
Ensuring the Effectiveness of e-Learning based on Online Technology
Analysis of Factors Influencing the Cognitive Independence of Students
Evgeniy A. Lavrov
1 a
, Viktoriya G. Logvinenko
2 b
, Viacheslav V. Osadchyi
3 c
,
Olga Ye. Siryk
4 d
and Yana I. Chybiriak
4 e
1
Sumy State University, 2 Rimsky-Korsakov Str., Sumy, 40007, Ukraine
2
Sumy National Agrarian University, 160 Herasyma Kondratieva Str., Sumy, 40000, Ukraine
3
Bogdan Khmelnitsky Melitopol State Pedagogical University, 20 Hetmanska Str., Melitopol, 72300, Ukraine
4
Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, 60 Volodymyrska Str., Kyiv, 01033, Ukraine
Keywords:
Cognitive Independence, E-Learning, Human Factor, Lifelong Learning, Distance Learning.
Abstract:
The problem of improvement of educational technologies in connection with the revealed problems, aggra-
vated in the conditions of COVID-19, is considered. A new approach to building a system of flexible learn-
ing, based on “tuning” the technologies of student interaction with the educational environment, is proposed.
Such adaptation is carried out using the mathematical model of educational process control developed by the
authors, the parameters of which are characteristic of the factors that form the cognitive independence of stu-
dents.The presented information technology for assessing the factors that shape the cognitive independence of
students can be integrated into any educational system due to the universal capabilities that Google services
provide. The developed technology is very useful for studying the real picture of individual factors of cognitive
independence in the educational process, organized with the help of electronic educational technology. The
main functional capabilities and advantages of the developed information technology are: the ability to orga-
nize adaptive learning, the ability to organize questionnaires in any electronic educational system, simplicity
and ease of use, modular structure, and others.
1 INTRODUCTION
The current educational revolution (Reid, 2006;
Bersin, 2004; Blaschke, 2012; Cochrane et al.,
2013), the rapid technology of e-learning (caused by
COVID-19) (Joshua et al., 2016; Pereira and Ro-
drigues, 2013) and the concept of lifelong learning
(Al-Qahtani and Higgins, 2013; Voloshinov et al.,
2020) exacerbate the following problems:
• quality of e-learning environment (Verkhova and
Akimov, 2017; Lavrentieva et al., 2021),
• adaptive learning (Kotova and Pisarev, 2017;
Atto and Kotova, 2020; Haranin and Moiseienko,
2018),
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9117-5727
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0993-0821
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5659-4774
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9360-4388
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0634-7609
• ergonomic support of the educational system
(Lavrov et al., 2017),
• formation of cognitive independence (Burov,
2017; Pinchuk et al., 2020).
The analysis of these scientific articles shows that
the main task of improving and ensuring the effec-
tiveness of e-learning is to enhance the cognitive in-
dependence of students. In modern literature, cog-
nitive independence is defined as follows (Lavrov
et al., 2021): ”Cognitive independence is an integra-
tive property of a student who learns using a com-
puter, associated with the student’s initiative and the
search for various alternative ways to solve problems
without the participation of tutors”.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
A problem arises: “How to ensure the cognitive in-
dependence of students in the conditions of electronic
Lavrov, E., Logvinenko, V., Osadchyi, V., Siryk, O. and Chybiriak, Y.
Ensuring the Effectiveness of e-Learning based on Online Technology Analysis of Factors Influencing the Cognitive Independence of Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0011009500003364
In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2020) - Volume 2, pages 569-577
ISBN: 978-989-758-558-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
569

education?”.
Lavrov et al. (Lavrov et al., 2021) outlines ap-
proaches to the analysis of factors that affect the cog-
nitive independence of students. However, the ques-
tion remains: “How to implement such a study in
practice?”.
Consider the most well-known digital content
management systems designed to organize learning
processes using Internet technologies (table 1). For
almost all of these platforms, the main goal is to orga-
nize access to teaching materials, ensure interaction,
testing and reporting between teachers and students.
One of the most common distance learning sys-
tems in universities is the Moodle system, an educa-
tional platform that aims to connect teachers, admin-
istrators and students in a reliable, secure and inte-
grated system to create a personalized learning envi-
ronment (Moodle Docs, 2020; Abdula et al., 2020).
