
Fine-tuning Siamese Networks to Assess Sport Gestures Quality
Mégane Millan and Catherine Achard
Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et de Robotique, Sorbonne University, 4 place Jussieu, Paris, France
Keywords:
Deep Learning, Siamese Network, AQA, Fine-tuning.
Abstract:
This paper presents an Action Quality Assessment (AQA) approach that learns to automatically score action
realization from temporal sequences like videos. To manage the small size of most of databases capturing
actions or gestures, we propose to use Siamese Networks. In the literature, Siamese Networks are widely used
to rank action scores. Indeed, their purpose is not to regress scores but to predict a value that respects true
scores order so that it can be used to rank actions according to their quality. For AQA, we need to predict
real scores, as well as the difference between these scores and their range. Thus, we first introduce a new loss
function to train Siamese Networks in order to regress score gaps. Once the Siamese network is trained, a
branch of this network is extracted and fine-tuned for score prediction. We tested our approach on a public
database, the AQA-7 dataset, composed of videos from 7 sports. Our results outperform state of the art on
AQA task. Moreover, we show that the proposed method is also more efficient for action ranking.
1 INTRODUCTION
Skill assessment is fundamental during learning. In-
deed, getting a feedback about performance is a key
towards improvement, and it can provide information
about the progression curve. Furthermore, for some
sports, such as diving or gymnastics, performance as-
sessment is mandatory to determine the winner of a
competition.
However current quality assessment is usually
done manually, which renders the process tiresome
and time-consuming. Moreover assessment is rel-
evant only if it is done by an expert in the field.
In sports, for instance, a training coach has the
knowledge and experience to assess one’s perfor-
mance. However, learning sports or other actions, has
been democratized thanks to the internet and tutorial
videos. The problem of only learning with How-to’s
videos, is that no feedback is given to improve one’s
skills. Automatic Quality Assessment (AQA) is a so-
lution for trainees to get information about their per-
formance without the assistance of an expert and the
resulting workload.
In this context, the goal of the proposed approach
is to automatically score instances done by trainees
(Figure 1).
To automatize the process, a model is usually
trained on many realizations of an action. This re-
quires an annotated database with a large number of
instances. Nowadays only a few public annotated
Figure 1: Action Quality Assessment process.
datasets exist, with a limited number of samples. This
complicates the model training.
To overcome this problem, many solutions have
been proposed in the literature. A well-known one is
the use of Siamese architectures. They learn to com-
pare two inputs and determine which one is the best,
instead of directly evaluating action quality. Hence
Siamese networks lead to action ranking, rather than
score regression, i.e Siamese branches output mea-
sures that respect scores order and not true scores. A
limitation of ranking is that it does not allow to know
if actions are well done or not. The only extracted in-
formation is how the action is ranked compared to a
wide range of the same action.
In this article, Siamese Networks are adapted in
order to predict true scores instead of just trials rank.
A new loss function is introduced to estimate perfor-
mance gap between two achievements of an action.
Only changing the loss does not allow the network to
predict real scores, as an additive constant is present.
Thus, a single branch of the Siamese Network is ex-
tracted and the last fully connected layer is fine-tuned
Millan, M. and Achard, C.
Fine-tuning Siamese Networks to Assess Sport Gestures Quality.
DOI: 10.5220/0008924600570065
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2020) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
57-65
ISBN: 978-989-758-402-2; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
57

to regress true scores. The approach is generic enough
to be used in a large number of applications and from
various signals such as videos, kinematic data or any
other temporal sequences.
The proposed method has been tested on the
AQA-7 database (Parmar and Morris, 2018) com-
posed of videos from 7 Olympic sports. Results the
proposed method outperform state of the art ones on
the action quality assessment task. Moreover, we
show that even if the method has been designed to
predict action score, it also outperforms state of the
art methods in action ranking.
2 RELATED WORK
Automatic skill assessment consists in rating how
well an action has been performed. In sports, only
a handful of studies evaluate gesture quality on mul-
tidimensional signals. Two kinds of approaches are
used: with a priori knowledge and without a priori
knowledge as explained in (Lei et al., 2019).
2.1 Automatic Skill Assessment with a
priori Knowledge
Among the approaches using a priori knowledge,
Burns et al. (Burns et al., 2011) designed kinematic
descriptors inherent to a specific sport. Those descrip-
tors are then used to analyze trials and provide an in-
teractive training tool for novices. This tool is dedi-
cated to a specific gesture and has to be redesigned for
every new gesture. Pirsiavash et al. (Pirsiavash et al.,
2014) designed an approach to automatically com-
pute performance scores in diving and figure skating.
