
A Blockchain-based Architecture for Enterprise Ballot
Paulo Henrique Alves
1 a
, Isabella Frajhof
1
,
´
Elisson Michael Ara
´
ujo
1
, Yang Ricardo Miranda
1 b
,
Rafael Nasser
1 c
, Gustavo Robichez
1
, Alessandro Garcia
1
, Cristiane Lodi
2
, Flavia Pacheco
2
and Marcus Moreno
2
1
Software Engineering Laboratory, Department of Informatics, Pontificial University Catholic of Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
2
Petrobras, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords:
Ballot, Electronic Voting Systems, Blockchain, Architecture.
Abstract:
Enterprise ballots are usually applied to support the decision-making process in voting-related scenarios. They
allow its members to manifest their opinion and settle their position in regards to a specific topic, such as the
approval of budgets and the acquisition of goods and services. Even though we are living in a data-driven
society, highly digitized, enterprise ballots still rely on a paper based process. Thus, migrating to an electronic
voting system, in which all the resolution process happens online, triggers various issues on verifiability,
correctness and secrecy. Blockchain plays a vital role in this environment, as it is able to provide a trustable
and secure enterprise decision-making system. Therefore, we developed BallotBR, an enterprise ballot system
under a permissioned blockchain platform, to address all the requirements based on a challenging enterprise
consortium context. This consortium is representative of many consortia across the oil and gas industry and
other domains. Furthermore, we contrasted the open-source proposals available in the literature with the
BallotBR needs. Also, we discussed how our solution addresses security and trustworthiness requirements
usually faced in e-voting systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Despite the tradition of some countries in the use of
e-voting systems for public and democratic elections,
this culture has not yet reached the enterprise am-
biance. Enterprise ballots (EB) are usually applied
to support the decision-making process in many sce-
narios (Yan et al., 2019). They allow stakeholders to
inform, discuss and settle their position on important
topics related to their business operation. Thus, EBs
can be understood to be a means by which an orga-
nization’s deliberative body discusses and deliberate
issues related to its operations. Through the exercise
of the stakeholders’ vote, such questions are decided
and the decisions executed.
The migration from a paper based ballot pro-
cess to an e-voting system requires the development
of systems that provide verifiability, correctness and
secrecy, common security requirements in crypto-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0084-9157
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7414-1899
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6118-0151
graphic e-voting systems (Juels et al., 2010), (Clark-
son et al., 2008), (Specter et al., 2020). The prevailing
goals of such requirements are to: (i) guarantee the
correct execution of the company rules regarding its
resolutions, (ii) verify that the votes were counted as it
were cast, and (iii) maintain the secrecy (iii.a) regard-
ing the voter identity and how s/he voted, avoiding
the coercion and influence on how one should vote,
and/or (iii.b) restrict unauthorized access to the sys-
tem, maintaining the confidentiality of deliberation to
its participants. In a nutshell, electronic ballot sys-
tems must provide a secure resolution process in order
to ensure the legitimacy and trust of the results.
Given the aforementioned goals, blockchain-
based systems play a vital role in this environment
(Pawlak et al., 2018). Blockchain is a novel technol-
ogy with the potential for creating a new paradigm of
trust and cooperation when involving multiple parties
(Alves et al., 2020; Nasser et al., 2020; Paskin et al.,
2020). Blockchain is a decentralized data structure
responsible for storing data in a chronological, digital
and immutable manner. The registration of such data
depends on the network participants consensus, which
232
Alves, P., Frajhof, I., Araújo, É., Miranda, Y., Nasser, R., Robichez, G., Garcia, A., Lodi, C., Pacheco, F. and Moreno, M.
A Blockchain-based Architecture for Enterprise Ballot.
DOI: 10.5220/0010432102320240
In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2021) - Volume 2, pages 232-240
ISBN: 978-989-758-509-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

validates the transactions without the need of a cen-
tral authority (Pilkington, 2016). When applied to an
e-voting system, due to its properties, blockchain al-
lows for the verification of the stored data. Thus, par-
ticipants can verify the results and attest their correct-
ness, without the need of third parties (Pawlak et al.,
2018).
In this sense, we have listed the main require-
ments and features that an EB system must present.
Our analysis was based on the context of an oil and
gas consortium, the Libra consortium. This context
is challenging for manifold reasons. First, this con-
sortium is composed of five different organizations.
Therefore, the consortium dynamics depend on the
non-trivial coordination and discussion of these or-
ganizations, for which important decisions must be
deliberated through ballots. Such process is well reg-
ulated by the Libra consortium agreement, which the
ballot procedure must comply with.
Also, three open-source voting projects were eval-
uated to investigate the proposed features with the
Libra ballot requirements. Such requirements were
listed according to the Libra consortium Agreement,
and validated and complemented by stakeholders
during regular meetings. None of the open-source
projects have presented a complete environment to
manage enterprise ballots and satisfy the Libra con-
sortium specifications.
