
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models
for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
Louise Bloch
1,2 a
and Christoph M. Friedrich
1,2 b
1
Department of Computer Science, University of Applied Sciences and Arts Dortmund,
Emil-Figge-Str. 42, 44227 Dortmund, Germany
2
Institute for Medical Informatics, Biometry and Epidemiology (IMIBE), University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany
Keywords:
Interpretable Machine Learning, Alzheimer’s Disease Classification, Shapley Values, Alzheimer’s Disease
Neuroimaging Initiative, Australian Imaging and Lifestyle Flagship Study of Ageing.
Abstract:
Many research articles used difficult-to-interpret black-box Machine Learning (ML) models to classify
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) without examining their biological relevance. In this article, an ML workflow was
developed to interpret black-box models based on Shapley values. This workflow enabled the model-agnostic
visualization of complex relationships between model features and predictions and also the explanation of
individual predictions, which is important in clinical practice. To demonstrate this workflow, eXtreme Gradi-
ent Boosting (XGBoost) and Random Forest (RF) classifiers were trained for AD classification. All models
were trained on the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) or Australian Imaging and Lifestyle
flagship study of Ageing (AIBL) dataset and were validated for independent test datasets of both cohorts. The
results showed improved performances for black-box models in comparison to simple Classification and Re-
gression Trees (CARTs). For the classification of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) conversion and the ADNI
training dataset, the best model achieved a classification accuracy of 71.03 % for the ADNI test dataset and
67.65 % for the entire AIBL dataset. This RF used a logical long-term memory test, the count of Apolipopro-
tein E ε4 (ApoEε4) alleles and the volume of the left hippocampus as the most important features.
1 INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative
disease (Alzheimer’s Association, 2020), the most
frequent cause of dementia and a globally grow-
ing health problem (Patterson, 2018). Small brain
changes begin decades before clinical symptoms were
noted (Lloret et al., 2019). The early identification of
patients at risk is important to recruit and monitor sub-
jects for therapy studies as there currently is no causal
therapy (Alzheimer’s Association, 2020). Many ap-
proaches investigated the early AD diagnosis using
Machine Learning (ML). Some approaches used in-
terpretable models like Decision Trees (DTs) or logis-
tic regression to investigate general associations (Li
et al., 2020; Mofrad et al., 2018). However, black-
box models like eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XG-
Boost) (Chen and Guestrin, 2016), Random Forests
(RF) (Breiman, 2001) or Convolutional Neural Net-
works (CNNs) (LeCun et al., 2015) often achieved
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7540-4980
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7906-0038
improved performances (Bloch and Friedrich, 2019;
Grassi et al., 2019) but were challenging to interpret.
Moreover, most AD ML models lacked for external
validation (Samper-Gonz
´
alez et al., 2018).
Interpretable ML was developed to explain black-
box models. This is relevant in AD as it was not com-
pletely understood yet. Additionally, interpretable
ML enables the inspection of the biological relevance
of black-box ML models. There have been some ar-
ticles using interpretable ML in AD diagnosis. For
example, (Pelka et al., 2020) trained Long Short-
Term Memory (LSTM) (Hochreiter and Schmidhu-
ber, 1997) based Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN)
(Rumelhart et al., 1986) to classify Cognitive Normal
(CN) vs. Mild Cognitive Impaired (MCI) subjects.
The paper compared different techniques to fuse so-
ciodemographic and genetic data with Magnetic Res-
onance Imaging (MRI). The models were evaluated
for an AD subset (Dlugaj et al., 2010) of the Heinz
Nixdorf Risk Factors Evaluation of Coronary Calci-
fication and Lifestyle (RECALL) (HNR) (Schmer-
mund et al., 2002) (61 MCI and 59 CN) and the
Bloch, L. and Friedrich, C.
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0010211300870099
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 87-99
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
87

Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI)
(Petersen et al., 2010) study (397 MCI and 227 CN).
Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-
CAM) (Selvaraju et al., 2017) was used to visually ex-
plain individual model decisions. Initial observations
showed a focus on biologically plausible regions.
(Das et al., 2019) presented a new interpretable
model, based on distinct weighted rules. The model
was evaluated for 151 subjects of the ADNI cohort
(97 AD and 54 CN). The framework was trained in
two stages, the first stage used plasma features to train
the interpretable model. Subjects with an unclear pre-
diction were propagated to the second stage, where a
Support Vector Machine (SVM) (Cortes and Vapnik,
1995) was trained using invasive Cerebrospinal Fluid
(CSF) markers. The evaluation included both, Cross-
Validation (CV) and an independent test dataset. For
the test dataset an Area Under the Receiver Operating
characteristics Curve (AUC) of 0.81 was reached.
(Hammond et al., 2020) used RF feature im-
portance to examine the predictive influence of β-
amyloid plaques, tau tangles and neurodegeneration
during the disease progress. The experiments were
performed for 405 ADNI subjects (148 CN, 147
MCI and 110 AD). β-amyloid Positron Emission
Tomography (PET) was used to detect β-amyloid
plaques, invasive CSF features surrogated tau-tangles
and MRI and Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET scans
were used to determine neurodegeneration. Models
trained to classify the early AD stages preferred fea-
tures representing tau tangles and β-amyloid-plaques,
whereas models for later stage classification favoured
surrogates for neurodegeneration. The observations
were reproduced using SHapley Additive exPlana-
tions (SHAP) (Lundberg and Lee, 2017) and Gradient
Tree Boosting (GTB) (Friedman, 2001). The RF clas-
sifier and the entire feature set reached accuracies of
73.17 %, 71.01 %, and 90.34 % for the CN vs. MCI,
MCI vs. AD, and CN vs. AD classifications.
(Rieke et al., 2018) compared the four heatmap
visualisation methods sensitivity analysis (Simonyan
et al., 2014), guided backpropagation (Springenberg
et al., 2015), occlusion (Zeiler and Fergus, 2014) and
brain area occlusion inspired by (Yang et al., 2018) for
3D-CNNs. The CNN model was trained using 969
MRI scans of 344 ADNI subjects (151 CN and 193
AD). It is important to ensure independent training
and test datasets if multiple scans per subject were
used (Wen et al., 2020) which was unclear for this
article. Thus, the CV accuracy of 77 % ± 6 %, was
questionable. The heatmaps of all the methods were
focused on AD-related anatomical brain areas.
(Wang et al., 2019) introduced an interpretable
deep learning model, consisting of a Generative Ad-
versarial Network (GAN) (Goodfellow et al., 2014)
to extend the training dataset, a regression network
to generate feature vectors from adjacent visits and
a classification model. The regression model itera-
tively estimated the feature vector at a prospective
visit and the classification model does the final pre-
diction. Longitudinal volumetric MRI features were
used to classify 101 progressive MCI (pMCI) vs. 115
stable MCI (sMCI) ADNI subjects. The model out-
performed SVMs and artificial neural networks.
In this article, an ML workflow was developed, to
interpret black-box models based on model-agnostic
Shapley values. In comparison to classical feature im-
portance methods, the advantage was to obtain an in-
dividual explanation for each subject and to observe
complex relationships between the features and the
prediction. The workflow was evaluated by train-
ing XGBoost and RF models to inspect different AD
stages but was not limited to those models. Two
different cohorts were used for model training, the
ADNI and the Australian Imaging and Lifestyle flag-
ship study of Ageing (AIBL) (Ellis et al., 2009). Each
model was trained on one cohort and evaluated for the
independent test datasets of both cohorts. The train-
ing has been performed for two different non-invasive
feature sets. Section 2 describes the datasets and in-
terpretation methods. The ML workflow is delineated
in Section 3. The experimental results are explained
in Section 4. Section 5 finally discusses the results
and gives an outlook about future work.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Dataset
Data used in the preparation of this article were ob-
tained from the ADNI (Petersen et al., 2010) and
the AIBL (Ellis et al., 2009) cohorts. The datasets
included 1700 ADNI and 612 AIBL subjects. The
ADNI dataset consisted of 512 CN, 853 MCI and
335 AD subjects. The MCI subjects were split into
two subsets. 401 Baseline (BL) MCI subjects had
no diagnostic changes in all visits and were classi-
fied as sMCI subjects. 319 BL MCI subjects con-
verted to AD at subsequent visits and were classified
as pMCI. BL MCI subjects, who reverted to CN for
at least one visit, pMCI subjects who reverted to MCI
and subjects with no follow-up diagnosis assigned to
none of these two classes. ADNI subjects from the
study phases ADNI-1 (809 subjects), ADNIGO (127
subjects) and ADNI-2 (764 subjects) were included.
