
Development of Future Foreign Language Teachers’ Soft Skills by Means
of ICT in Ukrainian Universities
Natalia V. Bondar
1
, Tetiana V. Konovalenko
1 a
and Ivan G. Riznitskii
2
1
Bogdan Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Pedagogical University, 20 Hetmanska Str., Melitopol, 72300, Ukraine
2
State University of Economics and Technology, 5 Stepana Tilhy Str., Kryvyi Rih, 50006, Ukraine
Keywords:
Hard Skills, E-Learning, Soft Skills, Online Technology Analysis, Distance Learning.
Abstract:
The aims of this paper are to overview the main aspects of soft skills development by means of ICT in higher
education Ukraine. The ways of future foreign language teachers’ soft skills development are identified within
the core and selective parts of the curriculum of Bachelor’s level. The article discusses the essence of soft
skills, their difference from hard skills and the main recent tendencies of their development by means of ICT
in Ukrainian higher education. The idea of creating educational-professional hub and its programme aimed at
future foreign language teachers’ soft skills development is outlined.
1 INTRODUCTION
Significant changes in science, economics and soci-
ety for the last two decades have influenced the de-
velopment of the education sector, setting the objec-
tive of training employable professionals who are able
to respond to today’s challenges and adapt to various
working conditions. Recently, in Ukrainian higher ed-
ucation the so-called soft skills and their importance
for the employability of graduates are frequently dis-
cussed. According to the opinion polls, most employ-
ers prefer a candidate who has developed soft skills,
while purely professional skills (hard skills) are of
primary importance for only 20% of the employers
(Mitchell, 2008). The reason for this is that having
professional knowledge and skills (hard skills) is not
enough to perform a wide range of professional tasks.
A person must have the universal skills needed in any
activity: the ability to think critically, find the nec-
essary information, work in a team, be resistant to
stress, rationally plan his or her time, etc.
The European Commission declared that “a large
number of Europeans, particularly highly-qualified
young people, work in jobs that do not match their
talents and aspirations. At the same time, 40%
of European employers report that they cannot find
people with the right skills to grow and innovate”
(ec.europa.eu, 2016). Council Recommendation on
Key Competences for Lifelong Learning (EC, 2018)
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4867-324X
was suggested as the way to help more people “ac-
quire the core set of skills necessary to work and live
in the 21st century with a special focus on promot-
ing entrepreneurial and innovation-oriented mind-sets
and skills” (ec.europa.eu, 2016). The issue is espe-
cially relevant to Ukrainian context as there are more
and more employers focusing on European standards
and requirements for employees’ hard and soft skills.
In Ukraine, the first sociological investigation of
digital skills demonstrated that 53% of Ukrainian
population are below the average mark, 15.1% of
them do not have any digital skills at all (Diia, 2019).
Digital skills are soft skills for all except IT special-
ists; moreover they can help to develop a range of
other soft skills.
Such skills will be useful not only in professional
activities, but also in everyday life, and will help to
better arrange the living space, solve various life is-
sues as well as establish relationships with others.
The study of the soft skills development has become
increasingly popular among scientists. On the one
hand, scientists and managers who are engaged in
business research and looking for the ways to train
competitive workers discuss the feasibility of soft
skills development. On the other hand, the impor-
tance of soft skills development is considered not only
as a significant advantage in the business sphere, but
also in any other field, including education.
Any teacher must have his or her soft skills devel-
oped as they interact with various people every day:
students, parents, colleagues. It is important for them
Bondar, N., Konovalenko, T. and Riznitskii, I.
Development of Future Foreign Language Teachers’ Soft Skills by Means of ICT in Ukrainian Universities.
DOI: 10.5220/0010932400003364
In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2020) - Volume 2, pages 425-433
ISBN: 978-989-758-558-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
425

to be able to build relationships with others, present
themselves and their ideas, have leadership qualities.
The teachers face unpredictable situations every day,
so they are expected to act effectively both inside and
outside the school. The ability to efficiently behave
in both typical and critical situations is one of the
characteristic features of the developed soft skills of a
teacher (Konovalenko and Goncharova, 2018). New
trends in education lead to changes and the search
for new models of future teachers’ training, which fo-
cuses on the student-centredness, forms the image of a
new generation teacher, teacher-facilitator, colleague,
educator, project manager, communicator, researcher,
innovator. Without developed soft skills it will be im-
possible for a teacher to perform this role.
The most prominent feature of the modern educa-
tional process is the active involvement of ICT in the
classroom, which is undoubtedly an extreme need of
the information society. The continuing development
of digital technologies provides teachers with unlim-
ited opportunities for the implementing, development
and use of new methods and technologies in the edu-
cational process, helping to improve it, adapt to new
labour market requirements, and to make the process
of acquiring knowledge by students more engaging
and productive.
