
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative
Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center
Joshua J. Levy
1,2,3,* a
, Christopher R. Jackson
3
, Aravindhan Sriharan
3
, Brock C. Christensen
2 b
and Louis J. Vaickus
3
1
Program in Quantitative Biomedical Sciences, Geisel School of Medicine, Dartmouth, Lebanon, U.S.A.
2
Department of Epidemiology, Geisel School of Medicine, Dartmouth, Lebanon, U.S.A.
3
Department of Pathology, Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Dartmouth, Lebanon, U.S.A.
Keywords: Deep Learning, Histopathology, Image Translation.
Abstract: Evaluation of a tissue biopsy is often required for the diagnosis and prognostic staging of a disease. Recent
efforts have sought to accurately quantitate the distribution of tissue features and morphology in digitized
images of histological tissue sections, Whole Slide Images (WSI). Generative modeling techniques present a
unique opportunity to produce training data that can both augment these models and translate histologic data
across different intra-and-inter-institutional processing procedures, provide cost-effective ways to perform
computational chemical stains (synthetic stains) on tissue, and facilitate the creation of diagnostic aid
algorithms. A critical evaluation and understanding of these technologies is vital for their incorporation into
a clinical workflow. We illustrate several potential use cases of these techniques for the calculation of nuclear
to cytoplasm ratio, synthetic SOX10 immunohistochemistry (IHC, sIHC) staining to delineate cell lineage,
and the conversion of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain to trichome stain for the staging of liver fibrosis.
1 INTRODUCTION
The field of histopathology is the study of disease
using morphological and spatial distributions of
tissue features observed under a microscope as
performed by a board-certified pathologist. Tissue is
biopsied or excised, fixed via a combination of
formalin and heat processing, embedded in paraffin
to create formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded
tissue blocks (FFPE). The tissue is then sectioned via
a microtome into thin sheets (typically 2µM-8µM in
thickness), and chemically stained with various
reagents (most commonly hematoxylin and eosin,
H&E). Slides and tissue blocks are typically stored
for at least 10 years (depending on legal and
institutional regulations), although there is no
effective limit to their shelf life beyond slow
bleaching of dyes and degradation of DNA/RNA and
many academic institutions retain all tissue
indefinitely. Despite advancements in “gold-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8050-1291
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3022-426X
*Address correspondence to: joshua.j.levy.gr@dartmouth.
edu
standard” scoring metrics for tissue examination,
some diagnoses have a high inter-observer
disagreement between pathologists. Like other
medical professionals, pathologists are increasingly
overworked and reporting high levels of burnout
(Miller & Brown, 2018) which can significantly
impact turn-around-time (TAT) and in severe cases,
diagnostic accuracy. Moreover, maintaining a CLIA-
certified (Raab, 2000) histopathology laboratory
capable of performing special stains and
immunohistochemistry (IHC) is expensive and
requires specialized technologists, licenses,
instruments and reagents. Thus, there is a great need
for the development of accurate, interpretable,
quantitative medical decision aid algorithms and
workflows (Levy et al., 2020). In this article, we
evaluate the application of generative, quantitative
techniques in a variety of common scenarios in the
application of digital pathology to current analogue
workflows.
302
Levy, J., Jackson, C., Sriharan, A., Christensen, B. and Vaickus, L.
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center.
DOI: 10.5220/0009427603020311
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 302-311
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Generative modelling techniques aim to produce
partially or wholly synthetic data that has a similarly
high fidelity as the original or target data source. In
some cases, data produced by these generative
models can be used to enhance the performance of a
variety of downstream prediction or inference tasks
without the need to acquire additional, expensive,
expert annotated data. These modelling techniques
are useful in a wide variety of domains, including
inferring ties in social networks for modelling the
spread of healthy behaviors, robust translation for
hundreds of languages, and the imputation of
genomics data for the inference of more favorable
disease prognosis as it relates to therapy choices
(Lotfollahi et al., 2019; O’Malley, 2013; Young et al.,
2018).
An important application of these generative
techniques is the use of deep learning in medical
imaging. Deep learning approaches are data-driven
computational heuristics that “learn” to specify a
large set of nonlinear interactions between predictors
to understand their relationship with clinical
outcomes of interest through the use of artificial
neural networks (ANN) (Krizhevsky et al., 2012).
ANN are comprised of layers of nodes that represent
levels of abstraction of the data, where nodes
aggregate weighted information from the previous
layer of nodes, transform the data, and pass it to
downstream layers of nodes to characterize the tissue
image. We focus on a subclass of these methods,
generative adversarial networks (GANs).
GANs simultaneously train two ANN. The first
network generates an image of, for instance,
histological tissue, from a latent data distribution
(generator), and the other ANN discriminates whether
the supplied image is “real” or “fake”
(discriminator/critic). The number of publications on
GANs in medical imagery has rapidly increased in
recent years, with topics spanning medical image
segmentation, nucleus detection, style translation,
and upsampling of images (Yi et al., 2019).
A growing collection of studies have used GANs
to synthetically stain images of histological tissue
sections, which can save institutions time and money
(both in reagents and technologists’ time)
(Bayramoglu et al., 2017; Borhani et al., 2019; De
Biase, 2019; Lahiani et al., 2018; Quiros et al., 2019;
Rana et al., 2018; Rivenson, Liu, et al., 2019;
Rivenson, Wang, et al., 2019; Xu et al., 2019). GAN
models have also been used to remove artificial and
natural discolorations in images of stained
histological tissue sections that could perturb deep
learning analyses (Bentaieb & Hamarneh, 2018;
Ghazvinian Zanjani et al., 2018; Pontalba et al.,
2019). Other studies have sought to use GANs to
generate synthetic training data to increase the
generalizability of deep learning histopathology
models (Wei et al., 2019). A few studies used deep
generative techniques to derive nucleus masks
without the use of physician supplied annotations
(Bug et al., 2019; Gadermayr et al., 2019; Hollandi et
al., 2019; Mahmood et al., 2018).
