
Stacking BERT based Models for Arabic Sentiment Analysis
Hasna Chouikhi
1
, Hamza Chniter
2
and Fethi Jarray
1,2 a
1
LIMTIC Laboratory, UTM University, Tunisia
2
Higher Institute of Computer Science of Medenine, Tunisia
Keywords:
Arabic Sentiment Analysis, BERT Models, Stacking Approach, Large Scale Dataset.
Abstract:
Recently, transformer-based models showed great success in sentiment analysis and were considered as the
state-of-the-art model for various languages. However, the accuracy of Arabic sentiment analysis still needs
improvements. In this work, we proposed a stacking architecture of Arabic sentiment analysis by combing
different BERT models. We also create a large-scale dataset of Arabic sentiment analysis by merging small
publicly available datasets. The experimental study proves the efficiency of the proposed approach in terms of
classification accuracy compared to single model architecture.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sentiment Analysis (SA) is a Natural Language Pro-
cessing (NLP) research field that spotlights on look-
ing over people’s opinions, sentiments, and emo-
tions. SA techniques are categorized into symbolic
and sub-symbolic approaches. The former use lexi-
cal and ontologies (Dragoni et al., 2018) to encode
the associated polarity with words and multi-word
expressions. The latter consist of supervised, semi-
supervised and unsupervised machine learning tech-
niques that perform sentiment classification based on
word co-occurrence frequencies. Among all these
techniques, the most popular are based on deep neu-
ral networks. Some hybrid frameworks leverage both
symbolic and sub-symbolic approaches. SA can be
seen as a multi-step process including data retrieval,
data extraction, data pre-processing, and feature ex-
traction. The ultimate subtasks of sentiment clas-
sification allow three types of classification: polar-
ity classification, intensity classification, and emo-
tion identification. The first type classifies the text
as positive, negative or neutral, while the second type
identifies the polarity degree as very positive, posi-
tive, negative or very negative. The third classification
identifies the emotion such as sadness, anger or hap-
piness. Practically, Arabic language has a complex
nature, due to its ambiguity and rich morphological
system. This nature associated with various dialects
and the lack of resources represent a challenge for the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5110-1173
progress of Arabic sentiment analysis research. The
major contributions of our present work are:
• Creating a large-scale sentiment Arabic datasets
(LargeASA) for Arabic sentiment analysis’s task.
• Using an adjusted model ASA Medium BERT.
• Designing a new staking approach (also known
as Stacked Generalization ) for Arabic Sentiment
Analysis by combing three BERT based models
(Arabic-BERT (Safaya et al., 2020), AraBERT
(Antoun et al., 2020) and mBERT (Jacob et al.,
2019)).
2 RELATED WORK
The learning based approaches of ASA can be classi-
fied into two categories : classical machine learning
approaches, and deep learning approaches.
2.1 Classical Machine Learning
Approaches for ASA
Machine learning (ML) methods have broadly been
used for sentiment analysis. ML addresses senti-
ment analysis as a text classification problem. Many
approaches such as support vector machine (SVM),
maximum entropy (ME), naive Bayes (NB) algo-
rithm, and artificial neural networks (ANNs) have
been proposed to handle ASA. NB and SVM are
144
Chouikhi, H., Chniter, H. and Jarray, F.
Stacking BERT based Models for Arabic Sentiment Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0010648400003064
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2021) - Volume 2: KEOD, pages 144-150
ISBN: 978-989-758-533-3; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

the most commonly exploited machine learning algo-
rithms for solving the sentiment classification prob-
lem (Imran et al., 2018) Al-Rubaiee et al. (Al-
Rubaiee et al., 2016) performed polarity classifica-
tion, and rating classification by using SVM, MNB,
and BNB. They achieved 90% accuracy polarity clas-
sification and 50% accuracy rating classification.
2.2 Deep Learning Approaches for ASA
Using DL is less abandoned in Arabic SA than in
English SA. (Socher et al., 2013) proposed an RNN
(Recurrent neural network) based approach which is
trained on a constructed sentiment treebank and im-
proved the sentence-level sentiment analysis on En-
glish datasets. (Rangel et al., 2019) used CNN model
for SA tasks and a Stanford segmenter to perform
tweets tokenization and normalization. They used
Word2vec for word embedding with ASTD datasets.
(Alhumoud et al., 2015a) used a LSTM-CNN
model with only two unbalanced classes (Positive and
negative) among four classes (objective, subjective
positive, subjective negative, and subjective mixed)
form ASTD.
