
Computational Model for Changing Sedentary Behavior through
Cognitive Beliefs and Introspective Body-feelings
Fawad Taj
1,2 a
, Nimat Ullah
1,3 b
and Michel Klein
1c
1
Social AI group, Dept. of Computer Science, VU Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
2
Dept. of Computer Science, University of Swabi, Swabi, Pakistan
3
Dept. of Computer Science, FATA University, TSD Dara, Kohat, Pakistan
Keywords: Digital Health, Sedentary Behavior, Theory of Planned Behavior, Health Belief Model, Network Oriented
Modelling.
Abstract: Sedentary behavior has emerged as a serious risk factor for numerous health outcomes. However, little work
has been done to approach the problem through social-cognitive theories. In this study, a network model has
been proposed for sedentary behavior intervention based on Influential determinants from major social-
cognitive theories i.e., theory of planned behavior and health-belief model. Accounting for these determinants
means that we are influencing behavior with a peripheral route, for which we included the somatic markers
as a body-feelings in the model. An effective behavior change techniques from literature are used to affect
these determinants to change the sedentary behavior. The model has been mathematically represented and
simulated using a network-oriented modelling technique for an office employee.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sitting behaviour is characterized by any waking
behavior with an energy expenditure of ≤1.5
metabolic equivalents (METs). You can be sedentary
at work, at school, at home, when travelling or during
leisure time while watching television, studying or
working at a desk or computer. A person can do
enough physical activity to meet the guidelines and
still be considered sedentary if he/she spends a large
amount of his/her time sitting or lying down
(Weggemans et al., 2018). Moreover, low level or
moderate-to-vigorous level physical activity is not the
same as being sedentary for example, I cycle to the
office every day (which is Dutch culture) and then sit
at a computer for around 6-7 hours, so it is possible
for being highly sedentary and highly active at the
same time. Prolonged sitting has several adverse
health outcomes including increased risk of type 2
diabetes, higher risk of premature death and death
from cardiovascular disease (Australian Government
guidelines for sedentary behavior, 2019)
(Weggemans et al., 2018).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9049-1736
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0592-8380
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4119-1846
A number of theories and models from social and
behavioral sciences can assist us to make sense of
behaviour and the world around us. More specifically
for sedentary behavior, a number of ecological
model/theories are proposed, but they are seldomly
used. In a recent review (Huang, Benford, & Blake,
2019), 19 out of 63 digital interventions for sedentary
behavior are based on some theoretical grounds
(among them the theory of planned behavior is used
for 5 times and social cognitive theory for 4 times).
Whereas from digital technological prospective the
sedentary behavior intervention mostly uses mobile
apps and wearable sensors (Taj, Klein, & van
Halteren, 2019). Sedentary behavior interventions
usually follow ecological models that define
multifaceted determinants of the problem, including
individual, social, and environmental policy level
(Owen et al., 2011).
A shortcoming of the ecological model is that they
fail to acknowledge the role of psycho-social
variables in explaining sedentary behavior
(Prapavessis et al., 2015). On an individual level,
different characteristic like beliefs, motivation or
Taj, F., Ullah, N. and Klein, M.
Computational Model for Changing Sedentary Behavior through Cognitive Beliefs and Introspective Body-feelings.
DOI: 10.5220/0010247704430450
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 5: HEALTHINF, pages 443-450
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
443

intention etc. can influence sedentary behavior. For
understanding these types of determinants, socio-
cognitive theories are the best options to be reached
out (Sallis, Owen, & Fisher, 2015). Sedentary
behavior in the workplace is high; 71–77% of
working hours are being spent sedentary (Scherer,
2005). It requires minimal effort or conscious
planning and is highly habitual. To change workplace
sedentary behavior, we need to target these
determinants using effective behavior change
strategies, which will also be discussed later in the
paper.
In this paper, we focus on a conceptual model that
considers psycho-social determinants to reason about
sedentary behavior and use different behavior change
techniques to break a sedentary behavior.