The technical aspects of the system can be de-
scribed as follows:
• Moodle is written in PHP using a SQL database,
• Moodle is installation packages and detailed in-
stallation files,
• Moodle represents different categories of users:
administrators, teachers-developers, teachers, stu-
dents, and guests.
Moodle has a wide range of features that are spe-
cific to e-learning platforms (Moodle Docs, 2020).
This allows you to organize all stages of the learning
process: diagnosis, planning, training, management
of educational activities, evaluation of results.
To diagnose and assess certain learning phenom-
ena in the Moodle system, the following technologies
are provided:
1. Questionnaire module is an activity that provides
many proven survey tools used to assess and
encourage learning in the Internet environment.
Teachers can use them to collect data from stu-
dents to help them understand the class and think
about their own teaching (Moodle Docs, 2020).
There are three types of questionnaires:
• ATTLS – Attitudes toThinkingandLearning
Survey a questionnaire containing 20 questions,
designed to determine the level of students’ at-
titudes to distance learning,
• COLLES – Constructivist On-Line Learning
Environment Survey (questionnaire “Learn-
ing Environment withEelements of Construc-
tivism”) a questionnaire containing 20 ques-
tions, designed to determine the level of stu-
dents’ attitudes to distance learning,
• Critical Incidents (questionnaire “Critical Inci-
dents”) is a questionnaire in which students are
given the opportunity to assess certain events
and their attitude to what is happening.
2. Survey module (choice) – in the classroom, you
can ask questions and set switches, and students
can press these switches to choose from a number
of possible answers. They can choose one or more
options, and if pre-settings allow, they can update
their selection. The options can be used as a quick
survey to stimulate reflection on the topic, to allow
the class to vote for the direction of the course, or
to assess progress (Moodle Docs, 2020).
3. Module test is an activity that allows teachers to
develop and build tests of knowledge, consisting
of many types of questions, including multiple
choice questions, right or wrong questions, short
answers and correspondence, and numerical ques-
tions (Moodle Docs, 2020).
4. The provided technologies can diversify distance
learning courses and make them “alive”.
5. Although these technologies have certain diag-
nostic capabilities, we believe that the main dis-
advantage of the questionnaire module is its static
nature:
• you cannot edit the questionnaire,
• other questions cannot be entered (they can
only be used in the same form as specified by
the developer).
Therefore, when teachers want to create their own
questionnaires to diagnose certain aspects of assess-
ment of learning phenomena, problems arise because
this is not provided in the system.
As the analysis of the literature shows, modern e-
learning systems do not allow to investigate the im-
portance of factors that affect cognitive independence
(in order to increase the effectiveness of learning).
Modern e-learning technologies have a wide range
of organizational capabilities at all stages of learning,
including diagnostic tools, but they are static in na-
ture, and the scope of assessment of learning phenom-
ena in them is limited.
Thus, despite the large number of studies in the
field of adaptive learning, including (Osadchyi et al.,
2020), the practice of most universities has shown a
lack of effective online learning in a pandemic. The
following facts have been recorded: decreased moti-
vation, decrease in the quality of the educational pro-
cess, refusal to study, stressful situations both among
students and teachers.
The main issues are related to the following dis-
abilities: operational research of motivational param-
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
570
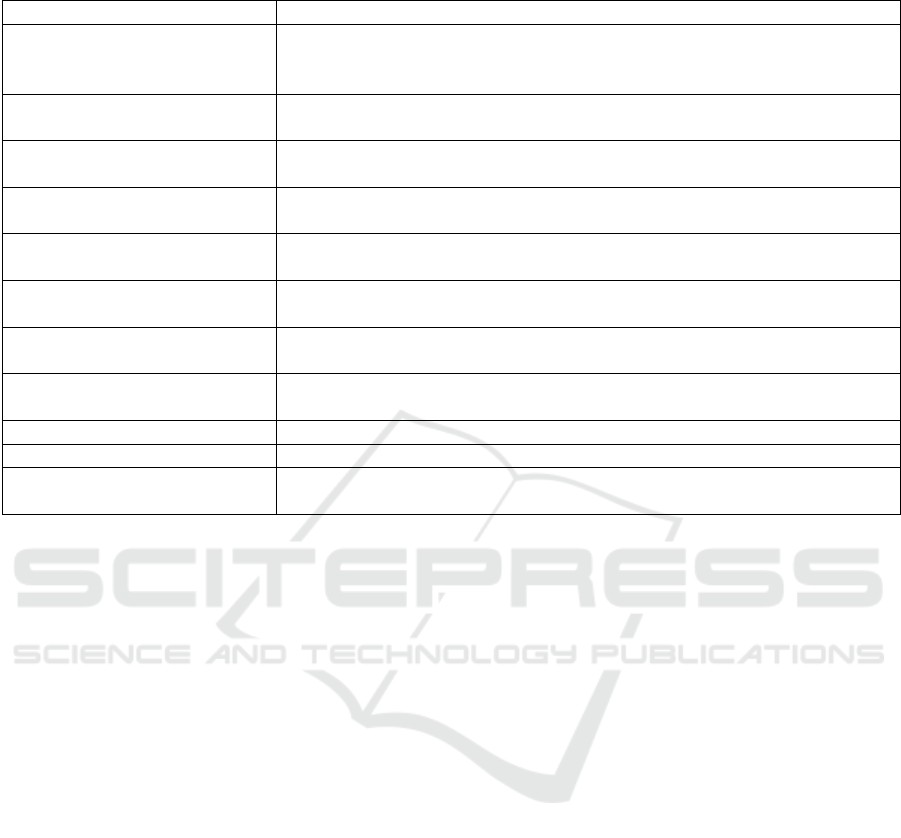
Table 1: The most popular educational platforms.
