
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing
Mehdi Stapleton
1,2
, Dieter Schmalstieg
1
, Clemens Arth
1,2
and Thomas Gloor
3
1
ICG, Graz University of Technology, Inffeldgasse 16/2, 8010 Graz, Austria
2
AR4 GmbH, Strauchergasse 13, 8020 Graz, Austria
3
Hilti Corporation, Feldkircherstrasse 100, 9494 Schaan, Liechtenstein
Keywords:
Sparse Registration, Active Perception, Active Localization, General Hough Transform.
Abstract:
Registering a known model with noisy sample measurements is in general a difficult task due to the problem in
finding correspondences between the samples and points on the known model. General frameworks exist, such
as variants of the classical iterative closest point (ICP) method to iteratively refine correspondence estimates.
However, the methods are prone to getting trapped in locally optimal configurations, which may be far from
the true registration. The quality of the final registration depends strongly on the set of samples. The quality
of the set of sample measurements is more noticeable when the number of samples is relatively low (≈ 20).
We consider sample selection in the context of active perception, i.e. an objective-driven decision-making
process, to motivate our research and the construction of our system. We design a system for learning how
to select the regions of the scene to sample, and, in doing so, improve the accuracy and efficiency of the
sampling process. We present a full environment for learning how best to sample a scene in order to quickly
and accurately register a model with the scene. This work has broad applicability from the fields of geodesy to
medical robotics, where the cost of taking a measurement is much higher than the cost of incremental changes
to the pose of the equipment.
1 INTRODUCTION
Localization within a new scene requires aligning ob-
served elements of the scene with prior knowledge of
the environment. The process is relevant to a wide-
ranging group of disciplines from Robotic Navigation
to Augmented Reality. When given a prior model of
the environment, the process is termed model-based
registration.
Classical approaches to model-based registration
rely on dense-sampling of the scene using dense
sensors, e.g., laser scanners, followed by optimiza-
tion routines to register the model with the obser-
vations (Ballard, 1981). However, the nonlinear na-
ture of the optimization routine leaves it prone to lo-
cal optima and sensitive to initialization – i.e., the
original sampling of the scene (Rusinkiewicz and
Levoy, 2001). Given the importance of the original
sampling, many works have attempted to tackle the
problem via geometry-based reductions of the origi-
nal dense-sampling to prevent spurious local optima
(Rusinkiewicz and Levoy, 2001). Sparse-sampling of
the scene has received considerably less attention, as
a small number of samples poses difficulties for ef-
fective reductions of the sample-set (Arun Srivatsan
et al., 2019). Sparse-sampling strategies will typically
be employed in cases where a single-measurement is
expensive either with regards to time taken or energy
consumed. Due to the effective limit on the number of
samples to be taken, sparse-sampling processes must
be judicious in their selection of good vantage points.
In this paper, we present an algorithm for effec-
tively sparse-sampling the environment to register it
with respect to a given model, i.e. model-based reg-
istration. We consider polygonal floor-plan models,
e.g. common in industrial construction and survey-
ing applications. We will present an approach based
on recent work using Active Localization (Chaplot
et al., 2018), combined with integration into a robust
method for localization. The algorithm will be a two-
stage approach. The first stage comprises carrying
out a robust and noise-tolerant sparse-sampling strat-
egy in a new environment. The second stage will re-
fine the registration using efficient sparse-registration
techniques (Arun Srivatsan et al., 2019). We will
demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on
sample floor-plans, and present interpretations of the
sampling strategies.
Stapleton, M., Schmalstieg, D., Arth, C. and Gloor, T.
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing.
DOI: 10.5220/0009172608350846
In Proceedings of the 15th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2020) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
835-846
ISBN: 978-989-758-402-2; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
835

2 RELATED WORK
Our approach learns active sampling strategies for
quickly and accurately registering a surrounding
scene with a model of the environment. The work
thereby lies at the intersection of active sensing and
geometric sub-sampling techniques.
2.1 Iterative-Closest-Point (ICP)
The work of Rusinkiewicz and Levoy (2001) formal-
ized the general process of ICP into six parts: point-
selection, neighbourhood-selection, point-matching,
weighting pairs, outlier rejection, and error minimiza-
tion. They emphasize the importance of the earlier
stages in order to guarantee that the final error mini-
mization would be well-conditioned. ICP techniques
are typically performed on dense point sets, which
helps to smooth out any sub-optimal behaviour in the
earlier parts. Evidently, the earlier parts, including
point-selection, become especially important when
we have a sparse number of measurements.
In the context of point-set registration (PSR),
many works have investigated different methods of
point-selection as means of constraining the down-
stream error minimization routine. Early works to
address this point-selection have looked at geomet-
rically stable model points (Gelfand et al., 2003), the
sampling of a diverse distribution of points based on
intrinsic point characteristics such as normal-vector
(Rusinkiewicz and Levoy, 2001), and selection of
points based on constraining motion in a local neigh-
bourhood of the point (Torsello et al., 2011).
It is along this line of research that we propose a
system for learning how best to select sample points
in a scene. The aforementioned methods are largely
based on sub-sampling a captured dense point-set of
a target object, and leveraging a priori knowledge of
how geometry plays with registration. Unlike these
methods, we learn a policy on how to perform point-
selection in an online manner. Moreover, we learn to
make decisions on whether or not to sample certain
regions of the scene based solely on our prior sam-
ples and a binary detector for topologically interesting
scene content.
Along with point-selection for registration, we
also simultaneously consider a dual-objective: we
would like to perform a point-selection in a minimal
amount of time as possible. Given a fixed time cost to
performing a measurement and moving the agent, this
can be reformulated as finding a minimal set of points
for accurate registration. In this respect, we may con-
sider our objective similar to active-sensing: We aim
to minimize the uncertainty in our registration belief-
space with each sample measurement.
2.2 Active Localization
Active Markov Localization (AML), popularized by
the work of Fox et al. (1998), takes an active approach
to controlling the robots actions in order to minimize
the expected future entropy of the system. This work
uses a grid for storing the belief of the robot pose.
Due to the large-size of the grid for moderate scene
sizes, efficient optimizations are needed to run the
algorithm. Foremost, the measurement likelihood is
pre-computed for every location within the grid, so
that the belief update corresponds to a handful of ta-
ble lookups. Another optimization is the belief map is
assumed to condense to only a small number of pos-
sible poses. Hence only the neighbourhoods about
those probable locations need to be considered. Sim-
ilarly, we use a grid-based localization scheme, but
we would like to avoid the onerous pre-computation
phase. We instead use a General Hough Transform
style method for updating our belief.
The more recent Active Monte Carlo Localiza-
tion (AMCL) work of K
¨
ummerle et al. (2008) uses
a particle filter for representing the belief. To avoid
costly ray-cast operations for each particle to evaluate
the information gain of a given action, the particles
are grouped into clusters. Each cluster then performs
a ray-cast operation from the mean of the cluster in
the information gain, i.e., utility function (Fox et al.,
1998).
2.3 Deep Reinforcement Learning
The work of Chaplot et al. (2018) and Gottipati et al.
(2019) specifically look at this dual-objective in the
context of active localization; a robotic agent must
determine its position within a map. Chaplot et al.
