
Probabilistic Analysis of an Impact of Information Security on
Standard Process Performance in a Life Cycle of Systems
Andrey Kostogryzov
a
Federal Research Center “Computer Science and Control” of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Analysis, Information Security, Management, Model, Process, Risk.
Abstract: A methodological approach is proposed that allows to analyse an impact of information security on the
performance of standard agreement processes, organizational project-enabling processes, technical
management processes and technical processes according to ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288. Using the proposed
probabilistic approach to risks prediction in a life cycle of systems helps to identify "bottlenecks" and define
measures and actions for reducing risks when performing standard processes, considering threats to system
information security. The usability of the approach is illustrated by examples.
1 INTRODUCTION
In conditions of multiple uncertainties for system life
cycle, various risks arise, including risks connected
with the violation of information security
requirements. Despite a lot of researches devoted to
risk management (Akimov, 2015, Artemyev, 2017,
Kostogryzov, 2008-2020), the problems associated
with the analysis of an impact of system information
security on standard system processes performance in
terms of predicted risks continue to be poorly studied.
For this reason, the topic of research related to the
probabilistic analysis of such impacts continues to be
acutely relevant. At the same time, standard system
processes according to ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288
"System and software engineering. Systems life cycle
processes" cover the agreement processes (i.e.
acquisition and supply processes), organizational
project-enabling processes (i.e. life cycle model
management, infrastructure management, portfolio
management process, human resource management,
quality management and knowledge management
processes), technical management processes (i.e.
project planning, project assessment and control,
decision management process, risk management,
configuration management, information
management, measurement and quality assurance
processes) and technical processes (i.e. business or
mission analysis, stakeholder needs and requirements
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0254-5202
definition, system requirements definition,
architecture definition, design definition, system
analysis implementation, integration, verification,
transition, validation, operation, maintenance and
disposal processes). In general, these processes
characterize the complete set of standard processes in
system life cycle.
In this paper an universal methodological
approach that allows to perform a probabilistic
analysis of an impact of information security on
performance of all above standard processes is
proposed.
2 GENERAL PROPOSITIONS
The focus on standard processes is justified by the
fact that on the one hand, the life cycle of any
complex system is woven from a variety of standard
processes deployed in time, and on the other hand, for
each of these processes, ISO/IEC / IEEE 15288
defines its possible purposes, outcomes and typical
actions.
For example the main purpose of the decision
management process is to provide a structured,
analytical framework for objectively identifying,
characterizing and valuating a set of alternatives for a
decision at any point in the life cycle and select the
most beneficial course of action. And as typical
Kostogryzov, A.
Probabilistic Analysis of an Impact of Information Security on Standard Process Performance in a Life Cycle of Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0010619300003170
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security (INFSEC 2021), pages 101-109
ISBN: 978-989-758-531-9; ISSN: 2184-9862
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
101

results of the successful performance of this process
are next outcomes: decisions requiring alternative
analysis are identified; alternative courses of actions
are identified and evaluated; a preferred course of
actions is selected; the resolution, decision rationale
and assumptions are recorded.
To obtain the identical results for every standard
process, one or more typical actions should be
performed using some assets for which information
security must be provided. It means the standard
processes are identical from the point of view of an
impact of information security on processes
performance.
In a life cycle of any system, both the reliable
performance of each of the standard processes used
and system information security, associated with this
process must be ensured. The term “reliability of
standard process performance” is defined as an ability
of this process to perform its necessary actions under
stated conditions for a specified period of time. The
reliability of standard process performance is
expressed in maintenance the values of corresponding
measures within the established limits during given
time.
To predict the risks for each of the standard
processes for a given prognostic time 𝑇
it is proposed
to use the following quantitative probabilistic
measures:
𝑅
𝑇
probability of failure to reliable
perform the necessary actions of the standard
process without consideration of threats to
system information security;
𝑅
𝑇
probability of violating information
security requirements;
𝑅
𝑇
integral probability of failure to
reliable perform standard process considering
system information security.
Corresponding risks are characterized by these
probabilistic measures against possible damage.
Note. According to ISO Guide 73 risk is defined
as effect of uncertainty on objectives considering
consequences. An effect is a deviation from the
expected — positive and/or negative.