The use of ICT as one of the tools in the process
of future foreign language teachers’ soft skills devel-
opment has not been revealed in the researches pro-
foundly enough. There are a lot of research and sci-
entific publications on the use of ICT in the process
of learning foreign languages in higher educational
institutions or secondary schools. Nevertheless, the
use of ICT as a means of soft skills development has
not been sufficiently studied, thus the topic of our re-
search is relevant in the context of recent world events
and challenges the system of higher education faces
today.
The aim of the article is to review the experience
of future foreign languages teachers’ soft skills de-
velopment and to outline the effective ways of their
development by means of ICT in Ukrainian universi-
ties.
2 METHODS
The methodology of our investigation is presented
with the standard procedure of action research as it is
one of the most dynamic, flexible and effective ways
of implementing new ideas in the education sphere.
According to Mertler (Mertler, 2018) we are fol-
lowing such stages:
• Identifying and limiting the topic
• Gathering information
• Reviewing the related literature
• Developing a research plan
• Implementing the plan and collecting the data
• Analysing the data
• Developing an action plan
• Sharing and communicating the results
• Reflecting on the research process.
This paper presents the beginning stage of the
study and action research cycle. So, it reveals the
topic relevance, discusses the world and Ukrainian
experience within the issue, describes the research
plan and the first data obtained.
This research describes the attempt to accumulate
the recent experience of educational community to
face the challenges of new educational environment,
to elicit what students and university teachers felt and
how they reacted to emerging factors, to synthesise
and communicate issues to be solved, and thereby
to stimulate implementing the best practices of soft
skills development by means of ICT. We suggest ex-
panding the lens of focus from individual effective
practices of university teachers to common use and
creating the new model of future foreign languages
teachers’ soft skills development in the process of
their training in Ukrainian universities.
We are going to involve all categories of stake-
holders into our research as it is necessary to know the
needs of students, university teachers, university man-
agement, their future school students, school admin-
istration, parents and authorities responsible for edu-
cation on national level. Thus, besides of literature
review, practical experience study, we need qualita-
tive and quantitative data as well as mixed methods to
engage the stakeholders to eliciting and synthesising
all relevant data and create the model of future foreign
languages teachers’ soft skills development by means
of ICT.
In this article we reveal our experience of finding
the answers to such research questions:
1. What is ‘soft skills’?
2. How have they been changing and what influences
their change?
3. Which soft skills are especially important for fu-
ture foreign language teachers?
4. What are the best practices for the development of
soft skills?
5. What issues have not been solved yet?
6. How can the use of ICT contribute to the develop-
ment of soft skills?
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
426

The answers to these questions will help us to col-
lect the necessary data and start designing the model
of future foreign languages teachers’ soft skills devel-
opment by means of ICT relevant to Ukrainian higher
education.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The concept of soft skills has become an integral part
of the labour market in many areas of the economy,
and there are some other closely related terms.
Cinque (Cinque, 2016), researching the develop-
ment of skills which we call ‘soft skills’, provides a
list of terms used by different organizations in differ-
ent periods:
Analysing these terms, we can see that they con-
tain the words ‘future’, ‘life’, ‘social’, ‘society’, i.e.
the presence of these skills is seen as a guaran-
tee of the success in the life of a particular person,
which leads to the success in society. And the verbs
‘transversal’ and ‘transferable’ indicate the universal
nature of these skills, the ability to use them in vari-
ous activities. The term ‘soft skills for talent’ empha-
sizes that the development of soft skills gives a person
more opportunities to realize his or her natural abili-
ties, and as a result increases success in the career life
and promotes self-realization, which in turn is the key
to harmonious and happy life.
The Oxford Dictionary defines ‘soft skills’ as
“personal qualities of a person that contribute to suc-
cessful communication with other people: the abil-
ity to work together, enthusiasm, emotional intelli-
gence” (www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com, 2021).
At the same time, life skills are defined as “skills nec-
essary or extremely useful for managing daily life:
the ability to work in a team, solve problems, liter-
acy and arithmetic skills. They also include such vi-
tal skills as the ability to cook or use a washing ma-
chine” (www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com, 2021).
Thus, although the terms ‘soft skills’ and ‘life skills’
are closely related, there is a difference between them.
The use of the term ‘life skills’ is more acceptable
when we talk about the formation of skills necessary
for a person primarily for independent living, adap-
tation to living conditions, solving life and everyday
problems. While the concept of ‘soft skills’ is more
often used in the context of training a person for fu-
ture professional activities.
