
Classification of Myoelectric Surface Signals of Hand Movements using
Supervised Learning Techniques
Marisol Cristel Galarza Flores
a
, Juan Felipe Miranda Medina
b
and Cristian L
´
opez del
´
Alamo
c
Universidad Nacional de San Agust
´
ın de Arequipa (UNSA), Arequipa, Peru
Keywords:
Electromyography, Support Vector Machines, Neural Networks, Wavelets, Principal Component Analysis.
Abstract:
This work presents a comparative study of techniques to classify four hand movements (flexion, extension,
opening and closure) using myoelectric signals measured at the forearm in two separate channels: the bra-
chioradialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) muscle. The process of signal acquisition is described, as well
as signal normalization, hybrid feature extraction and classification using two supervised learning techniques;
i.e., backpropagation and support vector machines. The classifiers were trained using the raw data from the
input signal. It was verified that the accuracy of the classification is improved by feature extraction up to
2.25%, yielding a successful average classification rate of 91.00%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Experiments related to electromyography (EMG) are
linked to the discovery of electricity in the late 16th
century (Kazamel and Warren, 2017). The array of
possibilities arising from the measurement of EMG
signals, however, was better understood only in the
20th century with the development of electronics and
programming: myoelectric prosthesis for amputees,
bionic exoskeletons, and teleoperated robots for mi-
crosurgeries or explosive deactivation are all current
applications that continue to be researched (Cabrera
and Jaramillo, 2010). The analysis of EMG signals,
however, is not exempt from challenges, since the
measured potentials present low amplitude and are
strongly non-stationary and the initial data is poorly
structured. There is thus the need to “develop new ef-
fective methods” for the analysis of EMG signals and
for their application to the study of human motricity
(Kurkin et al., 2019).
Earlier studies about the classification of myo-
electric signals deployed neural networks (Hudgins
et al., 1993; Haihua et al., 2005; Durgesh and Lekha,
2010), ARTMAP (Carre
˜
no and Vuskovic, 2005) and
Euclidean distance (Ferguson and Dunlop, 2002) as
classification methods. More recent research, such as
the survey by (Kehri et al., 2016) identifies Wavelets,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6419-0761
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5239-2718
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2568-650X
Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Support Vec-
tor Machines (SVM) and Neural Networks (NN) as
key techniques for EMG signal analysis. Further-
more, the studies by (Gupta et al., 2017) and (Sat-
apathy et al., 2019) emphasize on SVM and neural
networks as particularly relevant classification tech-
niques.
This work is aimed towards the classification of
four different hand movements (i.e., flexion, exten-
sion, hand opening and hand closure) utilizing mea-
surements of EMG signals in the forearm. In this
respect, the comparative study by (Wołczowski and
Zdunek, 2017) shows that in general, higher rates of
accuracy (approximately 95 %) with lower compu-
tational complexity can be achieved utilizing feature
extraction techniques, thus outperforming conven-
tional methods such as Principal Component Analy-
sis (PCA). This is a key motivation in the method-
ology of this work, since its chief contribution is a
comparison accross two different processes. The first
one refers to feature extraction, where we resort to
a hybrid approach combining (1) univariate selection
with a Chi-square distribution (henceforth referred to
as χ2) with Principal Component Analysis (PCA), (2)
χ2 with Wavelets, and (3) χ2 with PCA and Wavelets.
The second process corresponds to classification al-
gorithms; we present a comparison of classification
accuracy of back-propagation neural networks against
Support Vector Machines (SVM) for each of the three
feature extraction methods. Although the methods
Flores, M., Medina, J. and Álamo, C.
Classification of Myoelectric Surface Signals of Hand Movements using Supervised Learning Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0010281802430251
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 4: BIOSIGNALS, pages 243-251
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
243

deployed in this research have already been used by
other research groups for EMG signal classification,
the novelty of this work is the comparative study that
can be helpful to plan similar experiments in the fu-
ture.
2 PREVIOUS WORK
(Y
¨
ucel and Mehmet, 2001) and (Ferguson and Dun-
lop, 2002) proposed the extraction of signal features
prior to classification. For their study they deployed
the Wavelet transform with principal components as
a feature extractor. In 2004, hybrid feature vec-
tors were proposed. In this regard, (Kilby and Hos-
seini, 2004) made a comparison of different Wavelet
families with DWT and WPT, concluding that the
Wavelets that yielded the best results for EMG sig-
nals where Daubechies, Summlet and Coiflet. On
the other hand, (Hargrove et al., 2007) classified 6
patterns of movement based on surface EMG signals
and EMG intramuscular signals. Their hypothesis
was that crosstalk would be weaker in intramuscu-
lar signals, which would allow for a better classifi-
cation. Nevertheless, they found that there was no
significant difference in the accuracy of the classifica-
tion. In 2015, (Quinay
´
as-Burgos and Gaviria-L
´
opez,
2015) developed a two-channel system to detect the
intention of movement, achieving an accuracy per-
centage of 85 and 92.5% in the classification of four
different movements, utilizing a hybrid vector of sta-
tistical components as a feature extractor. In 2016
they developed a classifier based on a backpropaga-
tion neural network utilizing wavelength as the fea-
ture in the time domain for the feature extractor, ex-
tracting EMG signals to classify five different move-
ments, obtaining an accuracy percentage of 75.54%
± 5.17 and 67.37% ± 8.75. It was thus shown that
accuracy in movement classification is not dependent
on the number of electrodes deployed. A better classi-
fication rate can be achieved by placing the electrodes
on the main muscles relative to the movement being
performed, instead of utilizing a large amount of elec-
trodes (Irastorza-Landa et al., 2017).
