
Proxy Embeddings for Face Identification among Multi-Pose Templates
Weronika Gutfeter
a
and Andrzej Pacut
b
NASK - Research and Academic Computer Network, Warsaw, Poland
Keywords:
Biometrics, Face Identification, Proxy Embeddings, Multi-view Image Recognition.
Abstract:
Many of a large scale face identification systems operates on databases containing images showing heads in
multiple poses (from frontal to full profiles). However, as it was shown in the paper, off-the-shelf methods
are not able to take advantage of this particular data structure. The main idea behind our work was to adapt
the methods proposed for multi-view and semi-3D objects classification to the multi-pose face recognition
problem. The proposed approach involves neural network training with proxy embeddings and building the
gallery templates out of aggregated samples. A benchmark testing scenario is proposed for the purpose of the
problem, which is based on the linked gallery and probes databases. The gallery database consists of multi-
pose face images taken under controlled conditions, and the probes database contains samples of in-the-wild
type. Both databases must be linked, having at least partially common labels. Two variants of the proposed
training procedures were tested, namely, the neighbourhood component analysis with proxies (NCA-proxies)
and the triplet margin loss with proxies (triplet-proxies). It is shown that the proposed methods perform better
than models trained with cross-entropy loss and than off-the-shelf methods. Rank-1 accuracy was improved
from 48.82% for off-the-shelf baseline to 86.86% for NCA-proxies. In addition, transfer of proxy points
between two independently trained models was discussed, similarly to hyper-parameters transfer methodology.
Proxy embeddings transfer opens a possibility of training two domain-specific networks with respect to two
datasets identification schema.
1 INTRODUCTION
In many face identification applications there is a need
to identify low-quality in-the-wild samples against the
high-quality gallery with face images in several poses.
While this setup is typical for various surveillance
systems, police identification engines etc., problem
is not often distinguished from standard in-the-wild
identification scenario. Here we assume that at least
one part of the data can be more controlled and cover
a wider range of facial views. In fact, testing the be-
haviour of such systems require two specific linked
databases. One, which we call the gallery database,
consists of several face images in various poses for
each individual. The second database, namely, probes
database, typically contains many low-quality im-
ages. What is important, both databases must be
linked in a way that some individuals are represented
in both parts. Databases, that meet all these require-
ments, are hardly available, so it was necessary to put
some work into adjusting existing sets.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6359-8220
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3489-8990
The gallery face images should be of higher qual-
ity and are obtained under controlled conditions. Ac-
quisition procedure is usually designed by a spe-
cialists who define lighting, background, head po-
sitions and camera settings. These datasets usually
include multiple, but constant set of poses for each
subject, like the mug shot photography taken in po-
lice stations, or registries of people in administrative
databases. The second type of images, namely the
faces in-the-wild, are the most common type of im-
ages in the real-world recognition. They can be taken
in varying lighting conditions, with noisy background
and using different acquisition devices. Both types of
images need to be confronted in the face identifica-
tion applications. Two identification problems of the
above type can be considered. First, given a watch list
of gallery images, one wants to identify faces among
the in-the-wild set. Secondly, given the in-the-wild
image of face, one wants to identify its correspond-
ing gallery set label. We are interested here in the
latter problem, namely, identification of in-the-wild
samples in the multiple-pose gallery database. The
most important point is to make full use of the gallery
resources.
Gutfeter, W. and Pacut, A.
Proxy Embeddings for Face Identification among Multi-Pose Templates.
DOI: 10.5220/0009166505130520
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2020) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
513-520
ISBN: 978-989-758-402-2; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
513

Figure 1: Sample images from Quis-campi dataset. First
row: gallery images of a person in 3 predefined poses (im-
ages were cropped to show only the face areas). Second
row: same person, frames from an outdoor surveillance sys-
tem. Third row: a few frames sampled from a video of ro-
tating head having uniform green background.
It was noticed, that there exist plenty of a very
large datasets containing face images in-the-wild, for
example Labeled Faces in the Wild (Huang et al.,
2007) or the datasets which belong to NIST Face
Recognition Challenges, like IJCB-C IARPA Janus
Benchmark (Maze et al., 2018). We are aware that the
top algorithms submitted to solve the problems stated
in these benchmarks should also perform well in our
task. However, it is hard to construct linked databases
for in-the-wild to multi-view identification as we de-
fined here using only unconstrained datasets.
Proposed here methods are based on generating
face descriptors with deep convolutional networks.