3 THE PROPOSED APPROACH
There may be two cases for estimation the
probabilistic measure 𝑹
𝐫𝐞𝐥
𝑻
: the case of observed
repeatability and the case of assumed repeatability of
random events influencing reliability of the standard
process performance without consideration of threats
to system information security. For estimation the
probabilistic measure 𝑹
𝐬𝐞𝐜
𝑻
repeatability of
threats activation is assumed. For estimation the
integral probabilistic measure 𝑹
𝐢𝐧𝐭
𝑻
and
probabilistic analysis of an impact of information
security on standard process performance the
assumption of an independence of events connected
with reliability of standard process performance and
system information security is used.
3.1 The Case of the Observed
Repeatability
The inputs for calculations use statistical data
according to observed repeatability. For standard
process the quality of process performance results and
expected obtaining them in time are required. Failure
to perform the necessary actions of the process is a
threat of possible damage. From the point of view of
the composition of actions and/or the severity of
possible damage, all varieties of the standard process
can be divided into K groups, K ≥ 1 (if necessary).
Based on the use of statistical data, the probability of
failure to perform the actions of the process for the k-
th group for a given time is proposed to be calculated
by the formula
𝑅
𝑇
𝐺
𝑇
𝒌
/𝐺
𝑇
𝒌
, (1)
where 𝐺
failure
𝑇
𝒌
, 𝐺
𝑇
𝒌
- are accordingly, the
number of cases of failures when performing the
necessary actions of the process and the total number
of necessary actions from the k-th group to be
performed in a given time 𝑇
𝒌
.
The probability 𝑅
𝑇
of failure to reliable
perform the necessary actions of standard process
without consideration of threats to system
information security is proposed to be estimated for
the option when only those cases are taken into
account for which the actions were not performed
properly (they are the real cause of the damage)
𝑅
𝑇
1𝑊
1
𝑅
𝑇
𝐼
α
𝑊
,
(2)
where 𝑇 is the specified total time for a process
performance for the entire set of actions from
different groups, including all particular values 𝑇
,
taking into account their overlaps;
𝑊
is the number of actions taken into account
from the k-th group for multiple performances of the
process.
For the k-th group, the requirement to perform the
process actions using the indicator function
𝐼
α
is
taken into account
𝐼
α
1, if condition α
is peformed,
0, if condition α
isn
t peformed.
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
102
The condition α used in the indicator function is
formed by analysis of different specific conditions,
proper to the process. It allows to take into account
the consequences associated with the failure to
perform the necessary actions of the process – see (1),
(2). Condition α
means a set of conditions for all
process actions, subject to quality and time
constraints within the given time 𝑇
𝒌
for performing
the necessary actions from the k-th group.
3.2 The Case of the Assumed
Repeatability
For the case of the assumed repeatability the
probabilistic modeling approach is proposed. The
next interconnected ideas 1-7 are used.
Idea 1 is concerning the usual concept and
properties of probability distribution function (PDF)
(see for example Kostogryzov, 2020) for a continuous
random variable of time. PDF for a time variable τ is
nondecreasing function P(t) whose value for a given
point t≥0 can be interpreted as a probability that the
value of the random variable τ is less or equal to the
time value t, i.e. P(t)=P(τ≤t). Additionally P(t)=0 for
t<0, and P(t)→1 for t→∞. In general case the
solutions for modeling problems in decision-making
are based on using concept of the probabilities of
"success" and/or "unsuccess" (risk of "failure"
considering consequences) during the given
prognostic time period treq.. This probability is a
value for a point treq. and is defined by created PDF
in modeling.
