
Extracting Behavioral Determinants of Health from Electronic Health
Records: Classifying Yoga Mentions in the Clinic
Nadia M. Penrod, Selah Lynch and Jason H. Moore
a
Institute for Biomedical Informatics, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania,
3700 Hamilton Walk, Philadelphia, PA, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Electronic Health Records, Natural Language Processing, Machine Learning, Behavioral Determinants of
Health, Yoga.
Abstract:
Behavior-based interventions can prevent and/or treat many common chronic diseases, but few clinical re-
search studies incorporate behavioral data. Collecting behavioral data on a large-scale is time-consuming and
expensive. Fortunately, electronic health records (EHRs) are an incidental source of population-level behav-
ioral data captured in clinical narratives as unstructured, free text. Here, we developed and evaluated three
supervised text classification models for stratifying clinical chart notes based on use of yoga, a behavioral
determinant of health that is linked to stress-management and the prevention and treatment of chronic dis-
ease. We demonstrate that yoga can be extracted from the EHR and classified into meaningful use cases for
inclusion in clinical research.
1 INTRODUCTION
Modifiable behavioral risk factors are the key drivers
of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide
(Forouzanfar et al., 2016). These diseases, cardiovas-
cular disease, cancer, respiratory disease and diabetes,
are the leading causes of premature death and disabil-
ity, and the treatment and lost productivity costs they
incur have a tremendous impact on local economies
(Waters and Graf, 2018; Jakovljevic et al., 2019).
Even though we know behavior-based interventions
can, in many cases, prevent and/or reverse the course
of disease, incidence of chronic disease continues to
rise (World Health Organization, 2019). This is in
part because capturing relevant behavioral determi-
nants of health for inclusion in clinical research can
be an elusive task.
An underutilized but potentially abundant source
of behavioral data at the population level is the elec-
tronic health record (EHR). EHRs are an ever grow-
ing bank of patient data and clinical care data world-
wide. Secondary use of EHR data for clinical research
to improve patient care and conduct population-based
studies is an increasingly active area of research
(Jensen et al., 2012). There have been recent calls
to formalize and standardize the collection of social
and behavioral data by healthcare providers for inclu-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5015-1099
sion in EHRs (Adler and Stead, 2015). And electronic
portals that enable patients to contribute information
that may not be collected by their providers are on the
horizon (Mafi et al., 2018; Gheorghiu and Hagens,
2017). However, as it currently stands, behavioral
data is captured in the clinical narratives of the EHR
as unstructured, free text. Clinical narratives are in-
formation rich but difficult to analyze on a large-scale
because the data is not standardized; the format, level
of detail, and shorthand style of these notes vary at the
discretion of each clinician. Software packages that
use natural language processing have been developed
and, in some cases, widely adopted to perform named
entity recognition and information retrieval for med-
ical terms in biomedical and clinical text (Kreimeyer
et al., 2017; Soysal et al., 2017; Aronson and Lang,
2010; Savova et al., 2010). But there are no compara-
ble tools to explore behavioral risk factors embedded
in the EHR.
In this work, we developed and evaluated three
supervised classification models for stratifying clin-
ical chart notes based on use of the word “yoga”,
a practice based in controlled breathing, movement,
and meditation, as a behavioral determinant of health.
We focus on yoga because of its implications in
stress-management for the prevention and treatment
of chronic diseases (Pascoe and Bauer, 2015; Kiecolt-
Glaser et al., 2010). Stress is a pervasive, modifi-
Penrod, N., Lynch, S. and Moore, J.
Extracting Behavioral Determinants of Health from Electronic Health Records: Classifying Yoga Mentions in the Clinic.
DOI: 10.5220/0008936300770082
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 77-82
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
77

Annotation
“… exercise: yoga classes 3x per week …”
“… started yoga for osteoporosis …”
“… advised yoga for her neck and back pain…”
“… tried yoga in the past without benefit …”
“… only wearing stretchy yoga pants …”
n = 4,250
20%
80%
Test
Train: NLTK + sklearn
mNB
RF
SVM
5-fold CV
Features (ngrams)
Labels (annotations)
F1 score
Balanced accuracy
Features (ngrams)
Trained
Models
Predict labels
Classification
Figure 1: Extraction, annotation, and classification of yoga in the EHR.
able risk factor that drives other behavioral risk fac-
tors including: unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, and
alcohol and tobacco use. Small-scale studies suggest
yoga may effectively prevent and/or treat chronic dis-
eases by training the relaxation response to robustly
counter a protracted stress response. Larger validation
studies can be conducted on yoga and other behavior-
based interventions with EHR data, but first, we must
be able to identify relevant patient cohorts. Here, we
take an important step toward achieving this goal by
generating baseline models to classify health-related
behaviors documented in the unstructured text of the
EHR.
