
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development
of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions of
Adaptive Learning
Hanna B. Varina
1 a
, Kateryna P. Osadcha
1 b
, Svetlana V. Shevchenko
1 c
,
Valentyna V. Voloshyna
2 d
, Ivan G. Riznitskii
3
and Aleksandr D. Uchitel
3 e
1
Bogdan Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Pedagogical University, 20 Hetmanska Str., Melitopol, 72300, Ukraine
2
National Pedagogical Dragomanov University, 9 Pyrohova Str., Kyiv, 01601, Ukraine
3
State University of Economics and Technology, 5 Stepana Tilhy Str., Kryvyi Rih, 50006, Ukraine
Keywords:
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), Cloud Services, Cloud Technologies, ICT Com-
petence, Electronic Information and Educational Environment, Professional Stability, Working Capacity,
Self-Actualization, Motivation, Vital Capacity, Mental State.
Abstract:
The article considers practice-oriented possibilities of using cloud technologies in the process of development
of the main components of professional stability of the future specialist of socionomic direction in the con-
ditions of blended learning. The research is devoted to the use of cloud services in the formation of not only
ICT competence, but also the development of professional stability of the future specialist. The study sub-
stantiates the importance of cloud services and analyzes the use of cloud technologies Google Workspace for
Education, distance learning system Moodle in the modern information and educational environment of higher
education. The authors clarify the didactic capabilities of cloud services and identify the psychological and
pedagogical conditions for the development of components of professional stability, as a dominant integral
of the competitiveness of the future specialist. The methodical aspects of designing the process of develop-
ment of professional stability of the individual on the basis of the use of cloud services aimed at improving
the mental capacity of the applicant of higher education are highlighted. In the framework of theoretical
and methodological analysis of the problem of professional stability of the psychologist identified the follow-
ing main components: cognitive, motivational, behavioral, emotional and volitional. Professional stability is
closely interrelated with the processes of professional and personal development, professional adaptation, the
level of efficiency of the individual. In the process of implementing the program of implementation of cloud
technologies, the authors consider the professional stability of man as a dialectical synthesis of sustainability
and variability, preservation and development. The results of the formative stage revealed significant positive
changes in the manifestation of the components of professional stability of future professionals. Prospects
for further research are the development of a comprehensive program for the use of cloud technologies in
non-formal education and personalization of the process of professional development of future professionals.
1 INTRODUCTION
The field of education is experiencing a turning point,
which is accompanied by the reorientation of higher
education into an open educational system. Integra-
tion into the European educational environment re-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0087-4264
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0653-6423
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5140-0018
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4372-5824
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9969-0149
quires the introduction of the latest methods, based
on the use of information technologies, in the educa-
tional process of higher educational institution. To-
day, one of the main tasks of the educational system
is to provide everyone with a free and open access to
knowledge, taking into account their needs, abilities
and interests. So far, the state of informatization of
society has reached the point when innovations have
flooded all spheres of life: the pace of technology re-
newal is impressive and it forces the scientific com-
munity to respond immediately to today’s challenges.
The primary need of higher education in the personifi-
Varina, H., Osadcha, K., Shevchenko, S., Voloshyna, V., Riznitskii, I. and Uchitel, A.
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions of Adaptive Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0010928800003364
In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2020) - Volume 2, pages 101-114
ISBN: 978-989-758-558-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
101

cation and individualization of education, due to quar-
antine measures caused by COVID-19, causes a rapid
integration of cloud and innovative information tech-
nologies into the process of training a competitive,
professionally stable specialist of the new format. The
modern technologies are present at all levels and in all
aspects of pedagogical activity – from the use of in-
formation technology in teaching a certain discipline
to the implementation of systems of management in
higher educational institutions.
Among the modern technologies, cloud technolo-
gies occupy a prominent place, they are increasingly
penetrating the system of domestic education (Kiv
et al., 2019). Until recently, cloud technologies were
considered the prerogative of large corporations, but
today they are used by small and medium-sized busi-
nesses, government and the educational system in
general.
According to the latest statistics, about 77% of
companies have been already using or plan to use
the cloud technologies. 69% of them consider such a
transition to be a necessary condition for the survival
in a competitive changing world.
The cloud sphere, meanwhile, is actively develop-
ing and annually presents innovations in functionality
and applications. 2020 is a year of restructuring and
adaptation of a human being to the life in the new
economic, social conditions of society in the post-
coronavirus space. In the international press this year
was called “the year of cloud technology”. Market
giants IBM, Amazon and Microsoft started actively
offering cloud infrastructure and platform as a service
not only in the United States, which is the main coun-
try of data hosting, but also abroad, actively increas-
ing its presence in other countries.
The use of cloud technologies in the educational
process is one of the dominant areas for the enhance-
ment of the quality of higher education, individual-
ization and personalization of the educational pro-
cess. The educational process is not left out of the
renewal process, and one of the ways to solve the
problem of interaction of several remote systems sup-
porting the learning process, their mobility and cost-
effectiveness is the use of cloud computing, when data
resources are provided to final users as an Internet ser-
vice (Morze and Kusminska, 2011).
The Concept of Development of Digital Economy
and Society of Ukraine for 2018–2021 states the ne-
cessity of taking measures to implement appropriate
incentives for the digitalization of the economy, pub-
lic and social spheres. It also focuses on the issues
of raising the awareness of existing challenges, us-
ing tools for digital infrastructure development, and
developing digital competence. This Concept also
identifies critical areas, circles out the digitization
projects, plans stimulation of the domestic market of
production, use and consumption of digital technolo-
gies. It is noted that the integration of Ukrainian sci-
ence into the European research space will provide
an opportunity to develop advanced scientific ideas,
participate in interdisciplinary projects, focus on per-
spective ideas, technologies and innovations.
One of the important tasks is the formation of a
profound national policy of digitalization of educa-
tion as a priority component of educational reform,
and one of the key elements of the Digital Single Mar-
ket of Europe and a part of the paradigm “Open In-
novation – Open Science – Openness to the World”,
which is developing within the European scientific in-
novation space. There is also a need to develop a Eu-
ropean cloud of open science and a European data in-
frastructure. The implementation of the main postu-
lates of the Concept described above has been going
on for some time, in particular, various scientific re-
search works in this direction are being carried out in
Ukraine.
The dynamism of national processes, taking place
in modern Ukrainian society, creates a socio-cultural
and educational situation, the way out of which is di-
rectly related to the enhancement of the quality of
training and the increase of the level professional-
ism of future professionals who are capable of self-
transformation and are ready for full self-realization
in unstable, changing working conditions.
Future professionals’ awareness of the relation-
ship between the requirements of the profession and
their personal characteristics encourages the construc-
tion of their own personality in the framework of pro-
fessionalization, consequently it creates conditions
for becoming a professional.
The issue of students’ own social mobility, readi-
ness for self-education in the new information field,
in which integration competence plays an impor-
tant role, is becoming an urgent issue for modern
Ukrainian student youth.
