0.4 mg / L
*Efficiency = 65%
Dose Chlorine = DPC + Time chlorine =
1.18 mg / L + 0.4 mg / L = 1.58 mg / L
Requirement for 2.5 hours = 0.00327 kg
*Chlorination basin capacity = 1,242 m3
After the chlorination process, the treated water
supplied to the sump. As for the design of a tank
shown in Table 5. The calculation can be shown at
Table 4:
Table 4: Design Chlorination from WWTP Hospital.
Table 5: Design Sump from WWTP Hospital.
Generally, calculation of dimensions in the
planning of these is shown in Table 6:
6th FiAC 2020 - The Food Ingredient Asia Conference (FiAC)
104
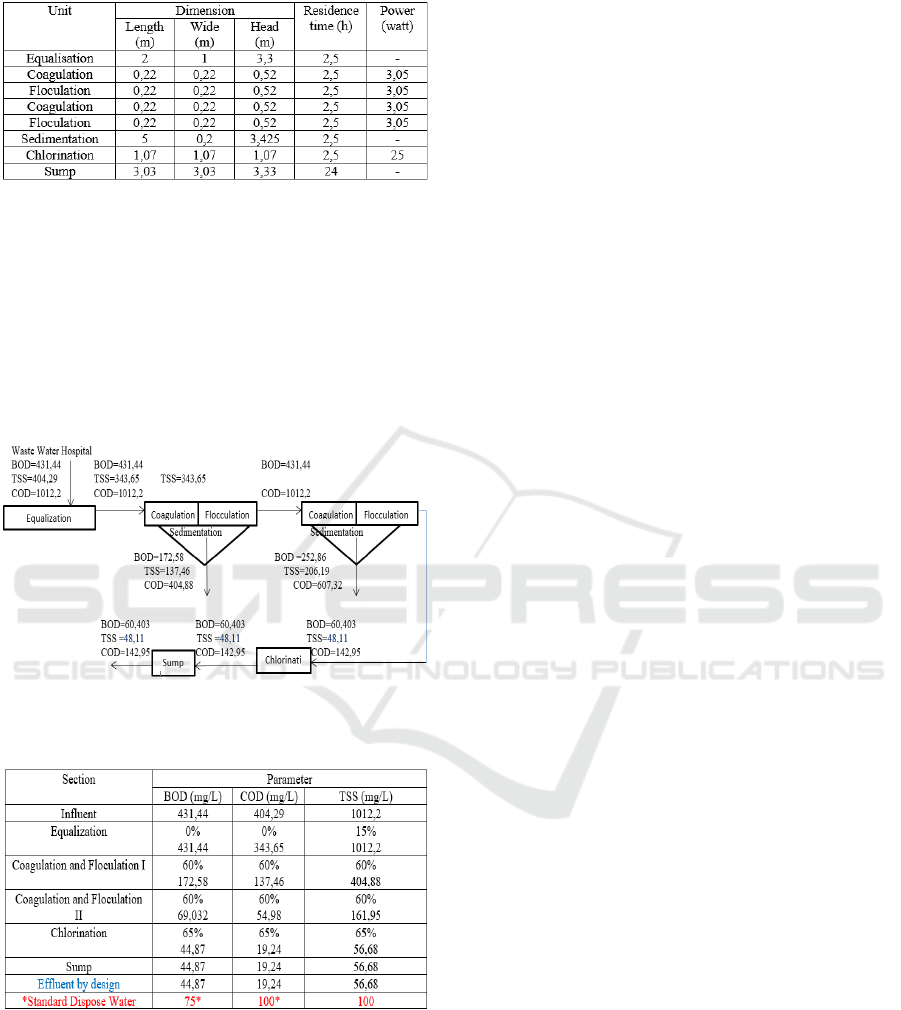
Table 6: Design WWTP Hospital.
5. Calculation Result WWTP.
In this planning, hospital waste flow of water
obtained as follows: 60 m
3
/ day so that calculation
Result WWTP refers to parameters of efficiency
reduction of some of the literature includes text book
Decentralised Wastewater Treatment in Developing
Countries and Treatment and Reuse Fourth Edition by
Metcalf and Eddy. After calculation can be shown at
Picture 3 dan Table 7:
Figure 3: Mass Balance Desain IPAL.
