
Video Action Classification through Graph Convolutional Networks
Felipe F. Costa
a
, Priscila T. M. Saito
b
and Pedro H. Bugatti
c
Department of Computing, Federal Unversity of Technology - Parana,
1640 Alberto Carazzai Ave., Cornelio Procopio, Brazil
Keywords:
Deep Learning, Graph Convolutional Network, Computer Vision, Action Classification.
Abstract:
Video classification methods have been evolving through proposals based on end-to-end deep learning archi-
tectures. Several works have testified that end-to-end models are effective for the learning of intrinsic video
features, especially when compared to the handcrafted ones. In general, convolutional neural networks are
used for deep learning in videos. Usually, when applied to such contexts, these vanilla deep learning networks
cannot identify variations based on temporal information. To do so, memory-based cells (e.g. long-short term
memory), or even optical flow techniques are used in conjunction with the convolutional process. However,
despite their effectiveness, those methods neglect global analysis, processing only a small quantity of frames
in each batch during the learning and inference process. Moreover, they also completely ignore the semantic
relationship between different videos that belong to the same context. Thus, the present work aims to fill these
gaps by using information grouping concepts and contextual detection through graph-based convolutional neu-
ral networks. The experiments show that our method achieves up to 87% of accuracy in a well-known public
video dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, there is a high availability of complex data
like images and videos. To cope with this huge vol-
ume of complex data, new methods needs to be de-
veloped to automatically retrieve and/or classify these
data. Moreover, due to the evolution of hardware re-
sources (e.g., GPUs), it was possible to use proposed
algorithms that were previously costly like convolu-
tional neural networks (CNNs) for CPU architectures
(Krizhevsky et al., 2012).
The greatest advances in deep learning for pat-
tern recognition in images was the use of convolutive
cores of the CNNs. It occurs because they are capable
of learning deep features robust to noise, distortions
and translations in images. The CNN, in terms of ro-
bustness and precision, was a new level reached in the
state-of-the-art and have been widely used in machine
learning for computer vision (LeCun et al., 1998).
A CNN applies convolution layers to extract fea-
tures from the image (or video frame), generating
maps that can consider color channels and also reduce
the spatial dimensions of the image, and finally reach
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7289-6032
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4870-4766
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9421-9254
a dense (fully connected) layer to perform the classi-
fication (end-to-end). This way of learning to extract
feature through convolutional kernels is clearly differ-
ent from obtain (handcrafted) features using a specific
image descriptor.
In recent years, as occurred in images, video clas-
sification techniques have been proposed using deep
learning (e.g., CNNs). However, the greatest diffi-
culty in working with videos is the time variable that
should be considered. This factor leads to several
problems such as changes in camera position, light-
ing, information variance due to the evolution of im-
age frames, among other complexities that the inclu-
sion of time adds to the relations of these sequential
static images.
Currently, the semantic characteristics of the
change in the temporal variable of videos are treated
by different ways in deep learning. There are so-
lutions that depend on CNNs to extract spatial fea-
tures from images, which are used as input to mod-
els that have temporal learning characteristics. Other
techniques apply long-short term memory structures
(Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997), or even use in-
dependent CNNs for static images in conjunction with
optical flow (Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014). How-
ever, all current methods do not capture and gather in
a well-suited fashion the context and interconnection
490
Costa, F., Saito, P. and Bugatti, P.
Video Action Classification through Graph Convolutional Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0010321304900497
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2021) - Volume 4: VISAPP, pages
490-497
ISBN: 978-989-758-488-6
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

of videos (or frames) that relate to each other to as-
sist the learning process. Thus, to mitigate this prob-
lem, we proposed a method based on graph neural
networks (GNNs and variants) capable of connecting,
through different policies, the frames and/or videos
from a given context. These connections are seam-
lessly integrated into the learning process enhancing
the model in a great extent. Therefore, the present
work aims to propose approaches to perform such ag-
gregation of information and achieve improvements
regarding video classification problems.
2 BACKGROUND
CNNs have been extremely successful in machine
learning problems in which the data representation
have a tensor structure (multidimensional) and need
robustness w.r.t. geometric transformations (invari-
ance and/or equivariance regarding translation, rota-
tion, among others).
