
Opportunities and Ways of using Laboratory Equipment in a Distance
Learning Environment
Liudmyla V. Vasylieva
1 a
, Denys Yu. Mikhieienko
1 b
, Iryna A. Getman
1 c
and
Maryna V. Kormer
2 d
1
Donbass State Engineering Academy, 72 Akademichna Str., Kramatorsk, 84313, Ukraine
2
State University of Economics and Technology, 5 Stepana Tilhy Str., Kryvyi Rih, 50006, Ukraine
Keywords:
E-Learning, Remote Labs, Virtual Laboratory Work, CNC, 3D Printing.
Abstract:
The paper considers the issue of possibility and ways of performing laboratory works in the conditions of
distance learning as well the experience of using virtual works as a forced replacement of traditional practical
training. The peculiarities of distance learning organization under conditions of coronavirus pandemic are
analyzed. The problems faced by the higher educational institutions in this situation based on the analytical
data of the international commissions are reviewed. The problems that arose in the use of laboratory equip-
ment for work in the conditions of the pandemic are analyzed. The advantages and disadvantages of remote
execution of laboratory works are discussed. The problems arising when replacing real laboratory work with
virtual ones are considered. The example of performing laboratory works under distant learning conditions by
providing remote access to them via the Internet on the example of bioelectronics and biomechanics laboratory
is considered. The directions of further development of virtual practical work at the department of computer
information technologies are formulated.
1 INTRODUCTION
Higher education institutions have faced transforma-
tion before with the porting of many educational ma-
terials and activities to online platforms such as Moo-
dle or Blackboard (Mintii, 2020). Recent measures
in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have brought
about an unprecedented transformation in higher edu-
cation (Bakhmat et al., 2021; Trubavina et al., 2021).
Almost all classrooms have moved from traditional
classrooms to virtual classrooms supported by video
conferencing platforms such as Zoom, Webex, Mi-
crosoft Teams, and others.
After the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic,
the Department of CIT DSEA, like most others, was
forced to switch to distance learning using appropri-
ate modern platforms. However, outside of distance
learning, there is often an important part of the educa-
tional process – laboratory work using special equip-
ment. This issue is especially acute for technical spe-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9277-1560
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1966-0618
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1835-4256
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6509-0794
cialties. It is impossible to imagine the process of
teaching technical specialties without its laboratory
component – this is due to the formation of the pro-
fessional competence of specialists with a high level
of training.
Therefore, the problem of organizing laboratory
work in the context of distance learning is very im-
portant.
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the pos-
sibilities and ways to conduct laboratory work in a
distance learning environment.
2 RELATED WORKS
Consideration of the specifics of conducting a labo-
ratory workshop in a distance learning environment
should begin with a consideration of the specifics
of education in the context of the coronavirus pan-
demic in general. The pandemic, on a global scale,
has affected not only all spheres of public life (Se-
merikov et al., 2020), but also each person individ-
ually, and not only on the physical but also on the
psycho-emotional levels (Velykodna, 2021). This was
Vasylieva, L., Mikhieienko, D., Getman, I. and Kormer, M.
Opportunities and Ways of using Laboratory Equipment in a Distance Learning Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0010930800003364
In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2020) - Volume 2, pages 275-282
ISBN: 978-989-758-558-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
275

especially acutely felt by the education sector since it
required a total transfer of all educational activities
to a distance mode. According to Executive Director
of Chandigarh University (India) S. K. Tripath, “The
new coronavirus has affected employment, education,
energy, agriculture and other areas of the global econ-
omy, including the emotional state of citizens. Higher
education institutions (HEIs), including universities,
colleges and other institutions of higher education, are
no exception” (UN, 2020). According to UNESCO,
the COVID-19 pandemic has led to the largest disrup-
tion in education systems in history, affecting nearly
1.6 billion students in more than 190 countries and on
all continents. School and other educational closures
have affected 94% of the global student population,
with 99% in low- and lower-middle-income countries
(International Commission on the Futures of Educa-
tion, 2020). According to the same UNESCO, 826
million students in the world do not have personal
computers, 706 million (43%) do not have access to
the Internet (Faek and El-Galil, 2020).