(2018) consider a robotic agent which can move in
four directions (up, down, right, left) with a forward
facing depth sensor. The work uses a fixed grid to
store the belief of the robotic location within a maze
and uses the belief map in its state representation. We
similarly use a belief map in our state representation;
however we use a novel grid-based localization algo-
rithm for generating the belief map.
Gottipati et al. (2019) train a residual neural net-
work to learn the likelihood map for a given state-
action pair via supervised learning, which it then
uses to update the prior belief during operation. The
robotic agent is equipped with a 360
o
laser scanner,
which is used as the measurement device. In con-
trast, our system uses a limited observation mech-
anism which is simply a binary topological indica-
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
836

tor which coarsely highlights areas of wall intersec-
tions. Our work additionally considers registration er-
ror with our objective to find a minimal set as quickly
as possible. Moreover, both prior works look at the
maximum of the belief map at the ground-truth pose
as the maximization objective; whereas we strive to
minimize the final registration error and the trajectory
cost (i.e., agent motion and measurement time penal-
ties).
2.4 Discussion
Our method’s computational cost is dependent on
the perimeter of the map as opposed to the interior.
In most scenes, the perimeter of the map is signifi-
cantly smaller than the interior area; hence we can
expect significant computational savings. Since we
are considering problems with a sparse number of
measurements possibly containing noise and outliers,
we cannot readily disqualify regions of the belief
space which may have gotten little consideration
after the first handful of samples. Therefore, we
need to consider the whole belief space throughout
our active-sensing routine. This means the sparse
sampling problem is ill-suited for optimizations
which only a consider a handful of poses early-on in
the algorithm.
We claim the following contributions:
• A system for learning active-sampling strategies
which considers both efficiency and accuracy for
the registration of a scene with a known model.
• A novel grid-based localization scheme, with
lower front-end computational load than classical
approaches.
• A full simulation environment for learning active-
sampling strategies, which includes map gen-
eration, localization, sparse-registration, and a
symmetry-aware evaluation module.
• An inspection tool for investigating deep policy
behaviour elicited by our active sampling strategy.
3 METHODOLOGY
We design a system for effectively sampling the sur-
rounding scene in a sparse manner. The sampling
strategy is learnt via a reinforcement-learning ap-
proach. Hence, we adopt the following terminology:
the agent denotes the entity performing the sampling,
the environment refers to the 2D or 3D scene sur-
rounding the agent, and the policy π(a|s) refers to how
the probability of the agent selecting an action a given
the current state s of the system.
The system is composed of four modules:
1. Our fast localization module, responsible for
coarsely hypothesizing the likelihood of the
agent’s pose within the environment
2. The active-sampling module, decides how to take
sample measurements
3. The refinement module, responsible for sparse-
registration of the scene with the model given a
coarse estimate
4. The evaluation module for assessing in a
symmetry-aware fashion the quality of the final
registration
We also introduce an inspection tool for easily in-
vestigating the decision-making process of the active-
sampling module.
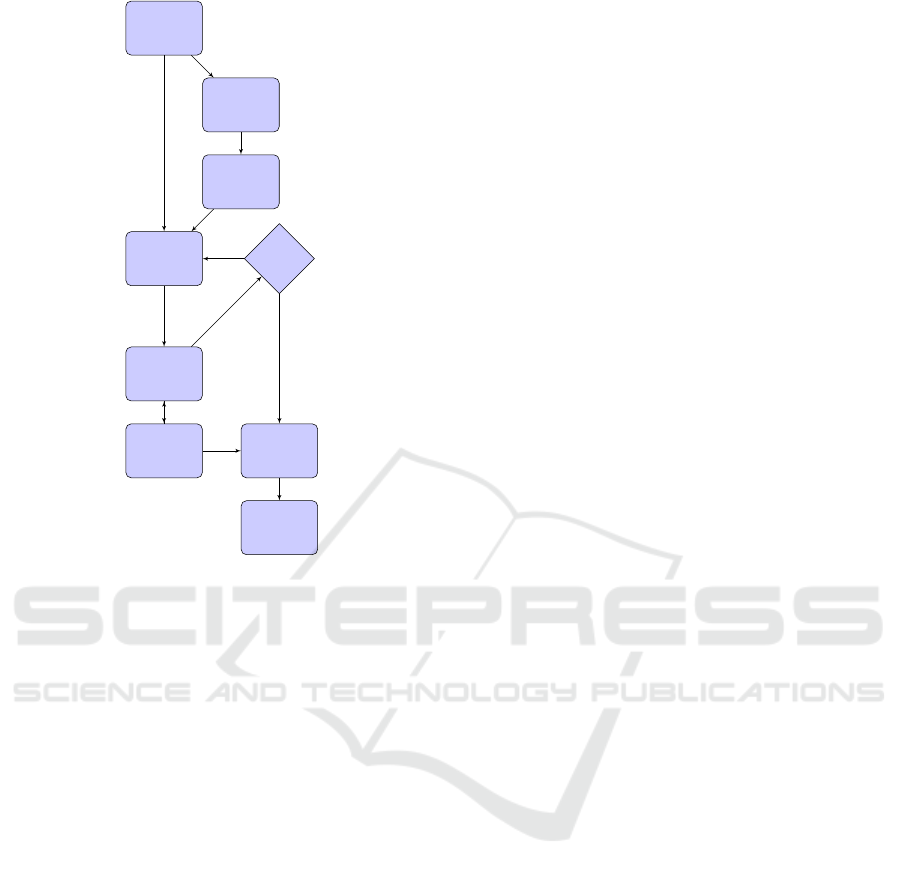
The sub-systems, shown in Figure 1, work in
concert in order to quickly and accurately register a
known model with the judiciously selected sample
measurements of the environment. We develop a sim-
ulation environment which generates outlines for ran-
dom floor-plans. The outlines represent single indoor
room scenes. We do not consider furniture or other
obstacles between the measurement device and the
walls of the room. Thereby, we concentrate on learn-
ing sampling strategies based purely on the room ge-
ometry. We allow the floor-plan outline to be a simple
non-convex polygon. The measurement device is as-
sumed to be level with respect to the ground-plane of
the simulated room, which can be achieved in prac-
tice by aligning the negative z-axis of the device ref-
erence frame with respect to the gravity vector given
by an on-board accelerometer. The simulation places
the agent (i.e., measurement device) at a random lo-
cation about the visual center of the room.
We use a quad-tree based algorithm to quickly
compute the visual center of our floor-plan. The dis-
tance between the visual center and the nearest wall
of the floor-plan determines the radius of a uniform
distribution about the visual center for placement of
the agent. We proceed to detail each individual sub-
system in the following sections in order of appear-
ance in our pipeline.
3.1 Learning Sampling Strategies
We frame the problem of effective sampling
as a Partially-Observed Markov Decision Process
(POMDP). In this process, the agent must learn a pol-
icy which maximizes the expected cumulative reward
(E[R]) over the course of an episode (τ). An episode
consists of a sequence of actions, which are drawn
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing
837
floorplan
generation
find visual
center
agent ini-
tialization
environment STOP?
policy
localization
sparse-
registration
error
evaluation
observation
action
no
yes
Figure 1: System overview of our environment. We pro-
vide a simulation environment for generating floor-plans.
The agent is initialized within room, about the visual center.
