
Multi-class Semantic Segmentation of Skin Lesions via Fully
Convolutional Networks
Manu Goyal
1 a
, Moi Hoon Yap
2 b
and Saeed Hassanpour
3 c
1
Department of Biomedical Data Science, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, U.S.A.
2
Visual Computing Lab, Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, U.K.
3
Departments of Biomedical Data Science, Computer Science and Epidemiology, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Skin Cancer, Fully Convolutional Networks, Multi-class Segmentation, Lesion Diagnosis.
Abstract:
Melanoma is clinically difficult to distinguish from common benign skin lesions, particularly melanocytic
naevus and seborrhoeic keratosis. The dermoscopic appearance of these lesions has huge intra-class variations
and high inter-class visual similarities. Most current research is focusing on single-class segmentation irre-
spective of classes of skin lesions. In this work, we evaluate the performance of deep learning on multi-class
segmentation of ISIC-2017 challenge dataset, which consists of 2,750 dermoscopic images. We propose an
end-to-end solution using fully convolutional networks (FCNs) for multi-class semantic segmentation to au-
tomatically segment the melanoma, seborrhoeic keratosis and naevus. To improve the performance of FCNs,
transfer learning and a hybrid loss function are used. We evaluate the performance of the deep learning seg-
mentation methods for multi-class segmentation and lesion diagnosis (with post-processing method) on the
testing set of the ISIC-2017 challenge dataset. The results showed that the two-tier level transfer learning
FCN-8s achieved the overall best result with Dice score of 78.5% in a naevus category, 65.3% in melanoma,
and 55.7% in seborrhoeic keratosis in multi-class segmentation and Accuracy of 84.62% for recognition of
melanoma in lesion diagnosis.
1 INTRODUCTION
Skin cancers are more common than all other can-
cers (Pathan et al., 2018). Malignant skin lesions are
classified as melanocytic, i.e. melanoma, and non-
melanocytic. The most common non-melanocytic
cancers are keratinocytic: basal cell carcinoma and
squamous cell carcinoma. Melanoma is less common
but is more likely to prove fatal than keratinocytic
skin cancers due to aggressive invasion and metastasis
(National Cancer Institute, 2017)(Dvo
ˇ
r
´
ankov
´
a et al.,
2017). Hence, early detection is important to save
lives. According to the prediction of the Melanoma
Foundation (Melanoma Foundation (AIM), 2017), the
estimated diagnosed cases of melanoma in the United
States in 2018 is 178,560 with 91,270 cases will be
invasive.
Melanocytic naevi and seborrhoeic keratosis
are very common benign skin lesions that may
be clinically difficult to differentiate from skin
cancer. Both melanoma and melanocytic naevi
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9201-1385
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7681-4287
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9460-6414
are melanocytic lesion as uncontrolled growth of
melanocytes (pigmented cells) results in melanoma
whereas non-cancerous growth in moles results in be-
nign melanocytic naevus. Seborrheic keratosis is a
type of non-melanocytic skin lesion. But, it is very
hard to distinguish the SK lesions from melanocytic
lesions (moles and melanoma) even with the help of
dermoscopy as these skin lesions share similar fea-
tures such as irregular shapes and multiple colors.
With the rapid growth of deep learning ap-
proaches, many researchers (Yuan et al., 2017), (Yu
et al., 2017), (Bi et al., 2017), (Goyal et al., 2019)
have proposed Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
for skin lesion segmentation (single-class). We have
found no previous research on multi-class semantic
segmentation for different types of skin lesions.
Our contributions are three fold. Firstly, we pro-
pose multi-class semantic lesions segmentation for
melanoma, seborrhoeic keratosis and naevus. To
overcome data deficiency, a two-tier transfer learn-
ing is used in skin lesions segmentation to train the
fully convolutional networks (FCNs). Secondly, we
design a hybrid loss function to handle class imbal-
ance in the multi-class segmentation. Thirdly, we as-
sess the performance of state-of-the-art deep learning
290
Goyal, M., Yap, M. and Hassanpour, S.
Multi-class Semantic Segmentation of Skin Lesions via Fully Convolutional Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0009380302900295
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 290-295
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Table 1: Distribution of images for multi-class segmenta-
tion task.
Naevi Melanoma Seborrheic Keratosis Total
Training set 1372 521 387 2000
Validation set 92 34 23 150
Testing set 393 117 90 600
Total 1843 521 386 2750
algorithms using our proposed multi-class segmenta-
tion and a post-processing method to determine le-
sion diagnosis on ISIC-2017 Challenge dataset. Our
proposed method can be generalised into other multi-
class segmentation tasks in medical imaging.
