
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information
Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
Alla V. Stepanyuk
1 a
, Liudmyla P. Mironets
2 b
, Tetiana M. Olendr
1 c
, Ivan M. Tsidylo
1 d
and
Maryna V. Kormer
3 e
1
Ternopil Volodymyr Hnatiuk National Pedagogical University, 2 Maksyma Kryvonosa Str., Ternopil, 46027, Ukraine
2
Sumy State Pedagogical University named afer A. S. Makarenko, 87 Romenska Str., Sumy, 40002, Ukraine
3
State University of Economics and Technology, 5 Stepana Tilhy Str., Kryvyi Rih, 50006, Ukraine
Keywords:
School Education, Mixed Learning, Smart Technologies, LearningApps.org, Website, Biology.
Abstract:
This paper considers the problem of integrated use of the LearningApps.org online resource in the process of
Biology studying in secondary schools and information devices. The appropriateness of moving to a mixed
form of learning that involves the creation of a polysubjective educational environment has been justified. The
article concretizes the essence of the notion “polysubjective educational environment” (teacher, pupil, online
resources, and information devices). It has been examined how well the scientific problem is developed in
pedagogical theory and educational practice. The methodology of using the LearningApps.org online resource
in the process of Biology studying in a basic secondary school, which involves the use of information devices,
the PlayMarket server applications, Smart technologies and a website has been created. In particular, a series
of exercises of the LearningApps.org online resource has been simulated, the implementation of which should
be integrated using a SMART Board, a mobile phone, a computer, a laptop, a tablet or other information
devices. Possibilities of their combination with the methodology of using information devices at the lesson in
the process of homework checking, learning new material, generalization and systematization of knowledge
have been revealed. The proposed assignments can be used as individual exercises for pupils at the lesson and
in extracurricular activities. The paper suggests the approach for homework checking, which involves besides
computer control of pupils’ learning outcomes, the use of Miracast wireless technology. The methodology of
conducting a mobile front-line survey at the lesson on the learned or current material in Biology in the test
form, with the help of the free Plickers application, has been presented. The expediency of using the website
builder Ucoz.ru for creation of a training website in Biology has been substantiated. The methodology of
organizing the educational process in Biology in a basic secondary school using the training website has been
developed. The effectiveness of the proposed methodology of using the LearningApps.org online resource in
combination with information devices in the process of Biology studying in a basic secondary school has been
substantiated.
1 INTRODUCTION
Specificity of the modern information society leads
to a change of the ways of human life. This causes
significant transformations in the educational system.
Its transition to a qualitatively new state requires the
optimization and management of the mechanisms of
interaction of all the subjects of learning environment.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3258-9182
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9741-7157
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1665-6413
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0202-348X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6509-0794
Its peculiarity is the functioning of multi-vector infor-
mation flows that need to be taken into account in the
educational process. There is a replacement of the
subject-subjective educational paradigm by a poly-
subjective one (Spivakovska, 2016). Within such a
system of relations, all the subjects of the educational
process interact with each other as active mutually in-
fluential participants. They interact with modern in-
formation technologies (IT), social networks, Internet
services, and others. That is why a new educational
communicative paradigm is actualized, which means
communication in a polysubjective learning environ-
ment.
452
Stepanyuk, A., Mironets, L., Olendr, T., Tsidylo, I. and Kormer, M.
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying.
DOI: 10.5220/0010932800003364
In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2020) - Volume 2, pages 452-465
ISBN: 978-989-758-558-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

New challenges, which face the society related to
the COVID-19 pandemic, have forced biology teach-
ers to reconsider the technical capabilities of informa-
tion technologies in distance learning (Bobyliev and
Vihrova, 2021). One of the advantages of using the
LearningApps.org online resource is the possibility to
integrate tasks into distance learning systems and self-
directed learning: pupils can remotely perform a va-
riety of tasks of biological content. The teacher does
not need to spend time checking assignments, because
the assessment automatically goes to his personal ac-
count.
Modern IT involve wide opportunities of various
social networks to the development of pupils. In con-
sequence of the potential of mass interactivity, immer-
sion, learning in joint activities, they become an effec-
tive tool of learning. The appropriateness of IT use
in the process of Biology school course studying is
caused by the specifics of the object of biological cog-
nition (life in all its manifestations) and the concept of
bio(eco)centrism, which recognizes the life of any or-
ganism as the highest value (Komarova and Starova,
2020).
Biology studying at secondary schools in Ukraine
is aimed at the formation of ten major key compe-
tencies (Shokaliuk et al., 2020), among which are the
following: information and digital competence and
key competencies in natural sciences and technolo-
gies. It is relevantly to form such competencies using
modern information devices in the educational pro-
cess. We consider a computer, an interactive white-
board Smart Board, a multimedia projector, a tablet, a
smartphone, Google Chromecast adapter, and others
to be the modern information devices.
A works (Doroshenko et al., 2005; Lavrentieva
et al., 2020; Matiash, 2004; Mironets and Tori-
anyk, 2018; Savosko et al., 2021; Nevedomska, 2007;
Shcherbakov, 2006; Stepanyuk, 2011) have dealt with
the possibilities of using a computer in the process
of Biology teaching. Matiash (Matiash, 2004) un-
derlines the necessity of using a computer during Bi-
ology school course to increase the effectiveness of
the lesson and the efficiency of the learning process.
Stepanyuk (Stepanyuk, 2011) studies the problem of
using computer learning tools in the methodologi-
cal training of future biology teachers. Nevedomska
(Nevedomska, 2007) considers the positive and neg-
ative aspects of the use of computer technologies in
Biology teaching while examining the levels of infor-
mation and computer systems that form the quality
criteria of the theoretical and practical implementa-
tion of pedagogical computer tools.
Theoretical aspects of mobile learning are dis-
closed in (Horbatiuk and Tulashvili, 2013; Kosyk,
2014; Malchenko et al., 2021; Mironets and Torianyk,
2018; Skrypka, 2015). Methodology of website us-
ing in the process of Biology teaching in a basic sec-
ondary school is revealed by Stepanyuk and Mironets
(Stepanyuk and Mironets, 2019). The essence and
possibilities of using the LearningApps.org online re-
source are described by Aman (Aman, 2019). Fe-
dosenko (Fedosenko, 2020), Bonch-Bruievych et al.
(Bonch-Bruievych et al., 2007) studied the use of
the LearningApps.org builder as one of the means of
SMART technologies in the process of Biology teach-
ing.
However, the analysis of scientific and pedagogi-
cal works shows that the practical aspect of using the
LearningApps.org online resource for conducting ed-
ucational studies in biology with the help of informa-
tion devices was not the subject of a separate study
and is not enough described. Therefore, there is a con-
tradiction between the innovative nature of the devel-
opment of information devices, online resources and
the development of scientific and methodological sup-
port for their implementation in the educational pro-
cess in biology.
The objective of this paper is to outline the pos-
sibilities, as well as the appropriateness of using the
LearningApps.org online resource in the process of
Biology school course studying with the application
of information devices.
The objective was realized through the following
tasks:
1. To clarify the state of development of the problem
at the levels of pedagogical activity and personal
property of pupils.