Two kinds of features are designed: low-level ones
that capture gradients and velocities from raw pixels,
and high-level ones based on human pose trajecto-
ries. Once features were extracted, a linear support
vector regressor (L-SVR) is trained to predict scores.
Works from Komura et al. (Komura et al., 2006) ex-
plore the evaluation of motions in martial arts. For in-
stance, gestures evaluation during a defense, is done
by exploiting motion energy, i.e less movements from
the defender equals an efficient defense. For classical
ballets, inter-limbs angles can be extracted, and after-
wards used to compare techniques (Ward, 2012).
2.2 Automatic Skill Assessment without
a priori Knowledge
Approaches that do not use a priori knowledge usu-
ally create a database of expert movements and after-
wards compute a metric to compare novice gestures
to expert ones.
Morel et al. (Morel et al., 2017) propose to use
Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) (Morel et al., 2018)
to build a model of experts gestures, and to afterwards
realign an unknown gesture with this model by com-
puting spatial and temporal errors.
Deep-learning-based methods have recently
emerged for skill assessment.
In surgery, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
have been designed to extract features from 1-D mul-
tidimensional signals and predict skill level among
three possible ones: Novice, Intermediate and Expert
(Wang and Fey, 2018)(Fawaz et al., 2018). These end-
to-end networks are trained on the JIGSAWS database
(Gao et al., 2014), one of the only annotated pub-
lic datasets available for skill assessment in surgery.
Using videos available in this dataset, Funke et al.
(Funke et al., 2019) designe a 3D-CNN to classify
stacks of frames according to skill level. Afterwards,
all stacks belonging to the same video are gathered,
and their predictions are aggregated to obtain overall
classification results.
In sports, Parmar et al. (Parmar and Morris, 2017)
predicte scores of Olympic events, using videos. Fea-
tures are first extracted from videos using a 3D-CNN
trained on another sports dataset (Tran et al., 2015).
Afterwards, these features sequences are used as in-
puts of a LSTM model trained to predict the score as-
sociated with the video. LSTM layer have also been
used to develop networks that assess performance in
basketball (Bertasius et al., 2016). Using first person
point-of-view videos, a convolutional LSTM layer
can detect events that are then used to build Gaussian
mixtures. These Gaussian mixtures are then aggre-
gated to form spatiotemporal features.
However the limited amount of annotated data is
an issue when automatizing skill assessment. To solve
this problem, data augmentation can be used. It has
been done for surgery. Each trial of the JIGSAWS
dataset has been divided into small clips using a fixed-
size sliding window (Wang and Fey, 2018). Anno-
tation for each clip is identical to the class label of