2 METHODOLOGY
This section discusses the publicly available ISIC-
2017 skin lesion dataset and its ground truth labeling,
the two-tier transfer learning approach, and the hybrid
loss function.
2.1 Datasets and Ground Truth
We used the publicly available ISIC-2017 Skin Le-
sion Analysis Towards Melanoma Detection Chal-
lenge dataset (Codella et al., 2017) to train the fully
convolutional deep learning models. RGB colorspace
is used to represent all the images in this dataset. It in-
cludes 3 skin lesion types using dermoscopy images:
naevi, melanomas and seborrhoeic keratosis. The seg-
mentation task on these dermoscopy images is very
challenging due to high inter-class similarity between
the 3 types of skin lesions. This dataset is imbalanced
as there are only a total of 521 melanoma and 386 seb-
orrheic keratosis compared to 1843 melanocytic naevi
dermoscopic images. There are a total of 2750 der-
moscopy images in the ISIC-2017 challenge dataset,
as summarised in Table 1.
In this dataset, the size of images varies between
540 × 722 and 4499 × 6748. To improve the per-
formance and reduce the computational cost, all the
images are resized to 500 × 375. In ISIC-2017 seg-
mentation challenge, the task is to segment the lesion
boundaries, which was a one-class segmentation task.
Here we are targeting on automatic multi-class seg-
mentation. The ground truths are all defined in RGB
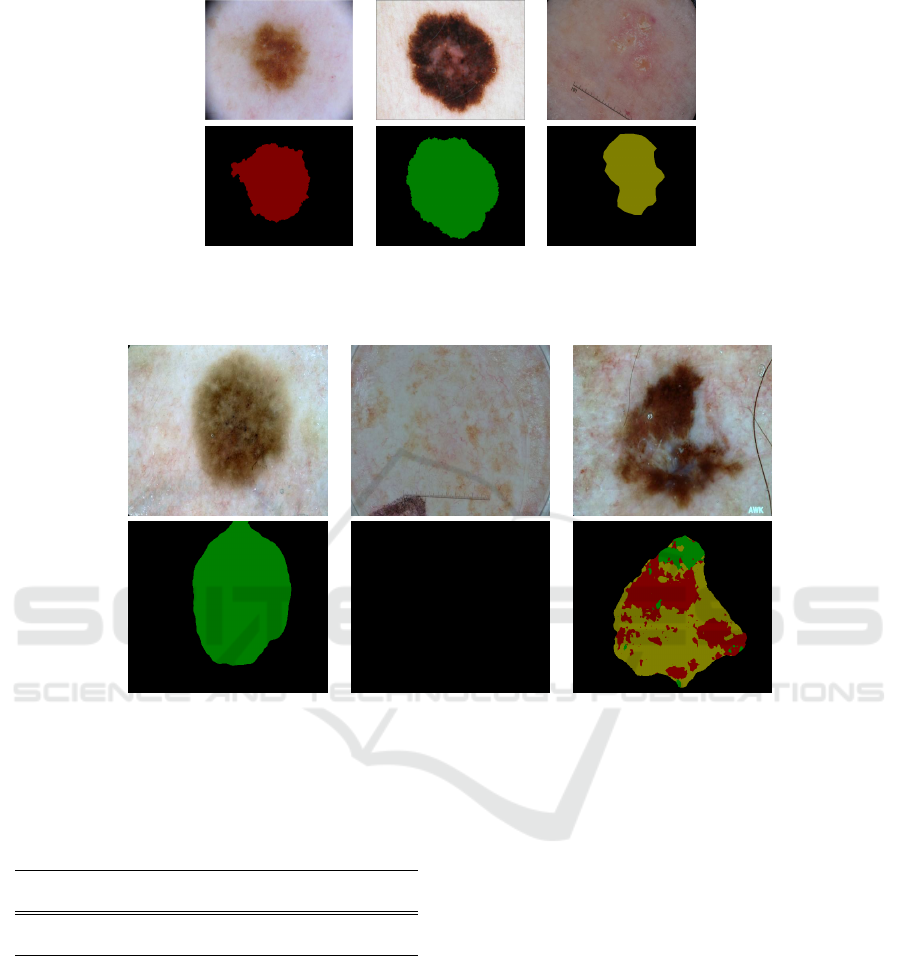
colorspace and 8-bit paletted images. Figure 1 illus-
trates the dermoscopic images with the correspond-
ing ground truth labeling in PASCAL-VOC format
(Garcia-Garcia et al., 2017)(Everingham et al., 2015).
