
High-resolution Controllable Prostatic Histology Synthesis using
StyleGAN
Gagandeep B. Daroach
1
, Josiah A. Yoder
1
, Kenneth A. Iczkowski
2
and Peter S. LaViolette
2
1
Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Milwaukee School of Engineering, Milwaukee, WI 53202, U.S.A.
2
Radiology and Biomedical Engineering, Medical College of Wisconsin, Wauwatosa, WI 53226, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Medical Imaging, Histology, Prostate, Prostate Cancer, Deep Learning, Machine Learning, Latent Space,
GAN, StyleGAN, StyleGAN2, Generative Adversarial Networks, Gleason.
Abstract:
For use of deep learning algorithms in clinical practice, detailed justification for diagnosis is necessary. Con-
volutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been demonstrated to classify prostatic histology using the same
diagnostic signals as pathologists. Using the StyleGAN series of networks, we demonstrate that recent ad-
vances in high-resolution image synthesis with Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can be applied to
prostatic histology. The trained network can produce novel histology samples indistinguishable from real
histology at 1024x1024 resolution and can learn disentangled representations of histologic semantics that sep-
arates at a variety of scales. Through blending of the latent representations, users have the ability to control the
projection of histologic semantics onto a reconstructed image. When applied to the medical domain without
modification, StyleGAN2 is able to achieve a Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) of 3.69 and perceptual path
length (PPL) of 33.25.
1 INTRODUCTION
Prostatic cancer is one of the most common ma-
lignancies in men across the globe, ranking second
after lung cancer (Rawla, 2019). Prostatic cancer
is diagnosed with a biopsy and often treated with
radical prostatectomy. Recent advances in the
machine learning medical imaging domain introduce
convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that can
assist pathologists with diagnosing Gleason patterns
indicative of patient prognosis from histology (Young
et al., 2019; Li et al., 2019; Araújo et al., 2017) and
generative adversarial networks (GANs) that are able
to reconstruct novel medical images from a latent
code or label (Kazeminia et al., 2018; Karras et al.,
2020). Efforts to improve automated Gleason grading
are ongoing (MICCAI, 2020). To best combine a
pathologist’s diagnostic skill with a neural network,
both the network and pathologist need to be able to
share explanations in support of their decisions with
one another. As a result, there has been much work
on interpreting how a deep neural network comes to
the decision that it does (Du et al., 2019; Li et al.,
2019).
Karras et al. demonstrate new techniques for
increased interpretability of image reconstruction
with the StyleGAN series of networks (ProgGAN,
StyleGAN, and StyleGAN2) (Karras et al., 2018;
Karras et al., 2019; Karras et al., 2020). In a
review of interpretable models, Du et al. point
out that many machine learning models sacrifice
accuracy for interpretability (Du et al., 2019). In
contrast, StyleGAN networks gain interpretability
while improving the state of the art. The modern
network architecture stabilizes reconstruction of
high resolution (1024x1024) images (Karras et al.,
2018) and layer normalization disentangles latent
representations for enhanced user control of image
semantics (Karras et al., 2019; Karras et al., 2020)
in diverse non-medical domains. For example when
reconstructing human face imagery, StyleGANs can
control facial features including smile, hair color, and
age (Karras et al., 2020; Karras et al., 2019; Karras
et al., 2018). StyleGAN2 eliminated high resolution
artifacts common in image reconstruction with an
updated style control mechanism (Karras et al., 2020)
while simplifying training complexity.
The Gleason grading system for prostatic adeno-
carcinoma originated in the 1960-70s and has been
developed further by the International Society of
Urologic Pathology in 2005 and 2014 (Chen and
Zhou, 2016). Both pathologists and clinicians need
Daroach, G., Yoder, J., Iczkowski, K. and LaViolette, P.
High-resolution Controllable Prostatic Histology Synthesis using StyleGAN.
