
Delayed Mutual Information to Develop Functional Analysis on Epileptic
Signals
Victor Hugo Batista Tsukahara
1 a
, Pedro Virgilio Basilio Jeronymo
1 b
, Jasiara Carla de Oliveira
2 c
,
Vinicius Rosa Cota
2 d
and Carlos Dias Maciel
1 e
1
Signal Processing Laboratory, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, University of S
˜
ao Paulo, S
˜
ao Carlos, Brazil
2
Laboratory of Neuroengineering and Neuroscience, Dept. of Electrical Engineering,
Federal University of S
˜
ao Jo
˜
ao Del-Rei, S
˜
ao Jo
˜
ao Del-Rei, Brazil
Keywords:
Epilepsy, Entropy, Delayed Mutual Information, Channel Capacity, Transmission Rate.
Abstract:
Epilepsy is the second most prevalent brain disorder affecting approximately 70 million people worldwide. A
modern approach to develop the brain study is to model it as a system of systems, represented by a network
of oscillators, in which the emergent property of synchronisation occurs. Based on this perspective, epileptic
seizures can be understood as a process of hyper-synchronisation between brain areas. To investigate such
process, a case study was conducted applying Delayed Mutual Information (DMI) to perform functional con-
nectivity analysis, investigating the channel capacity (C) and transmission rate (R) between brain areas —
cortex, hippocampus and thalamus — during basal and infusion intervals, before the beginning of generalised
tonic-clonic behaviour (TCG). The main contribution of this paper is the study of channel capacity and trans-
mission rate between brain areas. A case study performed using 5 LFP signals from rodents showed that the
applied methodology represents an another appropriate alternative to existing methods for functional analysis
such as Granger Causality, Partial Directed Coherence, Transfer Entropy, providing insights on epileptic brain
communication.
1 INTRODUCTION
Epilepsy is the second most common neurological
disease (Organization et al., 2017) and affects ap-
proximately 70 million people worldwide (Spiciarich
et al., 2019) representing a public health concern
(Niriayo et al., 2019). It is a chronic disease of the
central nervous system (CNS) that reaches people of
all ages in which it is commonly associated with so-
cial difficulties (Beghi, 2019) and can cause health
loss such as premature mortality and residual disabil-
ity (Beghi et al., 2019).
Epilepsy-based studies usually uses electroen-
cephalography (EEG) (Ibrahim et al., 2019) or local
field potentials (LFP) (Biasiucci et al., 2019) to check
brain electrical activity, although the use of electrodes
directly in brain tissue is an important option to map
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0713-9067
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1468-9051
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5170-1072
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2338-5949
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0137-6678
electrical activity of the brain with better spatial reso-
lution (Bartolomei et al., 2017).
The latest approach to study epilepsy is the analy-
sis of hyper-synchronisation of brain frequencies os-
cillations as a feature (Yu et al., 2019). (Olamat and
Akan, 2017) performed a nonlinear synchronisation
analysis in LFP epileptic data introducing this new
perspective. (Weiss et al., 2019) used the concept
to understand seizure genesis and spreading in hu-
man limbic areas and (Devinsky et al., 2018) reported
hyper-synchronisation to discuss epilepsy epidemiol-
ogy and pathophysiology. The brain is modelled as a
complex system where each region represents a sub-
system and synchronization is an emergent property
(Andrea Avena-Koenigsberger, 2017). Changes in
this feature during the occurrence of epileptic seizures
are an important aspect to understand the epilep-
tic brain network and synchronization (Mei et al.,
2019). The pathologic hyper-synchronisation of fre-
quencies oscillations give rise to seizures (Berglind
et al., 2018).
There is a hypothesis that high-frequencies oscil-
lations are related with the cortical local brain in-
Tsukahara, V., Jeronymo, P., Carla de Oliveira, J., Cota, V. and Maciel, C.
Delayed Mutual Information to Develop Functional Analysis on Epileptic Signals.
DOI: 10.5220/0008974900890097
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 89-97
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
89

formation processing whereas low-frequencies have
connection with larger cortical networks (Anastasi-
adou et al., 2019). Consequently, the brain interac-
tions through these areas can become complex be-
cause of interactions between oscillations at differ-
ent frequency bands (Anastasiadou et al., 2019). In
this situation, functional connectivity may be per-
formed to detect dependencies among neurophysio-
logical signals (Andrea Avena-Koenigsberger, 2017).
It can be assessed through different methods with
the aim to infer patterns of direct influences (Andrea
Avena-Koenigsberger, 2017).