The time between the BL and the final diagnosis for
sMCI and pMCI subjects ranged between 4.7 and
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
88

Table 1: ADNI demographics at BL. The mean and standard deviation are given for all continuous variables.
n Age (in years) Gender/ females (in %) MMSE CDR ApoEε4 (0/1/2) (in %)
CN 512 74.2±5.8 51.8 29.1±1.1 0.0±0.0 (71.3 / 26.2 / 2.3)
MCI 853 73.1±7.6 40.8 27.6±1.8 0.5±0.0 (49.4 / 39.5 / 10.8)
sMCI 401 73.2±7.5 40.4 27.8±1.8 0.5±0.0 (56.9 / 33.9 / 9.2)
pMCI 319 74.0±7.1 40.1 27.0±1.7 0.5±0.0 (34.2 / 49.5 / 16.3)
AD 335 75.0±7.8 44.8 23.2±2.1 0.8±0.3 (33.1 / 47.2 / 19.1)
Σ 1700 73.8±7.2 44.9 27.2±2.7 0.4±0.3 (52.8 / 37.0 / 9.9)
156.2 months. The same inclusion criteria were ap-
plied to the AIBL cohort. This resulted in 447 CN,
94 MCI, 16 sMCI, 18 pMCI and 71 AD subjects and
the time between the BL and the final diagnosis for
sMCI and pMCI subjects ranged between 16.9 and
55.1 months. The demographic data of the ADNI and
AIBL datasets are summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
For each subject, the BL 1.5 T or 3 T T1-weighted
Magnetization-Prepared Rapid Gradient-Echo (MP-
RAGE) MRI scan was selected. In this study, fully
preprocessed ADNI scans (Jack et al., 2015) were
used. There are no preprocessed AIBL MRI scans
available, thus unprocessed scans were used. Volu-
metric features were extracted from the MRI scans
using FreeSurfer v6.0 (Fischl, 2012). Volumetric
features of 34 cortical areas per hemisphere of the
Desikan-Killiany atlas (Desikan et al., 2006), 34 sub-
cortical areas (Fischl et al., 2002) and the estimated
Total Intracranial Volume (eTIV) were extracted. The
volumetric features were normalized by eTIV as rec-
ommended for volumes in (Westman et al., 2012).
The experiments were performed using two fea-
ture sets. Feature Set 1 (FS1) included 103 MRI fea-
tures, age, gender and count of Apolipoprotein E ε4
(ApoEε4) alleles (106 features). Gender and ApoEε4
were coded as two and three binary dummy variables.
APOE4.X (X∈{0,1,2}) indicated if a subject had X
ApoEε4 alleles. PTGENDER.MALE specifies if the
subject was male and PTGENDER.FEMALE if it was
female. All dummy variables had a value of one, if
the expression is true, and zero otherwise. In Feature
Set 2 (FS2) Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE),
Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR), and logical tests
to evaluate the long-term (Logical memory, delayed
(LDELTOTAL)) and the short-term memory (Logical
memory, immediate (LIMMTOTAL)) were added to
FS1 (110 features). The CDR score was excluded for
sMCI vs. pMCI classification due to small variance.
2.2 Interpretable ML
An overview of different methods to interpret ML
models can be found in (Molnar, 2019). Some mod-
els like DTs and logistic regression models are in-
terpretable by design. However, the interpretation
of black-box models, which often achieve better re-
sults, is more complicated. This article used model-
agnostic Shapley values. In contrast to the model-
specific approaches, it is suitable to explain any type
of ML model, and enabled comparability. Addition-
ally, Shapley values are local models, which explain
individual observations and thus achieve a high clini-
cal benefit and good performances.
2.2.1 Shapley Values
Shapley values (Shapley, 1953) are affiliated to coali-
tion game theory. The aim is to determine the effect
of a single feature of an observation on the overall
prediction. Shapley values explain the differences be-
tween the average model prediction and the prediction
of an observation by different features. Thus, Shap-
ley values are based on the additive linear explanation
model shown in equation 1. The model prediction
f (x) of an observation x is explained by the feature
effects Φ
j
and the average model prediction Φ
0
. x
0
is
a simplified representation of the observation x. For
tabular data, this is a binned binary feature represen-
tation. N is the number of simplified features.
f (x) = Φ
0
+
N
∑
j=1
Φ
j
x
0
j
(1)
Shapley values explain the overall prediction of an ob-
servation by fairly distributed feature effects. There-
fore, they are defined as the average contribution of
a feature expression for the prediction in all subsets,
described in equation 2. To calculate the Shapley
value Φ
i
of a feature i and an observation, it was re-
quired to determine all subsets S of the entire feature
set F. It was necessary to retrain and evaluate the
black-box model f
S
(S) for each subset S. The differ-
ences in model performance trained with ( f
S∪i
(S ∪ i))
and without ( f
S
(S)) the feature at interest i were cal-
culated. The Shapley value is the weighted average
difference of all subsets. The weights depend on the
total number of model features |F| and the number of
feature expressions |S| in the subset S. High weights
were assigned to both, subsets with few and with
many features, to support the estimation of the main
individual effects and the total effects.
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
89

Table 2: AIBL demographics at BL. The mean and standard deviation are given for all continuous variables.
n Age (in years) Gender/ females (in %) MMSE CDR ApoEε4 (0/1/2) (in %)
CN 447 72.5±6.2 57.0 28.7±1.2 0.0±0.1 (70.7 / 26.4 / 2.9)
MCI 94 75.3±7.0 46.8 27.1±2.2 0.5±0.1 (51.1 / 37.2 / 11.7)
sMCI 16 76.4±7.7 50.0 27.6±2.4 0.5±0.0 (56.2 / 37.5 / 6.2)
pMCI 18 78.0±7.1 50.0 26.8±2.0 0.5±0.0 (16.7 / 66.7 / 16.7)
AD 71 73.3±7.9 59.2 20.5±5.7 0.9±0.6 (32.4 / 49.3 / 18.3)
Σ 612 73.0±6.6 55.7 27.5±3.5 0.2±0.4 (63.2 / 30.7 / 6.0)
Φ
i
=
∑
S⊆F\{i}
|S|!(|F| − |S| −1)!
|F|!
f
S∪{i}
(S∪i)− f
S
(S)
(2)
The computational effort for the exact calculation of
Shapley values increases exponentially with the num-
ber of features. In this paper, Shapley sampling values
(
ˇ
Strumbelj and Kononenko, 2013) which are based on
Monte-Carlo sampling estimated the Shapley values
to avoid time-consuming repeated training and eval-
uation. The estimation of a Shapley value
b
Φ
i
(x) for
a feature i and an observation x is demonstrated in
equation 3. M is the number of Monte-Carlo simu-
lations and x
m
±i
is the observation x with some feature
expressions replaced by random values. In each simu-
lation, x
m
+i
and x
m
−i
are identical, except that the feature
i was randomly replaced in x
m
−i
and not in x
m
+i
. f is the
black-box model. Each Shapley sampling value is the
mean of the differences of M samples.
b
Φ
i
(x) =
1
M
M
∑
m=1
f (x
m
+i
) − f (x
m
−i
)
(3)
3 ML WORKFLOW
The ML workflow, shown in Figure 1 and im-
plemented using the programming language R ver-
sion 3.5.3 (R Core Team, 2019), allows the interpreta-
tion of black-box models trained to classify early AD.
Subject and feature selection and image process-
ing are described in Section 2.1. Feature fusion was
performed by a concatenation. The dataset was dis-
tinctly split into an 80 % training and a 20 % test
dataset. This split was performed within the diagnosis
groups. Model training, hyperparameter tuning and
model interpretation was carried out for the training
dataset and the performance evaluation was executed
for the independent test datasets of both cohorts.
