Pedestrian Tracking with Occlusion State Estimation
Akihiro Enomura
1
, Toru Abe
2 a
and Takuo Suganuma
2 b
1
Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University, 2-1-1 Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980-8577, Japan
2
Cyberscience Center, Tohoku University, 2-1-1 Katahira, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980-8577, Japan
enomura@ci.cc.tohoku.ac.jp, {beto, suganuma}@tohoku.ac.jp
Keywords:
Pedestrian Tracking, Tracking-by-Detection, Obstacle Area, Pedestrian Movement, Occlusion State.
Abstract:
Visual tracking of multiple pedestrians in video sequences is an important procedure for many computer vision
applications. The tracking-by-detection approach is widely used for visual pedestrian tracking. This approach
extracts pedestrian regions from each video frame and associates the extracted regions across frames as the
same pedestrian according to the similarities of region features (e.g., position, appearance, and movement).
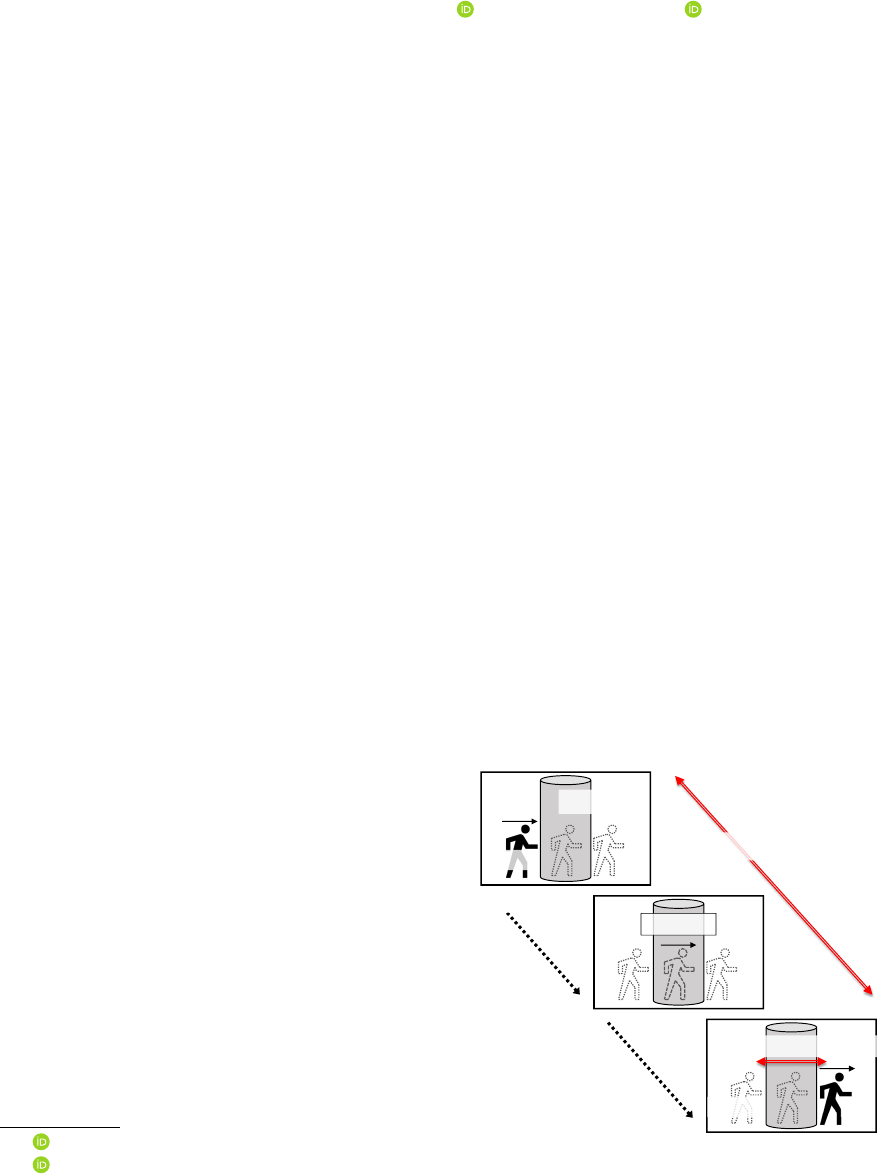
When a pedestrian is temporarily occluded by a still obstacle in the scene, he/she disappears at one side of the
obstacle in a certain frame and then reappears at the other side of it a few frames later. The occlusion state of
the pedestrian, that is the space-time interval where the pedestrian is missing, varies with obstacle areas and
pedestrian movements. Such an unknown occlusion state complicates the region association process for the
same pedestrian and makes the pedestrian tracking difficult. To solve this difficulty and improve pedestrian
tracking robustness, we propose a novel method for tracking pedestrians while estimating their occlusion
states. Our method acquires obstacle areas by the pedestrian regions extracted from each frame, estimates
the occlusion states from the acquired obstacle areas and pedestrian movements, and reflects the estimated
occlusion states in the region association process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Visual tracking of multiple pedestrians in video se-
quences is an important procedure for many com-
puter vision applications. The tracking-by-detection
approach is widely used for visual pedestrian track-
ing (Jiang and Huynh, 2018; Mekonnen and Lerasle,
2019). This approach extracts pedestrian regions
from each video frame and associates the extracted re-
gions across frames as the same pedestrian according
to the similarities of extracted region features (e.g.,
position, appearance, and movement). When a pedes-
trian is temporarily and fully occluded by a still ob-
stacle in the scene, as shown in Figure 1, he/she dis-
appears at one side of the obstacle in a certain frame
(position p in frame t) and then reappears at the other
side of it a few frames later (position p + ∆p in frame
t + ∆t). The occlusion state of the pedestrian, that is
the space-time interval where the pedestrian is miss-
ing, varies with obstacle areas and pedestrian move-
ments, which are not able to be determined in ad-
vance. Such an unknown occlusion state complicates
the region association process for the same pedestrian
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3786-0122
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5798-5125
and makes the pedestrian tracking difficult.