2. To develop and substantiate the methodology of
using the LearningApps.org online resource in the
process of Biology school course studying with
the application of information devices and to test
experimentally its effectiveness in a basic sec-
ondary school.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
To achieve the abovementioned objective and tasks,
a number of methods have been used, namely: the-
oretical – comparative analysis to find out differ-
ent views on the problem, identify areas of study;
modeling to develop a methodology for using the
LearningApps.org online resource in the process of
Biology school course studying with the application
of information devices; systematization and gener-
alization to formulate conclusions and recommenda-
tions for improving the educational process in biol-
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
453

ogy; empirical – generalization of pedagogical ex-
perience, scientific observation, interviews, content
analysis, questionnaires in order to determine the state
of implementation of the problem in practice and to
develop the content of experimental teaching method-
ology; pedagogical experiment, which provided veri-
fication of the effectiveness of the proposed method-
ology.
Experimental research has been carried out on
the basis of Ternopil general secondary schools No.
24, 26, 28, Terebovlia general secondary school No.
1 (Ternopil region) and Sumy general secondary
schools. Summative experiment involved 528 pupils,
212 biology teachers and 68 future biology teachers,
who are now students of the second (master’s) level of
higher education of Ternopil Volodymyr Hnatiuk Na-
tional Pedagogical University and Sumy State Ped-
agogical University named afer A. S. Makarenko.
Forming experiment lasted for two years (2018–2019
and 2019–2020 academic years) in 6th grades in the
process of Biology school course studying. 1006
pupils participated in it.
Effectiveness of the proposed methodology was
checked during the forming experiment.
The goal of the forming experiment was to test
the effectiveness of the developed methodology of us-
ing the LearningApps.org online resource in combi-
nation with information devices. We drew a conclu-
sion about the quality of the experimental method-
ology according to the criterion “coefficient of com-
pleteness of knowledge acquisition” (A. A. Kyveri-
alg’s method). It was determined using formula 1
(Kyverialg, 1980):
K =
∑
I
0
n · I
a
· 100%, (1)
where K – the coefficient of completeness of knowl-
edge acquisition;
n – the number of pupils who performed the work;
∑
I
0
– the sum of elements of knowledge acquired
by each pupil;
I
a
– the number of alements of knowledge com-
municated to each pupil.
According to the criteria of completeness of
knowledge acquisition, developed by Bespalko (Be-
spalko, 1968), the educational material was consid-
ered to be acquired, and knowledge formed if the
coefficient of knowledge acquisition was higher than
70%. It is believed that a pupil with such a coefficient
of knowledge acquisition is able to further improve
his knowledge through self-education.
The forming experiment was carried out in the
conditions of real educational process on Biology
studying in the 6th grade. It involved the creation of
experimental (EG) and control groups (CG) of pupils.
In EG pupils absorbed botanical knowledge (anatom-
ical, physiological, systematic, agronomic and eco-
logical notions) in the process of studying themes ac-
cording to our experimental methodology of using
the LearningApps.org online resource in combination
with information devices. Experimental training was
carried out during the study of Theme 3 “Plants” (ap-
proximately 20 hours) and Theme 4 “Plant diversity”
(approximately 12 hours) (MON, 2017). Pupils in CG
studied according to the traditional, dominant in mod-
ern secondary school, methodology of forming bio-
logical notions.
Thematic controls of the results of pupils’ from
control and experimental groups acquisition of ele-
ments of botanical knowledge (notions) – morpho-
logical, anatomical, physiological, systematic, agro-
nomic and ecological were carried out in three stages:
Stage I – after studying the themes “Root, steam:
structure and basic functions. Variety and modifica-
tions of vegetative organs. Photosynthesis as a char-
acteristic feature of plants, nutrition, respiration, plant
movements”; Stage II – after studying the themes
“Plant reproduction: sexual and asexual. Vegetative
reproduction of plants. Flower. Inflorescence. Pol-
lination. Fertilization”; Stage III – after studying the
themes “Algae. Mosses. Gymnosperms”.
The choice of these themes is determined by the
carried out content analysis of their content and the
results of the summative experiment. It proved that
the acquisition of anatomical, physiological and sys-
tematic notions causes significant learning difficulties
for schoolchildren.
After conducting each stage of thematic control,
the mistakes made by pupils, their causes, ways to
adjust and improve the methodology were analyzed.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
With the aim to study the state of the problem in the
practice of Biology teaching we carried out a survey
of 212 biology teachers and 528 pupils of the city
schools in Sumy and Ternopil regions. We analyzed
the way teachers train pupils to work with different
sources of information. Thus, 43.87% (93 teachers)
train pupils how to work with the catalogue, 73.58%
(156 teachers) train how to work with the textbook
orientation apparatus, 24.53% (52 teachers) form the
ability to search the necessary information on the In-
ternet.
198 teachers (93.40%) use computer as a tool for
Biology teaching, an interactive whiteboard Smart
Board is used by 46 teachers (21.70%), 86 teach-
ers (40.57%) use multimedia projector, a tablet and
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
454

a smartphone is used by 10 teachers (4.72%), and
8 teachers (3.77%) use Google Chromecast Adapter.
All the 212 teachers (100%) use computer during the
preparation to the lessons. However, only 154 teach-
ers (72.64%) give their pupils home task to search
for the additional information on the Internet, and
198 teachers (93.39%) offer pupils to prepare presen-
tations in the form of a report on the performance
of a specific task. There are the following reasons
for the inadequate use of modern information devices
by teachers in the educational process: insufficient
level of their own computer literacy – 104 teachers
(49.06%); lacking of material and technical as well
as educational and methodological support for Biol-
ogy school course teaching– 148 teachers (69.81%);
the reluctance of teachers to study phenomena and
processes of wildlife using a computer – 52 teach-
ers (24.53%). Only 10 teachers (4.72%) know that
a mobile device can be used as a tool for teach-
ing Biology. Only 23 respondents (10.85%) use the
LearningApps.org resource in the process of Biol-
ogy school course studying. At the same time only
13.04% out of them are aware of the feasibility of in-
tegrating this resource with mobile devices at the les-
son.
With the aim to find out main advantages and dis-
advantages of using the LearningApps.org software in
school practice, a survey of 64 future biology teach-
ers, who are now students of the second (master’s)
level of higher education was carried out. The stu-
dents were introduced to the LearningApps.org re-
source during practical classes in advance and com-
pleted a teaching practice, in the process of which
they modelled and conducted lessons using this online
resource. The results of the questionnaires showed
that future biology teachers identified the following
positive aspects of working with LearningApps.org:
many opportunities to create a variety of didactic
tasks (90.63%); expanding opportunities for the use
of visual and illustrative applications (67.19%); do-
ing exercises it is possible not only to check, but
also to correct mistakes (56.25%); exercises are ef-
fectively used to train pupils’ attention and memory
(39.06%); it is not necessary to print the material
on paper, it is enough to send it to the pupils’ per-
sonal account on the phone (100%); a large number
of convenient templates that are available and easy
to use (90.63%); the ability to view pupils’ learn-
ing outcomes statistics and control their knowledge
(78.13%); the exercise can be accessed using a spe-
cial QR-code, which facilitates pupils’ access to the
exercise and saves time at the lesson (75.00%); the
online resource is completely free (100%); possibility
to create tasks in Ukrainian (100%); possible acquain-
tance with exercises from different countries, which
were previously developed by other teachers and use
them in the own work (56.25%); availability of video,
audio and graphic materials (89.06%); the use of the
online resource is easy and saves a lot of time at the
lesson and when the teacher checks tasks (46.88%);
convenient use of the program during remote work
(100%); it is always possible to change, improve, ex-
pand and differentiate already created tasks by the
teacher (78.13%); the online resource is easy to use
for pupils’ independent work and learning additional
material (90.63%).
