
Knowledge Management for M&A Performance
Ksenija Lace and Marite Kirikova
Riga Technical University, Riga, Latvia
Keywords: Mergers & Acquisitions, Knowledge Management.
Abstract: This study focuses on knowledge management role in Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A). With high proportion
of M&A failure, it is important to define possible ways to increase M&A success rates. Knowledge acquisition
and management is the important part of M&A initiative, as it forms the foundation for M&A decisions. But
with M&A high complexity, uncertainty and ambiguity, effectively organized knowledge management of
M&A can become a challenge. In this article authors review current research on knowledge management in
general and M&A specific knowledge management, identify the levels of M&A knowledge hierarchy, namely
– individual M&A initiative scope, M&A initiatives in scope of one company, M&A initiatives in scope of
the same industry. For each level success factors and obstacles for the effective knowledge management are
defined. As a result, a proposal for M&A knowledge management high level framework is presented,
accumulating all knowledge management levels, and defining the knowledge structure and flow between them.
1 INTRODUCTION
Performance of Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
initiatives is a popular topic in the recent research. It
is noticed that proportion of so-called successful
M&A is relatively low and only third part of them is
later evaluated as positive change (Jie-mei, 2011).
One of the challenges for M&A is the ability to
transfer the knowledge about merging parties and
build on competences to make respective decisions
in a fast and efficient way, learn from the previous
M&A activities to make smarter decisions next time,
and learn from other companies experience to
not make the same mistakes (Jie-mei, 2011),
(Schumann & Tittmann, 2008). As an organizational
learning (accumulating, transferring and processing
knowledge) is a part of the effective knowledge
management, we can conclude that effective
knowledge management can contribute to the
overall M&A success (Vásquez-Bravo & Sánchez-
Segura & Medina-Domínguez & Amescua, 2014),
(Lohrkea & Frownfelter-Lohrkea & Ketchen, 2016).
But with M&A complexity, uncertainty and time
limitations, M&A knowledge management faces
known difficulties (Gruber & Paneva, 2014),
(Keizer, 2012).
This research explores how knowledge
management activities can be integrated in the scope
of M&A initiative, defines success factors and
obstacles that can impact M&A knowledge
management. As a result, several knowledge
management hierarchy levels are defined and M&A
knowledge management framework is proposed,
specifying knowledge management levels, activities,
and enabling factors. Research results can be used
later in the real-life M&A case studies.
In the next section each of knowledge
management levels is explored, current practices and
approach are summarized, success factors and
obstacles are identified, and framework architecture
is created. In the last section overall knowledge
management framework is described.
2 KNOWLEDGE LEVELS IN
M&A
With importance of learning in M&A projects, it is
crucial to inspect how knowledge transfer is
organized during specific M&A, as well as between
several linked M&A activities. This research analyzes
M&A knowledge management from the perspective
of the knowledge accumulating, transferring and
processing for learning on different hierarchical
M&A levels, which can be seen as M&A knowledge
management hierarchy levels (levels have been
obtained by amalgamating findings of 9 related
works) (see Figure 1):
Lace, K. and Kirikova, M.
Knowledge Management for MA Performance.
DOI: 10.5220/0010640100003064
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2021) - Volume 3: KMIS, pages 83-89
ISBN: 978-989-758-533-3; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
83

Level 1: Scope of each specific M&A initiative
- knowledge acquisition and integration during
the individual M&A activity (Jie-mei, 2011),
(Horie & Ikawa, 2014), (Eisenman &
Paruchuri, 2019);
Level 2: Scope of M&A initiatives for one
specific acquiring company - knowledge
processing during and after M&A for learning
and developing capabilities for future M&A
initiatives (Vieru & Rivard, 2012), (Zollo &
Singh, 2004), (Ellis & Lamont, 2004);
Level 3: Scope of M&A initiatives for different
acquiring companies – industry knowledge
accumulation and structuring to formalize
M&A processes (Wijnhovena & Spila &
Stegweea, 2006), (Hwang, 2004), (Ravikumar,
2017).