Idea 2. An interested system or process modelled
are in general case a complex system and may be a
subsystem or element of comprehensive complex
system. It means the used integrated PDF of time
between losses of system integrity can’t be banal
exponential PDF. It must consider complexity in
modeling any process, predict of “success” or
“failure” on time line and allow to define zone
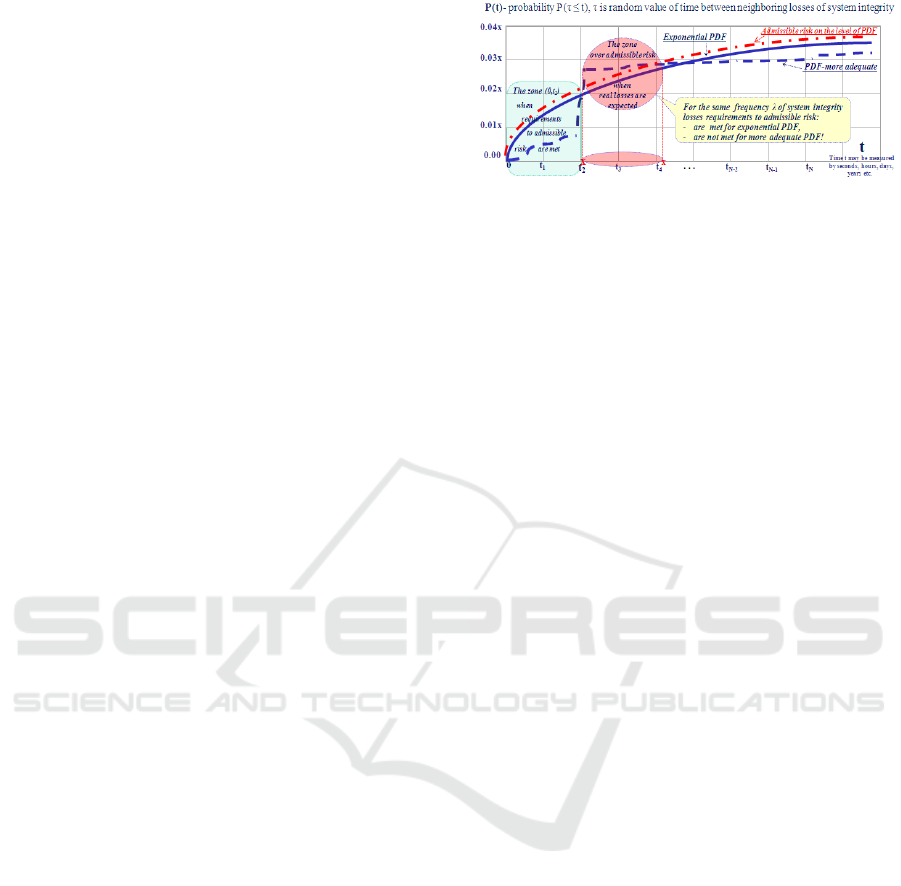
focused on limitations to admissible risks – see Figure
1 (fragment of exponential and an adequate PDF of
time between losses of system integrity with identical
frequency of system integrity losses is illustrated in
conditional units).
Figure 1: Example when all requirements to admissible risk
are met for an adequate PDF of time between losses of
system integrity.
Note. Integrity of system or process modelled is
defined as such state when purposes (of system or
process) are achieved with the required quality and in
time.
Idea 3. The proposed approach for modeling
should allow a generation of probabilistic models for
prediction of “success” or “failure” in uncertainty
conditions. In general case an input for generated
models should consider system complexity,
periodical diagnostics, monitoring between
diagnostics, recovery of the lost integrity for every
element of system or processes modelled. As an
output of such generated models adequate PDF of
time τ between losses of integrity should be produced
in analytical form
Idea 4. Input for probabilistic modeling can be
formed from gathered real data or from hypothetical
data.
For the approach implementation the next
probabilistic models are proposed.
3.2.1 “Black box” Formalization
The models below implemented ideas 1 – 3(see for
example Akimov, 2015, Artemyev, 2017,
Kostogryzov, 2008-2020).
As modelled system are considered:
“Black box” with virtual random events
influencing reliability of the standard process
performance without consideration of threats to
system information security – for estimating
𝑅
𝑇
;
“Black box” with virtual random events
influencing system information security before
or during the standard process performance
(with threats activation) – for estimating
𝑅
𝑇
.
In general case successful modelled system
operation is connected with counteraction against
various dangerous influences on process performance
integrity - these may be counteractions against
Probabilistic Analysis of an Impact of Information Security on Standard Process Performance in a Life Cycle of Systems
103

failures, defects events, “human factors” or computer
viruses events on time line, etc.
To analyse an impact of information security on
the performance of standard processes there are
proposed the formalization for the general technology
used in process performance. The technology is based
on periodical diagnostics of modelled system
integrity, that is carried out to detect danger sources
penetration into a modelled system or consequences
of negative influences (see Figure 2). The lost
modelled system integrity can be detect only as a
result of diagnostics, after which the system recovery
is started. Dangerous influence on modelled system
is acted step-by step: at first a danger source
penetrates into the system and then after its activation
begins to influence. The system integrity can’t be lost
before penetrated danger source is activated. A
danger is considered to be realized only after a danger
source has influenced on the modelled system.
Figure 2: Some accident events in modelled system.