In high school, the use of web-based distance ed-
ucation is expanding rapidly. This requires constant
improvement of the technological and methodologi-
cal support of the educational process. Failure in ed-
ucation is a serious threat to the entire society. There-
fore, educational institutions must respond quickly
and ensure the continuity of educational processes.
Research is underway to develop technical, organiza-
tional, and pedagogical changes that educational in-
stitutions must implement to use different methods
of interaction, ensure continuity and provide high-
quality education (Bojovi
´
c et al., 2020).
Research on the advantages and disadvantages of
distance education is important (www.eztalks.com,
2017). Many universities are researching to examine
the effectiveness of distance learning at universities
in light of the coronavirus pandemic and to identify
the barriers that university students face. Bataineh
et al. (Bataineh et al., 2021) is pointed out that dis-
tance learning requires an exceptional environment,
ability, and IT skills in addition to smart devices and
applications that enable video conferencing. Another
important area is the study of methods and means
for involving students in the online learning process
(Chen et al., 2021). An important step in the transi-
tion to online of many laboratories that are used in
higher education, especially in STEM fields. This
is important for students of those specialties that re-
quire access to physical objects: devices, sensors,
control devices. One of the ways to solve this prob-
lem is to use Remote Lab and Virtual Lab technolo-
gies when programming an embedded system and ap-
plying them to managing technical objects (Zub
´
ıa and
Alves, 2011; Sancristobal et al., 2012). A virtual lab-
oratory is a software and hardware complex that al-
lows research without direct contact with real pro-
duction or educational equipment, or in the absence
of it (Sancristobal et al., 2012). The Remote Lab in-
cludes real technological equipment, software, and
hardware for controlling the technological complex
and analog-digital conversion of measuring signals
from sensors installed on the equipment. At the same
time, it should be ensured: the operation of the equip-
ment, a reliable access channel via the Internet, access
dispatching and accounting of work performed, video
stream transmission using appropriate equipment, etc.
These tasks are solved, for example, in the GOLDi
system (GOLDi, 2021). Within the GOLDi Remote
Lab, interactive content objects can be offered to stu-
dents to digitally support learning processes. These
are digital, immersive tools that allow you to explore
learned content with predefined or self-created ex-
amples. Virtual Lab emulates laboratory equipment
through the use of mathematical models (Vasilyeva
and Portnyagin, 2017; Tarasov et al., 2020b). It is
also necessary to improve the technologies of the ed-
ucational process based on the use of IT.
To ensure a proper response to emerging prob-
lems, universities need to focus on changing not only
teaching methods but also the very approaches to
teaching, organizing the educational process, and to
do this quality and quickly. On the other hand, it
became necessary to abandon the traditional method
of planning and implementing educational programs.
A regulatory component of the educational process
during a pandemic in the Donbass State Engineer-
ing Academy was the “Regulations on distance learn-
ing for applicants for higher education at the Don-
bass State Engineering Academy in special condi-
tions” (DSMA, 2020). The implementation of this
provision is based on the expansion of distance learn-
ing opportunities through the digitalization of educa-
tion, which, on the one hand, requires an analysis of
the digital infrastructure of the academy, and on the
other, its management. This analysis led to the so-
lution of a global problem for technical universities
– how to implement a laboratory practice on special
equipment in this mode.
All laboratory work can be classified according to
the type of disciplines where they are used. This ap-
plies more to special disciplines, where the student is
often given the task of measuring the characteristics
of any process using real devices or maintaining the
process occurring in a given state. It is also possible
to set some target state, which should be achieved in
the process of laboratory experiment by appropriate
actions of the student (Tarasov et al., 2020a).