3.1 Hyperparameter Tuning
Bayesian optimization (Mo
ˇ
ckus, 1975) was imple-
mented using the R package rBayesianOptimization
version 1.1.0 (Yan, 2016) to tune the model hyper-
parameters. The idea is, to model the dependency
of the hyperparameters and the model performance
by a Gaussian Process (GP). Ten nearly random ini-
tial parameters were defined by a Latin hypercube
design (LHD) (McKay et al., 1979), which was im-
plemented using the R package SPOT version 2.0.3
(Bartz-Beielstein et al., 2005). The range of each
parameter was split into ten intervals to randomly
choose one sample per interval. The resulting ten
samples per parameter were randomly matched across
the parameters.
The ML model was evaluated for these combi-
nations using 10 × 10-fold CV (Refaeilzadeh et al.,
2009) to estimate the model performance for the test
dataset using the hyperparameters. 10 × 10-fold CV
was implemented by splitting the training dataset
into ten distinct folds using the R package caret ver-
sion 6.0-82 (Kuhn, 2019). The splits were executed
separately for each diagnosis. Ten iterations were per-
formed, each with a different fold used as validation
dataset (10 %). The training dataset included the re-
maining nine folds (90 %). This procedure was re-
peated for ten times, with shuffled data in each run.
The GP was fitted to predict the average CV ac-
curacy for the initial parameter combinations. After-
wards, the model was optimized to choose the next
parameter combination. Here, the Upper Confidence
Bounds (UCB) acquisition function (equation 4) was
used. ˆµ
Θ
is the performance estimation of the GP and
ˆ
Σ
Θ
is the covariance at parameter combination Θ. κ
weights the influence of exploitation and exploration
during the optimization. A high κ-value preferred ex-
ploration and small values favour exploitation. All
experiments used the default value of 2.576.
UCB(Θ) = ˆµ
Θ
+ κ ·
ˆ
Σ
Θ
(4)
Iteratively, the new hyperparameter combination was
evaluated using CV and the results were added to re-
fine the GP and to determine a new combination. This
procedure was repeated 25 times. The best combina-
tion was chosen to train the final model.
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
90
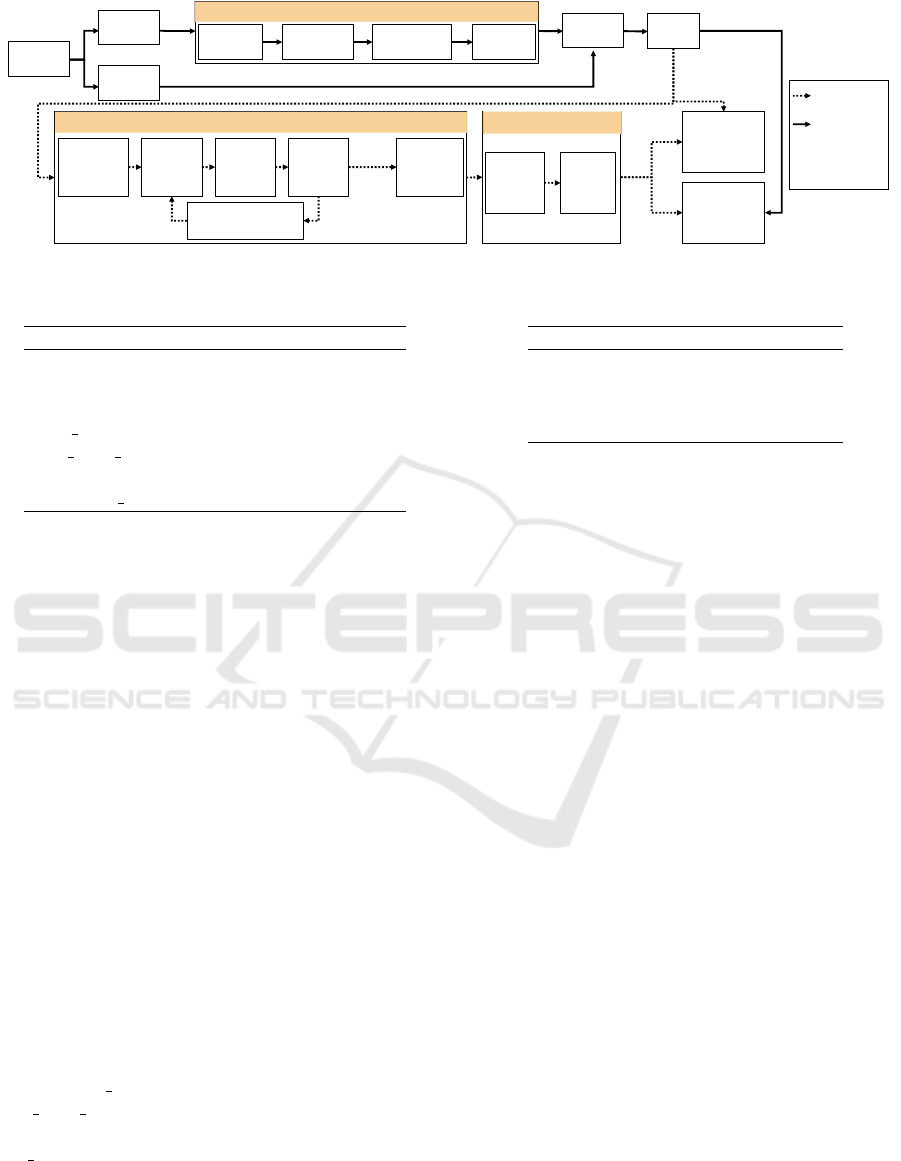
Final model generation
Volume
calculation
SegmentationRegistration
Pre-
processing
Hyperparameter tuning
Evaluation
Image processing
Data
splitting
Subject
selection
Model
training
Resampling
Pre-
processing
Model
training
Pre-
processing
Test dataset
Training
dataset
Initialize
parameter
combinations
Determine promising
parameter combination
Determine
best
parameter
combination
Met exit
condition
Continue
parameter tuning
Feature
selection
MRI scan
selection
Feature
fusion
Generate
interpretation
model
Training cohort
Training and
External
Validation
cohort
Figure 1: ML workflow.
Table 3: XGBoost hyperparameters and intervals.
Name Minimum Maximum
nrounds 1 500
eta 0 1
gamma 0 20
max depth 1 20
min child weights 1 30
subsample 0 1
colsample bytree 0 1
3.2 Model Training
The preprocessing included centering, scaling, me-
dian imputation and Synthetic Minority Over-
sampling Technique (SMOTE) (Chawla et al., 2002)
to compensate class imbalances. It was implemented
using the R package caret version 6.0-82 (Kuhn,
2019). Afterwards, the ML models were trained.
XGBoost (Chen and Guestrin, 2016) is an im-
plementation of gradient boosting (Friedman, 2001),
distributed as an open-source software library. The
idea of boosting algorithms is, to iteratively combine
multiple weak classifiers to get a strong joint clas-
sifier. Gradient boosting meets this assumption by
learning the gradients of the previous classifier. The
sum of the weak classifier results is the final predic-
tion. The main advantages of XGBoost are scalability,
parallelization and distributed execution. The XG-
Boost hyperparameters are summarized in Table 3.
nrounds sets the number of boosting iterations and
eta was the learning rate, which controls the prefer-
ence of classifiers at early iterations. The minimum
loss reduction required to split a node is defined by
gamma, max depth sets the maximum tree depth and
min child weights was the minimum number of ob-
servations in a child node. subsample and colsam-
ple bytree set the proportion of randomly subsampled
training instances and features per iteration. An XG-
Boost tree classifier was implemented using the R
package xgboost version 0.82.1 (Chen et al., 2019).
RF (Breiman, 2001) is an ensemble black-box
Table 4: RF hyperparameters and optimization intervals.
Name Minimum Maximum
mtry 2 # features
ntree 250 1250
nodesize 1 30
maxnodes 50 100
model based on multiple DTs and was implemented
using the R package randomForest version 4.6-14
(Liaw and Wiener, 2002). Each DT was trained us-
ing randomly chosen features and bootstrap sampling
(Efron and Tibshirani, 1986) of the training dataset.