To solve this kind of difficulty and improve the
robustness of pedestrian tracking in video sequences,
we propose a novel method for tracking pedestrians
while estimating their occlusion states. The proposed
method, which is based on the tracking-by-detection
approach, firstly acquires still obstacle areas in the
frame t
obstacle
occlusion
occlusion space interval
frame t+Δt
position p p+Δp
occlusion time interval
position p
Figure 1: Occlusion space-time interval.
scene by the foot positions of pedestrian regions ex-
tracted from each frame, secondly estimates the oc-
clusion states from the acquired obstacle areas and
pedestrian movements, and thirdly reflects the esti-
mated occlusion states in the region association pro-
cess. In our method, the positional relations in depth
direction (in front or behind) between pedestrians and
obstacles are determined by focusing on the foot po-
sitions of extracted pedestrian regions, and thus the
occlusion states of the pedestrians are estimated ac-
curately.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows: Section 2 presents the schemes to deal with oc-
clusion problems in the existing methods for track-
ing multiple objects including pedestrians in video
sequences, Section 3 explains the details of our pro-
posed method for tracking pedestrians while estimat-
ing their occlusion states, Section 4 presents the re-
sults of pedestrian tracking experiments, and Sec-
tion 5 concludes this paper.
2 RELATED WORK
For tracking multiple objects including pedestrians
in video sequences, many methods based on the
tracking-by-detection approach have been proposed.
Most of them take account of occlusion problems and
have some procedures to deal with these problems.
One of such procedures is to set a spatial-temporal
search range for each target object region according to
its position in the current frame and associate the tar-
get region with extracted regions in adjacent frames
within the search range as the same object. Thus,
when a target object disappears at a certain position
in a certain frame due to occlusion, the methods using
this procedure wait the region association for the tar-
get object until it reappears in the consecutive frames
within the search range. The search range needs to
be adjusted appropriately according to the occlusion
state of the target object, that is the space-time inter-
val where the target object is missing, however most
existing methods use a fixed range determined in ad-
vance. The following summarizes how the existing
methods determine the temporal search range for an
occlusion time interval and the spatial search range
for an occlusion space interval.
• Temporal Search Range
Several methods determine the temporal search
range manually (Huang et al., 2008; Mitzel and
Leibe, 2011; Possegger et al., 2014; Ju et al.,
2017; Zhu et al., 2018). Through preliminary
experiments, they choose the number of frames
which obtains good tracking performance as the
appropriate temporal search range. Some meth-
ods use very small temporal search ranges. For
example, the method in (Bewley et al., 2016) al-
lows the region association only between consec-
utive two frames. While this method prevents in-
correct region associations, it is difficult to pro-
ceed the region association for the same object af-
ter occlusion.
• Spatial Search Range
In (Salvi et al., 2013; Possegger et al., 2014; Ju
et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2018), the spatial search
range is determined manually. As with the tem-
poral search range described above, the spatial
search range which obtains good tracking perfor-
mance is determined through preliminary exper-
iments. In many cases, the spatial search range
corresponds to the width of an obstacle in the
scene. Compared to those, the method in (Ju
et al., 2017) sets the spatial search range automat-
ically according to the width of a target object re-
gion within a manually-set upper range limit. In
(Huang et al., 2008), the spatial search range is
extended to the entire field of the frame, when the
target object is lost. While this method can deal
with occlusion caused by unknown size obstacles,
it is likely to associate the target region with in-
correct object regions. The method in (Bochinski
et al., 2018) associates a target region with spa-
tially overlapped regions across frames. This is
equivalent to confine the search range to the im-
mediate vicinity of the target region in the cur-
rent frame without any regard for a long occlusion
space interval.
These methods cannot cope with unknown occlusion
states effectively. If the search range is set too large,
target regions are likely to be associated with incor-
rect object regions. If, on the other hand, the search
range is set too small, it is difficult to proceed the re-
gion association for the same object after occlusion.