3 METHODOLOGY
Upon reviewing the state of the art, we concluded that
the classifier that was most deployed was the back-
propagation neural network. In order to have a ref-
erence of comparison for this classifier, we decided
to use support vector machines (SVM) as well. Re-
garding feature extraction, we chose a hybrid vector
with Wavelet transform components, for it was the
most deployed method. We chose principal compo-
nent analysis as well because it had the best results
in the literature and we added the univariate selection
method to our list, utilizing the Chi-square (χ2) dis-
tribution. The methodology we suggest is represented
in Figure 1.
In the development of this work, the following
activities were carried out: signal acquisition (Sec-
tion 3.1), signal preprocessing (Section 3.2), extrac-
tion of signal features (Section 3.3), signal classifica-
tion (Section 3.4), result comparison (Section 4) and
conclusions from test analysis and results (Section 5).
3.1 Signal Acquisition
3.1.1 Features of the EMG Signal
An EMG signal has a typical amplitude that varies
between 0 and 6mV, and its useful frequency lies in
the range of 0 to 500 Hz although most part of the
energy is concentrated between 50 and 150 Hz (Ger-
dle et al., 1999). According to the Nyquist-Shannon
theorem, if the highest frequency contained in an ana-
log signal x
a
(t) is F
max
= B and the signal is sampled
at a rate F
s
> 2F
max
≡ 2B, then x
a
(t) can be fully re-
covered. If this criterion is not satisfied, there will
be frequency overlapping, otherwise known as alias-
ing. For this project, the sampling frequency had to
be at least greater than 300 Hz, therefore we chose to
sample every 2 ms, which is equivalent to a 500 Hz
sampling frequency. On the other hand, according to
(Birkedal et al., 2002), the first 400 ms of a muscu-
lar movement are enough for the identification of the
movement, therefore the signals were recorded with a
window of 400 ms. With these considerations, sam-
ples of four movements were taken in 10 different
participants, 10 samples for each one of them. The
participants did not perform any significant physical
effort 24 hours prior to the experiment.
3.1.2 Electrode Placement
One of the most controversial aspects of surface EMG
is the placement of the electrodes (Aaron, 2010).
That is why, the Surface Electromyography for Non-
invasive Assessment of Muscles (SENIAM) standard
was elaborated in Europe to provide specific rec-
ommendations regarding the location, the size and
the shape of the electrodes (Hermens and Freriks,
1997). According to the SENIAM standard, the rec-
ommended value for the diameter of the electrodes
is 10 mm, while the inter-electrode distance, defined
as the center-to-center distance of the conductive area
of the electrodes, should be 2 cm. For the shape of
BIOSIGNALS 2021 - 14th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
244

Figure 1: Suggested methodology for signal classification. Source: prepared by the authors.
the electrode, defined as the conductive area that is
in touch with the skin, most of the literature recom-
mends a circular shape (Merletti and Parker, 2004).
In this study, the following signal characteristics
and process for signal acquisition where selected:
1. Superficial (non-invasive) Ag-Cl electrodes.
2. The participants’ skin was disinfected with alco-
hol. In addition, the electrodes carried the saline
solution for the transmission of the electric im-
pulse.
3. The participant’s initial posture for signal acquisi-
tion is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Initial position for signal acquisition. Source: pre-
pared by the authors.
4. For this study we chose the motor points of the
brachioradialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
(FCU) muscle as shown in Figures 3 and 4.
5. The inter-electrode distance is 2 cm, and the
grounded electrode will be placed in the area near-
est to the elbow.
6. After placing the electrodes, the signals will be
visually inspected on the oscilloscope.
3.2 Signal Preprocessing
3.2.1 Sensing of the EMG Signal
Myoelectric signals are characterized by low ampli-
tude levels (typically between 0 and 6 mV) and there-
fore the sensing mechanism must include a low noise
amplifier. A passband filter is also required since the
Figure 3: Electrode position in the brachioradialis. Source:
prepared by the authors.
Figure 4: Electrode position in the FCU muscle. Source:
prepared by the authors.
signal’s energy is concentrated around a 50 to 150 Hz
bandwidth. Furthermore, the signal must be condi-
tioned according to the input of the microcontroller
carrying out the signal processing. A sensor was fab-
ricated that included the stages of amplification, filter-
ing and conditioning following the method proposed
by (Gomero et al., 2009). Upon comparing its per-
formance to the MyoWare Muscle sensor (MyoWare.,
2015), however, the latter yielded better results and
was therefore chosen for this project.
The resulting architecture of the sensing interface
was compact: it consisted of two MyoWare muscle
sensors (each of which includes low-noise amplifica-
tion, passband filtering and signal conditioning), an
Arduino Mega microcontroller (that converts the ana-
log input into a digital binary stream), and an SD
memory that stores the digitized version of the elec-
Classification of Myoelectric Surface Signals of Hand Movements using Supervised Learning Techniques
245

tromyographic signal into a CSV file. The reason for
using two sensors rather than one is that, according
to our medical consultant Dante Condori, at least two
different channels are needed in order to detect four
different hand movements.