The aims of this research includes: Identifying
the key psycho-social determinants from different
health cognitive theories for sedentary behaviour.
Exploring the popular behavior change
strategies/techniques from literature to target these
determinants ans lastly, modeling the findings as a
computational network model and simulating an
office employee working scenario using the model.
In Section 2 of the paper, the background of the
constructs from different theories are given and
discusses the behavior change techniques (BCTs) that
can be used to influence these determinants. In
section 3, the conceptual and mathematical
representation of network-oriented model is
presented. Section 4 contains the scenario and the
simulation results. The paper has been concluded in
Section 5 with a brief insight into the future
directions.
2 BACKGROUND
This section provides the background for the model
we proposed. In the first part, theories and working of
its determinants/parameters are discussed with
linkage to sedentary behaviors. The second part of
this section discusses different behaviour change
techniques with its association to the determinants of
the theories.
2.1 Socio-psychological Determinants
Most of the health cognitive theories describe
possible relationships between the psycho-social
factors and sedentary behavior, but theory of planned
behavior (TPB) has been mostly used in this context
(Prapavessis et al., 2015). According to TPB, an
individual’s intention is the main determinant of
actual sedentary time. The intermediate determinants
of intention are attitude, subjective norms (SN), and
perceived behavioral control (PBC). Attitude
represents an individual’s evaluation of the perceived
benefits and cost of sitting, SN reflects a belief about
whether most people approve or disapprove an action,
and PBC refers to individual’s perception of their
ability to control the time they spend being sedentary
(Prapavessis et al., 2015, Ajzen, 2005).
Health belief model (HBM) is the theory mostly
used to identify the determinants which explain the
likelihood of engaging in health-promoting behavior.
Perceived outcomes and self-efficacy are the main
constructs in HBM. Similarly, from Social Cognitive
Theory (SCT), self-efficacy construct suggests a
setting of realistic and measurable goals to ensure
initial success and the outcome expectancies
construct would suggest highlighting the benefits of
reducing sedentary time e.g., reduced muscle stiffness
etc. (Owen et al., 2011). The application of social
cognitive theory for health behavior change has
focused predominantly on increasing self-efficacy,
for example, confidence in one’s own abilities
(Bandura, 1998). The perceived self-efficacy is
highly correlated with goal attainment, higher the
self-efficacy, higher the goals people set for
themselves (Bandura, 2004). There exists a fair
amount of cross-sectional studies that correlate social
cognitive constructs to workplace setting but the
association between social-cognitive factors and
sedentary behavior needs much more exploration
(Hadgraft et al., 2017).
Among different theoretical models, most of the
determinants are overlapping and most of the
researcher overload their studies with the dictum that
more is better (Bandura, 2004). The determinants
discussed above are basically the internal cognitive
beliefs of humans. We represented these determinants
as positive and negative beliefs, for example,
perceived benefit (HBM) and self-efficacy (HBM,
TPB, SCT) are the positive beliefs about the action.
Similarly, perceived severity and susceptibility to
disease/behavior (HBM) are the negative beliefs
about the outcomes. Moreover, subjective norms in
TPB corresponds to expected social outcomes for a
given behavior. Perceived behavioral control in TPB
overlaps with perceived self-efficacy in SCT
(Bandura, 2004).
2.2 Behavior Change Techniques
In any intervention, BCTs are an important active
ingredient that may explain study variation in-
effectiveness. Effective sedentary reduction
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
444

intervention depends on understanding and reasoning
about what works and why (Michie et al., 2013). A
taxonomy is available which describes 93 discrete
behaviour change techniques that can be used in
interventions within any behavioural domain e.g.
providing information on health consequences,
setting goals, restructuring the physical environment.
Behaviour change techniques represent the
observable and irreducible intervention components
that serve to perform one or more functions (Michie
et al., 2013).