the original trial. Using this strategy considerably in-
creases the number of examples, even if they are no
longer uncorrelated.
Another way to manage small databases is to cre-
ate global models by mixing sports or gestures in the
learning set. Some sports share sub-actions, such as
somersault that can be found in gym and diving. Thus,
training a global model is relevant and enables the
learning of more general features (Parmar and Mor-
ris, 2018).
Other solutions can be found in the literature re-
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
58
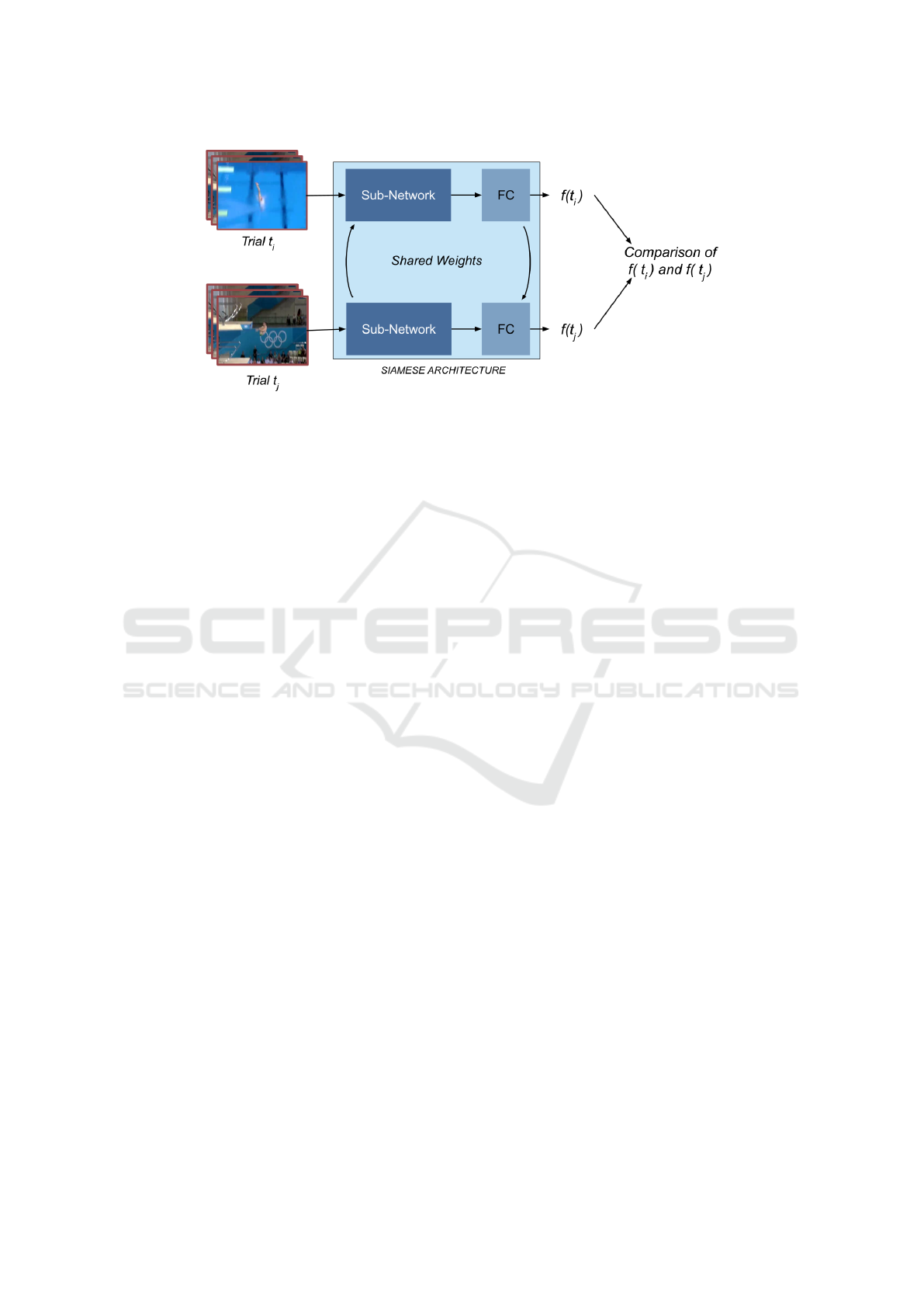
Figure 2: Overview of a Siamese network.
lated to few-shot learning.
2.3 Few-shot Learning
To train efficient neural networks with small datasets,
solutions have been proposed in literature (Chen et al.,
2019). In a classification context, generating new
data by transforming existing ones using geometric or
colorimetric transformations is possible. More elab-
orated methods have also been developed, such as
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) (Ledig et al.,
2017) to create new data. Data augmentation is suc-
cessful and easy to implement with images, but ex-
tending it to videos is tedious.
A other solution frequently used in literature is to
fine-tune an already existing model: network weights
are initialized by training a model on a problem close
to the one to solve and where larger databases are
available (Kim, 2014).
Both previous approaches are very popular when
the learning is based on images where data augmen-
tation is easy to implement and very large databases
with a lot of classes are available. Unfortunately,
data augmentation on video sequences is not so easy.
Moreover, the variety of gestures, actions or move-
ments is so large that there are currently no generic
databases, dealing with all videos types. The fine-
tuning to a particular application cannot be used on
videos.
Few shot learning using small databases, without
data-augmentation or fine-tuning can be done using
distance-metric-learning methods. A direct applica-
tion of those methods is the few-shot classification
problem, where the method learns to compare (Sung
et al., 2018), instead of directly estimating the score.
(Doughty et al., 2018) use Siamese Networks to com-
pare two video inputs and predict which one is the
best. They test their approach on a wide range of
actions, from dough rolling to surgery. Following
this work, an improved model has been developed
(Doughty et al., 2019). Attention modules were added
to the already existing model to use solely the skill-
relevant part of the input.
In a similar fashion, (Li et al., 2019) developed
a Siamese neural architecture with a spatial attention
module in a hand manipulation tasks context.
3 METHODOLOGY
In this section, the global framework used to assess
action quality – or score – is presented. Let us first in-
troduce some notations. For a given task, we consider
a set of K trials T = {t
i
, 1 < i < K} and their scores
s
i
.