Among the disadvantages of using the
LearningApps.org resource future biology teachers
named: the main condition for using the program
is the Internet connection (not all pupils may have
sufficient access to the Internet and not all schools
still have full access to the Internet) (100%); when
updating the interface of the LearningApps.org site,
some tasks may not work if there were changes in
the structure of the task template (56.25%); in some
templates, in the instructions to them the translation
into Ukrainian is not completely available (18.75%);
not all the exercises that are available for use are true
and may contain mistakes (39.06%); the teacher can
use only ready-made exercise templates, but cannot
create templates himself (18.75%); logging in to the
program is possible only through an Internet browser,
there is no specially created application that will
facilitate logging in (45.31%).
All the respondents had a positive attitude towards
the opportunity to use the LearningApps.org resource
in the process of practical activities and its combina-
tion with mobile devices.
The majority of pupils have shown moderate inter-
est to the TV programs about nature (77.65%). Only
7.20% claimed that they are not interested in such pro-
grams at all. 60.23% of pupils like observing plants
and animals and 16.10% demonstrate moderate inter-
est in such an activity. 74.43% of pupils sometimes
address the Internet sources to answer questions dur-
ing the lesson and 19.70% of the pupils often address
various information sources in this case. 5.87% of the
pupils stated that they don’t search for the answers in
additional sources.
The majority of teenagers (87.31%) possess mo-
bile devices (smartphones, tablets), but they use them
mainly for fun or socializing with peers in social net-
works. 18.56% of pupils know that a mobile device
can help in conducting a research both at school and
beyond it, but only 4.55% of respondents use smart-
phones for this purpose.
However, the study of the practice of modern
secondary schools and personal teaching experience
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
455

show that the use of the Internet facilitates bet-
ter learning of education material by pupils. The
LearningApps.org online resource is designed for de-
veloping and storing didactic multimedia interactive
tasks, through which the teacher can form, consoli-
date and test the acquired knowledge, skills and abil-
ities of each pupil in educational, play-based form,
which contributes to the formation of cognitive inter-
est, motivation to learn, critical thinking and indepen-
dence. At the same time the effectiveness of lessons
increases significantly and it encourages pupils to
study. The educational process is intensified through
the increase of its informativeness. Due to this, pupils
improve their ability to orient themselves in the infor-
mation space and, in this case, the teacher acts as a
mentor, consultant. All the above mentioned actual-
izes the necessity in the development of the methodol-
ogy of Biology studying using the LearningApps.org
online resource in combination with information de-
vices.
Our experimental methodology involves the use
of the LearningApps.org online resource in combina-
tion with the following information devices: a com-
puter, an interactive whiteboard Smart Board, a mul-
timedia projector, a tablet, a smartphone, and Google
Chromecast adapter. The main attention is paid to
the use of the m-learning technology. It is caused
by the main advantages of its use, namely: bring-
ing new technology into the classroom; possibility to
use portable devices to support the learning process;
possibility to use the technology as an additional tool
for learning; as a useful add-on tool for pupils with
special needs; available synchronous learning expe-
rience; allows widened opportunities for timing, lo-
cation, accessibility and context of learning (Striuk
et al., 2015).
The challenges of introducing m-learning technol-
ogy were also taken into account. Among them are
as follows: accessibility and cost barriers for users;
incompatibility of some mobile devices with other
applications and devices; frequent changes in device
models, technologies, functionality; number of file
(asset) formats supported by a specific device; risk of
distraction and fragmentation of learning; restriction
of educational information visualization; required
bandwidth for nonstop and fast streaming; tracking of
results and proper use of the information and the lack
of well-developed pupils’ self-control skills; insuffi-
cient “technical” training of school teachers in creat-
ing of mobile application (Tsesarska, 2002).
Smartphones and tablets based on the Android op-
erating system allow you to use online resources and
various free applications that are downloaded from
the PlayMarket server. Analyzing the PlayMarket
server, it has been found that it contains a lot of ap-
plications that are permanent helpers in the biology
learning with the possibility of free downloading. All
applications are installed on the teacher’s smartphone,
and using Google Chromecast adapter, they are dis-
played on the multimedia projector screen.
There are some examples of using templates of the
LearningApps.org online resource for teachers to cre-
ate their own exercises at the Biology lesson:
Exercise “Find a pair” is a universal task that can
be used by the teacher at any stage of the lesson and
in the process of studying various themes. Pupils
like images, text information, or videos to help them
match the right pairs. A bright example is to match
the image of the plant to its name (which taxonomic
link it belongs to). If a pupil forms a pair correctly,
the colour is green, but if a mistake is made, the pair
is shown in red.
Example: you can see images of the main rep-
resentatives of the Gymnosperms group and their
species names on the Smart Board (figure 1). Pupils
come up to the board in turn and try to match an im-
age and a species name. There is an exercise check at
the end (highlighting correct and incorrect answers in
colours).
Exercise “Classification” is used for selective sort-
ing of statements, notions, videos, audios, or images
according to a corresponding common theme. Prepar-
ing for a Biology lesson a teacher can use it for the
systematization of knowledge, matching, or consoli-
dating of the corresponding educational material.
Example: you can see statements on the board,
which can be referred to two groups: Gymnosperms
and Ferns. Pupils classify the statements, explaining
which of the groups it can be referred to. There is an-
swers check at the end (correct answer is highlighted
in green and incorrect answer is shown in red colour).
Figure 2 presents an illustration of the exercise
“Classification”, which should be used when study-
ing the types of inflorescences with the help of the
LearningApps.org online resource at different stages
of the lesson: perception of information, clarification
and expansion of knowledge, reproduction of infor-
mation, generalization and systematization of knowl-
edge.
Another bright example of this exercise is classi-
fication of statements. Pupils are offered to sort all
the statements according to their belonging to a cer-
tain class: Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons. If the
pupil’s answer is correct it is highlighted in green and
incorrect matching is shown in red colour.
Exercise “Simple ordering” the main goal of
which is to arrange the proposed statements, images
in a certain order (establishing a sequence). There is a
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
456

Figure 1: Illustration of the exercise “Find a pair”. Learning of plant species “Gymnosperms group” in the LearningApps.org
online resource (https://learningapps.org/display?v=pk1msmk7321).
numbering in the upper left corner, which is changed,
when you move the statements. It can be used during
Biology lessons for the sequential arrangement of de-
velopment cycles, body structure, physiological pro-
cesses, and others.
Example: during the lesson on the theme “Sub-
class Equisetidae” pupils get acquainted with differ-
ent stages of the equisetum development cycle. It
is necessary determine the correct sequence. The
stage which was correctly determined is highlighted
in green, false stage is shown in red (figure 3).
Exercise “Quiz (1 correct answer)” can be practi-
cally used when the teacher develops test tasks. Us-
ing clear instruction, the teacher can create questions
with different numbers of answer options. Questions
can be in text, audio or video format. The teacher
decides on the number of questions himself. Pupils’
answers are sent to the teacher’s personal account,
which makes it easier to check the tasks and does not
take much time.
Exercise “Fill in the blanks” is used for filling in
certain parts of the text. Pupils are offered certain part
of the text with blanks in it. It is necessary to fill in the
blanks: choosing from the list of proposed options, or
choose the statement independently from the learned
material. Each of the pupils can do this exercise us-
ing his mobile phone. Advantages of use: each of
the pupils can test his knowledge himself, online dis-
cussion of this exercise is possible and the results of
the answers are automatically sent to the teacher’s ac-
count, pupils can also see and analyze the correctness
of the completed tasks themselves. The exercise can
be used at the stage of motivation, homework check-
ing, consolidation of knowledge, or reflection.