Platform Description
Moodle (https://moodle.org/) The platform integrates teachers, administrators and students (students) into a
reliable, secure and integrated system to create a personalized learning envi-
ronment
Google Classroom (https:
//classroom.google.com)
Google’s web service, designed for educational institutions to facilitate the
creation, distribution and classification of tasks, making them paperless
edX (https://www.edx.org/) A platform that provides a large number of courses for various purposes from
the best universities and colleges in the world
Coursera (https://www.coursera.
org/)
An educational platform that provides online courses from the world’s leading
universities and organizations
FutureLearn (https://www.
futurelearn.com/)
Online course platform in the UK
Khan Academy (https:
//www.khanacademy.org/)
Free online courses and courses
Schoology (https://www.
schoology.com/)
A virtual learning environment for schools and universities that allows users
to create, manage and share learning content
Classdojo (https://www.
classdojo.com/)
A communication platform for distance learning in school, used by teachers,
students, and parents
Seesaw (https://web.seesaw.me/) A platform for creating digital learning resources
Skooler (https://skooler.com/) Tools for turning Microsoft Office software into an educational platform
CenturyTech (https://www.
century.tech/)
A platform that has tools for distance learning
eters and characteristics of students’ cognitive inde-
pendence, and customizing the educational process
for the characteristics of the student.
In this regard, define the purpose of this study:
a) develop information technology for analytical re-
search of factors influencing the effectiveness of dis-
tance learning in conditions caused by a pandemic;
b) develop the principle of building a model that pro-
vides “customization of learning technology for a par-
ticular student studying in a particular educational en-
vironment”.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Development of an Approach to
Building a Model of Adaptive
Formation of Cognitive
Independence in the Context of
Pandemic Constraints
We will consider a typical situation typical for the or-
ganization of the educational process at the university
(Lavrov et al., 2017):
1. The working curriculum for the discipline has M
topics.
2. Each topic has a basic conceptual part (these are
the basic provisions of the topic that are stable
for a long time), as well as a variable part (edu-
cational material, the content of which may vary
depending on the technical process of the educa-
tional process, software of the educational pro-
cess, personal experience, own knowledge, scien-
tific or methodological advantages, etc.).
3. For each i-th topic in the program, the time t
i
,
which can be represented as t
i
= t
i1
+ t
i2
, is allo-
cated, where ti1 is the time allotted to the concep-
tual part and t
i2
is the time allotted to the variable
part.
4. For each i-th variable part, there are N
i
variants j
of its presentation.
5. With each i-th variant ( j = 1, N
i
) of the topic
i (i = 1, M), it is possible to connect some func-
tion of usefulness of presentation of the mainte-
nance of the j-th variant for formation of cognitive
independence. Usefulness cannot be measured di-
rectly. Its indirect assessment may be a number –
the rank of R
i jl
– which is attributed by the expert
to the j-th variant in the i-th topic from the stand-
point of the influence of educational material of
the j-th variant on the formation of the l-th compo-
nent of cognitive independence. Ranks are formed
by the method of rank correlations. According to
this method, the j-th variant is assigned a rank of
Ensuring the Effectiveness of e-Learning based on Online Technology Analysis of Factors Influencing the Cognitive Independence of
Students
571

1, if in the opinion of the expert, this variant is the
most useful for the formation of the cognitive in-
dependence in the i-th topic; the second most im-
portant variant of presentation is assigned a rank
of 2, etc. Ranking of variants of teaching material
is carried out for each l-th informative component
of the cognitive independence.