Traditional unconditional GANs generate data by
using the discriminator to estimate and match the
distribution of the generated data to the real data.
Conditional GANs such as Pix2Pix (Isola et al., 2018)
are conditioned on the original labelled data while
attempting to directly match the target image. This
requires the pairing of images to learn the mapping
from source to target domain (Figure 1a). In
histopathology, perfectly registered paired images of
differentially stained tissue can often be difficult to
acquire (even when stereotactic sections are only
separated by 5µM) and therefore require accurate
annotation and registration, in which the images must
be warped, rotated and translated to most accurately
match the source domain. These registrations are not
entirely accurate and assume that the matched tissue
has no artifacts present (Borovec et al., 2019).
Additionally, the computational resources required to
register high resolution WSI with up to
80,000x80,000 pixels per color channel can be
exceedingly high. Another GAN architecture resolves
these issues: unconditional image-to-image
translation models such as CycleGAN (Zhu et al.,
2018) and UNIT (Zhu et al., 2018). In addition to
distributional matching of the real and synthetic target
and source domains, CycleGAN models learn to
recapitulate the source/target domain after using a
generator to construct the target/source image and
another generator to reconstruct the original image
(Figure 1b), which obviates the need to include
matched images. A mathematical description of these
two deep learning techniques have been included in
the appendix.
In light of the successes of these GAN techniques
in other domains, we sought to explore their
applications to the WSI’s generated during clinical
operations at the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical
Center Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Medicine (DHMC-PLM, a mid-sized National
Cancer Institute Cancer Center, NCI-CC). In this
study, we present preliminary results for the
application of the CycleGAN and Pix2Pix techniques
in calculating the nuclear to cytoplasm ratio of cells
in urine cytology specimens, the conversion of H&E
stains to predicted SOX10 immunohistochemistry,
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center
303
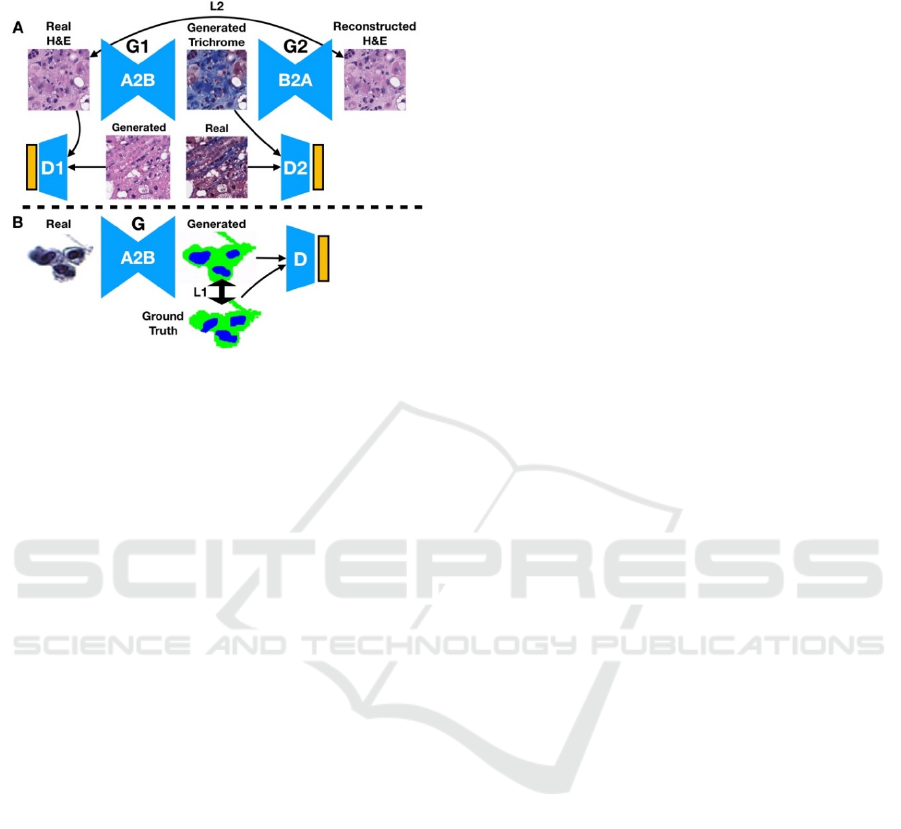
and the trichrome staining of liver tissue for fibrosis
analysis.
Figure 1: Illustration of (A) CycleGAN and (B) Pix2Pix
Deep Learning Techniques. (A) Trichrome stain is
generated from an H&E input image, which is in turn is
used to generate a reconstruction of the original H&E
image. The reconstructed image is compared to the original
via a reconstruction loss: the distribution of generated stains
are compared to the distribution of original stains via a
discriminator. The same process is used when converting
trichrome to H&E. (B) The urine segmentation mask is
generated from the real image. Real and generated
distributions are parameterized and compared both via the
discriminator and directly between paired generated masks
and ground truth segmentation masks.
2 METHODS
2.1 Data Preparation
Liver core needle biopsies obtained by various
approaches were fixed in formalin and processed into
FFPE tissue blocks; tissue sections were cut at 5μm
thickness and stained with H&E and trichrome stains
on adjacent levels, then scanned using the Leica
Aperio-AT2 scanner at 20x magnification. The
resulting images were stored natively as SVS files
and then converted to NPY and ZARR files for
preprocessing using PathFlowAI (Levy et al., 2020).