The results of the DTs were finally summarized using
a majority voting. The hyperparameter ntree sets the
number of DTs. Each split considered a random sub-
set of mtry features. The minimum size of leaf nodes
was defined by nodesize and maxnodes determines the
maximum number of leaf nodes per DT. Table 4 sum-
marizes the RF hyperparameters.
Classification and Regression Trees (CARTs)
(Breiman et al., 1984) were chosen as interpretable
models and implemented using the R package rpart
version 4.1-13 (Therneau and Atkinson, 2018). Dur-
ing the training of CARTs, successively decision rules
of the form x ≤ t for numerical or x ∈ t for categorical
features were learned with t as a threshold or a subset.
Each possible split was ranked by the Gini-coefficient
(equation 5) to find the best rule. In this equation, c is
the total number of classes and p(i), is the proportion
of observations of class i in a node.
f (p) =
c
∑
i=1
p(i) ·
1 − p(i)
(5)
This method was iteratively repeated as long as no
split with a minimum improvement of the complexity
parameter cp can be performed. This hyperparameter
was tuned in a range between 0 and 1.
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
91

3.3 Interpretation Model
Shapley sampling values were implemented using the
R package fastshap version 0.0.5 (Greenwell, 2020)
to explain the black-box models. All experiments per-
formed 5000 Monte-Carlo simulations to estimate the
Shapley values. The SHAP force plot in Figure 3 ex-
plains the model prediction of an individual observa-
tion. The plot shows, that the individual prediction
consists of the sum of all feature Shapley values and
the average model prediction. Feature expressions
with high positive Shapley values had a strong pos-
itive effect on the prediction and small negative Shap-
ley values represent small negative effects.
SHAP summary plots (Lundberg et al., 2018) ex-
plain the model results for the entire training dataset.
Each point shows a Shapley value for a subject and a
feature and is colored depending on the feature value.
The vertical axis represented the features, ordered by
the mean absolute Shapley values, and their distribu-
tion. The plots were limited to the top ten features.
4 RESULTS
The results of the experiments with FS1 and FS2 are
summarized in Tables 5 and 6. For both feature sets,
the best results were achieved for CN vs. AD clas-
sification. For example, a perfect CV accuracy was
achieved by training an RF with FS2 of the ADNI
dataset. The CART, trained with FS2 of the ADNI
dataset, reached a perfect classification for the ADNI
test dataset. The best accuracy for the AIBL test
dataset was 99.05 % and was achieved by training an
XGBoost model with FS2 of the AIBL dataset.
Only 16 sMCI and 18 pMCI AIBL subjects were
selected, thus, AIBL was only used for external vali-
dation in this case. For FS1 and FS2 the RF achieved
the best results to classify MCI conversion. The FS2
model yielded an accuracy of 71.03 % for the inde-
pendent ADNI and 67.65 % for the AIBL test dataset.
For FS1, accuracies of 68.28 % for the ADNI and
79.41 % for the AIBL test datasets were reached.
4.1 Feature Set 1 vs. Feature Set 2
In general, the performances reached with FS2 (Ta-
ble 6) outperformed the results achieved with FS1
(Table 5). Adding cognitive test results to FS1 im-
proved the distinction of the BL diagnoses. Minor im-
provements were noted for the MCI conversion pre-
diction. For example, the RF trained with FS2 for
MCI conversion prediction outperformed the model
trained with FS1 by 2.75 % for the ADNI test dataset
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
lh_inferiorparietal_volume
lh_middletemporal_volume
Right.Hippocampus
rh_entorhinal_volume
Right.Inf.Lat.Vent
APOE4.1
Right.Amygdala
Left.Amygdala
Left.Hippocampus
APOE4.0
LDELTOTAL
−0.10 −0.05 0.00 0.05 0.10
Shapley value
Feature
Low High
Feature value
Figure 2: SHAP summary plot of the RF trained with ADNI
and FS2 for sMCI (0) vs. pMCI (1). APOE4.X (X∈{0,1,2})
indicates if a subject had X ApoEε4 alleles. A value of 1
(purple) indicates a true expression, and 0 (yellow) a false.
but for the AIBL dataset the FS1 model performed
11.76 % better.
Figure 2 shows a SHAP summary plot of the
RF trained with FS2. The most important feature
of this model was the LDELTOTAL cognitive test
score. Small LDELTOTAL scores, exhibited high
Shapley values, thus the model identified subjects
with small LDELTOTAL scores as pMCI subjects. It
was detected, that subjects with no ApoEε4 alleles
(APOE4.0 = 1) were more likely classified as sMCI
as subjects with one or two alleles (APOE4.0 = 0).
Consistently, the presence of a single ApoEε4 allele
(APOE4.1 = 1) was associated with pMCI subjects.
The two most important MRI features of this model
were the volumes of the left hippocampus and the left
amygdala. For both features, high values predomi-
nantly have Shapley values smaller zero and were thus
associated with sMCI subjects. The other MRI fea-
tures consistently show biologically plausible associ-
ations, corresponding to AD neurodegeneration (De-
Ture and Dickson, 2019).
Figure 3 shows a SHAP force plot of this model
to explain the individual prediction of an ADNI pMCI
subject. SHAP force plots are helpful to present in-
dividual contributions for clinical observations. The
Shapley values are visualized as arrows to explain
the differences between the average model prediction
(0.395) and the prediction of the individual observa-
tion (0.61). Here, the individual prediction was the
probability of the subject of being classified as pMCI.
The length of an arrow indicated the Shapley value.
Feature expressions with high Shapley values like the
LDELTOTAL score were visualized with long arrows.
Pathogenic feature expressions were colored in red.
For example, a small normalized feature expression
of 0.09 was measured for LDELTOTAL. This expres-
sion had the highest positive Shapley value of 0.034
to explain the overall prediction. Protective feature
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
92

Table 5: Classification results and hyperparameters for FS1. Comparison of CART, RF and XGBoost models trained on
ADNI and AIBL datasets. The best results in each section are highlighted in bold. Hyperparameters: CART: (cp), RF: (mtry,
ntree, nodesize, maxnodes), XGBoost: (max depth, nrounds, eta, gamma, colsample bytree, min child weight, subsample).
Model Trai-
ning
dataset
Hyperparameters CV accuracy
(mean±sd)
in %
Accuracy
test dataset
ADNI in %
Accuracy
test dataset
AIBL in %
CN vs. AD: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 60.59, AIBL: 85.71
CART ADNI (0.013) 82.62±4.42 81.76 89.52
RF ADNI (27, 735, 1, 92) 88.14±4.05 90.00 88.57
XGBoost ADNI (2, 417, 0.120, 0.371, 0.349, 17.08, 0.746) 88.82±4.04 90.59 88.57
CART AIBL (0.803) 86.45±1.06 60.59 85.71
RF AIBL (1, 707, 9, 69) 89.27±5.19 83.53 95.24
XGBoost AIBL (1, 297, 0.246, 0.237, 0.436, 2.158, 0.732) 87.99±4.96 81.76 91.43
MCI vs. AD: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 71.85, AIBL: 55.88
CART ADNI (0.441) 71.79±0.33 71.85 55.88
RF ADNI (10, 1250, 20, 100) 73.11±4.28 78.15 58.82
XGBoost ADNI (19, 259, 0.088, 9.922, 0.696, 19.255, 0.595) 72.42±4.12 75.63 55.88
CART AIBL (0.207) 58.42±13.58 57.14 55.88
RF AIBL (1, 1250, 7, 89) 71.93±12.22 66.81 70.59
XGBoost AIBL (19, 259, 0.088, 9.922, 0.696, 19.255, 0.595) 64.36±12.41 68.91 70.59
CN vs. MCI: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 62.41, AIBL: 82.57
CART ADNI (0.028) 65.80±4.31 63.87 44.18
RF ADNI (23, 1250, 1, 100) 69.49±4.20 67.52 48.62
XGBoost ADNI (2, 417, 0.120, 0.371, 0.349, 17.080, 0.746) 68.89±4.07 68.98 40.37
CART AIBL (0.545) 82.65±0.96 37.59 82.57
RF AIBL (1, 1250, 20, 50) 79.91±4.59 55.84 83.49
XGBoost AIBL (2, 500, 0.109, 12.111, 1.000, 30.000, 0.157) 82.65±0.95 37.59 82.57
sMCI vs. pMCI: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 55.86, entire AIBL dataset: 52.94
CART ADNI (0.063) 65.26±5.97 63.45 70.59
RF ADNI (17, 250, 18, 50) 67.94±5.49 68.28 79.41
XGBoost ADNI (2, 417, 0.120, 0.371, 0.349, 17.080, 0.746) 67.18±5.10 64.83 64.71
Figure 3: SHAP force plot for an ADNI pMCI subject (PTID = 123 S 0050) to explain the prediction of the RF trained with
ADNI and FS2 for sMCI (0) vs. pMCI (1). The arrow length indicates a Shapley value of the feature expression. Pathogenic
feature expressions are shown as red and protective expressions as blue arrows. The normalized feature expressions with the
highest absolute Shapley values are explained below the arrows. Mean prediction value (base value): 0.395. ApoEε4 and
gender were dummy coded (e.g. APOE4.0 = 1 means, that the subject had no ApoEε4 alleles).