Another example of this exercise is the work with
a textbook (Matiash, 2004). Pupils should study a part
of the theme on the basis of the textbook, namely on
the example of the main features of flowering plants
(Angiospermae). The text without answer options is
provided on the board, or on the mobile phone (if the
teacher sends the task to pupils in advance), pupils in
turn at the board (or on the mobile phone indepen-
dently) fill in the answers, according to the learned
material. The correct answer is highlighted in green;
the incorrect answer is shown in red colour. The an-
swers are sent to the teacher’s account, then there is a
mutual reflection with the class and correction of mis-
takes with pupils’ explanations and if it necessary the
teacher may add something.
Exercise “Crossword (puzzle)” has a user-friendly
interface for building a layout and creating tasks. Us-
ing the template, the teacher only needs to create
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
457
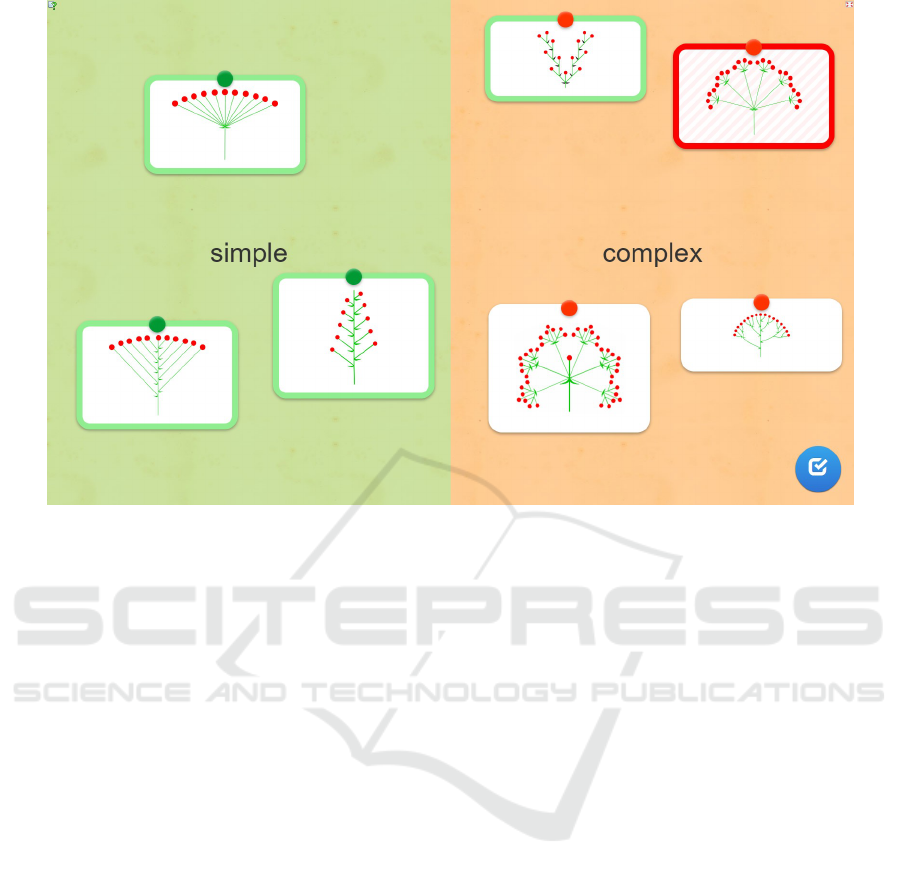
Figure 2: Illustration of the exercise “Classification”.
questions and choose the correct answers to them.
The program itself builds a crossword puzzle by plac-
ing words vertically and horizontally and determines
the appropriate intersections of words. The teacher
can also choose a keyword that is relevant to the
theme of the lesson. The exercise can be used at
the stage of motivation, revision of the learned ma-
terial, consolidation of knowledge. The development
of this exercise is quite easy and clear and can be used
for independent pupils’ work, in the case of sufficient
knowledge how to use the LearningApps.org online
resource. Example:
1. In the life cycle of the considered groups pre-
vails... ? (Sporophyte)
2. What do extinct plant species form? (Coal).
3. Where does photosynthesis take place in horsetail
(Equisetum)? (Stem).
4. What is the limiting factor in fertilization of the
considered groups (Water).
5. What is the underground part of Lycopodium?
(Root).
6. How are horsetails (Equisetidae) dispersed? (In
groups).
7. Where are spores of the considered groups
formed? (Strobilus).
8. Give a clear name for the sexual generation of
horsetails (Equisetidae) and lycophytes? (Game-
tophyte).
9. What is the photosynthetic organ of Lycopodium?
(Leaf).
10. What do young steams of horsetail (Equisetum)
contain in great amounts? (Starch).
11. What part of lycophytes is used to make baby
powder? (Spores).
12. What is the indicator for soils with high acidity?
(horsetail (Equisetum)).
Pupils can see the illustration of crossword puz-
zle on the Smart Board, and they immediately answer
the questions on it, checking the correctness of the
answers at the end.
Exercise “Find the words” is used as an educa-
tional game. Pupils are offered a list of questions
to answer and find them on the word search board
one next to the other. The program creates the word
search board itself where the words are arranged hor-
izontally, vertically and diagonally. This exercise is
used at all stages of Biology lessons, especially it is
offered for knowledge actualization. Example:
Questions:
1. Embryonic leaves that are found and developed in
the seed? (Cotyledon).
2. Modified steam of flowering plants (Angiosper-
mae) group? (Flower).
3. What fertilization (give the name) leads to the for-
mation of a seed and fruit? (Double).
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
458
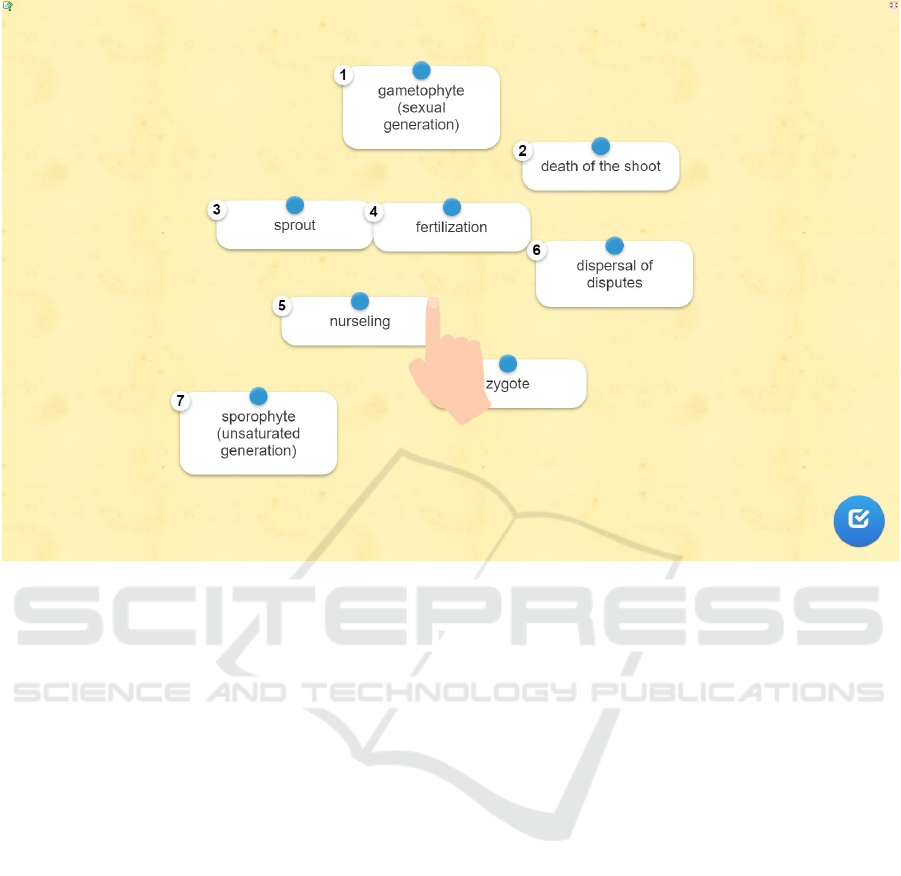
Figure 3: Illustration of the exercise “Simple ordering” – arrange stages of the life cycle of field horsetail (Equisetum arvense)
in the right order using the LearningApps.org online resource.