3.2.2 Signal Normalization
Each channel was normalized separately subtracting
the average offset amplitude to each measured input
signal. This is because each participant had a different
average offset amplitude value which corresponds to
the average of the signal measurement when the arm
is at rest.
3.3 Feature Extraction
3.3.1 Wavelet Transform
The Wavelet transform provides simultaneous infor-
mation both in the time and the frequency domains.
One of its most important parameters is the resolution
of the transform, associated with the level of decom-
position to be deployed (Mallat, 1991). The Wavelet
transform is used to analyze time series that contain
non-stationary signals in a wide frequency range (Tor-
rence and Compo, 1998), and is given by:
W
f
(s, τ) =
Z
f (t)ψ
∗
s,τ
(t)dt , (1)
where f (t) is the signal being analyzed, ψ
∗
s,τ
(t) is the
expansion function or basis, i.e., the Wavelet func-
tion, and W
f
(s, τ) is the resulting Wavelet transform.
Wavelets are generated from the translation and scale
variation of the same Wavelet function ψ(t), known
as the “mother Wavelet”. In this work, we deploy as
part of the characteristic vector of the EMG signal the
approximation coeficients (cA) of the mother Wavelet
Daubechies 4 (db4).
3.3.2 Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
The PCA algorithm starts from a mutually correlated
data set, and returns a set of information without any
linear correlation. The extractor of PCA character-
istics is most effective when there is a high correla-
tion in the variables of the input data (Daniel, 2015).
In this work, the first 100 principal components were
taken to form the characteristic vector.
1
1
The determination of the number of principal components
is also possible by means of statistical inference methods,
as the work of (Liu, 2017) illustrates.
3.3.3 Univariate Selection
This feature selection is based on picking the N char-
acteristics with greater correlation with the expected
output. The Chi-square function was chosen for this
test. It was used to compare the observed frequen-
cies with the expected frequencies. In our classifica-
tion method each of the four hand movements cor-
responds to a class. The classifier returns one of the
four classes as an output given the measured input sig-
nals for a given participant. To verify that the number
of observed results in each class corresponds approx-
imately to the expected number, we make use of hy-
pothesis contrast utilizing the Chi-square distribution:
χ
2
∗
=
k
∑
i=1
(O
i
− E
i
)
2
O
i
. (2)
From this equation we have that the lower the χ
2
∗
value is, the higher the correlation between the ob-
served and the expected frequencies.
3.4 Classifiers
3.4.1 SVM
Support vector machine (SVM) is a classification
technique based on exact mathematical models. To
achieve optimal results, cross-validation (Durgesh
and Lekha, 2010) on ten different test groups was de-
ployed.
SVM maps an input vector (input data) in a higher
spacial dimension, in which a maximal separation hy-
perplane is constructed. Two parallel hyperplanes are
constructed on each side of the hyperplane separating
the data. The separation hyperplane (MMH) is the
hyperplane that maximizes the distance between two
parallel hyperplanes. It is assumed that the higher the
margin or distance between the parallel hyperplanes,
the better the class separation will be (Vapnik, 2013).
If we consider Figure 5, we can see that the hy-
perplane of maximal margin is the medium line of
the widest “block” that we can insert between the two
classes so that they are perfectly separated.