Index 1 indicates naevus, index 2 indicates melanoma
and index 3 represents seborrhoeic keratosis.
2.2 Fully Convolutional Networks for
Multi-class Semantic Segmentation
FCNs and encoder-decoder CNNs can detect the mul-
tiple objects as well as localize the objects by using
pixel-wise prediction. This enables to learn which
pixel of an image belongs to which class of ob-
ject. Recently, FCNs have become the state-of-the-art
methods for segmentation tasks on both non-medical
and medical imaging, which are superior to conven-
tional machine learning and other deep learning meth-
ods. We used the four different variants of FCNs
(FCN-AlexNet, FCN-32s, FCN-16s, and FCN-8s)
and assessed their performance on multi-class skin le-
sions segmentation.
The first variant FCN-AlexNet is a modified ver-
sion of original state-of-the-art classification model
called AlexNet, which won ImageNet ILSVRC-2012
competition in the classification category (Long et al.,
2015)(Krizhevsky et al., 2012). The FCN-AlexNet
enables the pixel-wise prediction by using the de-
convolutional layers which up-sample the features
learned by the earlier convolutional layers. We have
trained the FCN-AlexNet on the Caffe deep learning
framework (Jia et al., 2014). The input and ground
truth images are both 500×375. We have fine-tuned
the network parameters to allow the method more
time to learn the features from dermoscopy images
by using 100 epochs, stochastic gradient descent with
a learning rate of 0.0001.
The other FCNs variants, FCN-32s, FCN-16s
and FCN-8s, are based on another state-of-the-art
classification network called VGG-16, which won
the localization challenge and was in second posi-
tion for the classification challenge in the ImageNet
ILSVRC-2014 competition (Simonyan and Zisser-
man, 2014)(Long et al., 2015). The differences be-
tween these models are the up-sampling layers with
different pixel stride. As the name suggested by
these FCNs variants, in FCN-32s, up-sampling is per-
formed with the help of 32-pixel stride whereas 16-
pixel stride is used for FCN-16s and 8-pixel stride for
FCN-8s. With the small pixel stride, the models were
able to predict finer-grained analysis of the objects.
The same network parameters as FCN-AlexNet were
used to train these models.
2.3 The Two-tier Transfer Learning
Approach
Convolutional neural networks generally require a
huge dataset to learn the features and detect objects
Multi-class Semantic Segmentation of Skin Lesions via Fully Convolutional Networks
291
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 1: Original images (first row) and PASCAL-VOC format (second row). The skin lesion diagnosis from left to right:
(a) naevus, (b) melanoma and (c) seborrhoeic keratosis.
(a) Single-detection (b) No-detection (c) Multi-detection
Figure 2: Examples of different types of semantic segmentation in ISIC-2017 testing set: (a) result with one class lesion type;
(b) result with no lesion detected; and (c) result with multiple lesion types. Where green color represents melanocytic naevus,
red color represents melanoma, and yellow color represents seborrhoeic keratosis.
Table 2: Number of cases for each type of inference in ISIC-
2017 Testing Set.
Inference Single-detection Multi-detection No-detection
Testing Set 395 192 13
in images (LeCun et al., 2015). Since, we have
RGB images in dermoscopic images, it is good to use
two-tier transfer learning from huge datasets in non-
medical backgrounds such as ImageNet and Pascal-
VOC dataset to converge the weights associated with
each convolutional layer of networks (Russakovsky
et al., 2014)(Everingham et al., 2015)(Goyal et al.,
2017). The transfer learning transfers the feature
learned by previous models on huge non-medical
datasets to medical image datasets. There are two
types of transfer learning, i.e. partial transfer learning
in which only the features from few convolutional lay-
ers are transferred, and full transfer learning in which
features are transferred from all the layers of previ-
ous pre- trained models. For the first tier of two-tier
transfer learning, we used partial transfer learning by
transferring the features from the convolutional lay-
ers trained on ImageNet. For the second tier, we used
full transfer learning from a model trained on Pascal-
VOC.