Multi-pose gallery properties enable to aggregate the
face descriptors belonging to the same subject. Ag-
gregation can be realized at various processing stages:
or by pooling descriptors or by altering the struc-
ture of network and merging the features inside the
model. Approach with descriptor averaging can be
applied also to off-the-shelf methods, referenced be-
low as baseline methods. However, in sec. 4.1 it
is shown that the solution based on watch-list cre-
ated with aggregated baseline gallery templates only
slightly outperform accuracy of the baseline system
that uses frontal images. In other words, multi-pose
properties do not boost the identification quality with-
out re-training the underlying networks. We therefore
decided to focus on improving algorithms for gener-
ating multi-view face templates.
2 DATASETS PREPARATION
In the proposed identification scenario we require face
images database to be consisted of two datasets. One
dataset, called here the gallery, includes controlled
images, where each person is represented by multiple
images with various head poses. Controlled images
are understood as the images having uniform back-
ground, good lighting conditions, no occlusions and
showing a face in one of a predefined views. The sec-
ond dataset, called here the probes set, contains im-
ages in-the-wild of the same individuals as the ones
present the gallery subset. Assembling these datasets
was quite challenging. Aside from the widely avail-
able separate multi-view face databases and large in-
the-wild databases, it is difficult to find face databases
with two linked dataset: gallery and in-the-wild, with
non-empty set of common individuals.
A publicly available database of images closest to
our requirements is Quis-campi database (Quis-campi
dataset, 2015). Its size is yet not sufficient consider-
ing current trends in training and testing face recogni-
tion algorithms. Unprocessed version of this database
contains images of 280 users but the common part of
the gallery and the probes subsets consisted only of
images of 170 different persons.
2.1 Quis-Campi - Face and Silhouette
Database
Quis-campi is a database for biometric recognition in
surveillance environments. It was collected in the SO-
CIA Lab at the University of Beira Interior in Covilh
˜
a,
Portugal. A part of it was utilised in facial identifi-
cation competition (Proenc¸a et al., 2018). It is com-
posed of various types of imaging data divided into
two subsets which reflect the division introduced be-
fore: gallery set and probes set (faces in-the-wild).
In the gallery dataset every person is represented
by three high quality photographs of the full silhou-
ette in frontal, left profile and right profile pose. Ad-
ditionally, the gallery set includes video sequences
showing rotating head of the same person. The video
frames have high resolution, do not contain any ad-
ditional objects occluding faces and are captured in-
doors on green uniform background. The second
dataset, namely the probes set is acquired using an
outdoor surveillance system. Frames containing faces
were extracted automatically by the system and then
manually labeled by the authors of database. These
images show people from a distance, not looking into
a camera and in poor lighting conditions.
Data from Quis-campi required many processing
steps to be functional as a component of training neu-
ral networks procedure. We needed to merge some
parts of it to create the coherent subsets. Faces were
detected automatically using dlib face detector (King,
2009) and then cropped to contain only the face areas.
The resulting 3 face images per person in the gallery
are not enough for further processing, so the gallery
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
514

was extended by selected frames from the rotating
head videos. We hand-picked the frames that con-
tain head in a certain pose, and cropped the images.
From each video sequence, 5 frames were extracted:
1 with frontal face, 2 with profiles (left and right), 2
with half-profiles (left and right). Therefore we ended
up with 10 gallery samples per person having prede-
fined labelled poses. The pose labels were saved and
known during the training. The probes subset was
processed using the same face detector, but the pose
remained unknown. Some identity labels were manu-
ally adjusted, especially in cases where the probe im-
age contained more than one face. For the purpose of
our experiment we excluded individuals which were
only in a single dataset (gallery or probes). Even-
tually, we gathered 1700 images in a gallery subset
with 170 individuals, and 2806 images in probes sub-
set with the same 170 individuals. Every person was
represented by exactly 10 gallery samples, and on the
average 16.5 probe samples.
3 MULTI-POSE FACE
TEMPLATES WITH PROXY
EMBEDDINGS
The main idea behind the proposed method is to adapt
some of the novel algorithms for the multi-view im-
age recognition to the considered task of multi-pose
face identification.
The basic approach of working with face images
of high pose variation is to apply the pose correc-
tion techniques. Images are transformed to contain
faces in one common view. In case of face frontaliza-
tion, every face is turned into a frontal portrait. The
frontalization improves the performance of recogni-
tion, what was shown in paper (Banerjee et al., 2018),
yet it causes some information loss due to uniformity
of such transformation.
To address the problem of effective use of multi-
pose images, many other solutions were proposed.
Solutions are predominantly based on specialized
deep network models that accept the input in form
of multi-view image sequence, like in the mv-cnn ap-
proach (Su et al., 2015). In mv-cnn identification, fea-
tures from distinct samples presenting the same sub-
ject are pooled at one of network layers to generate
a single aggregated descriptor. The aggregated de-
scriptor is capable of learning 3D characteristics of
subject shown from various perspectives. However,
in the case of pure convolutional architecture of net-
work, the number of views representing one subject is
often expected to be fixed.
