
3DSAL: An Efficient 3D-CNN Architecture for Video Saliency Prediction
Yasser Abdelaziz Dahou Djilali
1,3
, Mohamed Sayah
2
, Kevin McGuinness
3
and Noel E. O’Connor
3
1
Institut National des T
´
el
´
ecommunications et des TIC, Oran, Algeria
2
Universit
´
e Oran1, FSEA, Oran, Algeria
3
Insight Center for Data Analytics, Dublin City University, Dublin 9, Ireland
Keywords:
Visual Attention, Video Saliency, Deep Learning, 3D CNN.
Abstract:
In this paper, we propose a novel 3D CNN architecture that enables us to train an effective video saliency
prediction model. The model is designed to capture important motion information using multiple adjacent
frames. Our model performs a cubic convolution on a set of consecutive frames to extract spatio-temporal
features. This enables us to predict the saliency map for any given frame using past frames. We comprehensively
investigate the performance of our model with respect to state-of-the-art video saliency models. Experimental
results on three large-scale datasets, DHF1K, UCF-SPORTS and DAVIS, demonstrate the competitiveness of
our approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human attention was considered first in philosophy,
later in psychology and neuroscience, and most re-
cently as a computer vision problem in the field of com-
puter science (Mancas et al., 2016). Thanks mainly to
advances in deep learning, the development of com-
putational models of human attention has received re-
newed research interest in recent years (Mancas et al.,
2016). Computational models have been proposed for
imitating the attentional mechanisms of the Human
Visual Systems (HVS) for both dynamic and static
scenes. Dynamic fixation prediction, or video saliency
prediction, is very useful for understanding human at-
tentional behaviors for video content and has multiple
practical real-world applications e.g. video captioning,
compression, question answering, and object segmen-
tation (Wang et al., 2018). It is thus highly desirable
to have robust high-performance video saliency pre-
diction models.
Recently introduced benchmarks, such as
DHF1K (Wang et al., 2018) and LEDOV (Jiang
et al., 2018a), have allowed researchers to effectively
train deep learning models in an end-to-end manner
by formulating saliency as a regression problem.
However, the reported performances on video
(dynamic scene) datasets according to commonly used
saliency metrics are still far from those reported for
images (static scene). This is most likely due to the
rapid transition of video frames that makes dynamic
saliency prediction very challenging. Latent video
saliency deep learning based models separate spatial
features from temporal features. This is implemented,
for example, by a CNN module to extract spatial
features, which can then be aggregated into an LSTM
module to capture the temporal features (Hochreiter
and Schmidhuber, 1997).
In this paper we propose a novel video saliency
model that uses a 3D CNN architecture (Ji et al., 2013).
When performing a cubic convolution, our model cap-
tures spatio-temporal features in one 3D CNN module.
The dimensions
r
and
s
of the cube extract the spatial
features while the
t
axis extracts the temporal features.
In this way, the model learns saliency by fusing spatio-
temporal features for calculating the final saliency map.
Our key contribution is a 3D CNN architecture for pre-
dicting human gaze in dynamic scenes, which explic-
itly learns the hidden relationship between adjacent
frames for accurate saliency prediction.
This paper is organized as follows: Section
2 provides an overview of related video saliency
works. Section 3 gives a detailed description of
the proposed deep saliency framework. Section 4
compares the experimental results to state-of-the-art
methods. Finally, we conclude this work in Sec-
tion 5. The results can be reproduced with the
source code and trained models available on GitHub:
https://github.com/YasserDA/Saliency-3DSal.
Djilali, Y., Sayah, M., McGuinness, K. and O’Connor, N.
3DSAL: An Efficient 3D-CNN Architecture for Video Saliency Prediction.
DOI: 10.5220/0008875600270036
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2020) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
27-36
ISBN: 978-989-758-402-2; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
27

2 RELATED WORK
In this section we review the relevant literature on
saliency models for both static and dynamic scenes.
2.1 Static Saliency Models
Saliency prediction for images has been widely studied
during the last few decades. As a pioneer, (Itti et al.,
1998) derived bottom-up visual saliency using center-
surround differences across multi-scale image features.
Other static saliency models e.g. (Bruce and Tsot-
sos, 2006; Garcia-Diaz et al., 2009; Seo and Milanfar,
2009; Goferman et al., 2012; Gao and Vasconcelos,
2005) are mostly based on computing multiple visual
features such as color, edge, and orientation at mul-
tiple spatial scales to produce a saliency map. More
recent deep learning based static saliency models e.g.
(Huang et al., 2015; K
¨
ummerer et al., 2014; Liu et al.,
2015; Kruthiventi et al., 2017; Cornia et al., 2016; Pan
et al., 2016; Pan et al., 2017) have achieved remark-
able improvements relying on the success of neural
networks and the availability of large-scale saliency
datasets for static scenes, such as those described in
(Bylinskii et al., ; Jiang et al., 2015; Borji and Itti,
2015).
(Vig et al., 2014) and (Kruthiventi et al., 2017)
were the first to use CNNs for saliency prediction when
introducing eDN and DeepFix respectively. DeepFix
initialized the first 5 convolution blocks with VGG-16
weights, then added two novel Location Based Convo-
lutional (LBC) layers to capture semantics at multiple
scales. Pan et al. (Pan et al., 2017) used Generative Ad-
versarial Networks (GANs) (Goodfellow et al., 2014)
to build the SalGAN model. The network consists
of a generator model whose weights are learned by
back-propagation computed from a binary cross en-
tropy (BCE) loss over existing saliency maps. The
resulting prediction is processed by a discriminator
network trained to solve a binary classification task
between the saliency maps generated by the generative
stage and the ground truth ones.
