
AI-Rehab: A Framework for AI Driven Neurorehabilitation
Training - The Profiling Challenge
Yuri Almeida
1,2
a
, Manisha Sanjay Sirsat
2 b
, Sergi Berm´udez i Badia
1,3 c
and Eduardo Ferm´e
1,2 d
1
Universidade da Madeira, Portugal
2
NOVA-LINCS, Portugal
3
Madeira Interactive Technologies Institute, Portugal
Keywords:
Long Term Care in Cognitive Neurorehabilitation, Profiling Challenges, Machine Learning, Belief Revision.
Abstract:
One of the health clinic challenges is rehabilitation therapy cognitive impairment that can happen after brain
injury, dementia and in normal cognitive decline due to aging. Current cognitive rehabilitation therapy has
been shown to be the most effective way to address this problem. However, a) it is not adaptive for every
patient, b) it has a high cost, and c) it is usually implemented in clinical environments. The Task Generator
(TG) is a free tool for the generation of cognitive training tasks. However, TG is not designed to adapt and
monitor the cognitive progress of the patient. Hence, we propose in the BRaNT project an enhancement of
TG with belief revision and machine learning techniques, gamification and remote monitoring capabilities to
enable health professionals to provide a long-term personalized cognitive rehabilitation therapy at home. The
BRaNT is an interdisciplinary effort that addresses scientific limitations of current practices as well as provides
solutions towards the sustainability of health systems and contributes towards the improvement of quality of
life of patients. This paper proposes the AI-Rehab framework for the BRaNT, explains profiling challenge in
the situation of insufficient data and presents an alternate AI solutions which might be applicable once enough
data is available.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cognitive deficits are common after brain injury, de-
mentia and normally due to aging. These impact the
performance of activities of daily living and limit peo-
ple’s independence, with a high monetary and societal
cost. Moreover, many cognitive rehabilitation tools
lack flexibility to be adapted to each patient needs.
Cognitive rehabilitation has been shown to be the
most effective way to address this problem. However,
current rehabilitation has some limitations:
• Rehabilitation tools are not adaptive and may not
be adequate for every patient. Hence, a sub-
optimal set of exercises limits the impact of re-
habilitation and reduces engagement in rehabili-
tation;
• Interventions are time consuming and have a high
cost, and are usually implemented in clinical envi-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3213-7514
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5696-3602
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4452-0414
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9618-2421
ronments. Thus, the lack of monetary and human
resources prevent public health systems to imple-
ment ideal long-term rehabilitation.
Neuropsychological assessments (NPAs) are use-
ful instruments to evaluate cognitive skills. How-
ever, current cognitive interventions are sub-optimal
in terms of lack of adaptability according to the NPAs
results (Williams and Sims, 2000; Parsons, 2015).
Besides, the tools are not flexible enough to cover the
needs of all patients and traditional therapy has a high
cost both on human and monetary resources (Solana
et al., 2014). Here we propose bridging NPAs and
computational modelling to deliver a highly personal-
ized tool that allows for the creation of interventions
through Information and Communication Technolo-
gies (ICT). A tool that could generate validated cog-
nitive training tasks, parameterizedper patients needs,
which intelligently adjusts difficulty over time, mon-
itors changes and communicates with the patient’s
healthcare team. We start by creating an extension
and enhancement of an existing tool, the Task Gen-
erator (TG
1
) (Faria and Berm´udez i Badia, 2015), to
1
http://neurorehabilitation.m-iti.org/TaskGenerator/
Almeida, Y., Sirsat, M., Bermúdez i Badia, S. and Fermé, E.
AI-Rehab: A Framework for AI Driven Neurorehabilitation Training - The Profiling Challenge.
DOI: 10.5220/0009369108450853
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 845-853
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
845

generate the appropriatecognitive training tasks using
the patient profile as an input. The TG is a free web
based tool for the procedural generation of cognitive
training tasks. TG tasks are parametrized in terms
of training difficulty and cognitive demands, but are
not designed to monitor the evolution of the patient,
which is essential to adjust training for the patient’s
evolution. In the BRaNT project, we are develop-
ing an extension of TG with extended and improved
training content. This project uses two artificial in-
telligence modules (based on belief revision and ma-
chine learning techniques), gamification and remote
monitoringcapabilities to enable Health Professionals
(HP) to provide long-term personalized cognitive re-
habilitation therapy at home. AI-Rehab is the frame-
work behind the personalization and adaptation of
training, and relies on the results of validated NPA
used to evaluate patient and create a computational
Cognitive Profile (CP) of the patient. By comparing
this profile with the Normative Data (ND) accord-
ingly to the Socio-Demographic Information (SDI)
of the patient, we infer the patient’s Cognitive Sta-
tus (CS). After this, the HP can decide on a set of
training tasks for that patient. The patient trains at
home and the performance is communicated to Be-
lief Revision Engine (BR-E), which assesses evolu-
tion of the patient and manages task personalization
over time. The proposed system will be able to con-
tact the HP if something unexpected happens. This
framework tackles three important Artificial Intelli-
gence (AI) challenges: patient profiling, task selec-
tion and parameterization, and adaptive training. In
this paper we propose a solution for the patient pro-
filing challenge. In the Section 2, we review some
literature about assessment of cognitive impairment
and AI in cognitive rehabilitation field whereas, Sec-
tion 3 gives detailed explanation on each step of pro-
posed AI-Rehab framework. Section 4 describes the
patient’s profiling challenge and finally, its AI solu-
tion is reported in the Section 4.1, including task set-
ting and iterative training.