A learnt policy then interacts with the environment via the
agent’s actions and makes observations of the scene. Dur-
ing interactions, a belief map maintains a coarse distribu-
tion over the likely pose of the model with respect to the
scene. Once the policy dictates termination, then the current
coarse estimate is fed to the sparse-registration module for
refinement of our registration of the model with respect to
the scene. Finally, we evaluate the error using a symmetry-
aware pose-distance.
from a discrete action set, until completion of a task
or allotted time. We design a reward signal which pe-
nalizes excessively lengthy action sequences and re-
wards low final registration error (Sections 3.2 and
3.3). Each action from the discrete set has an in-
trinsic cost. In practice, the cost of a measurement
action greatly outweighs the cost of a small robotic
manipulation of the agent (e.g., change of pose of the
on-board sensor). We observe this behaviour in any
robotic platform outfitted with a high accuracy mea-
surement device, e.g., electronic distance measure-
ment (EDM) devices used in surveying applications,
which are designed for reliable and robust operation.
The length of an action sequence measures the sum of
action costs, e.g., expensive measurement actions and
cheap rotations. By penalizing the length of the action
sequence, we elicit behaviour which strives to find a
correct registration as quickly as possible. The cost
associated with the accuracy of the final registration
provides a natural negative feedback mechanism for
the length. This feedback mitigates the agent learn-
ing shortcuts to a quick-and-dirty registration, which
is ill-suited for proceeding to sparse registration re-
finement, or prone to getting trapped in a local sub-
optimum.
We use the coarse registration error as an indicator
of episode completion, i.e., once the coarse localiza-
tion (Section 3.2) is able to approximately register the
scene with the model, the action sequence terminates
and proceeds to the next stage in the pipeline (Sec-
tion 3.3). We use the final registration error (i.e., after
refinement) to penalize the final reward signal.
Our objective function is the expected cumulative
reward argmax
π
E
τ
[R|π] with
R =
T −1
∑
t=0
γ
t
r
t
(1)
where T is the maximum length of the episode, r
t
is
the reward at time-step t, and we use a discounted cu-
mulative reward with the discount factor γ ∈ (0, 1].
We parameterize our policy using a functional ap-
proximator, π
θ
, with θ denoting the free parame-
ters of our function. Policy gradient methods have
been shown to be an effective technique to optimizing
Equation 1 (Sutton and Barto, 2018) given we follow
the same policy we optimize (i.e., on-policy learning).
The policy gradient is given as follows,
∇
θ
E
τ
[R] =
E
τ
"
T −1
∑
t=0
∇
θ
logπ(a
t
|s
t
, θ
t
)
T −1
∑
t
0
=t
γ
t
0
−t
r
t
0
−V
π
(s
t
)
!#
(2)
We express the policy with respect to the parameters θ
and emphasize its interpretation as a conditional prob-
ability over the next action selection (a
t
) given the
current state of the system (s
t
). Noteworthy, we use
the value function V
π
,
V
π
(s) = E
τ
"
T −t−1
∑
l=0
γ
l
r
t+l
s
t
= s
#
(3)
as a baseline to reduce the variance of our gradient
estimate from Equation 2.
We use the Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic
(A3C) policy gradient method (Mnih et al., 2016)
to maximize the expected cumulative reward. We
choose A3C over other contemporary approaches
such as proximal policy optimization (PPO) (Schul-
man et al., 2017) due to the demonstrated efficacy of
A3C on a similar class of problems (Chaplot et al.,
2018).
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
838

The inner term of Equation 2 represents the ad-
vantage seen for an action sequence over the expected
cumulative reward V
π
(s
t
). Hence, action sequences
with positive advantage will act to nudge the param-
eters to encourage future similar action sequences,
whereas a negative advantage, i.e., an observed cu-
mulative reward below baseline, will nudge parame-
ters away from such action sequences. The param-
eters will act on the individual actions through the
log-probability of selecting such an action in a given
state. Many algorithms wrestle with providing a reli-
able estimate of the advantage without having to wait
until the episode terminates to perform a parameter
update. A central bias-variance trade-off lies at the
heart of algorithm development. Similar to the imple-
mentation of Chaplot et al. (2018), we use the Gener-
alized Advantage Estimator (GAE) (Schulman et al.,
2015) for computing an estimate. The GAE provides
an extra lever for controlling the bias-variance trade-
off through a parameter λ,
δ
t
= r
t
+ γV
π
(s
t+1
) −V
π
(s
t
)
A
π,γ
t
=
T −t−1
∑
i=0
(γλ)
i
δ
t+i
(4)
where A
π,γ
t
denotes our estimate of the advantage for
time-step t, based on our policy - π(a|s).
The training procedure performs simulation as
previously described, with periodic parameter up-
dates based on the experiences of the most recent seg-
ment of the episode. Therefore, we perform more fre-
quent policy updates.
We primarily compose our state representation the
belief-space of the agent’s pose within the scene, sim-
ilar to Chaplot et al. (2018), and a history of recent
coarse narrow field-of-view (FOV) topological scans
of the scene from the agent pose. The scans act as a
proxy for a conservative wall-intersection detector.
In case of pathological lighting conditions or oc-
clusions, we can at best assume a coarse indicator of a
wall intersection within a narrow FOV of the agent’s
bearing. We manage the belief-space of the agent’s
pose from all sample measurements up to the current
time, by using a grid-based localization system of our
own design, details in Section 3.2.
As shown in Figure 2, we modify the Actor-Critic
architecture of Chaplot et al. (2018) to supply the col-
lection of scans through a fully-connected network
along with the current step count within the episode
and the recent action history.
16 16
N
x,y
16 16
N
x,y
16 16
N
x,y
200
Scans
100
80
Actions
8
Length
444
Projection
4(5)
Actor
4(5)
SoftMax
1
Critic
Figure 2: Architecture of our policy model. We mod-
ify the architecture of Chaplot et al. (2018) to accom-
modate our topological scans. The inputs comprise the
|N
x
| × |N
y
| × |N
ξ
| belief map (Section 3.2) - top left, the
recent topological scans, the recent action history, and the
current step index in the episode.
3.2 Localization
We design the localization module with multiple con-
siderations in mind. The module should be able to
withstand noise and especially outliers, as well as pro-
viding a good degree of accuracy. Our primary con-
cern is robustness, since the downstream sparse reg-
istration module (Section 3.3) will be able to help en-
sure a final accurate estimate. Due to complete or par-
tial symmetries, the localization technique should be
able to accommodate multi-modal belief space distri-
butions. Critically, the module needs to present the
belief map over the agent pose in a form digestible
by the active-sampling module (Section 3.1). The
latter constraint disqualifies classical particle-filter-
based localization techniques (K
¨
ummerle et al., 2008,
Thrun et al., 2005), due to resultant complexity in
communicating the belief, i.e., collection of parti-
cles, to the active-sampling module. With all these
considerations, we decide to employ a novel Hough
Transform-based approach. Specifically, we rely on
the Generalized Hough Transform (GHT) (Ballard,
1981) for accumulating votes into the belief over the
agent pose.