(left – correct operation, right – a lose of integrity
during prognostic period T
req
)
There are recommended some “Black box”
models for which probabilistic space (
, B, P) is
created (see for example Kostogryzov, 2008, 2012,
2020 etc.), where:
- is a limited space of elementary
events; B – a class of all subspace of
-space,
satisfied to the properties of
-algebra; P – is a
probability measure on a space of elementary events
. Because,
={
k
} is limited, there is enough to
establish a reflection
k
p
k
=P(
k
) like that p
k
0
and
1
k
k
p
.
It is supposed that used diagnostic tools allow to
provide necessary integrity recovery after revealing
danger sources penetration into modelled system or
the consequences of influences. Using the
probabilistic models (described in details in
Kostogryzov, 2008, 2012) the measures 𝑅
𝑇
and
𝑅
𝑇
can be estimated in terms “success” or
“failure” considering uncertainty conditions,
periodical diagnostics, monitoring between
diagnostics, recovery of the lost integrity for “Black
box”. There are the next input for probabilistic
modeling (Kostogryzov, 2008-2020):
- frequency of the occurrences of potential
threats (or mean time between the moments of the
occurrences of potential threats which equals to
1/frequency);
- mean activation time of threats;
T
betw
- time between the end of diagnostics and the
beginning of the next diagnostics;
T
diag
- diagnostics time;
T
recov
- recovery time
T - given prognostic period.
3.2.2 About Modeling for Complex System
For a complex systems with parallel or serial
structure there are proposed the next method to
generate adequate probabilistic models
(Kostogryzov, 2008-2020 etc.) This method uses the
usual way of probability theory for independent
random variables, it is described below.
Let's consider the elementary structure from two
independent parallel or series elements. Let’s PDF of
time between losses of i-th element integrity is В
i
(t)
=Р (τ
i
≤ t), then:
1) time between losses of integrity for modelled
system combined from series connected independent
elements is equal to a minimum from two times τ
i
:
failure of 1st or 2nd elements (i.e. the modelled
system goes into a state of lost integrity when either
1st, or 2nd element integrity is lost). For this case the
PDF of time between losses of modelled system
integrity is defined by expression
В(t) = Р[min (τ
1
,τ
2
)≤t] =1- Р[min (τ
1
,τ
2
)>t] =
= 1- Р(τ
1
>t)Р(τ
2
> t)= 1 – [1-В
1
(t)] [1- В
2
(t)], (3)
2) time between losses of integrity for modelled
system combined from parallel connected
independent elements (hot reservation) is equal to a
maximum from two times τ
i
: failure of 1st and 2nd
elements (i.e. the modelled system goes into a state of
lost integrity when both 1st and 2nd elements have
lost integrity). For this case the PDF of time between
losses of modelled system integrity is defined by
expression
В(t)=Р[max(τ
1
,τ
2
)≤t]=Р(τ
1
≤t)Р(τ
2
≤t)=В
1
(t)В
2
(t)
(4)
Applying recurrently expressions (3) – (4), it is
possible to build PDF of time between losses of
integrity for any complex system with parallel and/or
series structure and theirs combinations.
Using these probabilistic models and methods
(described in details in […]) the measures 𝑅
𝑇
and 𝑅
𝑇
can be estimated in terms “success” or
“failure” considering uncertainty conditions, system
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
104

complexity, periodical diagnostics, monitoring
between diagnostics, recovery of the lost integrity for
every element of system or processes modelled.
3.3 Estimation of Integral Measure
The integral probability of failure to reliable perform
standard process considering system information
security 𝑅
𝑇
for the period T is proposed to be
calculated by the formula:
𝑅
𝑇
.
11𝑅
𝑇
1
𝑅
𝑇
.
(5
)
Here the probabilistic measure 𝑅
𝑇
and
𝑅
𝑇
are estimated according to proposition of
3.2.1 and 3.2.2 considering the possible damage.
4 EXAMPLES
Without violating the general understanding of the
proposed approach, the examples are given with
reference to the standard decision management
process.
Let some enterprise organize production
management, focusing on the requirements of IEC
62264-1 “Enterprise-control system integration - Part
1: Models and terminology” for the integration of
enterprise management systems.
Without going into the details of integrated
management systems in terms of the production
process, maintenance process, quality control process
and inventory process, the example demonstrates the
proposed approach to analysing the impact of
information security on the implementation of the
decision management process. Consider performing
the following actions: action 1 - planning decision
management; action 2-gatheing, processing, and
analysing information for decision making; action 3 -
decision making and decision management.
To estimate the probabilistic measures on
examples the following actions and assets are selected
– see verbal description on Figure 3
Figure 3: Verbal description.