In order to solve such trade-off problem, the size
of search range should be adjusted according to oc-
clusion states. This requires the front-behind rela-
tions of obstacles and target objects in the scene to
predict the occlusion states. Some methods directly
identify the position of the obstacle by acquiring the
depth of a scene. A depth sensor based method is used
in (Meshgi et al., 2016) and a multi-view stereo based
method is used in (Osawa et al., 2007) for acquiring
the scene depth. The front-behind relations between
obstacles and target objects are estimated from the ac-
quired scene depth, and then reflected in adjusting the
size of search range. Although these methods can ad-
just the search range appropriately, their applicable
environments are limited. Only a few methods (Hof-
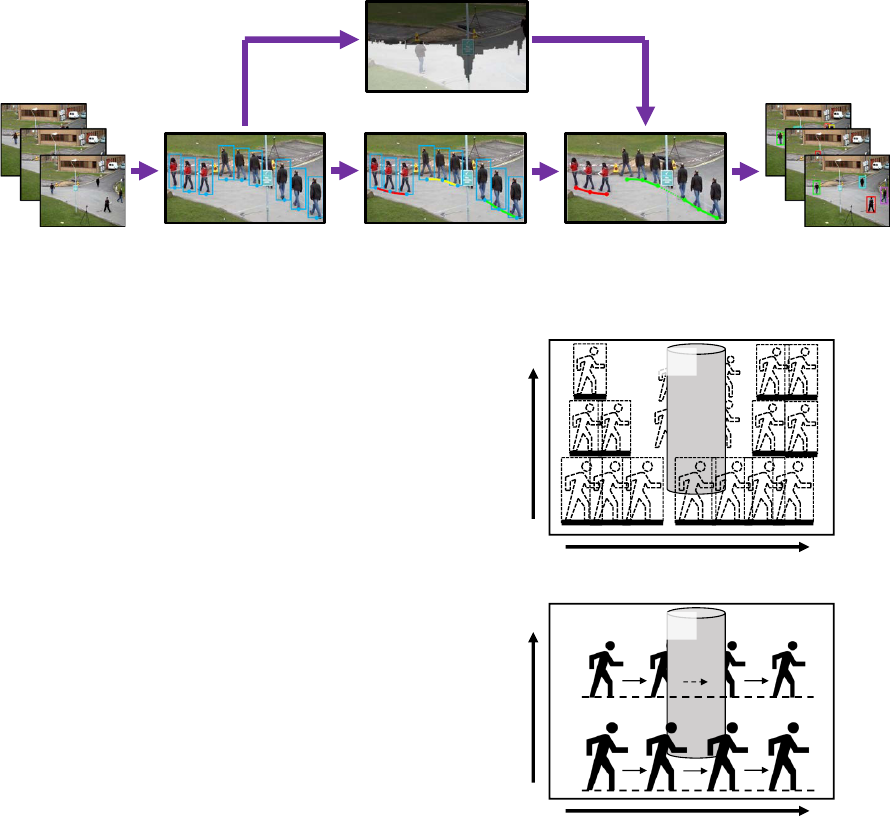
Extract pedestrian regions
Acquire obstacle areas
Generate tracklets Associate tracklets
(+ Estimate occlusion states)
Input video Tracking results
Figure 2: The overview of the proposed method.
mann et al., 2013) set obstacle areas manually in the
scene beforehand, however they cannot effectively es-
timate the front-behind relations between obstacles
and target objects and cannot flexibly adapt to use in
various different scenes.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
Figure 2 shows the overview of the proposed method.
In our method, firstly, pedestrian regions are extracted
from each video frame. From these extracted pedes-
trian regions, obstacle areas in the scene are acquired.
At the same time, short tracks “track lets” of individ-
ual pedestrians, each of which is an intermediate re-
sult of associating regions across frames as the same
pedestrian, are generated from the extracted regions.
The occlusion states are estimated from the relation
of the acquired obstacle areas and the generated track-
lets. By the equivalent process as dynamically adjust-
ing the size of search range according to the estimated
occlusion state, our method reflects the estimated oc-
clusion states in the association process for tracklets
and achieves robustly tracking of multiple pedestrians
in the scenes with obstacles.
3.1 Obstacle Area Acquisition
To acquire obstacle areas in the scene, firstly, by using
all pedestrian regions extracted as bounding boxes in
a video sequence, the extraction frequency F(x,y) of
bounding box bases is counted at each pixel (x, y) for
all video frames. The value of F(x, y) is regarded as
the total number of pedestrian foot positions which
overlap at (x, y) as shown in Figure 3 (a). It would
appear that pedestrian regions whose bounding box
bases are at (x, y) aren’t occluded by obstacles in the
video frame (image) where F(x, y) is large. However,
this doesn’t consider the distances from a camera to
pedestrians and obstacles.
obstacle
y
x
0
(a) Pedestrian foot positions (bounding box bases).
obstacle
y
u
y
l
y
x
0
(b) Pedestrians and obstacles in the scene.
Figure 3: Front-behind relations in the image.