expressions were colored in blue. In this plot, the ab-
sence of ApoEε4 alleles (APOE4.0 = 1) had a protec-
tive influence (Shapley value of -0.020) on the overall
prediction. The individual diagnosis of the subject at
interest was based on a large number of feature ex-
pressions and the most important ones are named in
the figure below the arrows.
The largest differences between the results of FS1
and FS2 were observed for the CN vs. MCI classifi-
cation. All models trained on the ADNI dataset with
FS2 achieved CV performances of 99.82 % ± 0.41 %
and accuracies of 98.91 % for the ADNI and 92.66 %
for the AIBL test dataset. The models trained with
FS1 performed worse with the best CV accuracy of
69.49 % ±4.20 % reached by the RF. This model also
achieved the best accuracy of 48.63 % for the AIBL
test dataset. The XGBoost model achieved a result of
68.98 % for the independent ADNI test dataset.
Corresponding observations were made for the
AIBL models. The best CV accuracy was 94.26 % ±
3.79 % and yielded by the RF trained with FS2. The
RF, CART and XGBoost models all achieved the
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
93

Table 6: Classification results and hyperparameters for FS2. Comparison of CART, RF and XGBoost models trained on
ADNI and AIBL datasets. The best results in each section are highlighted in bold. Hyperparameters: CART: (cp), RF: (mtry,
ntree, nodesize, maxnodes), XGBoost: (max depth, nrounds, eta, gamma, colsample bytree, min child weight, subsample).
Model Trai-
ning
dataset
Hyperparameters CV accuracy
(mean±sd)
in %
Accuracy
test dataset
ADNI in %
Accuracy
test dataset
AIBL in %
CN vs. AD: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 60.59, AIBL: 85.71
CART ADNI (0.625) 99.40±0.94 100.00 95.24
RF ADNI (16, 808, 16, 96) 100.00±0.00 99.41 96.19
XGBoost ADNI (2, 417, 0.120, 0.371, 0.349, 17.080, 0.746) 99.90±0.43 99.41 96.19
CART AIBL (0.147) 96.10±2.58 92.35 96.19
RF AIBL (44, 250, 1, 74) 97.02±2.60 97.65 98.10
XGBoost AIBL (10, 175, 0.020, 1.509, 0.448, 11.268, 0.403) 96.85±2.64 96.47 99.05
MCI vs. AD: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 71.85, AIBL: 55.88
CART ADNI (0.020) 89.79±2.62 92.02 73.53
RF ADNI (29, 1068, 18, 52) 90.59±2.79 90.76 86.67
XGBoost ADNI (6, 227, 0.229, 16.431, 0.591, 8.248, 0.367) 89.73±2.94 91.18 73.53
CART AIBL (0.084) 86.51±9.94 79.41 92.86
RF AIBL (25, 754, 19, 50) 86.95±9.20 92.02 73.53
XGBoost AIBL (7, 483, 0.324, 19.399, 0.753, 1.000, 0.955) 85.71±8.97 90.76 79.41
CN vs. MCI: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 62.41, AIBL: 82.66
CART ADNI (0.289) 99.82±0.41 98.91 92.66
RF ADNI (16, 808, 16, 96) 99.82±0.41 98.91 92.66
XGBoost ADNI (11, 279, 0.886, 18.605, 0.959, 2.285, 0.733) 99.82±0.41 98.91 92.66
CART AIBL (0.519) 94.21±3.79 98.91 91.74
RF AIBL (60, 1127, 1, 66) 94.26±3.79 98.18 91.74
XGBoost AIBL (16, 416, 0.110, 9.783, 0.761, 1.000, 1.000) 94.05±3.84 98.91 91.74
sMCI vs. pMCI: No information rate test dataset: ADNI: 55.86, entire AIBL dataset: 52.94
CART ADNI (0.099) 64.14±6.38 68.28 58.82
RF ADNI (19, 250, 1, 64) 69.59±5.78 71.03 67.65
XGBoost ADNI (6, 500, 0.090, 3.031, 0.918, 26.771, 0.853) 69.27±5.67 68.97 64.71
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
CDGLOBAL
−0.6 −0.4 −0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4
Shapley value
Feature
Low High
Feature value
Figure 4: SHAP summary plot of the XGBoost model
trained with ADNI and FS2 for CN (0) vs. MCI (1).
same results of 91.74 % for the AIBL test dataset.
The CART and XGBoost models achieved the best
results of 98.91 % for the ADNI test dataset. Worse
results were achieved using FS1. The best results
were 55.84 % (no information rate: 62.41 %) and
83.49 % (no information rate: 82.57 %) for the ADNI
and AIBL test datasets achieved by the RF. Figure 4
shows the SHAP summary plot for the model trained
with FS2 of the CN vs. MCI ADNI dataset. The CDR
score was the only feature included in this model.
A high CDR score was associated with MCI sub-
jects. Figure 5 shows the SHAP summary plot of
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Left.VentralDC
X4th.Ventricle
Left.Thalamus.Proper
Left.Amygdala
Left.Hippocampus
rh_caudalanteriorcingulate_volume
rh_lingual_volume
APOE4.0
lh_parstriangularis_volume
Right.Inf.Lat.Vent
AGE
−0.1 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3
Shapley value
Feature
Low High
Feature value
Figure 5: SHAP summary plot of the FS1 ADNI XGBoost
model trained for CN (0) vs. MCI (1). APOE4.0 indicates
if a subject had no ApoEε4 alleles. A value of 1 (purple)
expresses a true expression, and 0 (yellow) a false.
the same model trained with FS1. This model used
a huge number of MRI volumetric features. For ex-
ample, the model learned the unexpected connection,
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
94

that younger age was associated with MCI. Overfit-
ting might be a possible explanation. Some volu-
metric features, like the right inferior lateral ventricle
and the left pars triangularis, corresponded with the
neurodegenerative AD progress in this model. Other
areas like the right lingual gyrus or the right caudal
anterior cingulate gyrus showed contradictive results.
Subjects with no APOEε4 alleles (APOE4.0 = 1) were
associated with pMCI diagnosis. The Shapley feature
importance ranking only partially coincided with the
model-specific XGBoost feature importance ranking.
4.2 Comparison ADNI and AIBL
This section examines the portability of models
trained with the ADNI and AIBL datasets. Models
trained on the ADNI dataset were therefore validated
for the AIBL test dataset and vice versa. In Table 6, all
models exceed the no information rate for the external
test dataset and thus seemed to be portable. For exam-
ple, the CART trained on the ADNI dataset as well as
the RF trained on the AIBL dataset achieved the best
results of 92.02 % for MCI vs. AD classification and
the ADNI test dataset. The best accuracy of 98.91 %
for the ADNI test dataset and CN vs. MCI classifica-
tion was achieved by all three ML algorithms trained
on the ADNI dataset and by the CART and XGBoost
models trained on the AIBL dataset. The best accu-
racy for the AIBL test dataset and CN vs. MCI clas-
sification was 92.66 % and was reached by all three
ML algorithms trained on the ADNI dataset.