The issue of professional stability is also an im-
portant one, which is also a practical aspect of
a broader problem – the problem of competitive-
ness, efficiency and readiness for professional self-
realization in today’s unstable conditions of profes-
sional activity. Accordingly, it is also very important
to find priority ways to provide educational services,
taking into account the future specialist’s individual
psychological characteristics and innovative trends of
cloud technologies use in the process of future profes-
sionals’ training.
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
102

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The issue of creating cloud services is very popular
in today’s world, where the priority is a rapid devel-
opment of information technologies and their use in
public spheres. Many analytical companies study the
development market, build cloud services and imple-
ment them into practice. The main purpose of pro-
fessional training is to develop such a potential of a
specialist, which would ensure not only the quality
of his professional duties, but also professional self-
improvement. In the conditions of transformation of
a society the problem of adaptation of future experts
to fast changes both in social and economic, and in
cultural and educational spheres of life acquires spe-
cial sense. Today’s dynamic, competitive society re-
quires the training of a new type of professionals,
namely those who could be creative, unconventional
in decision-making, be mobile and effectively carry
out professional activities. Forrester Research has as-
sessed the current dynamics of cloud storage popular-
ization and concluded that by 2020 the cloud comput-
ing market will be $ 241 billion (Thompson, 2008).
In the world’s developed countries, the technol-
ogy of cloud computing is becoming more and more
widespread. In the domestic market, they are also ac-
tively penetrating public infrastructure.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a model of pro-
viding on-demand remote access to a common pool of
configurable computing resources (cloud infrastruc-
ture) with the ability to manage them independently.
The foundations for the creating and rapid devel-
opment of cloud technologies were:
• technical progress, rapid development of hard-
ware: the ever-increasing power of processors, de-
velopment of multi-core architecture and increase
of the hard disk storage capacity;
• high power Internet channels;
• ”large” Internet services, cloud data storage;
• impact of quarantine conditions caused by
COVID-19, combined with the need to perform
certain activities.
Cloud storage is a model of online storage in
which data is stored on numerous networked servers
which are provided to customers mostly by a third
party. Data is stored and processed in the cloud,
which is, from the client’s point of view, one large
virtual server. It should be noted that the cloud is
not the Internet itself, but the whole set of hardware
and software that provides processing and execution
of customer’s requests. There are not many author-
itative sources that define the concept of cloud com-
puting. The most comprehensive and fundamental ap-
proach to this issue was proposed by Mell and Grance
(Mell and Grance, 2011): they define cloud comput-
ing as a model of providing convenient on-demand
network access to a shared set of parameters, com-
puting resources (e.g., networks, servers, data stor-
ages, applications and/or services) which the user can
quickly use, when executing their own task, and free
up while minimizing the number of interactions with
the service provider or their own management efforts.
This model is aimed at the increase of the availabil-
ity of computing resources and combines five main
features, three service models and four deployment
models.
Characteristics of cloud computing:
1. Self-service on demand. The consumer, when he
or she needs it, can use computing capabilities,
such as server time or automatic network storage,
without interaction with the staff of the service
provider.
2. Wide availability via the network (Internet). Op-
portunities are available online; they are accessed
on the basis of standard mechanisms; it ensures
the use of heterogeneous thin and thick client plat-
forms (e.g., mobile phones, laptops, PDAs).
3. Combining the resources into a pool. The
provider combines its computing resources into
a pool in order to serve a large number of cus-
tomers using the principle of multitenancy. Dif-
ferent physical and virtual resources are dynami-
cally distributed and redistributed according to the
user’s needs. There appears a sense of location
independence when the customer does not know
where the computing resources they use are, but
may be able to identify their location on a more
abstract level (e.g. country, region or data cen-
ter). Examples of resources can be data storage,
computing power, RAM, bandwidth, virtual ma-
chines.
4. Ability for quick adaptation. Computing capabil-
ities can be quickly and flexibly reserved (often
automatically) for prompt scaling according to the
customer’s tasks, and also quickly vacated. From
the consumer’s point of view, the available op-
tions often look unlimited and can be purchased
in any quantity and at any time.
5. Measurable service. Cloud systems automatically
control and optimize resource utilization by mea-
suring some abstract parameters. The parame-
ters vary depending on the type of service. For
example, they may be: data storage size, com-
putation power, bandwidth and/or number of ac-
tive user’s records. Resource use is tracked, con-
trolled; reports are generated. Thus, both the
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions
of Adaptive Learning
103

provider and the consumer receive transparent in-
formation about the range of services provided
(consumed).
Cloud technologies represent a new paradigm that
provides a distributed and remote processing, data
storage; they lead us to a new concept of using In-
ternet resources in today’s educational environment.
The analysis of modern scientific research works
has shown that there exists the experience of using
cloud platforms and virtualization technologies, in-
cluding those based on the virtual machines from Mi-
crosoft, Amazon, Google, Yandex, for the organiza-
tion of universal workplaces for students with unifi-
cation of system and application software for individ-
ual learning. Shevchuk et al. (Shevchuk et al., 2020)
studied the main advantages of cloud software over
traditional academic tools used in the educational en-
vironment. The authors paid attention to the organi-
zation of a virtual workplace in order to increase the
effectiveness of learning both in the educational insti-
tution and outside the classroom.
Analyzing the possibilities of using cloud tech-
nologies as a component of future specialists’ pro-
fessional training, taking into account personal psy-
chological characteristics, Kolesnyk et al. (Kolesnyk
et al., 2020) demonstrated a structural model of in-
formation and media literacy of university entrants
and the use of cloud technologies in the educa-
tion for sustainable development. Kolesnyk et al.
(Kolesnyk et al., 2020) analyze the levels of for-
mation of such type of entrants’ literacy in the
process of their sustainable development (cognitive,
constructive-exploratory, creative and productive lev-
els). Kolesnyk et al. (Kolesnyk et al., 2020) devel-
oped a method of interaction of information and me-
dia literacy with cloud technologies in the educational
process.
Osadcha et al. (Osadcha et al., 2020) research
the current state and relevance of the use of adap-
tive learning systems and cloud technologies as use-
ful tools for the development of an individual learn-
ing path leading to the highest level of intellectual
development in accordance with natural abilities and
inclinations. Taking into account the technological
progress and the actualization of STEM education,
the priority is the research work done by the Valko
et al. (Valko et al., 2020), they focused on a detailed
description of the introduction of cloud sources in the
development of robotic systems.
Analyzing the combination of traditional class-
room education and distance learning, Petrenko et al.
(Petrenko et al., 2020) focused on the possibilities of
using cloud technologies in the process of organizing
distance learning and the implementation of a com-
prehensive competency-oriented approach.