The concepts of soft skills and hard skills origi-
nated in the 1960s and 1970s in military affairs and
were expressed in the doctrine of “Military Training
Design Systems”: hard skills were used to denote
machine skills and soft skills – to work with people
and papers. Subsequently, the terms began to be ac-
tively used in business. Robles (Robles, 2012) con-
sidered the need to develop soft skills in students as
one of the important factors in preparing them for suc-
cessful business communication. Mitchell (Mitchell,
2008) wrote about the importance of integrating soft
skills into business school curricula, which would
contribute to the further successful employment of
students and their competitiveness in the labour mar-
ket of the 21st century. There is a growing talk about
the need to develop soft skills in any profession and
emphasise the need to include the development of soft
skills in educational programs as one of the manda-
tory components, along with training for specialised
professional skills.
Thus, the modern education faces the necessity of
training primarily teachers who have well-developed
hard and soft skills, and who are able to contribute
to the further effective development of these skills
of their future students. That is why in the Reg-
ulations on Accreditation of Study Programmes in
Higher Education, one of the important sub-criteria
(sub-criterion 2.6) is the following: “The study pro-
gramme envisages the development of soft skills in
students that meet stated objectives” (NAQA, 2019),
which will help graduates succeed in their workplace.
The ratio of soft skills and hard skills may dif-
fer for individual professions. There are professions
that provide accurate calculations, drawings, exper-
iments, and in these professions the hard skills are
more important, because the level of their develop-
ment mostly influences the result of the task fulfilled.
Whereas the professions which are directly related to
communication with people, planning, trade, art, re-
quire more focus on soft skills. However, it should
be noted that, for example, researchers in a laboratory
with advanced communication skills will have a bet-
ter chance of professional growth, as they will be able
to present themselves and their ideas better than their
colleagues, whose soft skills are less developed.
When compared with the hard skills, the soft skills
are based more on personal values and in response
Development of Future Foreign Language Teachers’ Soft Skills by Means of ICT in Ukrainian Universities
427

to certain actions the models of human behaviour are
engaged. The development of soft skills is slower and
reaching a certain level is not guaranteed. Soft skills
under certain conditions have a tendency to reverse
development, while hard skills have almost no such
tendency (Dlugunovych, 2014).
There are many universal skills that may be
needed in a profession and for life in general. A
study by Simona (Simona, 2015) among teachers in
the UK, Denmark, Spain, Romania and Portugal iden-
tified such life skills as:
• Numeracy skills
• Literacy and communication
• ICT skills
• Interpersonal skills
• Use of foreign languages
• Entrepreneurship
• Job seeking
• Learning to learn
Most of these life skills can be attributed to soft
skills. Among the proposed list, teachers had to
choose the most important in their opinion. The study
found that the most desirable skills to be included in
school curricula were: literacy and communication
for Danish, British, Romanian and Spanish teachers,
ICT skills for Portuguese and Romanian respondents,
interpersonal skills for British respondents, learning
to learn for Danish Spanish and Portuguese teachers,
use of foreign languages for Danish respondents. The
most acceptable means to implement the involvement
of these flexible skills in the curriculum, according
to the author, are the method of case-study and role-
playing games (Simona, 2015).
The World Economic Forum in 2015 highlighted
the 10 most important qualities needed in 2020 for
successful employment, the so-called Davos concepts
(Lazorenko and Krasnenko, 2019):
1. Complex problem solving
2. Critical thinking
3. Creativity
4. People management
5. Coordinating with others
6. Emotional intelligence
7. Judgement and decision making
8. Service orientation
9. Negotiation
10. Cognitive flexibility
This list has been transformed to a shorter one, so
there are four competences on it now (Lazorenko and
Krasnenko, 2019):
1. Critical thinking
2. Communication
3. Creativity
4. Collaboration
Each profession requires greater development of
certain soft skills. Thus, in the typical program
“Methodology of teaching English” for future teach-
ers of English, the need to create opportunities for
the development of essential life skills (which corre-
sponds to our understanding of soft skills) that tran-
scend subject boundaries, is emphasised. Accord-
ing to the programme, these important skills include
(Bevz et al., 2009):
1. Communication
2. Collaboration
3. Creativity
4. Critical thinking
5. Information literacy
6. Intercultural awareness
7. Problem-solving
8. Time management
As skills are different, approaches, methods and
tools for their development will be different. So that
the teacher could work effectively with students and
help them develop the above mentioned skills, he
must plan the expected results and the program of ac-
tion that will help students to develop the appropriate
soft skills. The use of ICT in the educational process
will greatly facilitate the formation of soft skills, and
at the same time students’ awareness of higher educa-
tion latest trends will be greatly enhanced with digital
and ICT literacy. Kuybida et al. (Kuybida et al., 2019)
states that the development of digital skills is one of
the conditions for developing the digital market of any
country, a necessary condition for successful cooper-
ation and interaction in ‘innovation ecosystems’.