Developing intervention based on theories and
models suggest using the available systematically
verified BCTs to effectively target the determinants
noted in the above section. For example, from SCT
and TPB the use of self-efficacy construct suggests
the use of goal-setting e.g. setting a walking goal to
the corridor door after every 30 minutes of work, and
self-monitoring e.g. maintains sitting time record
book (Owen et al., 2011). BCT taxonomies are new
and are seldom reported in digital behavior change
interventions (Direito et al, 2016). It has been
observed that only 10 out of potential 93 BCTs were
present (mean of 2.42 BCTs were present in each app)
(Dunn, 2017). Table 1 shows the description of each
of the determinant with scale description, source
theory/model, and some of the effective BCT to target
these determinants, coded from recent BCTs
taxonomy (Michie et al., 2013). The best resource
available to find the linkage between BCT and the
above-mentioned determinants (mechanism of
action) is the human behaviour change project
(https://www.humanbehaviourchange.org/). In one of
the studies in this project, they published the
triangulating evidence of links made by authors in
published scientific studies and by expert consensus
(https://theoryandtechniquetool.humanbehaviourcha
nge.org/).
3 NETWORK-ORIENTED
MODEL
Network-oriented temporal-causal network
modelling approach (Treur, 2016) has been used for
modelling the above concepts. The temporal
dimension enables the modelling of cyclic causal
relations with exact timing. The reason for
representing it as a causal network lies in the fact that
most of the determinants are subjective beliefs and
they are causally linked like a network. There are two
types of beliefs presented in the model, the positive
and negative beliefs; self-efficacy and perceived
benefit are presented as positive beliefs about the
current sedentary behaviour and the perceived
susceptibility and severity are negative beliefs about
sedentary behaviour. The two types of actions i.e.,
sedentary behaviour (sitting) and non-sedentary
behaviour (walk) are inversely influenced by these
positive and negative beliefs.
The network-oriented models can be represented
in two ways i.e., graphical representation and
numerical representation. Fig. 1 shows the graphical
representation of the proposed model. In section 3.1,
the graphical representation is converted into a
numerical or mathematical representation.
In the model, a person sedentary behavior is
represented with the states i.e., preparation for action
(ps
) and execution of action (es
). Whereas, the
walking behavior is represented with states i.e.,
( ps
) and execution of action ( es
). The
determinants discussed in section 2 are represented by
different states in the network for example, perceived
susceptibility and severity are represented with state
name srs
.
, srs
.
respectively. The
scenario discussed in section 4, shows how perceived
susceptibility and severity of the action affects the
actions execution and how after the intervention,
efficacy and perceived benefits increases.
This shift in beliefs is model used the Damasio’s
somatic marker hypothesis, i.e., introspective
feelings. It plays a critical role in the ability to make
fast, rational decisions in complex and uncertain
situations (Damasio, 1998). The feeling actually
serves a kind of monitoring and helps in choosing the
best possible options for action. This feeling state is
affected by predictive as-if body loop, which gives a
sense of preview and valuing the action before it has
actually been performed.
3.1 Mathematical Representation
A network-model illustrated in fig. 1 involves states
that reflect actual world anomalies, and the arrows
indicate the causal connection between the two
entities. Important notions for each of the state and
connection are as follow:
• Connection(ω
X,Y
): represents the connection
value between the states (x,y). The value represents
the strength of causality and its value ranges between
[-1, 1].
Speed Factor (η
Y
): How fast the state value going to
change with incoming causal impact.