2 METHODS
We mined EHR data at Penn Medicine, a large re-
gional medical center, to explore if the practice of
yoga could be identified and classified into meaning-
ful use cases for inclusion in clinical research. The
steps we took to extract, annotate, and classify the
data are described in the following subsections.
2.1 Data Collection
To identify medical charts with yoga mentions, we
used PennSeek, a tool that enables search in the un-
structured text of EHRs. We queried the EHR for the
word “yoga” in outpatient clinical chart notes written
between November 15, 2006 and November 16, 2016.
The results were filtered to exclude notes correspond-
ing to patients under the age of 19, leaving 61,976
unique chart notes with yoga mentions. To develop
a supervised classifier, we took a random sample of
4,250 yoga notes for use as the corpus for this paper.
2.2 Annotation
Use of the word yoga in clinical chart notes is
generally straightforward and can be represented by
five annotation classes: lifestyle, treatment, recom-
mendation, asynchronous, and miscellaneous. The
lifestyle class includes clinicians recording a patient’s
lifestyle-based yoga practice, e.g., “exercise: yoga
classes 3x a week”. The treatment class includes
clinicians recording a patient’s use of yoga as self-
directed treatment for a specified medical condition,
e.g., “started yoga for osteoporosis”. The recom-
mendation class includes clinicians proposing yoga as
treatment to a patient for a specified medical condi-
tion, e.g., “advised yoga for her neck and back pain”.
The asynchronous class includes clinicians recording
a patient’s past use of yoga or an intention for future
use, e.g., “tried yoga in the past without benefit” and
“she is interested in doing yoga or something because
of her hypertension”. And the miscellaneous class in-
cludes mentions of the word yoga that are not relevant
to the patient’s health-related behavior, e.g., “she re-
ports only wearing stretchy yoga pants”.
2.3 Classification
We developed and evaluated three supervised classi-
fiers to classify the annotated yoga notes. Our goal
was to determine if we could meaningfully separate
the annotated classes with an automated classification
pipeline.
The models were trained, tuned, and tested on the
set of 4,250 annotated yoga notes (Figure 1). We used
a stratified 80/20 split to generate training and test
sets. Following standard preprocessing steps to re-
move symbols, punctuation, and case, each note was
represented by a short yoga-containing phrase based
on a given context window, i.e., a set number of words
before and after “yoga”. We experimented with fea-
ture sets of unigrams and bigrams generated from
HEALTHINF 2020 - 13th International Conference on Health Informatics
78

Table 1: Classifier performance by context window. The context windows are centered on the word yoga. mNB: multinomial
Na
¨
ıve Bayes, RF: random forest, SVM: support vector machine.
Macro-averaged F1 score Balanced accuracy
Context
window mNB RF SVM mNB RF SVM
4 0.726 0.742 0.751 0.786 0.798 0.804
8 0.722 0.715 0.748 0.775 0.773 0.795
12 0.696 0.691 0.728 0.752 0.758 0.782
16 0.670 0.686 0.696 0.728 0.760 0.746
context windows of length 4, 8, 12, and 16. An exam-
ple of a context window of length 4 is, “patient reports
she started yoga for osteoporosis last month”. From
this context window we generate nine unigrams: ‘pa-
tient’, ‘reports’, ‘she’, ‘started’, ‘yoga’, ‘for’, ‘osteo-
porosis’, ‘last’, ‘month’, and eight bigrams: ‘patient
reports’, ‘reports she’, ‘she started’, ‘started yoga’,
‘yoga for’, ‘for osteoporosis’, ‘osteoporosis last’, ‘last
month’. Context windows were used because most
notes have a single context-dependent mention of the
word yoga among hundreds of words of unrelated
text.