2.2 Dynamic Saliency Models
Visual information constantly changes due to egocen-
tric movements or the dynamics of the scene being
observed. Dynamic saliency is then dependent on
both current scene saliency as well as the accumulated
knowledge from previous time instants (Borji and Itti,
2013). Video saliency prediction is extremely more
challenging than image saliency prediction (Borji,
2018). In this task, viewers have much less time to
explore each video frame (
∼ 1/30
seconds) compared
to the 3-5 seconds typical for viewing still images.
Early video saliency models such as (Leifman
et al., 2017; Garcia-Diaz et al., 2012; Zhang and
Sclaroff, 2013; Leboran et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2017;
Guo et al., 2008; Rudoy et al., 2013), rely on existing
static saliency models with additional motion features.
They generally use linear or nonlinear combination
rules to fuse spatial and temporal information. How-
ever, using a simple fixed weight to combine spatial
and temporal information can drive the model to lose
the intrinsic relationship between these two comple-
mentary aspects.
A few works have investigated deep learning based
video saliency prediction models (Bak et al., 2018;
Jiang et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2018; Adel Bargal et al.,
2018). These are mainly based on two distinct net-
work modules to deal with spatial and temporal fields
separately. These works exhibit strong performance
and show the potential of using neural networks to the
video saliency problem. (Bak et al., 2018) were the
first to leverage deep learning when they used a two-
stream CNN architecture for video saliency prediction.
Video frames and motion maps were fed to the two
streams. (Wang et al., 2018) proposed a CNN-LSTM
network architecture with an attention mechanism to
explicitly encode static saliency information, thus al-
lowing the LSTM to focus on learning a more flexi-
ble temporal saliency representation across successive
frames. (Linardos et al., 2018) introduced a temporal
regularization for their previous model SalGAN (Pan
et al., 2017) for static saliency prediction. In terms of
architecture, they added a convolutional LSTM layer
on top of the frame-based saliency prediction to adapt
it for dynamic saliency prediction.
All these works consider the spatial domain as the
most influential aspect, and use very little accumulated
knowledge from the past (
∼ 70ms
), while the aver-
age human eye reaction time, is of the order of
284ms
(Saslow, 1967). We propose that more importance
needs to be given to the temporal domain for video
saliency prediction. In our approach, we exploit the
temporal and spatial domain in an equal manner via
the use of 3D CNN, with a view to more appropriate
spatio-temporal feature learning (see Fig. 1). Further-
more, we smooth adjacent frames to obtain good eye
fixation quality saturation by introducing the tangent
hyperbolic weighting function on the input sequence
frames.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
28

3 OUR APPROACH
3.1 Overview
Fig. 2 represents the overall architecture of our video
saliency model. The framework takes
i
consecu-
tive input frames:
{F
t−i
∈ R
224×244×3
: i ∈ {0,...,5}}
.
Since the latency for saccadic eye movement is about
284
ms (Saslow, 1967), when watching a 30 fps video,
the human eye is sensitive to exactly
(0.284ms × 30
fps)
' 8
frames. Thus, we set the number of input
frames to six to approximate the ideal threshold and
save computing capacity at the same time. Each frame
is fed into the spatial feature extraction function mod-
eled with a pre-trained VGG-16 (Simonyan and Zis-
serman, 2014) after removing the fully connected lay-
ers. This choice was motivated by the reduction of
complexity while improving accuracy. Since VGG-16
was trained on large-scale ImageNet dataset (1.4M im-
ages) (Deng et al., 2009), VGG-16 provides excellent
feature extraction performance. The output of the spa-
tial feature extraction function is six feature cuboids:
F
∗
t−5
,F
∗
t−4
,.....,F
∗
t
∈ R
14×14×512
, with
G(F
x
) = F
∗
x
, (1)
and where the function
G
is modelled by the truncated
VGG-16 model (for more details see (Simonyan and
Zisserman, 2014)).
3.2 Weighting Cuboid Coefficients
The eye motion on a given object has been intuitively
considered as a tangent hyperbolic activation func-
tion (Nwankpa et al., 2018). To preserve the consis-
tency of human vision and avoid computing complex-
ity in time and space, we considered six frames to
define the motion features for the human eyes. This
enables us to use a suitable
tanh
function, to weight the
motion frames by parameters
c[i]
where
i ∈ {1,..., 6}
–
see bold weights in Table 1.
Considering the vector of parameters
c =
[0.4,0.5,0.6, 0.7,0.8,0.98]
as illustrated in Table 1, we
can reach the eye fixation quality saturation in the 6
th
spatial frame. As such, the temporal dimension is
Figure 1: 3D Convolution operation over adjacent frames.
Table 1: Fixation quality motion.
Weight Fixation Quality Quality
Quality Variation Saturation
c[i] tanh(c[i]) tanh(c[i+1]) tanh(c[i+1])
−tanh(c[i]) +tanh(c[i])
0.1 0,044 - -
0.2 0,088 0.044 0.13
0.3 0,134 0.046 0.22
0.4 0.184 0.050 0.32
0.5 0.239 0.055 0.42
0.6 0.301 0.062 0.54
0.7 0.377 0.076 0.68
0.8 0.477 0.100 0.85
0.98 0.998 0.521 1.47
- 0,998 0,0 2.00
defined as a continuation of six
c
-weighted consecu-
tive frames. In each iteration, the
6
th
spatial frame
is determined via an adversarial process in which the
spatial frames
F
t−5
,F
t−4
,F
t−3
,F
t−2
, and
F
t−1
are used
to compute the
F
t
saliency map. Finally, each of the six
cuboids, weighted with respect to their importance in
the learning process, are adjusted in a temporary order
to construct one spatio-temporal feature map. Note
that the six frames do not represent a large variation of
space and that their concatenation preserves the spa-
tial information when finding the correlation in time
for each pixel location. Later, a spatio-temporal fea-
ture map of
6×
frames determines the spatio-temporal
units
S ∈ R
6×14×14×512
. The 3D CNN takes
S
as an
input, to perform a spatio-temporal fusion, in order to
learn saliency. Then, a saliency map
P ∈ R
224×224
is
generated to represent the saliency map for F
t
.