4. Which class do the Lily and Cereal families be-
long to (give the name of the class)? (Mono-
cotyledons).
5. What type of root system do Dicotyledons have?
(Taproot).
6. The diversity of which organs of flowering plants
(Angiospermae) group improves and increases the
species composition of vital functions perform-
ing? (Vegetative).
7. What class do Rosaceae and Asteraceae families
belong to? (Dicotyledons).
8. Name the type of Dicotyledons venation? (Retic-
ulate).
9. The root system of Monocotyledons is. . . ? (Fi-
brous).
10. Where is the seed protected by a pericarp that has
an adaptation to the dissemination? (Fruit).
Pupils are given a table with encrypted words and
questions to them. They answer the questions and find
the appropriate answer in the table. The correct an-
swer is highlighted in colour.
We present examples of educational applications,
involved in our methodology.
In our previous research (Stepanyuk et al., 2019)
the effectiveness of using such free applications of the
PlayMarket server as “Anatomy 4D”, “Animal 4D+”,
“Augmented Reality Dinosaurs – my ARgalaxy”,
“BioInc – Biomedical Plague, BioInc” , “Plan+Net”
in the process of Biology studying in a basic sec-
ondary school was proved. Their choice is caused
by the specifics of the object of biological cogni-
tion (life in all its manifestations) and the concept of
bio(eco)centrism, which recognizes the life of any or-
ganism as the highest value. Comparison of the con-
tent of these applications with the content of the pro-
gram material in Biology for the 6th grade allowed
us to conclude that it will be the most appropriate
to use the “Plan+Net” application for our experimen-
tal methodology, which is a powerful tool to identify
plants in the photo. During an excursion the teacher
takes a picture of an unknown plant by his smartphone
and then using the mobile application analyzes the re-
ceived information. After the work completing, plant
details can be checked using printed version of a plant
catalogue. Pupils can use such an educational appli-
cation not only at Biology lessons, but also during
their individual work in the process of research at the
centers of research and experimental activities.
The use of information devices at a lesson at the
stage of homework checking allows to diversify the
forms of pupils’ learning outcomes control. Thus, in
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
459

addition to computer testing, Miracast wireless tech-
nology can be used for this purpose. This requires the
owning of a smartphone, a multimedia projector and
Google Chromecast adapter. There is a great deal of
educational content available on Google Play Market
application of your smartphone, including programs
for pupils’ learning outcomes control. One of them is
Plickers. This web server lets you survey your class at
the lesson and conduct instant checks for understand-
ing of the learned and current material in a test form.
To start working with it, it is necessary to down-
load a free application Plickers to the teacher’s smart-
phone. Then, in a separate application, prepare the
tests and print a set of cards. One set of cards can
be used for different classes. Each pupil is assigned a
unique Plickers card that has a black and white image
similar to a QR code. The number of the card cor-
responds to each pupil (according to the list). Then
you will need to take your smart device, choose the
Plickers application.
Choose the class and necessary question from the
list. The chosen on your mobile device question
will be automatically displayed on the screen with
the help of a projector. Using the scanner of your
smartphone scan your pupils’ cards and record their
answers. Pupils should hold their cards so that the
letter of the correct answer is located at the top. Col-
ored highlighting helps to find out how well the pupils
answer the questions quickly: grey marks the pupils
who haven’t answered yet, red means incorrect an-
swers of pupils, and green stands for correct answers.
The use of Smart technologies makes it possible
to solve the following topical issues: use the latest IT
in training; improve the skills of pupils’ independent
work in information databases, the Internet; improve
the pupils’ knowledge, skills and abilities; make the
learning process more interesting and meaningful; de-
velop creative potential; control through testing and a
system of questions for self-control; increase the cog-
nitive activity of pupils due to various video and audio
information (Doroshenko et al., 2005).
Smart Board is a touch screen, which is connected
to a computer. Multimedia projector transmits an im-
age from the computer screen to the Smart Board. The
latter acts as an interactive touch screen monitor for
the computer. By touching the Smart Board, the user
is able to click on buttons, highlight text and drop and
drag items right from the Smart Board.
An interactive whiteboard helps the teacher to
work with a variety of multimedia visual aids that al-
lows you to display an object in a variety of ways.
In the course of his work a biology teacher can use
everything that the pupil is able to perceive clearly.
While working with the Smart Board, there is a
rapid increase in the amount of visual information,
which in its turn increases the quality and effective-
ness of the lessons. Unique possibilities of Smart in-
volve pupils in active cognitive activity and enhance
their creative potential. There is a chance to work with
a large amount of information at the lesson that cre-
ates the optimal conditions for pupils’ individual re-
search work in biology. Pupils work with computer
models, during such work they can carry out experi-
ments and check hypotheses.
During the work with the Smart Board a num-
ber of traditional didactic principles are being im-
plemented: sequence, systematic character, scientific
approach, visual training, pupils’ activity and con-
sciousness, connection of theory with practice, avail-
ability and duration of knowledge. The principles of
visualization, availability and systematicity are real-
ized through adding tables, video and audio materi-
als, and analysis of materials of electronic textbooks
during the explanation of new material. However, the
interactive whiteboard is mostly used during the prin-
ciple of visualization due to which you can present
educational material in the form of schemes, dynamic
algorithms or generalizing tables, which are a concise
statement and an illustration of the main conceptions
of the material and its use at the lesson.
Our methodology involves the use of a website as
a means of increasing the effectiveness of the learning
process. Nowadays any teacher can create a website.
There are hundreds of different website building plat-
forms and website builders. You can get either free or
for the payment information-technological base and
real resource in the form of electronic space, modules,
templates, control systems.
Site pages can be simple static file sets or cre-
ated by a special computer program on the server. It
can be either custom-made for a specific site, or be
a ready-made product designed for a specific class
of sites. The structure of a website consists of two
parts: internal and external. The internal part of the
structure is represented by the headlines, sub sections,
site sections, labels and other navigation elements.
The external part of the structure of a website is a
scheme of the content blocks, that is, how the header,
the main content, the comment block, and other ele-
ments of the site are located. A well designed website
layout, where convenient and interesting interface is
combined with actual information is a very important
point in the development of this resource and it is bet-
ter perceived by users (Skrypka, 2015).
Having analyzed the functions and tasks of var-
ious websites, we chose the website builder Ucoz.