We evaluated three classifiers - multinomial Na
¨
ıve
Bayes (mNB), support vector machine (SVM), and
random forest (RF). For hyperparameter optimiza-
tion and feature selection for each classifier, we used
stratified 5-fold cross validation in the training set.
Classifiers were evaluated based on macro-averaged
F1-scores and balanced accuracies across classes and
by precision and recall in individual classes. Text
processing and classification were done in Python
version 3.6.5 with the Natural Language Toolkit
(NLTK version 3.4.1) and Scikit-learn (sklearn ver-
sion 0.21.2) (Bird et al., 2009; Pedregosa et al., 2011).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Annotation
In this data set, use of the word yoga is context-
dependent and generally unambiguous to the human
reader. The entire 4,250 note corpus was annotated
by one annotator (first author). From this corpus, ap-
proximately 10% of notes (n = 429) were selected at
random for annotation by a second independent an-
notator (second author). The inter-annotator agree-
ment was κ = 0.82 (Cohen’s Kappa). The annota-
tors disagreed on 52 notes. This discrepancy was
almost entirely focused on notes reporting symptom
onset and/or injury during a yoga practice, e.g., “she
feels hip pain was caused by yoga”. One annotator
labeled these cases lifestyle because the notes imply
the patient uses yoga. The other annotator labeled
these cases asynchronous because it is not clear when
the event occurred or if the patient regularly or cur-
rently uses yoga. A consensus was reached to la-
bel these notes asynchronous with consideration for
downstream analyses that will require knowing if a
patient is using yoga at the time of a clinical en-
counter.
In total, 2,408 (57%) yoga notes were annotated as
lifestyle; 717 (17%) were annotated as asynchronous;
541 (13%) were annotated at treatment; 400 (9%)
were annotated as recommendation; and 184 (4%)
were annotated as miscellaneous. Class imbalance
was expected due to variability in patient behaviors,
patient reporting, and clinician documentation. The
uneven distribution of yoga notes across classes un-
derscores the need for a classification pipeline that
can identify the minority class use cases. Consistent
identification of the treatment and recommendation
classes in particular will be important for downstream
analysis.
3.2 Classification
Classifier performance is presented in Table 1. The
macro-averaged F1 scores and balanced accuracies
are shown for each classifier, by context window.
Here, the context windows correspond to short
phrases centered on “yoga” ± 4, 8, 12, or 16 words.
The mNB, RF, and SVM have similar average F1
scores within each context window. For all three clas-
sifiers, the average F1 scores decrease as the length of
the context window increases. The F1 scores for indi-
vidual classes showed some variation as the size of the
context window changed, but in all classes except the
miscellaneous class, models using the shortest context
window (length 4) achieved the highest scores.
We used balanced accuracy as a weighted met-
ric to account for the class imbalance in our dataset.
The differences in balanced accuracies between the
mNB, RF, and SVM models within each context win-
dow are negligible. Consistent with the average F1
Extracting Behavioral Determinants of Health from Electronic Health Records: Classifying Yoga Mentions in the Clinic
79
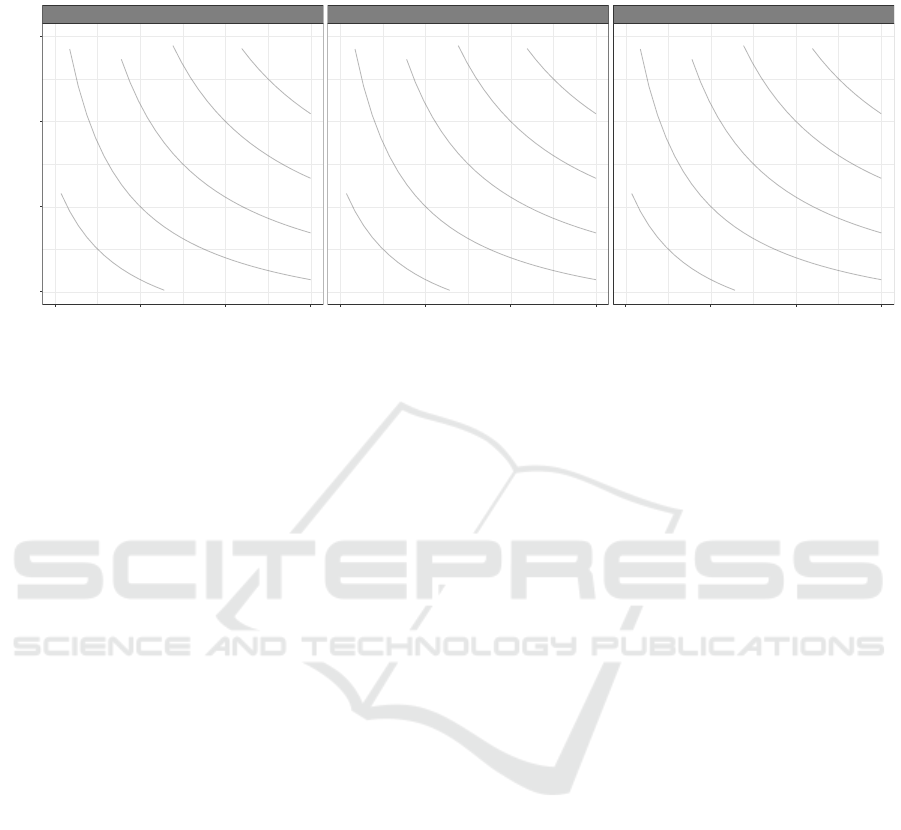
●
●
●
●
●
lifestyle
treatment
recommendation
asynchronous
miscellaneous
F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5
F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6
F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7
F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8
F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9
●
●
●
●
●
lifestyle
treatment
recommendation
asynchronous
miscellaneous
F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5
F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6
