
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of
Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies:
A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
Lukas Hellwig
1,2 a
, Jan M. Pawlowski
1,2 b
and Michael Schäfer
2c
1
Institute of Information Systems, University of Jyväskylä, Jyväskylä, Finland
2
Institute of Computer Science, Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences, Bottrop, Germany
Keywords: Digitalized Innovation Environment, Knowledge Transfer, Digital Innovation, Open Innovation, Digital
Transformation, Innovation Capacity, Acceptance Model.
Abstract: Digital Innovation Environments (DIE) as an umbrella term for facilities such as FabLabs, Makerspaces and
Innovation Laboratories are already well known in the private and academic sectors. We focus on exploring
the business aspects of DIEs and their role in digital transformation and creation of new opportunities for
companies to increase their knowledge transfer and innovation capabilities. This research is dedicated to
factors influencing the usage behavior of company employees of a DIE. From seven guided interviews, a total
of 27 influencing factors in seven topics were identified through successive in-depth analysis and criterion-
guided interpretation. These factors show the complexity of DIEs and at the same time lay the foundation for
further research. In addition, they are a valuable insight for practice, as they can be used as a basis for
developing new integration and cooperation structures.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital transformation is an irreversible process that
has now infiltrated all areas of our lives and is
challenging existing structures and processes (Vial,
2019). This affects both private and business
perspectives, so it is not surprising that this
phenomenon is a much-discussed field both in
scientific research (Bharadwaj et al., 2013; Piccinini
et al., 2015) and in practice (Fitzgerald et al., 2014;
Westerman et al., 2011). Since digital transformation
affects all areas of life and has many facets, it is also
the subject of research in a variety of research
disciplines and is viewed from a wide range of
perspectives.
In this paper, we focus on the business perspective
and explore the basis on which digital transformation
and DIEs create new opportunities for companies to
increase their knowledge transfer and innovation
capabilities. The nature of innovation has changed
fundamentally over the past decades. From the former
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7287-7923
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7711-1169
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3521-0975
Schumpeterian model of a single inventor who has an
idea and commercializes it (Schumpeter, 1943),
innovation has become a complex process involving
a variety of different actors (Hippel, 2007; Tidd &
Bessant, 2016). Thus, two different developments can
be observed: On the one hand, innovation processes
are increasingly opening up and integrating external
actors to get new stimuli, which leads to
interdisciplinary innovation teams. This development
is a well-known innovation approach under the term
of Open Innovation (Chesbrough, 2003) and is a
permanent object of the research landscape. Another
striking development is Digital Innovation, which
supports innovations through the use of digital
technologies and methods or leads to digital products
(Iansiti & Lakhani, 2014; Nambisan et al., 2017). Due
to their scalability, these digital products and services
enable enormous growth potential, so that many of
the world's most valuable companies are based on
these digital innovations (e.g. Amazon, Apple,
Microsoft, Alphabet, Alibaba and Facebook (Kantar
Millward Brown, 2020)). Comparatively low
90
Hellwig, L., Pawlowski, J. and Schäfer, M.
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0010650000003064
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2021) - Volume 3: KMIS, pages 90-101
ISBN: 978-989-758-533-3; ISSN: 2184-3228
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

investment costs also enable smaller companies to act
as innovation drivers. Thus, potentially disruptive
innovations are no longer reserved for large and
established companies but can also be realized by
flexible start-ups or small enterprises. The pressure to
innovate has grown steadily due to the new
developments and companies are in a constant
competition for innovation leadership. Faster
iteration cycles are required to keep pace with
progress, otherwise there is a risk of missing
important market trends. The basis of these two
innovation approaches is an efficient transfer of
knowledge between all the players involved.
Based on the mechanisms of open innovation and
digital innovation, innovation environments have
developed in recent years in the private and university
context, which are characterized by their
interdisciplinary users and the use of digital
technologies to implement ideas (Cutcher-
Gershenfeld et al., 2018). There are various names for
comparable facilities such as Makerspaces, FabLab,
Coworkingspace, living Labs, innovation hubs and
innovations laboratory (Capdevila, 2013). In this
paper, we will summarize these facilities under the
umbrella term of Digitalized Innovation
Environments (DIE), as they are all characterized by
the use of digital technologies and methods to support
innovation while providing open access to a wide
range of players (Capdevila, 2018). It is this
combination that leads to faster iteration cycles
through the faster realization of initial prototypes
through the use of digital manufacturing technologies
such as 3D printing and CNC milling (Wolf et al.,
2014). The interdisciplinary exchange between users
on a non-hierarchical ground also supports creativity
in the solution approaches. In the private context,
these environments are used by hobbyists and do-it-
yourself users, the so-called makers, to realize
personal ideas (Dougherty, 2012; Hartmann et al.,
2016). In the academic context, these environments
are often used for hands-on teaching of digital
competencies using concrete examples of
implementation (Konopek et al., 2018).