If the camera is set horizontally, and besides,
pedestrians and obstacles stand perpendicularly on
the flat ground, the distance from the camera to each
pedestrian or each obstacle in the scene is reflected
on the vertical coordinate of it in the image. Roughly
speaking, as shown in Figure 3 (b), a pedestrian or an
obstacle at a longer distance from the camera is ap-
peared on the upper part in the image, whereas it at
a shorter distance from the camera is appeared on the
lower part in the image. Accordingly, for the same
horizontal coordinate x in the image, if F(x, y
u
) is
large at its upper part (x, y
u
), then pedestrians are un-
likely to be occluded by obstacles also at its lower
part (x, y
l
) where y
l
< y
u
. From this, the proposed
method computes F
b
(x, y) and binarizes it to obtain
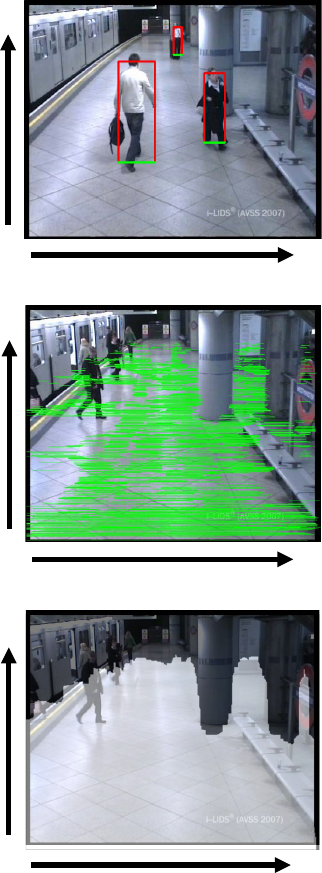
x
y
0
(a) Pedestrian regions (bounding boxes)
x
y
0
(b) F(x, y)
x
y
0
(c) F
∗
b
(x, y)
Figure 4: Examples of acquired obstacle areas.
F
∗
b
(x, y) = {0, 1} by
F
b
(x, y) =
∑
y≤h≤y
max
F(x, h), (1)
F
∗
b
(x, y) =
(
1, F
b
(x, y) > t
b
,
0, otherwise,
(2)
where y
max
is the vertical coordinate at the top of the
image and t
b
is a given threshold.
For a pedestrian region whose bounding box base
is at (x, y), obtained F
∗
b
(x, y) indicate whether or not
there are obstacles occluding it, i.e, if F
∗
b
(x, y) = 0
then there is an obstacle area and the pedestrian re-
gion is occluded by the obstacles otherwise it isn’t
occluded. Thus, the front-behind relations of obsta-
cles and pedestrians in the scene can be reflected in
tracking process by referring to F
∗
b
(x, y). Example
of acquiring obstacle ares is shown in Figure 4. Fig-
ure 4 (a) shows an example of pedestrian regions ex-
tracted as bounding boxes (red lines) and their bases
(green lines), (b) shows overlapped bounding box
bases F(x, y), and (c) shows acquired obstacle ar-
eas F
∗
b
(x, y), where white areas indicate F
∗
b
(x, y) = 1
(none obstacle areas).
3.2 Pedestrian Tracking
Tracking pedestrians is carried out by pursuing re-
gions corresponded to the same pedestrian. Pursu-
ing process consists of two stages. First, matching
regions between adjacent frames to generate trajec-
tory fragments (called ”tracklet”). Multiple tracklets
are generated for the same pedestrian before and after
occlusion. Second, we represents the relation of each
tracklets extracted in first step frames as a graph, and
apply the approach, which utilizes the minimum cost
of a flow network to handle multiple object tracking,
for pursuing tracklets of the same object.
3.2.1 Generating Tracklets
Following (Shu et al., 2012; Ju et al., 2017), generate
tracklets by one-to-one correspondence of pedestrian
regions detected between adjacent frames. Assuming
that the gap of same object’s spatial position between
adjacent frames is tiny, regions are matched by the
minimum binary matching that sets matching cost as
the gap of pedestrian’s position (Euclidean distance).
We introduce the threshold t
g
to avoid switching tar-
gets, never regions whose cost exceeds the threshold.
Each tracklet is represented as L
i
where i is the track-
let number as shown in Figure 5 (a).
3.2.2 Pursuing Tracklets
We pursue tracklets based on (Zhang et al., 2008) al-
gorithm. The concept of flow network model of pur-
suing tracklets is shown in Figure 5 (b). In this graph,
the start and goal of tracking are denoted as nodes s
and t. Each tracklets L
i
is represented by two nodes
u
i
, v
i
and a green edge. u
i
is head, v
i
is tail of L
i
. Rela-
tionship of tracklets is represented by red edges, each
of which has a corresponding cost and unit capacity.