The practice-oriented research of the staff of the
research laboratory “Cloud Technologies in Educa-
tion” of Kryvyi Rih National University and the In-
stitute of Information Technologies and Textbooks of
NAES of Ukraine demonstrates ways to implement
models of cloud services SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, which
should be used in the process of doing the courses
on mathematical, natural cycles while organizing fu-
ture specialists’ professional-practical training in the
field of information technology (on the example of
software engineering, computer science and computer
engineering). Scientists have identified the most sig-
nificant advantages of using cloud technologies in fu-
ture specialists’ training in information technology,
namely the possibility of using modern parallel pro-
gramming tools as the basis of cloud technologies
(Markova et al., 2019). Thus, cloud technology is not
only a modern trend of effective use of information
and communication technologies in professional ac-
tivities, but also a proven tool of educational activities
(Fedorenko et al., 2020).
Analysis of literature sources has shown that the
issue of development and implementation of cloud
services in the process of training of competitive fu-
ture professionals is an important area and it requires
additional practice-oriented empirical research in or-
der to expand the possibilities of creating cloud tech-
nologies and to implement them successfully not only
in the sphere of education but also in other no less im-
portant areas of human activity.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
Interdisciplinary research was conducted as part of re-
search work carried out at the expense of the general
fund of the state budget: “Adaptive system for in-
dividualization and personalization of future profes-
sionals’ training in the conditions of blended learn-
ing”, state registration number: 0120U101970. Tak-
ing into account the pandemic conditions and social
isolation, from 2019 to 2020 on the basis of Bogdan
Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Pedagogical University
in the context of the program “Development of pro-
fessional stability of the future specialist in the condi-
tions of information and educational transformations”
the implementation of the psycho-correctional pro-
gram, based on the elements of cloud technologies,
was proposed. The following methods were used in
the research process: method of theoretical analysis
of literature sources on the introduction of cloud tech-
nologies in the educational process of higher educa-
tional institution and on the implementation of dis-
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
104

tance learning based on the principles of adaptive and
personalized learning; analysis of modern experience
of psychological and pedagogical support of integra-
tive process of future specialist’s professional stability
development; systematization of practical experience
of enhancing the person’s working capacity in higher
educational institution; analysis of the practical im-
plementation of Google Workspace for Education in
the program of the future specialist’s professional sta-
bility development; a set of psychodiagnostic exami-
nations using Google Form; experimental study con-
sisting of two stages: ascertaining and formative.
4 RESEARCH RESULTS
4.1 Theoretical Foundations
Modern information and educational environment of
the university is analyzed in the context of the elec-
tronic display of various aspects of the university ac-
tivity on the Internet. There are different plans for
designing the e-learning environment that take into
account the interests of different groups of network
users. From the socio-psychological standpoint, the
electronic educational environment of the university
takes an active part in the improvement of educational
technologies, emergence of new aspects of teaching
activity, and creation of the conditions of students’
self-realization.
Example of modern cloud-based services for edu-
cational institutions is Google Workspace for Educa-
tion. Google’s online services for educational insti-
tutions have a number of advantages, which makes it
possible to use them in any educational environment
where there is an Internet connection (figure 1).
Modern computer technology allows students,
teachers and researchers to use several devices for
the communication and work: laptops, computers,
smart phones, mobile phones, etc. Google Workspace
tools are supported by a variety of devices, so it is a
widely available and universal IT technology to work
with in the modern educational environment. Google
Workspace include more than sixty free services that
can be connected to one domain, including video
hosting service YouTube, CMS Blogger, Google Ana-
lytics, organization chart service Lucid Chart, graphic
editor Aviary, etc. They are easy to use, are serviced
by Google and do not require downloading, installing
or maintaining hardware or software. In addition to
its diversity, which meets any needs of the modern
teacher, Google applications have such characteristics
as accessibility, simplicity, reliability, low cost, sta-
bility, variability, quality. The additional arguments
in favor of choosing Google services and other ser-
vices for the educational purposes are the availability
of special applications for phones and tablets, central-
ized data storage, information security and Ukrainian
interface. Google Workspace for Education combines
a number of useful services, such as:
• Gmail – a free e-mail service;
• Classroom – assistance of learning;
• Drive – file hosting using cloud technologies;
• Calendar – time planning;
• Vault – archiving and management of user’s data;
• Docs – a set of tools for working with office files;
• Sheets – processing of data presented in the form
of spreadsheets;
• Forms – creating online forms and conducting
surveys;
• Slides – creating presentations, regardless of the
available device;
• Sites – a platform for hosting and a designer for
creating sites;
• Meet – interactive communication and video con-
ferencing tool.
The above mentioned services can be used both
separately and in combination, as a complement to
each other.
Today, one of the most well-known and widely
used services for organizing learning of students
is Google Classroom (https://classroom.google.com).
Its use allows you to organize effective interaction of
all participants of the educational process, distribute
educational materials and provide the execution of
various educational tasks with necessary software,
assessment of students’ learning outcomes. Google
Classroom provides a user-friendly interface for cre-
ating and managing training courses. It gives a wide
range of opportunities for the organization of the ed-
ucational process in higher educational institutions.
The service has all necessary facilities for the com-
munication, task setting and testing. Also, the use of
Google Classroom helps to increase learning motiva-
tion; saves time for the preparation; provides clear and
interactive information, so it contributes to better as-
similation of information. The use of Google Class-
room in the process of future professionals’ training
systematizes the work of all participants of the educa-
tional process and takes it to a higher level.
Taking into account the dominant advantages of
using Google Classroom in the organization and mon-
itoring of the educational process in the university
and certain quarantine restrictions due to COVID-19,
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions
of Adaptive Learning
105

Figure 1: Main features of Google Workspace for Education use in education from the user’s point of view.
the priority in the context of our study was given
to the development, testing and implementation of
a comprehensive program “Development of profes-
sional stability as a factor of future specialist’s psy-
chological security in terms of information and edu-
cational transformations”. This program was being
piloted during 2019–2020 as part of the scientific and
practical online course “Modern innovative technolo-
gies in education and psychology” (Osadchyi and Va-
rina, 2020). The purpose of this online course is a
practice-oriented implementation of the competence-
based approach in the process of training future spe-
cialists in socionomy. It also aimed at the improve-
ment of future educators and psychologists’ profes-
sional skills and competencies in order to create better
opportunities for the use of modern practice-oriented
technologies in the educational process. This online
course consists of four modules and is based on the
use of Google Classroom. It is 90 hour, 3 ECTS credit
online course which includes four modules:
Module 1. Worldview foundations of professional
development of specialists of socionomic
professions
Content lines:
1. Information part. State strategy of ed-
ucation development. Legislative sup-
port of the system of education and
professional development of teachers in
Ukraine. A healthy and safe environ-
ment of an educational institution as a
component of professional well-being
and development.
2. Practice-oriented part. Value and activ-
ity principles of teacher and psycholo-
gist’s professional development. Spe-
cialist’s speech competence. Informa-
tion and media literacy as a key com-
petence of a digitalized society and the
main condition for quality education.