Therefore, we developed BallotBR, an EB system
under a permissioned blockchain and evaluated the
open-source voting projects (Section 4). This system
addresses Libra consortium agreement needs, and its
architecture was developed considering further adap-
tation to be reused in other enterprise contexts (Sec-
tion 5). We also discuss how we addressed security re-
quirements, which are often faced in electronic voting
systems: correctness, verifiability and privacy (Sec-
tion 6). Section 7 presents conclusions and future per-
spectives.
2 BACKGROUND
The migration to e-voting systems means that all
the resolution process happens online (from partici-
pants authentication to ballot tallying). This migra-
tion can provide for a more efficient, easy, engag-
ing, and sustainable process. However, this transfor-
mation can trigger security issues, especially regard-
ing the system’s verifiability, correctness, and pri-
vacy. Even though paper based and electronic bal-
lots (Silva, 2019) are not exempted from this criti-
cism, researchers are constantly aware of those issues
when developing e-voting systems (Juels et al., 2010;
Clarkson et al., 2008; Specter et al., 2020). Thus,
mapping and addressing such vulnerabilities become
a fundamental step towards the development of a safe
and reliable e-voting system.
Electronic voting systems raise many technical
challenges that must be dealt within democratic elec-
tions, which are potentially exacerbated in an elec-
tronic voting system (Juels et al., 2010). The main
security requirements that must be dealt are: verifia-
bility, correctness and secrecy.
Attacker-aware Correctness and Verifiability.
Juels et al. (Juels et al., 2010) identify, among others,
two security requirements that an electronic voting
scheme must deal with: correctness and verifiability.
Correctness is defined with a twofold meaning. First,
an attacker “cannot pre-empt, alter, or cancel” the
vote of the participants. Second, the attacker must not
be able to vote two times for the same person. Thus,
it means that votes must be counted once, according
to the intention of the voter. Verifiability is defined
as the ability of the voters to confirm if the vote was
correctly computed, in which the system must be able
to detect voting misbehaviors. Clarkson et al. (2008)
affirm that verifiability can also be considered an in-
tegrity property (Clarkson et al., 2008). The integrity
of the election means that participants must be con-
vinced that their votes were correctly counted.
Voting Security Requirements. Moreover,
Specter et al. (Specter et al., 2020) organize the main
security requirements and their definitions in the vot-
ing system literature, which are: (i) correctness and
usability, (ii) secret ballot and (iii) end-to-end verifi-
ability. According to the authors, correctness and us-
ability are defined as the system’s capacity to demon-
strate that “votes were cast as intended, collected as
cast, and counted as collected”. End-to-end verifia-
bility means that the participant must have proof that
his vote was cast as intended and unmodified. This
verification must be done “without the need to trust
any separate authority to do so”.
Ballot Secrecy. The concept of ballot secrecy
refers to the need to maintain the anonymity of the
voter identity and to his/her vote to avoid voter coer-
cion and vote buying. We questioned the Libra con-
sortium if anonymity was an important element for
the ballot context, which was not. The votes of each
organization are kept open for all members of the con-
sortium. Although we recognize that anonymous vot-
ing can be demanded in other EB contexts, we did not
deal with such feature, since it was not a priority.
Nevertheless, in BallotBR secrecy can be defined
as the need to avoid unauthorized access to the ballot
and to the shared documents during resolutions. In
this sense, there is the need to implement a robust user
A Blockchain-based Architecture for Enterprise Ballot
233

authentication procedure. Overall, electronic voting
systems must be developed taking in consideration
such aforementioned security requirements. In sec-
tion 6 we demonstrate how the BallotBR architecture
attends to such specifications. Complying with such
requirements is important to guarantee a secure voting
procedure, hence, a legitimate and trustworthy result.
3 RELATED WORK
This section aims to describe the state of art of
open-source electronic voting systems. Five selected
projects also proposed the usage of blockchain tech-
nology. The goal is to understand the proposed so-
lutions’ gaps to build a more accurate, verifiable and
secure system in the enterprise scenario.
Hardwick et al. presented an e-voting system un-
der the private Ethereum network destined for pub-
lic elections
1
(Hardwick et al., 2018). They defined
six requirements that such system should satisfy and
how their system dealt with them: (i) fairness, (ii) el-
igibility, (iii) privacy, (iv) verifiability, (v) coercion-
resistance, and (iv) forgiveness. The use of a pub-
lic blockchain does not allow for the creation of data
sharing options and all network members have access
to registered information. An EB needs to assure that
shared information during a deliberation is kept pri-
vate and restricted to its members. This can be im-
plemented with the use of a permissioned blockchain,
such as Hyperledger Fabric (HF).
Dagher et al. proposed the BroncoVote, a verifi-
able e-voting system also designed under Ethereum
blockchain (Dagher et al., 2018). The system tests
were performed in the Ropsten public network (Kim
et al., 2018). The authors mentioned that blockchain
smart contracts (BSCs) could be deployed on an
Ethereum private network. However, (Hardwick
et al., 2018) identified limitations regarding such ap-
proach, for instance, the majority of encryption proto-
cols require larger numbers than 256 bits available on
solidity unsigned int. Thus, HF emerges as a secure
option to overcome this.
Hj
´
almarsson et al. (Hj
´
almarsson et al., 2018) and
Patil et al. (Patil et al., 2019) defended the usage of
permissioned blockchains in the voting scenario as an
alternative to public blockchains to provide secrecy.