In the meantime, companies have also become
aware of the potential of such digitalized innovation
environments and are trying to integrate them into
their own innovation processes (Zakoth & Mauroner,
2020). Large companies are taking the path of setting
up their own innovation environments, but these are
usually reserved for the research and development
department, so that they cannot benefit from the
interdisciplinary knowledge transfer and the
innovation potential of their other employees (Lo,
2014). Cooperation between such DIEs and
companies has been underrepresented in the research
landscape to date, although initial studies at the meta-
level have shown promising approaches. The already
hypothetically identified potentials, which result from
a cooperation, could not be retrieved in a structured
way so far (Ruberto, 2015b; Suire, 2016). It has not
yet been possible to unlock the potential known from
the private and academic context and make it fully
usable for companies, although these approaches are
seen as promising drivers of innovation capacity
(Bergner, 2017). This is partly due to the very small
number of companies that have tested
interdepartmental cooperation, so that the empirical
material is very limited.
Against this background, this paper first
empirically examines the basis on which such
cooperation can operate and which factors influence
the integration of DIEs. In our paper, we thus start
from the basic assumption that extended use of DIEs
in companies is a prerequisite for exploiting the
innovation potentials that are already known from
other contexts. This results in the following research
question:
Which factors influence employees´ usage behavior
of Digitized Innovation Environments in companies?
This explorative approach attempts to form an
empirical basis for subsequent research regarding the
integration of such DIEs in companies by identifying
the underlying conditions. The so far only sporadic
use of the potentials known in other contexts suggests
that obstacles and barriers arise here, which must first
be overcome. At this point, the study makes a far-
reaching contribution to the Information Systems (IS)
research landscape by empirically identifying
relevant factors moderating the usage behavior of a
DIE in a company. These results are useful for further
research as a starting point for the development of
suitable cooperation models, as well as for
practitioners for a more targeted integration of DIEs
into their innovation processes. The findings are to be
used as a basis for future theories that have the
potential to take into account the “New Logics of
Theorizing About Digitization of Innovation” by
(Nambisan et al., 2017, p. 227). DIEs, with their
complex interplay of diverse actors and extensive
digital technologies, address all four logics indexed
by Nambisan et al. (2017) and can provide a platform
on which the postulated research questions can be
addressed.
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
91

2 DIGITALIZED INNOVATION
ENVIRONMENTS
Environments in which targeted innovations are to be
supported and which offer a platform for sharing
knowledge and equipment are already known
instruments, especially in the private and academic
context (Boutillier et al., 2020; Suire, 2016).
However, the first comparable approaches can also be
observed in the commercial sector in the form of
coworking spaces and LivingLabs (Capdevila, 2014).
LivingLabs and their underlying innovation methods
have already been identified as element of user
innovation, which is characterized by its real-life
environment and the user as co-creator (Almirall et
al., 2012). Particularly in the private and academic
contexts, a new way of innovating has developed in
recent years through the integration of a wide variety
of digital components and tools. For example, 3D
printers and CNC milling machines paired with in-
house electronics development enable the short-term
implementation of functional prototypes without
comprehensive craftsmanship (Gershenfeld, 2012).
This allows new user groups to participate in the
innovation process and to be involved by means of
digital communication channels. Based on the new
opportunities made possible by these technologies, a
wide range of different innovation environments have
developed under various names. Fablabs,
Makerspaces, InnovationLabs, Hackerspace or
Cocreation Laboratory are some examples. These
environments have emerged in different contexts and
differ in individual areas with regard to their focus,
orientation and user groups. However, differentiation
by naming is not possible because there is no uniform
understanding of the terms. There is only a Fab
Charter that defines some very generic requirements
of a FabLab (The Fab Charter, 2015). Initial
approaches to differentiate the individual approaches
from one another have produced only insufficient
selectivity and have excluded the digital aspect (cf.
Aryan et al., 2020; Capdevila, 2017). Each innovation
environment is adapted to its specific context and
makes use of a wide variety of elements from the
different streams. In order to respect this richness of
facets, the term "Digitized Innovation Environment"
will be introduced as an umbrella term for these
facilities. These environments are physical spaces
that use a variety of different digital technologies to
support innovation, but are not themselves digital.
They are therefore Digitalized Innovation
Environments rather than digital/digitized innovation
environments such as virtual-reality environments
would be, which convert analog material into a digital
format. We use the following definition of
"Digitalized Innovation Environments":
Digitalized Innovation Environments are physical
spaces that provide both traditional and digital tools
and state of the art technologies to support
collaborative and interdisciplinary innovation and
knowledge transfer.