6. To implement the selection process, a logical vari-
able x
i j
, is introduced, which takes on the value 1
if the j-th option is selected when presenting the
i-th topic, and the value 0 otherwise.
Given the assumptions made, the task of forming
cognitive independence can be formulated as follows:
Known:
• the number M of topics of educational material of
the discipline,
• the time t
i j
, allocated for each j-th variable part in
each i-th topic,
• the number N
i
of j variants of the presentation of
each variable part,
• the structure of the properties l (l = 1, k) of the
student’s personality, the list of which is custom-
ary to explicate cognitive independence (in other
words, personality properties that form cognitive
independence),
• R
i jl
ranks assigned by experts to the j-th variant of
presentation of the i-th topic according to the level
of its influence on the l-th parameter of cognitive
independence.
It is necessary to choose the following options j
for each topic i to maximize the total effect of the ed-
ucational material on the formation of cognitive inde-
pendence.
Thus, it is necessary to maximize the sum of
ranks, which determines this effect:
M
∑
i=1
N
i
∑
j=1
k
∑
l=1
R
l
i j
x
i j
→ max, (1)
with restrictions:
• on the study of the discipline
M
∑
i=1
N
i
∑
j=1
t
i j
≤ T, (2)
• on the obligatory presentation of all topics
N
i
∑
i=1
x
i j
= 1, (i = 1, M), (3)
• on the obligatory choice of at least one version of
the presentation in each topic
M
∑
i=1
x
i j
= 1, ( j = 1, N
i
), (4)
• for integer variables
x
i j
∈ 0, 1, (5)
Explication of the concept of “cognitive indepen-
dence” allows us to identify a list of personality traits
that form a complex quality of personality “cognitive
independence”, which can be called components of
cognitive independence (factors).
Consider an example of a fragment of a set of
such factors (determined by experts of Sumy National
Agrarian University and the Ukrainian Academy of
Engineering and Pedagogy):
• the need and desire to master the knowledge and
methods of activity,
• cognitive motive and interest,
• interest in the results of their independent cogni-
tive activity,
• interest in the future profession,
• initiative,
• basic knowledge (possessed by the individual),
• acquired basic skills and abilities, computer skills
and possession of previously learned software,
• acquired knowledge of the discipline of the com-
puter cycle being studied,
• acquired skills and abilities in the discipline of
computer cycle, computer skills and possession of
learned software,
• use of scientific and methodological literature,
means of communication, the Internet,
• attentiveness,
• strong-willed efforts,
• purposefulness,
• persistence,
• contact with the teacher during independent cog-
nitive activities in order to obtain information,
• contact with other students during independent
cognitive activities in order to obtain information,
• ability to set and achieve the goals of cognitive
activities,
• ability to plan their cognitive activities,
• ability to assess their potential in performing cog-
nitive activities,
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
572

• ability to evaluate the results of their cognitive ac-
tivities.
In the notation of the above model, a list of k prop-
erties of the student’s l personality is formed (l = 1, k).
Such sets of factors will be different:
• for different universities,
• for different groups of students,
• for different age groups,
• for different learning technologies, etc.
Therefore, it is necessary to be able to model them
in each problem situation.
The main problems of this model are:
• Pr1 – how to embed the model in the distance
learning system;
• Pr2 – how to generate source data that really re-
flects the current problem situation.
We solved the Pr1 problem by creating a spe-
cial technology of intelligent agent-manager, which
is built into any system of distance education (Lavrov
and Lavrova, 2019). To solve the Pr2 problem, we
offer a special online survey technology, which is de-
scribed below.
3.2 Information Technology for the
Analytical Study of the Factors
Influencing the Effectiveness of
Distance Learning in the Context of
Constraints Caused by a Pandemic
Basic principles of technology:
• use of modern Google Script technology familiar
to students and teachers,
• online questionnaire for all categories of partici-
pants in the learning process:
– all teachers,
– all students
• preliminary formation of factors to be considered
(special expert group of teachers and students),
• embedding the questionnaire in the educational
process management system,
• formation of results:
– for each student,
– for all teachers together.