3.3 3D CNN Architecture
We believe that a 3D ConvNet is more appropriate for
spatio-temporal feature learning. Compared to a 2D
ConvNet, a 3D ConvNet has the ability to model tem-
poral information better by virtue of 3D convolutions
and 3D pooling operations. In 2D ConvNets, convo-
lution and pooling operations are only performed spa-
tially. 3D ConvNets perform those operations spatio-
temporally to preserve temporal information in the
input signals resulting in an output volume (see Fig. 1).
The same phenomena is applicable for 2D and 3D
pooling (Tran et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 2, we built a five block decoder
3D CNN network to learn saliency in a
slow f usion
manner. Each block consists of Deconv3D and opera-
tions, with a ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) activation
function. The role of Deconv3D is to up-sample the
feature map resolution and Conv3D to construct the
3DSAL: An Efficient 3D-CNN Architecture for Video Saliency Prediction
29

Figure 2: Network Architecture of 3DSAL. (a) Feature extraction function with the truncated VGG-16. (b) Composition of
adjacent feature maps via the use of Tanh activation function. (c) Spatio-temporal feature fusion with 3D CNN.
spatio-temporal features for saliency learning. We de-
note the triplet
(t,r,s)
as the kernel size for Deconv3D
and Conv3D layers. We use the
t
axis in the kernel
to cover the temporal dimension in the kernel, while,
(r, s)
denotes the spatial kernel size. Consider a convo-
lutional layer
l
and the input spatio-temporal units
S
.
The
i
th
output unit
V
i,K
(l)
for the layer
l
is computed
as:
V
(l)
i,K
(x,y,z)
!
=
C
∑
c=1
T
∑
t=1
R
∑
r=1
S
∑
s=1
W
(l)
i,K,c
(t,r,s)
× U
(l−1)
i,c
(x+t,y+r,z+s)
!
+
B
(l)
i,K
!
,
(2)
where
C
is the channel number for the layer
(l)
and
x,y, z
are the cubic spatial dimensions. The parame-
ter
K
is considered as the channel dimension for the
output unit
V
(l)
. The
W
(l)
i,K,c
term denotes the weights
connecting the
i
th
unit at position
(x,y, z)
in the feature
map of layer
(l − 1)
and the
i
th
unit in the layer
l
with
K
channels. Finally, the
B
(l)
∀i,K
term is the bias vector
with length K.
The authors of (Li et al., 2016) and (Tran et al.,
2015) demonstrated that the most suitable kernel size
for 3D convolution is
3 × 3 × 3
. Hence, we set the
3D convolution kernel size to
3 × 3 × 3
with stride
1 × 1 × 1
. Since the ground truth saliency map can
be seen as a distribution probability, where each pixel
represents the probability to be fixated by a human, at
the final block, we use the sigmoid as an activation
function to get a normalized predicted saliency map in
0,1] with a size 224 ×224.
Loss function
. The saliency loss is computed on
a per-pixel basis, where each value of the predicted
saliency map is compared with its corresponding peer
from the ground truth map. We denote the predicted
saliency map as
P ∈
0,1]
224×224
and the continuous
saliency map as
G ∈
0,1]
224×224
. The continuous
saliency map
G
is obtained by blurring the binary fixa-
tion map
FM
with a 2D Gaussian kernel. The fixation
map FM is a binary image with:
FM
i j
=
(
1 if location (i, j ) is a fixation
0 otherwise,
and the variance of the Gaussian is selected so the
filter covers approximately 1-degree of visual angle,
as done in (Judd et al., 2012). The saliency task can be
seen as a similarity measure between the predicted
saliency map
P
and the ground truth
G
. The loss
function must be designed to maximise the invariance
of predictive maps and give higher weights to locations
with higher fixation probability. An appropriate loss
for this situation is the binary cross entropy, defined
as:
L
BCE
(G,P) = −
1
N
N
∑
i=1
(G
i
log(P
i
) + (1 − G
i
)log(1 − P
i
))
(3)
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
30

Table 2: Architecture of the 3D CNN.
Layer Depth Kernel Output Params Act
/Pool Shape #
Conv3D 1 1 512 3 × 3 × 3 (6,14,14,512) 7078400 ReLU
Conv3D 1 2 512 3 × 3 × 3 (6,14,14,512) 7078400 ReLU
MaxPool3D 1 – 4 × 2 × 2 (3,7,7,512) 0 –
Batch-Norm – – (3,7,7,512) 2048 –
Deconv3D 1 512 1 × 3 × 3 (3,14,14,512) 2359808 ReLU
Conv3D 2 1 512 3 × 3 × 3 (3,14,14,512) 7078400 ReLU
Batch-Norm – – (3,7,7,512) 2048 –
Deconv3D 2 256 3 × 3 × 3 (3,28,28,256) 3539200 ReLU
Conv3D 2 1 256 3 × 3 × 3 (3,28,28,256) 179728 ReLU
Conv3D 2 2 256 3 × 3 × 3 (3,28,28,256) 179728 ReLU
MaxPool3D 2 – 3 × 1 × 1 (1,28,28,256) 0 –
Batch-Norm – – (1,28,28,256) 1024 –
Deconv3D 3 128 1 × 3 × 3 (1,56,56,128) 295040 ReLU
Conv3D 3 1 128 1 × 3 × 3 (1,56,56,128) 147584 ReLU
Conv3D 3 2 128 1 × 3 × 3 (1,56,56,128) 147584 ReLU
Batch-Norm – – (1,56,56,128) 512 –
Deconv3D 4 64 1 × 3 × 3 (1,112,112,64) 73792 ReLU
Conv3D 4 1 64 1× 3 × 3 (1,112,112,64) 36928 ReLU
Conv3D 4 2 64 1× 3 × 3 (1,112,112,64) 36928 ReLU
Batch-Norm – – (1,112,112,64) 2048 –
Deconv3D 5 32 1 × 3 × 3 (1,224,224,32) 18464 ReLU
Conv3D 5 1 32 1× 3 × 3 (1,224,224,32) 9258 ReLU
Conv3D 5 2 16 1× 3 × 3 (1,224,224,16) 4624 ReLU
Conv3D 5 3 1 1 × 3 × 3 (1,224,224,1) 145 Sigm
Total Params: 31,447,841
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Experimental Setup
Datasets
. DHF1K (Wang et al., 2018), LEDOV (Jiang
et al., 2018b), HOLYWOOD (Mathe and Sminchis-
escu, 2015), UFC-SPORT (Mathe and Sminchis-
escu, 2015) and DIEM (Mital et al., 2011) are the
five datasets widely used for video saliency research.