To estimate the dependency between time series
there are several methods (Gribkova et al., 2018) and
Mutual Information is one of them. It is an Informa-
tion Theoretic and nonparametric approach that mea-
sures generalized, both linear and nonlinear, interde-
pendence between two variables (Akbarian and Erfa-
nian, 2017). This meets the accepted vision that real
world time series usually are nonlinear and non sta-
tionary (Wan and Xu, 2018).
Usually, the Information Theoretic approaches do
not make any hypothesis about the dependency be-
tween time series (Nichols et al., 2005). The use
of time Delayed Mutual Information (DMI) seeks to
quantify the information shared between time series
taking into account the previous information content
as function of time (Endo et al., 2015). (Li et al.,
2018) demonstrated that DMI is a suitable option to
develop analysis of nonlinear systems as in the case
of neuroscience data. (Kim et al., 2018) used DMI to
analyse information transmission of an EEG set from
groups of people with mild Alzheimer disease. (Li
et al., 2017) applied DMI to characterise hippocam-
pal theta-driving neurons. (Chapeton et al., 2017) per-
formed a study using intracranial EEG to identify ef-
fective connections in the brain that exhibit consistent
timing across multiple temporal scales.
The objective of this paper is, in performing a case
study using Delayed Mutual Information, to develop
functional connectivity analysis in rodents LFP sig-
nals, investigating the channel capacity (C) and the
transmission rate between brain areas. In addition,
Surrogate method is used to evaluate the DMI mea-
sures. In section 2, it is presented the theory related
to DMI and Surrogate. Section 3 describes the LFP
data used and the applied methodology. Section 4
presents the achieved results, and in Section 5 the re-
sults are discussed. Finally Section 6 brings forward
paper conclusions.
2 THEORY
This section presents the main theory required to de-
velop this paper. First it is introduced Mutual In-
formation explaining the main concepts of channel
capacity and transmission rate. Then the Surrogate
method, used to assess statistical significance of the
performed analysis, is defined.
2.1 Delayed Mutual Information
The measure of how deterministic is a given variable
can be determined through its entropy (H), defined by
(Cover and Thomas, 2012):
H(X) = −
∑
x∈χ
p(x)log
a
p(x) (1)
where X is a discrete random variable, p(x) = P{X =
x} is the probability of X equal to x, x ∈ χ, i.e. the
probability mass function of X, and a is the logarithm
base that provides the entropy measure in bits in the
case of a = 2. Given a signal X and another signal
Y , the Mutual Information may quantify the informa-
tion shared between this signals, which means how
much it is possible to reduce the uncertainty of sig-
nal X given the knowledge of signal Y (Cover and
Thomas, 2012).
The Delayed Mutual Information (DMI) accord-
ing to (Nichols et al., 2005) is the quantification of
information shared between X and Y
τ
where Y
τ
is the
signal displaced by a lag τ. It is mathematically de-
fined as:
I(X;Y
τ
) =
∑
x
n
∈χ
∑
y
τ
∈γ
p(x
n
, y
y−τ
)log
a
p(x
n
, y
n−τ
)
p(x
n
)p(y
n−τ
)
(2)
According to (Cover and Thomas, 2012) the chan-
nel capacity (C) represents the maximum measure of
Mutual Information:
C = maxI(X, Y ) (3)
and according to (Proakis and Salehi, 2001) the chan-
nel capacity for DMI is quantified by its peak value.
Also according to (Proakis and Salehi, 2001), the
transmission rate estimation (R) can be written as a
function of channel capacity and signal bandwidth
(BW) in Hertz:
R = 2.BW.C (4)
If the entropy is measured in bits, the transmission
rate is going to be measured as bits/s.
BIOSIGNALS 2020 - 13th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
90

2.2 Surrogate for Hypothesis Test
The investigation of information sharing between
brain regions sometimes require the assertion of sta-
tistical significance for confidence in the functional
analysis performed. In this case Surrogate may be
useful (Lancaster et al., 2018).
One of the techniques to apply this method is
the IAAFT technique, proposed by (Schreiber and
Schmitz, 1996). It consists of generating a surro-
gate data from the original signal, keeping the same
power spectrum and randomizing Fourier phases, cre-
ating uncorrelated signals. Applying DMI on surro-
gate data represents the measures that are expected
when signals do not share any connectivity. There-
fore, when comparing the statistics from original sig-
nals and the surrogate data statistics, the null hypothe-
sis can be accepted or rejected. Some literature can be
reviewed in neuroscience related to the use of Surro-
gate to assist the type of interdependency among elec-
troencephalographic signals (Pereda et al., 2005; Faes
et al., 2010; Subramaniyam and Hyttinen, 2015; Ad-
kinson et al., 2019).