There are two implications for equivariance, the
first is the equivariance measurement (symmetry for
functions from one space with symmetry to another)
and the second is the invariance. For instance, a
given image I can be translated to I
0
(for the new
coordinates of (x
0
m
, y
0
m
)) with the original coordinates
(x
m
, y
m
) through (x
m
− u, y
m
− v). Therefore, m
0
= m
is equivalent to the final measurements of convolu-
tions (through geometric coefficients from the convo-
lutional kernels). In other words, it means that the
location of a given object in the image should not be
static to be detected.
Although the CNNs present translational equivari-
ance and invariance they are not capable to establish
contextual connections between different objects or
images (e.g., frames from a video). As a matter of
fact, a core assumption of CNNs is that instances are
independent of each other. However, these connec-
tions are the cornerstones to reach a suitable context
recognition. Then, to aggregate such information to
the state-of-the-art CNNs we can use the Graph Neu-
ral Networks (GNNs).
GNNs (and their variants) are categorized in deep
learning as geometric models. The idea of these mod-
els is to work with multidimensional metrics consid-
ering the equivariance proposed by the CNNs. Just
as a convolution kernel consists of working with a
fixed coefficient of a geometric aspect in the image
(i.e., matrix of pixels), the GNN tries to general-
ize these filters by normalizing the distance between
points (e.g., pixels) in the non-euclidean space.
A variant of GNN is the so-called graph convolu-
tional network (GCN). The idea of a GCN architec-
ture is to use the automatic learning potential based
on convolution kernels to tackle problems with arbi-
trarily structured graph approaches. The proposal of
GCN was to bridge the gap between spectral-based
approaches and spatial-based approaches. Some
works proposed to generalize CNN models through
adaptations (Duvenaud et al., 2015; Li et al., 2016)
to allow non-euclidean spaces. Other works, using
the spectral graph theory (Bruna et al., 2014; Henaff
et al., 2015), defined filters based on classic CNN.
However, we considered GCNs because the filters are
shared for the entire graph.
The goal of graph-based neural networks is to
learn a set of input signals from a graph G = (ν, ε)
with an adjacency matrix A and input matrix X
N×D
,
where N is the number of nodes and D is the number
of features (dimensionality). Each layer produces an
output Z
N×F
where F represents the number of fea-
tures per node. Thus, the linear Equation 1 can be
formally defined:
H
(l+1)
= f (H
(l)
, A) (1)
where H
(0)
= X, Z = H
(l)
and l refers to the lth-layer.
It is possible to note that the definition is linear. How-
ever, to solve non-convex problems we need to con-
sider non-linearity. Then, a formalization to this is
given by Equation 2.
f (H
(l)
, A) = σ(AH
(l)
W
(l)
) (2)
where σ is a non-linear function (e.g., rectified linear
unit, sigmoid, among others), and W a weight matrix
per layer l that will be learned.
However, there is a problem in multiplying with
an adjacency matrix A. For each graph’s node the fea-
ture vectors of all its neighbors are aggregated, ex-
cept the node itself. To solve this issue, an identity
matrix I to the adjacency matrix A is considered, re-
sulting in
ˆ
A. Another problem is that multiplying by
matrix A it will change the scale of the feature vec-
tors. To cope with this problem it is used the degree
matrix D where all the lines add up multiplying
ˆ
A
by D
−1
. Then, Equation 3 formalizes the propagation
f (H
(l)
, A) in a normalized way.
f (H
(l)
, A) = σ(
ˆ
D
−
1
2
ˆ
A
ˆ
D
−
1
2
H
(l)
W
(l)
) (3)
Regarding video classification, several deep learn-
ing approaches are not only computationally expen-
sive, but also present problems w.r.t. the temporal
dimension. CNN models are well established to de-
scribe static images and applied in many video clas-
sification problems. However, they present several
problems related to the temporal reasoning. For in-
stance, vanilla CNNs does not consider global fea-
tures of the video. According to the literature, similar
Video Action Classification through Graph Convolutional Networks
491

to images, there are two main approaches to perform
video classification. The first one is to obtain hand-
crafted features and the other to reasoning through a
deep learning model (deep features).