3.4.2 Non-linear SVM
Not every problem is linearly separable. Therefore,
different kernels are required depending on the sets of
classes that are separated. The use of other kernels
offers a greater flexibility, allowing for a greater sep-
arability margin of non-linear and multidimensional
classes. SVM allows for non-linear kernels such as
the polynomial and radial kernels shown in Figure
BIOSIGNALS 2021 - 14th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
246
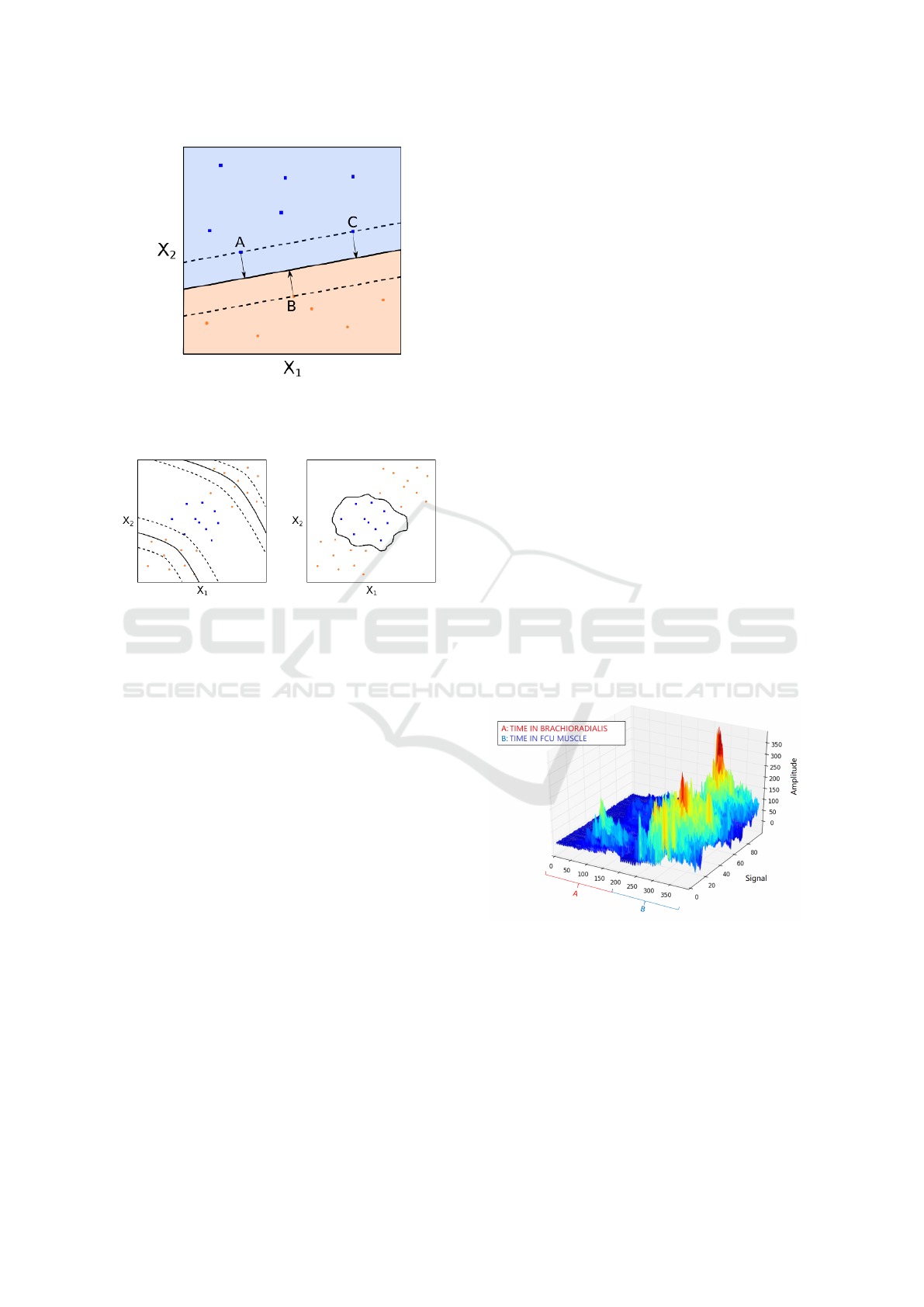
Figure 5: Maximal margin of the hyperplane with SVM for
points A, B and C. X
1
and X
2
represent each dimension of
a linearly separable two-dimensional hyperplane. Source:
(Quantstart., 2014).
Figure 6: SVM classification with polynomial and radial
kernels, respectively. X
1
and X
2
represent each a dimen-
sion of a two-dimensional non-linearly separable hyper-
plane. Source: (Quantstart., 2014).
6. In this work, the radial kernel was deployed be-
cause the set of signals was not linearly separable, and
cross-validation was utilized for tests.
3.4.3 Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks are a computational repre-
sentation of complex biological systems formed by
numerous nervous cells that work in parallel and im-
plement learning functions in the form of iterative
adaptation of their parameters. They aim at charac-
teristics such as auto-organization, learning capacity,
generalization capacity and robustness against failure
(Anderson, 1995).
For this research we used a backpropagation neu-
ral network with a sigmoid activation function shaped
as a hyperbolic tangent that maps values in the range
(−1, 1). The network has two hidden layers, the first
one with 100 neurons and the second one with 30 neu-
rons. This was the distribution that performed best in
a number of trials varying the number of neurons and
hidden layers.
4 TESTS AND RESULTS
Two classifiers were proposed: the support vector ma-
chine (SVM) and backpropagation neural networks.
Four different hand movements were studied (flexion,
extension, hand opening and hand closure) and hun-
dred samples were extracted for each movement. This
data was gathered from ten test participants.
Figures 7, 8, 9 and 10, display the hundred regis-
tered signals for the movements of flexion, extension,
hand opening and hand closure, respectively. In the X
axis an interval of 400 is observed which represents
the first 200 movement takes of the corresponding
movement in the brachioradial muscle and the sec-
ond 200 takes represent the corresponding movement
in the FCU muscle. In the Y axis an interval of 100
is observed, where each number is a registered sig-
nal (from the 100 signals taken for each movement).
Low and high amplitudes of the input in the Z axis
correspond to blue and red colors, respectively.
The figures show that there are clear identifica-
tion patterns for each movement, where the pattern
of the brachioradialis and FCU muscle is different in
amplitude and activation instant for each movement.
This is why a supervised learning method can clas-
sify these patterns in one of the four movements that
this work studies. All tests were conducted using
cross-validation as a technique for statistical analysis
to guarantee that the results are independent from the
partition between training data and test data.
Figure 7: Signals for the flexion movement. The X axis rep-
resents the 200 takes in the brachioradialis and FCU muscle.
The Y axis represents each registered signal, and the Z axis
represents the signal amplitude. Source: prepared by the
authors.