Related with the number of surrogate data to be
created, there is a well established rank-order test,
proposed by (Theiler et al., 1992), that can be used
(Schreiber and Schmitz, 2000). First, assume Ψ is the
probability of false rejection, then, define the level of
significance (S) as:
S = (1 − Ψ) · 100% (5)
The number of surrogate data to be created (M) is
defined as follows:
M =
K
Ψ
− 1 (6)
where K is an integer number defined by the type
of test - 1 if it is one-sided and 2 in the case of a two-
sided test. Usually, K = 1 is adopted due to compu-
tational effort to generate surrogates (Schreiber and
Schmitz, 2000).
3 METHODOLOGY
The section details the methodology used to analyse
the local field potential signals, in order to assess mu-
tual information, channel capacity and transmission
rate between brain areas. Furthermore, it describes
the methodology employed to acquire the LFP signals
and the computational environment.
3.1 Applied Methodology
The diagram presented in Figure 1 depicts the applied
methodology. The first step — blue box in Figure 1
— is to calculate the LFP signals entropy for cortex
(Cx), hippocampus (Hp) and thalamus (Th).
Then, in the second step, the optimal number of
bins to apply Mutual Information is determined — or-
ange box in Figure 1 — as follows: The rodents LFP
signals are discretized with different number of bins
— 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 where used — and DMI
is applied among brain areas. Next, the DMI mea-
sures are compared to find the best number of bins
- the DMI curve for a given number of bins that is
closest to highest DMI curve. Figure 2 explain better
the method. Another important measure performed is
the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to compare the group
of rodents to check if there is a statistical difference
between groups.
The third step is to apply Delayed Mutual Infor-
mation to understand the information sharing and de-
pict the lag where there the maximum value occurs,
therefore determining the channel capacity. In the
fourth step, surrogate data is created with Iterative
Amplitude Adjusted Fourier Transform (IAAFT) al-
gorithm for cortex, hippocampus and thalamus sig-
nals. In this case study, 35 signals for 97% signifi-
cance level were generated. In the fifth step, each sur-
rogate is combined with other two original signals to
perform DMI analysis, investigating the connectivity
significance between brain areas.
The surrogate data is compared with the origi-
nal DMI measures by means of Kolmogorov-Smirnov
(KS) test. In this paper, p-value = 5% was chosen to
evaluate the maximum mutual information and its val-
ues. The last step is to apply Fast Fourier Transform
to verify the signal’s bandwidth and, finally, calculate
the transmission rate between brain areas.
The applied methodology described was used to
investigate two periods of LFP signals: basal and con-
vulsant drug infusion, until generalized tonic-clonic
(TCG) behaviour. The analysis was performed in the
recordings of five rats.
Simulations were developed in Python language,
using the packages: Matplotlib, Nolitsa, Numpy, Pan-
das, Scipy, Seaborn and Time. The code was exe-
cuted on a computer with an Intel i7 processor, 8GB
of RAM, running MAC OS 10.14.6 operational sys-
tem.
3.2 Database for Case Study
We used LFP signals database from Interventional
Laboratory of Neuroengineering and Neuroscience
Delayed Mutual Information to Develop Functional Analysis on Epileptic Signals
91

LFP discretization
and entropy
calculation
DMI
Different bins
Transmission
Rate
FFT
LFP signals
Channel
Capacity (C)
Figure 1: Summary of applied methodology: First, the LFP signals are discretized and their entropy are calculated. Then,
DMI with different bin sizes are computed to determine the value that best fits the dataset. After the optimal number of bins
is identified, DMI is calculated among all rodent brain signals (Cx, Hp and Th) and channel capacities are determined. To
calculate the transmission rate between brain areas, Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied to all LFP signals to check the
signal’s bandwidth. Finally, the channel capacity and signal’s bandwidth are used to find the transmission rate between brain
areas.
Figure 2: Delayed Mutual Information performed with dif-
ferent number of bins between two brain areas (τ is given
in samples). As can be observed the highest curve is pre-
sented for 256 bins. In this case the better resolution for
DMI is 256 bins. However, if the 256 bins curve would
not exist, only the other curves, it is possible to check three
curves with almost same values (32, 64 and 128 bins). In
that case it could be possible to choose 32 bits to perform
analysis because the results are similar to 128 bins curve
and the computational processing would be smaller.
(LINNce) from Federal University of S
˜
ao Jo
˜
ao Del
Rei. The laboratory employs male Wistar rats weigh-
ing between 250 and 350 grams coming from the Uni-
versity Central Biotherm to acquire data and evaluate
methods of electrical stimulation. All described pro-
cedures are in according to ethics committee under-
protocol 31/2014.