Computational Model for Changing Sedentary Behavior through Cognitive Beliefs and Introspective Body-feelings
445
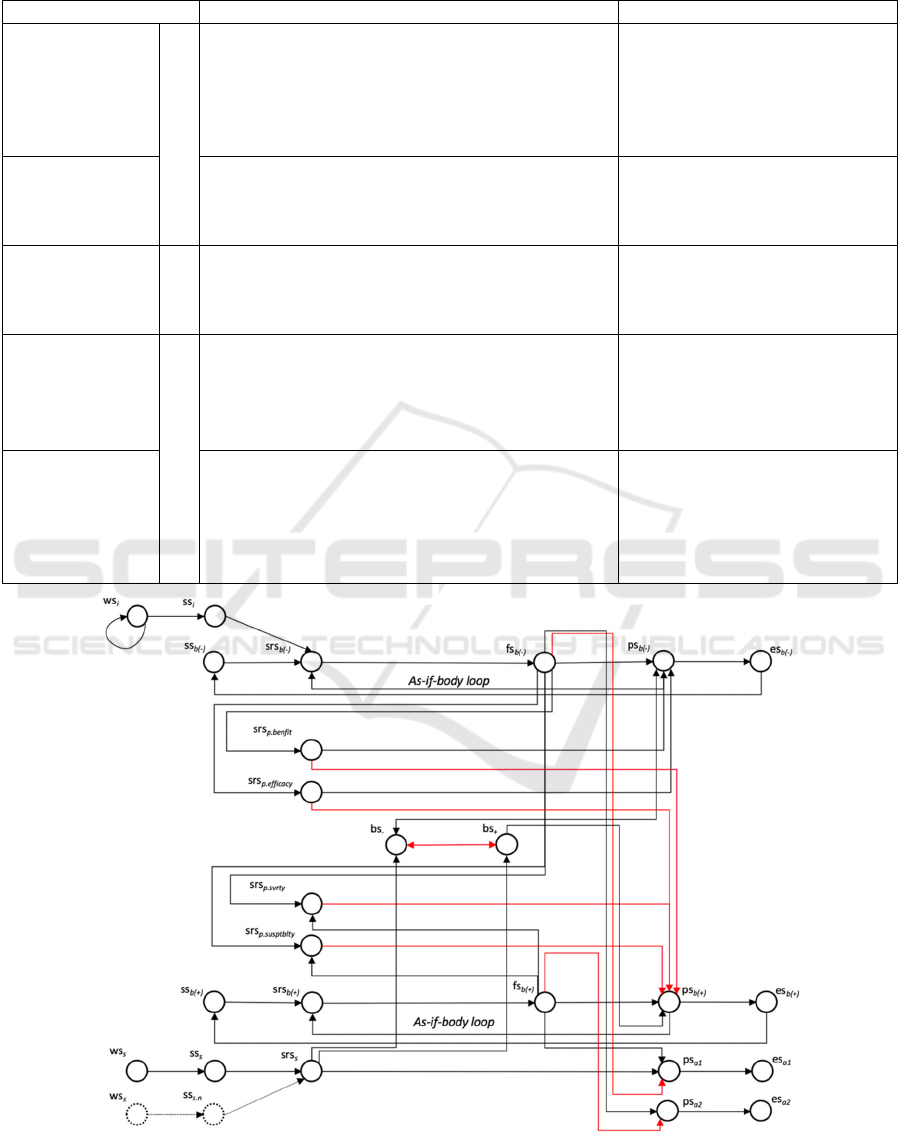
Table 1: Determinants with scale description and coded behavior change techniques.
Determinan
t
Scale Description BCT
Perceived
Severity
(HBM)
Negative beliefs
One's belief of how serious a condition and its
consequences are
E.g. How confident are you that long sitting can
cause serious chronic illnesses.
BCT: 5.1. Information about
health consequences
BCT: 9.2. Pros and cons
BCT: 10.1. Material incentive
(behaviour)
BCT: 10.10. Reward (outcome)
Perceived
Susceptibility
(HBM)
One's belief of the chances of getting a condition.
E.g. How confident are you that your health will
not be with long sitting.
BCT: 5.1. Information about
health consequences
BCT: 5.2 Salience of
consequences
Social norms
(SCT, TPB)
Perceived organization/social support for less
sitting at work.
E.g. My workplace environment has an open
choice to stand or move more at work.
BCT: 6.3. Information about
others’ approval
BCT: 6.2. Social comparison
Perceived
Benefits
(HBM)
Positive beliefs
One's belief in the benefit of the advised action to
reduce the risk or seriousness of the impact
E.g. How confident are you that small breaks after
every 30 minutes will help me avoiding chronic
disease.