The appropriateness of this website builder choice is
caused by the fact that it contains all the necessary
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
460

components for creating namely a training website
and allows to create multy-functional universal web-
sites free of charge. It involves a sufficiently large
number of educational category templates, with an
appropriate interface, convenient ways to add and edit
existing web pages, site management options from
both the control panel and the admin panel that re-
jects force majeure during learning, because if you
have problems with logging into the admin panel, the
teacher will be able to manage the site through the
control panel. This builder contains a specific, com-
prehensible control panel which requires registration
and has a definite password used to log in. It will
protect the site against hacking, illegal spreading of
information which is stored on it, as the website ad-
ministrator has certain copyrights.
In the context of experimental learning we have
developed a methodology for organizing a biology
teaching process in a basic secondary school using
the LearningApps.org resource and various informa-
tion devices. We used them variously at lessons of
different types: at the introductory lesson, to acti-
vate the cognitive process and to report new knowl-
edge; at the lesson of studying new material; at the
combined lesson in order to expand and deepen the
pupils’ knowledge; at the lesson of checking and cor-
rection of knowledge for final control and correction
of knowledge.
The LearningApps.org resource was used together
with other information devices at different stages of
the lessons: at the stage of actualization basic knowl-
edge: tests (Plickers application), video clips (Smart
Board), models of objects and phenomena (Smart
Board); at the stage of learning activity motivation:
coloured drawings, animated snippets, virtual biolog-
ical experiments, website; at the stage of learning new
material: photos, slideshows, animated plots, inter-
active models (website), video clips (Smart Board);
at the stage of summing up of the studied material:
multiple-choice tests (Plickers application), mute pic-
tures (Smart Board), establishment of sequence of bi-
ological processes (Smart Board); at the stage of gen-
eralization and systematization of obtained knowl-
edge: thematic control with automatic verification
(Plickers application), control – diagnostic tests (web-
site).
They were also used in various forms of learn-
ing: during the class work and practical classes (web-
site); during virtual excursions (Smart Board); dur-
ing pupils’ individual work and research (website);
while doing pupils’ homework (website, mobile ap-
plications).
Conducted research allows to make a conclusion
that using a training website in biology teaching pro-
cess greatly facilitates pupil-teacher interaction. It is
advisable to use a training website to prepare pupils
for independent work on the tasks that the teacher
places in advance in the suitable section on the web-
site. At the lesson preceding the lesson of general-
ization and systematization of knowledge, the home
assignment will be as follows: the pupils should re-
fer to the website, the address of which is reported
by the teacher, and in the section “Preparing for in-
dependent work” do the assigned tasks (there may be
different variants). At the lesson of generalization and
systematization of knowledge it is necessary to do the
tasks placed on the site, or to use them as a plan for
the survey of pupils. Thus, they can revise, gener-
alize, systematize the obtained knowledge and fill in
the gaps. By using the website in preparation for the
pupils’ independent work, we give them more time
to prepare and diversify the process, which will then
have a positive impact on the learning outcomes.
Using a website is also productive at the lesson
that precedes practical work. Biology teaching in-
volves performing such practical work that requires
certain conditions that cannot be created in the class-
room. For the fairness of the experiment and obtain-
ing accurate results, it is better to ask pupils to carry
out this practical work at home with the help of their
parents, and to place the plan of work and instructions
how to carry it out in the section “Practical work” on
the website before conducting it and, to discuss the
results at the stage of actualization knowledge at the
next lesson.
It is convenient to place some research themes on
this training website, as this will help to prepare for
pupils’ conferences, because they will be able to get
the theme at the beginning of the academic year and
work at it throughout the year and after that to defend
it at conferences. The website can store all the the-
oretical information necessary for conducting lessons
so that the pupil can access it at any time. This way of
placement is convenient for pupils who were absent
from the lesson, as they can independently study the
material which was missed in the home environment.
Generalized results of the thematic assessment on
the themes, during which the experimental methodol-
ogy of using the LearningApps.org online resource in
combination with information devices in the 6th grade
was implemented are presented in table 1.
Analyzing the data of table 1, we can see that
pupils acquired knowledge in all the themes which
were taught using experimental methodology. This is
evidenced by the average value indicator of the coef-
ficients of teaching information acquisition (76.42%).
The results of the Stage I of pupils’ thematic as-
sessment on the themes “Root, steam: structure and
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
461

Table 1: Results of acquisition the elements of knowledge by pupils of the experimental group.
No. Program themes
Elements of
knowledge (notions)
I
a
n n ·I
a
∑
I
0
K, %
1
Root, steam: structure and basic
functions. Variety and modifications of
vegetative organs. Photosynthesis as a
characteristic feature of plants.
morphological 6 491 2946 2254 76.51
anatomical 3 491 1473 1089 73.93
physiological 6 491 2946 2185 74.16
agronomic 1 491 491 405 82.48
2
Plant reproduction: sexual and asexual.
Vegetative plant reproduction. Flower.
Inflorescence. Pollination. Fertilization
morphological 11 503 5533 4188 75.69
anatomical 1 503 503 386 76.73
physiological 3 503 1509 1104 73.16
agronomic 1 503 503 437 86.87
3 Algae. Mosses. Gymnosperms
morphological 2 482 1928 1467 76.08
anatomical 2 482 964 773 80.18
physiological 5 482 2410 1695 70.33
systematic 3 482 1446 1115 77.10
agronomic 2 482 964 710 73.65
basic functions. Variety and modifications of vegeta-
tive organs”, Photosynthesis as a characteristic feature
of plants, nutrition, respiration, plant movements” are
shown in figure 4.
Figure 4: Coefficients of pupils’ acquisition of the elements
of botanical knowledge (Stage I of the thematic assess-
ment).
According to the state requirements for the level
of pupils’ general educational background, laid down
in the current program in Biology, the study of the
themes “Root, steam: structure and basic functions.
Variety and modifications of vegetative organs”, Pho-
tosynthesis as a characteristic feature of plants, nutri-
tion, respiration, plant movements” involves pupils’
learning of morphological, anatomical, physiological
and agronomic notions. Analysis of the results of
doing the tasks with morphological content showed
that pupils have learned this educational material
(K = 74.36% – in CG and K = 76.51% – in EG).
As it can be seen in figure 4, the coefficient
of pupils’ acquisition of the anatomical and phys-
iological notions has considerably increased in EG
(from 56.66% and 58.86% to 73.93% and 74.16%,
respectively). We believe that the effectiveness of
knowledge acquisition is connected with the pro-
posed methodology of teaching pupils using the
LearningApps.org online resource. The formation
of such notions as “photosynthesis”, “respiration”,
“evaporation”, “transportation of substances in the
plant” is possible only with a rational combination of
traditional visual aids (tables, diagrams, experiments)
and the use of multimedia fragments, that what the
experimental methodology included.
A comparison of the answers to the questions with
agronomic content showed that the results of thematic
assessments of pupils’ academic achievements from
CG and EG did not differ significantly (76.21 and
82.48, respectively).
A comparison of the thematic assessment results
on the themes “Plant reproduction: sexual and asex-
ual. Vegetative plant reproduction. Flower. Inflores-
cence. Pollination. Fertilization” is shown in figure 5.