F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7
F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8
F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9
●
●
●
●
●
lifestyle
treatment
recommendation
asynchronous
miscellaneous
F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5F1 = 0.5
F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6F1 = 0.6
F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7F1 = 0.7
F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8F1 = 0.8
F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9F1 = 0.9
mNB
RF
SVM
0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
Recall
Precision
Figure 2: Precision and recall performance metrics for multinomial Na
¨
ıve Bayes (mNB), random forest (RF), and support
vector machine (SVM) for each of five classes used to annotate clinical chart notes containing the word “yoga”. The feature
set is comprised of unigrams and bigrams generated from a context window of length 4 centered on yoga. iso-F1 curves
connect pairs of precision and recall scores that generate the labeled F1 scores.
scores, for all three classifiers the balanced accuracy
is marginally higher when the feature space is gen-
erated by a shorter context window. Within classes,
the accuracies across models and context windows
showed more pronounced variation. We see accu-
racies of 83-95% for the lifestyle class, 54-61% for
the treatment class, 69-80% for the recommendation
class, 36-69% for the asynchronous class and 62-76%
for the miscellaneous class. This variation highlights
the importance of the feature space and suggests the
context window can be optimized to prioritize perfor-
mance on an individual class. For the remainder of
this paper, we use the results generated with a context
window of length 4.
To determine if we could identify meaningful use
cases of yoga from mentions in the EHR, we evalu-
ated the precision and recall performance of the mNB,
RF, and SVM classifiers for each class. Figure 2
shows the trade-off between precision and recall by
class and classifier. For this task, we are most in-
terested in the three classes that represent use cases
of yoga: lifestyle, treatment, and recommendation.
The lifestyle class has substantially more training in-
stances than the other classes and, while mNB has the
highest precision (0.867) and RF has the highest recall
(0.946) for this class, all three classifiers are able to
correctly identify most cases of lifestyle-based yoga.
For the treatment class, the RF model achieves the
highest precision score (0.757) and the SVM model
returns the highest recall score (0.583). The precision
score shows a reasonable positive predictive value to
identify treatment-based use of yoga, but the low re-
call score reflects a high false negative rate. In the
recommendation class, the RF model has the highest
scores for both precision (0.813) and recall (0.763),
showing a respectable performance in the identifica-
tion of clinician-recommended yoga use cases.
Although the macro-averaged F1 scores and bal-
anced accuracies in Table 1 suggest only trivial per-
formance advantages for any given model, the pre-
cision and recall plots illustrate the underlying vari-
ability in classifier performance by class. The per-
formance discrepancies are attributable to both the
number of training instances per class and, perhaps
to an even greater extent, to the specificity and unifor-
mity of the vocabularies. For example, the vocabulary
in the lifestyle, treatment, and asynchronous classes
is largely shared, containing phrases such as, “do-
ing yoga” in different contexts (i.e., “is doing yoga
weekly”, “is doing yoga for anxiety”, “was doing
yoga”). We see evidence for this in the confusion ma-
trices (Figure 3). Among all misclassifications of the
lifestyle class, 50-60% are labeled as asynchronous
and 24-25% are labeled as treatment. Similarly, 52-
78% of treatment misclassifications are labeled as
lifestyle and 20-30% are labeled as asynchronous.