Nowadays ICT play a crucial role in future for-
eign language teachers’ soft skills development. In
our research we will use such understanding of ICT –
“a set of methods, production processes, software and
hardware, integrated for collecting, processing, stor-
ing, transmission, demonstrating and the use of data
in the interests of their users” (Shvachich et al., 2017).
The notion of ICTs will be considered not only as
hardware and software, but also as the more advanced
scheme of (Shvachich et al., 2017):
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
428

1. Theoretical principles (concepts and laws of com-
puter science).
2. Methods of solving problems (modeling, system
analysis, system design, methods of transmis-
sion, collection, production, accumulation, stor-
age, processing, transmission and protection of in-
formation).
3. Means for achieving tasks:
• hardware (personal computer and its compo-
nents; local and global networks, modern pe-
ripheral equipment);
• software (system, applied, universal, special,
instrumental).
Nowadays ICTs are widely used in the educational
process and in many cases due to the use of ICT it has
become possible to create virtual universities that do
not require students to stay in the classroom, but allow
them to adjust their curriculum, study outside the city
or country. This surely provides more opportunities to
implement a lifelong learning strategy in order to en-
rich people’s knowledge, improve skills and abilities
necessary for effective adaptation to new professional
and living conditions.
The use of ICT also promotes the implementation
of interactive learning within the system “teacher –
computer – student” and helps primarily to develop
communication skills, the ability to establish emo-
tional contact. Interactivity is a key feature of ICT in
the learning process, it contributes greatly to the im-
plementation of other didactic qualities of ICT, such
as communication, adaptability, productivity and cre-
ativity (Gurevich et al., 2012).
Thus, we see that the basic didactic qualities of
ICT coincide with the basic soft skills that a person
must develop to be successful in today’s world.
In the educational process, ICT can act as a sub-
ject of study, as a learning tools, as a means of manag-
ing the educational process, and as a tool for manag-
ing research and scientific and methodological work
(Gurevich et al., 2012). Speaking about the process
of learning foreign languages and preparing for fu-
ture teaching activities in the context of developing
students’ soft skills, ICT would be considered a learn-
ing tool, a means for managing the learning process,
research and methodological work.
The pandemic of 2020 promoted the massive use
of virtual classrooms and video conferencing soft-
ware. They are often used now as a tools for or-
ganization classes while distance learning. Such
programmes and platforms as Zoom, Google Meet,
Panopto, Microsoft Teams are useful helpers for ev-
ery teacher. In the context of soft skills development
it is worth to mention that all of them contribute to
communication skills development as well as to team-
building development. Being at a distance from each
other, students have a possibility to continue commu-
nication and collaboration. Teachers can use these
tools to split students into groups (break-out rooms),
ask them to write messages in the chat (e.g. in pairs),
share a screen, video, audio or files etc. The use of
software for videoconferences facilitates future teach-
ers’ new understanding of classroom management in
terms of making digital classroom as close to a phys-
ical one as it is possible.
The ICT as a learning tool stands for various soft-
ware, platforms, Internet sources used while learning
foreign languages and obtaining competences needed
for future teachers. One of the most useful foreign
languages learning tools are social services in the In-
ternet, for example, social nets, blogs, mind maps,
imitators of 3D space, which are called Web 2.0 tech-
nology (Kazhan et al., 2020). All these tools allow
students to communicate with native speakers of for-
eign languages, representatives of different cultures
and nationalities, that is much more useful for learn-
ing and more effective than the study of this material
with the help of coursebooks. It also promotes the
development of such students’ soft skills as commu-
nication skills, collaborating, negotiations, emotional
intelligence, intercultural awareness and others.
Mind maps or virtual boards are a good tool to de-
velop critical, systemic and creative thinking as well
as communication skills and team-building. The term
‘mind map’ was proposed by Tony Buzan in 1970s
and later in 2007 the first program (MindMeister) for
creating visualized schemes was made (Ivanova et al.,
2020). At modern stage of ICT development there
is a big variety of such programmes. The most pop-
ular ones are MindMeister, Padlet, Jamboard, Miro,
Coogle, Xmind, BubblUs, MindMup, Canva. These
programmes can be used as auxiliary means for brain-
storming to share thoughts and ideas online. Brain-
storming is one of the most effective methods for crit-
ical and creative thinking development. Mind maps
can also be used for creating notes while lectures and
conferences as well as for planning that can greatly
contribute to the development of time management
skills.
