
Evaluation of Stair Climbing as an Approach for Estimating Heart Rate
Recovery in Daily Activities
Daivaras Sokas
1
, Andrius Rapalis
1,2
, Andrius Petr
˙
enas
1,2
, Saulius Daukantas
1
and
Vaidotas Marozas
1,2
1
Biomedical Engineering Institute, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania
2
Department of Electronics Engineering, Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania
Keywords:
Stair Climbing, Heart Rate Recovery, Daily Activities, Fitbit, YMCA.
Abstract:
Post-Exercise heart rate recovery (HRR) is a convenient approach to assess cardiovascular autonomic function.
Ordinary stair climbing can be viewed as an alternative HRR test performed in daily activities, and also well-
suited for implementation in wrist-worn devices. This study compares HHR parameters estimated after stair
climbing to those obtained by performing the conventional YMCA bench step test using a custom-made wrist-
worn device and a consumer smart wristband Fitbit Charge 2. The results show that most HHR parameters are
underestimated after stair climbing but still comparable to those obtained from the bench step test. The lowest
relative error, 8–11% on average, was found for the decay of heart rate in 30, 60, and 120 s after the recovery
onset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Post-exercise heart rate recovery (HRR) is a simple
non-invasive approach to assess cardiovascular auto-
nomic function (Jouven et al., 2005; Pec¸anha et al.,
2017). Slower HRR is associated with decreased
physical fitness, cardiovascular diseases, and is a pre-
dictor of death (Jouven et al., 2005; Pec¸anha et al.,
2017). HRR can be improved by cardiac rehabilita-
tion (Streuber et al., 2006; Hai et al., 2010) and even
weight loss (Thomson et al., 2010). Therefore, HRR
trend monitoring could be useful for assessing the ef-
fectiveness of exercise training at home environment.
HRR is assessed using standardised tests that re-
quire specialised equipment and supervision. Hence,
it is inconvenient for use outside the clinical setting.
Improvement in wearable device technology gives op-
portunity to evaluate HRR by using a photoplethys-
mogram (PPG) signal (Sokas et al., 2019). Since stair
climbing is a common daily activity that require phys-
ical effort, and is usually followed by slow walking or
rest, this activity can be considered as an alternative
HRR test performed in free-living conditions.
Our previous work reported the feasibility of esti-
mating HRR parameters after stair climbing using the
wrist-worn device with the embedded PPG and baro-
metric pressure sensors (Sokas et al., 2019). However,
it is unclear how the new approach compares to the
conventional bench step test. Accordingly, the aim of
this study is to compare the agreement of HRR param-
eters estimated after stair climbing to those obtained
by performing the bench step test.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Study Population and Data
Acquisition
Fifty-four healthy volunteers (18 women), 25.5 ± 8.1
(mean ± SD) years old (range 18 to 50 years), with a
height of 177.4 ± 8.5 cm, weight of 73.7 ± 14.4 kg,
and body mass index of 23.3 ± 3.9 kg/m
2
were en-
rolled in the study.
The study was performed according to the pro-
tocol given in Figure 1. Participants were asked to
climb four floors (96 stairs in total) three times at dif-
ferent climbing rate: 48, 72, and 96 steps per minute.
After each activity, the participants had to rest in a
standing position for five minutes, slowly descend
to the ground floor and rest for three minutes be-
fore the next activity. The YMCA bench step test
was performed using the protocol described in (Gold-
ing, 2000) during which a participant has to step on
a 30.5 cm high bench for 3 min at a stepping rate
Sokas, D., Rapalis, A., Petr
˙
enas, A., Daukantas, S. and Marozas, V.
Evaluation of Stair Climbing as an Approach for Estimating Heart Rate Recovery in Daily Activities.
DOI: 10.5220/0010184500210025
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 21-25
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
21

5 min
rest
48
steps/min
72
steps/min
96
steps/min
5 min
rest
5 min
rest
5 min
rest
3 min
rest
3 min
rest
3 min
rest
15 min
rest
96
steps/min
3 min
test
Figure 1: The protocol of consecutive stair climbing at different rates and the bench step test. All activities are separated by
rest periods.
of 96 steps per minute (288 steps in total) and to sit
down for 5 min after the exercise is finished. An elec-
tronic metronome ensured steady stepping rate for
both tests.
Data were acquired using the custom-made wrist-
worn device (Biomedical Engineering Institute, Kau-
nas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania) on
the left wrist and the consumer smart wristband Fit-
bit Charge 2 (Fitbit Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA) on
the right wrist. A wrist-worn device synchronously
acquires electrocardiogram (ECG) at a sampling rate
of 500 Hz, photoplethysmogram (PPG) at a sampling
rate of 100 Hz, and barometric pressure at a sampling
rate of 50 Hz with an altitude resolution of 10 cm.