The results are processed in a special way (Lavrov
et al., 2021). Based on expert data, the average value
of the degree of P
avi
manifestation in the structure of
cognitive independence, the variance of S
i
expert as-
sessments, the confidence interval V
i
, as well as upper
confidence limit P
upi
values of the informativeness of
cognitive independence parameters, lower confidence
limit P
lowi
values of the informativeness of cognitive
independence parameters, and the R
Pupi
rank of the
values of the upper limits of the confidence intervals
are calculated for each factor. In addition, a line graph
for R
Pupi
and P
lowi
is built.
Figure 1 and figure 2 show the results that are au-
tomatically generated by the system after
• conducting a survey,
• processing questionnaires and determining the in-
formativeness of the parameters of cognitive inde-
pendence.
It is clear that for each student we receive the indi-
vidual estimations (figure 1), and it allows system to
adjust educational process.
If we analyze the ranks of the factors obtained as
a result of the analysis of teachers and students of
Sumy National Agrarian University, the most impor-
tant (fragment) for the conditions of the pandemic (a
total of 20 factors were estimated) were identified:
• rank 1 – contact with other students during the
performance of independent cognitive activities in
order to obtain information,
• rank 2 – the ability to evaluate the results of their
cognitive activity.
• rank 3 – contact with the teacher during the per-
formance of independent cognitive activity in or-
der to obtain information.
Such studies allow us: a) to change the general
technology of training organization; b) to adjust the
learning process for each student.
The main functional capabilities and advantages
of the developed information technology are:
• the possibility of organizing adaptive learning,
• the possibility of organizing a questionnaire in
any electronic educational system to determine
the level of factors in the study of any discipline,
• an opportunity, for example for educational insti-
tutions, to introduce disciplines in solving prob-
lems related to the quality of teaching,
• simplicity and ease of use,
• modular structure,
• the ability to reach a wide audience of test takers,
with access to the Internet,
• the ability to store answers in Google spread-
sheets,
Ensuring the Effectiveness of e-Learning based on Online Technology Analysis of Factors Influencing the Cognitive Independence of
Students
573
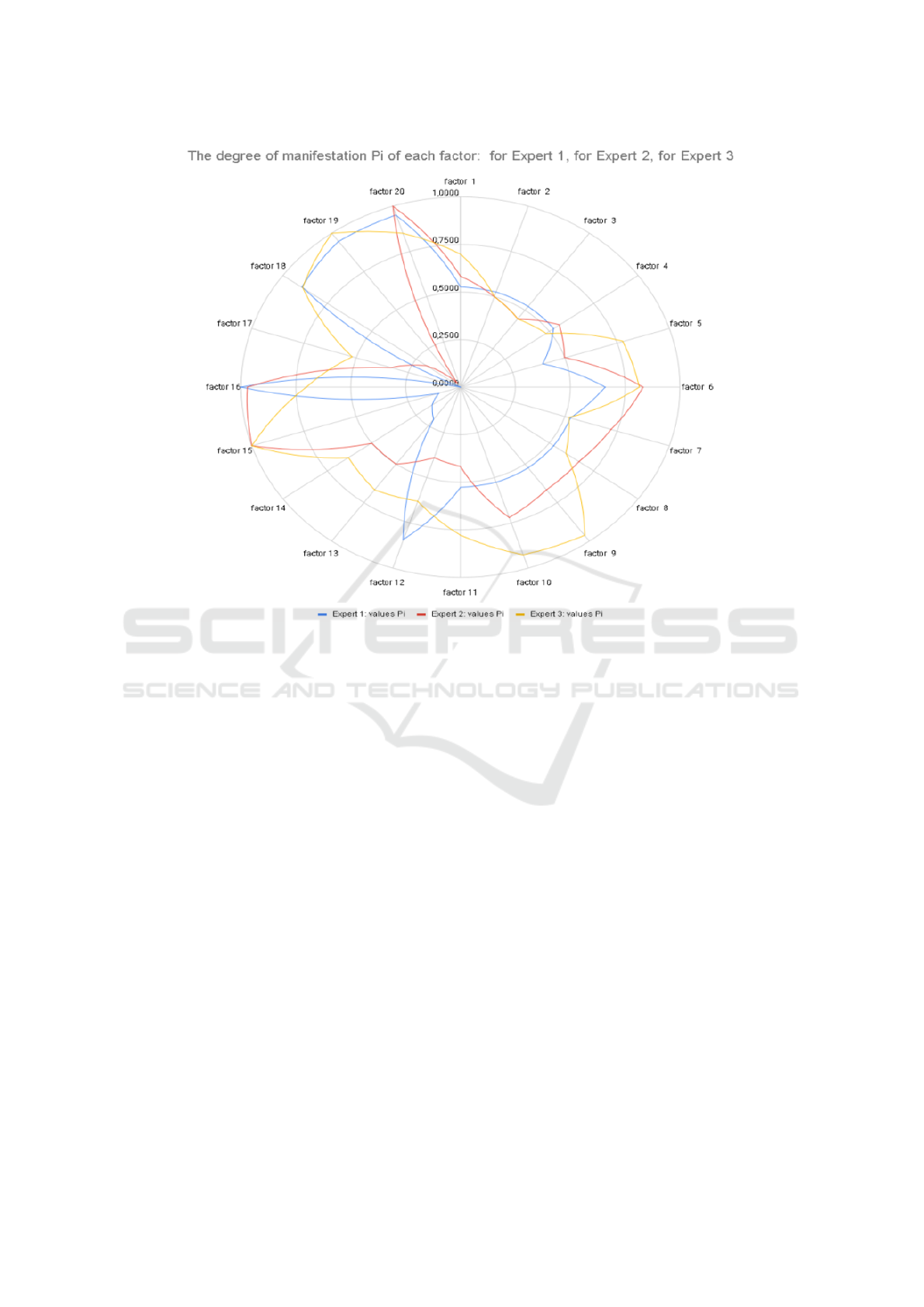
Figure 1: Results (fragment) of data processing by three experts (students) – the degree of manifestation of the components
of cognitive independence.
• survey results are stored on Google Drive,
• allows you to set a deadline for receiving answers
to questions,
• has sufficiently reliable protection, this applies to
both the content of the surveys and the results of
the surveys.
3.3 Use of Technology for the Formation
of Individualized Training Focused
on the Conditions of the Pandemic:
Experimental Studies