We consider a fixed grid underlying our grid-
based localization scheme. The fixed size reduces
the complexity of down-stream processing in the
active-sampling module. We define the robot pose
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing
839
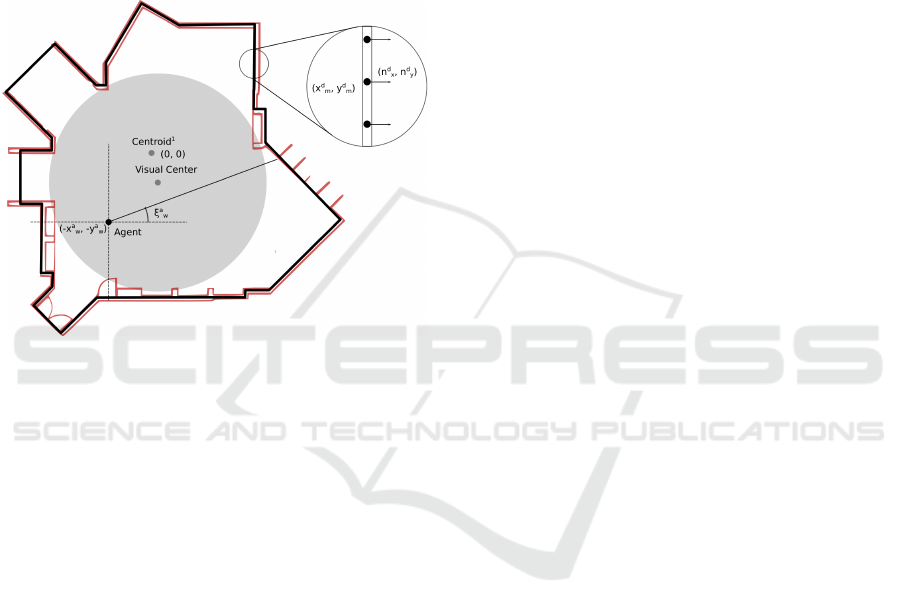
by the tuple x
:
= (x
offset
w
, y
offset
w
, ξ
a
w
) ∈ N
x
× N
y
× N
ξ
representing the translation and the orientation of
the agent. We adopt a special convention in light
of the use of the GHT. The translation components
(x
offset
w
, y
offset
w
) represent the offset between the agent
position (x
a
w
, y
a
w
) and the centroid of the surrounding
scene (x
scene
w
, x
scene
w
) in the world coordinate frame W.
The orientation component ξ
a
w
represents the rotation
of the agent in the world coordinate frame. An anno-
tated illustration of a sample floor-plan with our la-
belling convention is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Illustration of floorplan diagram.
The grid dimensions are given as |N
x
| × |N
y
| ×
|N
ξ
|. The grid will hold the belief of the robot pose,
which will be updated based on the measurement like-
lihood via classical Bayesian filtering,
p(x
t+1
|o
0:t+1
, a
0:t
) ∝
p(o
t+1
|x
t+1
)
Z
x
t
p(x
t+1
|x
t
, a
t
)p(x
t
|o
0:t
, a
0:t
)dx
t
,
(5)
where the o
t
and a
t
are the observation and action
taken at time-step t, respectively. Our grid would hold
the current belief at each time t, i.e, p(x
t
|o
0:t
, a
0:t
). At
each time-step, a new action is taken, which induces
the convolution over the motion model p(x
t+1
|x
t
, a
t
),
and a new observation is taken following the action
which weights the motion-updated belief with the
measurement likelihood p(o
t+1
|x
t+1
). For large grid
sizes, the process of applying the time-update and
measurement-update can be computationally expen-
sive. Hence, classical approaches must perform sev-
eral cost-saving measures to run in real-time. Firstly,
the measurement likelihood for each cell of the grid
is pre-computed, i.e. a ray-casting operation is per-
formed to compute p(o
t+1
|x
t+1
) for all |N
x
| × |N
y
| ×
|N
ξ
|. Secondly, the belief space is assumed to coa-
lesce around only a small number of modes; hence,
only a small number of belief clusters need to be
maintained. Essentially, the latter assumption relaxes
the grid-based localization to an approximate multiple
hypothesis Kalman filter.
The large up-front cost of the ray-casting pre-
computations can be prohibitive, especially, for op-
erations where the map may be parametrizable and
therefore changes every iteration. Therefore, we want
our approach to avoid the large up-front cost, while
being able to maintain a real-time computational load
during the measurement update phase.
With regards to the previously mentioned relax-
ation, the assumption of the belief space coalescing
around only a small number of modes is, in general,
inappropriate for cases where only a sparse number
of measurement will be taken overall. In our case, the
number of samples is small and each measurement
could be corrupted by noise or outliers. The outlier
case means that we can not readily discard considera-
tion of low belief regions, since it may be attributable
to an unfortunate erroneous measurement early-on.
In practical scenarios, we find indoor room scenes
to comprise of at least one large open space. In these
cases, the enclosed area of the floor-plan greatly ex-
ceeds the perimeter of the delineating outline. A clas-
sical grid-based localization technique would need to
consider every interior cell of the model and perform a
large up-front ray-casting operation; thereby working
from the inside-out Thrun et al. (2005). In contrast,
due to the computational load, we opt to instead dis-
cretize the perimeter of the floor plan, e.g., walls, and
work from the outside-in. A reasonable discretization
of the perimeter can be significantly smaller than the
encompassing area. The discretization can be carried
out very quickly, since it only requires traversing a
series of line segments. We can construct a lookup ta-
ble for each discrete point along the perimeter which
stores the position of the model centroid relative the
point position, (−x
d
m
, −y
d
m
). We assume the model to
be centered at the origin. We also store the outward-
facing normal at each discrete point (n
d
x
, n
d
y
). This
fast lookup table construction process is repeated for
|N
ξ
| rotated versions of the model, to construct a table
LUT(d, ξ) similar to an R-table in the GHT algorithm.
Given a new observation, we iterate through our
table LUT(d, ξ) for each discrete point and possi-
ble rotation. We perform several pre-filtering checks
to confirm whether we need to accumulate a vote
based on feasibility conditions such as the hypothe-
sized pose being within the model and the incidence
angle being feasible. Hence, we avoid unnecessary
computation both online as well as via any large up-
front pre-computations. We outline the preconditions
in Algorithm 1 and our voting scheme in Algorithm 2.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
840
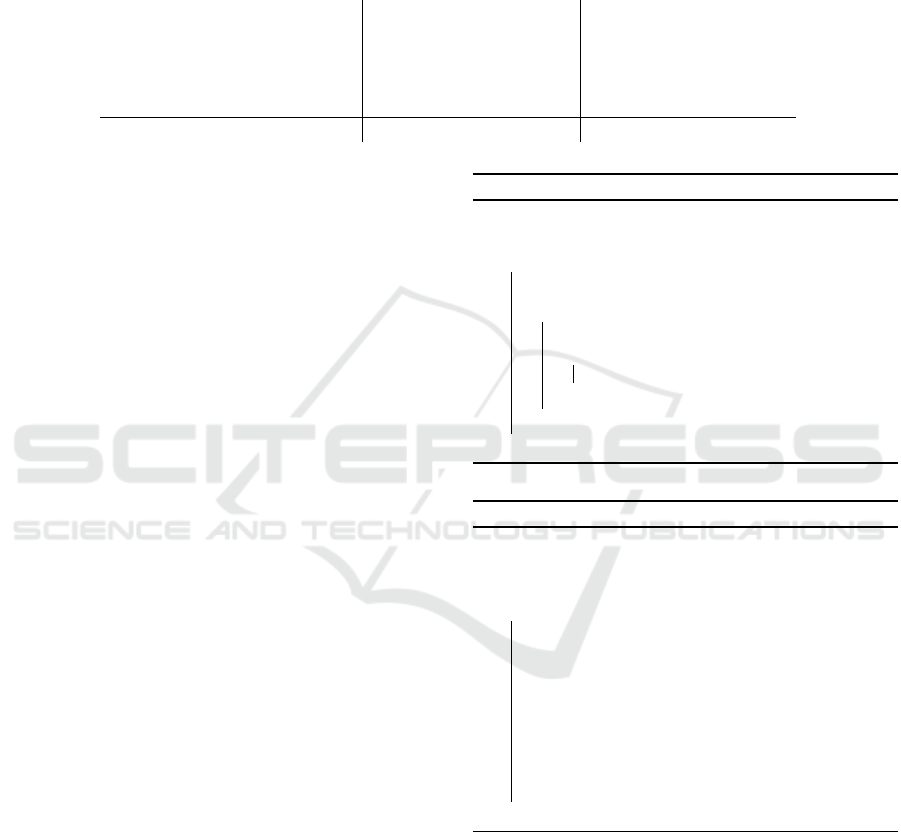
Table 1: Computational comparison between our approach and classical approach to grid-based localization with fixed-grid
size. We assume we consider the full belief space at each iteration, since we consider a sparse number of measurements and
possible outliers. The computational difference stems from the size of the area of the floor-plan A versus the resolution of
the perimeter discretization D. For the majority of floor-plans, a large open area surrounds the visual center of the floor-plan
model; hence, a convex approximation of this space can clearly illustrate the computational advantage of our approach for a
limited set of measurements. Our computation for each accumulation phase is slightly larger; however, our up-front cost is
dramatically less. Especially for cases of dynamic map models, where only a small number of measurements are made with
a given map configuration under consideration, our approach can be seen to be more efficient.