The results for FS1 provided contradictive ob-
servations for the MCI vs. AD and CN vs. MCI
classification. For example, the ADNI RF model
achieved an accuracy of 48.62 % for the AIBL test
dataset (no information rate: 82.57 %) for the CN
vs. MCI classification. The respective AIBL RF
model reached an accuracy of 55.84 % (no informa-
tion rate: 62.41 %) for the ADNI test dataset. The
SHAP summary plots of the models trained with the
ADNI and the AIBL dataset are shown in Figures 6
and 7. Both models used the number of APOEε4 al-
leles as the most important feature. No ApoEε4 alle-
les (APOE4.0 = 1) were associated with CN subjects.
However, the Shapley values of the AIBL model were
smaller, which means that a larger number of features
was included in each prediction. Both interpretation
models seemed biologically plausible. The ten most
important model features of both models agreed for
the four features APOE4.0, and the volumes of the
left inferior lateral ventricle, the left amygdala and
the right hippocampus. Additionally, for both models,
the Shapley feature importance ranking mainly coin-
cided with the model-specific RF feature importances.
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
lh_inferiortemporal_volume
Right.Hippocampus
lh_temporalpole_volume
lh_parstriangularis_volume
lh_entorhinal_volume
Left.Hippocampus
Left.Amygdala
rh_lingual_volume
Right.Inf.Lat.Vent
AGE
APOE4.0
0.0 0.1 0.2
Shapley value
Feature
Low High
Feature value
Figure 6: SHAP summary plot for the ADNI RF trained
with FS1 for CN (0) vs. MCI (1). APOE4.X (X∈{0,1,2})
indicates if a subject had X ApoEε4 alleles. A value of 1
(purple) indicates a true expression, and 0 (yellow) a false.
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Left.Amygdala
rh_parahippocampal_volume
lh_precuneus_volume
Left.Inf.Lat.Vent
Right.Inf.Lat.Vent
rh_precuneus_volume
Right.Hippocampus
APOE4.1
rhCortexVol
lhCortexVol
APOE4.0
−0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02
Shapley value
Feature
Low High
Feature value
Figure 7: SHAP summary plot for the RF trained with AIBL
and FS1 for CN (0) vs. MCI (1). APOE4.X (X∈{0,1,2})
indicates if a subject had X ApoEε4 alleles. A value of 1
(purple) indicates a true expression, and 0 (yellow) a false.
However, the ADNI dataset was highly imbalanced
for MCI vs. AD and the AIBL dataset for CN vs. MCI
classification. The classification of CN vs. AD and
sMCI vs. pMCI subjects led to results higher than the
no information rate for the external test dataset. The
portability of those models seemed to be possible.
4.3 Black-box Models vs. CARTs
In comparison to the CARTs, the black-box models
showed exceeding results. For example, the CART
trained with FS1 and the CN vs. AD AIBL dataset
achieved the no information rate for the ADNI and
the AIBL test datasets. This model learned to assign
the more frequently occurring CN class to all subjects
without using the feature values and is thus a random
classifier. One possible cause for this result might be
the strong class imbalance for this problem. The same
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
95

rh_parahippocampal_volume < 0.15
Left.Putamen < 0.28
MCI
0.57
100%
AD
0.38
58%
AD
0.20
39%
MCI
0.75
19%
MCI
0.83
42%
yes
no
Figure 8: CART trained with AIBL and FS1 for MCI vs.
AD. Features are centered and scaled. Nodes: (most fre-
quent class; MCI class probability; coverage).
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
APOE4.0
lh_cuneus_volume
Left.Pallidum
Left.Amygdala
X4th.Ventricle
rh_inferiortemporal_volume
Left.Hippocampus
AGE
Left.Putamen
rh_parahippocampal_volume
lh_precentral_volume
−0.10 −0.05 0.00 0.05 0.10
Shapley value
Feature
Low High
Feature value
Figure 9: SHAP summary plot for the FS1 AIBL XGBoost
model trained for MCI (0) vs. AD (1). APOE4.0 indicates
if a subject had no ApoEε4 alleles. A value of 1 (purple)
expresses a true expression, and 0 (yellow) a false.
applied for the FS1 CARTs trained for the MCI vs.
AD ADNI dataset and the CN vs. MCI AIBL dataset.
The CART trained with FS1 of the AIBL dataset
for MCI vs. AD classification is depicted in Figure 8.
All decision values were centered and scaled in this
figure. For each node, the most frequent class, the
MCI class probability and the coverage in the train-
ing dataset were given. The model was exclusively
based on the volume of the right parahippocampal
gyrus and the left putamen. For both features, subjects
with high volumes were classified as MCI and sub-
jects with small volumes as AD, which is biologically
plausible but seems to be incomplete, as was noted by
the poor classification accuracies of 57.14 % for the
ADNI and 55.77 % for the AIBL test dataset. The RF
and XGBoost black-box models outperformed this
model. The XGBoost model trained on the same
dataset achieved a result of 68.91 % for the ADNI and
70.59 % for the AIBL test dataset. Figure 9 depicts
the SHAP summary plot of this model, which showed
more complex interactions. The most important fea-
ture was the volume of the left precentral gyrus and
high feature values were associated with AD, which
was not biologically plausible. The same applied to
the volume of the left cuneus. All the other detected
associations agreed with the AD neurodegeneration.
Both features included in the CART were present in
the top ten features of the XGBoost model.
Table 6 shows smaller differences between the
CARTs and the black-box models. For example, all
models trained on the CN vs. MCI ADNI dataset re-
ceived the same results of 99.82 % ± 0.41 % during
the CV, 98.91 % for the ADNI and 92.66 % for the
AIBL test dataset. The SHAP summary plot of the
XGBoost model is visualized in Figure 4. This model
was only based on the CDR score. The respective
CART model also used only the CDR score. Since
both models achieved the same classification accura-
cies, there was no need to use a complex black-box
model. In conclusion, using black-box models was
more worthwhile for FS1 than for FS2 and sMCI vs.
pMCI classification than the BL diagnoses.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work, several RF, XGBoost and CART mod-
els were trained to classify different AD stages on the
ADNI or AIBL dataset. The models were validated,
using CV and the independent test datasets of both
cohorts. SHAP summary plots were used to visualize
and interpret those models. The experimental results
showed improved accuracies for black-box models
over CARTs. This observation was more clear for the
MCI conversion prediction and for BL diagnoses with
FS1. Simple CARTs were sufficient to classify BL
diagnoses with FS2. One reason for this observation
is that the diagnoses of both cohorts were based on
the cognitive test scores and a neurological examina-
tion (Petersen et al., 2010; Ellis et al., 2009). Conse-
quently, models which included cognitive test scores
achieved better results for the BL classification than
models which excluded those features. SHAP sum-
mary plots helped to understand the black-box mod-
els and enabled comparisons between the ADNI and
the AIBL datasets. Those comparisons showed strong
portability for models trained with FS2. Thus, the di-
agnoses and the cognitive test results were similar in
both datasets. Portability of the models between the
ADNI and the AIBL dataset for the CN vs. AD and
sMCI vs. pMCI classification with FS1 was also ob-
served. However, no portability between the models
trained for the classification of MCI vs. AD and CN
vs. MCI with FS1 was observed. This pointed to rele-
vant differences in the preprocessing or the recording
protocol of the MRI scans in the two studies. Thus,
future experiments should use raw ADNI scans.
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
96

In future, every article, which uses black-box
models to investigate AD, should also include an in-
terpretation method to explain the model and prove
the biological plausibility. Shapley values provide
suitable model explanations but are not sufficient
to guarantee their biological relevance (Slack et al.,
2020). State-of-the-art methods to measure feature
importance like the RF or the XGBoost feature im-
portance provide a single value per feature. Shap-
ley values, however, enabled to observe complex re-
lationships between feature values and their prognos-
tic relevance, since one Shapley value was calculated
per feature and observation. In these experiments,
the most associations between the feature values and
the predictions were biologically plausible. Individ-
ual predictions, which are important in clinical prac-
tice, can be interpreted using SHAP force plots.