The vocabulary in the recommendation class includes
specific words such as, “suggested”, “recommended”,
and “encouraged”. Nonetheless, the recommendation
class vocabulary is not unique; it includes phrases that
appear in multiple contexts like, “do yoga”, as in, “I
encouraged her to do yoga”, which is also included
in notes that read: “he continues to do yoga”, or “she
can no longer do yoga”. In the confusion matrices,
HEALTHINF 2020 - 13th International Conference on Health Informatics
80

●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
6
2 1 1 27
31 8 9 93
2
10
5
60
5
0
31 63 3
11
0
440 10 6 25
1
RF
lifestyle
treatment
recommendation
asynchronous
miscellaneous
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
8
2 1 1
25
26 8 10 98
1
7
3 59
11
0
24
62 8
14
0
424
19 8 29
2
mNB
lifestyle (n = 482)
treatment (n = 108)
recommendation (n = 80)
asynchronous (n = 143)
miscellaneous (n = 37)
lifestyle
treatment
recommendation
asynchronous
miscellaneous
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1
6
1 1 1
28
48
4
9 80
2
11
3 61
5
0
43 53
1 11
0
456 9 3 13
1
SVM
lifestyle
treatment
recommendation
asynchronous
miscellaneous
Figure 3: Confusion matrices comparing performance of multinomial Na
¨
ıve Bayes (mNB), random forest (RF), and support
vector machine (SVM) in the task of predicting annotations for clinical chart notes containing the word “yoga”. Rows are the
true annotation labels and columns are the predicted labels. The numbers are counts, white indicates correct classifications,
black indicates misclassifications, and the size and coloring of the circles correspond to the percent of notes by row.
33-58% of recommendation misclassifications are la-
beled lifestyle and 25-52% are labeled asynchronous.
The results of these models provide a baseline for
classifying mentions of “yoga” in clinical narratives.
The differences we observe in precision and recall by
class and classifier demonstrate that one model is not
the best in all cases. An ensemble method that lever-
ages the strengths of each model may improve classi-
fication accuracies. In addition, analysis of the mis-
classifications underscores the challenges of work-
ing with common vocabularies and suggests perfor-
mance improvements may require a curated feature
set or more sophisticated methods like word embed-
dings based on neural networks.
Despite the inherent challenges of working with
unstructured text in clinical narratives, the results of
this study demonstrate that yoga can be extracted
from the EHR and classified into meaningful use
cases for clinical research. Identifying use cases of
yoga in the EHR provides an opportunity to con-
duct observational studies on the use and effective-
ness of yoga in large patient populations including,
for example, how yoga interfaces with mainstream
medicine, how patients use yoga as treatment, and
how yoga contributes to disease prevention (Penrod
et al., 2019). Although this paper is focused on yoga,
all behavioral determinants of health present a multi-
class classification problem and the lifestyle, recom-
mendation, and asynchronous labels are likely to be
recurrent themes. Together, the baseline performance
of three classifiers in this task and the broad applica-
tion potential motivate our ongoing efforts. We will
extend this work by building more advanced models
to ensure the minority classes can be reliably identi-
fied in this domain, and ultimately, to develop a clas-
sification pipeline that generalizes beyond yoga.
4 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we demonstrated that the practice of
yoga, a behavioral determinant of health, can be ex-
tracted from the unstructured text of the EHR and
classified into meaningful use cases for clinical re-
search. The classification results we presented sug-
gest the context window and the classification mod-
els can be optimized to maximize the precision, re-
call, or F1 scores to prioritize performance on indi-
vidual classes. We provide these results as a baseline
to which more sophisticated text classification models
can be compared. This paper is a step in the direction
toward more integrated clinical research that includes
the effects of behavioral factors on health and disease.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to acknowledge the Clinical Research
Informatics Core at the Perelman School of Medicine
at the University of Pennsylvania for assistance in
data acquisition. This study was supported by gen-
erous funds from Penn Medicine at the University of
Pennsylvania and NIH grant UL1 TR001878.