Since its appearance in 2018, many pretrained ver-
sions of BERT (Devlin et al., 2018) has been pro-
posed for sequence learning such as ASA. The recent
trend in sentiment analysis is based on BERT repre-
sentation. Let’s briefly describe and remind BERT
and the different versions that handle Arabic texts.
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers) is pre-trained by conditioning on both
left and right context in all layers, unlike previous lan-
guage representation models. Applying BERT to any
NLP task needs only to fine-tune one additional out-
put layer to the downstream task (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: BERT based architecturefor ASA.
The multilingual BERT (mBERT) (Jacob et al.,
2019) model is trained on many languages including
Arabic and it serves as a universal language modeling.
(ElJundi et al., 2019) developed an Arabic spe-
cific universal language model (ULM), hULMonA.
They fine tune mBERT ULM for ASA. They col-
lected a benchmark dataset for ULM evaluation with
sentiment analysis. (Safaya et al., 2020) proposed
ArabicBERT which is a set of pre-trained trans-
former language models for arabic language. They
used a base version of arabic BERT model (bert-base-
arabic). (Antoun et al., 2020) created AraBERTv02
based on the BERT model. It was trained on Arabic
corpora consisting of internet text and news articles
of (8.6B tokens). (Lan et al., 2020) introduced Gi-
gaBERTv3 which is a bilingual BERT for English
and Arabic. It was pre-trained on a large corpra
(Gigaword, Oscar and Wikipedia). (Abdul-Mageed
et al., 2020) designed MARBERT and ArBERT.
Both are built based on the BERT-based model ex-
cept for MARBERT. ArBERT was trained on a col-
lection of Arabic datasets which are mostly books and
articles written in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA).
While MARBERT trained both Dialectal (DA) and
MSA tweets, it does not output the next sentence pre-
diction (NSP) objective as it is trained on short tweets.
Additionally, MARBERT and ArBERT were experi-
mented on the ArSarcasm dataset (Farha and Magdy,
2020). Finally (Abdelali et al., 2021) trained QARiB
(QCRI Arabic and Dialectal BERT) on a collection of
Arabic tweets and sentences of text written on MSA.
3 PROPOSED APPROACHES
In this paper, we realised a stacked generalization
BERT model by stacking designing training a meta
learning algorithm to combine the predictions of
three BERT models dedicated to the Arabic language
(Arabic-BERT, mBERT and AraBERT).
The Data pipeline consists of the following steps:
• We first apply tokenization to break up the input
texts into tokens. Figure 2 presents the result of
Arabic-BERT and mBERT tokenizers applied to
an example sentence (S). We observe that Arabic-
BERT tokenizer is more appropriate for Arabic
because it considers the characteristic of Arabic
morphology.
• Afterward, we convert each text to a BERT’s for-
mat by adding the special [CLS] token at the be-
ginning of each text and [SEP] token between sen-
tences and the end;
Stacking BERT based Models for Arabic Sentiment Analysis
145
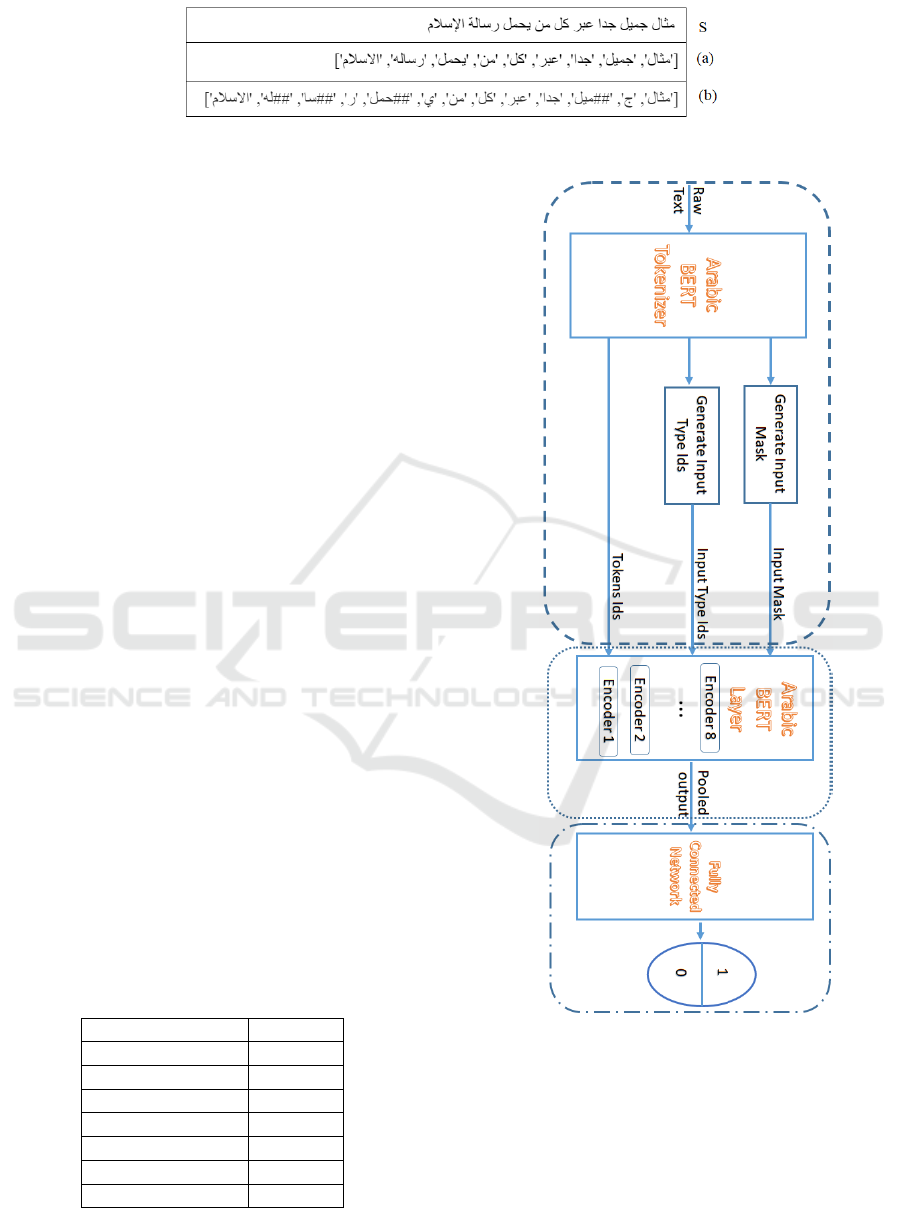
Figure 2: Comparison between Arabic BERT (a) and mBERT (b) tokenizer.
• We map each token to an index based on the pre-
trained BERT’s vocabulary.
3.1 ASA based on Arabic BERT Model
(ASA-medium BERT)
In this section, we propose an ASA based on the
Arabic BERT model. As mentioned on the orig-
inal paper, Arabic BERT is delivered in four ver-
sions: bert-mini-arabic, bert-medium-arabic, bert-
base-arabic and bert-large-arabic. We applied a grid
search strategy to find the best Arabic BERT ver-
sion with the best hyperparameters (Chouikhi et al.,
2021) . Table 1 represents hyper-parameters of Arabic
BERT for ASA used after our fine-tuning. We used
the AJGT dataset (Alomari et al., 2017) as a testing
dataset.
Among all cited works, the approach of Ali Safaya
(Safaya et al., 2020) is the closest to our approach.
Figure 3 depicts the proposed architecture for ara-
bic SA. Our architecture is composed of three blocks.
The first block describes the text pre-processing step
where we used an arabic BERT tokenizer to split
the word into tokens. Second block is the training
model. Arabic BERT model is used with only 8 en-
coder (Medium case (Safaya et al., 2020)). The out-
put of last four hidden layers is concatenated to get
a size representation vector 512x4x128 with 16 batch
size. The pooling operation’s output is concatenated
and flattened to be later on crossed a dense layer and
a Softmax function to get the final label. Third block
is about the classifier where we used a dropout layer
for some regularization and a fully-connected layer
for our output.
Table 1: Hyper-parameters of ASA-medium BERT.
Hyper-parameters Value
Batch-size 16
dropout 0.1
Max length 128
Hidden size 512
lr 2e-5
Optimizer AdamW
Epochs 10/20/50
Figure 3: ASA-medium BERT architecture.
Table 1 displays the hyperparameters of the pro-
posed model. The overall model is trained by AdamW
optimizer. We note that with hyperparameters opti-
mization by grid search strategy, we outperform the
approach of (Safaya et al., 2020).