Most existing methods set threshold value as a fixed
spatial search range SR
S
, and temporal search range
SR
T
to cut the edges where the distance between two
regions is greater than SR
S
or the frame interval is
greater than SR
T
. Proposed method calculates brute
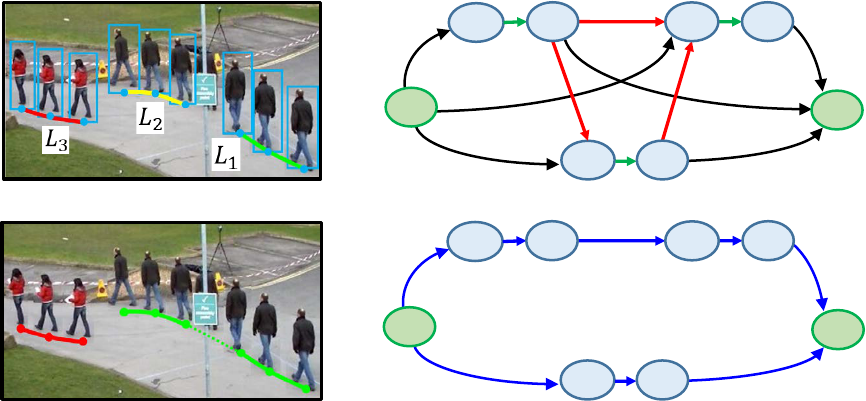
(a) Generating tracklets
u
1
u
3
t
v
3
u
2
v
2
s
v
1
(b) Making tracklets graph
(c) Pursuing tracklets
u
1
u
2
t
v
2
u
3
v
3
s
v
1
(d) Searching minimum cost path
Figure 5: The concept of flow network based model of pursuing tracklets.
force edges for all tracklets, unlike existing methods.
For a flow from s to t, the path that has the minimum
sum of corresponding costs is determined as a track-
ing pedestrian trajectory (Figure 5 (d)).
Generally, the corresponding cost C
i, j
is computed
from the similarity S
i, j
between tracklets L
i
and L
j
by:
C
i, j
= −log(S
i, j
) (3)
where S
i, j
is determined from the similarities in such
features as position, appearance, and movement be-
tween L
i
and L
j
. The larger the similarity, the smaller
the corresponding cost, and pursuing tracklets is also
easier.
In the proposed method, to deal with the difficulty
caused by the space-time occlusion interval, new cost
terms reflecting a pedestrian occlusion state is added
to C
i, j
. The new corresponding cost C
0
i, j
between L
i
and L
j
is determined by
C
0
i, j
= −log(S
i, j
) + αP
i, j
+ βT
i, j
(4)
where α,β are positive constants, and P
i, j
,T
i, j
are the
cost terms reflecting pedestrian occlusion state.
The cost terms P
i, j
, T
i, j
are determined as the error
between predicted appearance of L
i
after occlusion
and actual measurement of L
j
. The position where
L
i
appears again after occlusion is denoted p
i
(Plane
coordinates), and the time is denoted t
i
(frame num-
ber). These are predicted values considering the oc-
clusion state in Eq. (2). The actual position of L
j
is
expressed as p
0
j
, and the time as t
0
j
. Cost terms P
i, j
and
T
i, j
are calculated as space and time errors as shown
in Eqs. (5) and (6).
P
i, j
= |p
i
− p
0
j
| (5)
T
i, j
= |t
i
−t
0
j
| (6)
According to Eq. (4), small P
i, j
,T
i, j
decreases the cor-
responding cost C
0
i, j
, therefore pursuing L
i
between L
j
will be easier. This is similar to provide a SR around
the space-time position where L
i
is predicted to ap-
pear. By this way, the proposed method introduces
the pedestrian occlusion state into the corresponding
cost, and accomplishes the equivalent process as ad-
justing SR according to the pedestrian occlusion state.
3.2.3 Appearance Prediction of Li after
Occlusion
To predict position p
i
and time t
i
where L
i
appears
again after occlusion, we assume that pedestrians
move at a constant speed and on a straight line in the
real world while he is occluded. Pedestrians appear at
the boundary between F
∗
(x, y) = 0 (with occlusion)
and F
∗
(x, y) = 1 (with no occlusion). The pedestrian’s
trajectory is determined by applying the exponential
moving average method to the position of the pedes-
trian regions constituting the tracklet L
i
.
4 EXPERIMENTS
To demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method,
we carry out pedestrian tracking experiments. We
present our results using two type datasets and com-
pare our method with conventional methods.
4.1 Experiment Overview
For evaluation using actual video AVSS2007 (720 ×
576pixels, 25fps) (AVSS2007, 2007), 2400 frames
Camera
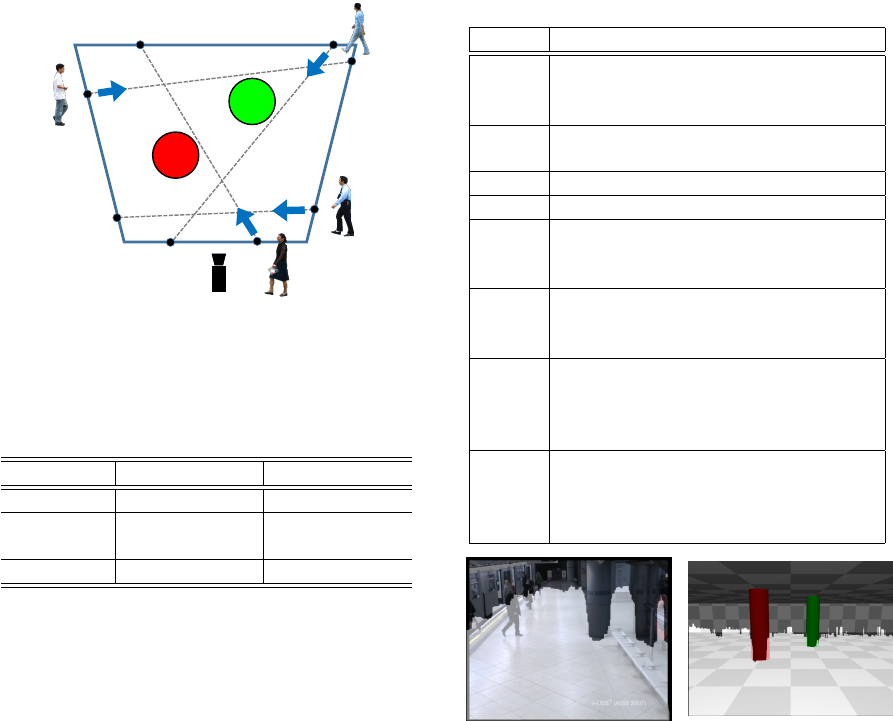
Figure 6: Example of pedestrian trajectory in the simulator
(Pedestrians are initially placed on blue line, red and green
circle represent obstacles (cylinder), gray dashed line is tra-
jectory of each pedestrian).