3. The part is aimed at developing the
professional stability of the individual.
Implementation of practical tasks and
group training exercises on “Profes-
sional resilience as a means of over-
coming complex professional tasks and
life situations”. The main directions
of the introduction of innovative psy-
chotechnologies:
• Styles of overcoming behavior in the
decision-making process under condi-
tions of uncertainty while performing
professional tasks;
• Resource components of personality
and their development;
• Social environment as a resource for
the development of professional sta-
bility. Team building and corporate
ethics of interpersonal interaction.
Module 2. Development of modern specialist’s psy-
chological and pedagogical competence.
Content lines:
1. Information part. Fundamentals of in-
clusive education, children with spe-
cial educational needs: peculiarities of
learning and development, psychologi-
cal and pedagogical conditions for their
assistance in the educational process,
universal design in education. Estab-
lishment of the safe educational envi-
ronment, prevention of bullying and its
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
106

overcoming in the educational institu-
tion, modern problems of adaptation
and socialization of the students; for-
mation of students’ social competen-
cies in the process of neuromanage-
ment. Pedagogy of partnership: inter-
action with teachers, parents, local au-
thorities, and community. Psychologi-
cal support of talented children.
2. Practice-oriented part. Development
of specialists’ emotional competence.
Specialists’ psychological competen-
cies: psychological features of the
child’s development at different age
stages, strategies and tactics of profes-
sional and personal burnout prevention,
psychology of team building; psychodi-
agnostics of student’s personality, psy-
chodiagnostics of educational manage-
ment.
3. The part is aimed at developing the pro-
fessional stability of the individual. In
this block, group lessons were imple-
mented aimed at developing the emo-
tional component of professional stabil-
ity and goal-setting skills:
• Professional stability and psychologi-
cal well-being as determinants of the
competitiveness of a future specialist;
• Professional stability as an alternative
to learned helplessness;
• The art of setting and achieving pro-
fessional goals;
• Personal formula for professional suc-
cess
Module 3. Organizational and methodological prin-
ciples of the development of specialist’s
professional competencies.
Content lines:
1. Information part. Practical psycholo-
gist’s educational and preventive work
in the educational institution. Counsel-
ing as a method of psychological influ-
ence. The use of art-therapeutic tech-
niques in the educational process. Con-
flict prevention and resolution using re-
newable techniques. Functioning of
psychological service in the system of
education in the conditions of the New
Ukrainian school: legislative base.
2. Practice-oriented part. Development of
a practical psychologist’s digital com-
petence:
• protection of personal data on the In-
ternet, safe use of digital technologies
and services; legal and ethical require-
ments for the use of information and
communication and digital technolo-
gies in professional activities;
• cloud services in the professional ac-
tivity of a specialist; streamlining digi-
tal educational resources, ensuring ac-
cessibility, organizing the interaction
of participants in the educational pro-
cess;
• use, creation, design and distribution
of digital educational resources;
• use of distance learning technologies;
virtual class: an overview of the re-
sources for creating a virtual class;
creation and organization of the edu-
cational process;
• preparation of a distance course: se-
lection of a platform for webinars, ed-
ucational process planning, prepara-
tion of a scenario for a webinar; pro-
viding interactive distance interaction
of participants in the educational pro-
cess;
• specialist’s digital portfolio; working
with documents; creating and compil-
ing a portfolio using a site (blog).
3. The part is aimed at developing the pro-
fessional stability of the individual. In
this block, a personality-oriented ap-
proach is implemented in the process
of updating the creative potential of fu-
ture specialists. Students researched
and used the mechanism of creativity
for the development of resource com-
ponents of professional sustainability.
The following group training sessions
were held:
• Creative creativity as a resource for
development professional stability;
• Professional and personal potential as
the foundation of creative creation.
To achieve an effective result, students
are familiar with the “Quest of resilience”
methodology to prevent the devaluation of
their own achievements in the process of
solving practical professional problems.
Module 4. Introduction of innovative technologies
into various spheres of psychological and
pedagogical activity.
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions
of Adaptive Learning
107

The subject of study – modern practice-
oriented technologies and methods of psy-
chological assistance of individuals and
groups. The purpose – acquaintance with
and internalization of innovative practice-
oriented technologies in practical psy-
chologist’s activity.
Content lines:
1. Information part. Innovative technolo-
gies for working with children with
special educational needs. Develop-
ment of interhemispheric interaction by
the method of kinesiology. Innova-
tive coaching technologies in a mod-
ern specialist’s activities. Innovative
art-therapeutic technologies in various
spheres of public practice. Case-study
technology in a modern specialist’s ed-
ucational work. Supervision in psycho-
logical practice: modern realities.
2. Practice-oriented part. Within this
block, future specialists developed, im-
plemented and analyzed the effective-
ness of the developed training program,
focused on solving current social prob-
lems. Based on the results of the imple-
mentation, students wrote down in on-
line format a qualitative and quantita-
tive analysis of the effectiveness of the
implementation of a personal training
program.
3. The part is aimed at developing the pro-
fessional stability of the individual. In
this block of the module, group lessons
are implemented, focused on the devel-
opment of the general level of individ-
ual resilience:
• Development of communication skills
as an element of “involvement” (ac-
cording to S. Maddy);
• Development of teamwork skills,
conflict-free communication skills as
an element of “involvement” (accord-
ing to S. Maddy);
• Development of skills of confident be-
havior as an element of “involvement”
(according to S. Maddy);
• Development of skills of stress-
resistant behavior as an element of
“control” (according to S. Maddi);
• Teaching relaxation skills, self-control
emotions as an element of “control”
(according to S. Maddy);
• Development of the ability to set a
goal as an element of “control” (ac-
cording to S. Maddi);
• Development of self-knowledge as
an element of “risk taking” (by S.
Maddy);
• Development of a positive Yconcep-
tion as an element of “risk taking” (ac-
cording to S. Maddy)
Due to the practical orientation of this online
course, its structure includes a comprehensive train-
ing program “Development of professional stability
of the future specialist in the conditions of infor-
mation and educational transformations”, which was
conducted using Google Classroom cloud technology.
In order to provide feedback and stimulate sharing
with the participants of the training group, the tech-
nical capabilities of Google Meet and the Trapscan
application (psychological diary) are used. The ap-
plication uses one of the main methods of cognitive-
behavioral therapy – ABC analysis. The role of
thoughts in shaping the mood and well-being of the
individual is very significant and it is not the situation
that affects what emotions a person feels, but the per-
ception of this situation. The application allows you
to keep a diary and analyze personal reactions, work
with your thinking, improving the quality of your life.
Duration of this training: 18 hours (9 classes of 2
hours each). The duration of each class may slightly
vary depending on the degree of participants’ interest
and the actualization of their problems.