An SQL database was created containing patches
with 95% or greater non-white space. We extracted
500,000 and 290,000, unpaired, 256 pixel x 256 pixel
subimages from 241 H&E and Trichrome stained
WSI respectively as training data for a CycleGAN
model. Seventy-five percent of the liver WSI (n=178
specimens with both H&E and trichrome WSI) were
used to train the model, while 25% of the data was
reserved for testing (n=63 specimens with both H&E
and trichrome WSI).
For the urine cytology dataset, a total of 217
ThinPrep® urine cytology slides were collected and
scanned at 40x magnification using a Leica Aperio-
AT2 scanner to 80K x 80K SVS files. These files
were extracted to TIF images and resized to 40K x
40K. Via a process of background deletion and
connected component analysis (Vaickus et al., 2019)
we created libraries of cells from each of the WSI and
randomly sampled 10,936 cell images from the
25×10
6
extracted cellular objects. Manually
annotated and algorithmically (AutoParis) derived
segmentation masks delineating pixel-by-pixel areas
of the nucleus, cytoplasm and background were
paired with the original cell images (Vaickus et al.,
2019). The cell images were separated into 60%
training, 20% validation and 20% testing sets for
Pix2Pix.
For the SOX10 IHC, an unpaired dataset
containing a total of 15,000 H&E and 15,000 IHC,
256 pixel x 256 pixel subimages of skin and lymph
node histology were acquired to train a CycleGAN
model. Next, 30,000 paired H&E and IHC patches
were registered to each other using an alignment
technique that constructs a coarse pose
transformation matrix to perform an initial alignment
of the tissue, then dynamically warps and finetunes
the IHC to the respective H&E tissue. Alignments
with significantly poor warping were filtered out to
yield 15,000 paired images for training a Pix2Pix
model. The Pix2Pix IHC model data was split into
60% training, 20% validation and 20% testing. The
CycleGAN model data was split into 60% training
and 20% validation sets and shared the same test set
with the Pix2Pix model. An additional 20 melanoma
and 18 nevus cases (split into 224 x 224 pixel
subimages) were processed for subjective grading of
Pix2Pix and CycleGAN model outputs.
2.2 Analytic Approach
A CycleGAN model was fit on the liver dataset with
the purpose of converting H&E stained images into
trichrome stained images. We prioritized the ability
of the model to identify pronounced fibrous tissue
(portal tracts, large central veins, cirrhosis:
highlighted in blue by the trichrome stain).
Accordingly, highly blue patches were upsampled (as
determined by blue color channel thresholds) and the
reconstruction loss of trichrome stained tissue of the
CycleGAN was upweighted to 0.8 versus H&E
reconstructions (a process we are still fine-tuning).
The model was trained for a total of 6 epochs and then
the resulting model was utilized to construct entire
C2C 2020 - Workshop on COMP2CLINIC: Biomedical Researchers Clinicians Closing The Gap Between Translational Research And
Healthcare Practice
304

synthetic trichrome WSI from H&E WSI in the test
set. As a preliminary analysis, these synthetic images
were qualitatively evaluated for their fidelity to the
original trichrome (understain, equivalent, overstain)
and then a pathologist scored the synthetic and real
trichromes for the presence or absence of advanced
fibrosis (bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis).
Pix2Pix was used to predict nucleus and
cytoplasm segmentation masks for cells contained in
urine cytology specimens. The Pix2Pix model was
trained for 200 epochs using the default settings of a
publicly available repository and then evaluated on a
ground truth, hand-annotated test set. Pixel-level
accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of each
segmentation assignment (nucleus, cytoplasm,
background) to the original ground truth was
calculated and then the nucleus to cytoplasmic ratio
(NC) was compared using the R
2
correspondence.
We utilized 1000-sample nonparametric bootstrap
estimates to derive 95% confidence intervals for each
of these estimates.
For the SOX10 dataset, both CycleGAN and
Pix2Pix models were fit to the synthetic IHC dataset
and each model was trained for approximately 150
epochs. These models were then utilized to convert
H&E images into SOX10 IHC stained images. Color
deconvolution algorithms were able to decompose
both the real and generated IHC stained images into
SOX10-positive (via 3,3 ′ -Diaminobenzidine
(DAB) color deconvolution) and SOX10-negative
(via hematoxylin color deconvolution) binary masks
using color thresholding. Since there was imperfect
registration between the H&E and IHC images, the
resultant binary masks for each of the stains could not
be directly compared. Instead, the area of the SOX10
positive and SOX10 negative stains were compared
between the real and generated images across the test
set via 1000-sample nonparametric bootstrap
estimates of the 95% confidence intervals of the
correlation coefficient between the area of real and
generated positive and negatively stained tissue.
The architectures for the generators for both the
CycleGAN and Pix2Pix models utilized residual
neural network blocks (He et al., 2015).
3 PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Herein, we present our initial results from the
application of the aforementioned tasks:
3.1 Cytology Segmentation
Figure 2: Examples of original cell images (left), ground
truth segmentation masks (middle), and predicted
segmentation masks (right) for: (A) poor segmentation and
(B) excellent segmentation.
Table 1: Performance of Pix2Pix Urine Cell Nuclear and
Cytoplasm Segmentation.