For the visualization of information, graphic
recording is used. Such new techniques of process-
ing and presentation of information as scribing and
sketch-noting can became a good alternative to usual
notes in paper notebooks or presentation. To make
a video with the help of scribing or to write a lec-
ture with the help of sketch-noting one should analyse
and choose the most important facts among the vari-
ety of information proposed by a lecturer or books
Development of Future Foreign Language Teachers’ Soft Skills by Means of ICT in Ukrainian Universities
429

and media. The future teachers should reconceptu-
alise everything and present in the most appropriate
way. All these activities train their thinking mak-
ing it more creative and critical as well as training
their ability to solve complex problems. Among pro-
grammes that can be used for scribing there are Pow-
Toon, GoAnimate, Sparkol Videoscribe, Animaker,
apps used for sketch-noting are Paper by Fifty Three,
Explain Everything, Sketchbook Express, Notability.
These types of visualization are especially valuable
for students participating in project-based multimedia
learning.
In the context of both hard and soft skills devel-
opment CLIL method will be also relevant as joint
learning foreign languages and computer science has
a high potential for enhancing employable teacher
training (Merzlykin et al., 2018).
While considering ICT to be the means of achiev-
ing our research purposes, we studied the current sit-
uation of students’ digital skills development. There
are the survey results realised by a team of researchers
from Bogdan Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Pedagog-
ical University, Kherson State Maritime Academy
and Dmytro Motornyi Tavria State Agrotechnolog-
ical University. According to it “most of the stu-
dents (40.6%) who participated in the survey would
like to study using the mixed learning technology
(combining online, traditional technologies and self-
study), 20.8% of the students prefer studying tradi-
tionally (lectures and practical lessons in the class-
room), 13.9% of the students would like to study in
groups (to get the project task and work on the result),
9.9% of the students would like to study on an individ-
ual schedule, 8/9% of the students would like to study
distantly, 5.9% of the students have pointed out that
there is no matter what technology is used” (Voloshi-
nov et al., 2020). The investigation took place before
the pandemic. Now we know that both students and
teachers faced a lot of challenges mostly associated
with the lack of digital skills.
We conducted a survey among teachers and stu-
dents of Bogdan Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Peda-
gogical University in order to learn the level of aware-
ness of methods for soft skills development and to
identify the most important skills. 10 teachers and
53 students took part in the survey. The survey was
conducted by means of Google Forms. Two question-
naires with similar questions were proposed to each
group.
1. Do you know what soft skills are?
2. How can you define soft skills?
3. What skills from the suggested list are important
in today’s professional and everyday life? (several
possible answers). If necessary, add to the list.
(a) Complex Problem Solving
(b) Critical Thinking
(c) Creativity
(d) People Management
(e) Coordinating with Others
(f) Emotional Intelligence
(g) Judgment and Decision making
(h) Service Orientation
(i) Negotiation
(j) Cognitive Flexibility
4. What skills from the suggested list are important
for a future foreign language teacher? (several
possible answers). If necessary, add to the list.
(The same list)
5. Have you attended trainings, seminars, webinars,
which cover the topic of soft skills development?
6. What methods, techniques would you like the
teachers use in the classroom to improve your soft
skills? (a question for students) / What methods,
techniques do you use in the classroom to develop
students’ soft skills? (a question for teachers)
7. What ICT would help you to improve your soft
skills? (a question for students) / What ICT do
you use in the classroom in order to develop stu-
dents’ soft skills? (a question for teachers).
The study revealed that 90% of teachers have an
idea of what soft skills are, among students the fig-
ure was lower, only 47.8% answered that they know
exactly what soft skills are.
Among the skills a person needs in everyday life,
most teachers chose Critical Thinking (100% of re-
spondents) and Cognitive Flexibility (80%), as well as
Coordinating with Others (80%), Judgment and De-
cision making (70%) and Complex Problem Solving
(70%).
Coordinating with Others (84.9%) was in the first
place for students. Other important features in the
opinion of students are Judgment and Decision mak-
ing (83%) and Creativity (77.4%).
In the questions about the skills necessary for
a future foreign language teacher, Creativity (90%)
and Coordinating with Others (90%) are preferable
from the point of view of teachers. Critical Thinking
(80%) and Cognitive Flexibility are also considered
by teachers to be important qualities for future teach-
ers.
Almost similar results on this issue were obtained
in a survey of students: they consider Coordinating
with Others (86.8%) and Creativity (86.8%) the most
useful skills for future teachers, as well as Cognitive
Flexibility (69.8%) and Negotiation (52.8%).