The argument concerns the BSC execution and trans-
action costs. They argue that this involves not only
performance, i.e., permissioned blockchains perform
1
Private Ethereum Network. Available at: https://geth.
ethereum.org/docs/interface/private-network Accessed at:
11/06/2020.
better than the public blockchains in regards to trans-
action per second, but permissioned blockchains also
deliver more data privacy. However, the authors only
evaluated an election voting scenario instead of an
EB.
Last but not least, the authors in (Specter et al.,
2020) analyze and criticize the security of the Voaz
blockchain-based system for Federal Elections in
the U.S. under a permissioned blockchain. Even
though Voatz developers affirm that a permissioned
blockchain is used, they do not specify which plat-
form. Furthermore, the authors address privacy con-
cerns and discuss system vulnerabilities that would al-
low hacker attacks. However, the proposed solution
does not comply with the enterprise requirements for
balloting processes, as demonstrated by (Villalobos
et al., 2019). Thus, the gap of the blockchain plat-
forms for EBs is still an open discussion.
Regarding non-blockchain-based e-voting solu-
tions, Helios and Civitas are open-source platforms
proposed by (Alonso et al., 2018) and (Clarkson et al.,
2008). Concerns regarding the coercion resistance in
public and democratic elections scenario were pre-
sented. However, other useful features that we could
approach were also presented, e.g., approval rates
and abstention behavior configuration. Therefore, we
have considered both platforms to develop our solu-
tion and the comparative analysis (Section 4.3).
Thus, as none of the previous work proposed a so-
lution for the EB environment, neither the use of a
permissioned blockchains in such domain, we devel-
oped BallotBR. Our proposal considered the gaps pre-
sented by previous works. Also, our system is based
on the Libra consortium requirements, and must deal
with security issues related to the correctness, veri-
fiability and secrecy of the system (Section 2). The
details of our study are described in the following sec-
tions.
4 REQUIREMENTS ANALYSIS
4.1 Application Scenario
Libra “was offered in the first bidding round executed
by the Brazilian government under the new Produc-
tion Sharing Contract for presalt areas, in 2013” (Car-
lotto et al., 2017). Currently, it is one of the seventeen
contracts in force in Brazil
2
. Libra is explored by
five companies that compose the consortium: Petro-
2
Available at: http://www.presalpetroleo.gov.br/
ppsa eng/sharing-contracts/sharing-contracts Accessed at:
11/27/2020.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
234

bras (Operator, upholding 40%), Shell Brasil (20%),
Total (20%), China National Petroleum Corporation
(CNPC) (10%), and China National Offshore Oil Cor-
poration (CNOOC) (10%). The Production Shar-
ing Contract establishes that PPSA (Pre-Sal Petroleo
S.A.), a public company, must be part of the con-
sortium to represent the Federal Government’s inter-
ests. The company chairs the Operational Committee
and is responsible for managing the sharing contracts.
One of the company’s role is to ensure that the con-
sortium complies with the agreement rules.
Hence, PPSA presents an essential role during the
deliberation process of the Operational Committee. A
ballot must take place whenever the consortium needs
to acquire goods and services. When a ballot is pro-
posed, such companies’ participation is proportion-
ally distributed to allow the involvement of PPSA.
Thus, in the deliberation process, which is called “res-
olution” in the consortium agreement, each company
will have the following participation: Petrobras with
20%, Shell Brasil and Total with 10% each, CNPC
and CNOOC with 5% each, and PPSA with 50%.
Moreover, other than the ballot, there is another
communication mechanism called notice, which con-
sists of a notification. Both ballot and notice are cur-
rently part of paper-based processes. These manual
activities delay the decision-making process and re-
quire many manual interventions to initiate and end
resolutions. Thus, in order to automate this proce-
dure and provide more efficiency, we mapped bal-
lot requirements of the Libra consortium to stream-
line the development of the BallotBR, an enterprise
blockchain-based ballot system.
The BallotBR had to be strictly adherent to the Li-
bra consortium Agreement. Such requirements were
listed according to that legal document, and vali-
dated and complemented by stakeholders during reg-
ular meetings. The decision to develop such a sys-
tem was motivated after the analysis of three open-
source voting projects. Non of these open-source
projects fully satisfied the requirements and features
demanded by the Agreement and stakeholders. Some
of these were: a flexible configuration of the resolu-
tions, well-defined roles, system availability and full
transparency. The use of a permissioned blockchain
was essential to reinforce key aspects of electronic
voting systems listed in Section 2, as well as to pro-
vide a transparent and legitimate ballot process.
4.2 BallotBR Requirements
Enterprise ballots require the creation of voting
groups to deliberate on different topics. Hence, such
systems must provide the creation of a committee,
group companies and voting sections. In Libra con-
sortium, the deliberation process is named resolution.
Additionally, a specific feature of Libra consor-
tium is the use of the notice instrument. The notice is
used on behalf of the operator of the consortium for
the acquisition of goods or services. Due to its value,
the operator only informs the other members, not re-
quiring a resolution. Situations where a notice is nec-
essary, and not a ballot, are listed in the Consortium
Agreement.