We propose to use Siamese network to assess ac-
tion quality. This kind of architecture is popular
for tasks where relationships exist between two in-
puts. For instance, in face recognition, face verifi-
cation (Taigman et al., 2014), signature verification
(Bromley et al., 1993) or even person re-identification
(Chung et al., 2017), Siamese networks are efficient
solutions since, during training, they learn to rank in-
puts, or to discriminate inputs.
Indeed, Siamese networks are composed of two
identical sub-networks, each one processing one
input. These sub-networks share parameters and
weights and lead to two measures f (t
i
) and f (t
j
) as-
sociated to input trials t
i
and t
j
.
Outputs of the two branches are then joined to
form the final output of the Siamese network, as it
is shown in Figure 2.
Usually, Siamese networks are trained using a
pairwise ranking framework where annotations are
easy to obtain since they do not require a real evalua-
tion of each sample but only a comparison of samples:
Fine-tuning Siamese Networks to Assess Sport Gestures Quality
59

Figure 3: Overview of the proposed method.
D(t
i
,t
j
) =
1 if t
i
performs better than t
j
−1 if t
j
performs better than t
i
0 if no preference.
Using this output and pairs such that D(t
i
,t
j
) = 1,
the pairwise loss function is defined by (Li et al.,
2019), (Doughty et al., 2019), (Yao et al., 2016),
(Wang et al., 2014):
L =
∑
i
max(0, m − f (t
i
) + f (t
j
)) (1)
where m is the Siamese margin.
By removing the constraint D(t
i
,t
j
) = 1 and
working on all pairs (t
i
,t
j
), this loss function can be
rewritten:
L =
∑
i
max(0, m − sign(s
i
− s
j
)( f (t
i
) − f (t
j
))) (2)
This loss allows to estimate a measure f (t
i
)
associated to each trial t
i
that respects true scores
order. The problem is that the estimated measure
f (t
i
) can be far from the real score s
i
given by
annotators. Furthermore, once f (t
i
) − f (t
j
) > m, the
pair (t
i
,t
j
) stops contributing to the loss.
As our goal is to estimate the scores s
i
, we propose
in this article to estimate the score gap between t
i
and
t
j
, ∆
i j
= s
i
− s
j
rather than the order between inputs,
using the Siamese network. To achieve this, we use
the Mean Square Error (MSE) loss function:
L =
∑
i
f (t
i
) − f (t
j
) − ∆
i, j
2
(3)
Once the Siamese model has learned to regress
score differences ∆
i, j
, the predicted measure f (t
i
) can
be shifted (additive constant) from the true score s
i
.
To solve this problem, a branch is extracted from the
Siamese architecture and fine-tuned over single inputs
with their scores. The loss function used to train this
last layer is the MSE loss function as represented in
Figure 3. During this second learning, weights of the
sub-network branch are frozen.
4 EXPERIMENTS
The approach presented in Section 3 was tested on the
publicly available dataset AQA-7. The two metrics
used to evaluate our results are:
• The Spearman’s Rank Correlation between s
i
and
b
s
i
that is defined by:
ρ = 1 −
6
∑
i
d
i
2
N(N
2
− 1)
(4)
where d
i
= rank(s
i
) - rank(
b
s
i
) is the rank difference
for trial t
i
and N is the number of trials. This met-
ric is relevant for score ranking evaluation.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
60

(a) Diving (b) Gym Vault (c) Ski Big Air
(d) Snowboard Big Air (e) Synchronized Diving 3m (f) Synchronized Diving 10m
Figure 4: Snapshots of the 6 sports in the AQA-7 database.
• The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) defined by:
RMSE =
s
1
N
∑
i
s
i
−
b
s
i
2
(5)
This metric is relevant for score prediction evalu-
ation.
Each experiment was run ten times to ensure the rele-
vance of the statistical analysis of the average.
4.1 Dataset: AQA-7
This dataset includes videos from 7 sports: single
10m diving, gymnastic vault, big air skiing, big air
snowboarding, synchronous 3m diving, synchronous
10m diving and trampoline. All videos were recorded
either during Winter or Summer Olympics. The
database comprises a total of 1106 videos. Snapshots
from the dataset are presented in Figure 4.
Except trampoline, each video shows only one fig-
ure and the score depends on the performance. For
this reason, trampoline was excluded from our tests
as it was done in (Parmar and Morris, 2018).