The handcrafted approaches consist of creating
descriptors, based on an a priori knowledge about
the problem, so that the learning model provides cor-
rect classifications. Generally, these works are based
on proposing new description methods (feature ex-
traction) in videos with compact dimensions, for in-
stance using Harris 3D outlines (Laptev, 2005), Hes-
sian measures (Dollar et al., 2005), cuboid model-
ing or even techniques that use optical flow to extract
dense trajectories (Wang et al., 2011). These captured
features are normally passed to a histogram.
Generally, video classification using deep learning
approaches considers end-to-end architectures (i.e.,
comprises the learning of deep features and the clas-
sification task at the same pipeline). There are sev-
eral techniques that can be used in video classification
to create temporal semantics. However, several mod-
els present restrictions w.r.t. the number of frames
analyzed. For instance, 3D conversion networks (Ji
et al., 2013; Karpathy et al., 2014) can only apply
partial clips with frames to learn features from a sin-
gle tensor. In (Karpathy et al., 2014) the authors
demonstrated that their model is only a fraction better
than CNN when trained with individual frames from
a video. It is important to note that convolutions are
employed locally and limited to a few frames, due to
restrictions of huge tensors to be allocated in memory
at once.
Some other approaches made an effort to trans-
mit temporal information to the networks. For in-
stance, in (Simonyan and Zisserman, 2014) the au-
thors passes the optical flow as an input parameter for
inference, limited to 10 frames only. However, this
model suffers from the same restriction problems of
local video information, since important information
from any frame may be lost. Moreover, it was not
so superior to a naive approach where single frames
passed to a 2D CNN.
Instead of trying to learn the spatio-temporal re-
sources limited to short-time periods, some works
aggregates CNNs with long-short term architectures
(LSTMs). It is consistent to use CNN architectures
to extract the features, and then apply them to LSTM
units. This allows to understand the patterns accord-
ing to the temporal variable (Baccouche et al., 2010).
However, LSTMs present high computational cost
and limited accuracies.
Other works (Yue-Hei Ng et al., 2015; Jain et al.,
2013) attempted to not use additional information, as
those provided by LSTM. They proposed variations
regarding the pooling layers at the video level to di-
minish the computational cost. Despite that, their ac-
curacies were similar to the LSTM approaches.
3 PROPOSED APPROACH
The motivation to our work is that, usually, the lit-
erature proposals neglect global analysis, processing
only short-time sequences due to computational costs.
Besides, they also ignore the semantic relationship
between different videos that belong to the same con-
text.
Thus, in this work we propose a new approach ca-
pable to create and explore the relationship between
different videos and/or frames of a given context, im-
proving the state-of-the-art results. To do so, we use
information grouping concepts and contextual detec-
tion through graph-based convolutional neural net-
works, and create a relationship between feature maps
from the videos.
Figure 1 shows the pipeline of our proposed ap-
proach. In step 1 we extracted deep features using a
given CNN architecture. Any CNN from the literature
can be used in this step. Moreover, to reduce the com-
putational cost, transfer learning (e.g., through Ima-
geNet) is also used, and frame sampling methods too.
To simplicity purpose we omitted these conditional
steps from Figure 1. Considering the step 2 each deep
feature vector is mapped into a graph node. In step
3 a relationship/connection policy is used to link the
graph nodes. Then, with the set of nodes and their
connections we generate an adjacency matrix to rep-
resent the global structure of the graph. It is important
to highlight that currently our approach consider only
undirected graphs. Finally, in step 4 we pass the adja-
cency matrix to a graph convolutional neural network
that consider the relationship between different nodes
to learn a model. Clearly, this pipeline describes the
training phase of our approach.
These are the general steps of our approach. How-
ever, different policies can be applied to each step.