4.1 Instruction on how to
perform behavior — how,
where, when
5.3 Information about social and
environmental consequences.
Self-Efficac
y
(HBM, SCT,
TPB)
Confidence in one's ability to act. Provide training,
guidance, and positive reinforcement
E.g. How confident would have been that you
could have stood up during the meeting.
BCT: 1.2. Problem solving
BCT: 8.7. Graded tasks
BCT: 4.1. Instruction on how to
perform behaviour
BCT: 6.1. Demonstration of the
b
ehaviou
r
Figure 1: The network model for sedentary behavior change. The red lines show the negative connections and black lines are
the positive connections.
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
446

• Combination Function (c
Y
(...)): is used to
combine the causal impact of multiple incoming
states. This approach provides a library of currently
40 combination functions for the aggregation of
multiple (incoming) causal impacts.
Impact
X,Y
= ω
X,Y
X(t)
(1)
Total aggregated impact on state Y at time t combined
by combination function.
aggimpact
Y
(t) = c
Y
(impact
X1,Y
, impact
X2,Y
,
impact
X3,Y
, …)
= c
Y
(ω
X1,Y
X
1
(t), ω
X2,Y
X
2
(t), ω
X3,Y
X3(t), …)
(2)
The aggimpact
Y
(t) will have upward or downward
effect at time point t, but how fast this change takes
place depends on the speed factor η
Y
,
Y(t+
Δt) = Y(t) + η
Y
[aggimpact
Y
(t) – Y(t)] Δt
(3)
The following difference (eq.4) and differential
equation (eq.5) can be obtained for state Y:
Y(t+
Δt) = Y(t) + η
Y
[cY(ω
X1,Y
X1(t),
ω
X2,Y
X2(t), ω
X3,Y
X3(t), …) – Y(t)]Δt
(4)
dY(t)/dt = ηY [c
Y
(ω
X1,Y
X1(t), ω
X2,Y
X2(t),
ω
X3,Y
X3(t), …) – Y(t)]
(5)
3.2 Parameters Formalization
The states represented in the model are cognitive
states having continuous one-dimensional value e.g.
sad vs happy. The causal connections shown by black
and red arrow shows the positive and negative
influence of one state on other, respectively. We have
scaled all type of values in the range of [-1,1] and
simulation time (t) is set for 200 steps.
The parameters required to define the network
models are: initial value, connection value,
combination function, and speed factor for each state.
The initial value for each of the state are set according
to the situation e.g., in simulation below for ws
s
and
ws
i
have initial values of 1 and 0.11, respectively and
rest of the state’s initial value are set to 0. To combine
the incoming effect on any state, a number of options
available for choosing among the different
combination function. In the proposed model, the
identity and advanced logistic sum combination
alogistic
σ,τ
(…) functions are used as the standard
combination function. The parameters for
combination functions (
τ, σ )and speed of factors (η) of
the states for the scenario (discussed below) are given
in Table 3.
4 SCENARIO AND SIMULATION
RESULTS
Consider an office situation where an employee,
Mavrik works in front of a computer from 9 to 5. He
is not aware of the severity and susceptibility of being
sedentary and do not have the self-belief that he
should overcome this behaviour. The organization
started a campaign (intervention) for providing
information to the employees about the negative
consequences of sitting more than consecutives 30
minutes and offered them 10 minutes break after each
1 hour of work (reward). With this campaign, the
employee starts realizing the severity and
susceptibility of the prolonged sitting, which leads to
an increase in his attitude towards taking a break after
each hour. Now with the campaign, the employee
starts perceiving the benefit of walking and his
efficacy gets increased, so it reduces the sedentary
behaviour. To simulate the above scenario, the
connection values and the combination functions are
described in the table 2 & 3.