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
276

3 CASE STUDY
Consider the possibilities and ways of remote use of
laboratory equipment of laboratories of bioelectron-
ics and biomechanics of the Department of Computer
Information Technologies of Donbass State Engineer-
ing Academy. They are equipped with modern re-
search and production equipment that was purchased
as part of the work in the international project BioArt
Erasmus+ and allows research on the use of modern
computer information technology in electronics, me-
chanics, biomechanics, and mechatronics. The pro-
duction equipment of the laboratories includes ma-
chines with computer numerical control (CNC) and
a 3D printer. This equipment allows to significantly
expand the experience of students in the field of com-
puter modeling and automated design in such CAD-
systems as AutoCAD (2D modeling) SolidWorks and
PTC Creo (3D modeling) by moving from computer
models of objects to their material embodiment.
Computer numerical control means a computer-
ized control system that reads the instructions of a
specialized programming language and controls the
drives of metal, wood, and plastic machining ma-
chines and machine tools. The CNC system inter-
preter translates the program from the input language
to the control commands of the main drive, feed
drives, controllers of the machine units (enable / dis-
able cooling, for example). To determine the required
trajectory of the working body as a whole (tool/work
piece) by the control program (CP) uses an interpo-
lator that calculates the position of the intermediate
points of the trajectory specified in the program end.
CNC machining increases productivity and accuracy
of operations, guarantees a constant level of quality,
which in most cases far exceeds the quality of tra-
ditional manual machining. Many orders that previ-
ously had to be abandoned can now be fulfilled eas-
ily and effortlessly, which in the meantime is consid-
ered exclusive and is the category of the largest profit
(Mikhieienko, 2020b).
CNC machines are represented by the following
models. CNC machine Krechet-4060 manufactured
by the Ukrainian company “CNC machines” (fig-
ure 1). This machine can be used for 2D and 3D
milling of all types of plastics, wood, plywood, MDF,
foam, composite, and light metals. The working field
of the machine 400 x 600 mm, stroke on the Z-axis
100 mm, processing error 0.08 mm.
These are the Sherline 5410 CNC drilling and
milling machine and the Sherline 4410 CNC lathe
(figure 2). Sherline is located in the United States
and is widely known in the world for quality small
machines. These machines allow you to perform ma-
chining of parts in both software and manual control
mode. The free version of Mach 3 is used as soft-
ware for controlling motor controllers. It is enough to
control the processing of medium-sized parts.
The Sherline 5410 CNC drilling and milling ma-
chine have a motor power of 0.6 kW, a spindle speed
range of 70–2800 rpm, axial movement: X/Y/Z –
220/127/159 mm, respectively. Stepper motors to
control the movement of the axes with a capacity of
0.2 kW.
The Sherline 4410 CNC lathe has a motor power
of 0.6 kW, spindle speed range 70–2800 rpm, spindle
bore diameter 10 mm, rear headstock quill stroke 45
mm, rear headstock quill cone – MK1, turning diam-
eter over frame 180 mm, turning diameter above the
transverse caliper 90 mm, the distance between the
centers 430 mm, the course of the transverse caliper
110 mm. Stepper motors to control the movement of
the axes with a capacity of 0.2 kW. There is a com-
plete set of equipment that allows you to process not
completely cylindrical parts and cut threads. The ma-
chine allows to carry out processing with simultane-
ous movement of the tool on two coordinates.
Additive technologies have made a big qualita-
tive leap in recent years, moving from the category
of industrial equipment to personal devices. Due to
this, there is an opportunity for the widespread intro-
duction of this technology in the educational process.
This allows not only to refine and expand the clas-
sic laboratory workshop but also to increase students’
motivation and develop their competencies in the field
of new technologies and their practical application.
In the conditions of active modernization of ed-
ucation, equipping universities with modern com-
puter technology and transition to various forms of
e-learning, there is an active introduction into the ed-
ucational process of various virtual simulators and
complexes designed to replace real physical experi-
ment, the base of which is often not updated and ob-
solete over time. But a real physical experiment plays
a very important role in the learning process. It allows
not only to instill skills in working with equipment,
but also to develop research and cognitive interest in
students (Mikhieienko, 2020a).