Example 1 is devoted to estimate predicting the
risk of a violation of the reliability of the
implementation of the decision management process
without taking into account the quality of the
information used (based on the results of collecting,
processing and analysing information for decision-
making) and information security requirements.
Example 2 is devoted to predicting the risk of
violating information security requirements. Example
3 illustrates the analysis of an impact of information
security on the performance of the standard decision
management process at the integral risk level.
4.1 Example 1
Verbal description on Figure 4 allows to form a
structure of modelled system in the form of a structure
of the following consecutive elements associated with
actions – see Figure 4. By definition, the reliability of
the decision management process is considered to be
ensured during a given period, if during this period
"And" for the production process, "And" for the
maintenance process, "And" for the quality control
process "And" for the inventory process, the actions
"And" for planning decision management (by
elements 1, 2, 3, 4), "And" on decision-making and
decision management (for elements 5, 6, 7, 8).
Figure 4: Structure of modelled system.
The input for estimations by the model
(Kostogryzov, 2008, 2012) using the methods of 3.2.2
is presented in Table 1.
Probabilistic Analysis of an Impact of Information Security on Standard Process Performance in a Life Cycle of Systems
105

Table 1: Input for example 1.
Input for
each
element 1-8
Value of element 1-8 in production, maintenance, quality control and inventory processes
-
frequency of
the
occurrences
of potential
threats
Threats for elements 1)-4) are the threats of hard-software, technology and human errors made during
planning:
1) - 5 times in a year (due to insufficient qualifications or knowledge);
2, 3, 4) - 1 time in a year (because of staff).
Threats for elements 5)-8) are the threats of damage from making unreasonable decisions:
5) - 2 times in a year (due to insufficient qualifications or knowledge);
6, 7, 8
)
- 1 time in a
y
ear
(
because of staff
)
- mean
activation
time of
threats
For elements 1)-4) these are the mean time to possible damage after critical hard-software, technology,
or human errors made during planning:
1)- 2 weeks (this is commensurate with the modeling time for the justification of the production plans);
2, 3, 4) - 1 year (this is commensurate with the time between critical errors in planning of maintenance,
quality control and inventory process).
For elements 5)-8) it is the mean time to possible damage after critical hard-software, technological, or
human errors made in decision-making:
5) – 6 months (this is commensurate with the time of gradual failure of production equipment);
6) – 6 months (this is explained by the preservation of the minimum system capabilities to function in
an outdated environment);
7) – 2 months (this is explained by the average time to complaints due to quality control errors
8
)
–
6 months
(
this is ex
p
lained b
y
the avera
g
e time to
p
roduction downtime due to critical errors
T
betw
- time
between the
end of
diagnostics
and the
beginning of
the next
diagnostics
For elements 1)-4) it is equal to 8 hours, this time is determined by the regulations for monitoring the
readiness of personnel for work – 1 time per shift with an 8-hour working day;
5) – 1 hour, it is determined by the equipment control regulations;
6, 7, 8) – 1 week, it is determined by the regulations for maintenance, quality control and inventory
processes
T
diag
-
diagnostics
time
For elements 1)-4) it is equal to 10 minutes, it is determined by the time of the medical examination
before work.
5, 7, 8) – 30 seconds, indicates the duration of automatic diagnostics in monitoring equipment and
assets integrity.
6
)
–
1 hour, it is duration of the dia
g
nostics of e
q
ui
p
ment condition
d
urin
g
maintenance
p
rocess
T
recov
-
recovery
time
For elements 1)-4) – 30 minutes, this is time to replace the person who has been suspended from
performing the duties, and to assign the necessary functional responsibilities to the replacement person
to perform the planning functions;
5) – mean recovery time for equipment;
6, 8) – 8 hours, this is recovery time for maintenance and inventory processes;
7)
–
30 minutes, this is time to re-install the software of quality control system
T - given
prognostic
p
erio
d
From 1 month to 1 year
(to estimate guarantees period to maintain admissible risks)
The analysis of calculation results showed that for
production, maintenance, quality control and
inventory process the probability of failure to reliable
perform the necessary actions of the standard process
without consideration of threats to system
information security during the year will be about
0.142 - see Figure 5. This means that actions for
planning decision management in the production
process (element 1) and actions for decision making
and decision management in the quality control
process (element 7) are the most significant in the
generalized risk in probabilistic terms ( see Table 1.