The consumer smart wristband provides a pulse rate
at intervals of 5 s or longer, depending on the quality
of the PPG signal.
The study was conducted by following the ethi-
cal principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Identi-
fiable information was removed to ensure participant
anonymity.
2.2 Estimation of Heart Rate Recovery
Heart rate normally recovers exponentially thus it can
be approximated by a mono-exponential model. The
exponential model is fitted in a 5 min time interval
after the physical activity and the time-constant τ of
exponential decay is estimated. Detection of the re-
covery onset, i.e., the end of stair climbing, in heart
rate series was performed relying on the procedure
described in (Sokas et al., 2019). The quality of ex-
ponential fitting is assessed via the coefficient of de-
termination which should exceed a fixed threshold of
0.5 to consider the fitting acceptable.
The rapid heart rate decay immediately after the
recovery onset is characterized by the short-term time
constant T30 (Pec¸anha et al., 2017). T30 is found by
fitting a line to the logarithm of heart rate and is the
negative inverse of the slope of the resulting line, ex-
pressed as -1/slope. The decay of heart rate in 30 s,
60 s and 120 s after the recovery onset is denoted
HR30, HR60, and HR120, respectively. The differ-
ence between the maximal heart rate at recovery onset
and the baseline heart rate (i.e., minimal heart rate at
the end of the recovery period) is denoted ∆HR.
3 RESULTS
Figure 2 shows the Bland-Altman plots of HRR pa-
rameters estimated from the reference ECG after stair
climbing at rate of 96 steps/min and the YMCA bench
step test. Given that ordinary stair climbing is less
intense activity than the bench step test, it is unsur-
prising that most parameters are underestimated, with
the exception of HR120 and T30. No bias in estimat-
ing HR120 can be explained by return of heart rate to
baseline, whereas T30 might be less affected by ac-
tivity intensity since it depends on the heart rate slope
rather than on absolute values.
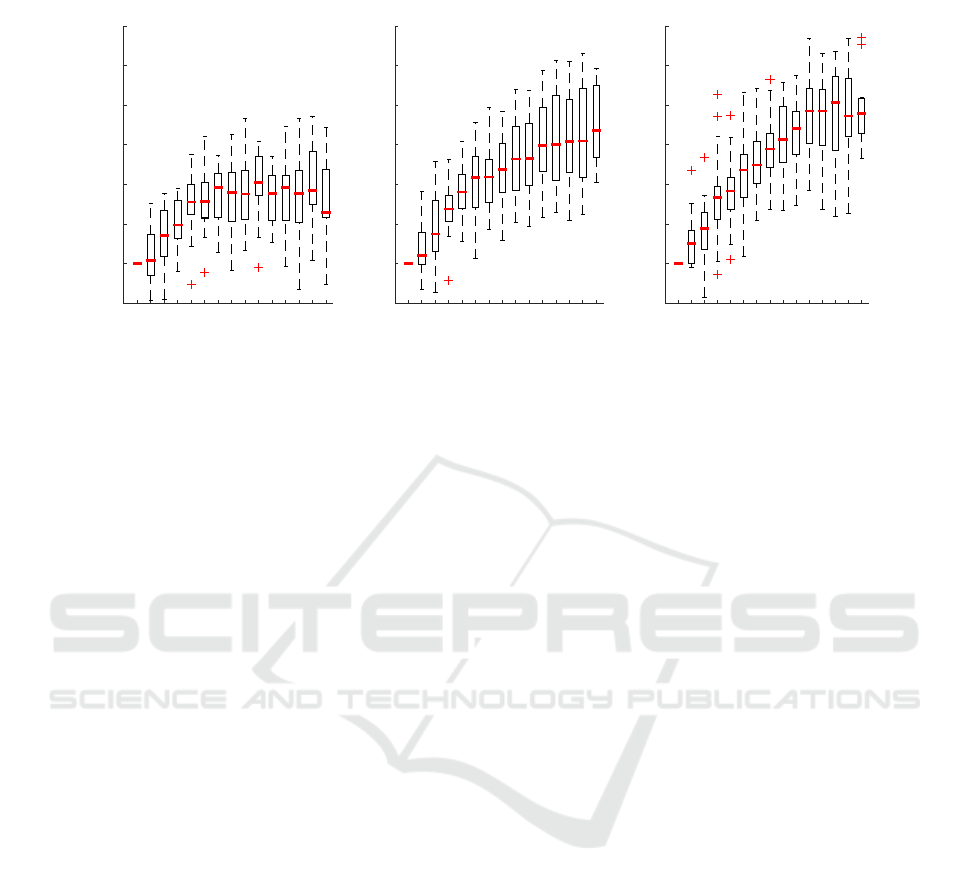
Figure 3 shows that lowest absolute and relative
errors are obtained for HR30, HR60, and HR120,
whereas are larger for the remaining parameters. In-
terestingly, absolute and relative errors estimated us-
ing wrist-worn devices are similar to those obtained
from the reference ECG, suggesting PPG as a useful
signal for HRR estimation.