2 STATE OF THE ART
Cognitive impairments following brain injury are
common, and are present in approximately 70% of
patients in the acute stages of recovery (Morris et al.,
2012), causing problems in activities of daily life and
social participation. Stroke commonly includes focal
disorders such as aphasia and neglect, and more dif-
fuse abnormalities such as slowed information pro-
cessing and executive dysfunction (Cumming et al.,
2013). Cognitive rehabilitation is designed to re-
store, substitute, or compensate for the lost of cog-
nitive abilities, and is the treatment of choice for
these deficits (Bott and Kramer, 2017). The Amer-
ican Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine conducted
systematic reviews on a total of 370 cognitive rehabil-
itation studies for people with acquired brain injury,
published from 1971-2008 (Cicerone et al., 2000; Ci-
cerone et al., 2005; Cicerone et al., 2011). Cogni-
tive rehabilitation was shown to be of greater benefit
than conventional rehabilitation in 94.1% of the stud-
ies. Thus, cognitive rehabilitation is the best avail-
able form of treatment for people with neurocognitive
impairment (Cicerone et al., 2011). Unfortunately,
the efficacy of cognitive training highly depends on
the intensity of treatment over an extended period of
time. The traditional intervention model is very time
consuming for teams to manage personalized rehabil-
itation programs; patients move to the clinical center,
making the duration of the treatment conditional to
patient’s availability; interventions are subject to the
availability of vacancies and transportation (Solana
et al., 2014). This results in a very high cost, com-
promising sustainability, accessibility and scalability,
resulting in a large economic burden to both the health
system and families (Carod-Artal et al., 2000).
The ICT based solutions such as gaming, virtual
reality or computer simulations have been shown to
have an enormous potential for enhancing cognitive
rehabilitation by supporting the ability to carry out
controlled and highly adaptive valid tasks (Berm´udez
i Badia et al., 2016). Over the past few years, sev-
eral computer based solutions have been proposed
to increase the availability and quality of cognitive
training, flooding the marketplace with commercial
brain exercise programs that claim to improve cogni-
tion and have diagnostic abilities (George and White-
house, 2011) such as the CogWeb and the Guttmann
Neuro Personal Trainer. Through these platforms it is
possible to deliver a training program to a patient, an-
alyze results and transfer them to the Hospital Infor-
mation System. Nevertheless, none of these tools ad-
dresses multiple domains of cognitive functioning in
a systematic and quantitative manner relying on vali-
dated NPAs.
2.1 Assessment of Cognitive
Impairment
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA)
(Nasreddine et al., 2005) is a well-known test which
is the recommended instrument in Portugal for global
cognitive screening measurement. It addresses (i)
short-term memory, (ii) executive functions, (iii)
visuospatial abilities, (iv) language, (v) attention,
Cognitive Health IT 2020 - Special Session on Machine Learning and Deep Learning Improve Preventive and Personalized Healthcare
846
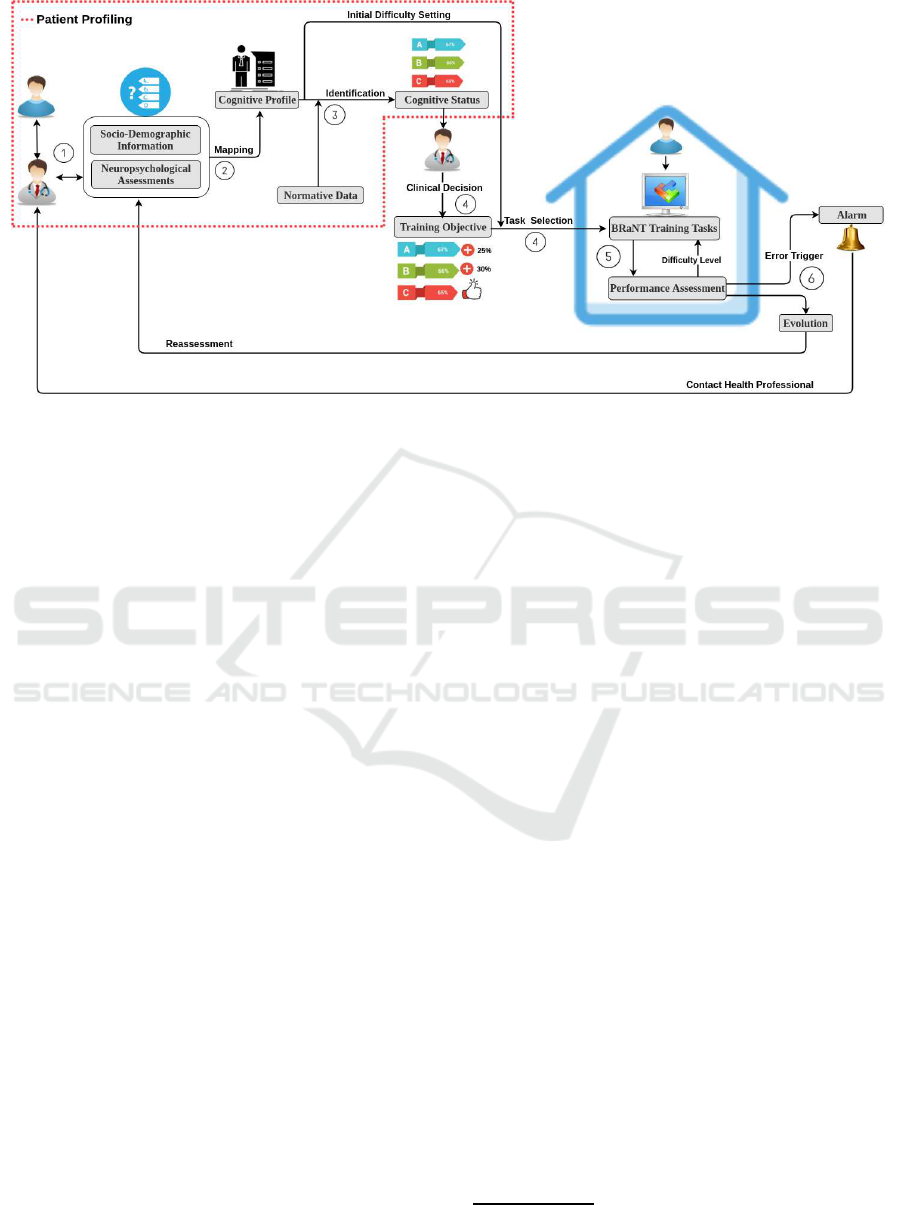
Figure 1: The AI-Rehab framework for the BRaNT project.