When indentifying the essential characteristics of
specialist’s professional stability, we took into ac-
count the following methodological ideas:
• stability is a qualitative characteristic of any ob-
ject, system or individual; thus, quality means
some certainty of the subject or the individual pos-
sessing certain specific features;
• stability is manifested in holistic systems, self-
organization of which is impossible without the
existence of a hierarchical structure of internal
factors;
• stability of the psychologist’s personality is
formed in the process of self-identification and
professional development and is manifested in the
work and active self-organization;
• stability is the result of the functioning of mech-
anisms that actively counteract the negative influ-
encing factors (Moore and Foxx, 2020).
The developed model of structural components
of future specialist’s professional stability acts as a
theoretical and methodological basis for the devel-
opment and implementation of this training program
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
108

(figure 2). As a result of theoretical analysis, we have
identified the following components in the structure
of the future specialist’s professional stability.
Based on the model of development of future spe-
cialist’s professional stability, as a factor of effective
mental capacity of the individual, all structural parts
of the training were divided into the following blocks:
• formation of psychological readiness to work in
new transformational conditions;
• development of psychological awareness of vari-
ous aspects of professional activity;
• enhancement of personal efficiency and working
capacity;
• development of specialists’ personal stress resis-
tance to the growth of mental load and work in
the new information conditions;
• formation and development of professionally sig-
nificant cognitive qualities;
• development and improvement of skills and abili-
ties to establish psychological contact with differ-
ent categories of citizens;
• formation of skills of role behavior in different sit-
uations of professional activity;
• improvement of the ability to apply psychological
and pedagogical methods of influence in the com-
plicated conflict situations of communication;
• formation of the ability of psychological stability
in tense situations of professional activity;
• development of personality’s positive emotional
and volitional qualities, training of specialists in
self-regulation and self-management;
• formation of volitional activity and skills of voli-
tional actions;
• development of positive internal motivation to
carry out effective professional activity;
• preparation for mental overload at work.
The structure of each unit included three elements:
1) acquaintance with the characteristics of a particular
trait that was developed, a metaphorical explanation
of the content and objectives of the unit, “warming-
up” activities; 2) the main part; 3) reflection on the
unit as a whole.
The training program was designed and piloted
taking into account the following principles: the prin-
ciple of purposeful creation of emotionally colored
situations (active influence on the individual, creation
of appropriate conditions for the perception and as-
similation of new knowledge that is emotionally col-
ored and has personal significance); the principle of
personal developmental communication (understand-
ing, recognition and perception of personality); the
principle of using empathy as a psychological mech-
anism in the education of personality (includes two
cognitive components – the ability to distinguish and
name the emotions experienced by other people and
take another person’s position; and the emotional
component – the ability to respond emotionally); the
principle of systematic analysis of one’s own actions
and the actions of others (it contributes to the forma-
tion of the ability to predict the above mentioned re-
sults and has a positive effect on the development of
behavioral skills of overcoming instantaneous aspira-
tions, states, desires).
The program is created in accordance with the
principles of the Accelerated Learning Theory and
implies all the latest advances in the field of method-
ology of teaching adults.
4.2 Experimental Results of Research
While conducting a formative experiment based on
the piloting of a comprehensive training program
“Development of professional stability of the future
specialist in the conditions of information and edu-
cational transformations” we introduced the practical
online course “Modern innovative technologies in ed-
ucation and psychology” in order to identify the ef-
fective psychological and pedagogical conditions for
the development of professional stability, as a factor
the specialist’s mental capacity. After conducting the
formative experiment we compared the results of two
psychodiagnostic assessments. The sample was ran-
domized and consisted of 58 people who did practical
online course “Modern innovative technologies in ed-
ucation and psychology” – 30 people, future profes-
sionals in psychology, who participated in the train-
ing program and 28 people, future professionals, who
didn’t take part in the training program. The psy-
chodiagnostic unit of the study included a survey us-
ing Google Forms.
According to the analyzed structural components
of professional stability of the personality in the psy-
chodiagnostic block the following techniques were
carried out:
• For successful higher education and maintaining
the optimal level of professional stability of stu-
dents, it is important to have a valuable motivation
to study. For this purpose, we used the method of
“Motivation to study at university”;
• Methodology “Questionnaire to determine the
level of socio-psychological stress”, aimed at
identifying the level of manifestation of socio-
psychological stress in future professionals at dif-
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions
of Adaptive Learning
109
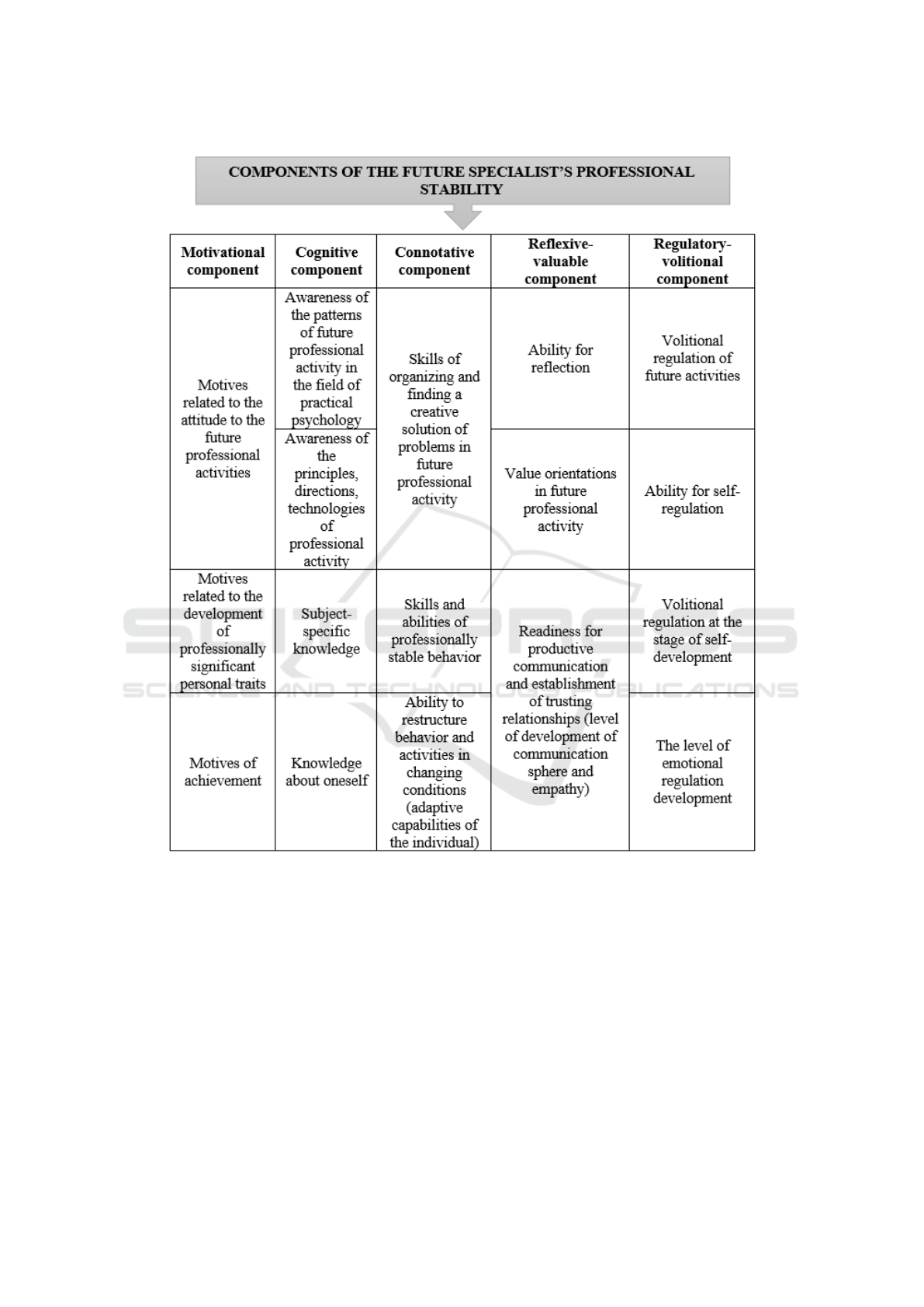
Figure 2: Structural components of future practical psychologist’s professional stability.