Figure 1: M&A knowledge management levels.
Effective knowledge management on each of
these levels, as well as well-established knowledge
transfer between these levels are key enablers for
M&A final success (Lodden, 2012). In the following
sections each of these levels is explored through the
following aspects based on the literature review:
What is the current knowledge management
approach and best practices on this level?
What are the success factors and obstacles
impacting effective knowledge management on
this level?
In the end, all findings are aggregated in the one
framework for knowledge management in the scope
of M&A activity set. This framework, in the further
research is intended to be applied across several
linked M&A initiatives to gather case study results
and cros-validate it in practice.
2.1 Knowledge Acquisition and
Integration during the M&A
Activity
The main goal for Level 1 is to integrate several
participants of the M&A. This level is the most
popular topic of the overall M&A research.
Knowledge management on this level covers the
following dimensions of the integration: (1) physical,
(2) cyber, (3) social. Many frameworks for M&A
organization are proposed (Ellis & Lamont, 2004),
(Wijnhovena & Spila & Stegweea, 2006), (Hwang,
2004), (Ravikumar, 2017), (Gasik, 2015), however
none of them looks on the M&A from the joint socio-
cyber-physical perspective.
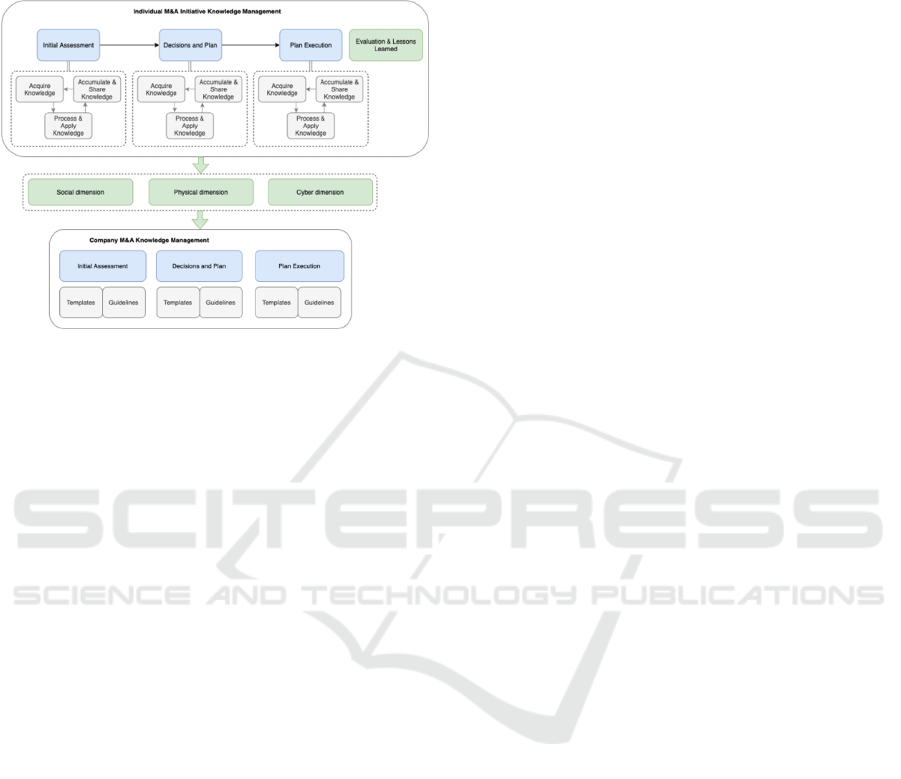
2.1.1 Proposed Approach
This knowledge management level is focused on
specific M&A initiative execution, and can be seen as
the following sequential activities (Chua & Goh,
2009), (Horie & Ikawa, 2012):
Initial assessment of the M&A participants;
Decisions on M&A approach and M&A
execution plan;
Execution of M&A plan, including partners
reorganization and knowledge integration.