Since in our database the number of multi-view
samples is not as large as it might be in other multi-
view objects datasets with hundreds of views per ob-
ject, it was hard to train new multi-view network.
Therefore multi-view descriptors [MV] are realized
as the averages of the single sample descriptors. The
probes images are always encoded in a single-view
mode. Nevertheless, we point the mv-cnn architec-
ture as the next step in the method development af-
ter collecting the data that will allow us to train the
model from scratch. Still, the aggregated descriptors
are found to be performing better than the single-view
ones [SV], see Sec.4.1.
The idea that we found particularly interesting for
the task of managing multi-view data was introduced
in (Ho et al., 2019). The authors proposed the Pose
Invariant Embeddings, which allows to train the net-
work simultaneously against multi-view and single-
view object representations by introducing a novel
similarity metrics. The training procedure was pre-
sented for 3 image classification and retrieval sys-
tems: the pose-invariant CNNs, the pose-invariant
proxies and the pose-invariant triplet centers. The
first is based on multi-view networks and the second
two utilize the concept of proxy learning proposed
in (Movshovitz-Attias et al., 2017). We follow some
of the concepts proposed in the last two papers and
train our network with two loss functions: the neigh-
bourhood component analysis-based function (NCA)
and the triplet margin loss.
3.1 Facial Features Embedding using
Neural Networks
The core part of our template modeling method is re-
alized using convolutional networks. We based on
VGG-Face model, which is described in paper (Parkhi
et al., 2015). Network transforms the input samples
X = {x
1
,x
2
..x
N
} into the feature embedding space
g(X) in which they can be compared. Values of the
embeddings g(X) are obtained from the descriptor
layer L
D
which is a fully connected layer set to have
predefined size. In case of VGG-Face model size of
descriptor layer L
D
is equal to 4096 and it is a penul-
timate layer in the whole structure. In our models the
size of this layer is set to 2048 (obviously excluding
the case when we test off-the-shelf methods). The
cross-entropy loss function requires additional clas-
sification layer L
C
to compute class-related probabili-
ties. Number of neurons in L
C
is adequate to the num-
ber of classes in the training dataset. In our case it is
equal to the number of users in Quis-campi dataset,
which is 170. The true label of a user for a sample
x is marked as c(x). Even if a loss is calculated on
Proxy Embeddings for Face Identification among Multi-Pose Templates
515

Figure 2: Toy example of learning with two-dimensional (size of network’s descriptor layer is equal to 2) proxy embeddings
for a 7-class dataset. Left: embeddings after the initialization. Colors represent the true class labels. For clarity, the 7 class
proxies (star-marked) are distributed uniformly on the unit hypersphere. Right: position of embeddings in final stage. Here
embeddings are not `
2
normalized (which is normally done in all other experiments). Embeddings of samples belonging to
the same class are well separated and enclosing their associated proxies.
the output of L
C
layer (cross-entropy approach), at the
validation stage sample similarities are computed on
the output of descriptor layer L
D
by employing near-
est neighbor classifier.
Distance learning technique, like triplet learning
with max margin loss, operates directly on descrip-
tors and do not need classification layer L
C
to be com-
puted. However, triplet learning requires forming the
input samples in a specific way. Triplets are formed
from 3 input samples (x, y+, z−). The first sample x
is called anchor, the second one is a sample belonging
to the same class as anchor c(x) = c(y), and the third
belongs to the impostor class c(x) 6= c(z). Because
of the large number of triplets combinations, training
procedure requires some mining techniques applied to
find the examples carrying the most meaningful infor-
mation.
3.2 Application of Proxies
One of the solutions to accelerate the training and to
limit the number of triplets is the idea of proxies pro-
posed in (Movshovitz-Attias et al., 2017). Proxies are
the points embedded in the same space as the descrip-
tors and are intended to represent the original training
set. They can play a significant role as a modification
of loss functions used for neural network training.
Each point in the training set has one proxy asso-
ciated with it. As we decided to use the static proxy
assignment, the proxies are directly associated with
class labels, and this association does not change dur-
ing execution of the algorithm. Having a set of prox-
ies P = {p
1
, p
2
,..., p
K
} and knowing the label c(x)
for each input point, we define the proxy of an in-
put point x as proxy of its class: p(x) = p
c(x)
. In our
method number of proxies is equal to the number of
class labels K, but in general they do not have to be
equal, however in the source paper this variant gives
the best results.
Idea of proxies is applicable to a wide range
of training methods. We test it with two types of
loss functions: the triplet loss (max-margin loss) and
the one based on neighbourhood component analysis
NCA described in paper (Goldberger et al., 2005).