In decision-making processes with multiple-
agent, an interaction guideline is important. In the
Libra consortium, members can require more details
or information when the resolution (or a notice) is
opened. Such resource decreases bureaucracy and
friction between members, as concerns are transpar-
ently addressed. This question and answer tool act as
a private forum, restricted to consortium members.
Moreover, EBs require different forms and
weights of participation. They demand more roles
than required by general election systems. Hence, we
incorporated six main user roles with different per-
mission rights:
Staff. This role provides committee members
(CMs) permission to: (i) create, edit, and delete reso-
lutions; (ii) create, answer, and resolve questions; (iii)
create notices; and (iv) remove companies from reso-
lutions and withdraw resolutions.
Representative. This role allows CMs to vote in
resolutions and answer questions from the committee
s/he is part.
Alternative. This role enables CMs to substitute
a Representative when necessary. The Alternative has
the same permissions as the Representative role.
Assistant. This role enables CMs to view resolu-
tions only. People with this role are restricted only to
visualize a resolution status.
Viewer. As the name suggests, this role allows
the CM-only to view resolutions and notices from the
committee s/he is part.
Partner Staff. This role allows the CM to create
notices, as well as create and answer questions.
The Libra consortium agreement sets different
participation percentages for each company, reflect-
ing percentage rates of the result. Hence, the system
should set distinct participation weights. Thus, EB
system must allow the configuration of approval rates
and abstention behaviors.
The approval rates calculate the required percent-
age to approve or disapprove a resolution, and de-
fines how absentee votes will be tallied. Therefore,
the EB system should allow the setup of percentages
of acceptance at the committee level and abstention
behavior at the resolution level. To do so, we present
A Blockchain-based Architecture for Enterprise Ballot
235
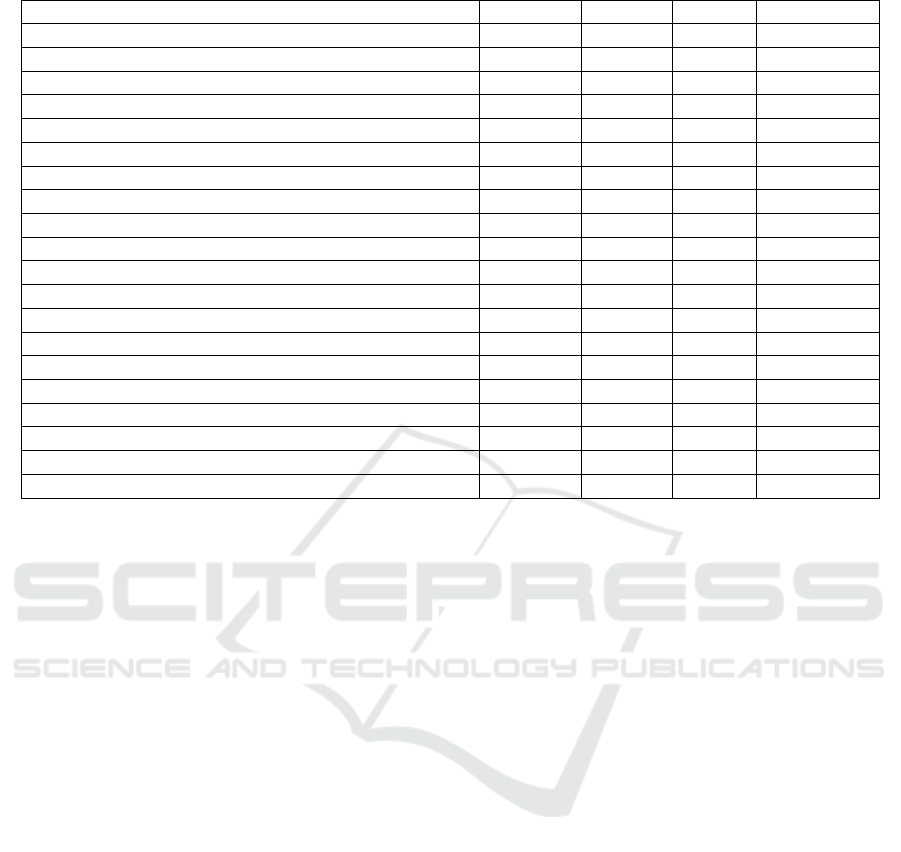
Table 1: Voting Systems Evaluation.
Feature BallotBR Helios Civitas BroncoVote
[F01] Account management Yes Partially Yes Yes
[F02]Committee management Yes No No No
[F03] Resolution management Yes Yes Yes Partially
[F04] E-mail notification Yes Yes No N/A
[F05] Dashboard of on-going resolutions Yes No No No
[F06] Resolution due date extension Yes Yes N/A No
[F07] Suspension of resolution Yes Yes N/A No
[F08] Withdraw resolution Yes No Yes No
[F09] Removal of participant in-progress Resolution Yes No N/A No
[F10] Approval rate configuration Yes Partially No No
[F11] Abstention Vote Behavior Configuration Yes Partially No No
[F12] Multiple Voting Options Configuration Yes Yes Yes Yes
[F13] Send notice Yes No No No
[F14] Resolution questions and answers Yes No No No
[F15] Notice questions and answers Yes No No No
[F16] Search questions and answers Yes No No No
[F17] Real time visualization of partial and final result Yes No No No
[F18] Export resolution result to PDF Yes No No No
[F19] Search attachments Yes No No No
[F20] Implemented in blockchain Yes No No Yes
two approval rates: majority and unanimity. However,
other acceptance percentages can also be set.