DOI: 10.5220/0010393901030112
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 2: BIOIMAGING, pages 103-112
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
103

to fully understand the principles and practice of
the Gleason grading system to effectively diagnose
patients. Classification of Gleason grade is done
solely based on visual morphologies in hematoxylin-
eosin stained histology (Chen and Zhou, 2016). The
principal motivation of this study is to investigate
how StyleGAN captures these morphologies and
relates histologic semantics in the input latent space.
The GAN reconstruction network learns to relate
visual morphologies during the unsupervised training
period with feedback from a CNN analyzing the
unlabeled histologic training data. The machine
learning developed relations in these convolutional
feature maps may provide new insights into Gleason
grading patterns.
In this paper, our contributions are:
• We demonstrate GANs can produce novel pro-
static histology at a high-resolution (1024
2
) and
accurately capture features of prostatic histology
including stroma, benign tissue, atrophy, low-
grade, and prostatic cancer. A pathologist was un-
able to distinguish between the real and generated
images (Section 5.1)
• We demonstrate StyleGAN and StyleGAN2 em-
bed histologic morphology to different generator
deep layers, isolating high (gland, lumen shape),
medium (epithelium and stroma texture), and low-
level (coloration, nuclear density) pathological
features for user control (Section 5.2)
• We propose a strategy for preparing whole slide
images into a high resolution training dataset to
maximize the performance of GAN image recon-
struction. (Section 4.1)
2 RELATED WORK
There is uncertainty in the literature as to whether
GANs improve interpretability over other deep net-
works. Some authors promote the use of GANs for
interpretation (Chen et al., 2018; Skandarani et al.,
2020) while others point out the work that remains
(Kazeminia et al., 2018). Themes for improving in-
terpretability include inverting images to the latent
space (Chen et al., 2018; Karras et al., 2020), demon-
strating separability of morphological labels in the
latent space (Skandarani et al., 2020; Quiros et al.,
2020), and combining the GAN with existing meth-
ods (Kazeminia et al., 2018; Skandarani et al., 2020).
In this study, we find that StyleGAN separates histo-
logic morphologies at different scales, correlates mor-
phologies with latent values, and maps stoichastic in-
formation in the noise channel to determine the spe-
cific placement of the image features.
Some authors have explored variations of the orig-
inal StyleGAN on medical images. Xu et al. use a
modified GAN architecture inspired from StyleGAN
components and MCGAN to draw non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) nodules onto chest CT imagery (Xu
et al., 2019). Given a 128
2
portion of a chest CT
and a patient’s protein profile, the GAN realistically
projects NSCLC nodules into the chest medical im-
age. Quiros demonstrate accurate prostatic histol-
ogy reconstruction at 224
2
and 448
2
resolution us-
ing PathologyGAN, inspired from the StyleGAN and
BigGAN networks, to achieve a FID of 16.65 (Quiros
et al., 2020). In this study, we use 1024
2
images as in
the original StyleGAN networks and explore which
histological features are captured at each layer.
Karras et al. explored training StyleGAN net-
works on limited data, including the breast histol-
ogy dataset BRECAHAD, proposing an adaptive data
augmentation technique for training algorithms on
small datasets containing only hundreds of 1024
2
images rather than tens of thousands (Karras et al.,
2020). In this study, we train on hundreds of thou-
sands of high quality images, so small-training set
techniques are not required.
3 BACKGROUND
Generative Adversarial Networks. The adversar-
ial learning framework is a pivotal contribution to
the data generation field, enabling synthesis net-
works capable of producing novel samples from high-
dimensional data distributions (Goodfellow et al.,
2014). An image GAN consists of an inverse CNN
synthesis network (generator or G) and a traditional
CNN classification network (discriminator or D).
Learning happens in three discrete stages. First D
classifies a batch of random images from the input do-
main as real or fake, embedding real image semantics
in its convolutional feature maps. Second G samples
a batch of random latent codes and presents fake data
to D. Third D grades the realism of the fake data, pro-
ducing a loss gradient for G to update with the infor-
mation in D’s convolutional feature maps. Training
concludes when D is unable to distinguish between
samples from the training distribution and the syn-
thetic distribution produced by G.