Our first policy is to extract features from a sample
of frames to diminish the computational cost. Frame
samplings are performed to consider regular exclu-
sion and frame selection intervals. For instance, if
there are F frames for a video and the intention to
get M frames (where F > M), then the ratio of F
to M is the increment value that will be used to se-
lect the frames (naive policy). After the selection of
frames per video, each one of them is given as input
to a CNN architecture, generating deep features. It
is important to note that in this step, several sampling
and/or clustering techniques from the literature can be
VISAPP 2021 - 16th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
492
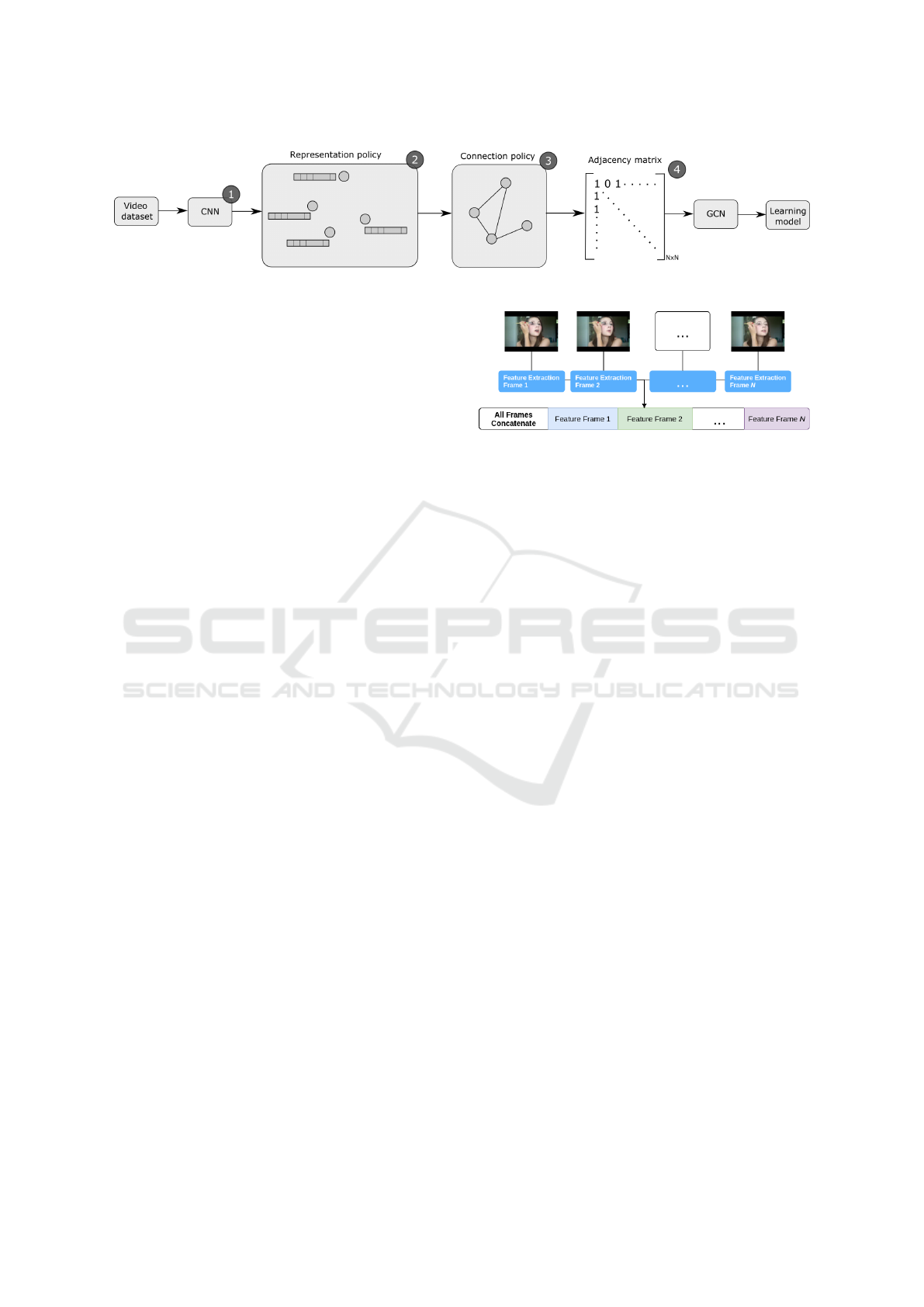
Figure 1: Pipeline of the proposed proposed aprroach.
used. To corroborate the efficacy of our approach we
create baseline (naive policies) instances of it. We fol-
low this plan because several literature papers (Zhang
et al., 2019; Luo et al., 2018; Lu
´
ıs Estevam Junior
et al., 2019), when analyzing the trade-off between
computational cost and accuracy, indicated that the
simpler the method, the better the trade-off.