Annotation
Type
Accuracy ±
SE
Sensitivity ±
SE
Specificity ±
SE
Background
0.98 ± 0.01 0.98 ± 0.01 0.98 ± 0.01
Cytoplasm
0.93 ± 0.05 0.91 ± 0.07 0.95 ± 0.05
Nucleus
0.94 ± 0.05 0.85 ± 0.16 0.96 ± 0.05
The NC ratio of urothelial cells is a metric that is
estimated by pathologists and considered in
combination with subjective measures of atypia to
screen urine cytology specimens for urothelial
carcinoma (bladder cancer) according to the gold
standard Paris System for Urine Cytology (Barkan et
al., 2016). The authors recently published a hybrid
morphometric and deep learning approach to
automating the Paris System utilizing a series of
specialists semantic segmentation networks for NC
ratio calculation requiring thousands of hand
annotated images (Vaickus et al., 2019). Improving
the quality and automation of cell compartment
segmentation could provide significant performance
gains to this and other automated techniques for the
performance of cytological cancer screening tests
(Layfield et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2019). Pix2Pix,
utilizing a rather small training set, achieved
remarkable segmentation performance, yielding an
macro-accuracy of 0.95 and an R
2
value of
0.74±0.019 between the ground truth and predicted
NC ratios across the test set (Table 1; Figure 2).
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center
305
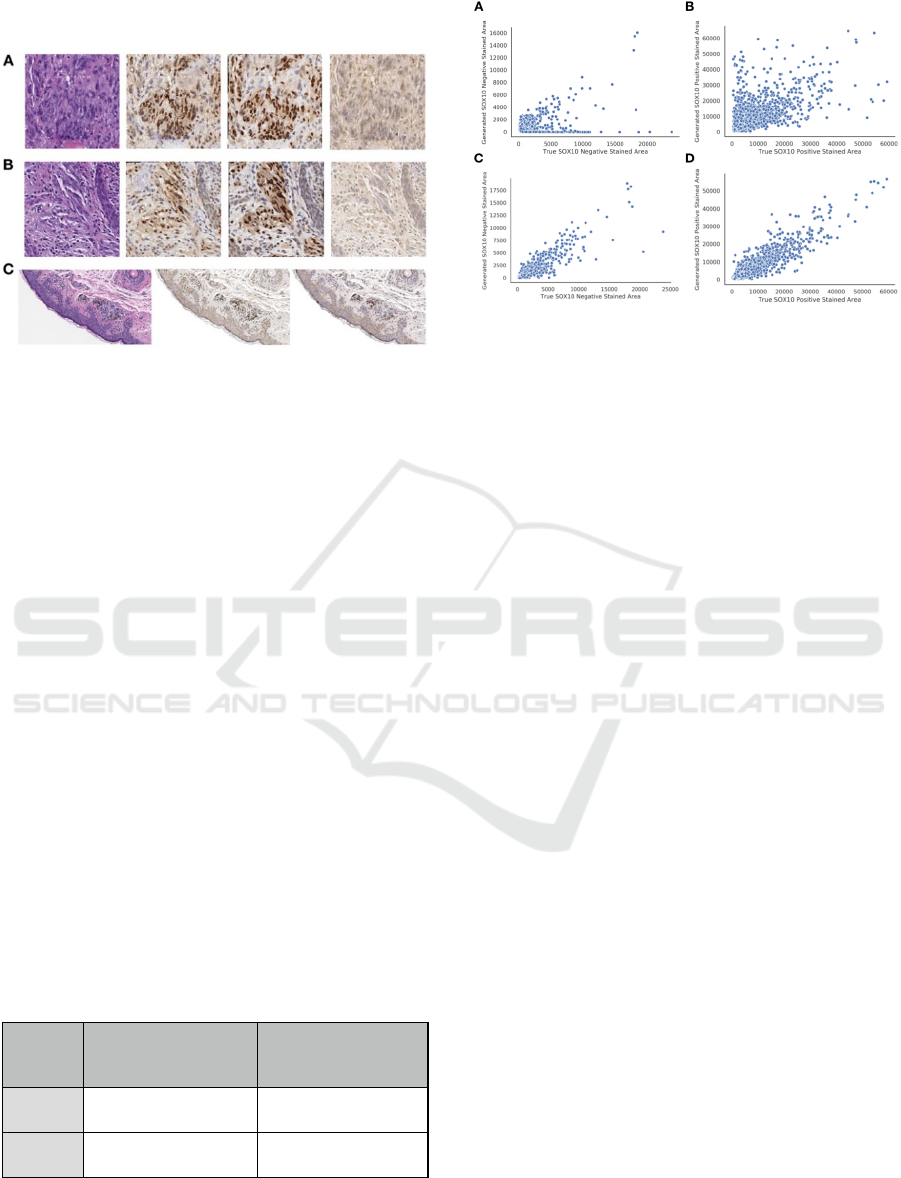
3.2 Synthetic IHC
Figure 3: Examples of Synthetic IHC Staining Technique
on: (A-B) Select image patches, organized by original H&E
(left), Pix2Pix generated IHC (left-center), True Registered
IHC (right-center), and CycleGAN generated IHC (right);
(C) Pix2Pix (center) and CycleGAN (right) IHC images
generated from large section of H&E stained tissue (left).
SOX10 is a nuclear transcription factor that is used in
IHC for the identification of cells with melanocytic/
Immunohistochemical stains generate a distinctive
brown color (DAB) on counterstained (hematoxylin)
tissue sections allowing for relatively simple color
deconvolution. Previous deep learning approaches
have been able to utilize mappings between H&E and
IHC tissue to learn antibody driven features in the
H&E that may be correspondent to the separation of
tumorous/non-tumorous tissue (Bulten & Litjens,
2018; Mohamed et al., 2013, p. 10; Willis et al.,
2015). The ability of a deep learning model to predict
the expression of DAB immunohistochemistry for a
nuclear transcription factor (SOX10) from an HE
stained image was first demonstrated by a resident
pathologist in our research program (Christopher
Jackson, MD) and presented at the 2019 meeting of
the American Society of Dermatopathology (full
manuscript currently in review) (Jackson, 2019).