4.1 Results
Three hybrid feature vectors were deployed in the
tests: (1) PCA and Chi-square, (2) Wavelet approx-
imation coefficients and Chi-square, and (3) PCA
Classification of Myoelectric Surface Signals of Hand Movements using Supervised Learning Techniques
247
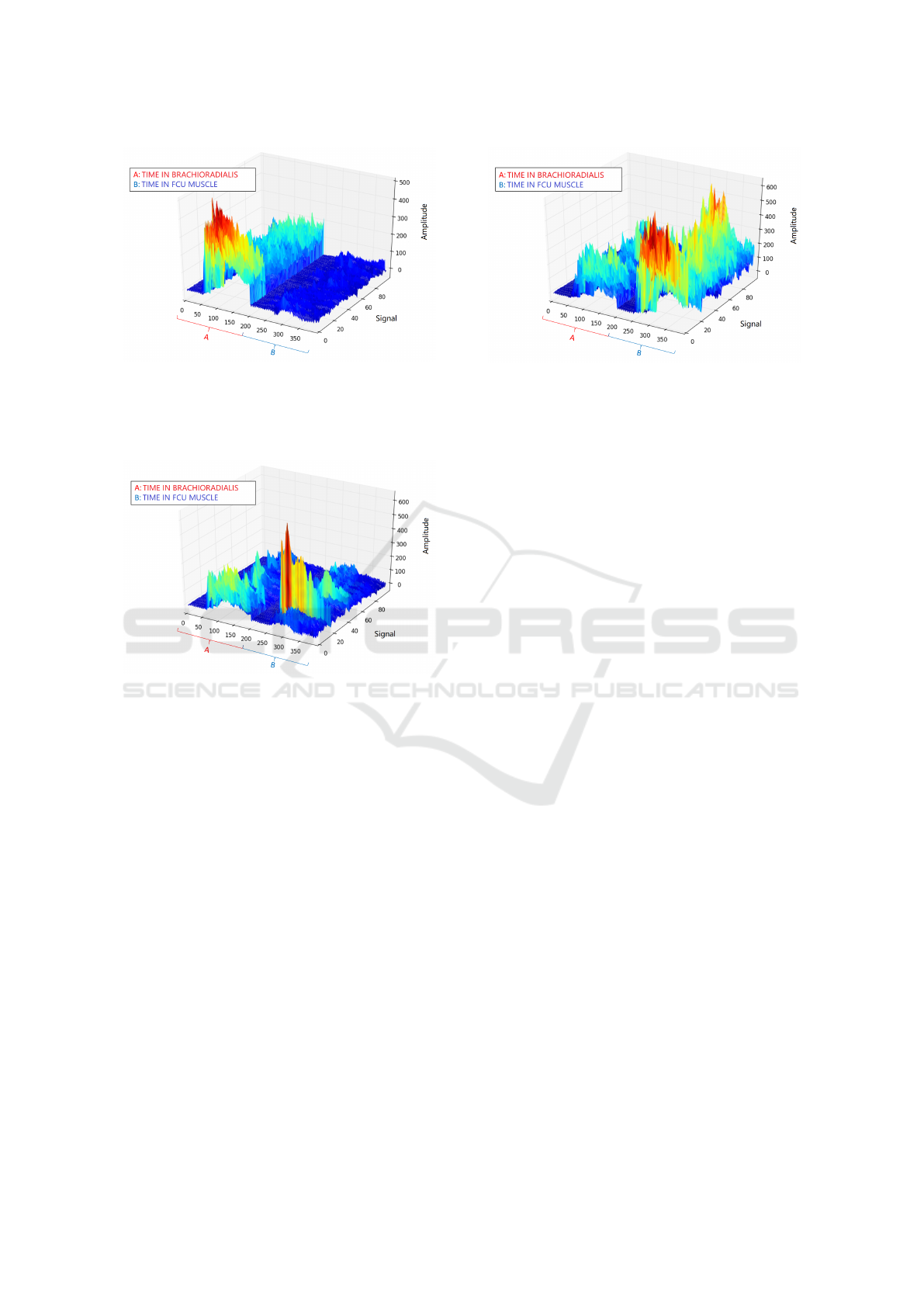
Figure 8: Signals for the extension movement. The X axis
represents the 200 takes in the brachioradialis and FCU
muscle. The Y axis represents each registered signal, and
the Z axis represents the signal amplitude. Source: prepared
by the authors.
Figure 9: Signals for the hand opening movement. The X
axis represents the 200 takes in the brachioradialis and FCU
muscle. The Y axis represents each registered signal, and
the Z axis represents the signal amplitude. Source: prepared
by the authors.
combined with Wavelet approximation coefficients
and Chi-square. Each of these vectors was tested with
the two classifiers, namely SVM and backpropagation
neural networks. Some tests were also conducted with
the normalized original data, using the same classi-
fiers, to test if the feature extraction improved the de-
tection percentaje of the corresponding class.
4.1.1 Results with SVM
In this work we utilized the radial basis function ker-
nel. Tests were conducted with the four movements.
The results were estimated on the sample of 100 sig-
nals for each movement, deploying cross-validation
with 10 different groups of 90 signals of training and
10 test signals.