In the construction stage of the graph, our ap-
proach also allows different policies. We can use
different node representations, edges’ weighting and
connection/pruning strategies. Considering as input
to the construction stage the selected frames (e.g.,
sampling), and their respective features, we proposed
different node representations. The first one is to con-
catenate each feature vector and then assign it to a
node (see Figure 2). In this policy each node has the
global representation of a video, and obviously, it will
impact in the nodes’ connection policies. It is easy to
see that many policies can be derived from our ap-
proach. For instance, instead of consider each node
as the entire video, we can represent each node by
a given frame from a video. It is interesting to note
that we can also join both policies, building an hierar-
chical representation of the videos as an hyper-graph.
Although this hierarchical policy is relevant, the fo-
cus of this work was in the proposal of the general
approach, since several policies can be derived and
exploited from it.
Regarding the nodes’ connections several policies
can also be applied. The most naive that we can
consider are self-connections of the nodes, that is,
connected only to themselves. The second one is to
consider a complete graph (i.e., connections between
all nodes). Another one is to build the connections
through a distance between the nodes (in our case the
dissimilarity between videos or frames depending of
the node representation policy).
Once we can use weighted connections between
the nodes this opens ways to pruning strategies. In
the present paper we consider naive dissimilarity mea-
sures (i.e., Euclidean distance) and pruning strategies
(i.e., threshold-based pruning) to testify the efficacy
of our approach even with baseline policies against
the four literature methods. Clearly, the policies are
not mutually exclusive - e.g., we can aggregate two or
more policies to generate a new one.
Figure 2: Connection of Frames.
4 EXPERIMENTS
The experiments were performed considering four
comparison models, the LRCN (Donahue et al., 2014)
and C3D (Tran et al., 2014), which are based on three-
dimensional convolutions. They are robust models
and describe relevant tests and results in their respec-
tive works. In addition, experiments were carried out
with other two models known from the literature, one
using CNNs aggretated to LSTMs (Hochreiter and
Schmidhuber, 1997) and another one using a multi-
layer perceptron (MLP) (Murtagh, 1991).
The execution conditions were taken based on the
complexity of the CNN architectures. Then, we cho-
sen the ResNet50 architecture (He et al., 2015) pre-
trained on ImageNet (i.e., transfer learning) to extract
the deep features. The same features were used as
input to the models based on LSTM and MLP.
4.1 Video Dataset Description
To perform the experiments we used the UCF101
dataset (Soomro et al., 2012). It is public, widely-
known and used in several literature works to achieve
video action recognition. Another reason to chose
UCF101 is that it undergoes a small change in volume
of samples per class (balancing) and presents a real
scenario with 13320 video clips. Basically, it consists
of web videos that are recorded in unrestricted envi-
ronments and, generally, considering: camera move-
ment, various lighting conditions, partial occlusion
and low quality frames. The name UCF101 makes
reference to the number of classes that comprises in
a collection divided into 5 general action categories
(human-object, human-human interaction, only body
Video Action Classification through Graph Convolutional Networks
493

Table 1: Experiment Settings.
Model Batch Size Frames Learning Rate Early Stopping
C3D 2 16 0.05 50
LCRN 76 10 0.05 50
MLP 128 3 0.05 50
LSTM 128 3 0.05 50
GCN (Ours) 39960 3 0.05 50
in motion, playing musical instruments and sports)
(Soomro et al., 2012).
The UCF101 dataset presents 180 frames on av-
erage, according to the duration and the frame rate
(25fps) of its videos. To perform the experiments, the
video memory of the GPU was limited to loading only
39,960 images as a total subset, both for testing and
training. It means that 3 frames were used to represent
a video (F = 3). This is a considerable restriction,
since each video from the dataset has 180 frames on
average. To obtain suitable results the approach needs
to capture effectively the contextual domain.