Table 2: Comparison of CycleGAN versus Pix2Pix
performance on synthetic SOX10 IHC staining.
Method Positive SOX10 Stained
Area Predicted vs True
PearsonR ± SE
Negative SOX10 Stained
Area Predicted vs True
PearsonR ± SE
CycleGAN
0.66±0.021 0.39±0.065
Pix2Pix
0.93±0.0061 0.90±0.013
Utilizing CycleGAN, we found that the area of
SOX10 positive and negative staining was weakly
associated between the predicted and true IHC stains
Figure 4: Breakdown of true versus predicted SOX10
stained area for: (A, B) CycleGAN; (C, D) Pix2Pix; (A, C)
SOX10 Negative Staining; (B, D) SOX10 Positive
Staining.
(Table 2; Figures 3-4). However, when we trained on
pairs of imperfectly registered images using Pix2Pix,
we found much stronger correlations in the area of
SOX10 staining between predicted and true IHC
stains (Table 2; Figure 4). We also investigated each
algorithm’s ability to identify melanocytic tissue for
subjective analysis by pathologists and residents, in
which the superior performance of the Pix2Pix model
was consistently noted (Table 2; Figure 3-4).
3.3 Synthetic Trichrome Staining of
Liver Tissue
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is
characterized by steatosis and chronic inflammation
causing progressive liver injury and fibrosis in
patients where no alcoholic, genetic, metabolic, or
medication-based causes for hepatitis have been
identified (Masugi et al., 2017). Progressive NASH
can lead to cirrhosis with morbidities including
ascites, sepsis, coagulopathies, and nutritional
deficiencies, and a markedly increased risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). End stage cirrhosis
requires transplantation which has a tremendous
financial impact on the healthcare system and is
associated with substantial patient morbidity and
mortality. Fibrosis progression is typically assessed
via liver biopsy. After core needle or wedge biopsies
of the liver are obtained, pathologists score the tissue
for features of NASH (percentage steatosis, presence
of inflammatory cells and ballooning hepatocytes)
using an H&E stain, then stage the degree of fibrosis
with a trichrome stain, on which collagen (fibrous
tissue) is highlighted blue. Here, we used CycleGAN
to convert an H&E stain to a synthetic trichrome stain
on small image patches and combined these patches
C2C 2020 - Workshop on COMP2CLINIC: Biomedical Researchers Clinicians Closing The Gap Between Translational Research And
Healthcare Practice
306

to recapitulate the entire WSI (Figure 5). In visual
assessment of gross trichrome stained area by a
pathologist, the model showed a propensity for
overcalling fibrosis with 58% deemed subjectively
overstained, 37.5% deemed subjectively equivalent
to the real trichrome, and 4.1% deemed subjectively
understained. When a pathologist staged each
synthetic and real trichrome stain for the presence or
absence of advanced fibrosis (bridging fibrosis,
cirrhosis), the accuracy of the synthetic trichromes
was 79%, the sensitivity was 100% and the specificity
was 67% (n=24, Table 3).
Table 3: Confusion matrix for synthetic trichrome in
pathologist scoring of advanced fibrosis (bridging fibrosis,
cirrhosis) versus non-advanced fibrosis.
N = 24 Real + Real - Accuracy
0.79
Synth +
11 6
Sensitivity
1.00
Synth -
0 12
Specificity
0.67
Figure 5: Examples of liver tissue specimen.(A) Original
H&E stained tissue; (B) generated trichrome stain; (C)
original matched trichrome stain.
4 DISCUSSION
In this study, we illustrated a few potentially useful
applications of CycleGANs and Pix2Pix in the
clinical workflow of a pathology department at a mid-
sized NCI Cancer Center. We found these synthetic
staining and segmentation techniques to yield
satisfactory performance in some situations, which
we will continue to evaluate with larger datasets in
the future. GANs are relatively difficult to train,
partially in light of the non-convergence of the
model’s objective function after training for a long
period of time. The oscillation of the model loss
during training reflects the dynamic min-max
objective function between the generator and
discriminator. For incorporation into the clinical
workflow, these technologies will have to be
packaged in ways that are accessible to the clinical
researcher and clinician through simple GUIs and
common workflow specifications (Amstutz et al.,
2016) as well as provide for robust model validation.
We noted that Pix2Pix was able to accurately
differentiate nuclei from cytoplasm in cells from
urine cytology specimens. However, we noticed
instances where the model both over and under-called
nuclear area. This may be remedied by training the
model on larger datasets with a more diverse
sampling of nuclear and cytoplasmic morphologies.
Automated conversion of H&E to IHC presents an
exciting opportunity to directly train models off of
objective molecular targets which may decrease the
bias present in physician annotations. Our
preliminary results highlight the importance of using
registration to assist with the accurate conversion of
H&E to IHC. Regardless, we plan to investigate more
robust measures of tissue similarity between ground
truth and predicted stains (e.g. correspondence in
circular objects detected using SURF and SIFT
features) (Bay et al., 2006; Lowe, 2004). Current
image registration techniques are also
computationally intensive and imperfect (in this study
it took 5 days to register 12 HE WSI to their
respective IHC WSI). Further improvements in
registration accuracy are likely to improve the
synthetic IHC staining accuracy and we intend to
invest significant research time in this area.