Algorithm Stage Classical Approach Our Approach
Ray-Casting Precomputations O(|E||A||N
ξ
|) N/A
R-table Construction N/A O(|E||D||N
ξ
|)
Preconditions N/A O(|D||N
ξ
|)
Accumulation (LUTs) O(|A||N
ξ
|) O(|D||N
ξ
|)
Total O((|E||A||N
ξ
| + |A||N
ξ
|) O(|E||D||N
ξ
| + |D||N
ξ
|)
The localization algorithm is a voting-based al-
gorithm; hence, it is able to cope with multi-modal
belief spaces. Classical Bayesian approaches to lo-
calization (Thrun et al., 2005) can suffer in the pres-
ence of outliers, due to the tendency for erroneous
likelihoods to null the posterior resulting in the per-
manent loss of information. Most of these meth-
ods will attempt to cope with outliers via additive
non-informative priors to account for outliers in the
measurement likelihood distribution (i.e., an additive
small uniform probability), which prevents zeroing of
the belief space. Contrarily, a voting-based approach
is non-destructive and hence can accommodate a high
percentage of outliers.
Our algorithm also checks several preconditions
prior to accumulating a given vote into the belief
space which further helps handle outliers. The pre-
conditions are sanity checks: require that the mea-
surement originate from within the model (i.e., fea-
sible measurement given assumption sensor is within
model) and require the incidence angle of the mea-
surement with the model surface is within a certain
tolerance of the surface normal (i.e., obtuse incidence
angles can be pruned, since they are unlikely to have
returned sufficiently strong sensor signal).
We present a side-by-side computational order
comparison with classical approaches (Fox et al.,
1998) in Table 1.
3.3 Sparse Registration
Once a coarse registration of the floor-plan model has
been made against the current scene, we use a sparse-
registration strategy to refine the registration estimate.
The sparse-registration performs an iterative process
similar to ICP; whereby, we alternate between phases
of correspondence-matching and optimization over
the pose of the model. Algorithm 3 details our work-
flow for sparse-registration. As with classical point-
set registration techniques, the optimization is prone
Algorithm 1: Check Preconditions.
Result: Whether to accumulate a vote
Given an input sample measurement;
for ξ ∈ N
ξ
do
if Scene normal (n
d
x
, n
d
y
) feasible given
sample then
if Hypothetical agent pose relative
scene lies within model then
Vote for Sample, Algorithm 2
end
end
end
Algorithm 2: Accumulate Vote.
Result: Whether to accumulate a vote
Given input sample measurement and rotation
angle of model;
for neighbourhood of vote location do
Compute vote-weight at neighbourhood
point, based on measurement model of
sensor;
Compute spatial proximity weight for
location;
Compute rotational proximity weight for
location;
Add combined vote-weight to location;
end
to converging to local optima or flat regions in the
registration error function due to the non-linear corre-
spondence matching. Our sparse registration follows
a similar workflow to Arun Srivatsan et al. (2019) by
perturbing our solution after every optimization rou-
tine. We anneal the perturbations gradually in magni-
tude as the registration routine approaches an optima.
The inner-optimization routine performs an ICP
algorithm, which solves for the registration pose T of
the model given a set of observations {o
i
∈ O}
N
O
i=0
.
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing
841

We perform correspondence-matching by projecting
each observation o
i
to the nearest point on the model
M , while satisfying a set of constraints C . If the
set of feasible points is empty, we relax the con-
straints and opt for the nearest point, albeit with a
lower weight assignment to that correspondence. In
practice, observations tend to be less reliable when
taken at oblique angles to the walls of a surround-
ing scene. Hence, we weight each correspondence by
the cosine of the incidence angle the ray cast of the
observation makes with the surface normal. We also
constrain the correspondence-matching to search for
nearest matches with a more natural incidence angle
before considering the more extreme oblique case.
We follow Rusinkiewicz and Levoy (2001) by per-
forming outlier-rejection on any correspondences in
the high percentiles in terms of distance error. The op-
timization routine minimizing the weighted error be-
tween our correspondences has an analytical solution
for
ˆ
T ∈ SE(2),
Γ = (M −
¯
m)
T
W(O −
¯
o)
ϑ = arctan
[Γ]
01
− [Γ]
10
tr(Γ)
t =
¯
o − R
ϑ
◦
¯
m,
(6)
where ϑ is the rotation angle between the current
model pose and scene, and M,
¯
m, O,
¯
o are the model
correspondents (stacked row-wise), the model cen-
troid, the observation correspondents (stacked row-
wise), and the observations’ centroid, respectively.
Algorithm 3: Sparse Registration.
Result:
ˆ
T ∈ SE(2)
Given initial estimate T
0
, k = 0;
while !converged do
Generate perturbations of estimate;
T
i
k
|T
k
+ ε
T
∼ N (0, σ);∀i ∈ N
0
∪ [0, M];
Select
ˆ
j = arg min
j
E(T
j
k
) ;
Solve
ˆ
T
k+1
= SparseICP(T
ˆ
j
k
);
if E(
ˆ
T
k+1
< E(T
j
k
) then
T
k+1
=
ˆ
T
k+1
;
else
T
k+1
= T
j
k+1
;
end
Update perturbation σ ∝
p
E(T
k+1
);
end
Algorithm 4: Sparse ICP.