concentration and working memory and (vi) temporal
and spatial orientation (Freitas et al., 2012c). MoCA
has been the subject of systematic research within the
Portuguese population and validation studies were
conducted on specific clinical groups like Mild Cog-
nitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease (Freitas
et al., 2013), Frontotemporal Dementia (Freitas et al.,
2012a), Vascular Dementia (Freitas et al., 2012b) and
Multiple Sclerosis (Freitas et al., 2018). Many studies
emphasize the psychometric characteristics of the test
(e.g. (Freitas et al., 2012c; Freitas et al., 2015; Freitas
et al., 2014), with norms for Portuguese population
(Freitas et al., 2011). Unfortunately, as a screening
instrument it can detect deficits but not quantify them
accurately. That can only be achieved with domain
specific NPAs. There are some NPAs such as Free
and Cued Selective Reminding Test, Semantic and
phonemic verbal fluency, Rey-Osterrieth Complex
Figure Test, clinical evaluation of dementia, etc. The
AI-Rehab is designed to receive information from
any NPA.
2.2 Artificial Intelligence in Cognitive
Rehabilitation
This section review the list of pilot studies of AI for
cognitive impairment and rehab. AI aims to bring
high precision in healthcare by employing computa-
tional intelligence in clinical tasks. Nowadays, the
most popular ML algorithms for structured data are
support vector machine, neural network (NN) and
deep learning (DL) whereas for unstructured data is
natural language processing (Jiang et al., 2017). Sev-
eral statistical learning (Hastie et al., 2009), ML clas-
sification (Fern´andez-Delgado et al., 2014) and re-
gression (Fern´andez-Delgado et al., 2018) and DL
techniques (LeCun et al., 2015) are available, by us-
ing them a few AI models are developed and these
really contribute for advancement of cognitive field.
For instance, the study (Chi et al., 2017) developed
personalized long-term and follow-up models to pre-
dict CS. First is sequential estimation of risk factors
to predict how cognition will change over long time
and second is observationof time-varyingrisk factors.
Likewise, (Ko et al., 2019) developed adaptive Least
Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO)
model to identify significant predictors of multivari-
ate NPAs and demographic variables for prediction of
cerebral amyloid beta abnormal level of status. Mem-
ory dysfunction is a crucial cognitive factor for early
detection of disease and one of the instruments to cal-
culate it is M-CRT. The binary classification (Berg-
eron et al., 2019) of cognitive health status (healthy or
unhealthy) and health related question (yes or no) is
modelled logistic regression using demographic data
and M-CRT test score.
Belief revision systems are logical frameworks
for modelling how agents modify their beliefs when
they receivenew information (sometimes inconsistent
with the previous beliefs)
2
. To integrate the new in-
formation, the agent will have to give up some in-
formation while preserving as much of the old in-
formation as possible. The AGM-framework (Al-
chourr´on et al., 1985) is the most popular framework
to guide the change of belief. The AGM model has ac-
quired the status of a standard model (for an overview,
2
For the sake of simplicity, we will assume that beliefs,
knowledge and data have the same status
AI-Rehab: A Framework for AI Driven Neurorehabilitation Training - The Profiling Challenge
847

see (Ferm´e and Hansson, 2011; Ferm´e and Hans-
son, 2018)). Several algorithms for the implementa-
tion of belief change operations were proposed. Most
of them were constructed to recognize which beliefs
are supported and how, and to perform changes while
minimizing the number of sentences to be changed,
thus preserving the maximum amount of the previ-
ous knowledge. Implementation also include pro-
posals by (Katsuno and Mendelzon, 1991; Williams
and Sims, 2000; Delgrande and Schaub, 2003; Pep-
pas and Williams, 2016). Katsuno and Mendelzon
(Katsuno and Mendelzon, 1991) also focused a lot
of their paper on trying to define a notion of dis-
tance between Knowledge Bases. This will be useful
later when comparing the CP at different stages. A
core aspect in implementation is the space and time
required for computation. Jin and Thielscher pro-
posed Reinforcement Belief Revision that combines
two desiderata for belief change implementations: It
satisfies the standard rationality postulates, and the
time and space required for its implementation can
be assessed. Recently, new studies of implementa-
tion belief revision by Horn Clauses have been initi-
ated (Booth et al., 2010; Delgrande, 2008; Delgrande
and Wassermann, 2010). Pagnucco (Pagnucco, 2006)
and (Zhuang et al., 2007) formalised a way of im-
plementing AGM operations using a knowledge com-
pilation technique involving prime implicates in or-
der to improve computational efficiency. The study
(Schwind et al., 2019) has proposed a change for-
mula, that given two know bases (or the same knowl-
edge base at different times) it is possible to determine
what caused the change in the belief set. Belief Re-
vision is still a relative new area of investigation and
there are not many examples we can draw from, so we
hope to contribute on this area.