Table 1: Search range (SR) setting in conventional method
(”width” is width of frame and ”fps” is frame rate of video).
Spatial SR Temporal SR
Method (a) width*0.03 fps*0.4
Method (b) width*0.20 fps*2.0
(set properly) (set properly)
Method (c) width*0.30 fps*4.0
(frame t = 2502650) are extracted, and manually as-
sociating detected regions is used as the ground truth.
Additionally, to obtain precise ground truth (pedes-
trian loci) and make scenes simple except occlusion,
simulation videos (CG animations) are used as input
videos. Twenty videos are created by using POV-Ray
(POV-Ray, 2019), each of which is 800 × 600pixels,
5fps, and 50frames. There are two obstacles (cylin-
der) in the scene, and four pedestrians walk. As
shown in Figure 6, pedestrian’s start line (blue trape-
zoid) is located around the obstacle, and four start
points are placed on each edge. Pedestrian moves
in straight line toward the opposite side of the trape-
zoid. Start points and end points are randomly deter-
mined. In the videos, various types of occlusion occur
to pedestrians by obstacles or other pedestrians.
The skeletons of pedestrians are extracted from
each frame by OpenPose (Cao et al., 2017), and a
bounding rectangle of every extracted skeleton is used
as a pedestrian region.
In Eq. (4), the similarity S
i, j
between pedestrian
regions L
i
and L
j
is set as
S
i, j
= S
p
× S
t
× S
a
× S
s
(7)
where S
p
, S
t
, S
a
and S
s
are the similarities between
L
i
and L
j
in position, time (frame), appearance, re-
gion size, respectively. The position similarity is de-
termined as S
p
= exp(−Euclidean distance between
Table 2: Evaluation metrics.
Metric Definition
FM The total number of times a trajectory
is fragmented (interrupted during track-
ing).
SW The total number of switches its
matched ground truth identity.
MS The total number of missed targets.
FP The total number of false positives.
MOTP Multiple Object Tracking Precision.
The misalignment between the anno-
tated and the predicted bounding boxes.
MOTA Multiple Object Tracking Accuracy.
This measure combines three error
sources: FP, MS and SW.
RS Ratio of tracks which are correctly re-
covered from Short occlusion. We de-
fine the occlusion is caused by other
target.
RL Ratio of tracks which are correctly re-
covered from Long occlusion. We de-
fine the occlusion is caused by static
obstacle.
(a) AVSS2007
(b) POV-Ray animation
Figure 7: Acquired obstacle areas.
L
i
and L
j
), the time similarity S
s
is determined as
S
p
= exp(−frame interval between L
i
and L
j
), the ap-
pearance similarity S
a
is normalized correlation be-
tween color histograms in L
i
and L
j
. Consequently,
S
i, j
ranges from 0 to 1.
We evaluate the tracking performance when a new
cost term P
i, j
, T
i, j
in Eq. (4) are introduced into the
matching cost (proposed method α, β > 0) and is not
introduced (conventional method α, β = 0). As shown
in Table 1, the space-time search range (SR) of the
conventional method is set to three variations, which
are named Method (a), (b), and (c), respectively. Spa-
tial SR is based on the width of the video, and tem-
poral SR is based on the frame rate of the video. As
shown in Table 1, (a) sets the search range extremely
small, and (c) sets it extremely large compared to
the occlusion interval. (b) manually sets the search
range which the method shows better performance
(that means fewer identity switches) in each dataset.
A summary and short description of the used mea-

Table 3: Quantitative results (↑:the higher is the better, ↓:the lower is the better).