Each of these activities consists of the following
knowledge management tasks with the goal also to
transfer the gathered or created knowledge to the next
activity (Chua & Goh, 2009), (Horie & Ikawa, 2012)
(see Figure 2):
Acquire knowledge about the M&A initiative,
as well as about merging parts;
Process and apply knowledge to make
decisions about M&A and define future state;
Accumulate and share knowledge to support
effective decision execution.
Figure 2: M&A knowledge management on an individual
initiative level.
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
84

2.1.2 Success Factors and Obstacles
There are several important factors, required for the
efficient knowledge management on this level (Jie-
mei, 2011), (Horie & Ikawa, 2012):
As each merging part shoud be pereceived as a
complex socio-cyber-physical system, all three
dimensions of the integration should be
covered as interrelated: social, physical and
cyber;
As it is extremely important to support cultural
merge and take only the best from all merging
parts - acquiring organization should
understand and respect and importance to learn
from acquired organization;
As for keeping engagement and motivation
high in both merging parts - acquired
organization should be encouraged to share the
opinions and should be involved in decision
making;
As for keeping the transparency and alignment
between all involved participants - acquiring
organization is interested to share knowledge
with acquired organization, especially if
reorganization and optimization is planned;
For the same reason knowledge should be
communicated properly between management
and execution levels of M&A project
participants (meaning - between process
planning and execution phases);
As it is important to base decisions on an actual
and complete facts about M&A initiative and
current state of merging parts - explicit
knowledge should exist and acquisition of
tactic knowledge should be properly planned
prior any decisions about M&A execution.
As can be noticed, success factors are related to
acquiring company’s culture and attitude to the
knowledge management, as well as with acquired
company motivation. But important prerequisites are
also availability of explicit knowledge.
There are also M&A specific factors, that can
negatively impact knowledge management efficiency
(Gruber & Paneva, 2014), (Lodden, 2012):
M&A complexity requires proper resource
allocation on in-depth investigation and
analysis of the current state before future state
definition;
As M&A uncertainty and unpredictability can
block the ability to gather knowledge upfront,
knowledge acquisition should be planned as an
integrated part of decision-making during
M&A execution;
M&A project time constraints usually do not
allow to spend required effort on knowledge
management. With that, predefined knowledge
management process, as well as reused
knowledge management assets from the
previous M&A initiatives could help to
optimize required resources.
These factors can be addressed by accumulating
experience and reusable knowledge in the previous
M&A initiatives. This ability is directly related to the
next M&A knowledge management level.
2.2 Knowledge Processing during and
after M&A for Learning and
Developing Capabilities for Future
M&A Initiatives
As M&A is one of the commonly used tools for
growth, often there is a sequence of M&A projects in
a company. As with any repeating process, it is good
to have lessons learned and best working practices
accumulated from the individual M&A initiatives,
that can be reused in the upcoming M&As. Research
of knowledge management on this (second) level is
not as frequent as on the M&A activity in general.
Main reasons for that are that each M&A is often
assumed to be unique (meaning – previous practice is
not applicable), as well as the fact that M&A can take
long time for accomplishing and evaluating the
results (meaning the next M&A activity can be started
before it is clear what worked and what did not in the
previous projects).
2.2.1 Proposed Approach
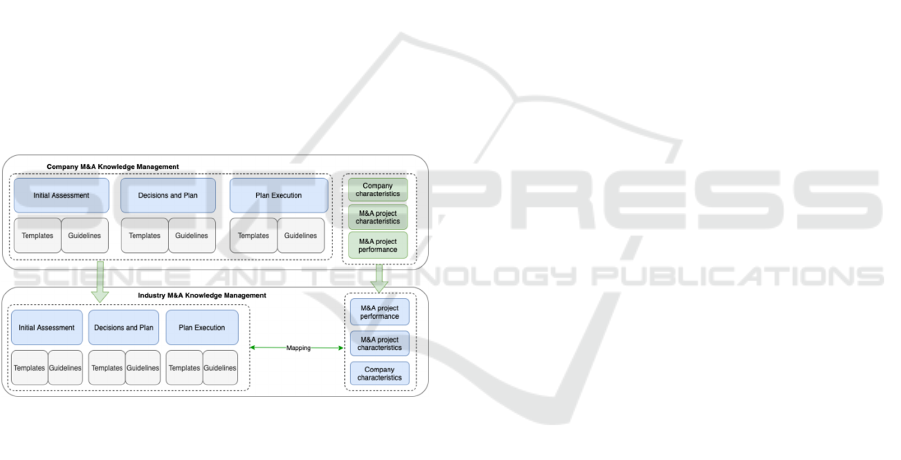
Aggregated M&A knowledge can be shared using
several approaches (see Figure 3):
Artefacts produced during previous M&A
projects, can be used in the future projects as
source of inspiration and reusable information.