Our initial attempt at training a liver H&E to a
synthetic trichrome staining model led to the gross
under-prediction of liver fibrosis. We remedied this
deficiency by supplying more images of highly
fibrous tissue areas in the training set and by
weighting to emphasise the reconstruction of fibrotic
tissue. As a result of this, the overall accuracy of
synthetic trichromes increased, but, perhaps
predictably, led to a moderate degree of
overestimation of fibrous tissue. Accordingly the
sensitivity of the model for advanced fibrosis was
high but the specificity was subpar. This result would
likely be acceptable for a screening test, but given that
the consequences of both over and under-calling liver
fibrosis level are severe, synthetic trichromes for liver
fibrosis staging would require very high sensitivity
and specificity to be clinically usable. Further tuning
of the model hyperparameters, architectures and/or
the application of other generative techniques will be
necessary to achieve better accuracy (Xu et al., 2019).
Given the superiority of the Pix2Pix in the synthetic
IHC task, we intend to attempt to register the H&E
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center
307

and trichrome training images (however imperfectly).
Considering that in every case the HE section is only
stereotactically separated from the trichrome section
by a 5 µM, this approach may prove successful,
however, it is largely reliant on expert sectioning and
placement of tissue slices by our histotechnologists.
Regardless, our results provide a framework to
improve upon these synthetic staining techniques for
incorporation into the clinical workflow.
In light of these investigations, we find that
generative models (CycleGAN, Pix2Pix) are well-
positioned to supplement engineering solutions that
are being developed to improve the efficiency and
accuracy of histopathological diagnosis. Generally,
clinicians at our institution are most interested in
digital aids that either cut-down on cost and time to
render a diagnosis or that automate tedious, error-
prone tasks (such as IHC quantitation). These
concerns are well met by our initial investigations. In
the future, we will consider applications of generative
models for the detection of cells for our clinical
workflow, for standardizing stains from a collection
of different institutions by translating to a common
synthetic stain, and for superresolution techniques
that may enable high-precision digital pathology from
low fidelity source material.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we assessed the ability of deep learning
image-to-image translation models to perform
nucleus/cytoplasm segmentation in cells from urine
cytology specimens, and synthetic trichrome and IHC
staining on liver and skin WSI respectively. These
initial investigations provide further evidence in favor
of the incorporation of generative models into the
core clinical workflow of a hospital pathology
service. These methods may reduce the costs and time
associated with chemical staining and manual image
annotations while providing unbiased means for the
molecular assessment of tissue. We will continue to
assess additional applications of these technologies
on new use cases with more robust measures of
concordance and larger repositories of data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by NIH grant
R01CA216265 and a grant from the DHMC Norris
Cotton Cancer Center, Cancer Fellows Program. JL is
supported through the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Big
Data in the Life Sciences at Dartmouth.
REFERENCES
Amstutz, P., Crusoe, M. R., Tijanić, N., Chapman, B.,
Chilton, J., Heuer, M., Kartashov, A., Leehr, D.,
Ménager, H., Nedeljkovich, M., Scales, M., Soiland-
Reyes, S., & Stojanovic, L. (2016). Common Workflow
Language, v1.0. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.
3115156.v2
Barkan, G. A., Wojcik, E. M., Nayar, R., Savic-Prince, S.,
Quek, M. L., Kurtycz, D. F. I., & Rosenthal, D. L.
(2016). The Paris System for Reporting Urinary
Cytology: The Quest to Develop a Standardized
Terminology. Acta Cytologica, 60(3), 185–197.
https://doi.org/10.1159/000446270
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., & Van Gool, L. (2006). SURF:
Speeded Up Robust Features. In A. Leonardis, H.
Bischof, & A. Pinz (Eds.), Computer Vision – ECCV
2006 (pp. 404–417). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/
11744023_32
Bayramoglu, N., Kaakinen, M., Eklund, L., & Heikkila, J.
(2017). Towards Virtual H&E Staining of
Hyperspectral Lung Histology Images Using
Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. 64–71.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2017.15
Bentaieb, A., & Hamarneh, G. (2018). Adversarial Stain
Transfer for Histopathology Image Analysis. IEEE
Transactions on Medical Imaging, 37(3), 792–802.
https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2017.2781228
Borhani, N., Bower, A. J., Boppart, S. A., & Psaltis, D.
(2019). Digital staining through the application of deep
neural networks to multi-modal multi-photon
microscopy. Biomedical Optics Express, 10(3), 1339–
1350. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.10.001339
Borovec, J., Kybic, J., & Muñoz-Barrutia, A. (2019, April
11). Automatic Non-rigid Histological Image
Registration challenge. https://doi.org/10.13140/
RG.2.2.12974.77126/2
Bug, D., Gräbel, P., Feuerhake, F., Oswald, E., Schüler, J.,
& Merhof, D. (2019). Supervised and Unsupervised
Cell-Nuclei Detection in Immunohistology.
Bulten, W., & Litjens, G. (2018). Unsupervised Prostate
Cancer Detection on H&E using Convolutional
Adversarial Autoencoders. https://openreview.net/
forum?id=Syoj0k2iG
De Biase, A. (2019). Generative Adversarial Networks to
enhance decision support in digital pathology.
http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:liu:diva-
158486
Gadermayr, M., Gupta, L., Klinkhammer, B. M., Boor, P.,
& Merhof, D. (2019). Unsupervisedly Training GANs
for Segmenting Digital Pathology with Automatically
Generated Annotations. International Conference on
Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, 175–184.
http://proceedings.mlr.press/v102/gadermayr19a.html
Ghazvinian Zanjani, F., Zinger, S., Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.,
van der Laak, J., & With, P. (2018). Stain normalization
of histopathology images using generative adversarial
networks. 573–577. https://doi.org/10.1109/
ISBI.2018.8363641
C2C 2020 - Workshop on COMP2CLINIC: Biomedical Researchers Clinicians Closing The Gap Between Translational Research And
Healthcare Practice
308

He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Deep Residual
Learning for Image Recognition. ArXiv:1512.03385
[Cs]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
Hollandi, R., Szkalisity, A., Toth, T., Tasnadi, E., Molnar,
C., Mathe, B., Grexa, I., Molnar, J., Balind, A., Gorbe,
M., Kovacs, M., Migh, E., Goodman, A., Balassa, T.,
Koos, K., Wang, W., Bara, N., Kovacs, F., Paavolainen,
L., … Horvath, P. (2019). A deep learning framework
for nucleus segmentation using image style transfer.