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
430
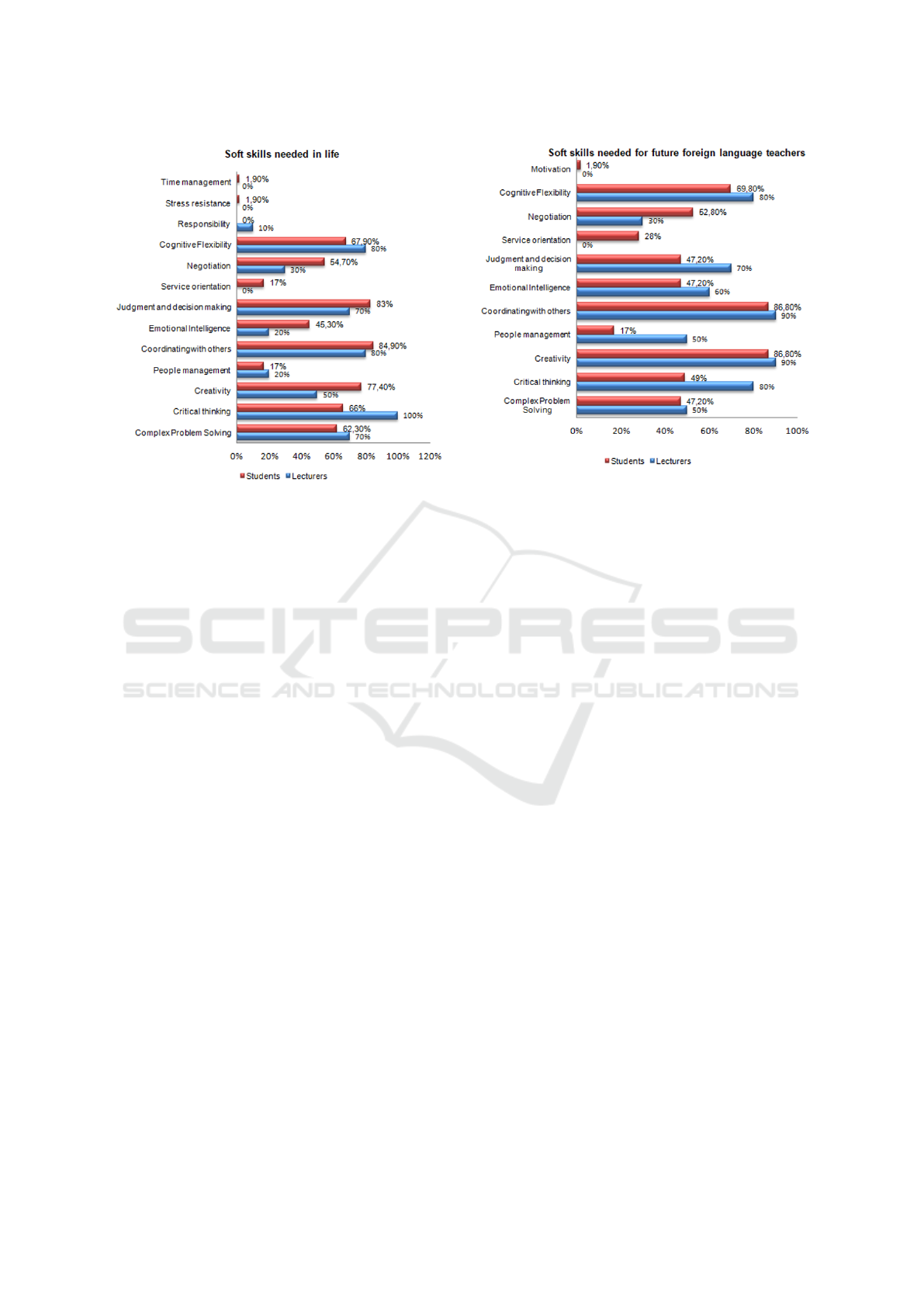
Figure 1: Students’ and lecturers’ attitude to soft skills
needed in life.
The survey also revealed that only 40% of teachers
and 17.8% of students attended trainings, seminars,
webinars dedicated to the soft skills development.
Teachers demonstrated greater awareness of the
methods and techniques used to develop soft skills
(group work, project technology, problem-based
learning, role playing game, business game, dis-
cussion, interactive communication, micro-teaching,
work in variable groups). As for students, most re-
spondents did not have a clear idea of the meth-
ods that can enhance the soft skills development.
Only a few students were able to answer clearly
(group work, business games, creative tasks, research
projects, trainings, interactive games and technolo-
gies). However, almost all respondents mentioned
methods and techniques related to creativity and ac-
tive interaction between people. Some students ex-
pressed their wish to develop time management and
public speaking as rather important skills.
Among ICT assisted methods and techniques used
by teachers in class to develop soft skills, there are
web quests, E-learning, Google Forms, Google Docs,
Jamboard, audio and video materials, case method,
review and analysis of Internet pages on the problem,
computer testing, multimedia equipment, e-mailing,
social networking, TED talks. There were some other
items mentioned though they can be called neither
methods nor techniques.