3 FRAMEWORK
The BRaNT project is an interdisciplinary effort to
create a new set of ICT for rehabilitation at home.
For this project, we propose the AI-Rehab framework,
which includes the steps shown in Figure 1. There
are clearly three distinct challenges in the framework.
First and foremost we need to find an optimal way
to consolidate whole data from all the different NPAs
into a consistent profile, that should be easily inter-
preted by HP. This is the Profiling Challenge. The
second challenge refers to the task selection and set-
tings definition. How will the system guarantee that
the tasks are always optimally configured for a partic-
ular patient’s profile? To achieve this, we will create
a Belief Revision Engine (BR-E) to generate a pre-
dictable profile given a set of difficulty and follow the
flow theory to keep the patient always engaged with
the training task in hand (Nakamura and Csikszentmi-
halyi, 2009). Finally, the third challenge is the adap-
tive training at home. The goal of this challenge is to
keep adapting the predicted profile and the game set-
tings to keep the patient in flow, all at the comfort of
his home, without updated NPAs data. The process of
the AI-Rehab framework (Figure 1) can be explained
as follows:
1. HPs use validated NPAs to assess the patient;
2. The result of NPAs data are then injected in a
database and mapped to values by applying equa-
tion 1 from section 4.1, which creates a normal-
ized patient’s CP where each factor (or cognitive
domain) is normalized from 0 to 100%;
3. Once the CP is created, it is compared with Nor-
mative Data (ND) to define the CS, so called
Identification, and for that it is necessary to in-
corporate new information of the patient (SDI)
along with ND;
4. The HP can then interpret the CS and specify
training objectives (For instance, A, B and C with
their percentages, shown in the Figure 1) for that
particular profile, where the set of number of pa-
rameters of the training tasks are suggested. Si-
multaneously, the initial difficulty of the training
is set based on the CP. At this time the BR-E tries
to predict the expected results of the training task
(ERTT);
5. The patient performs a gamified training task at
home and performance is communicated to the
BR-E. This compares the results of training with
ERTT and identifies:
(a) If patient performance is in the accordance to
expectation,
(b) Data shows patient evolution or involution, the
patient profile is updated and a new difficulty is
set,
(c) Statistically unlikely change or inconsistent
data is detected, and the HP is contacted to re-
assess the situation and train BR-E.
6. Finally, the HP will do a new NPA reassessment,
after intervention is completed to quantify the im-
pact of cognitive training with AI-Rehab and de-
cide if more therapy is required.
Hence, we aim at combining the advantages of ICT
with a participatory design approach involving health
professionals (such as rehabilitation physicians, ther-
apists and neuropsychologists) to develop a novel
portable tool for the generation of cognitive rehabili-
tation training for the home use (Paulino et al., 2018;
Cognitive Health IT 2020 - Special Session on Machine Learning and Deep Learning Improve Preventive and Personalized Healthcare
848

Paulino et al., 2019). This tool will be a free and
worldwide accessible for clinicians, able to generate
patient’s profile and personalized cognitive rehabili-
tation programs in digital form instead of paper-and-
pencil format. It will be composed by a set of stan-
dardized rehabilitation tasks gathered from clinical
settings and parameterized through a participatory de-
sign approach and will be able to procedurally gener-
ate a large number of tasks by specifying the values of
their intrinsic parameters. It addresses the following
task types as described below (Faria et al., 2018):
• Knowledge: Memory of Stories; Cancellation;
Questions of General Knowledge; Find Loca-
tions; Image Pairs.
• Comprehension: Differences between Similar
Scenarios; Categorization; Synonymous and
Antonyms; Association.
• Application: Mazes; Problem Resolution; Tan-
gram; Numeric Sequences; Navigation.
• Analysis: Action Sequencing; Visual Memory;
Puzzles; Word Search.
• Evaluation: Differentiation between Coherent and
Incoherent situations; Comprehension of Con-
texts.
These tasks will be implemented in an interactive dig-
ital environment, shaped as tasks through a gami-
fication approach to deliver an immediate feedback
and reinforcement on progress (Wilson and McDon-
agh, 2013), which is an important element to increase
the motivation and avoid dropouts. Besides, adaptive
training is the last challenge of the AI-Rehab frame-
work. After each iteration of the task training, the BR-
E will calculate a new temporary profile and cognitive
situation. These will be compared with the ERTT cal-
culated before to see if any adjustment needs to be
done. The authors (Katsuno and Mendelzon, 1991)
defined on their paper several operators that can be
used to calculate the differences between knowledge
bases. With this difference calculated, we can deter-
mine how that patient evolved during the previous it-
eration and we are able to use this information to ad-
just the parameters of the task. In this paper we will
only focus on the computational patient profiling.