Basically, the artefacts, created during each
phase of the individual M&A initiative, are
reused in the future projects;
The use of templates and guidelines created
based on the previous M&A lessons learned.
Lessons learned can be incorporated in the
individual M&A initiative as part of the process
(for example, retrospective after each phase),
or can be organized as a separate activity after
the project competition.
Knowledge Management for MA Performance
85
Artefact and template applicability for future
projects usually is evaluated subjectively by specific
executor (Eisenman & Paruchuri, 2019), (Lohrkea &
Frownfelter-Lohrkea & Ketchen, 2016).
Figure 3: M&A knowledge transfer between individual
M&A level and company level.
2.2.2 Success Factors and Obstacles
There are the following prerequisites for M&A
experience gathering and learning (Horie & Ikawa,
2012), (Morrison & James, 2002):
As already stated previously, all acquired
knowledge should cover three dimensions of
merging parts: social, cyber and physical, as
well as interrelationships between them;
To have clear responsibilities on M&A
knowledge sharing, dedicated M&A team in
the organization should be allocated on sharing
M&A experience across the organization;
As M&A previous experience is mentioned as
one of M&A success factors, individual M&A
initiative project team should be capable in
producing and sharing the knowledge about
M&A results;
This team also should have enough motivation
and planned time to share the knowledge
accumulated during the project and promote it
across the company and with future M&A
project teams;
For more efficient knowledge sharing, M&A
evaluation process should be established,
helping to identify similarities across several
M&A approaches and structure the M&A
knowledge to find relevant parts for the future
M&A initiative more easily. Otherwise,
applied inappropriately, previous knowledge
can compromise the usefulness of the
accumulated M&A knowledge.
Several M&A limitations can negatively impact
the learning process (Horie & Ikawa, 2014), (Zollo &
Singh, 2004):
As M&A is time limited, there should be well
defined balance which knowledge should be
documented, to which extent, and how it should
be populated;
It can take time to see and evaluate M&A
results, thus not always it is possible to foresee
which practices are successful or not.
These limitations can be addressed by
accumulating M&A knowledge on the industry level,
which is described in the next section.
2.3 Knowledge Accumulation and
Structuring to Formalize M&A
Processes
The third knowledge management level is focused on
the accumulating and aggregating knowledge from
several similar M&A initiatives (like same industry,
same acquisition size, same constraints, etc.) and
creating framework for the M&A knowledge
management organization. Research on this level is
very limited. Together with issues already mentioned
on the previous level (company level), Level 3
additionally faces issues related to the information
privacy.
2.3.1 Proposed Approach
Currently there is no any publicly available M&A
knowledge management framework, which would
accumulate best practices for different M&A
initiatives and would structure these practices per
M&A specific parameters, allowing to choose
appropriate practices for each specific M&A project.
However, there are many described M&A case
studies, which can be analyzed and processed to
extract best practices, guidelines and templates to be
used on the industry level of M&A knowledge
management (see Figure 4) (Jie-mei, 2011), (Horie &
Ikawa, 2014), (Eisenman & Paruchuri, 2019), (Zollo
& Singh, 2004).