Dataset Method FM↓ SW↓ MS↓ FP↓ MOTP↑ MOTA↑ RS↑ RL↑
Generating tracklets 121 55 61 912 0.8606 0.8297 0.00 ( 0/89) 0.00 ( 0/43)
Method (a) 57 62 63 912 0.8600 0.8272 0.28 (25/89) 0.00 ( 0/43)
AVSS2007 Method (b) 12 83 23 928 0.8632 0.8231 0.52 (47/89) 0.51 (22/43)
Method (c) 8 92 23 928 0.8625 0.8227 0.44 (40/89) 0.37 (16/43)
Proposed method 17 64 23 928 0.8639 0.8268 0.52 (47/89) 0.74 (32/43)
Generating tracklets 48 25 9 77 0.9516 0.9268 0.00 ( 0/28) 0.00 ( 0/24)
Method (a) 47 26 9 77 0.9514 0.9275 0.82 ( 6/28) 0.00 ( 0/24)
POV-Ray Method (b) 17 30 7 77 0.9525 0.9262 0.64 (18/28) 0.58 (14/24)
animation Method (c) 5 34 7 79 0.9507 0.9211 0.64 (18/28) 0.42 (10/24)
Proposed method 2 26 7 76 0.9535 0.9278 0.64 (18/28) 0.83 (20/24)
sures is given in Table 2. We use the widespread mea-
sures in (Bernardin and Stiefelhagen, 2008) called
Switch (SW), Miss (MS), False Positive (FP), Multi-
ple Object Tracking Accuracy (MOTA) and Multiple
Object Tracking Precision (MOTP). Additionally, we
apply further metrics that are presented in (Li et al.,
2009), that is Fragment (FM). To evaluate focusing on
robustness to occlusion, we use Recover from Short-
term occlusion (RS) and Recover from Long-term oc-
clusion (RL) are introduced in (Song et al., 2010).
These represent the Ratio of tracks which are cor-
rectly recovered from short/long occlusion. In the ex-
periment, RS is used as an evaluation metric for oc-
clusion between targets (pedestrian) , and RL is used
for occlusion due to static obstacles.
4.2 Experimental Results
First, show results of obstacle areas detection. To de-
tect obstacle areas, the threshold in Eq. (2) is set as t
b
= 0. Figure 7 shows detected obstacle areas F
∗
b
(x, y),
where white areas indicate F
∗
b
(x, y) = 1 (none obsta-
cle areas). Figure 7 (a) is the result obtained from
6879 pedestrian regions. Figure 7 (b) is the result ob-
tained from 3212 pedestrian regions of all 20 videos.
These detections include false positives. The detec-
tion result of the area without the pedestrian’s trajec-
tory (i.e. background excluding floor and obstacles)
can be ignored because it does not affect the subse-
quent tracking process.
Examples of tracking for each method are shown
in Figures 8 and 9. Each track is assigned a unique id
and a color rectangle. We refer to the performance of
each method by comparing the transition of tracking
in the same frame. Figure 9 also shows the top views
of pedestrian trajectories and tracking results in the
simulator. Each symbol represents the pedestrian tra-
jectory, and the colored lines represent the tracking
results (the colors match those of the rectangle in Fig-
ure 9). Focus on tracking example of Method (a) and
(c), these are examples of failed tracking. In Method
(a), the space-time SR is set small compared to the
occlusion interval, so the same pedestrian does not
appear in the SR after occlusion. It causes interrup-
tion of tracking, and increasing FM. In Method (b),
the space-time SR is set large, so many pedestrians
appear simultaneously in the search range after occlu-
sion. It causes an incorrect association, and increasing
SW. On the other hand, proposed method succeeds in
matching the same person after occlusion and achieve
lower FM/SW.
Table 3 presents quantitative results of each ap-
proach on two datasets. ”Generating tracklets” indi-
cates the tracking evaluation at the tracklet stage. All
the following methods pursue these common track-
lets. When SR of the conventional method expands
from (a) to (c), FM decreases and SW increases. In
such a trade-off relationship, Method (b) has an ap-
propriate SR and keep both metrics relatively low.
Among the conventional methods, method (b) shows
better results in MOTP. The proposed method shows
the best performance of all methods. Our stable track-
ing result is due to the adjustment of the matching cost
C
0
i, j
based on the obstacle areas detection.
FP and MS maintain almost constant values be-
tween the proposed method and the conventional
method. FP greatly depends on the performance of
the human detector. Also, since MS occurs in the
phase of generating tracklets, it is not affected by sub-
sequent processing (pursuing tracklets). Due to the
constancy of FP and MS, MOTA is greatly affected
by SW. Among the all methods, method (a) shows the
best results for MOTA, but leaves a very large FM
problem.
Proposed method shows relatively high RL. The
advantage of being able to adjust the SR according to
the occlusion state proves effective tracking for static
obstacles. Incidentally, Method (b) got high perfor-
mance in RS. Since occlusion between targets occurs
in a short or medium term, a method with appropriate
SR is advantageous.

Method (a) Method (b) Method (c) Proposed method
(Fragment id=8) (success id=4) (Switch id=1) (success id=4)
frame 1142
frame 1153
frame 1165
frame 1184
frame 1238
frame 1247
Figure 8: Examples of tracking results (AVSS2007).

Method (a) Method (b) Method (c) Proposed method
(Fragment id=4) (success id=3) (Switch id=3) (success id=3)
frame 10
frame 19
frame 27
frame 31
frame 36
frame 40
top views of pedestrian trajectories
Figure 9: Examples of tracking results (POV-Ray animation).