In regards to abstention behavior, the resolution
creator can set different behaviors. The absentee vote
can: (i) be proportionally distributed to the remaining
companies, (ii) follow the majority option, (iii) follow
the minority option, or (iv) not be tallied. Further-
more, the resolution creator can also require the jus-
tification for a vote option. For instance, the consor-
tium may always require a vote justification when a
participant intentionally votes for abstention or when
s/he disagrees.
The voting options in EB systems are different
from public and democratic e-voting systems. In en-
terprise systems, the possibilities are usually “agree”
or “disagree”. However, such systems should also al-
low other voting options. Therefore, we have enabled
such configuration (i.e, organization of an election).
Also, it is possible to link resolutions, e.g., a budget
resolution of 2019 may be related to the budget reso-
lution of 2020.
The Libra consortium also requires a transparent
business process to avoid friction. As partners have
to present evidence of expenses to share operational
costs, decisions must be securely stored and available
for auditing.
4.3 Systems Comparison
To position the BallotBR over the already proposed
e-voting solutions, Table 1 presents the main system’s
requirements and a comparative analysis between the
proposed solution and three open-source platforms:
(i) Helios (Alonso et al., 2018), (ii) Civitas (Clark-
son et al., 2008), and (iii) BroncoVote (Dagher et al.,
2018). Those requirements were listed with the stake-
holders before deciding to develop a system from the
very beginning.
There are three pillars that the system should pro-
vide to perform EBs: (i) account management, (ii)
committee management, and (iii) resolution manage-
ment. First, as information is not public in enterprise
solutions, they often require a restricted area for au-
thenticated users. So, the first step into the analysis is
the existence of user credential management. Second,
EBs usually require multiple and often related reso-
lutions during the corporation life cycle; hence, the
system should support the grouping of different bal-
lots from the same committee, or committee manage-
ment. Finally, the system should also allow resolution
management, i.e., a configuration of voting options,
approval rates, different ways for tallying votes, relat-
ing different resolutions, and definition of abstention
behavior.
We have based our evaluation on related works
that provide the code repository. Some of the listed
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
236

requirements Section 4.2 could not be evaluated be-
cause there is no information reported about them.
Such requirements were classified as N/A (not avail-
able). Furthermore, if a system addressed or not a
certain requirement, we gave three different values for
the response: (i) Yes, meet the requirement, (ii) Par-
tially meet the requirement, and (iii) No, it does not
meet the requirement.
Moreover, the system shall offer a dashboard to
evaluate the on-going resolutions and provide a space
for users to send questions to other enterprise mem-
bers while the resolution is open. Also, the sys-
tem needed to support default participants, i.e., non-
compliant financial status. Also, the system should
not allow the company participation during a resolu-
tion if it presents any financial issue. In this case, the
entity must not have a vote until the situation is fixed.
The Libra consortium presents two additional re-
quirements that the system should provide. First, the
notice event described above, when the operator an-
nounces a decision to the other consortium members
that does not demand a ballot. Second, the system
should also allow the visualization of partial and final
results.
Table 1 shows that the Helios platform fully at-
tends to the requirements [F03], [F04], [F06], [F07],
and [F12]. Also, Helios partially attends the fol-
lowing requirements: accounting management, ap-
proval rate and abstention vote behavior configura-
tion. As for Civitas, it fully attends to BallotBR re-
quirements [F01], [F03], [F08], and [F12]. How-
ever, Civitas does not partially attend to other require-
ments. Finally BroncoVote, meets BallotBR require-
ments [F01], [F12], and [F20]. On its turn, the plat-
form only partially attends to the resolution manage-
ment requirement.
Thus, Table 1 shows that no evaluated platform
adequately complies with the consortium agreement
requirements. The Helios platform (Alonso et al.,
2018) offered more features. However, even though
this platform provides an open-source project, we de-
cided not to use the Helios source-code given the lack
of documentation and the mismatch features regard-
ing our requirements.
5 BALLOTBR: AN ENTERPRISE
Ballot SYSTEM
In order to meet the identified requirements, we de-
signed the BallotBR architecture and fully developed
the system. Figure 1 depicts BallotBR software ar-
chitecture, which has two main layers: the BallotBR
interface, and the HF permissioned blockchain. The
former is responsible for providing most of the fea-
tures listed above as EB requirements. The architec-
ture persists data regarding the committee, resolution,
and notice in the Postgres database. This guarantees
that data will not be lost if any problem occurs while
it is not stored in the blockchain. The latter is respon-
sible for guaranteeing the ballot rules providing the
correctness, verifiability, and privacy required in EB.