4.2 Scenarios
To accomplish fair comparisons we tune the same hy-
perparameters for all methods. Table 1 shows the hy-
perparameters considered for each method. Indeed,
just the batch size and the number of frames were
modified. This was needed because of the specifica-
tions of some literature methods to be executed. For
instance, C3D and LRCN requires 16 and 10 frames,
respectively. Considering the LSTM-based method
and MLP we used 3 frames. It is important to note
that C3D and LRCN are not so flexible as the others.
Both literature methods represent the entire videos as
one sample. Hence, for experiments we also consid-
ered that each graphs’ node is represented by the con-
catenation of the deep features from its videos’ frames
(node representation policy, see Section 3)
The batch size was defined considering the mem-
ory restrictions. It is clearly to note that, as we are
using a vanilla GCN in our experiments, the entire
graph need to be into memory, then our batch size was
defined as the number of graphs’ nodes (e.g., 39960
because we employ the node representation that con-
sider each node as video from the dataset).
The test and training proportions were made in or-
der to separate 60% of the dataset for training and
40% for testing. The same samples were used for all
methods.
4.2.1 Threshold-based Policy
Considering the threshold-based pruning policy (see
Section 3) we focused on manipulating the connec-
tion threshold of the adjacency matrix. First, we cal-
culated the Euclidean distance among nodes (repre-
sented by the feature vectors of the videos). Then, a
given connection is created when two videos have a
greater similarity than the average distance consider-
ing a complete graph (see Equation 4).
d =
v
u
u
t
N
∑
j=1
(v
i
− v
j
)
2
(4)
where the adjacency matrix entry A(v
i
, v
j
) = 1 if d <
threshold, otherwise A(i, j) = 0.
We also considered dummy connections to sup-
port the proposed approach hypothesis. To do so, we
considered a complete graph construction policy and
a self-connection policy. Clearly, other dummy poli-
cies could be analyzed, such as a random construction
policy. However, this exhaustive analysis was not the
focus of the present paper.
4.3 Results and Discussion
According to the obtained results we can note that
our proposed approach not only provides a flexible
way to apply different strategies and policies, but
also reached competitive accuracies when compared
with literature methods. Table 2 shows the accuracies
achieved by the literature methods against our pro-
posed approach considering different instantiations
of it. We considered 3 different instances of our
proposed w.r.t. the connection policies, that were:
complete graph, self-loop connections and threshold-
based (more details about these policies see Sections
3 and 4.2.1).
From Table 2 we can see that our approach with
the complete graph policy obtained better accuracy
than C3D and LRCN, reaching an accuracy gain of up
to 1.9 and 3.1 times higher, respectively. Analyzing
our approach with the threshold-based we achieved
87% of accuracy. Therefore, it was better than us-
ing the complete graph policy (65% of accuracy) and
MLP, presenting an accuracy gain of up to 34% and
19%, respectively. Finally, our approach considering
the self-loop connections policy obtained an accuracy
of 92%, that was the best one regarding all the other
methods. It is also possible to note that LSTM almost
ties with our approach.
Surprisingly, the dummy connection considering
self-loops presents the best accuracy. Analyzing this
result we can argue that the complete graph and
threshold-based policies still introduce some kind of
contextual noise to the learning process. This is also
the reason that a simple MLP also obtained a good
accuracy, because it just consider the input video w/o
connections. We believe that, as mentioned in (Wu
et al., 2019) by the authors, adding self-loops to the
VISAPP 2021 - 16th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
494

Table 2: Models’ Accuracies.
Model Accuracy
C3D 33%
LRCN 21%
MLP 73%
LSTM 89%
Our approach - Complete Graph 65%
Our approach - Self-loop 92%
Our approach - Threshold-based 87%
graph shrinks the spectrum (eigenvalues) of the nor-
malized graph. In other words, the largest eigenvalue
of the graph becomes smaller. Hence, it is possible
to build more robust filters that does not degrade the
performance. However, we believe that deeper analy-
sis must be performed in the future to corroborate this
hypothesis considered in the present paper.
It is important to mention some results regarding
the early stopping variable and the number of epochs.