Following the training procedure proposed
in (Movshovitz-Attias et al., 2017), the standard
triplet formulation (x, y, z) is replaced by the triplets
using proxy embeddings (x, p(x), p(Z)), where p(x)
is a proxy representative of the positive example x,
and p(Z) is a representative of all negative compar-
isons. Note that the number of negative comparisons
is equal to K − 1 where K is the number of class
labels (and proxy points as well). It is dramatically
smaller than in the case of standard triplets.
Triplet loss function with proxy embeddings used
in this work will be referred further as the triplet-
proxies. It is based on standard max-margin loss func-
tion with the negative and positive embeddings re-
placed by its proxies.
L
T RI
(x, p(x), p(z)) = max
d(g(x), p(x))
−d(g(x), p(z)) + M, 0
(1)
where M is the margin parameter, d(g(x), p(x)) is
the Euclidean distance between the embedding g(x)
of sample x and its proxy embedding p(x), while
d(g(x), p(z)) is the distance between the sample em-
bedding g(x) and proxy embedding of the negative
class c(x) 6= c(z). The triplet margin loss is one of
the loss functions that represent the distance-learning
approach in deep neural networks.
Proxy embeddings can be applied to classification
learning as well. Neighbourhood component anal-
ysis (NCA) with proxy embeddings is an example
of such application. Identification made by model
trained with NCA loss will be referred further as
NCA-proxies.
L
NCA
(x, p(x), p(Z)) = −log
exp(−d(g(x),p(x)))
∑
p(z)∈p(Z)
exp(−d(g(x),p(z)))
(2)
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
516
where the meaning of x, p(x) and p(Z) are similar to
those in (1). Both the embeddings of the training set
g(X) and the proxy embeddings P are `
2
-normalized.
Proxy points are randomly initialized at the begin-
ning of each training fold and kept constant during
the training session.
In a multi-view variant [MV] of network train-
ing we use aggregated embeddings g(X
n
) in place
of single-view embeddings g(x ). Triplets must be
formed accordingly to loss functions modification
to contain set of samples instead of single sample
(X
n
, p(X
n
), p(Z)).
3.3 Evaluation Scenario and Batch
Sampling
For identification evaluation, we divided the database
into a training and a validation parts. As our dataset
has two components, we obtained four sets: the train-
ing gallery set, the validation gallery set, the training
probes set and the validation probes set. This specific
structure need to be considered in a cross-validation
division. In each fold, we take N
v
samples per per-
son from the gallery set and N
q
samples per person
from the probes set to be included in the validation
part. For that reason, it is required that each user in
the gallery set is represented by at least 2 ∗ N
v
samples
and by 2 ∗ N
q
samples in the probes set. In our experi-
ments employing Quis-campi database, N
v
and N
q
are
both set to 3. A single gallery images of a particular
view was drawn randomly in case of many samples of
the same view of an individual. Each result discussed
in our work is the average of 5 random folds created
according to the above guidelines. All of the data in a
training set was augmented using random crops, rota-
tion and small colour modifications.
The code used in our experiments was prepared
in Pytorch framework. VGG-Face with pre-trained
weights is used as a baseline model in comparisons.
At the validation stage the descriptors are compared
using the cosine distance metric. The ranking lists are
then formed and the cumulative match curves (CMC)
calculated. We evaluate the algorithms using Rank-
1 and Rank-3 identification metrics. However, in ta-
ble 1, a verification metric is also presented to show
the full picture of algorithms’ performance. In this or-
der we use the area under the receiver-operator curve
(ROC) index.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Baseline: Off-the-shelf Method
Evaluation
Identification of the probes images in the multi-pose
gallery set can be approached in various ways. One
of the simplest - baseline - approaches is to apply an
off-the-shelf facial recognition algorithm. Within this
line, we used the VGG-Face with pre-trained weights
and build several baseline tests. We used this model
without any modification - the penultimate layer of
the convolutional network produced the output of size
4096 to be used as the face descriptor g(x).