The parameter values shown in these tables can be
used to reproduce the results shown in fig. 2, 3 and 4
below. Moreover, only ws
s
and ws
i
have initial values
of 1 and 0.11 respectively. States with zero values for
τ and σ in table 3 suggest that Identity function has
been used for these sates.
Fig 2 displays all the states of the model. It can be
seen that initially the person’s negative belief about
his current sedentary behavior is almost zero. Which
means, the perceived susceptibility and severity of his
sedentary behaviour are also very low. Therefore, the
person keeps sitting for long time in office.
In the second half of the fig. 2, it’s observable that
a shift takes place in the dynamics of the states. This
shift is because of the intervention proposed for the
person for breaking the continuity of his sedentary
action. This intervention changes the person’s belief
by making him walk/move after certain amount of
time.
Computational Model for Changing Sedentary Behavior through Cognitive Beliefs and Introspective Body-feelings
447

Table 2: The connection values (
) between the two states.
Connection Weight Connection Weight Connection Weight
,
1
,
0.8
,
0.5
,
1
,
0.75
,
0.5
,
0.2
.
,
-0.2
,
0.8
,
.4
.
,
-0.2
,
-0.6
,
1
,
-0.8
,
0.8
,
1
,
0.6
,
.
0.4
,
0.4
,
1
,
.
0.45
,
0.9
,
-0.8
,
.
0.48
,
0.6
.
,
-0.6
,
.
0.55
,
-0.6
.
,
0.3
,
0.3
,
1
.
,
-0.6
,
1
,
.
0.1
.
,
0.3
,
0.5
,
.
0.1
,
1
,
0.8
,
0.3
,
1
,
0.8
Table 3: The parameter of alogistic
σ,τ
(…) combination function and speed factor for different states.
State
τ σ η
State
τ σ η
ws
0 0 0
srs
.
0.25 8 0.5
ss
0 0 1
bs
0.2 3 0.4
srs
0.4 8 0.2
bs
0.3 10 0.4
ps
0 0 0.5
srs
.
0.3 8 0.5
es
0 0 0.5
srs
.
0.3 8 0.5
ps
0 0 0.5
ws
0.2 8 0.02
es
0 0 0.5
ss
0.2 8 0.02
ss
0.35 8 0.4
ss
_
0.3 8 0.2
srs
0.35 8 0.4
srs
_
0.3 8 0.1
fs
0.35 8 0.4
fs
_
0.3 7 0.2
ps
0.4 8 0.4
ps
_
0.28 7 0.1
esb
0.4 8 0.4
es
0.3 8 0.1
srs
.
0.25 8 0.5
Figure 2: The simulation result of the model with the state values mentioned in table 2 & 3.
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200
Time