Some companies have already recognized the
potential of such DIEs and have made various efforts
to integrate them into their innovation processes
(Zakoth & Mauroner, 2020). However, collaboration
has so far mostly been limited to supporting the
research and development departments (Ruberto,
2015a). Some large concerns have gone the way of
making their own DIEs available to their
development teams, but even these have so far mostly
been reserved for a very limited user group and
therefore neglect to exploit the potentials of
interdisciplinary exchange known from the private
and academic context (Lo, 2014). Based on these
findings, potentials and functions that a DIE could
assume within a company has already been identified
(Hellwig et al.), but there is still a lack of knowledge
on how to implement them. As a result, the empirical
data on full-scale collaboration between DIEs and
companies is very limited, which means that only
very generic findings have been obtained so far.
There is a precise concept of use, instruction,
communication, and networking necessary (Bergner,
2017). Before such a concept can be developed, it is
first necessary to define the framework conditions
that influence the use of a DIE offering. Only if the
usability is ensured empirical data on the impact on
the innovation capacity of companies can be
collected. In the next step, this can lead to inductive
theory building, which is a far-reaching contribution
to the IS research landscape as well as to practice.
So far, there are only superficial findings
regarding the factors that influence the involvement
of DIEs in the innovation processes of companies.
This is because cooperation across all departments of
a company with a DIE has so far been a rare approach
to increasing knowledge transfer and innovation
capacity. Thus, the potential cases which allowed an
empirical investigation are very limited.
3 METHOD
Due to the limited prior knowledge in this research
area, an explorative approach was chosen to build a
data base for further investigations. For this purpose,
a qualitative in-depth analysis of an exemplary case
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
92

was to be conducted and findings were to be formed
by means of inductive theory building (Gregor,
2006). In the context of information systems research,
a case study is an inquiry into single or multiple
instances of observable complex phenomena with the
aim of identifying discrete units of analysis (Turnbull
et al., 2021). In our study, we explore a range of
influencing factors that impact DIE usage. As a
methodological approach, expert interviews (Kaiser,
2014) were conducted with employees from various
departments of a company which, at the time of the
survey, had its own FabLab on its own premises for a
year and which was freely accessible to all
employees. The guidelines for the interviews are
based on established theories and models from
comparable application areas, which were identified
through a literature search (Webster & Watson,
2002). The employees are in a position to report on
their own experiences and, due to their various
departmental affiliations, reflect a wide range of
perspectives and motives for use. In the following
evaluation and data analysis, we structured the
answers, identified influence factors and derived
initial recommendations for practice (Mayring,
2002). The detailed methodological steps are
explained in detail below.
3.1 Case Description
For the case study, we aimed at a company with broad
experiences to capture the broadest possible range of
experiences. For this purpose, we recruited a
company with a long-term cooperation of a company
with a DIE, which was made accessible to all
employees. This is the only way to ensure that the
interviewees can base their statements on experience
and that the greatest possible variance in perspectives
can be taken into account. Since this type of
cooperation is extremely rare, the search for suitable
research cases was limited. It was possible to recruit
a company in Germany for the study, which had been
operating its own FabLab for a year at the time of the
survey. This FabLab meets the definition of a
Digitalized Innovation Environment and houses a
variety of different digital tools and technologies. The
company is part of an international group, but forms
an autonomous unit at the location under
consideration with all the usual organizational units
for medium-sized companies. It is a manufacturing
mechanical engineering company with around 350
employees at the location of the DIE. The employees
are divided equally between the administration,
production and research and development
departments. All employees were free to access and
use the possibilities within the FabLab. At the
beginning, all employees were offered information
events and workshops on how to use individual
technologies. Over time, various concepts were tested
to simplify the integration of the FabLab into daily
business. Finally, one part of the development
department was permanently located in the FabLab
and serves as a contact person for other employees.
This must be taken into account in the upcoming data
evaluation.
In order to identify the widest possible range of
factors influencing usage behavior, employees were
also recruited at different hierarchical levels and from
different departments for an expert interview. A total
of seven stakeholders were identified, all of whom
had gained experience in the DIE but used its
opportunities to varying degrees. Two employees
each from Research & Development (R), Production
(P) and Marketing (M) as well as one employee from
Administration (A) were interviewed. Thus, the
sample represents a heterogeneous cross-section of a
medium-sized manufacturing company.