The signal recording is conducted with the aid of
electrodes (monopolar type and stainless steel cov-
ered by teflon) placed directly inside the right tha-
lamus and hippocampus of the rat’s brain through
stereotactic surgery (Cota et al., 2016). In addition,
two microsurgical screws were implanted (length 4.7
mm, diameter 1.17 mm, Fine Science Tools, Inc.,
North Vancouver, Canada) aiming the cortical regis-
tration of right hemisphere and to operate as reference
in frontal bone. The electrodes and screws were po-
sitioned with assistance of neuroanatomic atlas (Pax-
inos and Watson, 2013).
The LFP signals for each rodent was registered
while the subject was simultaneously filmed, to per-
form behavioural analysis (observe classic seizure
features such as facial automatisms, myoclonic con-
cussion, head myoclonus, anterior and posterior limbs
myoclonus, elevation and fall, generalized tonic-
clonic seizure) to allow their correlation with the elec-
trophysiological events observed during LFP record-
ing. For all rodents the time of recording was the same
with ten minutes of duration.
LFP recording was performed using 1 kHz sam-
pling rate. Signals were amplified 2000 V/V through
A-M Systems (model 3500) amplification system and
digitalized on National Instruments (PCI 6023E) A/D
converter controlled by developed LINNce Virtual In-
strument from LabView platform. Sequentially, they
were filtered using a second-order Butterworth filter
(0.3 to 300 Hz band).The power grid noise at 60 Hz
frequency was mitigated with use of shielded cables
and Faraday cage.
4 RESULTS
During basal and infusion intervals, stationarity was
observed, allowing the calculation of Shannon en-
tropy during each part of the signal. The Tables 1 and
2 display the entropy values (in bits) for all rodents
BIOSIGNALS 2020 - 13th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
92

used in the case study during basal and infusion inter-
vals respectively. To find the optimal number of bins
for Delayed Mutual Information different numbers of
bins were tested on the LFP signals and it provided
the number of 256.
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test performed with ro-
dents groups indicated that there is no difference be-
tween the groups at the level of p value equals 10%.
Next, Surrogate method was applied. Figure 3 depicts
an example of the power spectrum of original signal
in comparison to the power spectrum of the surrogate
data.
DMI was calculated for surrogate data and origi-
nal signals. An example result of DMI(Cx,Hp) for ro-
dent R048 can be seen in Figure 4. The lag with max-
imum mutual information can be also observed: τ = 0
for all rodents used in this case study. The Tables 5
and 6 exhibit the signals bandwidths for each rodent
during basal and infusion intervals respectively.
Tables 3 and 7 show, respectively, all channel
capacities and transmission rates, simulated during
basal interval. The similar results during infusion in-
terval can be verified in Tables 4 and 8. Boxplots in
Figures 5 and 6 depict the mean and standard devia-
tion of transmission rate between each brain area con-
sidering all the five rodents used to develop the case
study.
The computational time to perform this case study
was approximately 3 hours for each DMI. Three DMI
between each pair of brain areas were computed, re-
sulting in a total of 9 hours. Therefore, for each inter-
val, basal and infusion, it was spent 27 hours, reach-
ing 54 hours total.
Table 1: Entropy calculated for all rodents used in the case
study during basal interval. DMI is given in bits.
Rodent Cx Entropy Hp Entropy Th Entropy
R048 15.36 15.36 15.36
R052 13.28 13.28 13.28
R064 14.96 14.97 14.97
R065 15.05 15.05 15.05
R072 15.05 15.05 15.05
Table 2: Entropy calculated for all rodents used in the case
study during infusion interval. DMI is given in bits.
Rodent Cx Entropy Hp Entropy Th Entropy
R048 17.39 17.39 17.39
R052 17.02 17.02 17.02
R064 16.62 16.62 16.62
R065 17.14 17.14 17.14
R072 17.29 17.29 17.29
Table 3: Channel capacity in bits for each rodent during
basal interval.
Rodent Cx → Hp Cx → Th Hp → Th
R048 1.28 1.42 1.75
R052 3.00 2.93 3.72
R064 0.61 0.65 1.48
R065 1.53 1.51 1.25
R072 2.45 2.40 2.15
Table 4: Channel capacity in bits for each rodent during
infusion interval.
Rodent Cx → Hp Cx → Th Hp → Th
R048 0.91 1.26 1.10
R052 1.42 1.51 2.81
R064 0.70 0.71 1.47
R065 1.29 1.42 1.09
R072 2.61 2.72 2.29
Table 5: Bandwidth (BW) in Hertz for each rodent during
basal interval.