Many students found it difficult to answer this
question. Some of them mentioned artificial intel-
ligence, various messengers, social networks, video
conferencing, viewing of developing content, infor-
mation portals, mobile applications, media broad-
Figure 2: Students’ and lecturers’ attitude to soft skills
needed in professional activity.
casts, webinars, trainings, interactive quests.
Thus, having analysed the survey data, we can
conclude that both teachers and students have almost
the same idea of future foreign language teacher’s
soft skills. Both groups of respondents replied that
the focus should be made on the development of cre-
ative thinking, creativity and the ability to cooperate
with others. However, we observed a lack of aware-
ness and understanding among students about meth-
ods, techniques and tools to be used in the process of
soft skills development. Thus, it is necessary to pay
more attention to this issue in the educational process
and to integrate soft skills development in educational
programmes content and aims.
On the basis of information collected by us and
mentioned above with the further study of the topic,
we plan to develop a model for soft skills develop-
ment of future foreign language teachers, which will
be mostly associated with the use of modern ICT. It
is planned to implement the developed model into the
educational process of applicants for higher education
of Bogdan Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Pedagogical
University, who study in the specialty 014.021 Sec-
ondary education (English language and literature)
and check its effectiveness.
Now on our list of soft skills to primarily develop
are those offered in the typical program “Methodol-
ogy of teaching English” for Bachelor’s degree (Bevz
et al., 2009): communication, collaboration, creativ-
ity, critical thinking, information and digital literacy,
intercultural awareness, problem-solving, time man-
agement. Step-by-step, we are going to add other soft
skills to this list as modern reality is extremely dy-
Development of Future Foreign Language Teachers’ Soft Skills by Means of ICT in Ukrainian Universities
431

namic and requires flexibility and quick reaction to
everyday challenges in education.
Among methods and technologies to be used first
and foremost are the following:
1. Problem-based learning
2. Case-study method
3. Interactive learning technologies
4. Game technologies
5. Blended learning technologies and m-learning
technology
In the process of implementing the soft skills de-
velopment model, we will focus on classroom and
distance learning within the curriculum of the study
programme. Besides of activities in physical or vir-
tual classes there will be special focus on students’
self-study dealing with their learner autonomy and
other skills. One more component of our model will
be linked to students’ extracurricular activity. For
these purposes the list of recommended ICT tools will
be created to support students.
Our research plan comprises the idea of creation
an educational centre or a hub which will be a territory
for cooperation, collaboration and sharing experience,
a place for discussing issues related to methodology
of teaching foreign languages and various issues re-
lated to the educational process, current trends in ed-
ucation, of the national and world level, small-scale
and large-scale investigations. It is possible to involve
not only students and teachers of Bogdan Khmelnit-
sky Melitopol State Pedagogical University, but also
stakeholders: school teachers, methodologists, vari-
ous educational and cultural organizations represen-
tatives. Other universities, schools and colleges can
also be involved in the cooperation.
By participating in the educational hub, students
will be able to develop such soft skills as communica-
tion skills, skills of cooperation and critical thinking,
to expand their intercultural and international aware-
ness. Participation in seminars, trainings, etc. will al-
low students to prepare for future professional activ-
ities and expand their understanding of modern pro-
fessional requirements, combine their learning and re-
search. A special sequence of workshops with ICT as-
sisted professional development activities will be de-
livered, so that future teachers could handle with their
soft skills at present and be ready for that in future.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The process of training foreign language teachers for
professional activity, equipping them with hard skills
cannot and should not be limited to the development
of professional skills and abilities, it is also necessary
to develop universal skills that will help them be more
competitive in the labour market and more effective
organise their professional activity. In the modern
system of higher education in Ukraine, although there
appear researches of the need to focus on the meth-
ods and ways to develop soft skills of representatives
of various branches, but there are no effective pro-
grammes of action or models of implementing this
idea. So the issue remains relevant and needs further
consideration. We hope that the working out and im-
plementation of the model of future foreign language
teachers’ soft skills development will be effective and
help students feel more confident when starting their
professional career.
There are still a lot of issues waiting for further
study and finding solutions. For future employees in
any branch the framework of their professional train-
ing should contain not only hard skills and compe-
tences but also be focused on creating the opportu-
nities for their soft skills development. The list of
soft skills for each job should be compiled, the rec-
ommendations of the possible ways for their develop-
ment should be produced.