The presence of a large number of 3D printing
technologies on the one hand gives a wide field for
choice, on the other hand, imposes certain restrictions
on their implementation. One of the most common
3D printing technologies is FDM (fused deposition
modeling).
Among the main advantages of this type of print-
ing are the following:
• the use of fairly compact printing devices that do
not require special knowledge and skills in instal-
Opportunities and Ways of using Laboratory Equipment in a Distance Learning Environment
277

Figure 1: CNC machine Krechet-4060.
Figure 2: CNC machines: Sherline 5410 CNC and Sherline 4410 CNC.
lation and operation;
• relatively low (compared to devices that use other
technological processes) cost, both the devices
themselves and consumables;
• the principle of the press is simple and technolog-
ical that does not demand special places of instal-
lation;
• openness of technology, i.e. the possibility of its
improvement and modification (the possibility of
assembling a printing device from a ready-made
designer or set of components).
Equipment for additive production in laboratories
is represented by a 3D printer FARM2 (figure 3). This
3D printer has a printing area of 200x200x200 mm,
implements ULTIMAKER kinematics, and has the
ability to print the following types of plastic: PLA,
ABS, PVA, Nylon, HDPE, PCL, PET-G.
Let’s move directly to consider the possibility of
remote laboratory work on CNC machines and 3D
printers. Unfortunately, at the moment, for the full op-
eration of machines and printers, some operations can
only be performed by humans. For CNC machines it
is the installation and replacement of working tools,
blanks and finished products, chip cleaning. For 3D
printers, this is a replacement for plastic and printed
models. Although for some of these operations there
is already a solution for full or partial automation (tool
replacement and chip removal), laboratory work on
CNC machines and 3D printers without the interven-
tion of a teacher or laboratory assistant is currently
impossible. But, despite this, it is already possible
to remotely monitor the operation of CNC machines
and 3D printers, get the parameters of their work and
quickly adjust them. Consider ready-made solutions
in this area.
In (Rocha and Tostes, 2018) the possibility of
quality control and remote control of the device using
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
278
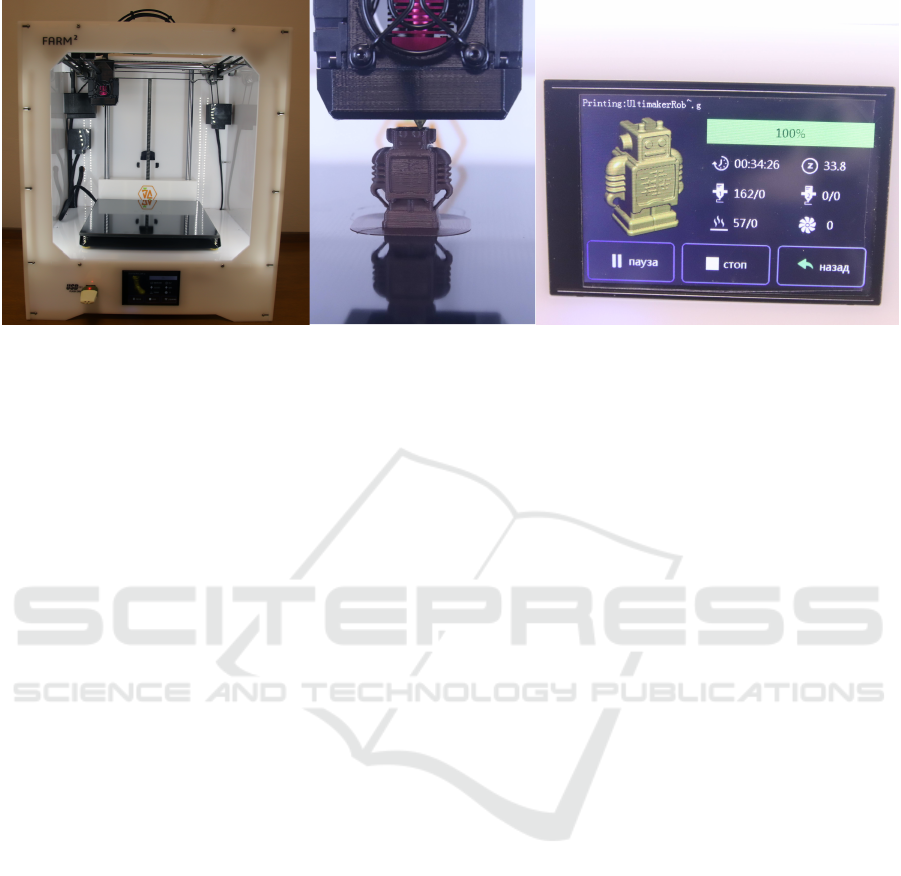

Figure 3: 3D printer FARM2.