The results of pupils’ educational information
acquisition proved that the most significant impact
the proposed methodology of using the online re-
source LearningApps.org in combination with infor-
mation devices has on the formation of anatomical
(K = 76.73%) and physiological notions (73.16%). At
the same time the difference in coefficients of knowl-
edge acquisition in CG and EG is + 11.38% and +
16.31%, respectively. It can be explained by the fact
that for the pupils of this age group (12-13 years old)
the physiological processes of “pollination”, “fertil-
ization” and “plant development” are difficult to un-
derstand and remember. It is difficult to show these
processes and to form the holistic visual representa-
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
462
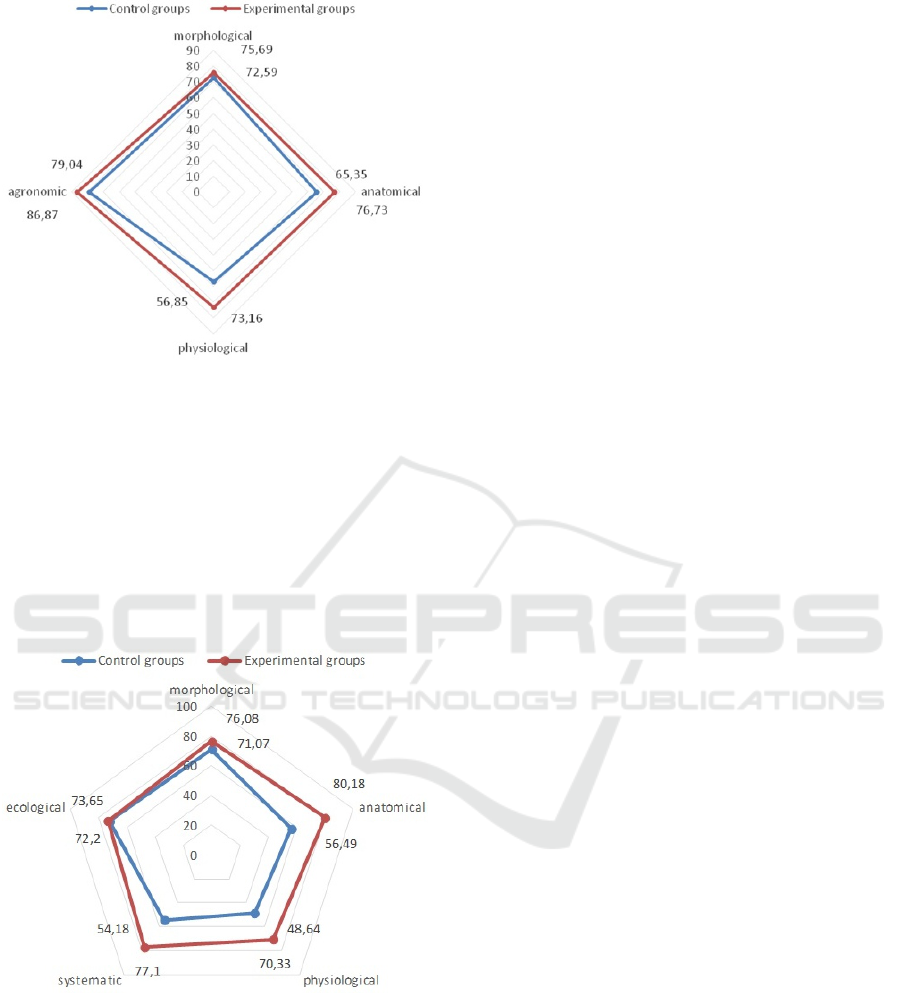
Figure 5: Coefficients of pupils’ acquisition of the elements
of botanical knowledge (Stage II of the thematic assess-
ment).
tion of the mechanisms of their occurrence with the
help of traditional static means of visualization.
The results of the Stage III of pupils’ thematic as-
sessment on the themes “Algae”. “Mosses”. “Gym-
nosperms” according to the coefficients of knowl-
edge elements acquisition (morphological, anatomi-
cal, physiological, systematic, and ecological) in con-
trol and experimental groups are shown in figure 6.
Figure 6: Coefficients of acquisition of the elements of
botanical knowledge (Stage III of the thematic assessment).
The analysis of the results of tasks on the themes
“Algae”, “Mosses”, “Gymnosperms”, which involved
the acquisition of morphological knowledge (figure 6)
showed that this knowledge is acquired by pupils at a
sufficient level (K = 71.07) using traditional teaching.
Undoubtedly, using of the LearningApps.org online
resource for training, in particular, the demonstration
of images of the organs of higher sporophytes and
gymnosperms promotes better memorization of edu-
cational information, as evidenced by the coefficient
of knowledge acquisition (K = 76.08).
The most significant impact of using the online
resource LearningApps.org in the process of study-
ing we observe at those stages where anatomical
(K = 56.49% in CG and K = 80.18% in EG) and
physiological (K = 48.64% and 70.33% respectively
in CG and EG) notions are formed. It is difficult to
form these notions using traditional mediums of in-
struction (tables, microscope, textbook). The use of
pedagogical software with dynamic multimedia frag-
ments helps to illustrate the complex processes of re-
production of higher sporophytes and algae, their bet-
ter visual perception.
In the process of pupils’ systematic notions ac-
quisition, it is important that they possess already
formed morphological, anatomical and physiological
notions. Since after using the LearningApps.org on-
line resource in EG, the coefficient of these notions
acquisition increased, this can explain the increase
of the coefficient of systematic notions acquisition
(K = 54.18% in control groups and K = 77.10% in
experimental groups).
Analysis of the answers to the questions with eco-
logical content allows to confirm that this material can
be considered to be learned as the coefficient of edu-
cational information acquisition both in CG and EG
is higher than 70%.
Thus, the comprehensive analysis of the results of
the forming experiment allowed us to conclude that
proposed by us methodology of using information de-
vices in the process of Biology school course studying
is effective.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
PERSPECTIVES OF FURTHER
RESEARCH
Modern IT allow to create a single information envi-
ronment, the basis of which is integrated computer
networks and communication systems, which gives
an opportunity to accompany and coordinate educa-
tional processes. When introducing online resources
and information devices into the educational process
in Biology, the principle of reasonable conservatism
and continuity must be observed. The computer can-
not substitute a teacher in the process of teaching; it
is only a means of broadening possibilities to acquire
new knowledge. The teacher always has to play the
key role in any educational innovation. This justi-
fies the appropriateness of moving to a mixed form
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
463

of training that involves the creation of a polysubjec-
tive educational environment (teacher, pupil, online
resource, information devices).
The LearningApps.org resource has a lot of ad-
vantages: availability of the service in different lan-
guages (including Ukrainian), access to unregistered
users, the ability to use tasks created by other users,
a wide range of task types, tips for completing and
developing tasks, easy to use, accumulation of own
exercises in a personal profile, creating pages to work
with different classes.
There are a great number of benefits of using this
digital app, but there are also some negative quali-
ties: some templates do not support Cyrillic script,
the school must be connected to the Internet, there are
some errors in the templates that cannot be corrected
manually, some exercise templates change or they are
removed from the site.
The use of the LearningApps.org service helps in
versatile and purposeful formation of pupils’ educa-
tional competencies and allows to achieve the goals
more effectively by involving each pupil in cognitive,
creative, active activities, combination of logical and
figurative thinking.
The methodology of using the LearningApps.org
service in combination with information devices in
the process of Biology studying in a basic secondary
school involves the use of the PlayMarket server ap-
plications, Smart technologies and a website. It is
relevantly to use free applications of the PlayMar-
ket server while studying Biology in a basic sec-
ondary school. They are as follows: “Anatomy 4D”,
“Animal 4D+”, “Augmented Reality Dinosaurs – my
ARgalaxy”, “BioInc – Biomedical Plague, BioInc”,
“Plan+Net”. Their choice is caused by the specifics
of the object of biological cognition (life in all its
manifestations) and the concept of bio(eco)centrism,
which recognizes the life of any organism as the high-
est value. During homework checking it is advisable
to use Miracast wireless technology besides computer
control of pupils’ learning outcomes. This demands
the owning of a smartphone, a multimedia projector,
and a Google Chromecast type adapter. It would be
appropriate to use the website builder Ucoz for cre-
ation of a training website in Biology.