DHF1K comprises a total of 1,000 video sequences
with 582,605 frames covering a wide range of scenes,
motions and activities. HOLLYWOOD-2 is a dynamic
eye tracking dataset. It contains short video sequences
from a set of 69 Hollywood movies, containing 12 dif-
ferent human action classes, ranging from answering
a phone, eating, driving and running. The UCF-Sports
dataset consists of 150 videos covering 9 sports classes
like golf, skateboarding, running and riding. LEDOV
contains videos with a total of 179,336 frames cover-
ing three main sub-categories: Animals, Man-made-
Objects and Human activities varying from social ac-
tivities, daily actions, sports and art performance.
We have chosen DHF1K and UFC-SPORT to train
our 3DSAL model. DHF1K characterises the free
viewing approach, in which subjects freely watch the
stimuli so that many internal cognitive tasks are en-
gaged, thereby making the generated saliency map
more difficult to predict. UFC-SPORT is a task driven
dataset, where subjects are more likely to follow the
main objects in the scene, affording the model preci-
sion. Training on two different paradigms helps ensure
more robust prediction.
Training Protocol.
We have two training modes:
(1) 3DSAL-base: Training the model without regres-
sion, where all frames are fed into the 3D CNN in an
equal manner, without multiplying by the weighting
coefficients. (2) 3DSAL-weighted: The use of weight-
ing coefficients, to indicate the frame importance in
the prediction process.
For DHF1K, we respect the original train-
ing/validation/testing partitioning (600/100/300). For
UFC-SPORT, as proposed by the authors in (Mathe
and Sminchisescu, 2015), the training/testing is split
(103/47). We test our model on: DHF1K, UFC-
SPORT and DAVIS (Perazzi et al., 2016) for both
quantitative and qualitative results.
Technical Specification.
We implemented our
model in Python using the Keras API running a Ten-
sorFlow backend. Due to the huge size of the train-
ing data (550k frames), we used the early stopping
technique on the validation set for optimal generaliza-
tion performance (Prechelt, 1998). The Adam Opti-
mizer (Kingma and Ba, 2014) initial learning rate was
set to
10
−4
and was dropped by 10 each 2 epochs. The
network was trained for 33 epochs. The entire training
procedure took about 7 days (160 hours) on a single
NVIDIA GTX 1080 GPU,which has a total of 8GB
global memory and 20 multiprocessors, and i7 7820
HK 3.9GHZ Intel processor.
Metrics.
To test the performance of our model,
we utilize the five widely used metrics: AUC-Judd
(AUC-J), Similarity metric (SIM), Linear Correlation
Coefficient (CC), shuffled AUC (s-AUC) and Normal-
ized Scanpath Saliency (NSS). A detailed description
of these metrics is presented in (Borji and Itti, 2013).
Competitors.
We compare the performance of our
model according to the different saliency metrics, with
six video saliency models: OM-CNN (Jiang et al.,
2017), Two-stream (Bak et al., 2018), AWS-D (Lebo-
ran et al., 2017), OBDL (Hossein Khatoonabadi et al.,
2015), ACLNet (Wang et al., 2018), (Linardos et al.,
2018). Benefiting from the work of (Wang et al., 2018),
which tested the performance of the previous mod-
els in three datasets (DHF1K, HOLYWOOD-2, UFC-
SPORT), we add our results to this work, to compare
the performance of our model with these works.
4.2 Results
Table 3 shows the comparative study with the afore-
mentioned models according to the different saliency
metrics on DHF1K and UFC-SPORT datasets (300/47)
test videos. Our model is very competitive in the two
3DSAL: An Efficient 3D-CNN Architecture for Video Saliency Prediction
31
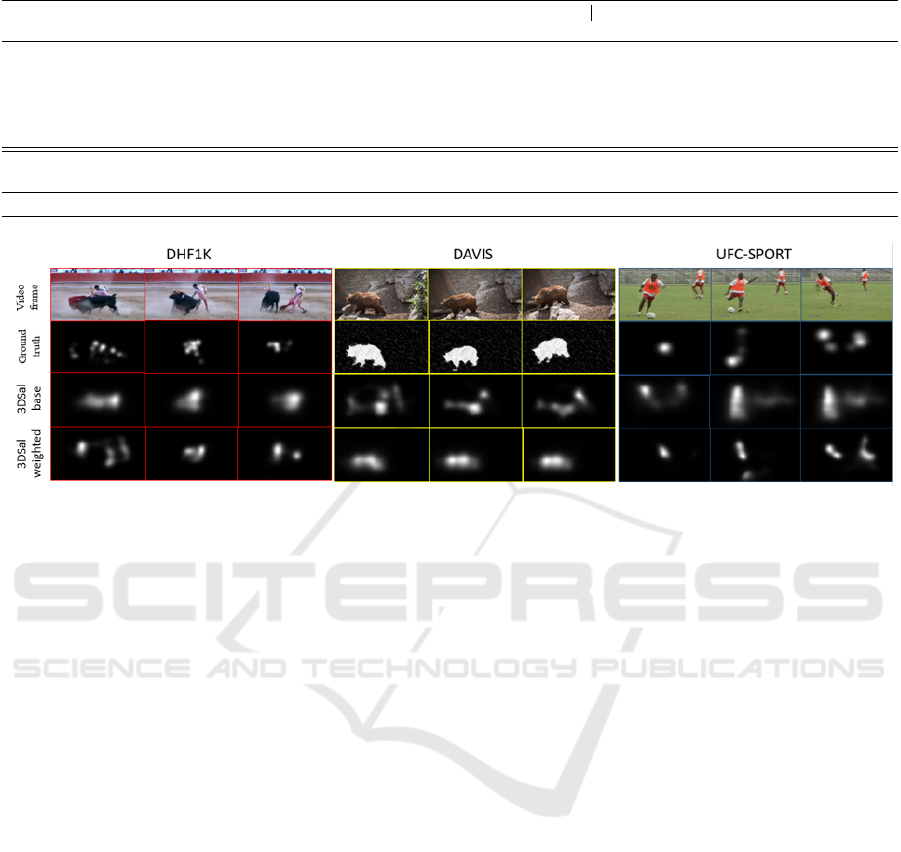
Table 3: Comparative performance study on: DHF1K, UFC-SPORT datasets.