Table 2 explain the architectural differences be-
tween ASA-medium BERT model, Arabic BERT
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
146

Table 2: Architectural differences between ASA-medium BERT, AraBERT and Arabic BERT models.
Batch-size Epochs Layers Activation function
ASA-medium BERT 16 5 8 Softmax
Arabic BERT (Safaya et al., 2020) 16/32 10 12 ReLU
AraBERT (Antoun et al., 2020) 512/128 27 12 Softmax
(Safaya et al., 2020) and AraBERT (Antoun et al.,
2020) ones. It shows that with an Arabic tokenizer
the number of encoders in the Arabic BERT model
influences the accuracy value.
3.2 Stacking BERT based Model for
ASA
A Stacking model is a hierarchical model ensemble
framework in which the predictions, generated by us-
ing various machine learning base modes, are used as
inputs for a meta-model. The objective of the meta-
model is to optimally combine the base model pre-
dictions to form a new classifier. In this work we
used Medium Arabic BERT (Safaya et al., 2020),
AraBERT (Antoun et al., 2020) and mBERT (Jacob
et al., 2019) as base model and a fully connected layer
as a meta-model (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Stacking BERT based model for ASA.
In the experiment section, we will envisage three
stacking scenarios: auto stacking of each BERT, pair-
wise stacking, and entire stacking of the three BERT
models.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
4.1 Datasets
In this paper we perform experiments on three avail-
able datasets HARD, LABR and AJGT (Table 3). All
were split into two subsets: 80% for training, and 20%
for testing.
• Hotel Arabic Reviews Dataset (HARD) (Elnagar
et al., 2018) contains 93,700 reviews. Each one
has two parts: positive comments and negative
comments. It covers 1858 hotels contributed by
30889 users.
• Large-scale Arabic Book Reviews (LABR) (Aly
and Atiya, 2013) contains over 63,000 book re-
views in Arabic.
• Arabic Jordanian General Tweets (AJGT) (Alo-
mari et al., 2017) contains 1,800 tweets annotated
as positive and negative.
• Large scale Arabic Sentiment Analyis
(LargeASA). We agragate HARD, LABRR,
and AJGT datasets into a large corpus for ASA.
This dataset is publicly available upon request.
Table 3: Statistics of used datasets.
Dataset Samples Labels
LABR 63,000 positive / negative
HARD 93,700 positive / negative
AJGT 1,800 positive / negative
LargeASA 158,500 positive / negative
Table 4 indicates the variation of the accuracy
value according to the used method and datasets. It
shows that we have a competition between our model
(ASA-medium BERT) and (Antoun et al., 2020) one.
Our model gives the best result for LABR, AJGT
and ArsenTD-Lev ((Baly et al., 2019)) datasets; while
(Antoun et al., 2020) works give the best result with
ASTD and HARD datasets. We found a slight dif-
ference in the accuracy value between the two works
( 92,6% compared to 91% for ASTD dataset ((Nabil
et al., 2015)) and 86,7% compared to 87% for LABR
datasets). However, our model gives a very good re-
sult with ArsenTD-Lev dataset (75% compared to an
Stacking BERT based Models for Arabic Sentiment Analysis
147

Table 4: Comparison between ASA-medium BERT and the previous ASA approaches.
Model \Dataset AJGT LABR HARD ASTD ArsenTD-Lev
CNN(Ghanem et al., 2019) - - - 79% -
LSTM (Shoukry and Rafea, 2012) - 71% - 81% -
LSTM-CNN (Alhumoud et al., 2015b) - - - 81% -
CNN-CROW(Eskander and Rambow, 2015) - - - 72.14% -
DE-CNN-G1(Dahou et al., 2019) 93.06% - - 82.48% -
LR(Harrat et al., 2019) - 84.97% - 87.10% -
GNB(Harrat et al., 2019) - 85% - 86% -
SVM(Aly and Atiya, 2013) - 50% - - -
Arabic-BERT base - - - 71.4% 55.2%
hULMonA (ElJundi et al., 2019) - - 95.7% 69.9% 52.4%
AraBERT 93.8% 86.7% 96.2% 92.6% 59.4%
mBERT 83.6% 83% 95.7% - -
ASA-medium BERT 96.11% 87% 95% 91% 75%
Table 5: Comparison between the base models.
Model \Dataset AJGT LargeASA LABR HARD
ASA-medium BERT 96.11% 90% 87% 95%
mBERT 83.6% 83% 85% 95.7%
AraBERT 93.8 % 85% 86.7% 96.2 %
Table 6: Auto stacking base models.