a server is considered. The development of a server
for CNC machine tool management is considered in
order to improve the user experience and expand the
capabilities of the device, including remote monitor-
ing of the device. The work is based on the implemen-
tation of synchronous engine control using such pa-
rameters as: Constant snap period, Constant jerk pe-
riod, Constant acceleration period, Constant velocity
period, and imposed snap bound. This set of param-
eters is a classic for CNC machines. To control the
device, it uses a simple built-in system (single-board
computer) Beaglebone Black with control through the
OS Linux kernel, acting as an operating system. Due
to the choice of OS Linux as the operating system, the
firmware software is open source.
To implement the firmware used a patch RTLinux
(Savant and Desai, 2007), designed to work with com-
ponents in real-time. The exchange of information
between blocks in real-time is through shared mem-
ory. A program in C++ using a server on Linux was
developed for remote device management. The pro-
gram works as a server processing client requests. To
implement the client part in the course of work were
considered 3 options: a console application on Linux,
a console application on Windows, and an application
with a graphical interface. PRUSS firmware was de-
veloped to perform real-time calculations. The server
application used writes data to the shared memory,
which uses the PRUSS firmware to generate control
signals and exchange their states via GPIO. The board
and computer interact via a TCP connection via an
Ethernet port.
One of the most common open-source firmware
for remote control of 3D printers is the RepRap sys-
tem. In (Liu et al., 2017) its application is consid-
ered. The web server is developed in Python in con-
junction with the Tornado framework. The authors
highlight some advantages of using the above frame-
work to implement the server. The main advantage is
the lightness of the system and the ability to scale to
service up to tens of thousands of open connections,
which is well suited for the operation of the printer
management system during long-term use of the con-
nection. The paper describes in detail the principle of
client-server communication based on the HTTP pro-
tocol, which allows studying in detail the process of
information transfer. The client part is a web page.
As a result of firmware research, promising directions
of technology development are proposed, including
improving the functionality of the remote Rep-Rap
server.
To improve the user experience when working
with printing devices, the capabilities of 3D printers
need to ensure their extensibility. One of these mod-
ifications is to provide full or partial tracking of the
behavior of device modules. Monitoring the printing
process requires access to readings from various types
of sensors and printer components. Monitoring the
printing process requires access to readings from var-
ious types of sensors and printer components. This
system allows you to automate the collection of in-
formation about the device for subsequent display of
data to the user to analyze the operation of the printer.