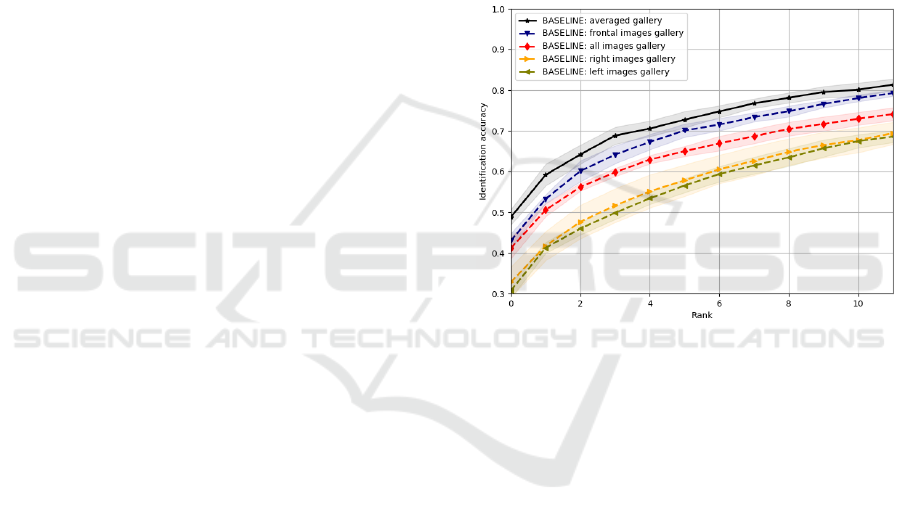
Figure 3: Multi-pose face identification using off-the-
shelf methods. Cumulative match score curves computed
for the Quis-campi dataset for 5 cases: all with the gallery
samples including all 3 poses with the most similar re-
trieved; frontal, left, and right, with the gallery images only
of certain poses, and averaged with the pose descriptors av-
eraged for each gallery sample. The shaded areas are within
1 − σ limits. While all the results are inferior, the average
case gives the best results, the frontal is the second, then all.
The left and right galleries are the worst.
First, we used the baseline approach to encode all
facial templates, regarding of pose (the all test). In
the next 3 baseline tests, we compare the probe with
only single-pose gallery images. For compatibility,
we follow the same cross-validation procedure (Sec.
3.3) for all tests. At every fold, three gallery images
are drawn that contain one frontal image, one left pro-
file and one right profile. We thus tested the probes
images with frontal-face-only watch-list (the frontal
test) and repeated testing with left-sided-only (the
left test) and right-side-only gallery lists (the right
test). The last option we considered is using a gallery
with the aggregated descriptor, namely with all three
gallery samples averaged (the average test). Note that
in the all test the gallery set is 3 times larger than in
Proxy Embeddings for Face Identification among Multi-Pose Templates
517
the other four cases. The first image with a correct
label is counted as the hit when determining the cu-
mulative match score (minimal distance strategy).
The results shown in graph 3 was the average of 5
cross-validation folds.
The highest Rank-1 accuracy is obtained for the
watch-list build with template aggregation approach
and it is equal to 48.78%. Next results in order be-
long to frontal images case (Rank-1=43.02%) and to
the all-images gallery (Rank-1=41.18%). Not surpris-
ingly, watch-lists constructed from profile pictures
dramatically decrease the accuracy (23.88% for left
profiles and 25.29% for right). The fact that the ag-
gregated descriptors give the best results is promising.
They are, however, very close to those obtained with
only frontal faces gallery. The profile images seem
to degenerate identification and without retraining the
network hence it is not very beneficial to include them
in the gallery watch-list at all.
4.2 Results: Proxy Embeddings in
Multi-Pose Face Identification
Evaluation of identification with proxy embeddings
is made for models trained with the use of 3 meth-
ods: cross-entropy with respect to class labels (called
shortly cross-entropy), NCA with proxy embeddings
(NCA-proxies) and triplet loss with proxy embedding
(triplet proxies). As the baseline, we used the best re-
sults obtained in previous experiment, namely base-
line frontal and baseline averaged.
We add identification accuracy computed with
VGG-Face model, where the gallery is created only
from frontal views (baseline - frontal) and from aver-
aged descriptors (baseline average. In every case, the
probes samples are identified within the gallery sam-
ples.
Two types of matching approaches are considered:
the first is to match a probe sample against a single
view SV) gallery sample, and second is to match a
probe sample against the multi-view gallery sample
MV).