Different characteristic vectors were explored thus
obtaining a classification accuracy of 88.75 % for the
original data without feature extraction, 91.00 % for
PCA and Chi-square, 91.00 % for Wavelet and Chi-
Figure 10: Signals for the hand closure movement. The
X axis represents the 200 takes in the brachioradialis and
flexor cubital muscles. The Y axis represents each regis-
tered signal, and the Z axis represents the signal amplitude.
Source: prepared by the authors.
square, 89.00 % for PCA, Wavelets and Chi-square.
The details of the classification for each movement
can be observed in Table 1.
From Table 1 we can see that the movement that
was hardest to detect with SVM was flexion, while
the movement that is detected with highest accuracy
is extension. The best results were achieved with hy-
brid features vectors: Chi-square and PCA; and Chi-
square and wavelets, where an average detection ac-
curacy of 91.00 % in the classification of the four
movements was achieved. These vectors improved in
2.25 % respect to classification without feature extrac-
tion. The vector composed of Chi-square, PCA and
Wavelets did not improve the classification accuracy
significantly.
4.1.2 Results with Neural Networks
The results are estimated from the sampling of 100
signals for each movement, using cross-validation
with 10 different test groups of 90 training signals and
10 test signals.
Different feature vectors were tested yielding a
detection accuracy of 86.25 % for the original data,
82.00 % for PCA and Chi-square, 82.00 % for
Wavelet and Chi-square, and 89.00 % for PCA,
Wavelet and Chi-square. The details of the classifi-
cation for each movement can be observed in Table 2.
From the Table 2 we can see that the movement
that was most difficult to detect using backpropaga-
tion neural networks is hand opening, while the move-
ment that is detected with the highest accuracy is ex-
tension. This movement is the same as the highest
detection accuracy movement using SVM. The best
results were obtained with the hybrid feature vector:
PCA, χ
2
and Wavelets, where an average detection
accuracy of 89 % was achieved in the classification of
BIOSIGNALS 2021 - 14th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
248
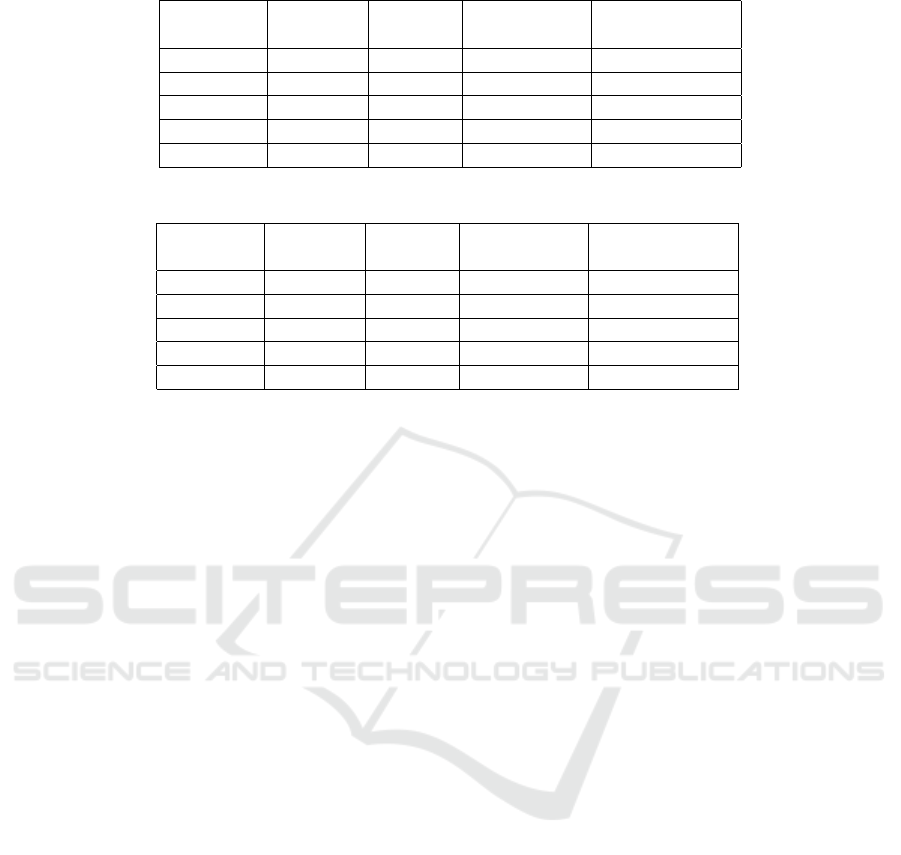
Table 1: Classification accuracy with SVM.
Raw data χ
2
, PCA χ
2
, Wavelets
PCA, Wavelets
χ
2
Flexion 86.00% 85.67% 85.67% 85.33%
Extension 94.67% 96.00% 96.00% 93.00%
Opening 86.00% 91.00% 91.00% 89.00%
Closure 88.33% 90.33% 90.33% 87.00%
Total 88.75% 91.00% 91.00% 89.00%
Table 2: Classification accuracy with backpropagation neural networks.