4 PATIENT PROFILING
CHALLENGE
This step starts with the task of specification the rel-
evant NPAs for a comprehensive evaluation of cogni-
tion. Screening tests are brief assessment triage tools
to identify patients cognitively at-risk that require a
fuller evaluation. Based on information from the clin-
ical process, which includes medical data, interview
data and scores on cognitive screening tests (such as
MoCA), the patient examined may be referred for a
more comprehensive NPA aimed at rehabilitation ob-
jectives. The NPA, instead, is a standard part of inte-
grated medical and psychological care, and is a nec-
essary step to implement and further evaluate rehabil-
itation procedures. The NPA has several objectives,
namely: (i) to identify and characterize cognitiveabil-
ities and activities of daily life, personality, emotional
functioning and behaviours of the person and to define
changes in these domains in comparison to the level
of premorbid functioning; (ii) to document and quan-
tify the nature and severity of cognitive and functional
deficits, symptoms and signs present, potentially as-
sociated with pathology, in the context of examining
the structural and functional integrity of brain func-
tioning, differentiating what is the associated decline
to the normal aging and deficits associated with cere-
bral dysfunction / neurodegenerative pathology; (iii)
to define a baseline in various domains of the cog-
nitive, emotional and behavioural functioning, which
can be examined in a longitudinal register, through
repeated evaluations, thus enabling monitoring of the
clinical evolution of the person, recovery of functions,
response to the intervention (e.g., rehabilitation, psy-
chotherapy, pharmacological) or the progression of
the disease; (iv) to identify personal resources and
preserved functions that are equally useful for plan-
ning and implementing rehabilitative/ therapeuticand
preventive intervention procedures, as well as evalu-
ating their effectiveness, with the aim of promoting
the person’s well-being and quality of life. Further
step is devoted to the factorization of the outcome
of these assessments and translation to a formal lan-
guage that allows creating automatically (by artificial
intelligence techniques) a profile of the patient that
can be used for defining a neurorehabilitation ther-
apy. This will give us the CP, shown in the Figure
1. The Identification part is more complicated. We
need to create a CS using the ND and the SDI, in or-
der to interpret how a particular patient CP compares
to the ND. This will produce the CS in the Figure 1,
which represents, in percentage, where the CP is lo-
cated compared to the rest of the population with sim-
ilar SDI. Hence, facilitating the interpretation of the
data by the HP.
4.1 Proposed Solution
This section reports on the AI solutions for AI-Rehab
framework. First and the most important challenge is
patient profiling. Then we need to solve the task set-
AI-Rehab: A Framework for AI Driven Neurorehabilitation Training - The Profiling Challenge
849

ting and iterative training challenge, which will not
be tackled in this paper. Here, we propose some tech-
niques without applying them on data which can be
useful to automatize the neurorehabilitation system.
The second step in AI-Rehab framework from Sec-
tion 3 is to map NPAs values to a consolidated CP
into the interval 0 to 100 and the equation 1 is used
for the Mapping. Note that it is formulated owing to
no data.
CP
k
=
n
∑
i=1
m
∑
j=1
Norm(NPA
i
F
j
).W
kij
(1)
Where,
W
kij
=
1/p, where p is count of factors,
contributing to CP
k
0, otherwise
NPA
i
F
j
= factor from a neuropsychological as-
sessment
CP
k
= cognitive domain K from CP
Norm= normalization function, interval is 0 and 100
W
kij
= weight function, interval is 0 to 1, which sums
to 1
m= number of times a F appeared in NPAs
n= number of NPAs
The way this formula works is that we take ev-
ery factor j from each NPA i (lets say, memory from
MOCA for instance) and multiply by the weight that
factor has on determining that specific cognitive do-
main (memory in this example). At the start, we will
inquire HPs to provide us with weights for each fac-
tor, as it seems a better solution to follow the pro-
fessionals intuition than to attribute arbitrary weights.
Once we have enough data, we can start using AI
algorithms to determine the weights which we have
explained at the end of this section. The weight W
should belong in the interval of 0 to 1. Given that, the
‘Norm’ function will give us a value between 0 and
100 and the sum of the weights is 1, the output CP
k
will be a value between 0 and 100, corresponding to
the weighted factor of the CP (in this example, mem-
ory). This is the Mapping process from the Figure 1.
Finally, the CP
k
is the aggregated result of a battery
of tests, instead of only one test, and CP is a set of
cognitive domain k.
The final step is to contextualize this profile. If
we interpret the CP using the ND from all the NPAs
taking into account the patient SDI, we will get a stan-
dardized cognitive profile. This process will generate
a profile that is compared to the population data. This
is the step which is needed for the identification of
deficits and the outcome of this is CS. Once again,
these process will be improved as we get actual data
from patients using the system.