The impact of stair climbing altitude and different
climbing rate on change in heart rate is illustrated in
Fig. 4. Heart rate tends to increase and then reaches
a plateau at 5 meters of altitude for low climbing in-
tensity (48 steps/min). For climbing rates of 72 and
96 steps/min, heart rate rises rapidly up to 10 me-
tres of altitude and then continues to increase only
marginally.
4 DISCUSSION
With this study we seek to take a further step towards
providing a more comprehensive information about
health status next to available heart rate and physical
activity parameters offered by most consumer wrist-
worn devices.
The stair climbing test has not yet been standard-
ised, probably due to different protocols applied in
BIOSIGNALS 2021 - 14th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
22

(HR30 + HR30
Y M CA
)/2, bpm
80 100 120 140 160 180
HR30 - HR30
Y M CA
, bpm
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
1.96 SD
-1.96 SD
Bias
21.5
-43.4
-10.9
HR30
(HR60 + HR60
Y M CA
)/2, bpm
60 80 100 120 140 160
HR60 - HR60
Y M CA
, bpm
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
1.96 SD
-1.96 SD
Bias
24.3
-36.4
-6.046
HR60
(HR120 + HR120
Y M CA
)/2, bpm
60 80 100 120 140
HR120 - HR120
Y M CA
, bpm
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
1.96 SD
-1.96 SD
Bias
26.4
-26.4
-0.006
HR120
(∆HR + ∆HR
Y M CA
)/2, bpm
30 40 50 60 70 80
∆HR - ∆HR
Y M CA
, bpm
-50
0
50
1.96 SD
-1.96 SD
Bias
3.8
-35.1
-15.7
∆HR
(τ + τ
Y M CA
)/2, s
20 40 60 80 100
τ − τ
Y M CA
, s
-100
-50
0
50
1.96 SD
-1.96 SD
Bias
27.6
-76.3
-24.3
τ
(T 30 + T 30
Y M CA
)/2, -1/slope
-1.2 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4
T 30 − T 30
Y M CA
, -1/slope
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.96 SD
-1.96 SD
Bias
0.5
-0.7
-0.1
T 30
Figure 2: Comparison of HRR parameters estimated after stair climbing (rate of 96 steps/min) and by performing the YMCA
bench step test. The parameters are estimated from the reference ECG.
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Absolute error, bpm
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Absolute error, bpm
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Absolute error, bpm
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Absolute error, bpm
ECGPPGFitbit
0
20
40
60
80
100
Absolute error, s
ECGPPGFitbit
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
Absolute error, 1/slope
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Relative error, %
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Relative error, %
ECGPPGFitbit
0
10
20
30
40
50
Relative error, %
ECGPPGFitbit
0
20
40
60
80
100
Relative error, %
ECGPPGFitbit
0
20
40
60
80
100
Relative error, %
ECGPPGFitbit
0
20
40
60
80
100
Relative error, %
Figure 3: Absolute (top row) and relative (bottom row) HRR parameter estimation errors when comparing stair climbing at a
rate of 96 steps/min to the YMCA bench step test.
Evaluation of Stair Climbing as an Approach for Estimating Heart Rate Recovery in Daily Activities
23
Altitude, m
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
∆HR, bpm
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
a)
Altitude, m
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
∆HR, bpm
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
b)
Altitude, m
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
∆HR, bpm
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
c)
Figure 4: ∆HR as a function of altitude for different climbing intensity: a) 48 steps/min, b) 72 steps/min, c) 96 steps/min.
Heart rate is averaged over 1 m of altitude. Altitude data was acquired using the custom-made wrist-worn device.
various studies. Common approach is to instruct pa-
tients (eg, after lung resection (Kubori et al., 2017)) to
climb the maximum number of stairs at a convenient
pace, and to stop only due to exhaustion, leg fatigue
or chest pain. The ability to climb the stairs largely
depends on respiratory system thus the total number
of climbed stairs can be complemented with HRR pa-
rameters to better represent the status of cardiorespi-
ratory system.