The use of a permissioned blockchain in the Bal-
lotBR solution was motivated by the technology’s
intrinsic characteristics and the Libra consortium’s
needs. In this sense, the integration of the BallotBR
to a permissioned blockchain can ensure important
properties to the ballot process.
The technology is able to reduce errors when ex-
amining ballot results, since the resolution rules are
hard-coded into immutable BSCs. This allows partic-
ipants to confirm that their votes were tallied accord-
ingly. Furthermore, the distributed consensus guaran-
tees that all members accept the ballot rules and trans-
actions before they are registered in the blockchain.
Also, data access can be restricted to specific mem-
bers of the network. Organizations can access the
results and verify their correctness depending on the
Certificate Authority’s previous authentication.
Hyperledger Fabric.The developed solution was
based on the HF framework (version 1.4). A strong
motivation for this decision was the offered possibili-
ties. Hyperledger allows creating different data access
and writing policies associated with the Channels and
Chaincodes. This means that data flow and access are
governed by immutable and self-enforcing rules pre-
viously defined.
Channel and Peers. The Channel is the layer that
allows data isolation and confidentiality. Each Chan-
nel has a specific ledger that is shared between the
Peers (the nodes in HF) of each organization, which
are part of the network. These nodes are associated
with the permission policies that rule each Channel.
For BallotBR, the Libra channel was created. Ac-
cess to this Channel is restricted to the Libra con-
sortium organizations (Petrobras, Shell Brasil, Total
CNPC, CNOOC and PPSA). Each organization has
its own Peer, Orderer, Fabric CA and API.
Chaincodes. The Chaincodes are the BSCs in HF.
They are instantiated and operated by the Peers. Their
role is to implement businesses rules that will vali-
date and modify the Channels’s states. These business
rules are part of the established consensus between
the organizations, which are represented by Chain-
codes’s methods. Each executed Chaincode method
represents a transaction that will be: evaluated, when
intended to validate or to consult the blockchain, and
submitted, when it wishes to change the state of the
A Blockchain-based Architecture for Enterprise Ballot
237

Figure 1: BallotBR architecture.
ledger related to the Channel (i.e., to share data with
other organizations).
Thus, BallotBR business rules are implemented
in the Chaincodes to create resolutions, notices and
exercise the right to vote. This is important for two
reasons: it means that the EB rules are hardcoded in
BSCs and that participants can confirm that their vote
was registered as intended, and counted correctly.
Endorsement Policies, Ordering Service and
Orders Node. Each submitted transaction called by
the Chaincode method should satisfy an endorsement
policy. It shall present a minimum quantity of spe-
cific signatures based on the standard configuration of
the Channel. If a transaction attends the endorsement
policy, it will be submitted to the Ordering Service,
responsible for ordering the block transactions by the
Orders nodes. Finally, these blocks are transmitted
to the Leading Peers of each organization, which will
replicate the transaction blocks between the associ-
ated Followers Peers, according to the HF Raft con-
sensus. In the end, the current states of the ledgers of
each associated Peer to a Channel are updated.
The endorsement policy is related to the dis-
tributed consensus of HF. For instance, when a vote is
cast, all Libra consortium organizations are commu-
nicated. Before registering the vote in the blockchain,
they must all validate such activity, and collectively
verify the vote before registering it.
Private Data. These transactions can also contain
a collection of private data that will be kept secret.
Only a subset of the Channel organizations can access
it, according to previous definition, which is similar to
the endorsement policy definitions. Non-authorized
organizations will only access the document hash of
the private data, not the data per se. The hash, thus,
is evidence of the transaction of the data and of its
ordering by the Order node.
This configuration of the architecture allows for
data governance, i.e., only specific organizations can
access certain data, and secrecy of shared informa-
tion. Also, the hash verifies the validity that a certain
transaction happened, without disclosing information.
Fabric CA. These mentioned functions are only
executed if the organization uses the HF Certificate
Authority (“Fabric CA”). The latter is responsible
for creating the digital identity (credentials) of each
member of an organization network, such as the nodes
types Peer and Orderer, and the clients of the appli-
cation. The credentials are issued by the Member-
ship Service Provider (MSP), which is an authorized
user responsible for issuing credentials to the network
members and creating affiliations and identities. The
use of these affiliations and the Organization Unity
(OU) of the digital certificate can create broad en-
dorsement policies and access to data.
Each organization in the Libra channel has its own
Fabric CA. This means that each company has auton-
omy and independence to issue its members’ digital
identity. Each digital identity has certain attributes
that follow the standard X.509 (Kinkelin et al., 2020),
such as: Common Name, which uses the corporate e-
mail; Organization, related to the companies that are
part of the Libra consortium (Petrobras, PPSA, Total,
Shell Brasil, CNPC or CNOOC), and Country.
Chaincode Server. The Chaincode Server is an
API that implements the integration between these
two applications: Client (i.e., BallotBR) and HF.
Moreover, another component, named Chaincode
Server, manages the user keys and issue the trans-
actions proposals or the submission of states to the
network to which the node is connected.