SCP
k
=
∑
n
i=1
Norm(ND
i
,SDI)
n
(2)
SDI= patient’s socio-demographic information
ND= normative data of k for each NPA used to
calculate CP
SCP
k
= standardized cognitive profile K from ND and
SDI
Norm= normalization function, interval is 0 and 100
n= number of NPAs
First, it is important to mention that we do not
have access to the normative value for the factors of
each NPA, we just have it for the result of the whole
NPAs. Also, since it is normative data, there is no
need to consider weights as it is already embedded in
the ND value itself. The value represented by the ND
and SDI pair is the average result of someone in the
closest socio-demographic group as the patient, since
the SDI is relative to her/him. This can be observed
for MoCA in (Freitas et al., 2018) for the Portuguese
population. For simplicity, lets consider only MoCA
and memory for an example. The result of this for-
mula would be the average of someone with a similar
SDI as the patient. By doing a simple cross multipli-
cation between the CP memory score and the result
of this function, we can get a relative value of the pa-
tient when compared with the ND. This value would
be, in this example, the memory domain in the CS of
the patient, where 50% means that you are as good
as it is expected for you group, 75% means you are
25% above average or 100% means you are twice as
good as expected. Eventually, we will have collected
patient’s CS with all the factors so HP can interpret
them and take clinical decision with ease. Eventually,
it gives solution for profiling challenge without data.
CP
k
=
n
∑
i=1
m
∑
j=1
Norm(NPA
i
F
j
).W
kij
(3)
Where, W
kij
belongs to (0≤W≤1) and
∑
n
i=1
W
kij
= 1
which is being determined by some AI techniques.
Once we get enough data, we can have AI solu-
tion for the W problem, appeared in the equation 1.
The equation 3 is a proposal solution for the weights
computation. Some statistical learning, ML or DL
techniques will apply on NPAs data to obtain highly
optimal W in the Mapping process, such as Princi-
pal Component Analysis, random forest or neural net-
work. Besides, if the number of F and NPA grow
over time then the system performance may decline
and the data will suffer with high dimentionality. To
overcome such problem, feature selection techniques
Cognitive Health IT 2020 - Special Session on Machine Learning and Deep Learning Improve Preventive and Personalized Healthcare
850

like Principal Component Analysis, LASSO, Ridge
or t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding can
be used. These techniques generate highly influential
parameters without loosing much information. Sub-
sequently, the next step is to create the Belief Revision
Engine (BR-E), a computational infrastructure based
on the Believe Revision that will enable the accurate
prediction of CPs for patients, over the iterative train-
ing process. The BR-E has three objectives:
1. At each iteration, register the difference between
the ERTT and the real result;
2. At each iteration, check for inconsistencies;
3. End finally, once the who training is completed,
after n iterations, it will compare the n
th
predicted
profile with the new real profile after the NPA re-
assessment.
The first point will allow us the tweak the difficulty
of the settings, with the goal of keep the patient in
flow (Nakamura and Csikszentmihalyi, 2009). It has
been proven that people at this level of concentration
and immersion are at their most effective, which will
lead to better rehabilitation results. If after each it-
eration, the new predicted profile is inconsistent, by
any reason, then an alarm must be risen and the HP
must be contact to evaluatethe situation. Finally, once
the patient has completed the trained and has been
re-evaluated, we can compare the n
th
predicted result
with the new real result. This will allow us the eval-
uate the performance of the system and to see if it
is performing as we want. The study (Schwind et al.,
2019) can help us to understand where the system pre-
dicted wrong, given the final result. Once all is done,
the loop restart until the HP decides that no more ther-
apy is necessary.
5 CONCLUSION
The BRaNT project goal is the development of a
novel cognitive rehabilitation tool to allow the health
professional the monitoring and adaptation of treat-
ment at home. To do this, we propose the usage of
Artificial Intelligence (AI) to improve the existing TG
tool. BRaNT proposes the usage of machine learn-
ing, deep learning and believe revision framework is
able to assess the patient’s deficits through the us-
age of the results battery of validated NPAs, generate
gamified cognitive training tasks adjusted to each pa-
tient profile, and support the continuum of healthcare
from the clinic to the home with a distributed archi-
tecture with remote monitoring capabilities. Conse-
quently, this paper proposes the AI-Rehab framework
for AI driven neurorehabilitation training and identi-
fies three challenges: patient’s cognitive profile, task
settings and iterative training. The present work only
focuses on profiling challenge and proposes a solu-
tion for Mapping and Identification process. Once
we have enough data, we will apply machine learning
algorithms. As for the BR techniques, (Katsuno and
Mendelzon, 1991) research will be crucial to mea-
sure the distance between the several profiles gathered
during the process and (Schwind et al., 2019) work
will help us understand what actually changed and
what needs to be adapted for the next training loop.
Presently, the framework targets only cognitive do-
mains. However, in future, it can easily be extended
to cognitive sub domains or to other domains such as
fitness.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We want to thank the BRaNT team for their support
and stimulating discussions. This research is sup-
ported by BRaNT - Belief Bevision applied to Neu-
rorehabilitation Therapy [project number PTDC/CCI-
COM/30990/2017],financed by FCT - Fundac¸˜ao para
a Ciˆencia e a Tecnologia. EF is partially supported
by UID/CEC/04516/2019.SBB is partially supported
by MACBIOIDI: Promoting the cohesion of Mac-
aronesian regions through a common ICT platform
for biomedical R - D - i” (INTERREG program
MAC/1.1.b/098)
REFERENCES
Alchourr´on, C. E., G¨ardenfors, P., and Makinson, D.
(1985). On the logic of theory change: Partial meet
contraction and revision functions. The journal of
symbolic logic, 50(2):510–530.