Dataset DHF1K UFC-SPORT
AUC-J ↑ SIM ↑ s-AUC ↑ CC ↑ NSS ↑ AUC-J ↑ SIM ↑ s-AUC ↑ CC ↑ NSS ↑
# OBDL (Hossein Khatoonabadi et al., 2015) 0.638 0.171 0.500 0.117 0.495 0.759 0.193 0.634 0.234 1.382
# AWS-D (Leboran et al., 2017) 0.703 0.157 0.513 0.174 0.940 0.823 0.228 0.750 0.306 1.631
OM-CNN (Jiang et al., 2017) 0.856 0.256 0.583 0.344 1.911 0.870 0.321 0.691 0.405 2.089
Two-Stream (Bak et al., 2018) 0.834 0.197 0.581 0.325 1.632 0.832 0.264 0.685 0.343 1.753
ACLNET (Wang et al., 2018) 0.890 0.315 0.601 0.434 2.354 0.897 0.406 0.744 0.510 2.567
Linardos et al (Linardos et al., 2018) 0.744 0.260 0.722 0.302 2.246 – – – – –
3DSAL-Base – – – – – 0.8111 0.3255 0.6088 0.3209 1.7119
3DSAL-Weighted 0.8500 0.3205 0.6234 0.3562 1.9962 0.8813 0.4783 0.7011 0.5902 2.8023
(#) Non deep learning models. The best score is marked in bold red. The second best score is marked in bold black.
Figure 3: Saliency map predictions over three datasets.
datasets. The 3DSAL-weighted repeatedly appears
in the best two scores, and exhibits the best score
for certain metrics. Also, it is clear that deep learn-
ing approaches outperform classic hand-crafted video
saliency methods.
DHF1K.
The diversity of this dataset makes the
prediction task very challenging, our model remains
very competitive since our scores are close to the state
of art model (ACLNet (Wang et al., 2018)). This is
due to the inclusion of temporal domain exploration
via the use 3D CNN for adjacent frames.
UFC-SPORT.
On the 47 test videos of UFC-
SPORT dataset, our model gains a remarkable advan-
tage against other models. This demonstrates the ca-
pacity of our model to predict task driven saliency,
when observers are more likely to track the main ob-
ject in the scene e.g. soccer player, horse rider, skate-
boarder, etc. Most UFC-SPORT fixations are located
on the human body zone.
The 3DSAL-weighted model outperforms the
3DSAL-base model in all situations for to the UFC-
SPORT dataset. 3DSAL-base faces the problem
of a centered saliency in the middle and consider-
ing the same weight for all frames (
c[i] = 1
) con-
fuses the model to predict saliency map in a highly
correlated space, which increases the false positive
rate. We solved this problem when using the
tanh
weighting function, which helped the 3D CNN learn
more accurate relationships between the features of
adjacent frames (e.g. AUC-J:
0.8111 → 0.8813
,
NSS:1.7119 → 2.8023).
Fig. 3 illustrates the prediction task on a sample
of frames from three datasets: DHF1K, DAVIS, UFC-
SPORT. It can be seen that the generated saliency maps
with 3DSAL-weighted are more comprehensive and
look remarkably similar to the Ground truth saliency
maps in terms of fixations. DAVIS (Perazzi et al.,
2016) is a video object segmentation dataset, thus, the
various saliency metrics are not applicable. However,
it is used in the qualitative study to show the effective-
ness of our model to capture the main objects in the
scene.