Note: according to methods 3.2.2 this generalized risk
isn’t equal to the arithmetical sum of risks for
elements 1-8). For elements 2-6, 8, the values of the
estimated risk do not exceed 0.019. When the
prognostic period changes from 1 month to 1 year, the
risk for all actions increases from 0.012 to 0.142. For
an admissible risk at the level of 0.05, a period of up
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
106
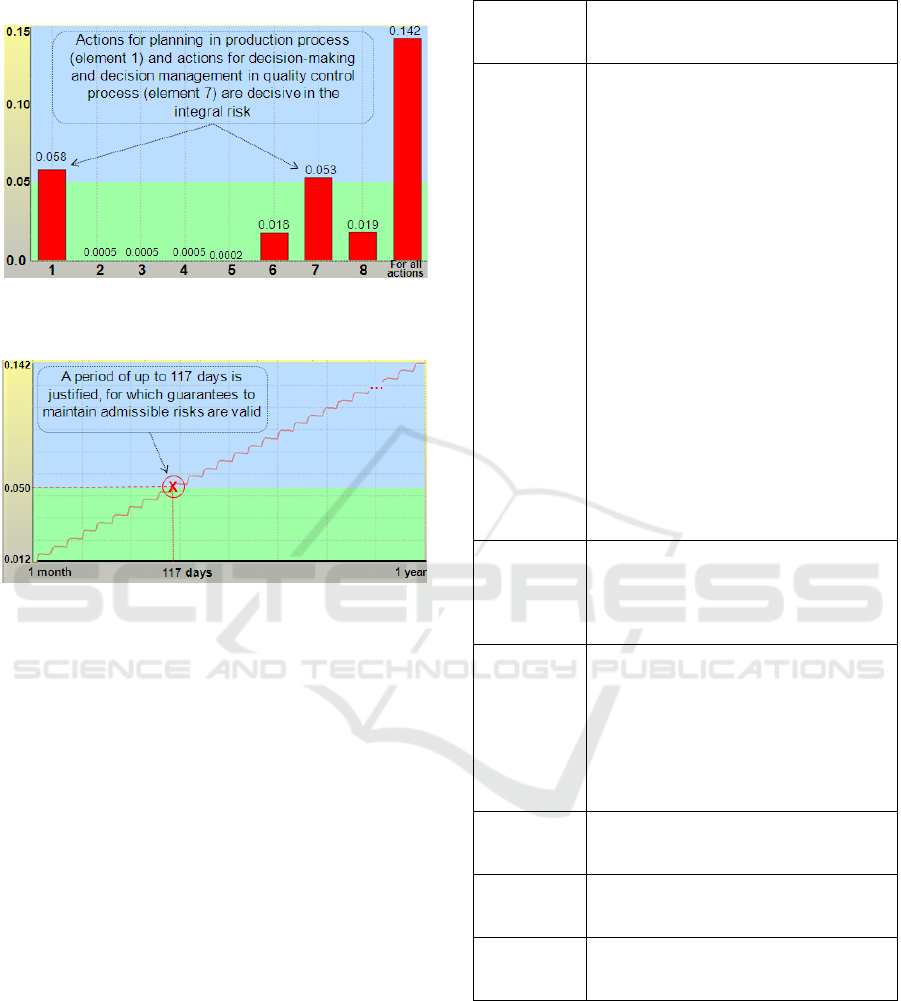
to 117 days is justified, for which guarantees to
maintain admissible risks are valid (see Figure 6).
Figure 5: Risks without taking into account information
security requirements (prognostic period =1 year).
Figure 6: Dependence of generalized risk on the prognostic
period lasting from 1 month to 1 year.
4.2 Example 2
Continuing with example 1, the focus to analyse is on
the structure of actions and protected assets defined
in Figures 3 and 4. The input for each of the 8
elements, taking into account possible vulnerabilities
in asset protection technologies, for estimations by
the same model (Kostogryzov, 2008, 2012): using the
methods of 3.2.2 is presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Input for example 2.