Result:
ˆ
T ∈ SE(2)
Given initial estimate T
0
, k = 0;
while !converged do
Apply transform to model M
k
= T
k
◦ M
k−1
;
Find correspondences between model and
observations;
(m
i
, o
j
)|m
i
v o
j
, m
i
∈ M
k
, o
j
∈ O ∀i, j ∈ N
0
;
Outlier rejection;
(m
i
, o
j
)|km
i
− o
i
k < ε
reject
;
Optimize
T
k+1
= argmin
T
∑
N
k
−1
i=0
kT ◦ m
i
− o
i
k
2
ω
i
;
end
3.4 Evaluation Metrics
Due to partial and complete symmetries in our ran-
domly generated floor-plans, we want to avoid penal-
izing the system for registering model with an equally
valid registration. A prototypical example would be a
square floor-plan, which has four equally valid regis-
trations, in the absence of any user-annotation indi-
cating a preferred option. If we were to provide four
different reward signals based on these four equally
valid registrations, we would confound the optimiza-
tion routine which must now harmonize this one-to-
many mapping. In this vein, we use the symmetry-
aware pose representation of Br
´
egier et al. (2018) for
each floor-plan.
We quantify the pose of a floor-plan by a transfor-
mation T ⊂ S E(2), which maps the outline compris-
ing the floor plan from a canonical inertial frame to
an object frame (Br
´
egier et al., 2018). Each floor-plan
belongs to its own group of proper symmetries G such
that the pose of the floor-plan is invariant to any trans-
formation belonging to this group. Our prototypical
square floor-plan would be invariant to 90
◦
rotations
about the centroid. We adopt the pose-distance d
P
(˙,
˙
)
proposed by Br
´
egier et al. (2018) for transformations
in SE(2),
d
P
(P
1
, P
2
) = argmin
G
1
,G
2
∈G
ˆ
d
P
(T
1
◦ G
1
, T
2
◦ G
2
)
ˆ
d
P
(T
1
, T
2
) =
r
1
L
Z
S
µskT
1
(s) − T
2
(s)k
2
ds,
(7)
where L is the perimeter length of the floor-plan and
S is the perimeter of the floor-plan. We can sim-
plify Equation 7 by assuming the floor-plan is cen-
tered about its center of mass. In practice, we will
choose a reference frame with its origin at the center
of mass of the model floor-plan when evaluating the
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
842

Table 2: Table of Pose Representatives in SE(2) from Br
´
egier et al. (2018).
Proper Symmetry Class Proper Symmetry Group Pose Representative
Circular Symmetry SO(∈) t ∈ R
2
No Proper Symmetry {I} (Λe
iθ
, t
T
)
T
∈ R
4
Cyclic Symmetry R
2kπ
n
|k ∈ Z ∪ [0, n] {(Λe
i(θ+
2kπ
n
)
, t
T
)
T
∈ R
4
|k ∈ Z ∪ [0, n]}
pose-distance between the scene and the registered
model. The simplification is as follows,
d
P
(P
1
, P
2
) = kt
1
− t
2
k
2
(8)
+ min
G
1
,G
2
∈G
1
L
Z
S
µskR
1
G
1
(s) − R
2
G
2
(s)k
2
ds
(9)
where we separate a transformation T
i
into its con-
stituent rotational R
i
∈ S O(2) and translational t
i
∈
R
2
parts. The group of symmetries can be treated as a
group of rotations about the center of mass of the ob-
ject; hence, a group member G
j
∈ G can be reduced
to a rotation G
j
∈ SO(2).
From Equation, 9, one can show (Br
´
egier et al.,
2018) that the pose distance between two transfor-
mations can be reduced to the Euclidean norm be-
tween two pose-representatives. Table 2 demon-
strates the pose-representative of a given floor-plan
depending on the symmetry class. Historically, at-
tempts at constructing metrics for comparing poses
in SE(2) or SE(3) had found it difficult to decide
how to weight the rotational and translational error.
The pose-representative uses the inertia matrix Λ to
weight the rotational error,
Λ =
Z
1
L
Z
S
µksk
2
ds. (10)
When evaluating the pose error in our final registra-
tion, we construct a pose-representative for our model
and our estimate. The pose-representative necessi-
tates that we detect symmetries present in the floor-
plan. We use the symmetry detection algorithm out-
lined in Wolter et al. (1985). The wall junctions of
the floor-plan can be represented as a collection of
points x
i
∈ R
2
. We use an edge-chain to encode the
sequence of points by the interior angle of each con-
secutive triplet of points, i.e x
i−1
, x
i
, x
i+1
and the dis-
tance to the next point in the chain, i.e., kx
i
− x
i+1
k
2
.
The encoded sequence is a vector of tuples, i.e.,
[s
0
, s
1
, ·, s
N
], where s
i
= (φ, ρ) ∈ [0, 2π] × R
+
.
By constructing the a 2N − 1-length sequence,
[s
1
, s
2
, ·, s
N
, s
0
, ·, s
N
] , we can perform fast symmetry
detection by sub-string matching the new sequence
against the original encoded sequence. We assign an
equivalence class for edge angles
ˆ
φ ∼ φ, ∀{
ˆ
φ|
ˆ
φ + ε
φ
∈
φ + j2π, j ∈ Z}, and the equivalence class for edge
distances
ˆ
ρ ∼ ρ, ∀{
ˆ
ρ|k
ˆ
ρ − ρk <
ε
ρ
ρ
}. The equivalence
classes provide a bit of freedom to detect near sym-
metries via the soft tolerances, ε
ρ
and ε
φ
.
3.5 Inspection Tool
We release a full simulation environment with our
work, which may benefit further research into learn-
ing active sampling strategies. Along with the simu-
lation environment and the previously discussed mod-
ules (Section 3.3,3.2, and 3.1), we also provide an
inspection tool for debugging learnt strategies. Be-
haviour learnt via reinforcement learning can be chal-
lenging to debug due to the changing system dy-
namics and state-dependent nature of the system.
Hence, we provide a tool which logs a minimal state-
trajectory, i.e., a trajectory comprising of the state at
each step along the episode, for offline debugging.
Our inspection tool can be run on the state-trajectory
to visualize the state-representation at each time-step
with easily accessible sliders for navigating to the de-
sired time-step. Since the dimensionality of the belief
space of the agent pose will, in general, be greater or
equal to 3D, we provide a slider for easily navigating
along the different channels of the belief space. The
most useful debug feature of the inspection tool is the
ability to toggle on and off a guided-backpropagation
view of the state-space (Springenberg et al., 2014).
The selected action at each time-step is used as the tar-
get class for the guided-backpropagation; therefore,
we are able to see heat-maps on each state compo-
nent showing the areas of the state most prominent in
eliciting the chosen action.
4 EXPERIMENTS
We evaluate our system in the context of fast and ac-
curate model-based sparse-registration within an in-
door scene. We consider the 2D floor-plan scenario,
since it allows for more concrete analysis on whether
our agent is learning effective sampling strategies.