Progressive Growing. ProgGAN introduced the
notion of progressive growing of image data to sta-
bilize training of higher-resolution images (Karras
et al., 2018). In StyleGAN the training images are
BIOIMAGING 2021 - 8th International Conference on Bioimaging
104

down-sampled to 4
2
resolution and doubled in spatial
size after each epoch until the target 1024
2
resolution.
Karras et al. hypothesize that lower-resolution data is
more stable to learn because there are fewer modes,
and as the learning progress the modes can be divided
while maintaining the structure shared by the modes.
In some sense, the course layers/features learned early
in training provide scaffolding for the later layers to
learn fine details.
Intermediary Latent Space. The input latent space
Z is modeled as a vector of uncorrelated Gaussian
noise. StyleGAN uses a multi-layer fully-connected
network (the transformer) to map the input Z space
onto an intermediary latent space W before feeding
into the synthesis network. The W space has an ad-
vantage over the Z space in that it is not constrained
to a multivariate single-modal Gaussian distribution.
If the space of training images is not naturally repre-
sented by a Z hyper-sphere, the transformer can learn
to map the hyper-sphere onto a more natural, disen-
tangled latent space W.
For instance, if G is trained on images that have
variations in H&E staining such that cribiform ap-
pears in dark purple stains and healthy stroma appears
in light pink stains, there may exist a combination of
cribiform in light pink and stroma in dark purple in
the W space although not explicitly in the training
data. In StyleGAN, the disentangled latent space can
map onto image semantics at multiple scales of the
synthesis network because the W space interacts with
each convolutional upsampling layer twice.
4 METHODS
4.1 Prostatic Histology Data
Preparation
Thirteen (13) patients with biopsy-confirmed pro-
static cancer were included in this study. Fol-
lowing radical prostatectomy, samples were sec-
tioned using patient-specific slicing jigs created
from the presurgical magnetic resonance images
(McGarry et al., 2019). Tissue sections were
paraffin-embedded, whole-mounted, stained with
hematoxylin-eosin (H&E), and then digitally scanned
using a Huron microscope at 40X magnification or
0.20 µm per pixel. JPEG compression reduced the
average ~120GB raw whole slide image (WSI) TIF
files into ~15GB TIF images while retaining 90% of
perceived image quality.
Each WSI was down-sampled by a factor of 2
to visualize both small cell features and large tissue
features at 1024
2
image size. A vector processing
pipeline approach (Martinez and Cupitt, 2005) was
applied to incrementally process each WSI into 1024
2
PNG images without loading the complete WSI into
computer memory. To remove white tiles and low-
quality tiles from the edges of the slide scan, an His-
tomicsTK algorithm was used to count the number of
nuclei in each tile (Gutman et al., 2017). Two datasets
were created for evaluation of the models. To con-
struct the Simple dataset, image tiles with 100 or more
nuclei were extracted, resulting in 87k tiles. For the
Augmented Dataset, first tiles with more than 20 nu-
clei were extracted, resulting in 100k tiles. Next each
image was augmented with a horizontal flip and four
90 degree rotations yielding eight tiles per each input
tile or 800k total images. In both datasets, each im-
age was down-sampled into nine levels with spatial
dimensions ranging from 4
2
to 1024
2
before feeding
into the progressive growing training process (Karras
et al., 2018).
4.2 StyleGAN Training
The StyleGAN (Karras et al., 2019) and StyleGAN2
(Karras et al., 2020) networks were each trained
twice, once on the Simple dataset and once on the
Augmented dataset. The networks from the official
NVLabs GitHub repositories were configured with
the default large network architecture Config-F. Each
training run was done with eight NVIDIA V100’s in
a DGX-1 system. StyleGAN trained through 25 mil-
lion real image impressions, and StyleGAN2 through
21 million.