The technology of revealing individual features of
students and the model of individual customization of
the educational process “for the student” during the
spring semester of 2019–2020 academic year and the
autumn semester of 2020–2021 academic year were
studied, implemented and tested at the Department of
Cybernetics and Informatics of Sumy National Agrar-
ian University (SNAU).
The content of the questions (20 questions in to-
tal) that were asked to students is described in clause
3.1 and complies with the recommendations (Lavrov
et al., 2021) (however, it is possible to formulate ar-
bitrary questions that are relevant for a particular uni-
versity).
The main advantage of the proposed method is the
ability to flexibly adjust the training to the characteris-
tics of the student and the recommendations of teach-
ers (see table 2).
Satisfaction with the forms of educational pro-
cess (percentage of positive assessments of the qual-
ity of technology, according to materials of the De-
partment of Cybernetics and Informatics of Sumy Na-
tional Agrarian University) in the pandemic is pre-
sented in figure 3.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Existing e-learning technologies do not offer the pos-
sibility of flexible operational analysis of factors that
determine the quality of the educational process from
the point of view of teachers and students, in particu-
lar the factors that shape the cognitive independence
of students.
In today’s e-learning environment, including due
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
574
Figure 2: Results (fragment) of data processing: R
Pupi
and P
lowi
– upper and lower confidence limits for the informativeness
values of the factors of cognitive independence (obtained during the survey of teachers for the conditions of studying the
discipline “Information Technology”, Faculty of Management, Sumy National Agrarian University).
Figure 3: Satisfaction with the forms of educational pro-
cess (percentage of positive assessments of the quality of
technology, according to the Department of Cybernetics and
Informatics of Sumy National Agrarian University) in the
pandemic.
to COVID-19 restrictions, this is a critical limitation.
In this regard, a modern management system of the
educational process requires a fundamentally new in-
formation technology developed as a result of this
study, which includes models and software:
• online surveys of students and teachers,
• prompt processing of survey results with the pos-
sibility of ranking the factors influencing cogni-
tive independence in different learning conditions
(including pandemics),
• adjustment of learning technologies to the param-
eters of students identified as a result of online
surveys.
The scientific novelty of the result lies in the fact
that in contrast to the existing models of adaptive
management of the learning process, focused on ex-
pert (or selective) assessment of student parameters
and learning technologies, built adaptation models
use online assessment technologies that allow you to
quickly configure the system to a “problem situation”.