2.4 Custom Hybrid Loss Function
For imbalanced dataset as summarized in Table 1, we
used a hybrid loss function, which is a combination of
softmax cross-entropy loss and Dice score loss func-
tion, to optimize the objective function. Dice Score
is a commonly used performance metric in medical
imaging segmentation. Softmax cross-entropy loss
function is a sum of per-pixel softmax cross-entropy
C2C 2020 - Workshop on COMP2CLINIC: Biomedical Researchers Clinicians Closing The Gap Between Translational Research And
Healthcare Practice
292
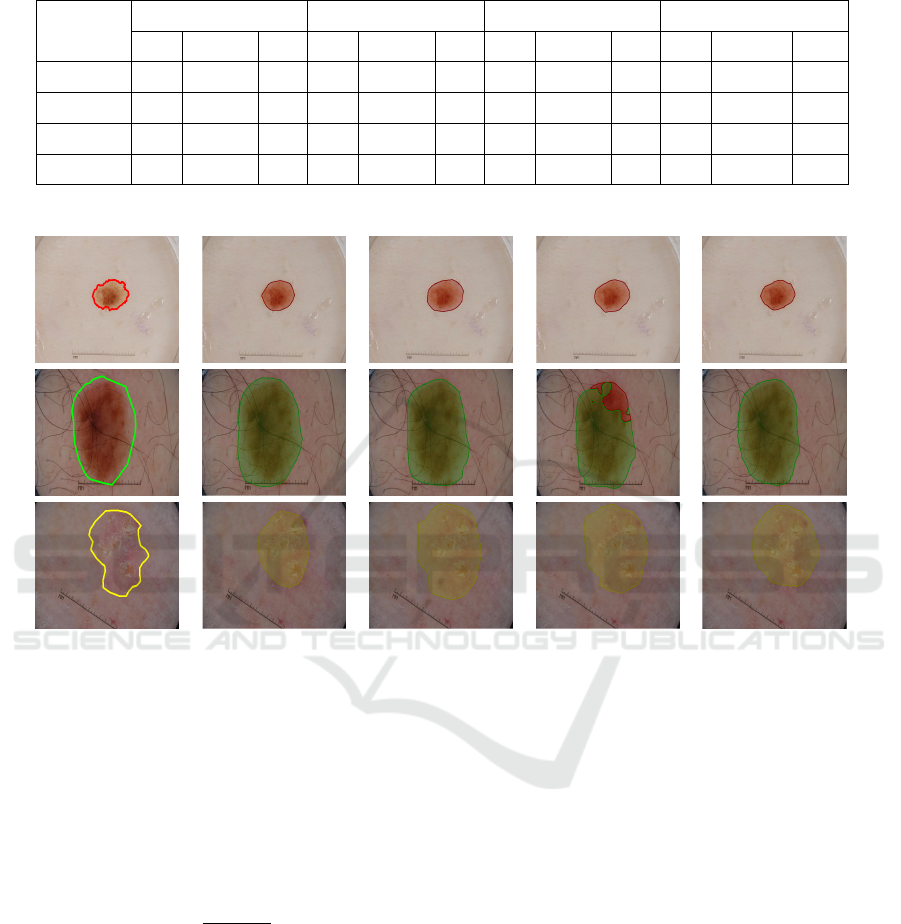
Table 3: Comparison of different FCN architectures using the ISIC-2017 Challenge Dataset (SK denotes Seborrheic Kerato-
sis).
Method
Dice Specificity Sensitivity MCC
Naevi Melanoma SK Naevi Melanoma SK Naevi Melanoma SK Naevi Melanomas SK
FCN-AlexNet 0.819 0.609 0.488 0.989 0.982 0.987 0.798 0.4864 0.456 0.814 0.541 0.484
FCN-32s 0.779 0.549 0.484 0.991 0.977 0.968 0.751 0.430 0.478 0.775 0.484 0.463
FCN-16s 0.761 0.590 0.506 0.988 0.979 0.978 0.706 0.471 0.466 0.764 0.528 0.501
FCN-8s 0.785 0.653 0.557 0.990 0.984 0.988 0.747 0.527 0.509 0.779 0.582 0.5683
Ground truth FCN-AlexNet FCN-32s FCN-16s FCN-8s
Figure 3: Illustration of segmentation results to visually compare the performance of ground truth delineation and four FCNs
on multi-class segmentation for a naevus (top row), a melanoma (middle row), and a seborrhoeic keratosis (bottom row).
loss whereas Dice score loss function take care of
overall segmentation score on whole image.
L
s
= So f tmax(cross −entropy) (1)
where L
s
is overall softmax cross entropy loss func-
tion and cross-entropy is per-pixel cross-entropy loss.
L
d
=
2|S ∩ G|
|S| + |G|
(2)
where L
d
is Dice score loss function, S is segmented
image and G is ground truth.