5 RESULTS
5.1 Quantifying Generator
Performance
The generator performance is measured using the
Fréchet inception distance (FID) and perceptual path
length (PPL). Rather than pixel-wise comparisons (as
done by the L2 norm), the FID metric uses a pre-
trained VGGnet CNN to compare visual similarity be-
tween real and synthetic images, mimicking human
perception (Heusel et al., 2017). PPL is an auxiliary
metric introduced in (Karras et al., 2020) that mea-
sures how well the disentangled latent space fits onto
correlated features and grades overall semantic con-
sistency within the reconstructed images. Like Kar-
ras, we calculated PPL based on path endpoints in W
and without the central crop. Results are presented in
Table 1.
High-resolution Controllable Prostatic Histology Synthesis using StyleGAN
105
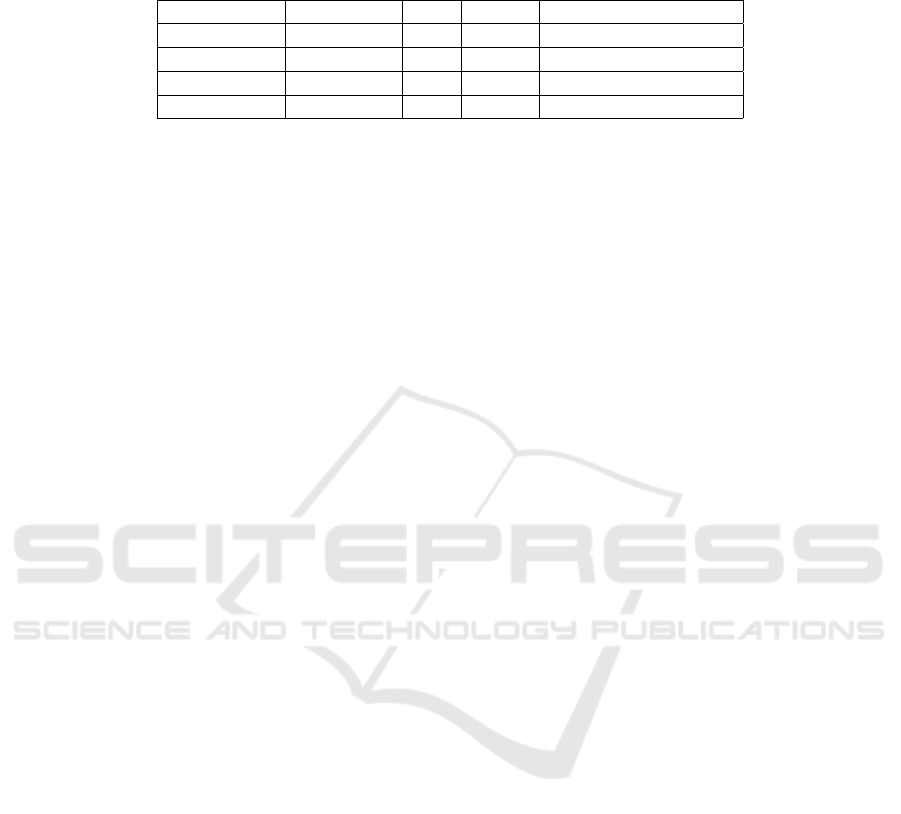
Table 1: Training Results. For each training run, we selected the final training snapshot to evaluate the metrics. A lower
FID indicates that the generator produced a distribution of images more similar the training data. A lower PPL indicates the
network was better able to generalize onto the training dataset. Best results in each column are indicated in bold.
Network Dataset FID PPL Training Time (days)
StyleGAN Simple 3.43 147.25 5d 10h 43m
StyleGAN2* Simple 3.69 33.25 10d 5h 11m
StyleGAN Augmented 2.86 139.34 5d 18h 51m
StyleGAN2* Augmented 5.70 47.31 11d 23h 28m
* Training results for StyleGAN2 terminated after 21 million image impressions. Results are shown for the last epoch completed.
We presented 80 samples of generated histology
and 80 samples of real histology from the training set
to a pathologist for evaluation. The pathologist was
unable to differentiate between the two groups with
45% prediction accuracy.