5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed a method for tracking
multiple pedestrians in video sequences. The pro-
posed method extracts pedestrian regions in each
video frame, detects obstacle areas in the scene from
the extracted pedestrian regions, and tracks pedestri-
ans while estimating their occlusion states from the
detected obstacle areas. The efficacy of our proposal
was demonstrated through experiments on simulation
video sequences. The experimental results showed
that the proposed method, which estimates the occlu-
sion states of pedestrians and reflects them on region
association process, improves the robustness in visual
tracking multiple pedestrians under situations where
pedestrians are temporary occluded by still objects.
In future work, we plan to investigate a method for
updating detected obstacle areas by new input video
frames, and extend the proposed method in order to
deal with situations where pedestrians are temporary
occluded by occasionally moving obstacles, e.g, tem-
porary parked cars and stacked objects.
REFERENCES
AVSS2007 (2007). i-Lids dataset for AVSS2007. http://
www.eecs.qmul.ac.uk/
∼
andrea/avss2007 d.html.
Bernardin, K. and Stiefelhagen, R. (2008). Evaluating
multiple object tracking performance: The CLEAR
MOT metrics. EURASIP J. Image Video Process.,
2008(1):Article ID 246309.
Bewley, A., Ge, Z., Ott, L., Ramos, F., and Upcroft, B.
(2016). Simple online and realtime tracking. In IEEE
Int. Conf. Image Process., pages 3464–3468.
Bochinski, E., Senst, T., and Sikora, T. (2018). Extend-
ing IOU based multi-object tracking by visual infor-
mation. In IEEE Int. Conf. Adv. Video Signal Based
Surv., pages 1–6.
Cao, Z., Simon, T., Wei, S.-E., and Sheikh, Y. (2017).
Realtime multi-person 2D pose estimation using part
affinity fields. In IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision Pattern
Recognit., pages 1302–1310.
Hofmann, M., Haag, M., and Rigoll, G. (2013). Unified
hierarchical multi-object tracking using global data
association. In IEEE Int. Workshop Perform. Eval.
Tracking Surv., pages 22–28.
Huang, C., Wu, B., and Nevatia, R. (2008). Robust ob-
ject tracking by hierarchical association of detection
responses. In Eur. Conf. Comput. Vision, pages 788–
801.
Jiang, Z. and Huynh, D. Q. (2018). Multiple pedestrian
tracking from monocular videos in an interacting mul-
tiple model framework. IEEE Trans. Image Process.,
27(3):1361–1375.
Ju, J., Kim, D., Ku, B., Han, D. K., and Ko, H. (2017).
Online multi-person tracking with two-stage data as-
sociation and online appearance model learning. IET
Comput. Vision, 11(1):87–95.
Li, Y., Huang, C., and Nevatia, R. (2009). Learning to asso-
ciate: HybridBoosted multi-target tracker for crowded
scene. In IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision Pattern Recog-
nit., pages 2953–2960.
Mekonnen, A. A. and Lerasle, F. (2019). Comparative eval-
uations of selected tracking-by-detection approaches.
IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., 29(4):996–
1010.
Meshgi, K., ichi Maeda, S., Oba, S., Skibbe, H., zhe Li, Y.,
and Ishii, S. (2016). An occlusion-aware particle filter
tracker to handle complex and persistent occlusions.
Comput. Vision Image Unders., 150:81–94.
Mitzel, D. and Leibe, B. (2011). Real-time multi-person
tracking with detector assisted structure propagation.
In IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vision Workshops , pages
974–981.
Osawa, T., Wu, X., Sudo, K., Wakabayashi, K., Arai, H.,
and Yasuno, T. (2007). MCMC based multi-body
tracking using full 3D model of both target and envi-
ronment. In IEEE Int. Conf. Adv. Video Signal Based
Surv., pages 224–229.
Possegger, H., Mauthner, T., Roth, P. M., and Bischof,
H. (2014). Occlusion geodesics for online multi-
object tracking. In IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision Pattern
Recognit., pages 1306–1313.
POV-Ray (2019). POV-Ray The persistence of vision ray-
tracer, persistence of vision raytracer pty. ltd. http:
//www.povray.org/.
Salvi, D., Waggoner, J., Temlyakov, A., and Wang, S.
(2013). A graph-based algorithm for multi-target
tracking with occlusion. In IEEE Workshop Appl.
Comput. Vision, pages 489–496.
Shu, G., Dehghan, A., Oreifej, O., Hand, E., and Shah, M.
(2012). Part-based multiple-person tracking with par-
tial occlusion handling. In IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision
Pattern Recognit., pages 1815–1821.
Song, B., Jeng, T.-Y., Staudt, E., and Roy-Chowdhury,
A. K. (2010). A stochastic graph evolution framework
for robust multi-target tracking. In Eur. Conf. Comput.
Vision, pages 605–619.
Zhang, L., Li, Y., and Nevatia, R. (2008). Global data asso-
ciation for multi-object tracking using network flows.
In IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision Pattern Recognit.
Zhu, J., Yang, H., Liu, N., Kim, M., Zhang, W., and Yang,
M.-H. (2018). Online multi-object tracking with dual
matching attention networks. In Eur. Conf. Comput.
Vision, pages 379–396.