Raw data χ
2
, PCA χ
2
, Wavelets
PCA, Wavelets
χ
2
Flexion 83.00% 81.33% 81.33% 88.67%
Extension 92.67% 92.00% 92.00% 92.00%
Opening 81.33% 72.67% 72.67% 82.33%
Closure 88.00% 82.00% 82.00% 92.00%
Total 86.25% 82.00% 82.00% 89.00%
the four movements. This vector improved in 2.75 %
the result of the classification. It is also observed that
the vectors formed by χ
2
and PCA; as well as χ
2
and
Wavelets, did not improve the accuracy of the classi-
fication without feature extraction.
In general, the highest average classification ac-
curacy obtained in this work (over 90 %) is at the
level of the state of the art in the literature utilizing
sofisticated but more complex methods such as ma-
chine learning (Mora Rubio et al., 2020), ternary pat-
tern and discrete wavelet based iterative feature ex-
traction (Tuncer et al., 2020) and convolutional neural
networks with intrinsic feature extraction capabilities
(Zia ur Rehman et al., 2018).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work has provided a comparison of different
methods for the classification of four different hand
movements (extension, flexion, hand opening, hand
closure) across two different lines. First, a compar-
ison of methods for feature extraction (χ
2
and PCA,
χ
2
and Wavelets) and second, a comparison of meth-
ods for classification (namely neural networks and
support vector machines). We have shown that the
SVM supervised classifier has a better performance
than backpropagation neural networks for the classifi-
cation of these four movements, and that these can be
recognized taking the first 400 ms of the brachioradi-
alis and flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (FCU) as an input.
With SVM, an accuracy of 91.00 % was achieved us-
ing a hybrid characteristic vector with components of
approximation coefficients of Wavelet transform and
Chi-square. Likewise, an accuracy of 91.00 % was
also achieved deploying a hybrid characteristic vec-
tor constituted by the hundred principal components
(PCA) and Chi-square.
It was also observed that for the SVM classifier,
flexion was the most difficult movement to detect,
while opening the hand was the most difficult move-
ment for neural networks. On the other hand, in all
confusion matrices, the movement causing the most
classification errors was closing the hand in the case
of SVM, while for backpropagation neural networks
both opening the hand and flexing were problematic.
A greater number of distinct movements could be de-
tected if more channels were used. Nevertheless, the
high accuracy obtained with SVM, i.e., over 90 % is
comparable to other methods in the state of the art that
are computationally more expensive.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the Univer-
sidad Nacional de San Agust
´
ın de Arequipa (UNSA)
for financing this research project with contract num-
ber N
◦
0091-2016-UNSA; to Imagine Labs team for
their valuable collaboration; to CiTeSoft UNSA, Al-
fredo Paz, Erasmo Sulla and Dante Condori for their
time and support; to Jorge Segura for his most gener-
ous technical contribution, and to all those who par-
took in this study, either as participants or motiva-
tional agents.
Classification of Myoelectric Surface Signals of Hand Movements using Supervised Learning Techniques
249

REFERENCES
Aaron, C. G. I. (2010). Dise
˜
no y construcci
´
on de un sistema
para la detecci
´
on de se
˜
nales electromiogr
´
aficas. PhD
thesis, Universidad Aut
´
onoma de Yucat
´
an, Mexico.
Anderson, J. A. (1995). An introduction to neural networks.
MIT press.
Birkedal, L., Collet, T., Dagilis, S., Delavernhe, G., and
Emborg (2002). Pattern recognition of upper-body
electromyography for control of lower limb prosthe-
ses. Institute of Electronic Systems, Aalborg Univer-
sity.
Cabrera, J. S. and Jaramillo, H. F. (2010). Mejora de pro-
cesos para el desarrollo de dispositivos prost
´
eticos de
mano. Ingenium, (21).
Carre
˜
no, I. and Vuskovic, M. (2005). Wavelet-based fea-
ture extraction from prehensile emg signals. 13th
NordicBaltic on Biomedical Engineering and Medical
Physics (NBC’05 UMEA), pages 13–17.
Daniel, L. (2015). Un ejemplo sencillo sobre an
´
alisis de
componentes principales (pca, principal component
analysis). https://dlegorreta.wordpress.com.
Durgesh, K. S. and Lekha, B. (2010). Data classification
using support vector machine. Journal of Theoretical
and Applied Information Technology, 12(1):1–7.
Ferguson, S. and Dunlop, G. R. (2002). Grasp recog-
nition from myoelectric signals. In Proceedings of
the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automa-
tion, Auckland, New Zealand, volume 1.
Gerdle, B., Karlsson, S., Day, S., and Djupsj
¨
obacka, M.
(1999). Acquisition, processing and analysis of the
surface electromyogram. In Modern techniques in
neuroscience research, pages 705–755. Springer.
Gomero, F. N. C., Campos, F. D. R., and Ch
´
avez,
S. J. Z. (2009). M
´
odulo de detecci
´
on, reg-
istro y presentaci
´
on de se
˜
nales electrooculogr
´
aficas.
Electr
´
onica-UNMSM, (24):3–12.
Gupta, T., Yadav, J., Chaudhary, S., and Agarwal, U.
(2017). Emg pattern classification using neural net-
works. In The International Symposium on Intelligent
Systems Technologies and Applications, pages 232–
242. Springer.
Haihua, L., Xinhao, C., and Yaguang, C. (2005). Wavelet
transform analyzing and real-time learning method for
myoelectric signal in motion discrimination. In Neu-
ral Interface and Control, 2005. Proceedings. 2005
First International Conference on, pages 127–130.