The experiments presented in this paper could be
expanded by including more cohorts like the Open
Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS) (Marcus
et al., 2010), a subset of the National Alzheimer’s
Coordinating Center (NACC) (Beekley et al., 2004)
cohort or the AD subset of the HNR study. All ex-
periments used ML models based on DTs. Since
the explanatory method is model-agnostic, the results
should be validated with more diverse ML models and
different interpretable ML methods (Molnar, 2019).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Data used in preparation of this article were ob-
tained from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimag-
ing Initiative (ADNI) and the Australian Imaging,
Biomarker & Lifestyle Flagship Study of Ageing
(AIBL) database. We thank the patients and ADNI
and AIBL for availability of the data.
The work of Louise Bloch was partially funded by
a PhD grant from University of Applied Sciences and
Arts Dortmund, Germany.
REFERENCES
Alzheimer’s Association (2020). 2020 Alzheimer’s Dis-
ease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia,
16(3):391–460.
Bartz-Beielstein, T., Lasarczyk, C. W. G., and Preuss, M.
(2005). Sequential parameter optimization. In Pro-
ceesings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Com-
putation, volume 1, pages 773–780.
Beekley, D. L., Ramos, E. M., van Belle, G., Deitrich,
W., Clark, A. D., Jacka, M. E., and Kukull, W. A.
(2004). The National Alzheimer’s Coordinating
Center (NACC) database: An Alzheimer Disease
database. Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders,
18(4):270–277.
Bloch, L. and Friedrich, C. M. (2019). Classification
of Alzheimer’s Disease using volumetric features of
multiple MRI scans. In Proceedings of the 41st An-
nual International Conference of the IEEE Engineer-
ing in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pages
2396–2401.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learning,
45(1):5–32.
Breiman, L., Friedman, J., Stone, C. J., and Olshen, R. A.
(1984). Classification and regression trees. CRC
press, New York, United States, 1st edition.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., and Kegelmeyer,
W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-
sampling Technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence
Research, 16(1):321–357.
Chen, T. and Guestrin, C. (2016). XGBoost: A Scalable
Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd
ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowl-
edge Discovery and Data Mining, pages 785–794,
New York, United States. ACM.
Chen, T., He, T., Benesty, M., Khotilovich, V., Tang,
Y., Cho, H., Chen, K., Mitchell, R., Cano, I.,
Zhou, T., Li, M., Xie, J., Lin, M., Geng, Y., and
Li, Y. (2019). xgboost: Extreme Gradient Boost-
ing. Manual of R package v0.82.1 https://CRAN.R-
project.org/package=xgboost, Last accessed: 2020-
09-12.
Cortes, C. and Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks.
Machine Learning, 20(3):273–297.
Das, D., Ito, J., Kadowaki, T., and Tsuda, K. (2019). An
interpretable machine learning model for diagnosis of
Alzheimer’s Disease. PeerJ, 7:e6543.
Desikan, R. S., S
´
egonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dick-
erson, B. C., Blacker, D., Buckner, R. L., Dale, A. M.,
Maguire, R. P., Hyman, B. T., Albert, M. S., and Kil-
liany, R. J. (2006). An automated labeling system
for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI
scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroIm-
age, 31(3):968–980.
DeTure, M. and Dickson, D. (2019). The neuropathologi-
cal diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecular Neu-
rodegeneration, 14:32.
Dlugaj, M., Weimar, C., Wege, N., Verde, P., Gerwig, M.,
Dragano, N., Moebus, S., J
¨
ockel, K.-H., Erbel, R., and
Siegrist, J. (2010). Prevalence of Mild Cognitive Im-
pairment and its subtypes in the Heinz Nixdorf Recall
Study cohort. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Dis-
orders, 30(4):362–373.
Efron, B. and Tibshirani, R. (1986). Bootstrap methods
for standard errors, confidence intervals, and other
measures of statistical accuracy. Statistical Science,
1(1):54–75.
Ellis, K. A., Bush, A. I., Darby, D., De Fazio, D., Fos-
ter, J., Hudson, P., Lautenschlager, N. T., Lenzo, N.,
Martins, R. N., Maruff, P., Masters, C., Milner, A.,
Pike, K., Rowe, C., Savage, G., Szoeke, C., Tad-
dei, K., Villemagne, V., Woodward, M., Ames, D.,
and AIBL Research Group (2009). The Australian
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
97

Imaging, Biomarkers and Lifestyle (AIBL) study of
aging: Methodology and baseline characteristics of
1112 individuals recruited for a longitudinal study of
Alzheimer’s Disease. International Psychogeriatrics,
21(4):672–687.
Fischl, B. (2012). FreeSurfer. NeuroImage, 62(2):774–781.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich,
M., Haselgrove, C., van der Kouwe, A., Killiany, R.,
Kennedy, D., Klaveness, S., Montillo, A., Makris, N.,
Rosen, B., and Dale, A. M. (2002). Whole brain
segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomi-
cal structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3):341–
355.
Friedman, J. H. (2001). Greedy function approximation:
A gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics,
29(5):1189–1232.
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. In
Advances in neural information processing systems,
pages 2672–2680.
Grassi, M., Rouleaux, N., Caldirola, D., Loewenstein,
D., Schruers, K., Perna, G., Dumontier, M., and
Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2019).
A novel ensemble-based Machine Learning algo-
rithm to predict the conversion from Mild Cogni-
tive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease using socio-
demographic characteristics, clinical information, and
neuropsychological measures. Frontiers in Neurology,
10:756.
Greenwell, B. (2020). fastshap: Fast Approximate Shapley
Values. Manual of R package v0.0.5 https://CRAN.R-
project.org/package=fastshap, Last accessed: 2020-
09-12.
Hammond, T. C., Xing, X., Wang, C., Ma, D., Nho, K.,
Crane, P. K., Elahi, F., Ziegler, D. A., Liang, G.,
Cheng, Q., Yanckello, L. M., Jacobs, N., and Lin, A.-
L. (2020). β-amyloid and tau drive early Alzheimer’s
Disease decline while glucose hypometabolism drives
late decline. Communications Biology, 3(1).
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long Short-
Term Memory. Neural computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Jack, C. R., Barnes, J., Bernstein, M. A., Borowski, B. J.,
Brewer, J., Clegg, S., Dale, A. M., Carmichael, O.,
Ching, C., DeCarli, C., Desikan, R. S., Fennema-
Notestine, C., Fjell, A. M., Fletcher, E., Fox, N. C.,
Gunter, J., Gutman, B. A., Holland, D., Hua, X., Insel,
P., Kantarci, K., Killiany, R. J., Krueger, G., Leung,
K. K., Mackin, S., Maillard, P., Molone, I., Mattsson,
N., McEvoy, L., Modat, M., Mueller, S., Nosheny, R.,
Ourselin, S., Schuff, N., Senjem, M. L., Simonson,
A., Thompson, P. M., Rettmann, D., Vemuri, P., Wal-
hovd, K., Zhao, Y., Zuk, S., and Weiner, M. (2015).
Magnetic Resonance Imaging in ADNI. Alzheimer’s
& dementia, 11(7):740–756.
Kuhn, M. (2019). caret: Classification and Regres-
sion Training. Manual of R package v6.0-82
https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=caret, Last ac-
cessed: 2020-09-12.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learn-
ing. Nature, 521(7553):436–444.
Li, M., Reisman, J., Morris-Eppolito, B., Qian, S. X.,
Kazis, L. E., Wolozin, B., Goldstein, L. E., and Xia,
W. (2020). Beneficial association of angiotensin-
converting enzyme inhibitors and statins on the occur-
rence of possible Alzheimer’s Disease after traumatic
brain injury. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 12(1).
Liaw, A. and Wiener, M. (2002). Classification and Regres-
sion by randomForest. R News, 2(3):18–22.
Lloret, A., Esteve, D., Lloret, M.-A., Cervera-Ferri, A.,
Lopez, B., Nepomuceno, M., and Monllor, P. (2019).
When does Alzheimer’s Disease really start? The role
of biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular
Sciences, 20(22):5536.
Lundberg, S. M., Erion, G. G., and Lee, S. (2018).