C3D, LRCN, LSTM and MLP, from a total of 1000
epochs, presented a saturation at the 691st, 431st,
250th and 300th epochs. Regarding GCN, since the
entire graph is allocated at memory, there is only one
batch per epoch. Then, we considered more epochs
because the weights are updated just when the en-
tire dataset is evaluated. It was defined a limit of
4000 epochs. Considering the threshold-based pol-
icy approach the experiments were interrupted at the
3213rd epoch. On the other hand, when we applied
the complete graph and self-loop connections poli-
cies, an early stopping occurred 2500 times.
In order to provide a deeper analysis regarding
the accuracy results, we also generated the confu-
sion matrix of each method under analysis. To bet-
ter visualize the results, since UCF101 presents 101
classes, we applied a mapping function into the con-
fusion matrices considering a heatmap, i.e., the hotter
the color, the higher the accuracy (white is the hottest
color and black is the coldest). Figures 3 to 9 illus-
trate these heatmaps obtained from the confusion ma-
trices according to C3D, LRCN, MLP, LSTM, our ap-
proach w/ complete graph, self-loop connections and
threshold-based policy, respectively.
Analyzing the heatmaps is clear to note that
C3D and LRCN presented several errors in different
classes, these methods obtained the worst results in
classes with actions like “Playing”. It is also inter-
esting to see that all methods failed in classify im-
ages from the “Jump Rope” class. Maybe, it occurs
because of the subtlety of the “rope” object into the
images.
Figure 3: Heatmap obtained by C3D.
Figure 4: Heatmap obtained by LRCN.
Figure 5: Heatmap obtained by MLP.
Video Action Classification through Graph Convolutional Networks
495

Figure 6: Heatmap obtained by LSTM.
Figure 7: Heatmap obtained by Our Approach w/ Complete
Graph.
Figure 8: Heatmap obtained by Our Approach w/
Threshold-based.
Figure 9: Heatmap GCN obtained Our Approach w/ Self-
loop
5 CONCLUSIONS
Video action recognition is a complex task. It also
presents high computational cost, because it requires
to deal with huge volume of data. Thus, it is im-
portant to reach the best trade-off between efficiency
and effectiveness. Therefore, this paper proposes a
new approach to create and explore the relationship
between different videos of a given context, improv-
ing the state-of-the-art regarding video action recog-
nition.
The proposed approach showed good results in the
classification of actions in videos using GCNs. To do
so, graph connections were generated in a simple way
and with low computational cost, considering that the
model is fully loaded into memory. When compared
to models based on three-dimensional convolutional
filters, such as C3D and its variations, the proposed
approach provided better flexibility w.r.t. representa-
tion mechanisms of the samples and higher accura-
cies.
The best results were reached using our approach
with one of the simplest policies (i.e., self-loop con-
nections), in which the computational cost to generate
the graph is extremely low. It is also important to con-
sider that models with more parameters tends to lead
to a higher time complexity. Moreover, they present
results that are often inferior and with a relatively bad
trade-off compared with our proposed approach (even
when comparing the amount of batches in memory
and the number of frames needed).
Despite the aforementioned factors, our approach
still presents some drawbacks. One of them concerns
the time to generate the graphs, since it is an expen-
sive task. However, this is an offline process, which is
VISAPP 2021 - 16th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
496

generated only once. Of course, if there is an incre-
ment in the video dataset, the graph must be generated
again, but this factor affects any other classification
method from the literature.
Thus, in general, the proposed approach proved
to be promising when compared with competing lit-
erature methods. In addition, it opens up many pos-
sibilities for future modifications, improvements and
analyzes. It is relevant to consider that it is possible
to try methods working in batch with models based
on geometric deep learning, providing other ways to
gain even more flexibility.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Coordination for the Im-
provement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES),
National Council of Scientific and Technological De-
velopment (CNPq), Fundac¸
˜
ao Arauc
´
aria, SETI and
UTFPR.
REFERENCES
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C., and
Baskurt, A. (2010). Action classification in soccer
videos with long short-term memory recurrent neural
networks. In ICANN, pages 154–159. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Bruna, J., Zaremba, W., Szlam, A., and Lecun, Y. (2014).