All videos from the dataset have a fixed length of
103 frames. Concerning scores, each sport has its own
scale. In order to compare them, they have been stan-
dardized to have zero-mean and a standard deviation
of 1.
4.2 Sub-network Overview and
Training Details
Training the model on videos would be inefficient,
considering the dataset size. Indeed, to efficiently
train a neural network on videos, millions of trials are
needed. Here, only hundreds of videos are available
per sport, so training the model using videos is not vi-
able. To solve this problem, we first extracted mean-
ingful features from 16-frame-length slices of videos
using the C3D-Network (Tran et al., 2015), as in (Par-
mar and Morris, 2018). C3D-Network has proven its
effectiveness in preserving temporal and spatial infor-
mation in videos, since it outperforms 2-CNN, when
used in video classification tasks (Tran et al., 2015).
Furthermore, this model was trained on the Sports-
1M dataset (Karpathy et al., 2014), which includes
many sports that are also present in the AQA-7 dataset
used to test our method.
The architecture used for the sub-network is
based on LSTM (Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997)
that has shown promising results in many sequence-
related tasks, such as machine translation, speech
recognition or even automatic text scoring, and also in
video-related task. Here we only use the last output of
the 256-cell LSTM layer, which can be considered as
a global representation of the whole sequence. A fully
connected layer is then added to predict a score from
this global representation. The network is presented
in Figure 5.
C3D Network weights are frozen during train-
ing. Weights of both layers (LSTM and FC) are ini-
tialized with a zero-mean Gaussian noise with stan-
Fine-tuning Siamese Networks to Assess Sport Gestures Quality
61
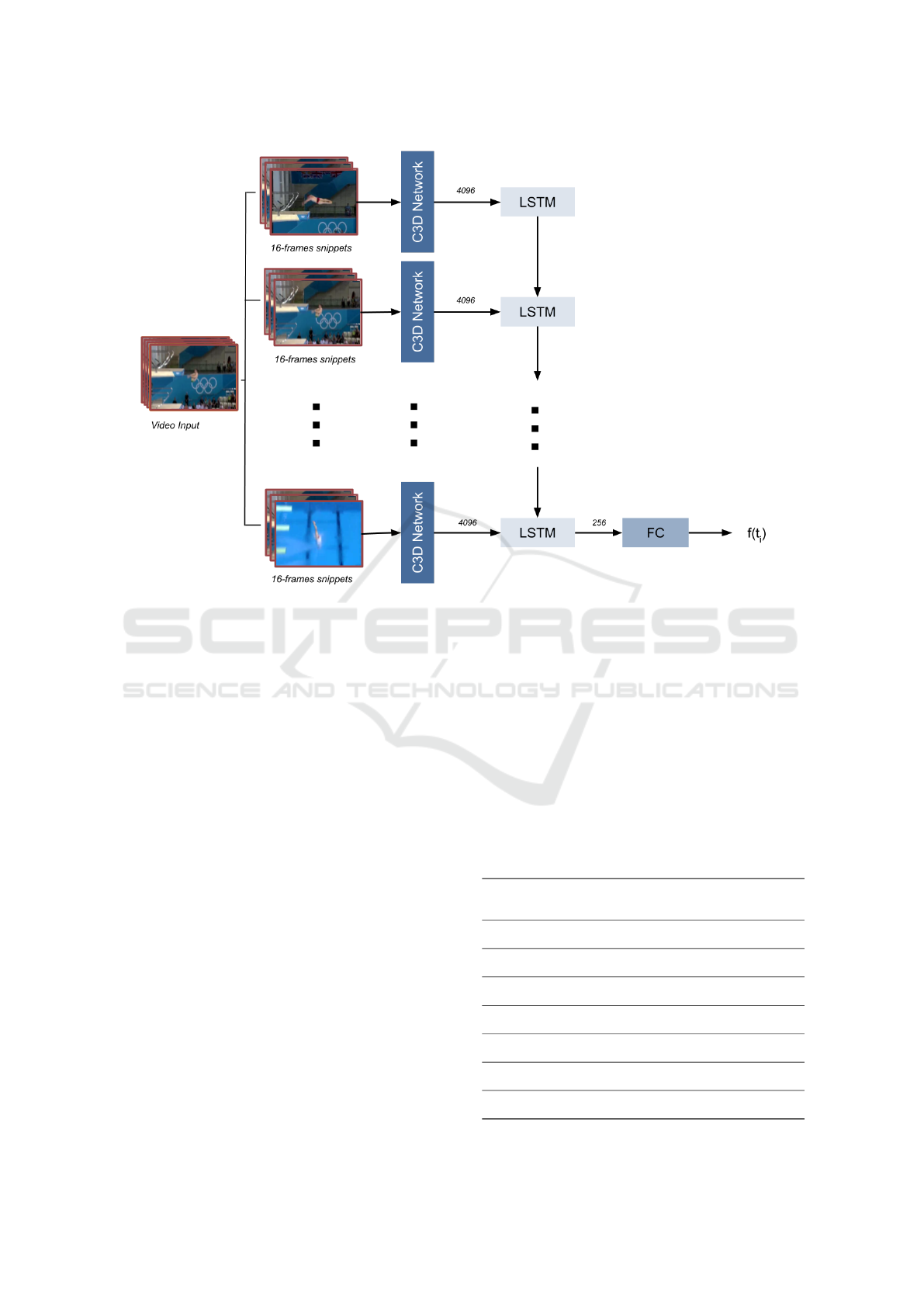
Figure 5: Overview of the LSTM network.