Input for
each
element 1-8
Value of element 1-8 in production,
maintenance, quality control and
inventor
y
p
rocesses
-
frequency of
the
occurrences
of potential
threats
The threats for all elements 1)-8) are
the threats to information security:
1, 5) - 1 time in a year (it is
commensurate with the frequency of
technical failure of the equipment);
2) - 1 time in a year (it is commensurate
with the error rate on the part of a
specialist -planner of average
qualification);
3, 4) – 2 times in a year (commensurate
with the frequency of errors on the part
of the man-controller and specialist –
inventory planner of average
qualification);
6) – 1 time in 5 years (it is explained by
the threats masking of failures in the
process of system maintenance by
highly qualified specialists);
7, 8) - 1 time in a year (it is
commensurate with the frequency of
errors on the part of the man-controller
and specialist –inventory planner of
average qualification)
- mean
activation
time of
threats
For all elements 1)-8) – 1 day (it is
assumed that because of masking, the
threat sources are not activated
immediately, but with a delay of at least
a day)
T
betw
- time
between the
end of
diagnostics
and the
beginning of
the next
diagnostics
For all elements 1)-8) – 1 hour (it is
determined by the rules for controlling
the integrity of the software and assets
used)
T
diag
-
diagnostics
time
For all elements 1)-8) – 30 seconds (it
is diagnostics time during automatic
software and asset integrity monitoring)
T
recov
-
recovery
time
For elements 1)-8) – 5 minutes,
including software reinstallation and
data recover
y
T - given
prognostic
p
erio
d
From 1 to 4 months
(to estimate guarantees period to
maintain admissible risks
)
The analysis of calculation results showed that for
the probability of violating information security
requirements during the month will be about 0.016 -
see Figure 7, and for elements 1-5, 7-8 - about 0.002,
for 6th element - 0.0003, i.e. all assets are protected
to a relatively equal degree. When the prognostic
period increases from one to four months, the risk
increases from 0.016 to 0.062. For an acceptable risk
at the level of 0.05, a period of up to 96 days is
Probabilistic Analysis of an Impact of Information Security on Standard Process Performance in a Life Cycle of Systems
107
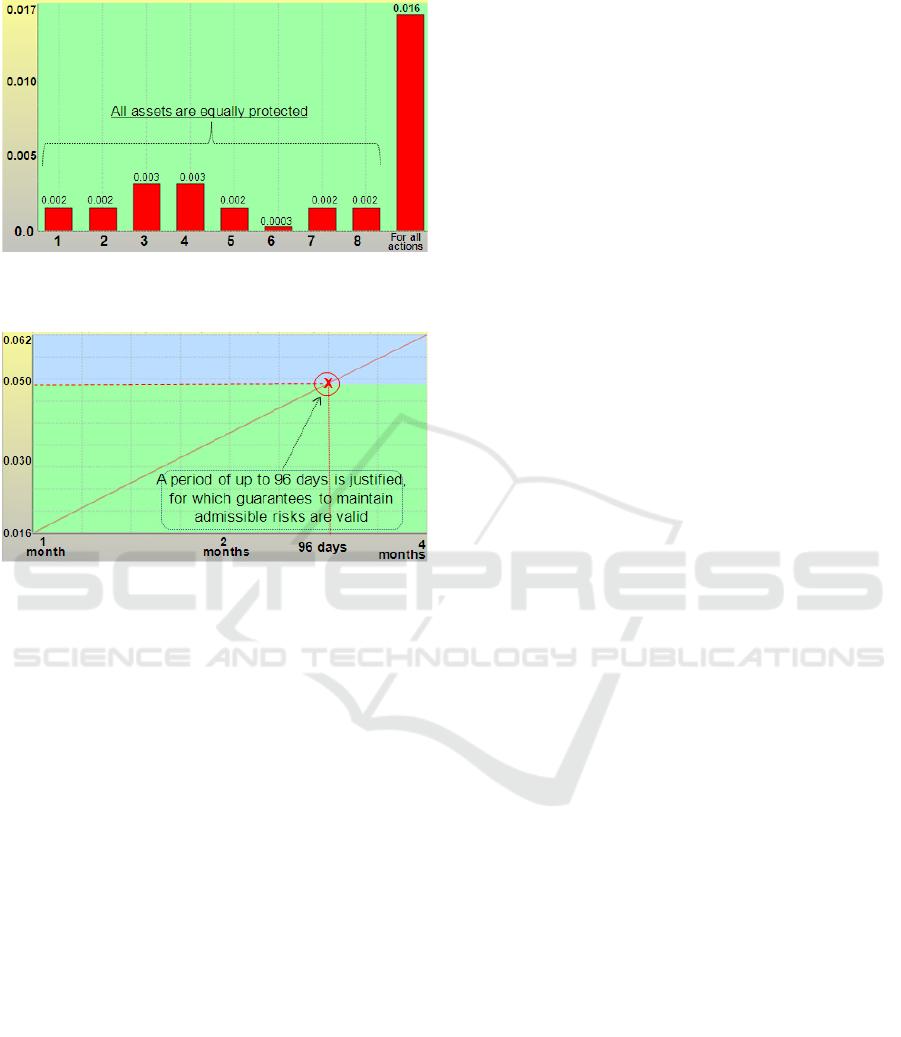
justified, for which guarantees to maintain admissible
risks are valid (see Figure 8).