Consistent individualized feature attribution for
tree ensembles. Computing Research Repository.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03888, Last accessed: 2020-
09-13.
Lundberg, S. M. and Lee, S.-I. (2017). A unified ap-
proach to interpreting model predictions. In Guyon,
I., Luxburg, U. V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fer-
gus, R., Vishwanathan, S., and Garnett, R., editors,
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
volume 30, pages 4765–4774. Curran Associates, Inc.
Marcus, D. S., Fotenos, A. F., Csernansky, J. G., Morris,
J. C., and Buckner, R. L. (2010). Open Access Series
of Imaging Studies: Longitudinal MRI data in nonde-
mented and demented older adults. Journal of Cogni-
tive Neuroscience, 22(12):2677–2684.
McKay, M. D., Beckman, R. J., and Conover, W. J. (1979).
A Comparison of three methods for selecting values of
input variables in the analysis of output from a com-
puter code. Technometrics, 21(2):239–245.
Mo
ˇ
ckus, J. (1975). On bayesian methods for seeking the
extremum. In Proceedings of the Optimization Tech-
niques IFIP Technical Conference, pages 400–404.
Springer.
Mofrad, R. B., Schoonenboom, N. S., Tijms, B. M., Schel-
tens, P., Visser, P. J., Flier, W. M., and Teunissen, C. E.
(2018). Decision tree supports the interpretation of
CSF biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s
& Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Mon-
itoring, 11(1):1–9.
Molnar, C. (2019). Interpretable Machine Learning:
A guide for making black box models explain-
able. https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-
book/, Last accessed: 2020-08-30.
Patterson, C. (2018). World Alzheimer report
2018 - The state of the art of dementia re-
search: New frontiers. Alzheimer’s Dis-
ease International, London, Great Britain.
https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerRepo
rt2018.pdf, Last accessed: 2020-08-26.
Pelka, O., Friedrich, C. M., Nensa, F., M
¨
onninghoff, C.,
Bloch, L., J
¨
ockel, K.-H., Schramm, S., Sanchez Hoff-
mann, S., Winkler, A., Weimar, C., Jokisch, M., and
for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
(2020). Sociodemographic data and APOE- 4 aug-
mentation for MRI-based detection of amnestic Mild
Cognitive Impairment using deep learning systems.
PLOS ONE, 15(9):1–24.
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
98

Petersen, R. C., Aisen, P. S., Beckett, L. A., Donohue,
M. C., Gamst, A. C., Harvey, D. J., Jack, C. R., Jagust,
W. J., Shaw, L. M., Toga, A. W., Trojanowski, J. Q.,
and Weiner, M. W. (2010). Alzheimer’s Disease Neu-
roimaging Initiative (ADNI). Neurology, 74(3):201–
209.
R Core Team (2019). R: A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statis-
tical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Manual v3.5.3
https://www.R-project.org/, Last accessed: 2020-09-
12.
Refaeilzadeh, P., Tang, L., and Liu, H. (2009). Cross-
Validation. In Liu, L. and
¨
Ozsu, M. T., editors,
Encyclopedia of Database Systems, pages 532–538,
Boston, United States. Springer.
Rieke, J., Eitel, F., Weygandt, M., Haynes, J.-D., and Rit-
ter, K. (2018). Visualizing Convolutional Networks
for MRI-based diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. In
Stoyanov, D., Taylor, Z., Kia, S. M., Oguz, I., Reyes,
M., Martel, A., Maier-Hein, L., Marquand, A. F.,
Duchesnay, E., L
¨
ofstedt, T., Landman, B., Cardoso,
M. J., Silva, C. A., Pereira, S., and Meier, R., editors,
Understanding and interpreting Machine Learning in
medical image computing applications, pages 24–31.
Springer International Publishing.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., and Williams, R. J. (1986).
Learning representations by back-propagating errors.
Nature, 323(6088):533–536.
Samper-Gonz
´
alez, J., Burgos, N., Bottani, S., Fontanella,
S., Lu, P., Marcoux, A., Routier, A., Guillon, J., Bacci,
M., Wen, J., Bertrand, A., Bertin, H., Habert, M.-O.,
Durrleman, S., Evgeniou, T., and Colliot, O. (2018).
Reproducible evaluation of classification methods in
Alzheimer’s Disease: Framework and application to
MRI and PET data. NeuroImage, 183:504–521.
Schmermund, A., M
¨
ohlenkamp, S., Stang, A., Gr
¨
onemeyer,
D., Seibel, R., Hirche, H., Mann, K., Siffert, W.,
Lauterbach, K., Siegrist, J., J
¨
ockel, K.-H., and Erbel,
R. (2002). Assessment of clinically silent atheroscle-
rotic disease and established and novel risk factors for
predicting myocardial infarction and cardiac death in
healthy middle-aged subjects: Rationale and design of
the Heinz Nixdorf RECALL study. American Heart
Journal, 144(2):212–218.
Selvaraju, R. R., Cogswell, M., Das, A., Vedantam, R.,
Parikh, D., and Batra, D. (2017). Grad-CAM: Vi-
sual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-
Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV),
pages 618–626.
Shapley, L. S. (1953). A Value for n-Person Games. In
Kuhn, H. W. and Tucker, A. W., editors, Contributions
to the Theory of Games (AM-28), volume 2, pages
307–318. Princeton University Press.
Simonyan, K., Vedaldi, A., and Zisserman, A. (2014). Deep
inside convolutional networks: Visualising image
classification models and saliency maps. Computing
Research Repository. http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6034,
Last accessed: 2020-08-30.
Slack, D., Hilgard, S., Jia, E., Singh, S., and Lakkaraju, H.
(2020). Fooling LIME and SHAP adversarial attacks
on post hoc explanation methods. In Proceedings of
the AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society.
ACM.
Springenberg, J., Dosovitskiy, A., Brox, T., and Ried-
miller, M. (2015). Striving for simplicity: The
all Convolutional Net. In Proceedings of the In-
ternational Conference on Learning Representations
(ICLR) (workshop track). http://lmb.informatik.uni-
freiburg.de/Publications/2015/DB15a, Last accessed:
2020-08-30.
ˇ
Strumbelj, E. and Kononenko, I. (2013). Explaining pre-
diction models and individual predictions with feature
contributions. Knowledge and Information Systems,
41(3):647–665.
Therneau, T. and Atkinson, B. (2018). rpart: Re-
cursive Partitioning and Regression Trees.
Manual of R package v4.1-13 https://CRAN.R-
project.org/package=rpart, Last accessed: 2020-09-
12.
Wang, X., Shen, D., and Huang, H. (2019). Interpretable
deep temporal structure learning model for early de-
tection of Alzheimer’s Disease. bioRxiv.
Wen, J., Thibeau-Sutre, E., Diaz-Melo, M., Samper-
Gonz
´
alez, J., Routier, A., Bottani, S., Dormont, D.,
Durrleman, S., Burgos, N., and Colliot, O. (2020).
Convolutional Neural Networks for classification of
Alzheimer’s Disease: Overview and reproducible
evaluation. Medical Image Analysis, 63:101694.
Westman, E., Aguilar, C., Muehlboeck, J.-S., and Simmons,
A. (2012). Regional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
measures for multivariate analysis in Alzheimer’s Dis-
ease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Brain Topogra-
phy, 26(1):9–23.
Yan, Y. (2016). rBayesianOptimization: Bayesian
Optimization of Hyperparameters. Man-
ual of R package v1.1.0 https://CRAN.R-
project.org/package=rBayesianOptimization, Last
accessed: 2020-09-12.
Yang, C., Rangarajan, A., and Ranka, S. (2018). Vi-
sual explanations from deep 3D Convolutional
Neural Networks for Alzheimer’s Disease clas-
sification. Computing Research Repository.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02544, Last accessed:
2020-08-30.
Zeiler, M. D. and Fergus, R. (2014). Visualizing and under-
standing Convolutional Networks. In Fleet, D., Pajdla,
T., Schiele, B., and Tuytelaars, T., editors, Proceed-
ings of the 13th European Conference on Computer
Vision (ECCV), pages 818–833. Springer International
Publishing.
Developing a Machine Learning Workflow to Explain Black-box Models for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
99