Bergeron, M. F., Landset, S., Tarpin-Bernard, F., Ashford,
C. B., Khoshgoftaar, T. M., and Ashford, J. W. (2019).
Episodic-memory performance in machine learning
modeling for predicting cognitive health status classi-
fication. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 70(1):277–
286.
Berm´udez i Badia, S., Fluet, G. G., Llorens, R., and
Deutsch, J. E. (2016). Virtual reality for sensorimo-
tor rehabilitation post stroke: Design principles and
evidence. In Neurorehabilitation technology, pages
573–603. Springer.
Booth, R., Meyer, T., Varzinczak, I., and Wassermann, R.
(2010). Contraction core for horn belief change: pre-
liminary report. Unpublished manuscript.
Bott, N. T. and Kramer, A. (2017). Cognitive rehabilitation.
Encyclopedia of Geropsychology, pages 544–551.
AI-Rehab: A Framework for AI Driven Neurorehabilitation Training - The Profiling Challenge
851

Carod-Artal, J., Egido, J. A., Gonz´alez, J. L., and Varela de
Seijas, E. (2000). Quality of life among stroke sur-
vivors evaluated 1 year after stroke: experience of a
stroke unit. Stroke, 31(12):2995–3000.
Chi, C.-L., Zeng, W., Oh, W., Borson, S., Lenskaia, T.,
Shen, X., and Tonellato, P. J. (2017). Personalized
long-term prediction of cognitive function: Using se-
quential assessments to improve model performance.
Journal of biomedical informatics, 76:78–86.
Cicerone, K. D., Dahlberg, C., Kalmar, K., Langenbahn,
D. M., Malec, J. F., Bergquist, T. F., Felicetti, T., Gi-
acino, J. T., Harley, J. P., Harrington, D. E., et al.
(2000). Evidence-based cognitive rehabilitation: rec-
ommendations for clinical practice. Archives of phys-
ical medicine and rehabilitation, 81(12):1596–1615.
Cicerone, K. D., Dahlberg, C., Malec, J. F., Langenbahn,
D. M., Felicetti, T., Kneipp, S., Ellmo, W., Kalmar, K.,
Giacino, J. T., Harley, J. P., et al. (2005). Evidence-
based cognitive rehabilitation: updated review of the
literature from 1998 through 2002. Archives of physi-
cal medicine and rehabilitation, 86(8):1681–1692.
Cicerone, K. D., Langenbahn, D. M., Braden, C., Malec,
J. F., Kalmar, K., Fraas, M., Felicetti, T., Laatsch, L.,
Harley, J. P., Bergquist, T., et al. (2011). Evidence-
based cognitive rehabilitation: updated review of the
literature from 2003 through 2008. Archives of physi-
cal medicine and rehabilitation, 92(4):519–530.
Cumming, T. B., Marshall, R. S., and Lazar, R. M. (2013).
Stroke, cognitive deficits, and rehabilitation: still an
incomplete picture. International Journal of stroke,
8(1):38–45.
Delgrande, J. and Wassermann, R. (2010). Horn clause
contraction functions: Belief set and belief base ap-
proaches. In Twelfth International Conference on the
Principles of Knowledge Representation and Reason-
ing.
Delgrande, J. P. (2008). Horn clause belief change: Con-
traction functions. In KR, pages 156–165.
Delgrande, J. P. and Schaub, T. (2003). A consistency-
based approach for belief change. Artificial Intelli-
gence, 151(1-2):1–41.
Faria, A. L. and Berm´udez i Badia, S. (2015). Development
and evaluation of a web-based cognitive task gener-
ator for personalized cognitive training: a proof of
concept study with stroke patients. In Proceedings
of the 3rd 2015 Workshop on ICTs for improving Pa-
tients Rehabilitation Research Techniques, pages 1–4.
ACM.
Faria, A. L., Pinho, M. S., and Berm´udez i Badia, S. (2018).
Capturing expert knowledge for the personalization
of cognitive rehabilitation: Study combining com-
putational modeling and a participatory design strat-
egy. JMIR rehabilitation and assistive technologies,
5(2):e10714.
Ferm´e, E. and Hansson, S. O. (2011). Agm 25 years. Jour-
nal of Philosophical Logic, 40(2):295–331.
Ferm´e, E. and Hansson, S. O. (2018). Belief Change: In-
troduction and Overview. Springer.
Fern´andez-Delgado, M., Cernadas, E., Barro, S., and
Amorim, D. (2014). Do we need hundreds of classi-
fiers to solve real world classification problems? The
Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1):3133–
3181.
Fern´andez-Delgado, M., Sirsat, M., Cernadas, E., Alawadi,
S., Barro, S., and Febrero-Bande, M. (2018). An
extensive experimental survey of regression methods.
Neural Networks.
Freitas, S., Batista, S., Afonso, A. C., Sim˜oes, M. R.,
de Sousa, L., Cunha, L., and Santana, I. (2018). The
montreal cognitive assessment (moca) as a screening
test for cognitive dysfunction in multiple sclerosis.
Applied Neuropsychology: Adult, 25(1):57–70.
Freitas, S., Prieto, G., Sim˜oes, M. R., and Santana, I.
(2014). Psychometric properties of the montreal cog-
nitive assessment (moca): an analysis using the rasch
model. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 28(1):65–83.
Freitas, S., Prieto, G., Sim˜oes, M. R., and Santana, I.