4.1 Dataset
We generate floor-plans using our simulation environ-
ment. We create floor-plans of single rooms based
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing
843
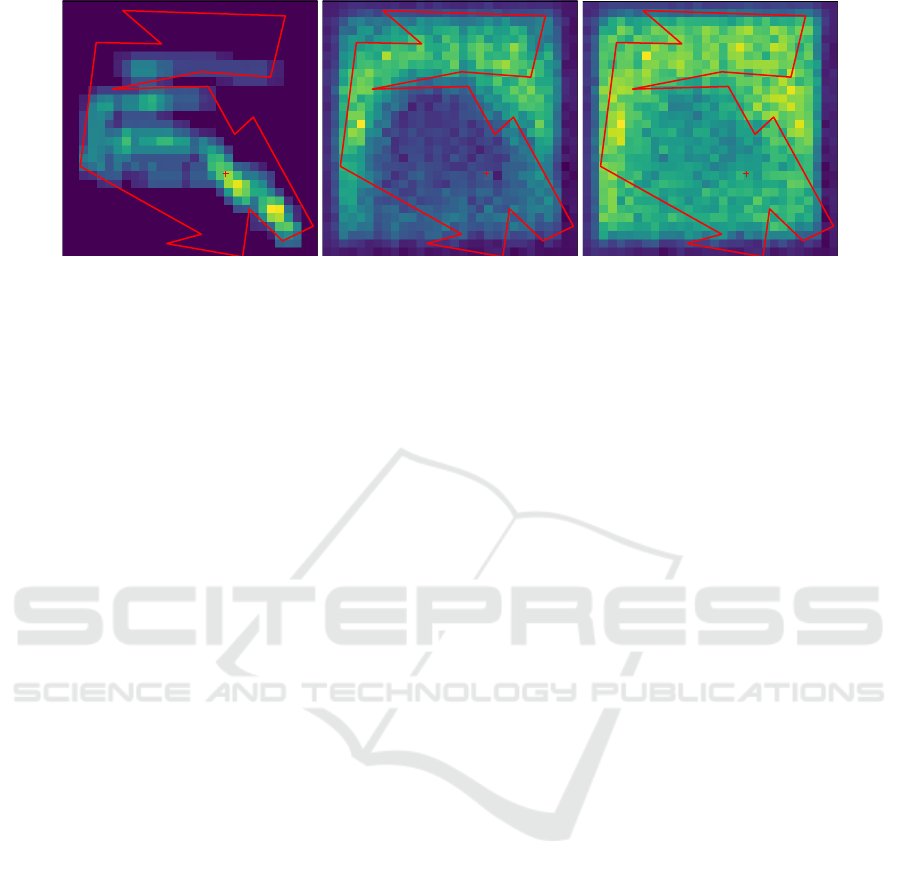
Figure 4: We use our inspection tool to slide through each time-step of a given active sampling episode. The inspector tool
uses Guided Back-Propagation Springenberg et al. (2014) to show which areas of the input belief map (left) are active when
the agent selects the measurement action (middle), or a rotation action (right). Evidently, the agent has learnt to use the belief
map as a form of prior on the agent pose (or coarse registration). We can interpret the activations as the following: If the belief
map indicates the agent is likely to be in an unexpected region of the scene, i.e., far from the visual center, it encourages the
agent to take more measurements. Similarly, the agent is encouraged to explore (rotate) when the current belief has unexpected
peaks, but not to the same extent as a measurement action. Noteworthy, we have normalized the activations for visualization
purposes.
on an underlying non-convex polygonal model. Each
floor-plan can be seeded by a random 32bit integer;
hence, we generate a training and evaluation set of
seed indices. We compute the floor-plans on-the-fly
during the training process, which facilitates quicker
debugging when making small changes to the algo-
rithm.
In our experiments, we configure our observations
of the environment to be topological scans of only 20
pixels wide, covering a 45
o
FOV. The reason for the
low dimensional observation is primarily due to its
portability to the real-world. We commonly refer to
porting algorithms trained in simulation to the real-
world as bridging the domain gap. The domain gap
is widened when training based on simulated high-
dimensional raw pixel representations of the environ-
ment. The gap can be narrowed when an efficient
meta-representation of the sensor readings can be re-
liably generalized to the real-world scenario. The
low-dimensional topological scans detect wall inter-
sections which could be readily extracted via passive
edge-detection techniques, assuming no large floor
to ceiling occluders. We have this in common with
early-work from Active Localization community, al-
beit with the motivation that the simulation of indi-
cators based topology are much more easily portable
and accessible to the real-world scenario.
4.2 Active-sampling Experiments
We train our approach on a larger dataset comprising
20,000 simulated floor-plans. The number of transla-
tion is set to 30, and we test two cases for the number
of rotation bins - 1 and 10. The maximum allotted
time to complete a registration is set to 500 actions.
The heuristic approaches are separated into two
categories: blind agents and heuristic agents. The
blind agents perform actions based on a fixed proba-
bility mass function; hence they effectively ignore any
observations or the current system state. The heuristic
agents perform different pragmatic strategies which
are intuitively well-suited for localization, such as
performing a sensor measurement intermittently with
a constant direction of rotation. The different heuris-
tic approaches are defined in Table 3.
We compare our approach against the previously
discussed collection of heuristic and blind alterna-
tives. The various sampling strategies are evaluated
on a collection of 1000 different floor-plans from a
test set. The agent is instantiated randomly about the
visual center of the floor-plan as a sample from a uni-
form distribution with a radius equal to the nearest
distance between visual center and any wall of the
floor-plan. The agent’s initial rotation is sampled uni-
formly from [0, 2π].
In the first experiment we use the coarse registra-
tion error as a termination condition. Therefore, the
agent tries to learn an efficient sampling strategy of
the scene in order to quickly reduce the uncertainty
based on our grid-based localization. We use penal-
ties for each measurement and rotation action under-
taken by the agent, with penalties of 0.05 and 0.005,
respectively. Evidently, the measurement cost is an
order of magnitude larger to represent the disparity
between the time needed for a small pose adjustment
versus a high-accuracy measurement sample. We pro-
vide a standard +1 reward if the agent is able to find
a coarse registration in the allotted time, and −1 if the
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
844

Table 3: Definition of Heuristic Approaches.
Heuristic Description
blind-0 Selects left rotation, and depth measurement 75%, and 25% of the time, respectively.
blind-1 Selects left rotation, and depth measurement 50% of the time.
blind-2 Selects right rotation, left rotation, and depth measurement 33%, 33%, and 34% of the time, respectively
heuristic-0 Alternates between a left rotation and depth measurement
heuristic-1 Rotates in only left direction and samples depth measurement every 6
th
action
heuristic-2 Rotates in only left direction and samples depth measurement every 18
th
action
heuristic-3 Rotates in only left direction and samples depth measurement every 54
th
action
allotted time is exceeded. We use a clipped quadratic
reward for minimizing the final registration error be-
low an acceptable threshold. To ensure the agent suf-
ficiently explores the state-space prior to converging
on a good strategy, we provide an exploration bonus,
which we decay as the inverse of the visitation fre-
quency (Audibert et al., 2009). We add the explo-
ration bonus to states based on their episode length. In
this way, the bonus acts akin to simulated annealing,
in that the agent explores lengthier sequences initially
before condensing on shorter sequences as the bonus
cools.
Table 4 shows the comparison results for our
learnt strategy against the heuristic approaches. Due
to the small number of measurements required to pro-
duce a coarse registration of the scene with a known
model, we find heuristic approaches provide a com-
petitive benchmark for evaluation.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Understanding Strategies
Given our learnt active-sampling strategy, we use the
inspection tool to glean insights into the behaviour of
our policy. The first insight comes from analyzing
successful runs of our system and checking which ar-
eas of the belief map are active, i.e., grid cells respon-
sible for encouraging the agent to take the action it
ultimately chooses.