L
h
= L
s
+ L
d
(3)
where L
h
is a hybrid loss function which is combina-
tion of both softmax cross entropy loss function and
dice loss function.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
We experimented with four state-of-the-art fully con-
volutional networks for our proposed segmentation
task as described above. We trained the models on the
ISIC-2017 training set of 2000 dermoscopic images
with an input-size of 500×375 using stochastic gradi-
ent descent with a learning rate of 0.0001, 60 epochs
with a dropout rate of 33%. In Table 3, we report Dice
Similarity Coefficient (Dice), Sensitivity, Specificity,
Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) as metrics
for performance evaluation of multi-class segmenta-
tion of skin lesions. We used the trained model based
on the best Dice score on the ISIC-2017 validation set
to perform inference on the ISIC-2017 test set.
Configuration of GPU Machine for Experi-
ments. (1) Hardware: CPU - Intel i7-6700 @
4.00Ghz, GPU - NVIDIA TITAN X 12Gb, RAM -
32GB DDR5 (2) Software: Caffe.
In performance measure for multi-class segmen-
Multi-class Semantic Segmentation of Skin Lesions via Fully Convolutional Networks
293

tation, we received three types of results from the
inference as shown in the Fig. 2 and number of
cases for each type of detection is shown in Table
2. In Table 3, we report the performance evaluation
of fully convolutional networks for multi-class seg-
mentation on ISIC-2017 test set. In the naevi cate-
gory, all FCNs achieved good segmentation results,
but FCN-AlexNet achieved the best results with Dice
score of 0.819, MCC score of 0.814, and Sensitivity is
0.798. In this category, FCN-8s performed 2nd best
with Dice score of 0.779 and MCC score of 0.779. In
the melanoma and seborrhoeic keratosis catergories,
FCN-8s has achieved Dice score of 0.653 and 0.557
respectively, which was also the best performer for all
the metrics. Fig. 3 visually compares the segmenta-
tion results on different lesion types. FCNs performed
best in the class of naevi because we have more im-
ages of naevi than melanoma and seborrhoeic ker-
atosis. Due to high intra-class and inter-class visual
similarities, performance for both melanoma and se-
borrhoeic keratosis suffer due to fewer images in the
dataset. Melanoma images are approx. 37% and ker-
atosis images are approx. 22% of the total of images
of naevi in the dataset.
The results demonstrated that deep learning tech-
niques are reliant on the size of dataset. The segmen-
tation results for melanoma and seborrhoeic keratosis
were notably poorer than for naevi as a consequence
of data deficiency. Despite the limitation on dataset,
we have provided a fully automated end-to-end solu-
tion for multi-class segmentation.
3.1 Post-processing Method to
Determine Lesion Diagnosis
We used a post-processing method to determine a sin-
gle label for lesion diagnosis especially for multi-
detection. We only used FCN-8s for this stage
as it provided best scores for the segmentation of
melanoma and seborrhoeic keratosis. For single-
detection, we directly assumed the detected lesion
class as same. There were very few cases of no de-
tection (13 cases out of 600) in testing set, we as-
sumed these cases as naevi for performance evalua-
tion. For multi-class detection, we adopted an prior-
ity based strategy for class prediction with preference
of the malignant lesions over the benign and number
of images in the training set according to the Table
4. For example, the (c) multi-detection case in Fig. 2
is classified as melanoma according to priority based
strategy.
In Table 5, we report the performance of selected
FCN-8s with post-processing method to determine le-
sion diagnosis. We achieved an Accuracy of 84.62%
Table 4: Priority strategy based on benign/malignant and
number of images in ISIC-2017 training set. Where SK is
seborrhoeic keratosis.
Priority Class Benign/Malignant No. of Images
1 Melanoma Malignant 541
2 SK Benign 387
3 Naevi Benign 1372
Table 5: The performance of FCN-8s with post-processing
method for lesion diagnosis on ISIC-2017 testing set.
Where SK is seborrhoeic keratosis.
Class No. of Cases Correct Incorrect Accuracy
Naevi 393 319 74 81.17
Melanoma 117 99 18 84.62
SK 90 67 23 74.44
Overall 600 485 115 80.83
for recognition of melanoma and 74.44% for sebor-
rhoeic keratosis with our proposed post-processing
method despite the poor performance of FCNs for
segmentation of melanoma and seborrhoeic keratosis.