In order to structure available case studies, the
classification of different M&A initiative types
should be introduced. There are already several
attempts to classify M&A initiatives and define
specific M&A process parameters, that can have an
impact on the overall project success (Ellis &
Lamont, 2004), (Hwang, 2004), (Ravikumar, 2017).
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
86
Some knowledge management efficiency related
parameters are (Ellis & Lamont, 2004), (Gruber &
Paneva, 2014):
Acquired company resource quality and
relatedness to acquiring company;
Differences and geographical distance between
acquisition parties;
The scope and depth of an integration and the
level of management replacement;
Documented integration knowledge
experience.
Still, the parameter list can be expanded to support
the variety of case studies, and a holistic model of
possible M&A characteristics could be established, as
well as M&A taxonomy could be created.
Nevertheless, for managing M&A complexity issue,
only knowledge management relevant characteristics
should be selected.
Additionally, more detailed M&A performance
criteria could be established, as different M&A may
have different goals and priorities and they have
direct impact on required knowledge management
activities.
Figure 4: M&A knowledge transfer between company level
and industry level.
2.3.2 Success Factors and Obstacles
There are several key success factors, enabling the
development of one common M&A knowledge
management process (Ellis & Lamont, 2004),
(Gruber & Paneva, 2014), (Keizer, 2012), (Lodden,
2012):
All three dimensions are represented also on
this level: social, cyber and physical;
As a lot of corporate knowledge stays inside the
specific companies and does not become
publicly shared, close collaboration between
researchers and industry is required, allowing
to access and process M&A experience
knowledge and transform it into publicly
available artefacts;
But as a lot of M&A knowledge is a subject of
limited access information, there should be
specific process how researchers can access
and use M&A knowledge and create publicly
available meta knowledge about M&A
projects.
There are several obstacles currently hindering
future research (Ellis & Lamont, 2004), (Gruber &
Paneva, 2014), (Keizer, 2012), (Lodden, 2012):
Some information about M&A projects still has
strictly limited access rights and will not be
available for external researchers;
Currently there is no taxonomy of different
M&A approaches, neither there are any
established standard M&A frameworks. Often
acquiring organization is developing its own
specific M&A approach, which later is hardly
comparable with approaches developed by
other organizations;
With M&A initiatives complexity and scope, it
is problematic to find correlations between
M&A characteristics, applied knowledge
management approach and M&A results.
To mitigate these obstacles, at least to some
extent, the integrated M&A knowledge management
framework is proposed in the next section.
3 M&A KNOWLEDGE
MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
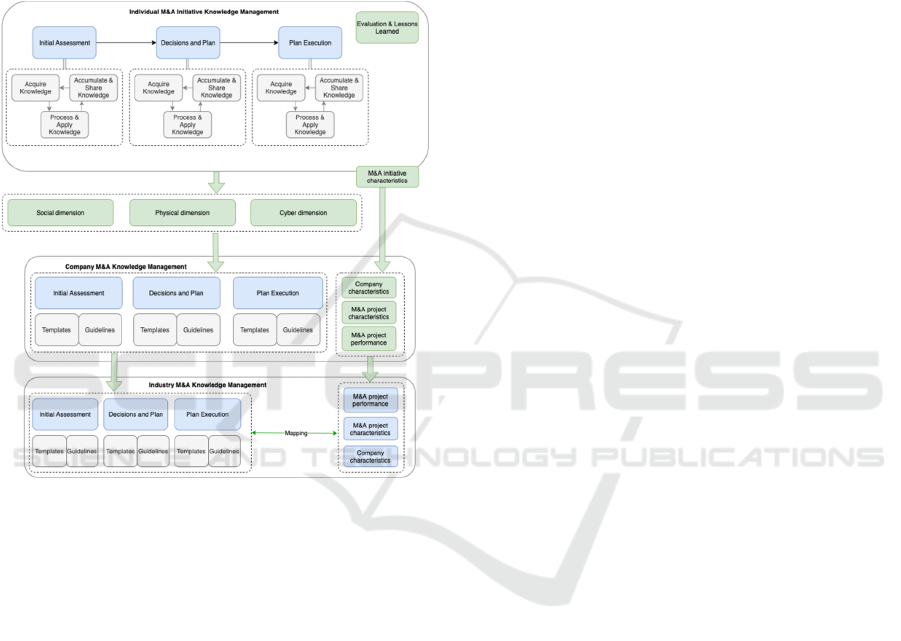
M&A knowledge management levels together with
corresponding success factors and obstacles,
discussed in Section 2, form the proposed M&A
knowledge management framework with a purpose to
accumulate and share gathered knowledge and
improve M&A performance.