REFERENCES
Bevz, O. P., Hembaruk, A., Honcharova, O. A., Zabolotna,
O. A., Zmiievska, O. O., Kalinina, L. V., Kamynin,
I. M., Konovalenko, T. V., Romanyshyn, I. M.,
Samoiliukevych, I. V., Taran, O. M., Tuchyna, N. V.,
and Khudyk, K. H. (2009). Core Curriculum. English
Language Teaching Methodology. Bachelor’s Level.
NAIR, Ivano-Frankivsk. http://eprints.mdpu.org.
ua/id/eprint/9187/1/Complete 31.10.2019 with%
20curriculum%20guidelines%20%283%29.pdf.
Cinque, M. (2016). “Lost in translation”. Soft skills de-
velopment in European countries. Tuning Journal for
Higher Education, 3(2):389–427.
Diia (2019). Digital literacy of the population of Ukraine.
https://osvita.diia.gov.ua/uploads/0/588-the first in
the history of ukraine research compressed.pdf.
Dlugunovych, N. A. (2014). Soft skills training as a nec-
essary component of IT professionals. Visnyk Khmel-
nytskogo natsionalnogo universytetu, (6(219)). http://
journals.khnu.km.ua/vestnik/pdf/tech/2014 6/47.pdf.
EC (2018). Council recommendation on key competences
for lifelong learning. https://tinyurl.com/pn2h5x47.
ec.europa.eu (2016). Ten actions to help equip people in
Europe with better skills. https://ec.europa.eu/social/
main.jsp?langId=en&catId=89&newsId=2556.
Gurevich, R. S., Kademiya, M. Y., and Shevchenko, L. S.
(2012). Information learning technologies: an inno-
vative approach. Glider, Vinnytsia.
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
432

Ivanova, H. I., Lavrentieva, O. O., Eivas, L. F., Zenkovych,
I. O., and Uchitel, A. D. (2020). The students’ brain-
work intensification via the computer visualization
of study materials. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2643:185–209.
Kazhan, Y. M., Hamaniuk, V. A., Amelina, S. M.,
Tarasenko, R. O., and Tolmachev, S. T. (2020). The
use of mobile applications and Web 2.0 interactive
tools for students’ German-language lexical compe-
tence improvement. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2643:392–415.
Konovalenko, T. V. and Goncharova, O. A. (2018). Future
english language teachers’ life skills development in
methodology course. Studies in comparative educa-
tion, (1 (35)):98–104. http://eprints.mdpu.org.ua/id/
eprint/5041/.
Kuybida, V., Petroye, O., Fedulova, L., and Androshchuk,
G. (2019). Digital competences as a condition for
shaping the quality of human capital. Collection of
scientific works of the National Academy of Public Ad-
ministration under the President of Ukraine, (1):118–
133.
Lazorenko, L. and Krasnenko, O. (2019). The importance
of developing 21st century skills for advanced stu-
dents. In New stages of development of modern sci-
ence in Ukraine and EU countries. Baltija Publishing.
Mertler, C. A. (2018). Action research communities: Pro-
fessional learning, empowerment, and improvement
through collaborative action research. Routledge.
Merzlykin, O. V., Topolova, I. Y., and Tron, V. V. (2018).
Developing of key competencies by means of aug-
mented reality at CLIL lessons. CEUR Workshop Pro-
ceedings, 2257:41–52.
Mitchell, G. W. (2008). Essential soft skills for success
in the twenty-first century workforce as perceived by
Alabama business/marketing educators. PhD the-
sis, Auburn University. https://etd.auburn.edu/handle/
10415/1441.
NAQA (2019). Regulations on accreditation
of study programmes in higher education.
https://en.naqa.gov.ua/wp-content/uploads/2020/
05/Accreditation Regulations 2019 ENG.pdf.
Robles, M. M. (2012). Executive perceptions of the top
10 soft skills needed in today’s workplace. Business
Communication Quarterly, 75(4):453–465.
Shvachich, G. G., Tolstoy, V. V., Petrechuk, L. M.,
Ivashchenko, U. S., Gulyaeva, O. A., and Sobolenko,
O. V. (2017). Modern information and communica-
tion technologies. NMetAU, Dnipro. https://nmetau.
edu.ua/file/ikt tutor.pdf.
Simona, G. (2015). Teacher training for embedding life
skills into vocational teaching. Procedia-Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 180:814–819.
Voloshinov, S., Kruglyk, V., Osadchyi, V., Osadcha, K.,
and Symonenko, S. (2020). Realities and prospects
of distance learning at higher education institutions of
Ukraine. Ukrainian Journal of Educational Studies
and Information Technology, 8(1):1–16.
www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com (2021). Ox-
ford Learner’s Dictionaries. https://www.
oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/.
Development of Future Foreign Language Teachers’ Soft Skills by Means of ICT in Ukrainian Universities
433