BioRxiv, 580605. https://doi.org/10.1101/580605
Isola, P., Zhu, J.-Y., Zhou, T., & Efros, A. A. (2018).
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional
Adversarial Networks. ArXiv:1611.07004 [Cs].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004
Jackson, C. (2019, October 17). Sox-10 Virtual
Immunohistochemistry: An Application of Artificial
Intelligence Using a Convolutional Neural Network.
ADSP 56th annual meeting.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2012).
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional
Neural Networks. In F. Pereira, C. J. C. Burges, L.
Bottou, & K. Q. Weinberger (Eds.), Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems 25 (pp. 1097–1105).
Curran Associates, Inc. http://papers.nips.cc/paper/
4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-
convolutional-neural-networks.pdf
Lahiani, A., Gildenblat, J., Klaman, I., Albarqouni, S.,
Navab, N., & Klaiman, E. (2018). Virtualization of
tissue staining in digital pathology using an
unsupervised deep learning approach.
ArXiv:1810.06415 [Cs]. http://arxiv.org/abs/
1810.06415
Layfield, L. J., Esebua, M., Frazier, S. R., Hammer, R. D.,
Bivin, W. W., Nguyen, V., Ersoy, I., & Schmidt, R. L.
(2017). Accuracy and Reproducibility of
Nuclear/Cytoplasmic Ratio Assessments in Urinary
Cytology Specimens. Diagnostic Cytopathology, 45(2),
107–112. https://doi.org/10.1002/dc.23639
Levy, J., Salas, L. A., Christensen, B. C., Sriharan, A., &
Vaickus, L. J. (2020). PathFlowAI: A High-Throughput
Workflow for Preprocessing, Deep Learning and
Interpretation in Digital Pathology. Pacific Symposium
on Biocomputing, 25, 403–414. https://doi.org/
10.1101/19003897
Lotfollahi, M., Wolf, F. A., & Theis, F. J. (2019). ScGen
predicts single-cell perturbation responses. Nature
Methods, 16(8), 715–721. https://doi.org/10.1038/
s41592-019-0494-8
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive Image Features from Scale-
Invariant Keypoints. International Journal of
Computer Vision, 60(2), 91–110. https://doi.org/
10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94
Mahmood, F., Borders, D., Chen, R., McKay, G. N.,
Salimian, K. J., Baras, A., & Durr, N. J. (2018). Deep
Adversarial Training for Multi-Organ Nuclei
Segmentation in Histopathology Images.
ArXiv:1810.00236 [Cs]. http://arxiv.org/abs/
1810.00236
Masugi, Y., Abe, T., Tsujikawa, H., Effendi, K.,
Hashiguchi, A., Abe, M., Imai, Y., Hino, K., Hige, S.,
Kawanaka, M., Yamada, G., Kage, M., Korenaga, M.,
Hiasa, Y., Mizokami, M., & Sakamoto, M. (2017).
Quantitative assessment of liver fibrosis reveals a
nonlinear association with fibrosis stage in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Masugi, Abe, et al.
Hepatology Communications, 2. https://doi.org/
10.1002/hep4.1121
Miller, D. D., & Brown, E. W. (2018). Artificial
Intelligence in Medical Practice: The Question to the
Answer? The American Journal of Medicine, 131(2),
129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.amjmed.2017.10.035
Mohamed, A., Gonzalez, R. S., Lawson, D., Wang, J., &
Cohen, C. (2013). SOX10 Expression in Malignant
Melanoma, Carcinoma, and Normal Tissues. Applied
Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology,
21(6), 506. https://doi.org/10.1097/
PAI.0b013e318279bc0a
O’Malley, A. J. (2013). The analysis of social network data:
An exciting frontier for statisticians. Statistics in
Medicine, 32(4), 539–555. https://doi.org/10.1002/
sim.5630
Pontalba, J. T., Gwynne-Timothy, T., David, E., Jakate, K.,
Androutsos, D., & Khademi, A. (2019). Assessing the
Impact of Color Normalization in Convolutional Neural
Network-Based Nuclei Segmentation Frameworks.
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 7, 300.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00300
Quiros, A. C., Murray-Smith, R., & Yuan, K. (2019).
Pathology GAN: Learning deep representations of
cancer tissue. ArXiv:1907.02644 [Cs, Eess, Stat].
http://arxiv.org/abs/1907.02644
Raab, S. S. (2000). The Cost-Effectiveness of
Immunohistochemistry. Archives of Pathology &
Laboratory Medicine, 124(8), 1185–1191.
https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-
9985(2000)124<1185:TCEOI>2.0.CO;2
Rana, A., Yauney, G., Lowe, A., & Shah, P. (2018).