When matching against multi-view gallery sam-
ples, the view set is created from 3 gallery samples
drawn with respect to frontal, left side, and right side
samples. Validation is performed by application of
the cumulative match score curve. In final compari-
son we consider Rank-1 and Rank-3 metric. All meth-
ods are based on the network are the same, except for
the training loss function (cross-entropy)
Detailed information about the identification and
recognition rates are summarized in Tab. 1. As it can
be observed in Fig. 4, the best results were obtained
for model trained with NCA-proxies. NCA-proxies
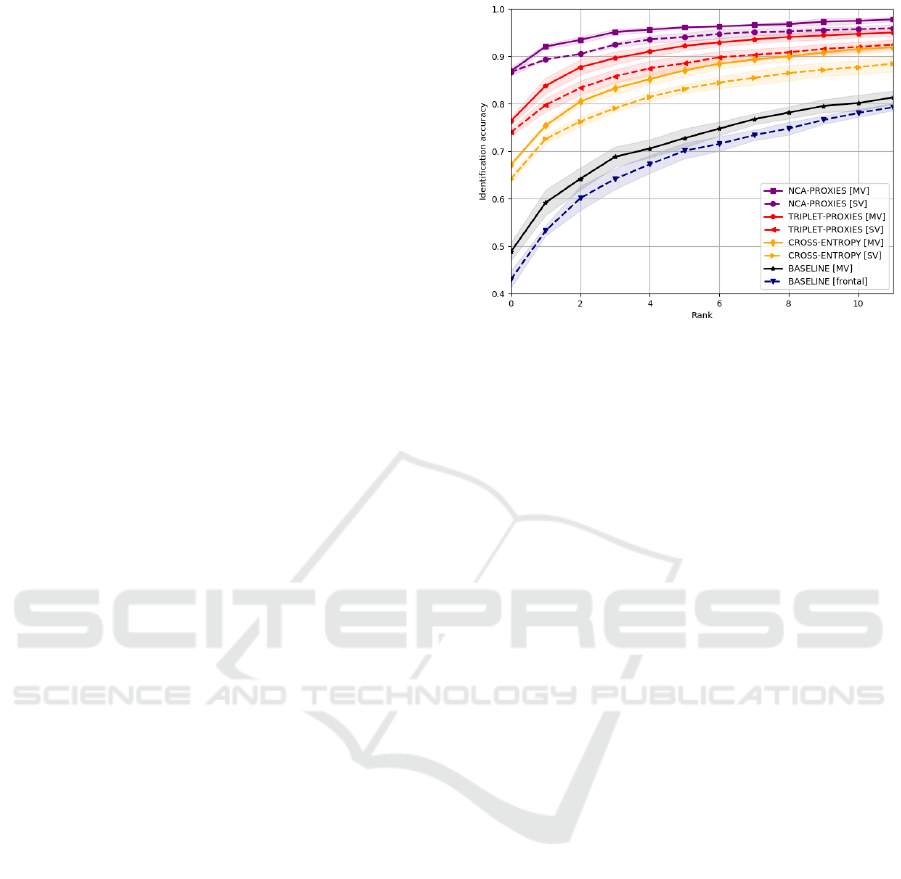
Figure 4: Multi-pose face identification with proxy em-
beddings. The CMC curves for identification of probes
samples in multi-pose Quis-campi dataset gallery. Each
classifier was trained with NCA-proxies and the cross-
entropy loss in two versions: with the list created from
single-view images (SV) and created from multi-view im-
ages (MV). For comparison, the best baseline result for un-
trained classifier using VGG-Face model is also shown.
method achieved Rank-1 of 86.67% for the single-
view gallery and 86.86% for the multi-view gallery.
triplet-proxies method is slightly worse in this case.
Rank-1 rate for triplet-proxies was 74.00% for single-
view and 76.35% for the multi-view gallery. Gallery
database built of multi-view descriptors gives in all
cases better results than for the single-view galleries.
Gain of Rank-1 accuracy for NCA-proxies is by about
78% as compared to the off-the-shelf method and by
32% compared to model trained with cross-entropy.
Results for face identification with proxy embed-
dings are very favorable, especially if we consider the
fact that it allows us to manipulate the classifier be-
haviour directly at the embedding layer. This conclu-
sion raises the question if it is possible to train two
models with the same set of proxy points and whether
the descriptors in these two models can be used to
match samples from different domains.