There are also more advanced technologies for track-
ing the printing process, in which the status of the
printer is monitored by analyzing readings from sen-
sors and the position of the head using a neural net-
work (Zhang et al., 2019). The article analyzes the
operation of the position sensor, which is used to col-
lect data on the status of the printer. It uses the pre-
diction root mean square error as an indicator to de-
scribe the operating state of the printer. As a prospect
for the development of technology, the introduction
of such analysis into the remote control system of a
3D printer should be considered, it will allow moni-
toring the quality of the printing process and remotely
Opportunities and Ways of using Laboratory Equipment in a Distance Learning Environment
279
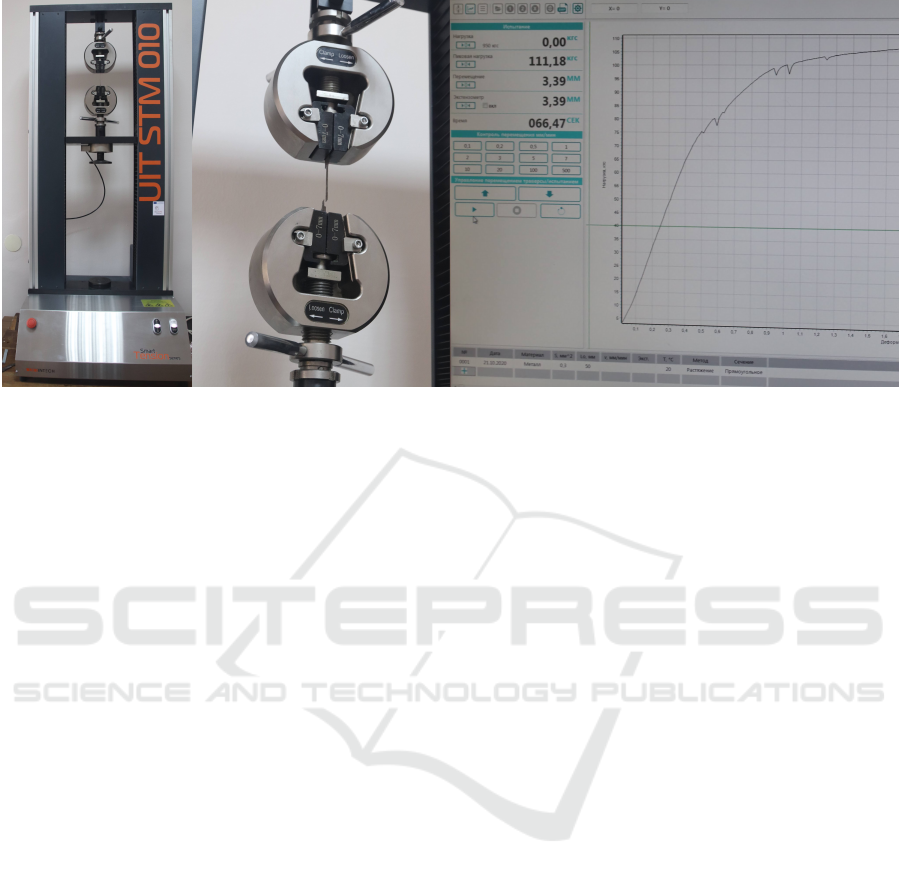
Figure 4: Universal testing machine UIT STM 001.
monitoring the health of the device.
Also, many amateur projects for remote control of
3D printers on the use of open-source software (more
often OctoPrint) and single-board computers Rasp-
berry Pi and Orange Pi are posted in the public do-
main.
Consider the ways of remote use of equipment for
research and development. The study of the mechani-
cal properties of medical purposes, for example, met-
als, composites, threads, are investigated on a uni-
versal testing machine UIT STM 001, which can be
completed with a variety of equipment and devices,
and the software allows testing according to various
standards (GOST, GB, ASTM, DIN, ISO, etc.) and
techniques (figure 4). Using an application program-
ming interface (API) allows you to develop software
products to extend the capabilities of the testing ma-
chine.
Full automation of the testing machine has the
same obstacles as the automation of machine tools
and 3D printers - human intervention is required, in
the case of a testing machine, to replace prototypes.
The ways of partial remote translation of laboratory
work on a testing machine are also similar – remote
monitoring and control.
But in the case of a testing machine, an alter-
native way is possible – replacing real laboratory
works with virtual ones. In (Vasilyeva and Portnya-
gin, 2017), a prototype of virtual laboratory work was
developed for use in the educational process in the
course ”resistance of materials”. The software pack-
age in real-time provides a full cycle of laboratory
work: preparatory stage (training), installation and re-
moval of the sample, performing measurements of the
sample before and after testing, test, plotting a tensile
diagram to determine the main mechanical strength
characteristics (figure 5). The tests have shown that
the use of modern technologies for performing vir-
tual laboratory work in the educational process sig-
nificantly increases the quality and efficiency of the
learning process and can be used in conjunction with
work on real equipment.