dard deviation of 0.015. To avoid over-fitting, L2-
regularization is used on weights of both layers with a
coefficient value of 0.1. The network is trained for 50
epochs with a batch size of 15 input pairs. For back-
propagation, the Adam solver (Kingma and Ba, 2015)
is used with an initial learning rate of 0.001. Every 15
epochs, the learning rate is halved. For the validation
process, we apply the same train/test-set division as
in (Parmar and Morris, 2018) to compare our results
to theirs.
After this first training, the network is extracted
from the Siamese architecture. LSTM weights are
frozen and the Fully Connected layer is fine-tuned
during 50 epochs with a batch size of 15 trials.
Just like for the Siamese Network training the Adam
solver is used with an initial learning rate of 0.001,
and the learning rate is halved every 15 epochs.
4.3 Results
To highlight the advantages of the proposed MSE loss
function, we compare it with others methods:
• A simple score regression using a MSE loss func-
tion, i.e a single branch network;
• A branch extracted from a Siamese network
trained with the pairwise loss function (equa-
tion 2);
• A branch extracted from a Siamese network
trained with the MSE loss function (equation 3)
(our).
A network is trained for each sport and methods pre-
sented above are compared according to metrics de-
fined in equation 4 and 5. Results are presented in Ta-
ble 1. RMSE was computed using standardized scores
in order to get a meaningful average of the RMSE.
Table 1: Comparison of 2 networks trained in a Siamese ar-
chitecture with different loss functions and a single-branch
network.
Regression
Single branch
Siamese network
Pairwise loss
Single branch
Siamese network
MSE loss (Ours)
Diving
ρ 0.70 0.71 0.69
RMSE 0.71 1.09 1.13
Gym Vault
ρ 0.70 0.72 0.72
RMSE 0.65 1.06 0.72
Ski
ρ 0.59 0.64 0.64
RMSE 0.74 1.31 0.77
Snowboard
ρ 0.52 0.54 0.54
RMSE 0.74 1.13 0.86
Sync Dive 3m
ρ 0.81 0.89 0.91
RMSE 0.63 0.83 0.66
Sync Dive 10m
ρ 0.83 0.83 0.87
RMSE 0.60 0.83 0.53
Average
ρ 0.69 0.72 0.73
RMSE 0.68 1.04 0.78
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
62

Considering Spearman’s Rank Correlation ρ must
be maximum, a simple regression leads to the worst
results. Rank correlation is improved by training the
same network in a Siamese architecture. During test-
ing, a single branch of the network is used. The MSE
loss function presented in this article achieves better
results than the pairwise loss function usually used
to train Siamese architectures. Thus, predicting score
gaps helps the network for the task of trial ranking.
Considering the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE),
the model trained to regress the score using a clas-
sical network achieves significantly the best results.
Indeed, networks extracted from a Siamese architec-
ture estimate either ranks or score gaps. Thus scores
are estimated up to an additive constant.
To improve RMSE obtained with Siamese Net-
works, one of the branch of the network is fine-tuned
to regress scores, as proposed in Section 3. This al-
lows to fix the additive constant problem. The com-
pared methods are the following:
• A simple score regression using a MSE loss func-
tion, i.e a single branch network;
• A fine-tuned branch extracted from a Siamese
network trained with the pairwise loss function
(equation 2);
• A fine-tuned branch extracted from a Siamese net-
work trained with the MSE loss function (equa-
tion 3).
Results are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Comparison of 2 networks fine-tuned from a
Siamese architecture with different loss functions and a
single-branch network.