4.3 Proxy Transfer
As well as the weights of the deep neural network,
the proxy points can be transferred between the train-
ing sessions. The main goal of the proxy-related loss
functions is to establish the embeddings of samples
that belong to a given class to be near the associated
proxy points. Consequently, the embeddings should
maintain this property when trained on two distinct
datasets. The embeddings created by two different
models, but estimated basing on the same set of proxy
points and also the same set of associations, can be
used in a single evaluation scenario. To check this
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
518
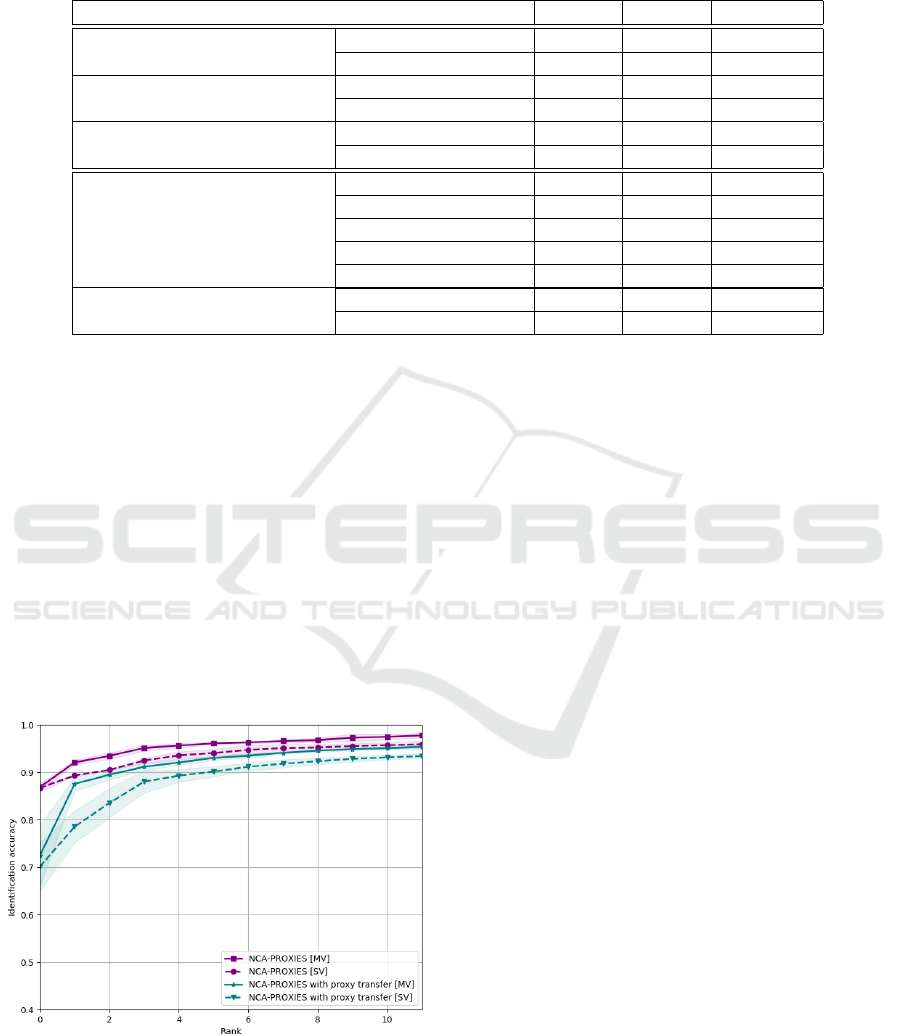
Table 1: Summary of evaluation metrics for the probe samples identification against the multi-pose gallery samples from the
Quis-campi dataset. Rank-1 and Rank-3 identification accuracies are presented along with the area under (AUC) receiver-
operator curve (ROC). The table covers the results of 3 experiments discussed in this works: the identification with off-the-
shelf methods (Fig. 3), the training with proxy embeddings (Fig. 4) and the application of proxy transfer (Fig. 5).
Method Rank-1 Rank-3 ROC-AUC
NCA-proxies
single-view [SV] 86.67% 90.49% 0.9930
multi-view [MV] 86.86% 93.43% 0.9941
Triplet-proxies
single-view [SV] 74.00% 83.33% 0.9817
multi-view [MV] 76.35% 87.69% 0.9842
Cross-entropy
single-view [SV] 60.47% 74.98% 0.9708
multi-view [MV] 65.88% 81.29% 0.9774
Baseline
all images gallery 41.18% 56.20% 0.8955
frontal images gallery 43.02% 60.12% 0.9033
left images gallery 30.78% 46.00% 0.8942
right images gallery 32.86% 47.65% 0.8964
averaged gallery 48.82% 64.20% 0.9259
Proxy transfer (NCA-proxies)
single-view [SV] 70.13% 83.53% 0.9827
multi-view [MV] 72.47% 89.47% 0.9869
idea, we set up an experiment in which we train two
independent models that share the architecture and
the dictionary of proxy points. By dictionary, we
mean the values of embeddings and label of the re-
lated classes. The models were trained on two ex-
clusive subsets of Quis-campi database: one on the
gallery set and one on the ‘in the wild’ probes set.
The evaluation is performed in the same way as in the
previous experiments. Both models were trained em-
ploying NCA with proxy embedding (NCA-proxies).
The gallery watch-list is built using the gallery model,
either in a form of single-view or multi-view descrip-
tors. The probes are encoded using the probes model
they are matched with the gallery descriptors during
evaluation.
Figure 5: Proxy transfer. CMC curve for the identifica-
tion of probe samples in the multi-pose Quis-campi dataset
gallery. For the proxy transfer, two distinct models were
trained, one only on the gallery samples and the second only
on the probe samples, with the same sets of proxy points set.
All models were trained using NCA-proxies loss.