Experience has shown that most students had no
problems with running the labs and completing them.
We believe that the best result is achieved when they
are conducted in real-time, with the teacher’s expla-
nations via video link and dialogue with the students.
4 CONCLUSION
Developed courses are at the stage of implementation
in the educational process. The study of the features
of laboratory work in the conditions of distance learn-
ing showed:
• at this point, it is impossible to make com-
plete automation of equipment for remote labo-
ratory work. Human intervention is required for
some operations. This makes it relevant to de-
velop communications between students, teach-
ers, and laboratory assistants using modern elec-
tronic means of communication, planning, and
optimization of the working time of laboratory
equipment;
• there are many ready-made solutions for remote
monitoring and control of laboratory equipment
using open source software, single-board comput-
ers, cloud services, server, and client applications;
• in some cases, an alternative to laboratory work
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
280

Figure 5: Program interface with three-dimensional models, interface, and mini cameras for simultaneous control of all
processes (Vasilyeva and Portnyagin, 2017).
on real equipment is to replace them with virtual
laboratory works.
The authors do not view the virtual labs as a
complete substitute for the real ones. However, we
think that they will organically complement class-
room work after the pandemic is over.
REFERENCES
Bakhmat, L., Babakina, O., and Belmaz, Y. (2021). Assess-
ing online education during the COVID-19 pandemic:
a survey of lecturers in ukraine. Journal of Physics:
Conference Series, 1840(1):012050.
Bataineh, K. B., Atoum, M. S., Alsmadi, L. A., and
Shikhali, M. (2021). A silver lining of coron-
avirus: Jordanian universities turn to distance educa-
tion. International Journal of Information and Com-
munication Technology Education, 17(2):138–148.
https://www.igi-global.com/gateway/article/260754.
Bojovi
´
c,
ˇ
Z., Bojovi
´
c, P. D., Vujo
ˇ
sevi
´
c, D., and
ˇ
Suh, J.
(2020). Education in times of crisis: Rapid tran-
sition to distance learning. Computer Applications
in Engineering Education, 28(6):1467–1489. https:
//onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cae.22318.
Chen, Z., Jiao, J., and Hu, K. (2021). Formative assessment
as an online instruction intervention: Student engage-
ment, outcomes, and perceptions. International Jour-
nal of Distance Education Technologies, 19(1):50–65.
https://www.igi-global.com/gateway/article/264397.
DSMA (2020). Polozhennia pro dystantsiine navchannia
zdobuvachiv vyshchoi osvity za dennoiu formoiu u
donbaskii derzhavnii mashynobudivnii akademii v os-
oblyvykh umovakh. https://tinyurl.com/r3nfs7e6.
Faek, R. and El-Galil, T. A. (2020). The shift to online
education in the arab world is intensifying inequality.
https://www.al-fanarmedia.org/2020/04/the-shift-to-
online-education-in-the-arab-world-is-intensifying-
inequality/.
GOLDi (2021). The Grid of Online Laboratory Devices
Ilmenau. http://goldi-labs.net/.
International Commission on the Futures of Educa-
tion (2020). Education in a post-COVID world:
Nine ideas for public action. United Na-
tions Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organiza-
tion, Paris. https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/
pf0000373717/PDF/373717eng.pdf.multi.
Liu, C., Jiang, P., and Jiang, W. (2017). Embedded-web-
based remote control for RepRap-based open-source
3D printers. In IECON 2017 - 43rd Annual Confer-
ence of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pages
3384–3389.
Mikhieienko, D. (2020a). The use of additive technologies
in the educational process of the department of com-
puter information technologies. In Modern education
- accessibility, quality, recognition, pages 109–111,
Kramatorsk. DSEA.