Regression
Fine-tuned
Siamese network
Pairwise loss
Fine-tuned
Siamese network
MSE loss (Ours)
Diving
ρ 0.70 0.69 0.69
RMSE 0.71 0.82 0.67
Gym Vault
ρ 0.70 0.68 0.72
RMSE 0.65 0.66 0.63
Ski
ρ 0.59 0.63 0.65
RMSE 0.74 0.73 0.72
Snowboard
ρ 0.52 0.54 0.55
RMSE 0.74 0.70 0.73
Sync Dive 3m
ρ 0.81 0.81 0.91
RMSE 0.63 0.75 0.39
Sync Dive 10m
ρ 0.83 0.85 0.86
RMSE 0.60 0.60 0.54
Average
ρ 0.69 0.70 0.73
RMSE 0.68 0.71 0.61
By fine-tuning, ranking abilities of the networks
are kept. Indeed, both fine-tuned models lead to better
correlation results than the regression model. Further-
more fine-tuning a branch of a Siamese architecture
significantly improves RMSE compared to non fine-
tuned branch. However, using a pairwise loss func-
tion to train a Siamese Network does not decreases
the RMSE compared to the same network directly
trained in regression. The same network trained in
a Siamese architecture with a MSE loss function and
fine-tuned afterwards, leads to the best RMSE results.
Thus, both in score ranking and in score regression,
the Siamese architecture trained with MSE as a loss
function, associated with fine-tuning of the last fully
connected layer leads to the best results.
Previous works on this AQA-7 database are lim-
ited, and only focused on one metric: Spearman’s
rank correlation (Parmar and Morris, 2018). This
metric allows non-linearity between the real score and
the predicted score since it only consider ranking.
Thus, it does not really provide information on the
true score prediction. Comparison results using this
metric are given in Table 3.
As we can see in Table 3, the proposed methods
outperforms state-of-the-art methods in rank correla-
tion on this datasets.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a new approach to assess action qual-
ity has been introduced. The approach is based on
Siamese Networks which enable networks to deal
with small datasets. Already used in automatic as-
sessment, Siamese Networks usually rank trials in-
stead of regressing true score or score differences.
Here, we propose to predict real scores of trials. Thus,
a first modification in Siamese Network is introduced
by using a loss function allowing to regress the gap
difference between two input samples, rather than a
ranking loss function as usually done. This change
provides predicted values with the same scale of vari-
ation than real values but with and additive offset. To
remove this offset the last layer of the Siamese Sub-
network is fine-tuned to predict real scores. This two
changes rescale and recenter outputs of the network
towards true scores.
The approach was tested on a sport-videos
database. To deal with such data, sub-networks of
the Siamese Networks are composed of LSTM cells.
Results are encouraging since the proposed method
outperforms state of the art results, both in score re-
gression and score ranking.
This work is only a step towards automatic feed-
back for action learning. In our future works, we plan
to give a constructive feedback to learner during task
training in order to accelerate the learning.
Fine-tuning Siamese Networks to Assess Sport Gestures Quality
63

Table 3: Performance of state of the art model (Parmar and Morris, 2017), (Parmar and Morris, 2018) and our Siamese
approach.
Diving Gym Vault Ski Snowboard
Sync Dive
3m
Sync Dive
10m
Average
Single-action
C3D-SVR
(Parmar and Morris, 2017)
0.79 0.68 0.52 0.4 0.59 0.91 0.69
Single-action
C3D-LSTM
(Parmar and Morris, 2018)
0.6 0.56 0.46 0.5 0.79 0.69 0.62
Finetuned All-action
C3D-LSTM
(Parmar and Morris, 2018)
0.74 0.59 0.6 0.44 0.74 0.81 0.65
Finetuned
Siamese Network
trained with MSE (ours)
0.69 0.72 0.65 0.55 0.91 0.86 0.73
REFERENCES
Bertasius, G., Stella, X. Y., Park, H. S., and Shi, J. (2016).
Am i a baller? basketball skill assessment using first-
person cameras. CoRR.
Bromley, J., Guyon, I., LeCun, Y., Säckinger, E., and Shah,
R. (1993). Signature verification using a siamese time
delay neural network. In NIPS.
Burns, A.-M., Kulpa, R., Durny, A., Spanlang, B., Slater,
M., and Multon, F. (2011). Using virtual humans and
computer animations to learn complex motor skills: a
case study in karate. In BIO Web of Conferences.