Rodent BW Cx BW Hp BW Th
R048 1.30 1.49 1.23
R052 1.73 1.71 1.71
R064 9.00 10.50 8.71
R065 10.00 10.00 10.00
R072 2.77 2.75 2.74
Table 6: Bandwidth (BW) in Hertz for each rodent during
infusion interval.
Rodent BW Cx BW Hp BW Th
R048 30.00 20.00 20.00
R052 20.00 13.95 10.43
R064 26.00 33.00 36.00
R065 30.00 27.00 30.00
R072 20.26 15.00 20.48
Figure 3: Power spectrum of original cortex signal and sur-
rogate data of cortex area for rodent R048. The power
density spectrum of the synthetic data is approximately the
same of the original signal.
Delayed Mutual Information to Develop Functional Analysis on Epileptic Signals
93

Table 7: Transmission rate (R) for each rodent during basal interval. Base 2 was used for DMI logarithm. Frequency was
measured in Hertz, resulting in C being provided in bits and R in bits/s.
Rodent Cx → Hp Cx → Th Hp → Th Hp → Cx Th → Cx Th → Hp
R048 3.33 3.69 5.22 3.81 3.49 4.31
R052 10.38 10.14 12.72 10.26 10.02 12.72
R064 10.98 11.71 31.08 12.81 11.32 25.78
R065 38.70 30.2 25.00 30.6 30.2 25.00
R072 6.79 6.65 5.91 6.74 6.58 5.89
Table 8: Transmission rate (R) for each rodent during infusion interval. Base 2 was used for DMI logarithm. Frequency was
measured in Hertz, resulting in C being provided in bits and R in bits/s.
Rodent Cx → Hp Cx → Th Hp → Th Hp → Cx Th → Cx Th → Hp
R048 54.60 75.60 44.40 36.40 50.40 44.40
R052 56.80 60.40 78.40 39.62 31.50 58.62
R064 36.40 36.90 97.68 46.20 51.12 105.80
R065 38.70 30.20 29.43 34.83 42.60 32.70
R072 52.88 55.10 34.35 39.15 55.70 46.90
Figure 4: Delayed mutual information between cortex and
hippocampus for rodent R048 using 256 bins. The blue line
is the DMI performed with original signals and the red lines
are the DMI with surrogate. Due to the difference between
the surrogate DMI it is not possible to distinguish the dif-
ference among surrogate data DMI because it was approx-
imately the same. It is important to note that the lag for
maximum mutual information is zero, the same found for
another rodents used to perform the case study.
5 DISCUSSION
The entropy for all rodents used in this case study
during basal interval were similar with exception of
rodent R052 which was slightly lower. During in-
fusion interval, the entropy was more uniform and
higher then calculated for basal interval. This in-
dicates that LFP signals become more probabilistic
during infusion, meeting the hypothesis of increase
Figure 5: Boxplot denoting the transmission rate in bits/s
between each brain areas, for all the 5 rodents used to per-
form the case study, during basal interval (black dots rep-
resent the rodents measures). It is important to observe
that the highest standard deviation is verified in transmis-
sion rate between hippocampus and thalamus. The black
dots represent the rodents in the boxplot.
of information rate, which in turn is compliant with
the perspective of understanding epileptic seizure as a
hyper-synchronisation phenomena.
It is possible to check that signal bandwidth during
infusion interval is bigger then the bandwidth during
basal interval. This indicates initially larger informa-
tion for each brain area during infusion, again indi-
cating the increasing communication among cortex,
hippocampus and thalamus.