The original StyleGAN results include drop-like
artifacts resulting from layer signal leakage due to
normalization removing channel magnitudes as de-
scribed in (Karras et al., 2020). We found StyleGAN
to generate the same droplike artifacts when trained
on prostatic histology and StyleGAN2 to similarly re-
move these reconstruction artifacts with its improved
architecture.
5.2 Style Mixing
To explore the resolution at which various histologic
features occur, two randomly-generated histology im-
ages were mixed at the inputs to the layers of the
generator (Fig. 1). In StyleGAN image synthesis,
each input latent code z is converted into a disentan-
gled latent code w by a multi-layered fully-connected
network. This w is then inserted into each upsam-
pling convolutional layer twice through style controls.
These style controls adjust the mean and standard de-
viation of each convolutional channel, modifying the
signal of specific projected feature maps onto the im-
age.
During style mixing, the w vector for one image
is used for most layers, and the w vector for the other
image is used for the remaining layers. No truncation
adjustment (Karras et al., 2019) was used for these
figures. We observe that large scale features (gland,
lumen location) are fixed at the course layers of the
network (the layers closest to the input). The middle
layers control epithelium and stroma textures. The
fine layers (those closest to the image) control col-
oration and nuclear density.
5.3 Capturing Stochastic Variation
In the StyleGAN networks, random noise is broad-
cast onto each layer to capture stochastic informa-
tion, such as the exact location of hair or freckles that
doesn’t change the overall appearance of an image
(Karras et al., 2019). Unlike natural images which use
a standard composition for the subject, histologic tile
samples are truly spatially invariant. Indeed, the pre-
cise locations of nuclei, cell boundaries, and glands
are modeled through the random channel. Figure 2
shows the effect of varying the input noise while leav-
ing the latent codes intact. It illustrates how the style
(inclusion/exclusion, color, thickness, texture) of cells
and glands is fixed by the latent code, but the locations
are specified by the random broadcast noise.
5.4 Classifying Generated Histology
Given 100 tissue samples, samples were grouped 8
distinct classes. We then averaged all w coordinates
each class and projected the mean into an image. Re-
sults are shown in Figure 3.
5.5 Generator Interpolation
The network has the ability to create realistic images
from latent codes that fall within the latent space.
Given two separate image samples, we have shown
the impact of style mixing when reconstructing those
images given the same latent code. With our work we
additionally investigate the impact of defining new la-
tent codes that exist along the path between labeled
latent codes (Fig. 4). Although the intermediary
samples are independently photorealistic, we find the
shortest path in latent space does not capture realistic
biochemical transitions in the underlying pathology.
6 DISCUSSION
While histology shares many characteristics in com-
mon with natural images (such as containing lines,
edges, and RGB color), there are many unique char-
acteristics that differentiate histology generation from
natural image generation. Progressive growing or res-
olution enhancement during training enabled high-
resolution image generation that captures histologic
structures at multiple scales. By training first on a
BIOIMAGING 2021 - 8th International Conference on Bioimaging
106

Figure 1: Disentangled latent mixing at generator levels. Using the same approach as the original StyleGAN literature(Karras
et al., 2019; Karras et al., 2020), we select two random input latent vectors z, generate pure images, then mix a select set of
w vectors from source B into source A at certain layers. In coarse styles, we mix B’s w layers into A layers 4
2
to 16
2
. In
middle styles, B mixed in at 16
2
to 128
2
. In fine styles, B mixed into all layers after 128
2
. Figure generated with StyleGAN2
on Simple dataset.
course resolution, the network embeds high-level his-
tologic features such as lumen or tissue mass into
coarse layer feature maps. Middle layers capture
stroma and epithelium textures. Later layers capture
low-level fine details like tissue color. Karras et al.
hypothesize that lower-resolution data is more sta-
High-resolution Controllable Prostatic Histology Synthesis using StyleGAN
107

(a) (b)
Figure 2: Impact of random noise on histologic features. (a) Varying input noise. Images are generated from the same latent
code but different noise at all layers. Noise impacts multi-scale changes in final image reconstruction, but does not change
many of the features important for diagnosis including cell texture and epithelium thickness. (b) Isolating input layers. In the
upper left image, all noise input is on. In the upper right image, all noise input is off. In the lower left image, noise is inserted
only into the coarse layers. In the lower right image, noise is inserted into only the fine layers. The random input in the course
layers control gland placement while those in the fine layers control cell placement.
ble to learn because there are fewer modes, and as
learning progresses the modes divide while maintain-
ing the structure shared by the modes (Karras et al.,
2018). The course layer feature maps learned early in
training provide scaffolding for the later layer feature
maps to project more complex fine details.