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
States Values
dynamic states
wss
sss
srss
psa1
esa1
psa2
esa2
ssb+
srsb+
fsb+
psb+
esb+
srsp.susptblty
srsp.svrty
bs-
bs+
srsp.efficacy
srsp.benefit
wsi
ssi
ssb-
srsb-
fsb-
psb-
esb-
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
448
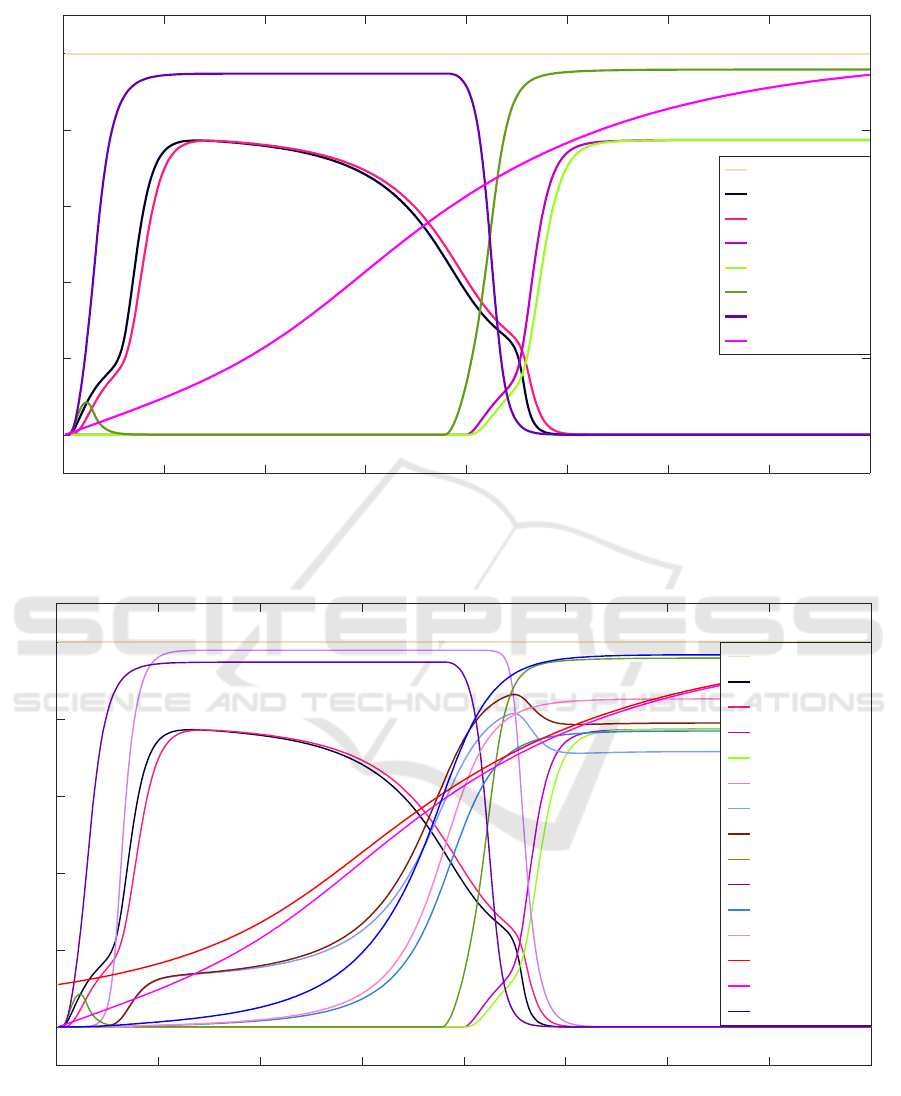
Figure 3: The sedentary behavior (esa(sedentary)) is high and the walking behavior (esa(active)) is low, but latter after with
intervention effect, the sedentary behavior went down and walking behavior got high.
Figure 4: All the cognitive belief states. The susceptibility and severity were initially too low and after the intervention it gets
high.
Fig. 3 shows that initially the person’s negative
belief (bs
-
) about his sedentary behaviour is low and
positive belief (bs
+
) is high. Hence his sedentary
action (ps
a1
,es
a1
) are high. In fig. 4, when the
intervention ws
i
and ss
i
gets activated to an enough
level, which changes the person’s belief, the
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200
Time
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
States Values
dynamic states
wss
psa(sedentary)
esa(sedentary)
psa(active)
esa(active)
bs-
bs+
ssi
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 20
0
Time
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
States Values
dynamic states
wss
psa1
esa1
psa2
esa2
fsb+
srsp.susptblty
srsp.svrty
bs-
bs+
srsp.efficacy
srsp.benefit
wsi
ssi
fsb-
Computational Model for Changing Sedentary Behavior through Cognitive Beliefs and Introspective Body-feelings
449

perceived susceptibility srs
p.susptblty,
and severity
srs
p.svrty
of the sedentary action get increased.
Negative belief (bs-) increases and positive belief
(bs+) decreases. As a result, the person’s non-
sedentary action i.e., preparation for action ‘2’ ps
a2
and execution of action ‘2’ es
a2
also increases while
sedentary behaviour i.e., preparation for action ‘1’
ps
a1
and execution of action ‘1’ es
a1
decreases
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (2005). Attitudes, personality, and behavior.