For more qualitative results, Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 show
the overlaid saliency maps on sample videos/frames
from DAVIS and DHF1K datasets for the 3DSAL-
Base, 3DSAL-weighted, and ACLNet. Two main
points can be derived from these figures:
•
In Fig. 4, as the scene progresses, the
3DSAL-weighted ignores some static objects and
only focuses on other moving objects, while
ACLnet (Wang et al., 2018) still considers them
salient. In video (b), both models considered the
car as a salient object in the first frame. Since
the car was static all over the scene, the 3DSAL-
weighted considered it as a background, and only
focused on dynamic objects (dog, ducks), while
ACLNet (Wang et al., 2018) took it as salient dur-
ing the whole scene. This demonstrates the effec-
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
32
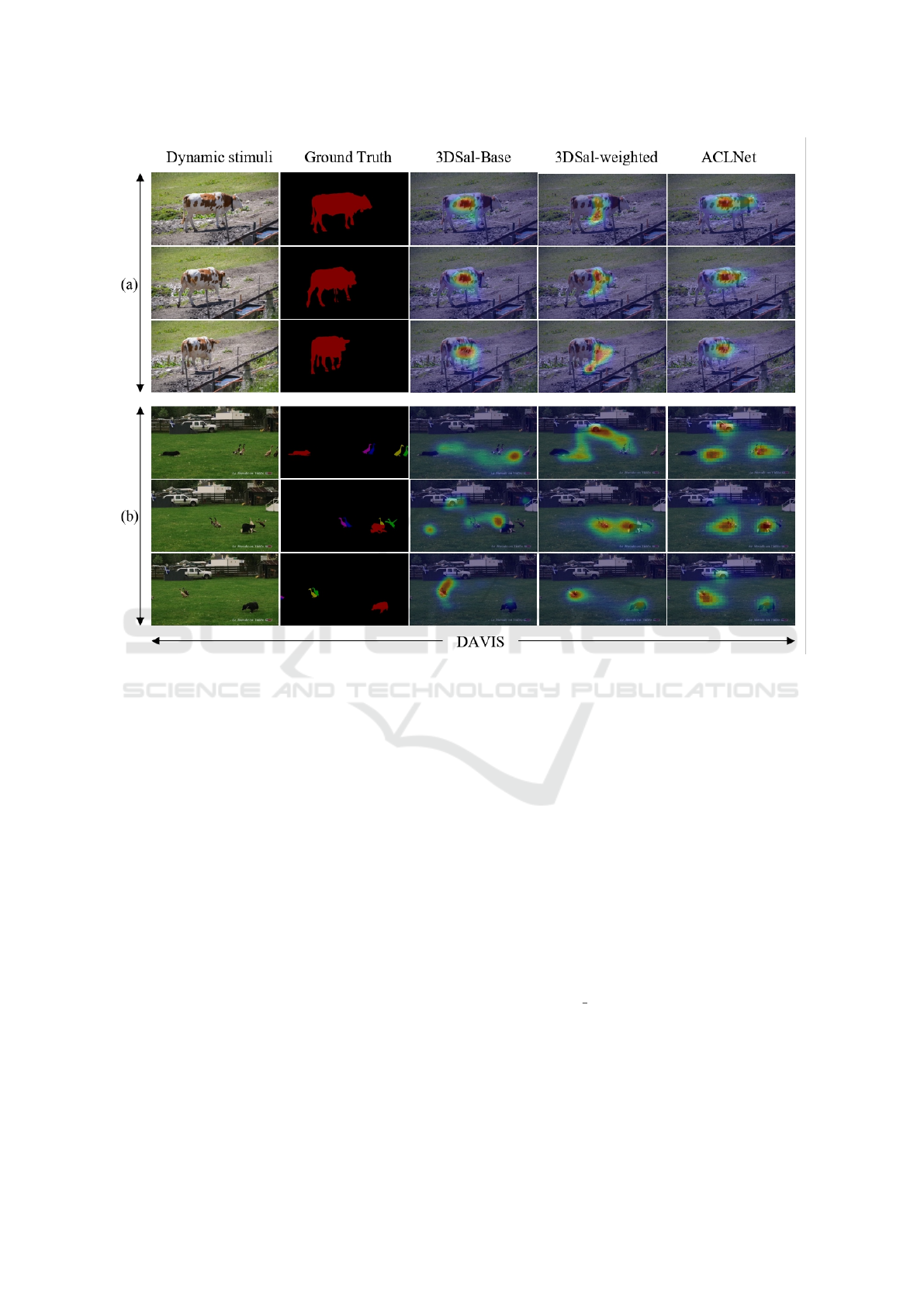
Figure 4: Qualitative results of our 3DSAL model and the ACLNet model (Wang et al., 2018) on two validation video samples
from the object segmentation dataset DAVIS. It can be observed that the proposed 3DSAL-weighted is able to capture the main
objects in the scene.
tiveness of 3D convolutions to capture motion.
•
In Fig. 5, it is noticeable that the generated saliency
maps using 3DSAL-base are sparse, this is due to
the large number of features in the latent space,
the model tends to give a high probability to a
given pixel, which makes it salient. In the 3DSAL-
weighted version, the use of the weighting function
forces the model to generate a more focused and
consistent saliency regions.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we target the problem of learning spatio-
temporal features for video saliency prediction using
3D ConvNets, trained on large-scale video saliency
datasets. We proposed the 3DSAL-weighted video
saliency model, which fuses the spatio-temporal fea-
tures from adjacent frames to accurately learn the hid-
den relationship that affects human behavior when
watching videos. We extensively tested the perfor-
mance of our model on: DHF1K, UFC-SPORT and
DAVIS datasets, and reported the performance of
our model compared with the state-of-the-art video
saliency models. It is worth noting the competitive-
ness of the proposed model, whereby results on UFC-
SPORT dataset outperform the state-of-the-art models.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of
Ericsson Algeria for the donation of GPUs used in
this work. This material is based on works sup-
ported by Science Foundation Ireland under Grant No.
SFI/12/RC/2289 P2.