Chen, W.-Y., Liu, Y.-C., Kira, Z., Wang, Y.-C. F., and
Huang, J.-B. (2019). A closer look at few-shot classi-
fication. ICLR.
Chung, D., Tahboub, K., and Delp, E. J. (2017). A two
stream siamese convolutional neural network for per-
son re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
1983–1991.
Doughty, H., Damen, D., and Mayol-Cuevas, W. W. (2018).
Who’s better? who’s best? pairwise deep ranking for
skill determination. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Doughty, H., Mayol-Cuevas, W. W., and Damen, D. (2019).
The pros and cons: Rank-aware temporal attention for
skill determination in long videos. Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition.
Fawaz, H., Forestier, G., Weber, J., Idoumghar, L., and
Muller, P.-A. (2018). Evaluating surgical skills from
kinematic data using convolutional neural networks.
Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted In-
tervention – MICCAI 2018, 11073.
Funke, I., Mees, S. T., Weitz, J., and Speidel, S.
(2019). Video-based surgical skill assessment using
3d-convolutional neural networks. International Jour-
nal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery.
Gao, Y., Vedula, S. S., Reiley, C. E., Ahmidi, N., Varadara-
jan, B., Lin, H. C., Tao, L., Zappella, L., Béjar, B.,
Yuh, D. D., Chen, C. C. G., Vidal, R., Khudanpur, S.,
and Hager, G. D. (2014). Jhu-isi gesture and skill as-
sessment working set ( jigsaws ) : A surgical activity
dataset for human motion modeling.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computation.
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Suk-
thankar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Large-scale
video classification with convolutional neural net-
works. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition.
Kim, Y. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for sentence
classification. In EMNLP.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. CoRR.
Komura, T., Lam, B., Lau, R. W., and Leung, H. (2006). e-
learning martial arts. In International Conference on
Web-Based Learning.
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszár, F., Caballero, J., Aitken, A. P.,
Tejani, A., Totz, J., Wang, Z., and Shi, W. (2017).
Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a
generative adversarial network. 2017 IEEE Confer-
ence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR).
Lei, Q., Du, J., Zhang, H., Ye, S., and Chen, D.-S. (2019). A
survey of vision-based human action evaluation meth-
ods. In Sensors.
Li, Z., Huang, Y., Cai, M., and Sato, Y. (2019).
Manipulation-skill assessment from videos with spa-
tial attention network. ArXiv.
Morel, M., Achard, C., Kulpa, R., and Dubuisson, S.
(2017). Automatic evaluation of sports motion: A
generic computation of spatial and temporal errors.
Image and Vision Computing.
Morel, M., Achard, C., Kulpa, R., and Dubuisson, S.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
64

(2018). Time-series averaging using constrained dy-
namic time warping with tolerance.
Parmar, P. and Morris, B. T. (2017). Learning to score
olympic events. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW).
Parmar, P. and Morris, B. T. (2018). Action quality assess-
ment across multiple actions. 2019 IEEE Winter Con-
ference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV).
Pirsiavash, H., Vondrick, C., and Torralba, A. (2014). As-
sessing the quality of actions. In ECCV.
Sung, F., Yang, Y., Zhang, L., Xiang, T., Torr, P. H. S., and
Hospedales, T. M. (2018). Learning to compare: Re-
lation network for few-shot learning. 2018 IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion.
Taigman, Y., Yang, M., Ranzato, M., and Wolf, L. (2014).
Deepface: Closing the gap to human-level perfor-
mance in face verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion, pages 1701–1708.
Tran, D., Bourdev, L. D., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., and
Paluri, M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features
with 3d convolutional networks. 2015 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
Wang, J., Song, Y. J., Leung, T. K., Rosenberg, C., Wang,
J., Philbin, J., Chen, B., and Wu, Y. (2014). Learn-
ing fine-grained image similarity with deep ranking.
2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition.
Wang, Z. and Fey, A. (2018). Deep Learning with Convolu-
tional Neural Network for Objective Skill Evaluation
in Robot-assisted Surgery. International Journal of
Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery.
Ward, R. E. (2012). Biomechanical perspectives on clas-
sical ballet technique and implications for teaching
practice. PhD thesis, Doctoral thesis, University of
New South Wales, Sydney.
Yao, T., Mei, T., and Rui, Y. (2016). Highlight detection
with pairwise deep ranking for first-person video sum-
marization. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 982–
990.
Fine-tuning Siamese Networks to Assess Sport Gestures Quality
65