Model \Dataset AJGT LargeASA LABR HARD
ASA-medium BERT x2 94% 90 % 90% 96%
mBERT x2 83% 86% 87% 95%
AraBERT x2 77 % 87 % 86% 96%
Table 7: Pairwise Stacking BERT models.
Model \Dataset AJGT LargeASA LABR HARD
ASA-medium BERT+ mBERT 94% 90% 90 % 96 %
ASA-medium BERT+ AraBERT 90% 90 % 88% 96 %
mBERT + AraBERT 78 % 88% 88% 95%
accuracy value that does not exceed 60% with others
models).
Table 5 shows a comparison between the three
base models that are used in the stacking approach. It
shows that Medium Arabic BERT is the most perfor-
mant and mBERT is the less performant. We will en-
visage different stacking strategies of these base mod-
els to strengthen them.
4.2 Auto Stacking Strategy
We aim to strengthen each base model by stacking it
with its self. The numerical results are displayed in
Table 6. By cross comparing Table 5 and Table 6, we
conclude that performance of the model did not im-
proved by auto stacking a model with itself. This is
may be due to the fact that we have only small num-
ber of classes; positive and negative and it may be
interesting to check the efficiency of auto stacking for
large number of classes such as the sentiment analysis
with intensity.
4.3 Pairwise Stacking Strategy
In this set of experiments, we stack the base models in
a pairwise manner. Table 7 details the results obtained
by applying two different models. It shows that the
other BERT based model can be strengthen by stack-
ing them with ASA-medium BERT .
4.4 Complete Stacking Strategy
Finally, we completely stack the three base models:
Arabic BERT, AraBERT and mBERT (see Table 8).
From all the stacking scenarios, we conclude that the
best way is to autostack ASA-medium BERT with it
self.
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
148

Table 8: Complete Stacking BERT models.
Model \Dataset AJGT LargeASA LABR HARD
ASA-medium BERT+ mBERT +AraBERT 93% 91% 88% 95%
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we proposed a stacked generalization
approach for Arabic sentiment analysis. We have
used Medium Arabic BERT, AraBERT and mBERT
as base models. Firstly, we proved that by implement-
ing a single arabic medium BERT model we outper-
form the state of the art for ASA. Secondly, the ex-
periment results showed that the stacking strategy im-
proves the accuracy. As a continuity of this contribu-
tion, we plan to generalize our results to the sentiment
analysis with intensities case.
REFERENCES
Abdelali, A., Hassan, S., Mubarak, H., Darwish, K.,
and Samih, Y. (2021). Pre-training bert on ara-
bic tweets: Practical considerations. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2102.10684.
Abdul-Mageed, M., Elmadany, A., and Nagoudi, E. M. B.
(2020). Arbert & marbert: Deep bidirectional trans-
formers for arabic. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.01785.
Al-Rubaiee, H., Qiu, R., and Li, D. (2016). Identifying
mubasher software products through sentiment analy-
sis of arabic tweets. In 2016 International Conference
on Industrial Informatics and Computer Systems (CI-
ICS), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Alhumoud, S., Albuhairi, T., and Alohaideb, W. (2015a).
Hybrid sentiment analyser for arabic tweets using r.
In 2015 7th International Joint Conference on Knowl-
edge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowl-
edge Management (IC3K), volume 1, pages 417–424.
IEEE.
Alhumoud, S., Albuhairi, T., and Alohaideb, W. (2015b).
Hybrid sentiment analyser for arabic tweets using r.
In 2015 7th International Joint Conference on Knowl-
edge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowl-
edge Management (IC3K), volume 1, pages 417–424.
IEEE.
Alomari, K. M., ElSherif, H. M., and Shaalan, K. (2017).
Arabic tweets sentimental analysis using machine
learning. In International Conference on Industrial,
Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intel-
ligent Systems, pages 602–610. Springer.
Aly, M. and Atiya, A. (2013). Labr: A large scale ara-
bic book reviews dataset. In Proceedings of the 51st
Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), pages 494–498.
Antoun, W., Baly, F., and Hajj, H. (2020). Arabert:
Transformer-based model for arabic language under-
standing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.00104.
Baly, R., Khaddaj, A., Hajj, H., El-Hajj, W., and Sha-
ban, K. B. (2019). Arsentd-lev: A multi-topic corpus
for target-based sentiment analysis in arabic levantine
tweets. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.01830.