ferent stages of professional genesis, which af-
fects the indicators of their overall level of pro-
fessional stability;
• Methodology “Coping behavior in stressful situ-
ations”, aimed at identifying the dominant cop-
ing stressful behavioral strategies in students. Ob-
taining these data allows a more thorough study
of the psychological conditions for the develop-
ment of their professional stability, because only
a constructive coping response to stress, aimed
at rational analysis of the problem and solve a
complex stressful situation, allows future profes-
sionals to overcome difficulties and successfully
solve professional problems without reducing per-
formance.
• “Questionnaire DORS – Differentiated assess-
ment of states of reduced efficiency (fatigue-
monotony-oversaturation-stress)”, which is aimed
at determining the degree of manifestation of each
of the physiological states of personality stability
(fatigue-monotony-saturation-stress). The devel-
opment of these states leads not only to a decrease
in resistance, but also affects the qualitative char-
acteristics of behavior and emotional coloring of
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
110

experiences, which provokes significant changes
in the motivational sphere of personality.
The analysis of the results of piloting the system
of psychological and pedagogical measures showed
the significant differences between the control and
experimental groups in terms of indicators of pro-
fessional stability and the development of its psy-
chological and pedagogical conditions. Significant
changes in the indicators have been traced according
to all the methods used. In order to identify the sig-
nificance of the changes that occurred after the cor-
rection work, we used the G-criterion (Varina and
Shevchenko, 2020). The G-criterion is used for the
establishment of the general direction of sign shift un-
der research. We put forward the hypotheses:
H
0
: The predominance of the typical direction of
shift between the obtained data is accidental.
H
1
: The predominance of the typical direction of
shift between the obtained data is not accidental.
This work contributed to the effective formation of
experimental group specialists’ value motivation for
learning (table 1).
As we can see from table 1, in the experimen-
tal group there was an increase by 16.66% in the
number of people wishing to master the profes-
sion (from 10.00% to 26.66%). It means that they
rethought themselves as future professionals; they
started demonstrating the desire to develop profes-
sionally important qualities, to become an educated
person and a high-caliber professional. In addition,
the number of people, who are focused on the acqui-
sition of certain professional knowledge, showing cu-
riosity, purposefulness and independence in the pro-
cess of knowledge acquisition, has slightly increased
(from 33.36% to 36.67%). Due to this, there was a de-
crease by 20.01% in the number of respondents who
considered getting a diploma or professional certifi-
cation as a priority of learning. That is, it can be
stated that after conducting some activities the moti-
vation for learning of the experimental group respon-
dents has become more valuable. Having analyzed
the indicators of the control group, we saw only a few
changes. There was a shift of only 3.57% in motives
of mastering the profession and getting a diploma.
Also, according to the results of correlation analysis it
was found out: with n = 108, typical shift is positive.
Negative shifts – 32.
G
contr
=
45(p 6 0.05)
42(p 6 0.01)
G
emp
– a number of untypical shifts, so
G
emp
= 32, G
emp
< G
contr
. It means that H
0
is not
proved, but H
1
is accepted.
It is also necessary to note significant changes in
the manifestations of the level of socio-psychological
stress of the experimental group students (table 2).
As we can see from table 2, after the introduction
of the training program, in the experimental group
there was an increase by 13.34% (from 33.33% to
46.67%) in the number of people with a low level
of stress and there were no people with a high level
of this indicator. Future professionals have stopped
perceiving the process of adaptation to the introduc-
tion of information, cloud technologies in the educa-
tional space as that associated with stress. There was
a slight decrease of the medium level of this indica-
tor (from 63.3% to 53.33%), which proves the effec-
tiveness of the development of the experimental group
students’ personal stress resistance, their ability to tol-
erate stress. There are only a few changes in the con-
trol group. Having used the G-criterion, we found out
that the changes were due to the implementation of
the correction program, but not thanks to the external
artifacts that threaten the internal and external validity
of the experiment. With n = 115, the typical shift is
positive. Negative shifts – 38.
G
contr
=
45(p 6 0.05)
42(p 6 0.01)
G
emp
– a number of untypical shifts, so
G
emp
= 38, G
emp
< G
contr
. It means that H
0
is not
proved, but H
1
is accepted.
The formation of the effective individual behav-
ioral styles to overcome stressors after conducting ex-
perimental activities is confirmed by the following
data (table 3).
The table 3 shows the increase in the percentage of
participants of the experimental group (from 23.33%
to 36.66%) who choose coping, focused on solving
the problem, and a significant decrease (from 70.00%
to 50.00%) in the number of people who prefer to
avoid coping in stressful situation. That is, thanks
to the work done, future specialists in situations of
stress and uncertainty have become more focused on
rational analysis of the problem, its constructive solu-
tion, they try to create and implement a plan to solve
a complex stressful situation, rather than just blindly
avoid their problems applying protective mechanisms
or compensating for problems as before. In addition,
in the experimental group, the number of people, who
prefer not to think about problems at all, involving
others in their experiences, trying to forget in a dream
or compensate for negative emotions with food, de-
creased by 6.67%. Analyzing the changes in the con-
trol group, we can state in general the same indica-
tors. With n = 58 typical shift is positive. No negative
changes were identified.