Furthermore, such server is agnostic to the Chain-
code. Its role is to abstract the transaction execution
and facilitate interaction with the Peer nodes. This is
made possible by the configuration archive, that con-
nects the different Channels which the Peers are as-
sociated. This simplifies IT activities and allows the
integration with different systems, being necessary
(i) the connection archive indicating the Peer nodes
and the Fabric CA; (ii) the user ID and password, is-
sued by the Fabric CA, necessary to obtain the keys;
(iii) the indication to the API of the transaction body,
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
238

including the names of the Channel, Chaincode, its
function and arguments, and/or private data (if any).
The API is responsible for validating digital iden-
tities and submissions of the transactions to the Libra
channel. Thus, the API plays an important role in the
authentication procedure and in confirming the eligi-
bility of the users that can participate of the BallotBR.
Challenges of the Architecture. HF has an in-
herent complexity related to its configuration. Before
implementing the network, it is necessary to define
what will be the network governance, such as: which
organizations will be part of the Channel; Certificate
Authorities creation (if each organization will have a
Fabric CA, or if only one Fabric CA will be consti-
tuted for the whole Channel); if an organization will
participate of the Channel of an Orderer; and which
Endorsement Policies will be implemented.
Moreover, creating a Channel can be done with
little complexity once the governance is defined.
However, once it is implemented, adding new par-
ticipants and updating the Endorsement Policies of
a Channel is still an operational challenge. Also,
managing different services that need to be integrated
raises traditional challenges of distributed networks
(i.e., communication, orchestrating containers, etc).
Finally, the deployment of this application allows
for the development of the Chaincode and how a
client application will interact with it, since all the
infrastructure details related to such application are
standardized by different applications. This allows
the allocation of time and effort to structure the con-
sortium organizations and how its applications will
interoperate with HF. Therefore, the blockchain layer
was essential to develop a verifiable, correct and se-
cure electronic voting system.
6 DISCUSSION
Generally, blockchain technology provides data in-
tegrity as, by definition, stored data are immutable.
Such technology supports append-only transactions
and creates a linked list of blocks identified by the
hash of such block. All blocks have the hashed in-
formation of the previous block. Hence, it enables
data integrity. Once the data is changed, its hash will
also be changed, which will generate an inconsistency
in the chain. This is a standard characteristic of all
blockchain solutions, either permissioned or not.
The permissioned blockchain allows the creation
of smaller networks and subgroups to share data.
Even though this approach is more susceptible to
availability issues, as it presents a smaller number of
nodes, other features are worth its usage. As a side
effect of this smaller network, the consensus mech-
anism performs better than the presented by public
blockchains. Moreover, the HF enables data gover-
nance, providing privacy management and creating
channels to share information between a specific sub-
set of participants.
Blockchain technology provides data availability.
As a subset of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
(Ølnes et al., 2017), all the information is distributed
among the participant nodes. Also, the possibility
of establishing data governance related to data access
and writing in the blockchain provides the necessary
secrecy in an enterprise consortium.
As an immutable distributed database, blockchain
technology also supports verifiability, which is neces-
sary to e-voting systems. Users can verify the trans-
actions in the blockchain without the need for a third
party. Moreover, such technology is a timekeeping
mechanism for the data structure, so the proof of data
history is easily reportable. Thus, the system correct-
ness and verifiability requirements were mitigated by
using permissioned blockchain and the system’s re-
quirements.
The blockchain layer, especially the Fabric CA,
plays an important role in authenticating user’s iden-
tity. This avoids the participation of an unauthorized
party in the resolution and offers a secure manner in
certifying who is eligible to participate. Also, the sys-
tem’s roles and their permission to interact in the Bal-
lotBR according to their responsibilities restrict unde-
sired and unauthorized behavior.
Blockchain immutability does not allow further
alterations of a registered transaction. Thus, the vote
can not be modified after it was cast. Even though
the system allows the participant to change its vote
throughout the resolution, once it is resolved, and all
votes are cast, the result is registered indefinitely and
irrevocably in the blockchain.
The technology also allows tracking users’ behav-
ior and actions in the BallotBR, i.e., creation of reso-
lution and notice, voting, etc, in a transparent and dis-
tributed manner. Additionally, the blockchain’s cryp-
tographic feature also allows participants to verify the
results and integrity of the votes individually.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper proposes BallotBR, an enterprise ballot
system implemented in a permissioned blockchain,
Hyperledger Fabric, applied to a company consor-
tium. The main contributions of this research are:
(i) the development of a permissioned blockchain-
A Blockchain-based Architecture for Enterprise Ballot
239

based architecture to enterprise ballot systems; (ii)
it is flexible enough to be applied to other contexts;
and (iii) it deals with the main security and trustwor-
thiness requirements of e-voting systems, due to its
architecture with the implementation of a blockchain
layer. Furthermore, we compared our enterprise so-
lution with related work approaches and revealed the
newly-developed features.
The developed architecture is modular and the de-
veloped API allows the BallotBR application layer to
be changed for other scenarios. Some limitations in-
clude: (i) the chosen scope, i.e., the Libra consortium
scenario; (ii) challenges related to vote anonymiza-
tion, as the consortium did not present any concern
on this issue; (iii) coercion issues were not expressly
dealt, (iv) interoperability issues may arise in the fu-
ture through the use of different blockchain platforms
(e.g., Corda, Ethereum), and (v) performance tests
were not available yet. Addressing these limitations is
the target of our future work. We also aim to develop
digital identity management applied to HF permis-
sioned blockchain systems as a complementary mod-
ule of BallotBR.