The framework illustrates how M&A knowledge,
covering all social, cyber and physical perspectives,
is gathered in the scope of one individual activity; is
transferred to the company level, where company
specific M&A experience is accumulated; and then
how company level M&A knowledge can be
aggregated into industry level M&A knowledge (see
Figure 5).
The framework represented in Figure 5
corresponds to the quality parameters that should be
present in any proposed reference model (Taylor &
Sedera, 2003). All these quality parameters can be
Knowledge Management for MA Performance
87
divided into three main quality aspects reviewed
below.
One quality aspect is a syntactic quality, related to
a language used in the model. From this perspective,
the model has both clear structure and clear language.
Model notation includes data structures and data
flow, represented by graphical elements commonly
used for data modelling. Definitions used in the
model are aligned with ones used in the M&A
scientific research.
Figure 5: M&A knowledge management framework.
Another quality aspect is a semantic quality,
related to a domain coverage in the model. Model
incorporates M&A domain and knowledge
management domain principles. Several hierarchical
knowledge management levels specific for M&A
initiatives is an important topic for both domains.
Despite the novelty of the structural hierarchy of KM
levels, the model still is easy to understand for all
M&A practitioners and does not require additional
trainings or clarifications.
And one more quality aspect is pragmatic quality,
linked to the fact how effectively the model can be
interpreted by the audience and applied in practice.
Two important specific quality parameters here are
pragmatics (accessibility and applicability) and
feasibility (economical efficiency). Analysis of these
quality characteristics are the matter of further
research as it requires the data gathered in rela world
applications of the proposed framework.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we highlighted the importance of M&A
knowledge management for overall M&A initiative
success. We reviewed and proposed models for
different hierarchy levels of M&A knowledge
management – specific M&A initiative level,
organizational learning between M&A initiatives,
cross organizational M&A knowledge management.
For each of the levels current practices were analyzed,
success factors and obstacles defined. Based on this,
and also, for M&A experience accumulation, overall
M&A knowledge management framework was
proposed that incorporates all three knowledge
management levels. This framework can help in
M&A knowledge management as it represents the
experience and scientific evidences in this area in a
structured and conceptually clear manner. It takes
into account three essential perspectives: social, cyber
and physical ones, combination of which becomes
more and more important in todays M&As. As a
future work, framework can be elaborated in more
details and the model of M&A specific knowledge
management can be created. Additionally, the
framework should be applied to real M&A initiatives
and potential improvements should be identified.
REFERENCES
Vieru, D., & Rivard, S. (2012, January). Working under
grey skies: Information systems development and
organizational identity in a post-merger context.
In 2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on
System Sciences (pp. 5267-5276). IEEE.
Chua, A. Y., & Goh, D. H. (2009). Why the whole is less
than the sum of its parts: Examining knowledge
management in acquisitions. International Journal of
Information Management, 29(1), 78-86.
Jie-mei, Z. (2011, August). The knowledge integration
strategy analysis after Geely acquisition of Volvo.
In 2011 2nd International Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, Management Science and Electronic
Commerce (AIMSEC)(pp. 3504-3507). IEEE.
Schumann, C. A., Tittmann, C., & Tittmann, S. (2008,
September). Merger of knowledge network and users
support for lifelong learning services. In IFIP World
Computer Congress, TC 3 (pp. 149-152). Springer,
Boston, MA.