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions
of Adaptive Learning
111
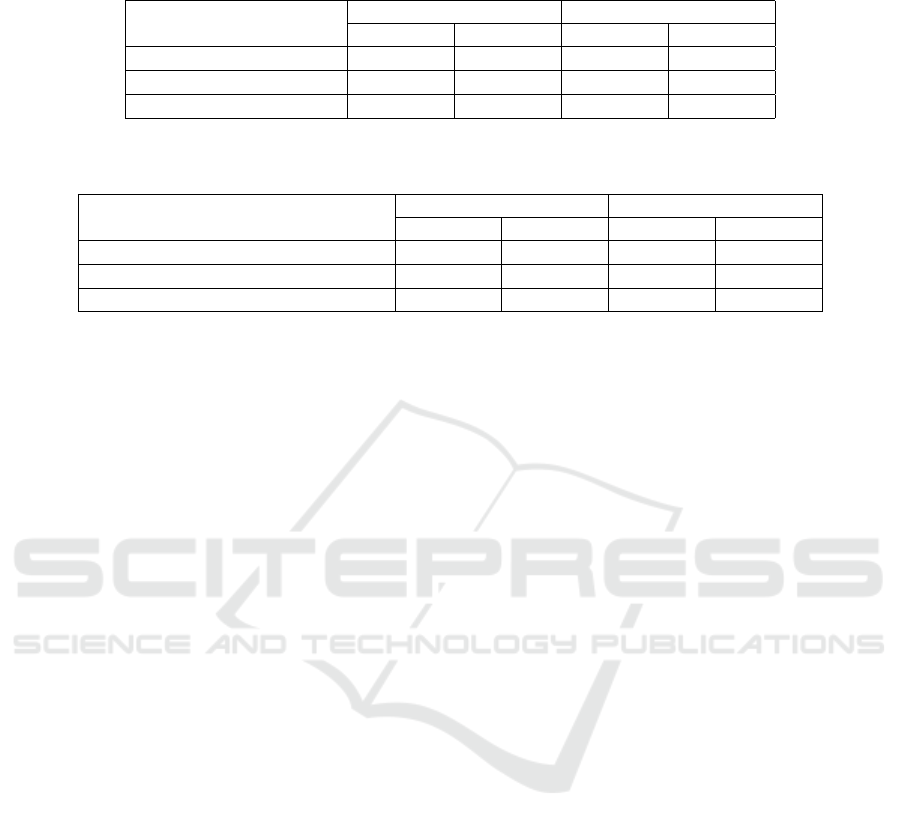
Table 1: Learning motives of the experimental group (n = 30) control group (n = 28) specialists according to the formative
experiment results.
Learning motives
Experimental group Control group
before after before after
Knowledge acquisition 33.36 (10) 36.67(11) 28.57 (8) 28.57 (8)
Mastering the profession 10.00 (3) 26.66 (8) 7.14 (2) 10.71 (3)
Getting the diploma 56.66 (17) 36.67 (11) 64.29 (18) 60.71 (17)
Table 2: Quantitative indicators (%) of levels of social-psychological stress of experimental (n = 30) and control (n = 28)
groups students after the formative experiment.
Level of social-psychological stress
Experimental group Control group
before after before after
Low level 33.33 (10) 46.67(14) 39.29 (11) 42.86 (12)
Medium level 63.33 (19) 53.33 (16) 57.14 (16) 53.57 (15)
High level 3.34 (1) 0 (0) 2.57 (1) 3.57 (1)
G
contr
=
13(p 6 0, 05)
10(p 6 0, 01)
G
emp
– a number of untypical shifts, so
G
emp
= 0, G
emp
< G
contr
. It means that H
0
is not
proved, but H
1
is accepted.
The introduction of the training program based on
the cloud technologies has had a positive impact on
all states of the reduced capacity, in particular among
the experimental group participants.
Thus, there was an increase of 10.00% (from
10.00% to 20.00%) in the number of people with a
low level of fatigue, which indicates that future pro-
fessionals perform mental work online without ex-
haustion and significant errors. Due to this, the num-
ber of respondents with medium indicators of this
state decreased by 3.33% (from 83.33% to 80.00%).
Future specialists gained skills of rational organiza-
tion of mental activity, which allowed them to get
rid of high-level indicators on this parameter (from
6.66% to 0), which proves the ability of students to
perform mental activities and tasks without deteriora-
tion of the working capacity. Analyzing the indicators
of this state manifestation in the control group, only
partial shifts were noted (a number of people with a
high level decreased by 3.57% and a number of peo-
ple with a medium level of fatigue increased accord-
ingly). With n = 58 typical shift is positive. Negative
shifts – 37.
G
contr
=
50(p 6 0, 05)
46(p 6 0, 01)
G
emp
– a number of untypical shifts, so
G
emp
= 37, G
emp
< G
contr
. It means that H
0
is not
proved, but H
1
is accepted.
Accordingly, the work, which was carried out,
also affected the indicators of monotony. It has to
be noted that significant changes are noticeable in
the experimental group. Therefore, the indicator of
a high level of monotony decreased by 6.66% (from
10.00% to 3.34%). The participants demonstrated an
increase of attention and the general ability to strong-
willed efforts, they showed their general inclusion in
innovative mental work. It should be noted that the
number of people with a medium level decreased by
3.33% (from 76.66% to 73.33%) and the number of
students with a low level of monotony decreased by
9.99% (from 13.34% to 23.33%). By developing the
ability to gradually approach the perception and per-
formance of intellectual actions, gradual mobilization
and appropriate adjustment of the body to more ef-
fective execution of these actions, students learned to
adaptively perceive the latest online intellectual ac-
tivity, while maintaining a high level of working ca-
pacity. Assessing the indicators of this state mani-
festation in the control group, we noted only partial
changes (there was a decrease in the high level by
3.58% and, accordingly, an increase in the medium
level of manifestation of monotony). With n = 40
typical shift is positive. There were no negative shifts
identified.
G
contr
=
14(p 6 0, 05)
12(p 6 0, 01)
G
emp
– a number of untypical shifts, so
G
emp
= 0, G
emp
< G
contr
. It means that H
0
is not
proved, but H
1
is accepted.
According to the indicator of mental oversatura-
tion, it was found out that due to the introduction
of highly efficient cloud technologies in the devel-
opment of professional stability (namely, diversifica-
tion and emotional saturation of mental activity in the
process of performing practice-oriented tasks), low
level of this state increased by 13.33% (from 26.67%
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
112

Table 3: Features of coping reactions to stress in experimental (n = 30) and control (n = 28) groups according to the results
of the formative experiment.
Coping-behaviour in stressful situations
Experimental group Control group
before after before after
Coping oriented for the solution of the problem 23.33 (7) 36.66 (11) 28.57 (11) 32.14 (9)
Coping oriented for the emotions 6.67 (2) 13.34 (4) 7.14 (2) 7.14 (2 )
Coping oriented for the avoidance 70.00 (21) 50.00 (15) 64.29 (18) 60.72 (17)
to 40.00%), so future professionals have learned to
perceive mental activity without a wish to stop it.