Clinical research shows that most established and
reproducible HRR parameters are the decay of heart
rate in 60, 120, and 300 s (Pec¸anha et al., 2017; Fec-
chio et al., 2019). While a single point measurement
is well-suited in a controlled environment (e.g., labo-
ratory), it is less reliable in free-living conditions be-
cause it requires accurate detection of the recovery
onset. Exponential fitting or a short-term time con-
stant should potentially be more stable than the de-
cay measures since a large part of the recovery phase
is involved for estimation. However, our current and
previous (Sokas et al., 2019) findings show that this
is not the case, probably due to sensitivity of these
parameters to the slope of the HRR curve, which is
affected by insufficient physical load reducing fitting
reliability.
HRR parameters often show increased repro-
ducibility after maximal exercise (Boullosa et al.,
2014), which is more similar to the YMCA bench step
test. Therefore, parameter estimation error can be re-
duced at higher climbing rates, assuming that the de-
cay phase will be better expressed. Our study shows
that 5 to 10 meters of climbing altitude is required to
increase heart rate by 20–30 bpm and reach plateau.
Due to simplicity and similarity to ordinary stair
climbing, we selected the YMCA bench step test as a
reference test in this study. However, the results may
differ if other stair climbing test is employed instead.
5 CONCLUSION
This study shows that most HHR parameters are un-
derestimated after stair climbing however are still
comparable to those obtained from the conventional
bench step test. The decay of heart rate in 30, 60, and
120 s was estimated with the lowest error.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was financially supported by the Research
Council of Lithuania (Agreement No. S-MIP-20-54).
REFERENCES
Boullosa, D. A., Barros, E. S., Del Rosso, S., Nakamura,
F. Y., and Leicht, A. S. (2014). Reliability of heart
rate measures during walking before and after run-
ning maximal efforts. International Journal of Sports
Medicine, 35(12):999–1005.
Fecchio, R. Y., Brito, L., Leicht, A. S., Forjaz, C. L.,
and Pec¸anha, T. (2019). Reproducibility of post-
exercise heart rate recovery indices: A systematic re-
view. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical,
221:102582.
Golding, L. A., editor (2000). YMCA Fitness Testing
and Assessment Manual. Human Kinetics Publishers,
Champaign, IL, USA, 4th edition.
Hai, J. J., Siu, C. W., Ho, H. H., Li, S. W., Lee, S., and Tse,
H. F. (2010). Relationship between changes in heart
BIOSIGNALS 2021 - 14th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
24

rate recovery after cardiac rehabilitation on cardiovas-
cular mortality in patients with myocardial infarction.
Heart Rhythm, 7(7):929–936.
Jouven, X., Empana, J. P., Schwartz, P. J., Desnos, M.,
Courbon, D., and Ducimeti
`
ere, P. (2005). Heart-rate
profile during exercise as a predictor of sudden death.
New England Journal of Medicine, 352(19):1951–
1958.
Kubori, Y., Matsuki, R., Hotta, A., Morisawa, T., and
Tamaki, A. (2017). Comparison between stair-
climbing test and six-minute walk test after lung
resection using video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
lobectomy. Journal of physical therapy science,
29(5):902–904.
Pec¸anha, T., Bartels, R., Brito, L. C., Paula-Ribeiro, M.,
Oliveira, R. S., and Goldberger, J. J. (2017). Meth-
ods of assessment of the post-exercise cardiac auto-
nomic recovery: A methodological review. Interna-
tional Journal of Cardiology, 227:795–802.
Sokas, D., Petr
˙
enas, A., Daukantas, S., Rapalis, A., Pali-
akait
˙
e, B., and Marozas, V. (2019). Estimation of heart
rate recovery after stair climbing using a wrist-worn
device. Sensors (Switzerland), 19(9).
Streuber, S. D., Amsterdam, E. A., and Stebbins, C. L.
(2006). Heart rate recovery in heart failure patients
after a 12-week cardiac rehabilitation program. Amer-
ican Journal of Cardiology, 97(5):694–698.
Thomson, R. L., Buckley, J. D., Noakes, M., Clifton, P. M.,
Norman, R. J., and Brinkworth, G. D. (2010). Heart
rate recovery improves after weight loss in overweight
and obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Fertility and Sterility, 93(4):1173–1178.
Evaluation of Stair Climbing as an Approach for Estimating Heart Rate Recovery in Daily Activities
25