Mikhieienko, D. Y. (2020b). Introduction of the use of
cnc machine in teaching the discipline of computer
design technology. In Automation and computer-
integrated technologies in production and education:
state, achievements, development prospects, pages
263–264. Cherkasy. https://conference.ikto.net/pub/
akit 2020 16-22march.pdf.
Mintii, I. S. (2020). Using Learning Content Management
System Moodle in Kryvyi Rih State Pedagogical Uni-
versity educational process. CEUR Workshop Pro-
ceedings, 2643:293–305.
Rocha, P. and Tostes, E. (2018). Development of an embed-
ded CNC control system. In 2018 13th IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Industry Applications (INDUS-
CON), pages 407–412.
Sancristobal, E., Mart
´
ın, S., Gil, R., Ordu
˜
na, P., Tawfik,
M., Pesquera, A., Diaz, G., Colmenar, A., Garc
´
ıa-
Zubia, J., and Castro, M. (2012). State of art, initia-
tives and new challenges for virtual and remote labs.
In 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Ad-
vanced Learning Technologies, pages 714–715.
Savant, B. and Desai, R. (2007). Deployment of RTLinux
on various platforms. In 2007 IET-UK International
Opportunities and Ways of using Laboratory Equipment in a Distance Learning Environment
281

Conference on Information and Communication Tech-
nology in Electrical Sciences (ICTES 2007), pages
1058–1062.
Semerikov, S., Chukharev, S., Sakhno, S., Striuk, A., Osad-
chyi, V., Solovieva, V., Vakaliuk, T., Nechypurenko,
P., Bondarenko, O., and Danylchuk, H. (2020). Our
sustainable coronavirus future. E3S Web of Confer-
ences, 166:00001.
Tarasov, A. F., Getman, I. A., Turlakova, S. S., Stashkevych,
I. I., and Kozmenko, S. M. (2020a). Methodical as-
pects of preparation of educational content on the ba-
sis of distance education platforms. CEUR Workshop
Proceedings, 2643:161–173.
Tarasov, O., Vasylieva, L., Altukhov, O., and Anosov, V.
(2020b). Automation of the synthesis of new design
solutions based on the requirements for the function-
ality of the created object. CEUR Workshop Proceed-
ings, 2711:161–175.
Trubavina, I., Dotsenko, S., Naboka, O., Chaikovskyi, M.,
and Meshko, H. (2021). Developing digital compe-
tence of teachers of humanitarian disciplines in the
conditions of COVID-19 quarantine measures. Jour-
nal of Physics: Conference Series, 1840(1):012052.
UN (2020). COVID-19 i Vysshee obrazovanie: Otuchitsia
ot prezhnikh navykov radi sozdaniia sistemy obrazo-
vaniia na budushchee (COVID-19 and Higher Educa-
tion: Unlearn Previous Skills to Build Education for
the Future). https://www.un.org/ru/85374.
Vasilyeva, L. V. and Portnyagin, A. S. (2017). Implementa-
tion of a simulator of a specialized explosive machine
for conducting virtual laboratory work. Scientific pa-
pers of Donetsk National Technical University: Infor-
matics, Cybernetics and Computer Science, 24(1):30–
35. http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Npdntu inf 2017 1 6.
Velykodna, M. (2021). Psychoanalysis during the COVID-
19 pandemic: Several reflections on countertransfer-
ence. Psychodynamic Practice, 27(1):10–28.
www.eztalks.com (2017). Advantages and
disadvantages of distance learning.
https://www.eztalks.com/elearning/advantages-
and-disadvantages-of-distance-learning.html.
Zhang, S., Sun, Z., Long, J., Li, C., and Bai, Y. (2019). Dy-
namic condition monitoring for 3D printers by using
error fusion of multiple sparse auto-encoders. Com-
puters in Industry, 105:164–176.
Zub
´
ıa, J. G. and Alves, G. R., editors (2011). Using Re-
mote Labs in Education: Two Little Ducks in Re-
mote Experimentation. University of Deusto, Bil-
bao. http://www.deusto-publicaciones.es/deusto/pdfs/
otraspub/otraspub01.pdf.
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
282