McGraw-Hill Education (UK).
Australian Governement guidleines for sedenteray
behavior. (2019). Retrieved from http://www.
health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/sbe
haviour
Bandura, A. (1998). Health promotion from the perspective
of social cognitive theory. Psychology and Health,
13(4), 623–649.
Bandura, A. (2004). Health promotion by social cognitive
means. Health Education & Behavior, 31(2), 143–164.
Damasio, A. R. (1998). Emotion in the perspective of an
integrated nervous system1. Brain Research Reviews,
26(2–3), 83–86.
Direito, A., Carraça, E., Rawstorn, J., Whittaker, R., &
Maddison, R. (2016). mHealth technologies to
influence physical activity and sedentary behaviors:
behavior change techniques, systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Annals
of Behavioral Medicine, 51(2), 226–239.
Dunn, E. E. (2017). Sedentary Behaviour, Physical
Activity, and Mobile Apps Among University Students.
Hadgraft, N. T., Winkler, E. A. H., Healy, G. N., Lynch, B.
M., Neuhaus, M., Eakin, E. G., Fjeldsoe, B. S. (2017).
Intervening to reduce workplace sitting: mediating role
of social-cognitive constructs during a cluster
randomised controlled trial. International Journal of
Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, 14(1), 27.
Huang, Y., Benford, S., & Blake, H. (2019). Digital
Interventions to Reduce Sedentary Behaviors of Office
Workers: Scoping Review. Journal of Medical Internet
Research, 21(2), e11079. https://doi.org/10.2196/11079
Michie, S., Richardson, M., Johnston, M., Abraham, C.,
Francis, J., Hardeman, W., Wood, C. E. (2013). The
behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93
hierarchically clustered techniques: Building an
international consensus for the reporting of behavior
change interventions. Annals of Behavioral Medicine,
46(1), 81–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-013-
9486-6
Owen, N., Sugiyama, T., Eakin, E. E., Gardiner, P. A.,
Tremblay, M. S., & Sallis, J. F. (2011). Adults’
Sedentary Behavior. American Journal of Preventive
Medicine, 41(2), 189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.amepre.2011.05.013
Prapavessis, H., Gaston, A., & DeJesus, S. (2015). The
Theory of Planned Behavior as a model for
understanding sedentary behavior. Psychology of Sport
and Exercise, 19, 23–32.
Sallis, J. F., Owen, N., & Fisher, E. (2015). Ecological
models of health behavior. Health Behavior: Theory,
Research, and Practice, 5, 43–64.
Scherer, K. R. (2005). What are emotions? and how can
they be measured? Social Science Information, 44(4),
695–729. https://doi.org/10.1177/0539018405058216
Taj, F., Klein, M. C. A., & van Halteren, A. (2019). Digital
Health Behavior Change Technology: Bibliometric and
Scoping Review of Two Decades of Research. JMIR
MHealth and UHealth, 7(12), e13311.
Taj, F., Klien, M., & Aart Van Halteren. (2020). An Agent-
Based Framework for Persuasive Health Behavior
Change Intervention. In 9th International Conference
on Health Information Systems (HIS 2020) 20-23
October 2020 (pp. 157–168). Amsterdam and Leiden,
Netherlands: Springer Lecture Notes in Computer
Science (LNCS). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-
61951-0_15
Treur, J. (2016). Dynamic modeling based on a temporal-
causal network modeling approach. Biologically
Inspired Cognitive Architectures, 16, 131–168.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bica.2016.02.002
Weggemans, R. M., Backx, F. J. G., Borghouts, L.,
Chinapaw, M., Hopman, M. T. E., Koster, A.,
Committee Dutch Physical Activity Guidelines 2017.
(2018). The 2017 Dutch Physical Activity Guidelines.
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and
Physical Activity, 15(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.1186/
s12966-018-0661-9.
HEALTHINF 2021 - 14th International Conference on Health Informatics
450