Computational Histological Staining and Destaining of
Prostate Core Biopsy RGB Images with Generative
Adversarial Neural Networks. 2018 17th IEEE
International Conference on Machine Learning and
Applications (ICMLA), 828–834. https://doi.org/
10.1109/ICMLA.2018.00133
Rivenson, Y., Liu, T., Wei, Z., Zhang, Y., Haan, K. de, &
Ozcan, A. (2019). PhaseStain: The digital staining of
label-free quantitative phase microscopy images using
deep learning. Light: Science & Applications, 8(1), 1–
11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-019-0129-y
Rivenson, Y., Wang, H., Wei, Z., Haan, K., Zhang, Y., Wu,
Y., Gunaydin, H., Zuckerman, J., Chong, T., Sisk, A.,
Westbrook, L., Wallace, W., & Ozcan, A. (2019).
Virtual histological staining of unlabelled tissue-
autofluorescence images via deep learning. Nature
Biomedical Engineering, 3. https://doi.org/10.1038/
s41551-019-0362-y
Vaickus, L. J., Suriawinata, A. A., Wei, J. W., & Liu, X.
(2019). Automating the Paris System for urine
cytopathology—A hybrid deep-learning and
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center
309

morphometric approach. Cancer Cytopathology,
127(2), 98–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncy.22099
Wang, S., Yang, D. M., Rong, R., Zhan, X., & Xiao, G.
(2019). Pathology Image Analysis Using Segmentation
Deep Learning Algorithms. The American Journal of
Pathology, 189(9), 1686–1698. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.ajpath.2019.05.007
Wei, J., Suriawinata, A. A., Vaickus, L., Ren, B., Liu, X.,
Wei, J., & Hassanpour, S. (2019). Generative Image
Translation for Data Augmentation in Colorectal
Histopathology Images. ArXiv, abs/1910.05827.
Willis, B. C., Johnson, G., Wang, J., & Cohen, C. (2015).
SOX10: A Useful Marker for Identifying Metastatic
Melanoma in Sentinel Lymph Nodes. Applied
Immunohistochemistry & Molecular Morphology,
23(2), 109. https://doi.org/10.1097/
PAI.0000000000000097
Xu, Z., Fernández Moro, C., Bozóky, B., & Zhang, Q.
(2019). GAN-based Virtual Re-Staining: A Promising
Solution for Whole Slide Image Analysis.
Yi, X., Walia, E., & Babyn, P. (2019). Generative
adversarial network in medical imaging: A review.
Medical Image Analysis, 58, 101552. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.media.2019.101552
Young, T., Hazarika, D., Poria, S., & Cambria, E. (2018).
Recent Trends in Deep Learning Based Natural
Language Processing [Review Article]. IEEE
Computational Intelligence Magazine, 13(3), 55–75.
https://doi.org/10.1109/MCI.2018.2840738
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., & Efros, A. A. (2018).
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-
Consistent Adversarial Networks. ArXiv:1703.10593
[Cs]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.10593
APPENDIX
Mathematical Description of CycleGAN
and Pix2Pix Objective Functions
GANs are tasked with learning a source/target
domain Y from latent noise vector Z via mapping G.
The loss function for a GAN is specified by:
,
1
(1)
The ideal generator is acquired through
alternating updates to the generator and discriminator
parameters:
G
∗
argmin
max
,
(2)
The objective is minimized with respect to the
generator parameters to maximize the discriminator’s
output for generated data D(G(z)) to attempt to fool
the discriminator, which aims to maximize the
separation between the real and generated data, as
parameterized by the discriminator. The loss is
maximized with respect to the discriminator’s
parameters. GANs can be difficult to train, thus
alterations to the objective such as the Wasserstein
distance and gradient penalties have been introduced.
The goal of Image-to-Image translation is to learn
a mapping from source domain/observed image X to
a target domain Y via a generator G: X →Y.
The generator for both of the Pix2Pix and
CycleGAN models compress input data X into a latent
subspace Z by subsequent applications of
convolutional and pooling/aggregation operators,
then decompress the latent information Z into the
target Y via upsampling and deconvolution operators.
Pix2Pix accomplishes the mapping G through
generation of Y from X and Z. The original image X
and target image Y are concatenated together, and
original image X and generated image G(x,z) are
concatenated. Both of these images are passed
through the discriminator via the objective:
,
,
,
,
1
,
,
(3
)
This loss function is supplemented by an L1-Loss
that compares the generated image with the target
image:
,,
|
,
|
(4)
The optimization process is identical to the GAN
training process and is performed on a weighted
combination of the conditional GAN (cGAN) and L1
objectives.
The CycleGAN model trains two generators, G: X
→ Y and F: Y→X, and utilizes discriminators,
and
for the source and target domains respectively.
The CycleGAN objective utilizes a cycle-consistent
loss, which assumes that original data X, mapped to Y
via G, then mapped back via F, should resemble the
original data source. This is expressed as:
,
λ
λ
(5)
There two weighting terms control the importance
of generating from one domain versus the other. The
final objective adds the cycle-consistent loss to
adversarial losses for the source and target domains:
C2C 2020 - Workshop on COMP2CLINIC: Biomedical Researchers Clinicians Closing The Gap Between Translational Research And
Healthcare Practice
310

,,
,
λ
,
,
,
(6)
A similar minmax optimization of the objective is
used to obtain the ideal parameterization of G and F
to realize the translation from X to Y when images are
unpaired.
Code and Data Availability
The CycleGAN and Pix2Pix models that were
utilized in this study were trained using PyTorch
1.3.0, code was adopted from GitHub repository
https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-
pix2pix. Additionally, we provide helper scripts and
small test datasets, which will undergo continuous
updating, in our GitHub repository:
https://github.com/jlevy44/PreliminaryGenerativeHi
stoPath. PathFlowAI, which was utilized to prepare
the data for the H&E to Trichrome analysis is
available at: https://github.com/jlevy44/PathFlowAI.
Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center
311