IEEE.
Hargrove, L. J., Englehart, K., and Hudgins, B. (2007). A
comparison of surface and intramuscular myoelectric
signal classification. IEEE transactions on biomedical
engineering, 54(5):847–853.
Hermens, H. and Freriks, B. (1997). The state of the art on
sensors and sensor placement procedures for surface
electromyography: a proposal for sensor placement
procedures. Deliverable of the SENIAM Project.
Hudgins, B., Parker, P., and Scott, R. N. (1993). A new
strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 40(1):82–
94.
Irastorza-Landa, N., Sarasola-Sanz, A., Shiman, F., L
´
opez-
Larraz, E., Klein, J., Valencia, D., Belloso, A.,
Morin, F., Birbaumer, N., and Ramos-Murguialday,
A. (2017). Emg discrete classification towards a my-
oelectric control of a robotic exoskeleton in motor re-
habilitation. In Converging Clinical and Engineering
Research on Neurorehabilitation II, pages 159–163.
Springer.
Kazamel, M. and Warren, P. P. (2017). History of elec-
tromyography and nerve conduction studies: A trib-
ute to the founding fathers. Journal of Clinical Neu-
roscience, 43:54–60.
Kehri, V., Ingle, R., Awale, R., and Oimbe, S. (2016). Tech-
niques of emg signal analysis and classification of
neuromuscular diseases. In International Conference
on Communication and Signal Processing 2016 (IC-
CASP 2016). Atlantis Press.
Kilby, J. and Hosseini, H. G. (2004). Wavelet analysis of
surface electromyography signals. In Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society, 2004. IEMBS’04. 26th
Annual International Conference of the IEEE, vol-
ume 1, pages 384–387. IEEE.
Kurkin, S. A., Khorev, V., Pitsik, E. N., Maksimenko, V. A.,
and Hramov, A. E. (2019). The approach to the detec-
tion of the movement precursor by electromyographic
signals. In ICINCO (1), pages 276–280.
Liu, Y. (2017). Statistical inference in principal component
analysis based on statistical theory. Italian Journal of
Pure and Applied Mathematics, (37):565–574.
Mallat, S. (1991). Zero-crossings of a wavelet trans-
form. IEEE Transactions on Information theory,
37(4):1019–1033.
Merletti, R. and Parker, P. A. (2004). Electromyography:
physiology, engineering, and non-invasive applica-
tions, volume 11. John Wiley & Sons.
Mora Rubio, A., Alzate Grisales, J. A., Tabares-Soto,
R., Orozco-Arias, S., Jim
´
enez Var
´
on, C. F., and
Padilla Buritic’a, J. I. (2020). Identification
of hand movements from electromyographic sig-
nals using machine learning. Preprints. DOI:
10.20944/preprints202002.0443.v1.
MyoWare. (2015). Myoware
TM
muscle sensor (at-04-001)
Datasheet. https://cdn.sparkfun.com/datasheets/
Sensors/Biometric/MyowareUserManualAT-04-001.
pdf.
Quantstart. (2014). Support vector machines: A guide
for beginners. https://www.quantstart.com/articles/
Support-Vector-Machines-A-Guide-for-Beginners/.
Quinay
´
as-Burgos, C. A. and Gaviria-L
´
opez, C. A. (2015).
Sistema de identificaci
´
on de intenci
´
on de movimiento
para el control mioel
´
ectrico de una pr
´
otesis de mano
rob
´
otica. Ingenier
´
ıa y Universidad, 19(1).
Satapathy, S. C., Raju, K. S., Shyamala, K., Krishna, D. R.,
and Favorskaya, M. N. (2019). Advances in Decision
Sciences, Image Processing, Security and Computer
Vision: International Conference on Emerging Trends
in Engineering (ICETE), Vol. 1, volume 3. Springer.
Torrence, C. and Compo, G. P. (1998). A practical guide to
wavelet analysis. Bulletin of the American Meteoro-
logical society, 79(1):61–78.
BIOSIGNALS 2021 - 14th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
250

Tuncer, T., Dogan, S., and Subasi, A. (2020). Surface EMG
signal classification using ternary pattern and discrete
wavelet transform based feature extraction for hand
movement recognition. Biomedical Signal Processing
and Control, 58:101872.
Vapnik, V. (2013). The nature of statistical learning theory.
Springer science & business media.
Wołczowski, A. and Zdunek, R. (2017). Electromyography
and mechanomyography signal recognition: Experi-
mental analysis using multi-way array decomposition
methods. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineer-
ing, 37(1):103–113.
Y
¨
ucel, K. and Mehmet, K. (2001). Emg signal classifica-
tion using wavelet transform and fuzzy clustering al-
gorithms. Istanbul, Turkey: Ayazaga.
Zia ur Rehman, M., Waris, A., Gilani, S. O., Jochum-
sen, M., Niazi, I. K., Jamil, M., Farina, D., and Ka-
mavuako, E. N. (2018). Multiday emg-based classifi-
cation of hand motions with deep learning techniques.
Sensors, 18(8):2497.
Classification of Myoelectric Surface Signals of Hand Movements using Supervised Learning Techniques
251