Table 7: Mass Balance and Efficiency Design WWTP.
*based on KEPUTUSAN MENTERI NEGARA
LINGKUNGAN HIDUP NO. 58 TAHUN 1995
TANGGAL 21 DESEMBER 1995
4 CONCLUSIONS
Hospital Waste water treatment at one of the hospitals
in Indonesia. debits 60 m
3
/ day. WWTP hospital
building consists of equalization bath, flocculation
coagulation bath, chlorination bath and sump.
Wastewater treatment plant at the hospital are
planned can be disposed into environment because
has fit to the standards.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors say thank you to the Hospital in
Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Ayu Taurini, Putri. 2014. Perencanaan Pengolahan Air
Limbah Sistem Setempat (On Site) dengan Sistem
Tangki Septik Bersusun dengan Filter pada Perumahan
PT Pertamina UP III Plaju Palembang). Fakultas
Teknik Jurusan Teknik Sipil, Universitas Sriwijaya.
Basak, NN. 2003. Environmental Engineering. Tata Mc
Graw Hill: New Delhi.
Batterman S. (2004). Findings on an Assessment of Small-
scale Incinerators for Health-care Waste. WHO,
Geneva, Switzerland.
Batterman S, (Website Updated April 9, 2008),
Mozambique Program for Healthcare facility waste
treatment, The Regents of the University of Michigan
School of Public Health (MSPH).
Crites, Tchobanoglous. 2003. Small and Decentralized
Wastewater Management System. McGraw-Hill.
Singapore.
Depkes RI, 2004. Keputuan Menteri Kesehatan
No.1204/MENKES/SK/2004 tentang Persyaratan
Kesehatan Lingkungan Rumah Sakit, Jakarta:
DepkesRI.
Eckenfelder, W Wesley Jr. 2000. Industrial Water
Pollution Control. The McGraw Hill Companies.
Singapore.
Ginting Perdana, 2007. Sistem Pengelolaan Lingkungan
dan Limbah Industri,Bandung : CV. Yrama Widya.
Hermana, Joni. 2010. Dasar - dasar Teknik Pengelolaan
Air Limbah. Jurusan Teknik Lingkungan. Institut
Teknologi Sepuluh November, Surabaya.
Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum. 2012. Pedoman
Pengelolaan Program Hibah Air Limbah, Direktorat
Jenderal Cipta Karya, Jakarta.
Kementrian Kesehatan RI. 2011. Seri Sanitasi Lingkungan:
Pedoman Teknis Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah
Dengan Sistem Biofilter Anaerob Aerob Pada Fasilitas
Pelayanan Kesehatan. Kementrian Kesehatan RI,
Direktorat Jenderal Bina Upaya Kesehatan.
Metcalf & Eddy, Inc. 2004. Wastewater Engineering:
Treatment, Disposal and Reuse 4th Edition. Mc Graw
Hill. New York.
Siregar A., 2005. Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah,
Yogyakarta: Kanisius.
Design of Waste Water Treatment Plant for Hospital
105

Said, Nusa Idaman, 2006. Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah
Rumah Sakit. Kelompok Tehnologi Pengolahan Air
Bersih dan Air Limbah, Pusat Pengkajian dan
Penerapan Lingkungan, BPPT, Jakarta.
Zaenal, A.Z, 2005. Analisis Bangunan: Menghitung
Anggaran Biaya Bangunan. Gramedia PustakaUtama,
Jakarta.
Wulanarum, Rina. 2008. Laporan Tugas Akhir:
Perancangan Sistem Penyaluran dan Bangunan
Pengolahan Air Buangan Domestik Kelurahan
Rejowinangun Selatan Kecamatan Magelang Selatan.
Teknik Lingkungan UNDIP. Semarang.
Verlicchi, P et al., “Hospital effluents as a source of
emerging pollutants: An overview of micropollutants
and sustainable treatment options.” Journal of
Hydrology: Elsevier, (2010).
6th FiAC 2020 - The Food Ingredient Asia Conference (FiAC)
106