(2015). Scaling cognitive domains of the montreal
cognitive assessment: an analysis using the partial
credit model. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology,
30(5):435–447.
Freitas, S., Sim˜oes, M. R., Alves, L., Duro, D., and Santana,
I. (2012a). Montreal cognitive assessment (moca):
validation study for frontotemporal dementia. Journal
of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 25(3):146–
154.
Freitas, S., Sim˜oes, M. R., Alves, L., and Santana, I. (2011).
Montreal cognitive assessment (moca): normative
study for the portuguese population. Journal of clin-
ical and experimental neuropsychology, 33(9):989–
996.
Freitas, S., Sim˜oes, M. R., Alves, L., and Santana, I.
(2013). Montreal cognitive assessment: validation
study for mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer
disease. Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders,
27(1):37–43.
Freitas, S., Simoes, M. R., Alves, L., Vicente, M., and
Santana, I. (2012b). Montreal cognitive assessment
(moca): validation study for vascular dementia. Jour-
nal of the International Neuropsychological Society,
18(6):1031–1040.
Freitas, S., Simoes, M. R., Marˆoco, J., Alves, L., and San-
tana, I. (2012c). Construct validity of the montreal
cognitive assessment (moca). Journal of the Interna-
tional Neuropsychological Society, 18(2):242–250.
George, D. R. and Whitehouse, P. J. (2011). Marketplace of
memory: what the brain fitness technology industry
says about us and how we can do better. The Geron-
tologist, 51(5):590–596.
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., and Friedman, J. (2009). The el-
ements of statistical learning: data mining, inference,
and prediction. Springer Science & Business Media.
Jiang, F., Jiang, Y., Zhi, H., Dong, Y., Li, H., Ma, S., Wang,
Y., Dong, Q., Shen, H., and Wang, Y. (2017). Arti-
ficial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and fu-
ture. Stroke and vascular neurology, 2(4):230–243.
Katsuno, H. and Mendelzon, A. O. (1991). Propositional
knowledge base revision and minimal change. Artifi-
cial Intelligence, 52(3):263–294.
Cognitive Health IT 2020 - Special Session on Machine Learning and Deep Learning Improve Preventive and Personalized Healthcare
852

Ko, H., Ihm, J.-J., Kim, H.-G., Initiative, A. D. N., et al.
(2019). Cognitive profiling related to cerebral amy-
loid beta burden using machine learning approaches.
Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 11.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Morris, K., Hacker, V., and Lincoln, N. B. (2012). The
validity of the addenbrooke’s cognitive examination-
revised (ace-r) in acute stroke. Disability and rehabil-
itation, 34(3):189–195.
Nakamura, J. and Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2009). Flow the-
ory and research. Handbook of positive psychology,
pages 195–206.
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., B´edirian, V., Charbon-
neau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., Cummings, J. L.,
and Chertkow, H. (2005). The montreal cognitive as-
sessment, moca: a brief screening tool for mild cogni-
tive impairment. Journal of the American Geriatrics
Society, 53(4):695–699.
Pagnucco, M. (2006). Knowledge compilation for belief
change. In Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, pages 90–99. Springer.
Parsons, T. D. (2015). Ecological validity in virtual reality-
based neuropsychological assessment. In Encyclope-
dia of Information Science and Technology, Third Edi-
tion, pages 1006–1015. IGI Global.
Paulino, T., i Badia, S. B., and Cameir˜ao, M. (2019). Us-
ability evaluation of an integrative exergaming system
for the senior population. In 2019 5th Experiment In-
ternational Conference (exp. at’19), pages 286–291.
IEEE.
Paulino, T., Mu˜noz, J., Berm´udez i Badia, S., and Cameir˜ao,
M. S. (2018). Design of an integrative system for con-
figurable exergames targeting the senior population.
In International Conference on Human Systems Engi-
neering and Design: Future Trends and Applications,
pages 287–292. Springer.
Peppas, P. and Williams, M.-A. (2016). Kinetic consistency
and relevance in belief revision. In European Confer-
ence on Logics in Artificial Intelligence, pages 401–
414. Springer.
Schwind, N., Inoue, K., Konieczny, S., Lagniez, J.-M., and
Marquis, P. (2019). What has been said? identifying
the change formula in a belief revision scenario. In
Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-19, pages
1865–1871. International Joint Conferences on Artifi-
cial Intelligence Organization.
Solana, J., C´aceres, C., Garc´ıa-Molina, A., Opisso, E.,
Roig, T., Tormos, J. M., and G´omez, E. J. (2014). Im-
proving brain injury cognitive rehabilitation by per-
sonalized telerehabilitation services: Guttmann neu-
ropersonal trainer. IEEE journal of biomedical and
health informatics, 19(1):124–131.
Williams, M.-A. and Sims, A. (2000). Saten: An object-
oriented web-based revision and extraction engine.
arXiv preprint cs/0003059.
Wilson, A. and McDonagh, J. (2013). Application of the
principles of gamification to facilitate acquisition of
self-management skills in young people with long-
term medical conditions. In European Conference on
Games Based Learning, page 579. Academic Confer-
ences International Limited.
Zhuang, Z. Q., Pagnucco, M., and Meyer, T. (2007). Imple-
menting iterated belief change via prime implicates.
In Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence, pages 507–518. Springer.
AI-Rehab: A Framework for AI Driven Neurorehabilitation Training - The Profiling Challenge
853