3DSAL: An Efficient 3D-CNN Architecture for Video Saliency Prediction
33
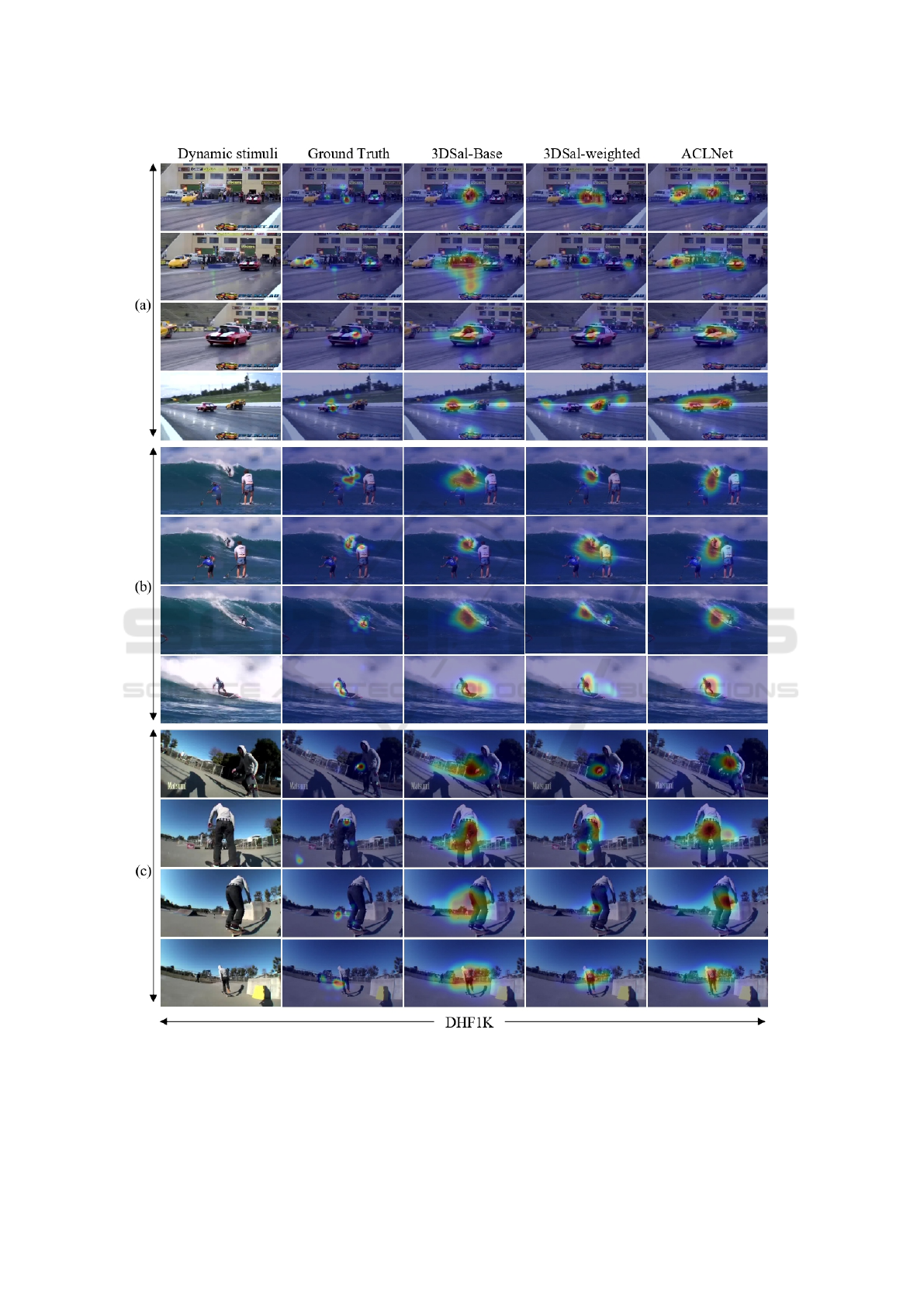
Figure 5: Qualitative results of our 3DSal model and ACLNet (Wang et al., 2018) on three validation video samples from
DHF1K dataset. It can be observed that the proposed 3DSal-weighted is able to handle various challenging scenes well and
produces consistent video saliency results.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
34

REFERENCES
Adel Bargal, S., Zunino, A., Kim, D., Zhang, J., Murino, V.,
and Sclaroff, S. (2018). Excitation backprop for rnns.
In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1440–1449.
Bak, C., Kocak, A., Erdem, E., and Erdem, A. (2018). Spatio-
temporal saliency networks for dynamic saliency pre-
diction. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 20(7):1688–
1698.
Borji, A. (2018). Saliency prediction in the deep learn-
ing era: An empirical investigation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.03716.
Borji, A. and Itti, L. (2013). State-of-the-art in visual atten-
tion modeling. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis
and machine intelligence, 35(1):185–207.
Borji, A. and Itti, L. (2015). Cat2000: A large scale fixation
dataset for boosting saliency research. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1505.03581.
Bruce, N. and Tsotsos, J. (2006). Saliency based on informa-
tion maximization. In Advances in neural information
processing systems, pages 155–162.
Bylinskii, Z., Judd, T., Borji, A., Itti, L., Durand, F., Oliva,
A., and Torralba, A. Mit saliency benchmark.
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Serra, G., and Cucchiara, R. (2016).
A deep multi-level network for saliency prediction. In
2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recog-
nition (ICPR), pages 3488–3493. IEEE.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., and Fei-Fei,
L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image
database. In 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision
and pattern recognition, pages 248–255. Ieee.
Gao, D. and Vasconcelos, N. (2005). Discriminant saliency
for visual recognition from cluttered scenes. In Ad-
vances in neural information processing systems, pages
481–488.
Garcia-Diaz, A., Fdez-Vidal, X. R., Pardo, X. M., and Dosil,
R. (2009). Decorrelation and distinctiveness provide
with human-like saliency. In International Conference
on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems,
pages 343–354. Springer.
Garcia-Diaz, A., Fdez-Vidal, X. R., Pardo, X. M., and
Dosil, R. (2012). Saliency from hierarchical adapta-
tion through decorrelation and variance normalization.
Image and Vision Computing, 30(1):51–64.
Goferman, S., Zelnik-Manor, L., and Tal, A. (2012). Context-
aware saliency detection. IEEE transactions on pattern
analysis and machine intelligence, 34(10):1915–1926.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-
Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Bengio, Y.
(2014). Generative adversarial nets. In Advances in
neural information processing systems, pages 2672–
2680.
Guo, C., Ma, Q., and Zhang, L. (2008). Spatio-temporal
saliency detection using phase spectrum of quaternion
fourier transform. In 2008 IEEE Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 1–8. IEEE.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Hossein Khatoonabadi, S., Vasconcelos, N., Bajic, I. V., and
Shan, Y. (2015). How many bits does it take for a
stimulus to be salient? In Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 5501–5510.