Although not designed explicitly for spatially in-
variant cellular medical domains, the StyleGAN is
successfully able to isolate stochastic information in
the synthesis network noise channels. The noise
can be adjusted to dramatically change the appear-
ance of the generated histology without changing the
histopathology. A latent code will generate simi-
lar histologic morphologies regardless of the random
broadcast noise. Additionally, the computer vision
improvements in StyleGAN2 with PPL and image ar-
tifact reduction carry over in the histology domain.
Conclusion. We have demonstrated that StyleGAN
and StyleGAN2 generate realistic prostatic histology
at high-resolution (1024
2
images). The GANs cap-
ture prostatic structure at multiple scales ranging from
gland layout through nuclei density. Image features
can be controlled by interpolating between points
within the latent space, mixing the inputs to the lay-
ers of the generator network, and adjusting the seed
for broadcast random noise at different scales.
Future Work. GANs hold much promise for pro-
viding interpretation of image data. Central to in-
terpretability is the projection of real clinical images
onto the projector’s latent space. This would en-
able pathologists to insert real image specimens into
the network for analysis. Extending the StyleGAN2
to learn an image-by-image inverse projection of the
generator during training, similar to (Chen et al.,
2018) would enable this. A network that produces
semantic masks or captions from the generator such
as epithelium or stroma segmentation would also en-
hance the interpretability of the network. Interpola-
tion in latent space could provide insight into disease
progression or production of 3D volumes between
histology slices. With pathologist collaboration, a
more rigorous analysis of the generator network con-
volutional feature maps in latent clusters may provide
insight into the correlation of new Gleason patterns
with Gleason grading. Although the default Style-
GAN configurations demonstrated success, additional
exploration in the length of the transformer network
and quality of the dataset could yield improved effec-
tiveness. With additional compute resources and high
quality prostatic histology, it is possible the Style-
GAN network may show stable image reconstruction
at higher 4096
2
resolution.
BIOIMAGING 2021 - 8th International Conference on Bioimaging
108
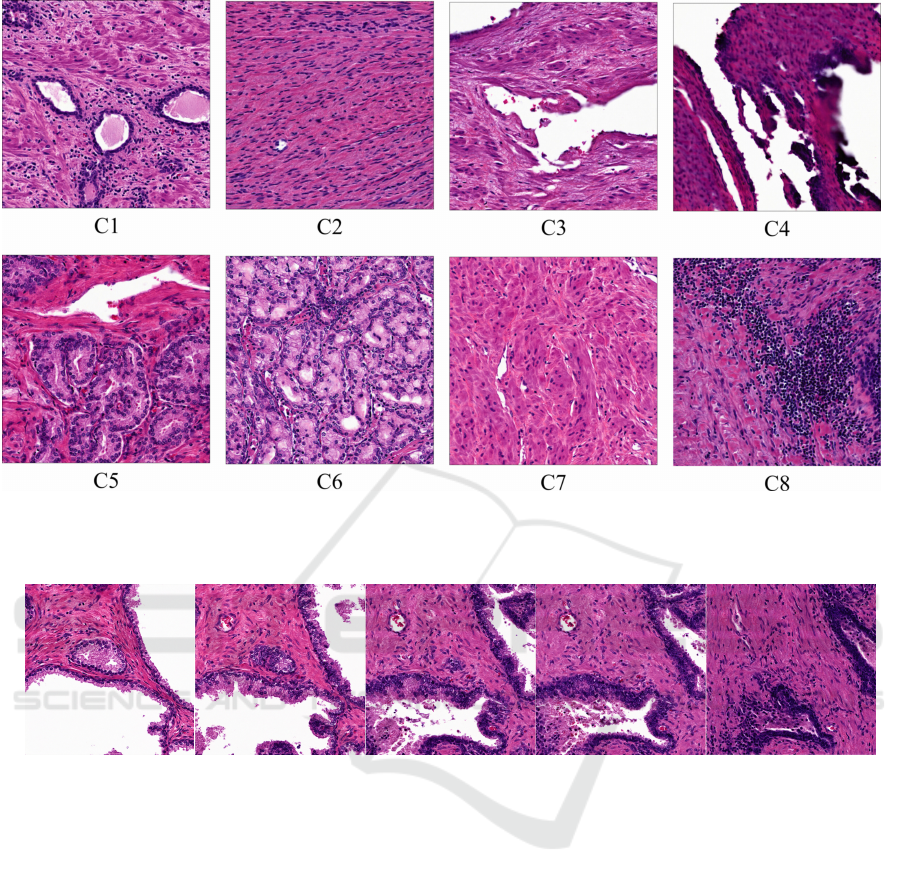
Figure 3: Histologic Morphology Means. Resulting generated histology from mean latent space vectors generated from empir-