Based on the synthesis of the obtained data, rec-
ommendations for the use of a Biology training web-
site were developed: the use of the website should
not be the only means of training; each lab work us-
ing a training website must be preceded by a manda-
tory introductory instruction; the information in the
sections should be precisely matched to the relevant
theme of the lesson; the answers to the questions for
self-examination should be mandatory checked, ei-
ther in the course of group activity at the lesson or
individually, in order to trace the gaps in the knowl-
edge of a particular pupil; take into account wishes
of the pupils, because in order to enhance their aca-
demic performance, socialization and improvement,
such a training website is created.
The educational process which involves the use
of the LearningApps.org service and information de-
vices encourages the independent work of each pupil,
creates a favorable communication situation and con-
ditions for the development of creative abilities of the
individual, which are especially important for each
pupil; increases the motivation and cognitive activity
of pupils, improves the individualization, differentia-
tion and intensification of the learning process, broad-
ens and deepens interdisciplinarary links, system-
atizes and integrates knowledge of certain subjects,
organizes systematic and reliable control, avoids sub-
jectivism in assessment. In addition the use of the
methodology of the LearningApps.org service and in-
formation devices integration in the process of Biol-
ogy studying significantly simplifies the interaction
between pupil and teacher, allows to combine the for-
mation of logical and figurative pupils’ thinking.
The prospects for further study consist in the
studying of the influence of the methodology of the
LearningApps.org service in combination with in-
formation devices on the formation of pupils’ gen-
eral and subject-based competencies in the process
of Biology studying; preparing of future biology
teachers to model educational activities using the
LearningApps.org service in combination with infor-
mation devices.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful for the opportunity to give us a chance
to present the findings of our study to the world’s sci-
entific community.
REFERENCES
Aman, I. S. (2019). Online service of multimedia
didactic exercises LearningApps. http://internet-
servisi.blogspot.com/p/learning-apps.html.
Bespalko, V. P. (1968). Experience in the development and
use of criteria for the quality of learning. Sovetskaia
pedagogika, 4:52–69.
Bobyliev, D. Y. and Vihrova, E. V. (2021). Problems and
prospects of distance learning in teaching fundamental
subjects to future mathematics teachers. Journal of
Physics: Conference Series, 1840(1):012002.
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
464

Bonch-Bruievych, H. F., Abramov, V. O., and Kosenko, T. I.
(2007). Methods of use of SMART Board technology
in education. KMPU imeni B. D. Hrinchenka, Kiev.
Doroshenko, Y., Semeniuk, N., and Semko, L. (2005). Biol-
ogy and ecology with a computer. Shkilnyi svit, Kiev.
Fedosenko, V. A. (2020). Learning Apps builder as one
of the tools of SMART technology in the process of
teaching biology. In Teoretychni ta prykladni aspekty
doslidzhennia z biolohii, heohrafii ta khimii, pages
193–196.
Horbatiuk, R. M. and Tulashvili, Y. Y. (2013). Mobile
learning as a new technology of higher education.
Naukovyi visnyk Uzhhorodskoho natsionalnoho uni-
versytetu, 27:30–34.
Komarova, E. and Starova, T. (2020). Majority values of
school biological education in the context of education
for sustainable development. E3S Web of Conferences,
166:10029.
Kosyk, V. M. (2014). Use of mobile devices and tablets
based on Android OS in the learning process. Kompi-
uter u shkoli ta simyi, 4:19–21.
Kyverialg, A. A. (1980). Methods of research in profes-
sional pedagogy. Valgus, Tallin.
Lavrentieva, O., Pererva, V., Krupskyi, O., Britchenko, I.,
and Shabanov, S. (2020). Issues of shaping the stu-
dents’ professional and terminological competence in
science area of expertise in the sustainable develop-
ment era. E3S Web of Conferences, 166:10031.
Malchenko, S. L., Tsarynnyk, M. S., Poliarenko, V. S.,
Berezovska-Savchuk, N. A., and Liu, S. (2021). Mo-
bile technologies providing educational activity dur-
ing classes. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
1946(1):012010.
Matiash, N. Y. (2004). Look at the problem of computeri-
zation of education. Biolohiia ta khimiia, 4:55–56.
Mironets, L. P. and Torianyk, V. M. (2018). Use of mod-
ern information tools in the process of control of
pupils’ educational achievements in biology. In Proc.
New Ukrainian School 17–18 May 2018, pages 95–98,
Ternopil. Vektor.
MON (2017). Biology 6-9 grades. curriculum for secondary
schools. https://mon.gov.ua/ua/osvita/zagalna-
serednya-osvita/navchalni-programi/navchalni-
programi-5-9-klas.
Nevedomska, Y. (2007). Computer technologies in the pro-
cess of biology studying. Biolohiia ta khimiia v shkoli,
4:10–14.
Savosko, V., Komarova, I., Lykholat, Y., Yevtushenko, E.,
and Lykholat, T. (2021). Predictive model of heavy
metals inputs to soil at kryvyi rih district and its use in
the training for specialists in the field of biology. Jour-
nal of Physics: Conference Series, 1840(1):012011.
Shcherbakov, A. H. (2006). Computer testing is an impor-
tant methodological tool of a contemporary teacher.
Kompiuter u shkoli ta simyi, 4:30–31.
Shokaliuk, S. V., Bohunenko, Y. Y., Lovianova, I. V., and
Shyshkina, M. P. (2020). Technologies of distance
learning for programming basics on the principles of
integrated development of key competences. CEUR
Workshop Proceedings, 2643:548–562.
Skrypka, G. V. (2015). The use of mobile applica-
tions for educational research in the study of natural-
mathematical subjects. Kompiuter u shkoli ta simyi,
3:28–31.
Spivakovska, Y. (2016). The notion of virtual multisub-
ject learning environment. Naukovyi visnyk Nat-
sionalnoho universytetu bioresursiv ta pryrodokorys-
tuvannia Ukrainy. Seriia “Pedahohika, psykholohiia,
filosofiia”, 253:269–279.
Stepanyuk, A. V. (2011). The use of computer learning tools
in methodological training of future biology teachers.
Pedahohichnyi almanakh, (12(1)):58–64.
Stepanyuk, A. V. and Mironets, L. P. (2019). The method-
ology of using the website in the process of teach-
ing biology in a primary school. Aktualni pytannia
pryrodnycho-matematychnoi osvity, (1(13)):56–62.
Stepanyuk, A. V., Mironets, L. P., Olendr, T. M., Tsidylo,
I. M., and Stoliar, O. B. (2019). Methodology of us-
ing mobile internet devices in the process of biology
school course studying. CEUR Workshop Proceed-
ings, 2643:535–547.
Striuk, M. I., Semerikov, S. O., and Striuk, A. M. (2015).
Mobility: A systems approach. Information Tech-
nologies and Learning Tools, 49(5):37–70. https:
//journal.iitta.gov.ua/index.php/itlt/article/view/1263.
Tsesarska, H. (2002). Reflections about benefits and harm
of computer network. Biblioteka, 5:36–37.
Integrated Use of the LearningApps.org Resourse and Information Devices in the Process of Biology School Course Studying
465