The lag with maximum MI was zero, found for
all rodents in this case study. Probably, this result
is related with the low sampling rate of LFP sig-
nals. All surrogate data created for this case study
maintained the power spectrum and randomized the
Fourier phases, as expected for IAAFT algorithm, as
BIOSIGNALS 2020 - 13th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
94
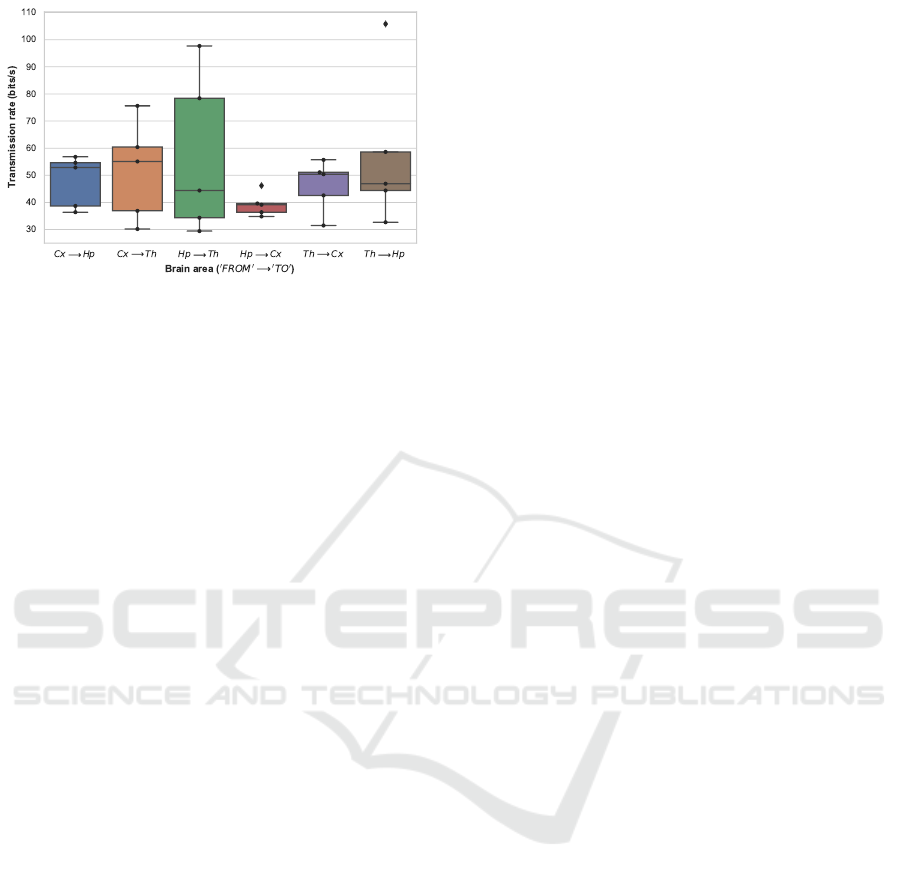
Figure 6: Boxplot denoting the transmission rate in bits/s
between each brain areas, for all the 5 rodents used to per-
form case study, during infusion interval (black dots rep-
resent the rodents measures). The values during infusion
interval are higher when compared with values measured
during basal interval. A possible reason for that difference
is a larger signal’s bandwidth. The DMI is approximately
the same among brain areas for both intervals, see Tables 3
and 4. The black dot represent the rodents in boxplot.
illustrated in Figure 3. This created uncorrelated sig-
nals, with whose measures, it was possible to vali-
date the DMI measures for original signals. For all
rodents, it was possible to observe that the measures
of the original signals were higher than surrogate data
measures.
DMI revealed different measures for each rodent
even Kolmogorov-Smirnov test indicated statistical
equality among groups for 10% significance. Yet,
during basal and interval the values for each rodent
was approximately the same, indicating that the chan-
nel capacity did not change during basal and infu-
sion intervals. Nonetheless, the bandwidth was differ-
ent between them, resulting in different transmission
rates as can be observed in Tables 7 and 8.
It is important to make clear that surrogate anal-
ysis assured 5% p-value using Kolmogorov-Smirnov
test indicating that signifcance level of comparison
between original signals DMI and surrogates DMI for
each rodent. When the results are compared between
rodents the results presented 10% p-value signifcance
level when Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was applied.
That is the reason for different Kolmogorov-Smirnov
p-values presented in this paper.
The increase of transmission rate, observed for all
rodents during infusion interval — in Figures 5, 6
and Tables 7, 8 — is an important result, meeting the
concept of hyper-synchronization phenomena that ap-
pears during epileptic seizures. DMI was able to cap-
ture the increase of communication among brain ar-
eas. Since there is more volume of information mov-
ing between brain areas during infusion, the uncer-
tainty (entropy) accordingly grows, as expected. The
channel capacity practically do not change between
intervals, pointing that the main reason for hyper-
synchronization is the growth of information sharing
between cortex, hippocampus and thalamus.