ically categorized histologic classes. C2 and C7 mimic stroma, C4 mimics inked prostatic edge, C8 lymphocyte inflammation
and C5 and C6 prostatic cancer. StyleGAN2 Simple Datset.
Figure 4: Interpolating between two latent code representations of histologic tiles (Sec. 5.5).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Funding: The State of Wisconsin Tax Check-off
Program for Prostate Cancer Research, NCI/NIH
RO1CA218144 (LaViolette), and MSOE Professional
Summer Development Funding (Yoder). We would
like to thank Allison Lowman for assistance with ob-
taining the dataset and Samuel Bobholz for insight
into data preparation strategy. We would like to thank
Dr. John Bukowy for domain expertise and Dr. Sean
McGarry for insights into the clinical applications of
deep networks.
REFERENCES
Araújo, T., Aresta, G., Castro, E., Rouco, J., Aguiar, P.,
Eloy, C., Polónia, A., and Campilho, A. (2017). Clas-
sification of breast cancer histology images using con-
volutional neural networks. PLOS ONE, 12(6):1–14.
Chen, J., Xie, Y., Wang, K., Wang, Z. H., Lahoti, G.,
Zhang, C., Vannan, M. A., Wang, B., and Qian,
Z. (2018). Generative Invertible Networks (GIN):
Pathophysiology-Interpretable Feature Mapping and
Virtual Patient Generation. arXiv:1808.04495.
Chen, N. and Zhou, Q. (2016). The evolving Gleason grad-
ing system. Chinese Journal of Cancer Research,
28(1):58–64.
Du, M., Liu, N., and Hu, X. (2019). Techniques for In-
terpretable Machine Learning. arXiv:1808.00033 [cs,
stat].
Goodfellow, I. J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative Adversarial Networks.
arXiv:1406.2661.
Gutman, D. A., Khalilia, M., Lee, S., Nalisnik, M., Mullen,
Z., Beezley, J., Chittajallu, D. R., Manthey, D., and
Cooper, L. A. (2017). The digital slide archive: A
High-resolution Controllable Prostatic Histology Synthesis using StyleGAN
109

software platform for management, integration, and
analysis of histology for cancer research. Cancer Re-
search, 77(21):e75–e78.
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., Nessler, B., and
Hochreiter, S. (2017). GANs Trained by a Two Time-
Scale Update Rule Converge to a Local Nash Equilib-
rium. arXiv:1706.08500.
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., and Lehtinen, J. (2018). Pro-
gressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Sta-
bility, and Variation. arXiv:1710.10196 [cs, stat].
Karras, T., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.,
and Aila, T. (2020). Training Generative Adversar-
ial Networks with Limited Data. arXiv:2006.06676
[cs.CV].