Accordingly, the indicators of the medium level of
oversaturation decreased by 13.33% (from 73.33%
to 60.00%), indicating the formation of respondents’
ability to accept subjectively uninteresting activities
without changing the stereotype of performing rea-
sonable actions. In the control group the oversatu-
ration indicator remained unchanged. With n = 58
typical shifts are positive. Negative sifts – 37.
G
contr
=
50(p 6 0, 05)
46(p 6 0, 01)
G
emp
– a number of untypical shifts, so
G
emp
= 37, G
emp
< G
contr
. It means that H
0
is not
proved, but H
1
is accepted.
Thanks to this work done, it was possible to in-
crease by 16.67% the number of people with a low
level of stress (from 20.00% to 36.67%), which indi-
cates an increase in their stress resistance and the for-
mation of skills of self-regulation of their own psy-
chophysiological state. Due to this, the number of
people with a medium level of this state decreased by
16.67% (80.00% to 63.33%), they have an experience
of overcoming a difficult stressful situation. In the
control group the indicators of stress remained almost
unchanged.
The training work helped to increase students’
neuro-psychological stability. According to the for-
mative experiment results, there was an increase in the
level of neuro-emotional stability in both experimen-
tal and control groups. But more significant changes
took place in the experimental group. In particu-
lar, the number of people with a low level of neuro-
emotional stability decreased by 10% (from 66.66%
to 56.66%) and the number of people with a high level
of this indicator increased by 10%. This states that
the respondents have become more optimistic about
the reality when doing the educational activities in
the online format under quarantine restrictions. They
adequately perceive new transformational innovative
requirements of the intellectual and educational en-
vironment. These shifts in the control group were
shown only partially (there was a decrease by 3.57%
in the number of people with a low level and, accord-
ingly, there was an increase in the number of people
with a high level of neuro-emotional stability).
Thus, the results of statistical processing of em-
pirical data proved the effectiveness of the training
program, based on cloud technologies, in the process
of developing the future specialists’ professional sta-
bility in the modern educational environment. The
corresponding program, in contrast to the traditional
training, has certain advantages, which were identi-
fied according to the feedback, received from the par-
ticipants:
• personal orientation and personification;
• possibility of in-depth study of personal prob-
lems;
• psychological and emotional security;
• free timing and autonomy in performing practice-
oriented tasks; selection of the tasks depending on
personal requests, etc.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
FUTURE RESEARCH
Despite the great variety of information and commu-
nication technologies, used in education, and the di-
versity of the educational environment, the innovative
systems, based on the use of cloud services, are sig-
nificant from the point of view of all participants of
the educational process. And if the traditional man-
agement system of the educational process is a “ver-
tical” educational technology that reflects the tradi-
tional model of learning in the modern educational
environment, the use of cloud technologies in the
revolutionary reform of education, implies “horizon-
tal” educational technology of cooperation, collabo-
ration, networking community. Thus, modern cloud
technologies provide an opportunity to design and
construct a new learner-centered information environ-
ment, taking into account the individual psychologi-
cal characteristics of students, so such system goes in
line with principles of personification and individual-
ization of modern information. It contributes to the
Main Determinants of the Use of Cloud Technologies in the Development of Professional Stability of the Future Specialist in the Conditions
of Adaptive Learning
113

introduction of new methods of educational process
construction, interaction and management. All men-
tioned above determines the psychological and peda-
gogical feasibility and didactic significance of the use
of cloud services for modeling and implementing the
components of the educational environment under the
conditions of quarantine and social isolation, which
can not be an obstacle to future specialists’ profes-
sional development and growth. There is also a need
to include the ability of students to create an educa-
tional environment with the help of cloud technol-
ogy services as part of future specialists’ information
competence.
The piloted model of the development of fu-
ture specialists’ professional stability with the help
of cloud services will not only form professionally
important competencies, but also generate students’
knowledge about the functions and capabilities of
modern information technologies and cloud services,
which will modernize education as a whole. Further
research should include the development of technolo-
gies for this model introduction, taking into account
the individual characteristics of students in the pro-
cess of online learning. We also see the perspectives
of the research in the integration of cloud technologies
in formal and non-formal education, identification of
conditions and opportunities for the monitoring of the
individualized and personalized training of future pro-
fessionals.
REFERENCES
Fedorenko, E. H., Velychko, V. Y., Omelchenko, S. O.,
and Zaselskiy, V. I. (2020). Learning free software
using cloud services. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2643:487–499.
Kiv, A. E., Soloviev, V. N., and Semerikov, S. O. (2019).
CTE 2018 – How cloud technologies continues to
transform education. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2433:1–19.
Kolesnyk, N., Kubrak, S., Yavorska, T., and Vitvytska, S.
(2020). Information and media literacy and ”cloud”
technologies in training of higher education appli-
cants: The sustainable development paradigm. Uni-
versal Journal of Educational Research, 8(6):2668–
2677.
Markova, O. M., Semerikov, S. O., Striuk, A. M., Shalatska,
H. M., Nechypurenko, P. P., and Tron, V. V. (2019).
Implementation of cloud service models in training
of future information technology specialists. CEUR
Workshop Proceedings, 2433:499–515.
Mell, P. and Grance, T. (2011). The NIST Definition of
Cloud Computing.
Moore, C. M. and Foxx, S. P. (2020). The development
and initial validation of the interpersonal stress scale-
counselor. Measurement and Evaluation in Counsel-
ing and Development, 0(0):1–19.
Morze, N. and Kusminska, O. (2011). Pedagogical as-
pects of cloud computing. Journal of Informa-
tion Technologies in Education (ITE), (9):020–029.
http://ite.kspu.edu/index.php/ite/article/view/445.
Osadcha, K., Osadchyi, V., Semerikov, S., Chemerys, H.,
and Chorna, A. (2020). The review of the adaptive
learning systems for the formation of individual ed-
ucational trajectory. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2732:547–558.
Osadchyi, V. and Varina, H. (2020). Future masters of psy-
chology training for professional activity in the con-
ditions of non-formal education. Ukrainian Journal
of Educational Studies and Information Technology,
8(3):49–61.
Petrenko, L., Kravets, S., Bazeliuk, O., Maiboroda, L., and
Muzyka, I. (2020). Analysis of the current state of dis-
tance learning in the vocational education and training
institutions. E3S Web of Conferences, 166:10010.
Shevchuk, M., Shevchenko, V., Chukalovskaya, E., and
Gramakov, D. (2020). Cloud platforms and virtual-
ization technologies in education. E3S Web of Confer-
ences, 210:22034.
Thompson, B. (2008). Storm warning for cloud computing.
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/7421099.stm.
Valko, N., Kushnir, N., and Osadchyi, V. (2020). Cloud
technologies for STEM education. CEUR Workshop
Proceedings, 2643:435–447.
Varina, H. and Shevchenko, S. (2020). The peculiarities
of using the computer complex HC-psychotests in the
process of psychodiagnosis of the level of develop-
ment of future specialists’ mental capacity. E3S Web
of Conferences, 166:10025.
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
114