4 CONCLUSION
We propose a fully automated multi-class semantic
segmentation for melanomas, naevi and seborrhoeic
keratosis in the ISIC 2017 Challenge dataset. Seg-
mentation of skin lesions is very challenging as there
are high intra-class variations and inter-class similar-
ities in terms of visual appearance, size and colour.
The literature on skin lesion segmentation only de-
scribes one-class solutions. Computer vision algo-
rithms can easily segment one class of skin lesion
from the surrounding healthy skin. But it remains a
major challenge to achieve good multi-class segmen-
tation results for multiple categories. We designed a
hybrid loss function and implemented two-tier trans-
fer learning and successfully established a new base-
line for multi-class segmentation for skin lesions. We
further investigated the post-processing method to im-
prove the lesion diagnosis of FCNs. With balanced
skin lesion dataset and expert annotation, the method
has potential to further improve the lesion diagnosis
with multi-class segmentation.
REFERENCES
Bi, L., Kim, J., Ahn, E., Kumar, A., Fulham, M., and
Feng, D. (2017). Dermoscopic image segmentation
C2C 2020 - Workshop on COMP2CLINIC: Biomedical Researchers Clinicians Closing The Gap Between Translational Research And
Healthcare Practice
294

via multi-stage fully convolutional networks. IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.
Codella, N. C., Gutman, D., Celebi, M. E., Helba, B.,
Marchetti, M. A., Dusza, S. W., Kalloo, A., Li-
opyris, K., Mishra, N., Kittler, H., et al. (2017).
Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A
challenge at the 2017 international symposium on
biomedical imaging (isbi), hosted by the international
skin imaging collaboration (isic). arXiv preprint
arXiv:1710.05006.
Dvo
ˇ
r
´
ankov
´
a, B., Szabo, P., Kodet, O., Strnad, H., Kol
´
a
ˇ
r,
M., Lacina, L., Krej
ˇ
c
´
ı, E., Na
ˇ
nka, O.,
ˇ
Sedo, A., and
Smetana, K. (2017). Intercellular crosstalk in human
malignant melanoma. Protoplasma, pages 1–8.
Everingham, M., Eslami, S. M. A., Van Gool, L., Williams,
C. K. I., Winn, J., and Zisserman, A. (2015). The pas-
cal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective.
International Journal of Computer Vision, 111(1):98–
136.
Garcia-Garcia, A., Orts-Escolano, S., Oprea, S., Villena-
Martinez, V., and Garcia-Rodriguez, J. (2017). A re-
view on deep learning techniques applied to semantic
segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.06857.
Goyal, M., Oakley, A., Bansal, P., Dancey, D., and Yap,
M. H. (2019). Skin lesion segmentation in dermo-
scopic images with ensemble deep learning methods.
IEEE Access, pages 1–1.
Goyal, M., Reeves, N. D., Rajbhandari, S., Spragg, J., and
Yap, M. H. (2017). Fully convolutional networks
for diabetic foot ulcer segmentation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1708.01928.
Jia, Y., Shelhamer, E., Donahue, J., Karayev, S., Long, J.,
Girshick, R., Guadarrama, S., and Darrell, T. (2014).
Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature em-
bedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM inter-
national conference on Multimedia, pages 675–678.
ACM.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In Advances in neural information process-
ing systems, pages 1097–1105.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. Nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., and Darrell, T. (2015). Fully con-
volutional networks for semantic segmentation. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition, pages 3431–3440.
Melanoma Foundation (AIM) (2017). Melanoma stats,
facts and figures. last access: 27/10/2017.
National Cancer Institute (2017). Cancer stat facts:
Melanoma of the skin. last access: 26/10/17.
Pathan, S., Prabhu, K. G., and Siddalingaswamy, P. (2018).
Techniques and algorithms for computer aided diag-
nosis of pigmented skin lesions—a review. Biomedi-
cal Signal Processing and Control, 39:237–262.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh,
S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla,
A., Bernstein, M., et al. (2014). Imagenet large
scale visual recognition challenge. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1409.0575.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep con-
volutional networks for large-scale image recognition.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
Yu, L., Chen, H., Dou, Q., Qin, J., and Heng, P.-A. (2017).
Automated melanoma recognition in dermoscopy im-
ages via very deep residual networks. IEEE transac-
tions on medical imaging, 36(4):994–1004.
Yuan, Y., Chao, M., and Lo, Y.-C. (2017). Automatic skin
lesion segmentation using deep fully convolutional
networks with jaccard distance. IEEE Transactions
on Medical Imaging.
Multi-class Semantic Segmentation of Skin Lesions via Fully Convolutional Networks
295