Extracting Behavioral Determinants of Health from Electronic Health Records: Classifying Yoga Mentions in the Clinic
81

REFERENCES
Adler, N. E. and Stead, W. W. (2015). Patients in context –
EHR capture of social and behavioral determinants of
health. N Engl J Med, 372(8):698–701.
Aronson, A. R. and Lang, F.-M. (2010). An overview of
metamap: historical perspective and recent advances.
J Am Med Inform Assoc, 17(3):229–236.
Bird, S., Klein, E., and Loper, E. (2009). Natural language
processing with Python: analyzing text with the natu-
ral language toolkit. ” O’Reilly Media, Inc.”.
Forouzanfar, M. H., Afshin, A., Alexander, L. T., An-
derson, H. R., Bhutta, Z. A., Biryukov, S., Brauer,
M., Burnett, R., Cercy, K., Charlson, F. J., et al.
(2016). Global, regional, and national compara-
tive risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmen-
tal and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters
of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the
global burden of disease study 2015. The Lancet,
388(10053):1659–1724.
Gheorghiu, B. and Hagens, S. (2017). Use and maturity of
electronic patient portals. In ITCH, pages 136–141.
Jakovljevic, M., Jakab, M., Gerdtham, U., McDaid, D.,
Ogura, S., Varavikova, E., Merrick, J., Adany, R.,
Okunade, A., and Getzen, T. E. (2019). Comparative
financing analysis and political economy of noncom-
municable diseases. J Med Econ, 0(0):1–6. PMID:
30913928.
Jensen, P. B., Jensen, L. J., and Brunak, S. (2012). Mining
electronic health records: towards better research ap-
plications and clinical care. Nat Rev Genet, 13(6):395.
Kiecolt-Glaser, J. K., Christian, L., Preston, H., Houts,
C. R., Malarkey, W. B., Emery, C. F., and Glaser, R.
(2010). Stress, inflammation, and yoga practice. Psy-
chosom Med, 72(2):113.
Kreimeyer, K., Foster, M., Pandey, A., Arya, N., Hal-
ford, G., Jones, S. F., Forshee, R., Walderhaug, M.,
and Botsis, T. (2017). Natural language processing
systems for capturing and standardizing unstructured
clinical information: a systematic review. J Biomed
Inform, 73:14–29.
Mafi, J. N., Gerard, M., Chimowitz, H., Anselmo, M., Del-
banco, T., and Walker, J. (2018). Patients contribut-
ing to their doctors’ notes: insights from expert inter-
views. Annals Intern Med, 168(4):302–305.
Pascoe, M. C. and Bauer, I. E. (2015). A systematic review
of randomised control trials on the effects of yoga on
stress measures and mood. J Psychiatr Res, 68:270–
282.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P.,
Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., et al. (2011). Scikit-learn:
Machine learning in python. J Mach Learn Res,
12(Oct):2825–2830.
Penrod, N. M., Lynch, S., Thomas, S., Seshadri, N., and
Moore, J. H. (2019). Prevalence and characterization
of yoga mentions in the electronic health record. The
Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine,
32(6):790–800.
Savova, G. K., Masanz, J. J., Ogren, P. V., Zheng, J., Sohn,
S., Kipper-Schuler, K. C., and Chute, C. G. (2010).
Mayo clinical text analysis and knowledge extraction
system (ctakes): architecture, component evaluation
and applications. J Am Med Inform Assoc, 17(5):507–
513.
Soysal, E., Wang, J., Jiang, M., Wu, Y., Pakhomov, S., Liu,
H., and Xu, H. (2017). Clamp–a toolkit for efficiently
building customized clinical natural language process-
ing pipelines. J Am Med Inform Assoc, 25(3):331–
336.
Waters, H. and Graf, M. (2018). The cost of chronic dis-
eases in the U.S. Technical report, Milken Institute.
World Health Organization (2019). Global Health Observa-
tory (GHO) data. https://www.who.int/gho/mortality\
burden\ disease/en/. Accessed May 10, 2019.
HEALTHINF 2020 - 13th International Conference on Health Informatics
82