Figure 4 depicts the outline of a generated floor-
plan overlaid on activation heatmaps for a measure-
ment (middle) and rotation (right) action. The regions
of higher activation are shown in brighter shades of
yellow, whereas the darker blue shades indicate low
activity. Evidently, the heatmap for the measurement
action illustrates a tendency for the agent to encour-
age measurement actions, when there is substantial
belief probability mass near the periphery of the floor-
plan. A similar pattern emerges with the rotation ac-
tion, albeit to a lesser extent, in that rotation actions
are encouraged when the belief map has mass near
the periphery, since the agents are initialized about
the visual center of the scene. We can interpret this
behaviour as the agent learning a prior over the agent
initialization within the floor-plan, and encouraging
exploratory, i.e., probing behaviour, when the belief
map deviates from this expectation. Another indi-
cation that the agent is learning effective behaviour
comes from its decision to exclusively choose either
left rotations or right rotations, but never both within
the same episode. This behaviour is arguably benefi-
cial for our experiments, since alternating rotation di-
rections would be inefficient once a certain direction
has been chosen.
5.2 Future Work
We use the success of our coarse registration algo-
rithm (Section 3.2 to determine the ground-truth lo-
cation (i.e., within coarse bounds) as a termination
condition on the action sequence. In practice, the
ground-truth pose of the agent within the scene is not
known; hence, the termination condition is subject to
the user’s discretion based on a feedback visualiza-
tion of the registration. Naturally, once the automatic
procedure finds an approximately correct registration
and the user signals completion, the system will then
perform a refinement step based on the sample mea-
surements which will exceed the accuracy percepti-
ble by the user. The envisioned user-interface is out-
of-scope of the current paper, which concentrates on
learning efficient sampling strategies. We see this in-
teraction in an Augmented Reality (AR) setting as
promising future work.
We note an improved performance margin of our ap-
proach over heuristic benchmarks with an increase
in the dimensionality of the pose-space. We expect
larger performance gains as the complexity of the task
increases, as would be the case in the 3D floor-plan
setting. We consider the 3D-setting and an expanded
evaluation including a variant of AMCL, applicable
to our dual-objectives, as future work.
Learning Effective Sparse Sampling Strategies using Deep Active Sensing
845

Table 4: Active sampling strategy versus Heuristic Approaches to sampling the scene. We allot each algorithm 100 actions to
find a coarse registration of the scene. The non-trivial rotation case, i.e. 10 rotation bins, is shown in parentheses along side
the rotation-free, i.e. 1 rotation bin, case. The heuristic methods present a competitive benchmark in the rotation-free case
due to the simplicity. Moreover, it presents a good scenario for eliciting insights on the inner workings of the active-sampling
strategy. Our approach can be seen to learn effective strategies relative to the pragmatic heuristic approaches as seen in our
high recognition rate and low pose-error, i.e. high registration accuracy.
Sampling Approach Recognition Rate Pose-Error Average # of Measurements Average # of Rotations
Our approach 0.997 (0.966) 0.0541 (0.0627) 4.084 (8.524) 9.777 (26.552)
blind-0 0.987 (0.862) 0.0595 (0.1740) 5.354 (13.355) 16.214 (39.891)
blind-1 0.977 (0.794) 0.0706 (0.2549) 11.179 (27.894) 11.146 (27.941)
blind-2 0.698 (0.243) 0.2150 (0.8040) 15.468 (28.837) 30.079 (56.506)
heuristic-0 0.989 (0.891) 0.0651 (0.1525) 9.323 (24.026) 8.544 (23.429)
heuristic-1 0.994 (0.940) 0.0507 (0.0921) 3.199 (7.248) 11.539 (32.390)
heuristic-2 0.951 (0.640) 0.0644 (0.3861) 2.439 (4.577) 25.506 (65.097)
heuristic-3 0.639 (0.115) 0.2117 (0.9036) 1.713 (1.961) 54.447 (93.563)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was enabled by the Competence Cen-
ter VRVis. VRVis is funded by BMVIT, BMWFW,
Styria, SFG and Vienna Business Agency under the
scope of COMET - Competence Centers for Excel-
lent Technologies (854174) which is managed by
FFG. We acknowledge the support of the Natural Sci-
ences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
(NSERC) [516801].
REFERENCES
Arun Srivatsan, R., Zevallos, N., Vagdargi, P., and Choset,
H. (2019). Registration with a small number of sparse
measurements. The International Journal of Robotics
Research, page 0278364919842324.
Audibert, J.-Y., Munos, R., and Szepesv
´
ari, C. (2009).
Exploration–exploitation tradeoff using variance esti-
mates in multi-armed bandits. Theoretical Computer
Science, 410(19):1876–1902.
Ballard, D. H. (1981). Generalizing the hough trans-
form to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern recognition,
13(2):111–122.
Br
´
egier, R., Devernay, F., Leyrit, L., and Crowley, J. L.
(2018). Defining the pose of any 3d rigid object and
an associated distance. International Journal of Com-
puter Vision, 126(6):571–596.
Chaplot, D. S., Parisotto, E., and Salakhutdinov, R.
(2018). Active neural localization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1801.08214.
Fox, D., Burgard, W., and Thrun, S. (1998). Active markov
localization for mobile robots. Robotics and Au-
tonomous Systems, 25(3-4):195–207.
Gelfand, N., Ikemoto, L., Rusinkiewicz, S., and Levoy, M.
(2003). Geometrically stable sampling for the icp al-
gorithm. In International Conference on 3-D Digital
Imaging and Modeling, 2003. 3DIM 2003. Proceed-
ings., pages 260–267. IEEE.
Gottipati, S. K., Seo, K., Bhatt, D., Mai, V., Murthy, K.,
and Paull, L. (2019). Deep active localization. IEEE
Robotics and Automation Letters, 4(4):4394–4401.
K
¨
ummerle, R., Triebel, R., Pfaff, P., and Burgard, W.
(2008). Monte carlo localization in outdoor ter-
rains using multilevel surface maps. Journal of Field
Robotics, 25(6-7):346–359.
Mnih, V., Badia, A. P., Mirza, M., Graves, A., Lillicrap, T.,
Harley, T., Silver, D., and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2016).
Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learn-
ing. In International conference on machine learning,
pages 1928–1937.
Rusinkiewicz, S. and Levoy, M. (2001). Efficient variants of
the icp algorithm. In International Conference on 3-
D Digital Imaging and Modeling, 2001. 3DIM 2001.
Proceedings., volume 1, pages 145–152.
Schulman, J., Levine, S., Abbeel, P., Jordan, M., and
Moritz, P. (2015). Trust region policy optimization. In
International conference on machine learning, pages
1889–1897.
Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., and
Klimov, O. (2017). Proximal policy optimization al-
gorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347.
Springenberg, J. T., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T., and Ried-
miller, M. (2014). Striving for simplicity: The all con-
volutional net. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6806.
Sutton, R. S. and Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement learn-
ing: An introduction. MIT press.
Thrun, S., Burgard, W., and Fox, D. (2005). Probabilistic
robotics. MIT press.
Torsello, A., Rodola, E., and Albarelli, A. (2011). Sampling
relevant points for surface registration. In 2011 Inter-
national Conference on 3D Imaging, Modeling, Pro-
cessing, Visualization and Transmission, pages 290–
295. IEEE.
Wolter, J. D., Woo, T. C., and Volz, R. A. (1985). Optimal
algorithms for symmetry detection in two and three
dimensions. The Visual Computer, 1(1):37–48.
VISAPP 2020 - 15th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
846