Our preliminary results in proxy transfer do not
surpass the single model approach, but they are
close despite the independent training. Rank-1 for
multi-view gallery identification with proxy transfer
is 72.47% and Rank-3 reaches the level of 89.47%.
However, validation results need to be improved be-
cause of the relatively high variance of Rank-1 (it is
visible in figure 5), σ of Rank-1 is about 5%. The re-
sults obtained with proxy transfer are still much better
than for off-the-shelf method.
Our intuition behind this approach is to create a
possibility of building two domain-specific models:
one for the multi-pose controlled images (possibly
based on some modification of mv-cnn architecture)
and the second for the data-in-the wild. The second
model can be adapted to the images acquired from the
particular source, e.g. for certain types of surveillance
systems.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, a new method for multiple-pose face
identification was proposed, based on proxy embed-
dings in combination with two loss functions: the
triplet loss and the neighbourhood component anal-
ysis loss. A benchmark scenario was introduced for
training and testing image recognition from uncon-
trolled in-the wild probes to multi-view gallery. The
application of the new method results in a large in-
crease of the identification rates. Alongside, it was
demonstrated that one cannot benefit from multi-pose
image databases without changing the model struc-
ture or retraining the network to the specific task.
There is still a space for increasing the full poten-
Proxy Embeddings for Face Identification among Multi-Pose Templates
519

tial of the presented methodology. The most impor-
tant step would consist of creating larger and more
diversified datasets. It would be then possible to per-
form parallel training on two models with different ar-
chitectures: one specialized in multi-pose controlled
face photographs and the second for uncontrolled im-
ages or for images coming from a predefined type of
capture device. It was shown here that the network
training can be set up in the way that embeddings in
both models are forced to enclose to same set of proxy
points.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by NCBiR grant DOB-
BIO7/18/02/2015. Computations made in this paper
would not be possible without the support of NVIDIA
Corporation that donated the GPU to author.
REFERENCES
Banerjee, S., Brogan, J., Krizaj, J., Bharati, A., Webster,
B. R., Struc, V., Flynn, P. J., and Scheirer, W. J.
(2018). To frontalize or not to frontalize: Do we really
need elaborate pre-processing to improve face recog-
nition? In 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applica-
tions of Computer Vision (WACV), pages 20–29.
Goldberger, J., Hinton, G. E., Roweis, S. T., and Salakhutdi-
nov, R. R. (2005). Neighbourhood components anal-
ysis. In Saul, L. K., Weiss, Y., and Bottou, L., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
17, pages 513–520. MIT Press.
Ho, C.-H., Morgado, P., Persekian, A., and Vasconcelos, N.
(2019). Pies: Pose invariant embeddings. In The IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion (CVPR).
Huang, G. B., Ramesh, M., Berg, T., and Learned-Miller,
E. (2007). Labeled faces in the wild: A database for
studying face recognition in unconstrained environ-
ments. Technical Report 07-49, University of Mas-
sachusetts, Amherst.
King, D. E. (2009). Dlib-ml: A machine learning toolkit.
Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10:1755–
1758.
Maze, B., Adams, J., Duncan, J. A., Kalka, N., Miller, T.,
Otto, C., Jain, A. K., Niggel, W. T., Anderson, J., Ch-
eney, J., and Grother, P. (2018). IARPA Janus Bench-
mark - C: Face Dataset and Protocol. In 2018 Inter-
national Conference on Biometrics (ICB), pages 158–
165.
Movshovitz-Attias, Y., Toshev, A., Leung, T. K., Ioffe, S.,
and Singh, S. (2017). No fuss distance metric learning
using proxies. CoRR, abs/1703.07464.
Parkhi, O. M., Vedaldi, A., and Zisserman, A. (2015). Deep
face recognition. In British Machine Vision Confer-
ence.
Proenc¸a, H., Nixon, M., Nappi, M., Ghaleb, E.,
¨
Ozbulak,
G., Gao, H., Ekenel, H. K., Grm, K., Struc, V., Shi,
H., Zhu, X., Liao, S., Lei, Z., Li, S. Z., Gutfeter, W.,
Pacut, A., Brogan, J., Scheirer, W. J., Gonzalez-Sosa,
E., Vera-Rodriguez, R., Fierrez, J., Ortega-Garcia, J.,
Riccio, D., and De Maio, L. (2018). Trends and con-
troversies. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 33(3):41–67.
Quis-campi dataset (2015). Biometric Recognition in
Surveillance Environments. http://http://quiscampi.di.
ubi.pt/. Accessed: 2020-01-01.
Su, H., Maji, S., Kalogerakis, E., and Learned-Miller, E. G.
(2015). Multi-view convolutional neural networks for
3d shape recognition. In Proc. ICCV.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
520