Delayed Mutual Information represented an an-
other appropriate alternative to existing methods be-
cause it was able to provide insights about the func-
tional connectivity among brain areas. It is a non lin-
ear method supporting the real world condition that
is not linear, do not require a large volume of data
when compared to another methods such as Transfer
Entropy and it is non parametric which means more
flexibility to data analysis.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The use of DMI to perform a case study with ro-
dents LFP presented insights about the communica-
tion among brain areas before the occurrence of an
epileptic seizure. It was observed that entropy during
infusion interval was higher than during basal inter-
val, being the first indicator that the communication
was increasing during infusion. The uncertainty about
signals was becoming higher. The second indicator
was the growth of LFP bandwidth for all signals. It
was also observed a consistent lag of zero for DMI
for all rodents. This last result may have being in-
fluenced by the relatively low sampling rate used to
record the LFP signals. The verified channel capac-
ity was different for each rodent, however, exhibited
the same behaviour of staying approximately equal
during basal and infusion intervals. Consequently,
the transmission rate was different between periods
mainly due to the change of signal’s bandwidth. It in-
dicates that communication is increasing essentially
due to the growth of information sharing among brain
areas. This is the last indicator, which is in agreement
with the idea of hyper-synchronisation phenomena as-
sociated with epileptic seizure. Therefore, DMI rep-
resented a helpful method to perform functional anal-
ysis on LFP signals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was supported by the Fundac¸
˜
ao de Am-
paro
`
a Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) [grant
number APQ 02485-15] and financed in part by
the Coordenac¸
˜
ao de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de
N
´
ıvel Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Delayed Mutual Information to Develop Functional Analysis on Epileptic Signals
95

REFERENCES
Adkinson, J. A., Karumuri, B., Hutson, T. N., Liu,
R., Alamoudi, O., Vlachos, I., and Iasemidis, L.
(2019). Connectivity and centrality characteristics of
the epileptogenic focus using directed network analy-
sis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Reha-
bilitation Engineering, 27(1):22–30.
Akbarian, B. and Erfanian, A. (2017). Automatic detec-
tion of ptz-induced seizures based on functional brain
connectivity network in rats. In 2017 8th Interna-
tional IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineer-
ing (NER), pages 576–579. IEEE.
Anastasiadou, M. N., Christodoulakis, M., Papathanasiou,
E. S., Papacostas, S. S., Hadjipapas, A., and Mit-
sis, G. D. (2019). Graph theoretical characteristics of
eeg-based functional brain networks in patients with
epilepsy: The effect of reference choice and volume
conduction. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13:221.
Andrea Avena-Koenigsberger, Bratislav Msic, O. S. (2017).
Communication dynamics in complex brain networks.
Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 19:17 – 33.
Bartolomei, F., Lagarde, S., Wendling, F., McGonigal, A.,
Jirsa, V., Guye, M., and B
´
enar, C. (2017). Defining
epileptogenic networks: Contribution of seeg and sig-
nal analysis. Epilepsia, 58(7):1131–1147.
Beghi, E. (2019). Social functions and socioeconomic vul-
nerability in epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior.
Beghi, E., Giussani, G., Abd-Allah, F., Abdela, J., Abde-
lalim, A., Abraha, H. N., Adib, M. G., Agrawal, S.,
Alahdab, F., Awasthi, A., et al. (2019). Global, re-
gional, and national burden of epilepsy, 1990–2016:
a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease
study 2016. The Lancet Neurology, 18(4):357–375.
Berglind, F., Andersson, M., and Kokaia, M. (2018). Dy-
namic interaction of local and transhemispheric net-
works is necessary for progressive intensification of
hippocampal seizures. Scientific reports, 8(1):5669.
Biasiucci, A., Franceschiello, B., and Murray, M. M.
(2019). Electroencephalography. Current Biology,
29(3):R80–R85.
Chapeton, J. I., Inati, S. K., and Zaghloul, K. A. (2017).
Stable functional networks exhibit consistent timing
in the human brain. Brain, 140(3):628–640.
Cota, V., Marcela Bacellar Drabowski, B., Carla de
Oliveira, J., and Moraes, M. (2016). The epilep-
tic amygdala: Toward the development of a neural
prosthesis by temporally coded electrical stimulation.
Journal of Neuroscience Research, 94:463–485.
Cover, T. M. and Thomas, J. A. (2012). Elements of infor-
mation theory. John Wiley & Sons.
Devinsky, O., Vezzani, A., O´Brien, T. J., Scheffer, I. E.,
Curtis, M., and Perucca, P. (2018). Epilepsy. Nature
Reviews Disease Primers, 4.
Endo, W., Santos, F. P., Simpson, D., Maciel, C. D., and
Newland, P. L. (2015). Delayed mutual information
infers patterns of synaptic connectivity in a proprio-
ceptive neural network. Journal of computational neu-
roscience, 38(2):427–438.
Faes, L., Porta, A., and Nollo, G. (2010). Testing
frequency-domain causality in multivariate time se-
ries. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,
57(8):1897–1906.
Gribkova, E. D., Ibrahim, B. A., and Llano, D. A. (2018). A
novel mutual information estimator to measure spike
train correlations in a model thalamocortical network.
Journal of neurophysiology, 120(6):2730–2744.