Figure 7: Risks of violating information security
requirements (prognostic period =1 month).
Figure 8: Dependence of generalized risk on the prognostic
period lasting from 1 to 4 months.
4.3 Example 3
Considering prognostic period T =1 month and the
calculating results 𝑅
𝑇
= 0.012 and 𝑅
𝑇
=
0.0160, than according to (5) integral probability of
failure to reliable perform standard process
considering system information security
𝑹
𝐢𝐧𝐭
𝑻
= 1 ─ (1─0.012)ꞏ(1─0.016) ≈ 0.028
This is less than the established acceptable level
of 0.05, and with similar damages and reasonable
costs, the reliability of the decision management
process is commensurate with the effectiveness level
of information security. It confirms for enterprise that
the planned or applied system engineering solutions
are balanced and allow to maintain admissible risks
during justified period.
5 CONCLUSIONS
A methodological approach allows to analyse an
impact of information security on the performance of
standard processes in system life cycle according to
ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288. It uses the integral measure for
uncertainty conditions – the integral probability of
failure to reliable perform standard process
considering system information security. Using the
proposed probabilistic measures the approach
application helps to confirm that the planned or
applied system engineering solutions are balanced, to
calculate justified period for maintaining admissible
risks, to identify "bottlenecks" and define measures
and actions that help reduce risks when performing
standard processes, considering threats to system
information security.
REFERENCES
Kostogryzov A.I. and Stepanov P.V. (2008). Innovative
management of quality and risks in systems life cycle.
Moscow, Armament. Policy. Conversion, Moscow.
Kostogryzov A., Nistratov G. and Nistratov A. (2012).
Some Applicable Methods to Analyze and Optimize
System Processes in Quality Management. Total
Quality Management and Six Sigma, InTech, 127-196.
Kostogryzov A., Nistratov G. and Nistratov A. (2013). The
Innovative Probability Models and Software
Technologies of Risks Prediction for Systems
Operating in Various Fields. International Journal of
Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT), 3(3),
146-155.
Akimov V., Kostogryzov A., Mahutov N. et al., (2015).
Security of Russia. Legal, Social&Economic and
Scientific&Engineering Aspects. The Scientific
Foundations of Technogenic Safety. Under the
editorship of Mahutov N.A. Znanie, Moscow.
Kostogryzov A.I., Stepanov P.V., Nistratov G.A., Nistratov
A.A., Grigoriev L.I. and Atakishchev O.I. (2015).
Innovative Management Based on Risks Prediction,
Information Engineering and Education Science –
Zheng (Ed.). Taylor & Francis Group, London, 159-
166.
Artemyev V., Kostogryzov A., Rudenko Ju., Kurpatov O.,
Nistratov G. and Nistratov A. (2017). Probabilistic
methods of estimating the mean residual time before
the next parameters abnormalities for monitored critical
systems. Proceedings of the 2nd International
Conference on System Reliability and Safety (ICSRS),
Milan, Italy, 368-373
Kostogryzov A., 2019. Mathematical models and methods
of system engineering for preventive risks control in
real time. Proceedings of the 6th International
Conference Actual Problems of System and Software
Engineering, Moscow, Russia, 12-14 November,
Published by the IEEE Computer Society, pages 1-9.
Kostogryzov A. and Korolev V. (2020). Probability,
combinatorics and control. Probabilistic methods for
cognitive solving problems of artificial intelligence
systems operating in specific conditions of
uncertainties, 3-34. IntechOpen.
INFSEC 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Computer and Information Security
108

Kostogryzov A., Nistratov A. and Nistratov G. (2020)
Analytical risks prediction. Rationale of system
preventive measures for solving quality and safety
problems. Modern Information Technology and IT
Education, Edtors: Sukhomlin, Vladmir, Zubareva,
Elena (Eds.), 1, pages 352-364.
Kostogryzov A. (2020). Risks Prediction for Artificial
Intelligence Systems Using Monitoring Data, CEUR
Workshop Proceedings, vol 2603, pages 29-33.
Probabilistic Analysis of an Impact of Information Security on Standard Process Performance in a Life Cycle of Systems
109