Testing under COVID-19 constraints has proven
Ensuring the Effectiveness of e-Learning based on Online Technology Analysis of Factors Influencing the Cognitive Independence of
Students
575
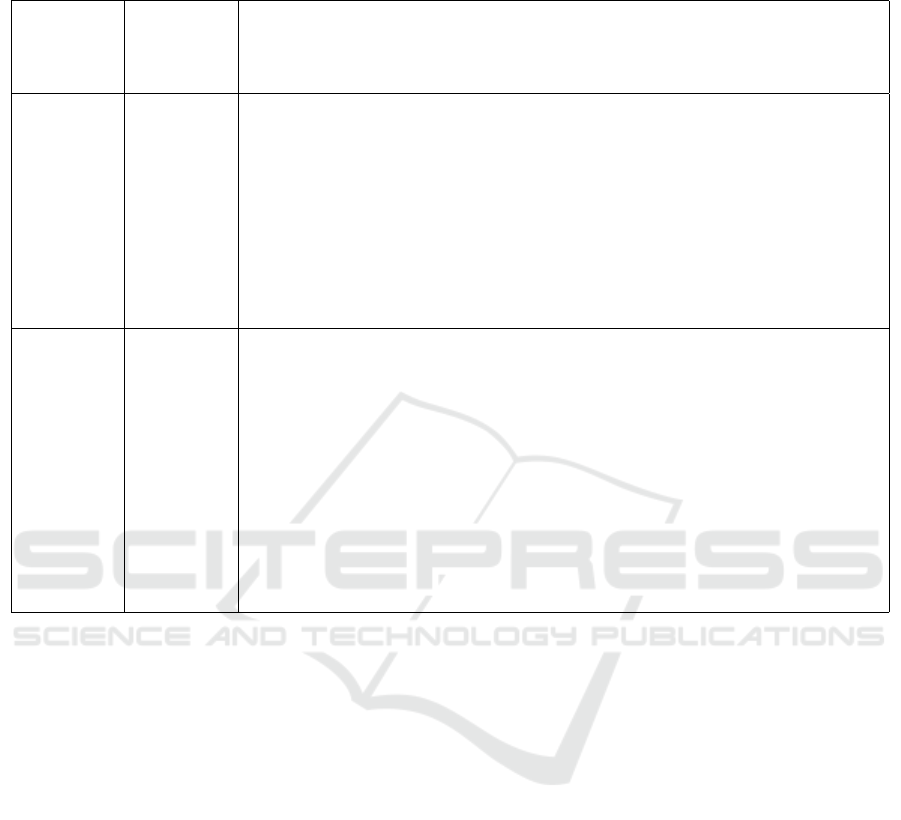
Table 2: Development of approaches to learning technologies (example based on materials of computer cycle disciplines,
teacher V. G. Logvinenko, SNAU, Ukraine).
Traditional
learning
(F1 –
Form 1)
Distance
learning
(F2 –
Form 2)
Flexible online learning in a pandemic (adaptive technology) (F3 – Form
3)
Lectures –
18 hours
Study of
lecture
materials
(on the
website) –
18 hours
The volume and forms are adjusted individually according to the results of the
online research:
• online lecture of the teacher,
• video lecture (record),
• study of materials for the lecture (text, presentation),
• discussion of problematic issues of the lecture with the teacher,
• discussion of problematic issues of the lecture in microgroups of students,
• games and debates based on lecture materials
Laboratory
work – 36
hours
Virtual
laboratory
work – 36
hours
The volume and forms are adjusted individually according to the results of the
online research:
• online preparation for laboratory work,
• video to study the technology of laboratory work (record),
• modeling problem situations “what will happen if”,
• discussion of problematic issues of laboratory work with the teacher,
• discussion of problematic issues of laboratory work in micro-groups of stu-
dents,
• games,
• passing a laboratory course
the effectiveness of the approach. The practical sig-
nificance of the results lies in the possibility (thanks
to the use of Google services) of embedding into any
learning process management system.
REFERENCES
Abdula, A. I., Baluta, H. A., Kozachenko, N. P., and Kas-
sim, D. A. (2020). Peculiarities of using of the Moo-
dle test tools in philosophy teaching. CEUR Workshop
Proceedings, 2643:306–320.