Ibrahim, F., Abd-Elateif El-Gindy, S., El-Dolil, S. M., El-
Fishawy, A. S., El-Rabaie, E.-S. M., Dessouky, M. I.,
Eldokany, I. M., Alotaiby, T. N., Alshebeili, S. A.,
and Abd El-Samie, F. E. (2019). A statistical frame-
work for eeg channel selection and seizure prediction
on mobile. International Journal of Speech Technol-
ogy, 22(1):191–203.
Kim, H.-R., Go, H.-J., and Kim, S.-Y. (2018). Discrimina-
tion of mild alzheimer’s disease patients using cluster
analysis of information transmission in eeg. Journal
of the Korean Physical Society, 73(3):377–387.
Lancaster, G., Iatsenko, D., Pidde, A., Ticcinelli, V., and
Stefanovska, A. (2018). Surrogate data for hypothesis
testing of physical systems. Physics Reports, 748:1 –
60. Surrogate data for hypothesis testing of physical
systems.
Li, S., Xiao, Y., Zhou, D., and Cai, D. (2018). Causal infer-
ence in nonlinear systems: Granger causality versus
time-delayed mutual information. Physical Review E,
97(5):052216.
Li, S., Xu, J., Chen, G., Lin, L., Zhou, D., and Cai, D.
(2017). The characterization of hippocampal theta-
driving neurons—a time-delayed mutual information
approach. Scientific reports, 7(1):5637.
Mei, T., Wei, X., Chen, Z., Tian, X., Dong, N., Li, D.,
and Zhou, Y. (2019). Epileptic foci localization based
on mapping the synchronization of dynamic brain net-
work. BMC medical informatics and decision making,
19(1):19.
Nichols, J., Seaver, M., Trickey, S., Todd, M., Olson, C.,
and Overbey, L. (2005). Detecting nonlinearity in
structural systems using the transfer entropy. Physi-
cal Review E, 72(4):046217.
Niriayo, Y. L., Mamo, A., Gidey, K., and Demoz, G. T.
(2019). Medication belief and adherence among pa-
tients with epilepsy. Behavioural neurology, 2019.
Olamat, A. E. and Akan, A. (2017). Synchronization analy-
sis of epilepsy data using global field synchronization.
In 2017 25th Signal Processing and Communications
Applications Conference (SIU), pages 1–4.
Organization, W. H. et al. (2017). Atlas: country resources
for neurological disorders 2004. geneva: World health
organization; 2004.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C. (2013). The Rat Brain in Stereo-
taxic Coordinates. Elsevier. 7th edition.
Pereda, E., Quiroga, R. Q., and Bhattacharya, J. (2005).
Nonlinear multivariate analysis of neurophysiological
signals. Progress in Neurobiology, 77(1):1 – 37.
Proakis, J. G. and Salehi, M. (2001). Digital communica-
tions, volume 4. McGraw-hill New York.
Schreiber, T. and Schmitz, A. (1996). Improved surrogate
BIOSIGNALS 2020 - 13th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
96

data for nonlinearity tests. Phys. Rev. Lett., 77:635–
638.
Schreiber, T. and Schmitz, A. (2000). Surrogate time
series. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 142(3-
4):346–382.
Spiciarich, M. C., von Gaudecker, J. R., Jurasek, L.,
Clarke, D. F., Burneo, J., and Vidaurre, J. (2019).
Global health and epilepsy: Update and future direc-
tions. Current neurology and neuroscience reports,
19(6):30.
Subramaniyam, N. P. and Hyttinen, J. (2015). Dynamics of
intracranial electroencephalographic recordings from
epilepsy patients using univariate and bivariate recur-
rence networks. Phys. Rev. E, 91:022927.
Theiler, J., Eubank, S., Longtin, A., Galdrikian, B., and
Farmer, J. D. (1992). Testing for nonlinearity in time
series: the method of surrogate data. Physica D: Non-
linear Phenomena, 58(1):77 – 94.
Wan, X. and Xu, L. (2018). A study for multiscale infor-
mation transfer measures based on conditional mutual
information. PloS one, 13(12):e0208423.
Weiss, S. A., Staba, R., Bragin, A., Moxon, K., Sperling,
M., Avoli, M., and Engel, J. (2019). Interneurons
and principal cell firing in human limbic areas at fo-
cal seizure onset. Neurobiology of Disease, 124:183 –
188.
Yu, H., Zhu, L., Cai, L., Wang, J., Liu, C., Shi, N., and
Liu, J. (2019). Variation of functional brain connec-
tivity in epileptic seizures: an eeg analysis with cross-
frequency phase synchronization. Cognitive Neurody-
namics, pages 1–15.
Delayed Mutual Information to Develop Functional Analysis on Epileptic Signals
97