Huang, X., Shen, C., Boix, X., and Zhao, Q. (2015). Salicon:
Reducing the semantic gap in saliency prediction by
adapting deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,
pages 262–270.
Itti, L., Koch, C., and Niebur, E. (1998). A model of saliency-
based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE
Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelli-
gence, (11):1254–1259.
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., and Yu, K. (2013). 3d convolu-
tional neural networks for human action recognition.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 35(1):221–231.
Jiang, L., Xu, M., Liu, T., Qiao, M., and Wang, Z. (2018a).
Deepvs: A deep learning based video saliency pre-
diction approach. In The European Conference on
Computer Vision (ECCV).
Jiang, L., Xu, M., Liu, T., Qiao, M., and Wang, Z. (2018b).
Deepvs: A deep learning based video saliency predic-
tion approach. In Proceedings of the European Confer-
ence on Computer Vision (ECCV), pages 602–617.
Jiang, L., Xu, M., and Wang, Z. (2017). Predicting video
saliency with object-to-motion cnn and two-layer con-
volutional lstm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.06316.
Jiang, M., Huang, S., Duan, J., and Zhao, Q. (2015). Sali-
con: Saliency in context. In The IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Judd, T., Durand, F., and Torralba, A. (2012). A benchmark
of computational models of saliency to predict human
fixations.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A
method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Kruthiventi, S. S., Ayush, K., and Babu, R. V. (2017). Deep-
fix: A fully convolutional neural network for predicting
human eye fixations. IEEE Transactions on Image Pro-
cessing, 26(9):4446–4456.
K
¨
ummerer, M., Theis, L., and Bethge, M. (2014). Deep
gaze i: Boosting saliency prediction with feature maps
trained on imagenet. arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.1045.
Leboran, V., Garcia-Diaz, A., Fdez-Vidal, X. R., and Pardo,
X. M. (2017). Dynamic whitening saliency. IEEE
transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelli-
gence, 39(5):893–907.
Leifman, G., Rudoy, D., Swedish, T., Bayro-Corrochano,
E., and Raskar, R. (2017). Learning gaze transitions
from depth to improve video saliency estimation. In
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 1698–1707.
Li, X., Zhao, L., Wei, L., Yang, M.-H., Wu, F., Zhuang,
Y., Ling, H., and Wang, J. (2016). Deepsaliency:
Multi-task deep neural network model for salient object
detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
25(8):3919–3930.
3DSAL: An Efficient 3D-CNN Architecture for Video Saliency Prediction
35

Linardos, P., Mohedano, E., Cherto, M., Gurrin, C., and
i Nieto, X. G. (2018). Temporal saliency adaptation in
egocentric videos.
Liu, N., Han, J., Zhang, D., Wen, S., and Liu, T. (2015).
Predicting eye fixations using convolutional neural net-
works. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 362–
370.
Mancas, M., Ferrera, V. P., Riche, N., and Taylor, J. G.
(2016). From Human Attention to Computational At-
tention, volume 2. Springer.
Mathe, S. and Sminchisescu, C. (2015). Actions in the
eye: Dynamic gaze datasets and learnt saliency models
for visual recognition. IEEE transactions on pattern
analysis and machine intelligence, 37(7):1408–1424.
Mital, P. K., Smith, T. J., Hill, R. L., and Henderson, J. M.
(2011). Clustering of gaze during dynamic scene view-
ing is predicted by motion. Cognitive Computation,
3(1):5–24.
Nwankpa, C., Ijomah, W., Gachagan, A., and Marshall, S.
(2018). Activation functions: Comparison of trends
in practice and research for deep learning. CoRR,
abs/1811.03378.
Pan, J., Ferrer, C. C., McGuinness, K., O’Connor, N. E., Tor-
res, J., Sayrol, E., and Giro-i Nieto, X. (2017). Salgan:
Visual saliency prediction with generative adversarial
networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.01081.
Pan, J., Sayrol, E., Giro-i Nieto, X., McGuinness, K., and
O’Connor, N. E. (2016). Shallow and deep convolu-
tional networks for saliency prediction. In Proceedings
of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, pages 598–606.
Perazzi, F., Pont-Tuset, J., McWilliams, B., Van Gool, L.,
Gross, M., and Sorkine-Hornung, A. (2016). A bench-
mark dataset and evaluation methodology for video
object segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 724–732.
Prechelt, L. (1998). Early stopping-but when? In Neural
Networks: Tricks of the trade, pages 55–69. Springer.
Rudoy, D., Goldman, D. B., Shechtman, E., and Zelnik-
Manor, L. (2013). Learning video saliency from hu-
man gaze using candidate selection. In Proceedings of
the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, pages 1147–1154.
Saslow, M. (1967). Effects of components of displacement-
step stimuli upon latency for saccadic eye movement.
Josa, 57(8):1024–1029.
Seo, H. J. and Milanfar, P. (2009). Static and space-time
visual saliency detection by self-resemblance. Journal
of vision, 9(12):15–15.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep con-
volutional networks for large-scale image recognition.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., and Paluri,
M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d
convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE
international conference on computer vision, pages
4489–4497.
Vig, E., Dorr, M., and Cox, D. (2014). Large-scale optimiza-
tion of hierarchical features for saliency prediction in
natural images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages
2798–2805.
Wang, W., Shen, J., Guo, F., Cheng, M.-M., and Borji, A.
(2018). Revisiting video saliency: A large-scale bench-
mark and a new model. In Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 4894–4903.
Xu, M., Jiang, L., Sun, X., Ye, Z., and Wang, Z. (2017).
Learning to detect video saliency with hevc features.
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 26(1):369–
385.
Zhang, J. and Sclaroff, S. (2013). Saliency detection: A
boolean map approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE
international conference on computer vision, pages
153–160.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
36