Spectral networks and locally connected networks on
graphs. In ICLR, pages 1–14.
Dollar, P., Rabaud, V., Cottrell, G., and Belongie, S. (2005).
Behavior recognition via sparse spatio-temporal fea-
tures. In PICCN, pages 65–72. IEEE Computer Soci-
ety.
Donahue, J., Hendricks, L. A., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan,
S., Guadarrama, S., Saenko, K., and Darrell, T.
(2014). Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Networks
for Visual Recognition and Description. arXiv e-
prints, page arXiv:1411.4389.
Duvenaud, D. K., Maclaurin, D., Iparraguirre, J., Bom-
barell, R., Hirzel, T., Aspuru-Guzik, A., and Adams,
R. P. (2015). Convolutional networks on graphs for
learning molecular fingerprints. In NIPS, pages 2224–
2232. Curran Associates, Inc.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2015). Deep Resid-
ual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv e-prints,
page arXiv:1512.03385.
Henaff, M., Bruna, J., and LeCun, Y. (2015). Deep con-
volutional networks on graph-structured data. CoRR,
abs/1506.05163.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computing, 9(8):1735–1780.
Jain, M., J
´
egou, H., and Bouthemy, P. (2013). Better
exploiting motion for better action recognition. In
CVPR, pages 2555–2562.
Ji, S., Xu, W., Yang, M., and Yu, K. (2013). 3d convolu-
tional neural networks for human action recognition.
IEEE TPAMI, 35(1):221–231.
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Suk-
thankar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Large-scale video
classification with convolutional neural networks. In
CVPR, pages 1725–1732.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In NIPS, pages 1097–1105. Curran Asso-
ciates, Inc.
Laptev, I. (2005). On space-time interest points. Interna-
tional Journal of Computer Vision, 64(2):107–123.
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., and Haffner, P. (1998).
Gradient-based learning applied to document recogni-
tion. In Proceedings of the IEEE, pages 2278–2324.
Li, Y., Tarlow, D., Brockschmidt, M., and Zemel, R. S.
(2016). Gated graph sequence neural networks.
CoRR, abs/1511.05493.
Lu
´
ıs Estevam Junior, V., Pedrini, H., and Menotti, D.
(2019). Zero-Shot Action Recognition in Videos: A
Survey. arXiv e-prints, page arXiv:1909.06423.
Luo, Z., Jiang, L., Hsieh, J.-T., Niebles, J. C., and Li,
F. F. (2018). Graph distillation for action detection
with privileged information. In Proceedings of ECCV,
pages 1–18.
Murtagh, F. (1991). Multilayer perceptrons for classifica-
tion and regression. Neurocomputing, 2(5):183 – 197.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Two-stream con-
volutional networks for action recognition in videos.
In NIPS, pages 568–576. Curran Associates, Inc.
Soomro, K., Zamir, A. R., and Shah, M. (2012). Ucf101:
A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in
the wild. CoRR, abs/1212.0402.
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., and Paluri,
M. (2014). Learning Spatiotemporal Features with
3D Convolutional Networks. arXiv e-prints, page
arXiv:1412.0767.
Wang, H., Kl
¨
aser, A., Schmid, C., and Liu, C. (2011). Ac-
tion recognition by dense trajectories. In CVPR, pages
3169–3176.
Wu, F., Souza, A., Zhang, T., Fifty, C., Yu, T., and Wein-
berger, K. (2019). Simplifying graph convolutional
networks. In ICML, pages 6861–6871. PMLR.
Yue-Hei Ng, J., Hausknecht, M., Vijayanarasimhan, S.,
Vinyals, O., Monga, R., and Toderici, G. (2015). Be-
yond Short Snippets: Deep Networks for Video Clas-
sification. arXiv e-prints, page arXiv:1503.08909.
Zhang, H.-B., Zhang, Y.-X., Zhong, B., Lei, Q., Yang, L.,
Du, J.-X., and Chen, D.-S. (2019). A comprehen-
sive survey of vision-based human action recognition
methods. Sensors, 19:1005.
Video Action Classification through Graph Convolutional Networks
497