REFERENCES
Alonso, L. P., Gasco, M., del Blanco, D. Y. M., Alonso, J.
A. H., Barrat, J., and Moreton, H. A. (2018). E-voting
system evaluation based on the council of europe rec-
ommendations: Helios voting. IEEE Transactions on
Emerging Topics in Computing.
Alves, P. H. C., Paskin, R., Frajhof, I., Miranda, Y. R.,
Jardim, J. G., Cardoso, J. J. B., Tress, E. H. H.,
da Cunha, R. F., Nasser, R., and Robichez, G. (2020).
Exploring blockchain technology to improve multi-
party relationship in business process management
systems. In ICEIS (2), pages 817–825.
Carlotto, M. A., da Silva, R. C. B., Yamato, A. A., Trindade,
W. L., Moreira, J. L. P., Fernandes, R. A. R., Ribeiro,
O. J. S., Gouveia Jr, W. P., Carminati, J. P., Qicai, D.,
et al. (2017). Libra: A newborn giant in the brazilian
presalt province.
Clarkson, M. R., Chong, S., and Myers, A. C. (2008). Civ-
itas: Toward a secure voting system. In 2008 IEEE
Symposium on Security and Privacy (sp 2008), pages
354–368. IEEE.
Dagher, G., Marella, P., Milojkovic, M., and Mohler, J.
(2018). Broncovote: Secure voting system using
ethereum’s blockchain. pages 96–107.
Hardwick, F. S., Gioulis, A., Akram, R. N., and Markan-
tonakis, K. (2018). E-voting with blockchain: An
e-voting protocol with decentralisation and voter pri-
vacy. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on In-
ternet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing
and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber,
Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE
Smart Data (SmartData), pages 1561–1567. IEEE.
Hj
´
almarsson, F., Hreiarsson, G. K., Hamdaqa, M., and
Hj
´
almt
`
ysson, G. (2018). Blockchain-based e-voting
system. In 2018 IEEE 11th International Confer-
ence on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), pages 983–986.
IEEE.
Juels, A., Catalano, D., and Jakobsson, M. (2010).
Coercion-resistant electronic elections. In Towards
Trustworthy Elections, pages 37–63. Springer.
Kim, S. K., Ma, Z., Murali, S., Mason, J., Miller, A.,
and Bailey, M. (2018). Measuring ethereum network
peers. In Proceedings of the Internet Measurement
Conference 2018, pages 91–104.
Kinkelin, H., von Seck, R., Rudolf, C., and Carle, G.
(2020). Hardening x. 509 certificate issuance us-
ing distributed ledger technology. In NOMS 2020-
2020 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Manage-
ment Symposium, pages 1–6. IEEE.
Nasser, R. B., Lodi, C., Alves, P. H. C., Frajhof, I. Z., Mi-
randa, Y. R., Araujo, E. M. F., Silva, F. P. T., Vianna,
R., and Moreno, M. V. B. (2020). Distributed ledger
technology in the oil and gas sector: Libra ballot use
case. Rio Oil and Gas.
Ølnes, S., Ubacht, J., and Janssen, M. (2017). Blockchain in
government: Benefits and implications of distributed
ledger technology for information sharing.
Paskin, R., Jardim, J. G., Miranda, Y. R., Frajhof, I., Alves,
P. H. C., Miranda, F. P., Gama, C., Ladeira, R., Nasser,
R. B., and Robichez, G. (2020). Blockchain digital
signatures in a big corporation: a challenge for costs
management sector. Rio Oil and Gas.
Patil, H., Ladkat, P., Jituri, A., Desai, R., Shinde, D.,
et al. (2019). Blockchain based e-voting system.
Blockchain Based E-Voting System (May 18, 2019).
Pawlak, M., Poniszewska-Mara
´
nda, A., and Kryvinska,
N. (2018). Towards the intelligent agents for
blockchain e-voting system. Procedia Computer Sci-
ence, 141:239–246.
Pilkington, M. (2016). Blockchain technology: principles
and applications. In Research handbook on digital
transformations. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Silva, M. P. (2019). A seguranc¸a da democracia e a
blockchain. Estudos eleitorais: vol. 13, n. 3 (set./dez.
2018).
Specter, M. A., Koppel, J., and Weitzner, D. (2020). The
ballot is busted before the blockchain: A security anal-
ysis of voatz, the first internet voting application used
in us federal elections. In 29th {USENIX} Security
Symposium ({USENIX} Security 20), pages 1535–
1553.
Villalobos, K. M., Altamirano, C., and Chandra, R. (2019).
Blockchain voting : Implementation and analysis.
Yan, Z., Liu, J., and Liu, S. (2019). Dpwevote: differ-
entially private weighted voting protocol for cloud-
based decision-making. Enterprise Information Sys-
tems, 13(2):236–256.
ICEIS 2021 - 23rd International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
240