Vásquez-Bravo, D. M., Sánchez-Segura, M. I., Medina-
Domínguez, F., & Amescua, A. (2014). Knowledge
management acquisition improvement by using
software engineering elicitation techniques. Computers
in Human Behavior, 30, 721-730.
Horie, N., & Ikawa, Y. (2014, July). Knowledge integration
in a product development organization for new
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
88

businesses: A case study of a precision device
manufacturer. In Proceedings of PICMET'14
Conference: Portland International Center for
Management of Engineering and Technology;
Infrastructure and Service Integration (pp. 1834-1840).
IEEE.
Eisenman, M., & Paruchuri, S. (2019). Inventor knowledge
recombination behaviors in a pharmaceutical merger:
The role of intra-firm networks. Long Range
Planning, 52(2), 189-201.
Zollo, M., & Singh, H. (2004). Deliberate learning in
corporate acquisitions: post‐acquisition strategies and
integration capability in US bank mergers. Strategic
management journal, 25(13), 1233-1256.
Horie, N., & Ikawa, Y. (2012, July). Adverse factors of
knowledge integration in a product development
organization after M&A: A case study of a precision
device manufacturer. In 2012 Proceedings of
PICMET'12: Technology Management for Emerging
Technologies (pp. 2570-2576). IEEE.
Morrison, M. J., & James, A. D. (2001, July). The role of
dedicated integration teams in the post-merger
management of technology. In PICMET'01. Portland
International Conference on Management of
Engineering and Technology. Proceedings Vol. 1:
Book of Summaries (IEEE Cat. No. 01CH37199) (Vol.
1, pp. 12-13). IEEE.
Morrison, M. J., & James, A. D. (2001, July). The role of
dedicated integration teams in the post-merger
management of technology. In PICMET'01. Portland
International Conference on Management of
Engineering and Technology. Proceedings Vol. 1:
Book of Summaries (IEEE Cat. No. 01CH37199) (Vol.
1, pp. 12-13). IEEE.
Ellis, K. M., & Lamont, B. T. (2004). “Ideal” acquisition
integration approaches in related acquisitions of
equals: A test of long-held beliefs. In Advances in
mergers and acquisitions. Emerald Group Publishing
Limited.
Wijnhoven, F., Spil, T., Stegwee, R., & Fa, R. T. A. (2006).
Post-merger IT integration strategies: An IT alignment
perspective. The Journal of Strategic Information
Systems, 15(1), 5-28.
Lohrke, F. T., Frownfelter-Lohrke, C., & Ketchen Jr, D. J.
(2016). The role of information technology systems in
the performance of mergers and acquisitions. Business
Horizons, 59(1), 7-12.
Hwang, M. (2014). Integrating Enterprise Systems in
Mergers and Acquisitions. In: 10th Americas
Conference on Information Systems, AMCIS 2004,
New York, USA, August 6–8, 2004, vol. 12, pp. 62–66.
Ravikumar, N. (2017, June). Post-Merger IS Integration:
Influence of Process Level Business-IT Alignment on
IT-based Business Value. In Proceedings of the 2017
ACM SIGMIS Conference on Computers and People
Research (pp. 195-196).
Paneva, I., & Gruber, J. (2014). The process of knowledge
transfer in mergers and acquisitions: A single-case
study of a Swedish manufacturing organization.
Keizer, M. (2012). A knowledge integration approach
within acquisitions: how to deal with innovative
acquired firms? Master's thesis, University of Twente.
Lodden, I. (2012). Knowledge transfer in mergers and
acquisitions: a case analysis of CISCO. Master's thesis,
Universitetet i Agder; University of Agder.
Gasik, S. (2015).
An analysis of knowledge management in
PMBOK® guide. PM World Journal, 4(1), 1-13.
Taylor, C., & Bandara, W. (2003). Defining the quality of
business process reference models. In Proceedings of
the 14th Australasian Conference on Information
Systems (pp. 1-10). Edith Cowan University.
Knowledge Management for MA Performance
89