Al-Qahtani, A. A. Y. and Higgins, S. E. (2013). Effects
of traditional, blended and e-learning on students’
achievement in higher education. Journal of Com-
puter Assisted Learning, 29(3):220–234.
Atto, K. and Kotova, E. (2020). Communicative strate-
gies simulation in intelligent learning environment. In
2020 IEEE Communication Strategies in Digital Soci-
ety Seminar (ComSDS), pages 37–39.
Bersin, J. (2004). The blended learning book: Best prac-
tices, proven methodologies, and lessons learned.
Pfeiffer.
Blaschke, L. M. (2012). Heutagogy and lifelong learning:
A review of heutagogical practice and self-determined
learning. The International Review of Research in
Open and Distributed Learning, 13(1):56–71.
Burov, O. Y. (2017). ICT for performance assessment of
emergent technologies operators. CEUR Workshop
Proceedings, 1844:127–138.
Cochrane, T., Narayan, V., and Oldfield, J. (2013). Ipada-
gogy: Appropriating the ipad within pedagogical con-
texts. Int. J. Mob. Learn. Organ., 7(1):48–65.
Haranin, O. M. and Moiseienko, N. V. (2018). Adaptive ar-
tificial intelligence in RPG-game on the Unity game
engine. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 2292:143–
150.
Joshua, D., Obille, K., John, E., and Shuaibu, U. (2016).
E-Learning platform system for the department of
library and information science, Modibbo Adama
University of Technology, Yola : A Developmental
plan. Information Impact: Journal of Information and
Knowledge Management, 7(1):51–69. https://www.
ajol.info/index.php/iijikm/article/view/144901.
Kotova, E. E. and Pisarev, A. S. (2017). Adaptive predic-
tion of student learning outcomes in online mode. In
2017 IEEE II International Conference on Control in
Technical Systems (CTS), pages 138–141.
Lavrentieva, O., Horbatiuk, R., Skripnik, L., Kuchma,
O., Penia, V., and Pahuta, M. (2021). Theoreti-
cal and methodological bases of designing the ed-
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
576

ucational institution information and consulting en-
vironment. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
1840(1):012060.
Lavrov, E., Barchenko, N., Pasko, N., and Borozenec,
I. (2017). Development of models for the formal-
ized description of modular e-learning systems for the
problems on providing ergonomic quality of human-
computer interaction. Eastern-European Journal of
Enterprise Technologies, 2(2 (86)):4–13.
Lavrov, E. and Lavrova, O. (2019). Intelligent adapta-
tion method for human-machine interaction in modu-
lar e-learning systems. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2393:1000–1010.
Lavrov, E., Logvinenko, V., Siryk, O., and Kyzenko, V.
(2021). Method for assessing the information con-
tent of factors forming the cognitive independence
of students. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,
1840(1):012066.
Moodle Docs (2020). Moodle 3.8 release notes. https://
docs.moodle.org/dev/Moodle 3.8 release notes.
Osadchyi, V., Krasheninnik, I., Spirin, O., Koniukhov, S.,
and Diuzhykova, T. (2020). Personalized and adaptive
ICT-enhanced learning: A brief review of research
from 2010 to 2019. CEUR Workshop Proceedings,
2732:559–571.
Pereira, O. R. E. and Rodrigues, J. J. P. C. (2013). Survey
and analysis of current mobile learning applications
and technologies. ACM Comput. Surv., 46(2).
Pinchuk, O., Burov, O., and Lytvynova, S. (2020). Learn-
ing as a systemic activity. In Karwowski, W., Ahram,
T., and Nazir, S., editors, Advances in Human Factors
in Training, Education, and Learning Sciences, pages
335–342, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Reid, C. D. (2006). Supporting e-learning: a guide for
library and information managers. Library Review,
55(7):452–453.
Verkhova, G. V. and Akimov, S. V. (2017). Electronic edu-
cational complex for training specialists in the field of
technical systems management. In 2017 IEEE II Inter-
national Conference on Control in Technical Systems
(CTS), pages 26–29.
Voloshinov, S., Kruglyk, V., Osadchyi, V., Osadcha, K.,
and Symonenko, S. (2020). Realities and prospects
of distance learning at higher education institutions of
Ukraine. Ukrainian Journal of Educational Studies
and Information Technology, 8(1):1–16.
Ensuring the Effectiveness of e-Learning based on Online Technology Analysis of Factors Influencing the Cognitive Independence of
Students
577