Karras, T., Laine, S., and Aila, T. (2019). A style-based
generator architecture for generative adversarial net-
works. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aittala, M., Hellsten, J., Lehtinen, J.,
and Aila, T. (2020). Analyzing and improving the im-
age quality of stylegan. In Proceedings of the Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 8110–8119.
Kazeminia, S., Baur, C., Kuijper, A., van Ginneken,
B., Navab, N., Albarqouni, S., and Mukhopadhyay,
A. (2018). GANs for Medical Image Analysis.
arXiv:1809.06222.
Li, W., Li, J., Sarma, K. V., Ho, K. C., Shen, S., Knudsen,
B. S., Gertych, A., and Arnold, C. W. (2019). Path
R-CNN for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Gleason
Grading of Histological Images. IEEE Transactions
on Medical Imaging, 38(4):945–954.
Martinez, K. and Cupitt, J. (2005). VIPS: a highly tuned im-
age processing software architecture. In IEEE Inter-
national Conference on Image Processing (31/08/05),
pages 574–577.
McGarry, S. D., Bukowy, J. D., Iczkowski, K. A., Un-
teriner, J. G., Duvnjak, P., Lowman, A. K., Jacob-
sohn, K., Hohenwalter, M., Griffin, M. O., Barring-
ton, A. W., Foss, H. E., Keuter, T., Hurrell, S. L., See,
W. A., Nevalainen, M. T., Banerjee, A., and LaVio-
lette, P. S. (2019). Gleason Probability Maps: A Ra-
diomics Tool for Mapping Prostate Cancer Likelihood
in MRI Space. Tomography, 5(1):127–134.
MICCAI (2020). Kaggle MICCAI 2020 prostate cancer
challenge.
Quiros, A. C., Murray-Smith, R., and Yuan, K. (2020).
PathologyGAN: Learning deep representations of
cancer tissue. arXiv:1907.02644 [cs, eess, stat].
Rawla, P. (2019). Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World
Journal of Oncology, 10(2):63–89.
Skandarani, Y., Painchaud, N., Jodoin, P.-M., and Lalande,
A. (2020). On the effectiveness of GAN generated
cardiac MRIs for segmentation. arXiv:2005.09026.
Xu, Z., Wang, X., Shin, H.-C., Yang, D., Roth, H., Milletari,
F., Zhang, L., and Xu, D. (2019). Correlation via syn-
thesis: end-to-end nodule image generation and radio-
genomic map learning based on generative adversarial
network. arXiv:1907.03728 [cs, eess].
Young, K., Booth, G., Simpson, B., Dutton, R., and Shrap-
nel, S. (2019). Deep neural network or dermatologist?
arXiv:1908.06612.
BIOIMAGING 2021 - 8th International Conference on Bioimaging
110

APPENDIX
Figure 5: Uncurated random generated histology samples from StyleGAN2 trained on the Simple dataset.
High-resolution Controllable Prostatic Histology Synthesis using StyleGAN
111

Figure 6: Preliminary experiments with inversion of images. In each pair of images, the image on the left is a generated
synthetic image used as an input and the image on the right is the result of the inversion process. To invert images, we
used the inversion algorithm in the NVLabs StyleGAN2 package. This adjusting the latent codes through backpropagation to
produce an output image as close to the input image as possible. We display this output image as the result of the inversion
process. Since the input image is generated by the algorithm, a latent code to generate a perfect match exists, but the inversion
process fails to find it. With some tuning, we were able to converge on the correct location of the glands and general color
scheme, but the structure of the epithelium tissue is often completely absent. We used our StyleGAN2 network trained on the
Simple dataset with a truncation scaling factor ψ = 1.0 (no scaling).
Figure 7: Exploring truncation psi trick on the Simple histology dataset with StyleGAN2. As ψ → 0.0, all histology samples
converge to the “mean” histology image in our training dataset. As ψ becomes negative, features are often replaced with their
opposites, such as thick vs. thin epithelium and large vs. small or absent glands.
BIOIMAGING 2021 - 8th International Conference on Bioimaging
112