Chouikhi, H., Chniter, H., and Jarray, F. (2021). Arabic
sentiment analysis using bert model. In 13th Interna-
tional Conference on Computational Collective Intel-
ligence (ICCCI). Springer, Cham.
Dahou, A., Elaziz, M. A., Zhou, J., and Xiong, S. (2019).
Arabic sentiment classification using convolutional
neural network and differential evolution algorithm.
Computational intelligence and neuroscience, 2019.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K.
(2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional trans-
formers for language understanding. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.04805.
Dragoni, M., Poria, S., and Cambria, E. (2018). Ontosentic-
net: A commonsense ontology for sentiment analysis.
IEEE Intelligent Systems, 33(3):77–85.
ElJundi, O., Antoun, W., El Droubi, N., Hajj, H., El-Hajj,
W., and Shaban, K. (2019). hulmona: The univer-
sal language model in arabic. In Proceedings of the
Fourth Arabic Natural Language Processing Work-
shop, pages 68–77.
Elnagar, A., Khalifa, Y. S., and Einea, A. (2018). Ho-
tel arabic-reviews dataset construction for sentiment
analysis applications. In Intelligent natural language
processing: Trends and applications, pages 35–52.
Springer.
Eskander, R. and Rambow, O. (2015). Slsa: A sentiment
lexicon for standard arabic. In Proceedings of the
2015 conference on empirical methods in natural lan-
guage processing, pages 2545–2550.
Farha, I. A. and Magdy, W. (2020). From arabic sentiment
analysis to sarcasm detection: The arsarcasm dataset.
In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Open-Source
Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools, with a Shared
Task on Offensive Language Detection, pages 32–39.
Ghanem, B., Karoui, J., Benamara, F., Moriceau, V., and
Rosso, P. (2019). Idat at fire2019: Overview of the
track on irony detection in arabic tweets. In Proceed-
ings of the 11th Forum for Information Retrieval Eval-
uation, pages 10–13.
Harrat, S., Meftouh, K., and Smaili, K. (2019). Machine
translation for arabic dialects (survey). Information
Processing & Management, 56(2):262–273.
Imran, A., Faiyaz, M., and Akhtar, F. (2018). An enhanced
approach for quantitative prediction of personality in
facebook posts. International Journal of Education
and Management Engineering (IJEME), 8(2):8–19.
Jacob, D., Ming-Wei, C., Kenton, L., and Toutanova, K.
(2019). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional trans-
formers for language understanding. In Proceedings
Stacking BERT based Models for Arabic Sentiment Analysis
149

of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chap-
ter of the Association for Computational Linguistics:
Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, Min-
nesota, June. Association for Computational Linguis-
tics, 1:4171–41862.
Lan, W., Chen, Y., Xu, W., and Ritter, A. (2020). An empir-
ical study of pre-trained transformers for arabic infor-
mation extraction. In Proceedings of the 2020 Con-
ference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language
Processing (EMNLP), pages 4727–4734.
Nabil, M., Aly, M., and Atiya, A. (2015). Astd: Arabic
sentiment tweets dataset. In Proceedings of the 2015
conference on empirical methods in natural language
processing, pages 2515–2519.
Rangel, F., Rosso, P., Charfi, A., Zaghouani, W., Ghanem,
B., and Snchez-Junquera, J. (2019). Overview of the
track on author profiling and deception detection in
arabic. In Working Notes of the Forum for Information
Retrieval Evaluation (FIRE 2019). CEUR Workshop
Proceedings. In: CEUR-WS. org, Kolkata, India.
Safaya, A., Abdullatif, M., and Yuret, D. (2020). KUISAIL
at SemEval-2020 task 12: BERT-CNN for offensive
speech identification in social media. In Proceedings
of the Fourteenth Workshop on Semantic Evaluation,
pages 2054–2059, Barcelona (online). International
Committee for Computational Linguistics.
Shoukry, A. and Rafea, A. (2012). Sentence-level arabic
sentiment analysis. In 2012 International Conference
on Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS),
pages 546–550. IEEE.
Socher, R., Perelygin, A., Wu, J., Chuang, J., Manning,
C. D., Ng, A. Y., and Potts, C. (2013). Recursive
deep models for semantic compositionality over a sen-
timent treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 confer-
ence on empirical methods in natural language pro-
cessing, pages 1631–1642.
KEOD 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
150