3.2 Expert Interviews
To ensure a balance between unbiased expression of
opinion and a minimum of structure, the expert
interviews were organized with the help of
predetermined interview guidelines. The employees
were asked to comment on pre-identified dimensions
relating to their usage behavior and were also given
the opportunity to comment on entirely new aspects
(Döring & Bortz, 2016). The interview could be
divided into three parts. In the first part, the
demographic information of the interviewees was
asked to be able to evaluate the subsequent
statements. Then questions regarding usage,
motivation, expectation, and cooperation were asked
to be able to identify first indirect influencing factors
and to gain a broader understanding of the
interviewees' context. he questions were derived from
the dimensions of customer orientation (CO)
(Handlbauer & Renzl, 2009), as this model has
already proven itself in comparable research
approaches and the employees have a customer
relationship with the DIE. In the third phase,
questions were also asked about specific factors
influencing usage behavior. To ensure a basic
structure, the dimensions to be considered were
derived from adjacent theoretical models. The
technology acceptance model (TAM3) (Venkatesh &
Bala, 2008) and the Innovation Diffusion Theory
(IDT) of Rogers (1983) were used as underlying
theories, as these are both established models and
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
93

Table 1: Dimensions and Guiding Questions within guided Expert Interviews.
No Dimension (Reference) Guiding Question
1 Demographic context
2 Utilization (CO) How have you used the FabLab so far?
3 Motivation (CO) What incentives are there for FabLab use?
4 Barriers (CO) What problems are associated with the use of the FabLab?
5 Expectations (IDT & TAM3) What future possibilities of use do you see in the FabLab?
6
Competencies
(IDT & TAM3)
To what extent do your own skills and knowledge support you in implementing your own
ideas in the FabLab?
7
Organization
(IDT & TAM3)
What influence do the organizational structures in the FabLab and at the company level have
on your usage behavior?
8
Social Aspects
(IDT & TAM3)
To what extent do social aspects influence your decision to use the FabLab?
9 Marketing (IDT & TAM3) How is the public presentation of the FabLab?
10 Feedback (IDT & TAM3) Do you receive feedback on your projects in the FabLab?
cover a wide range of potential influencing factors.
Since DIEs represent a complex structure that
attempts to integrate a variety of technologies into an
existing system, but at the same time can be
interpreted as an innovation itself, both the TAM3
and the IDT were used as a basis. Thus, the
complexity of DIEs should be considered and as
many perspectives as possible should be considered.
The influencing factors listed in the reference models
were generalized in such a way that they allowed
statements to be made regarding FabLab use, while at
the same time leaving room for supplementary
factors. This resulted in the ten dimensions in table 1
that were addressed in the expert interviews.
In addition to the guiding questions, sub-questions
were prepared for each dimension, but these were
optional depending on the progress of the interview.
As guiding questions were formulated to avoid
suggestion, and interviewees were directed only to
broad topics. The sequence of the questions was also
not predetermined. The interviewees were asked to
express themselves as freely as possible and were
encouraged during the interview to explain points that
were not explicitly asked for. An initial pretest with
two volunteers confirmed that the formulated guiding
questions were easy to understand without
prescribing answers to the interviewees. The actual
interviews were conducted in the company itself in an
appropriately relaxed atmosphere, alone with the
interviewer. This ensured that possible critical factors
were also openly communicated. The interviews
lasted between 40 and 65 minutes and were recorded.
3.3 Data Evaluation
Our explorative research approach aims at identifying
factors that influence the use of the company's
internal FabLab by a wide range of employees, a
qualitative data analysis approach was chosen. This is
suitable for explorative research approaches when a
database is to be created first (Döring & Bortz, 2016).
Therefore selective protocols were used. When
identifying influencing factors, the wording is of
secondary importance, which is why selective
protocolling according to Mayring (2002) provides
sufficiently precise results. Parallel to the creation of
the protocols, a category system is to be derived with
the help of the object-related theory formation (cf.
grounded theory (Glaser, 1978)), which permits an
allocation of the statements to differentiated aspects
(Urquhart, 2013). This methodology, which is known
from sociology, enables the formation of categories
already during the data collection or the rehearing of
the recordings by summarizing statements on
superordinate topics. The categorization could be
made inductively, which was further developed in an
iterative process during the recording of the various
interviews. This methodology already falls in part
into the data evaluation and is particularly suitable for
explorative studies (Mayring, 2002). In a further step,
the statements of the interviews were then assigned to
the developed categories. Finally, the statements
within the identified categories were generalized into
precise statements with the help of a qualitative
content analysis (Mayring, 2002). In this way, it was
possible to successively reduce the complex
statements of the interviewees to individual
influencing factors together with their impact on
usage behavior. The evaluation is done in four
analysis steps: paraphrasing, generalization to a
defined abstraction level, first reduction and second
reduction (Mayring, 2002). The results of the data
analysis are presented below.
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
94
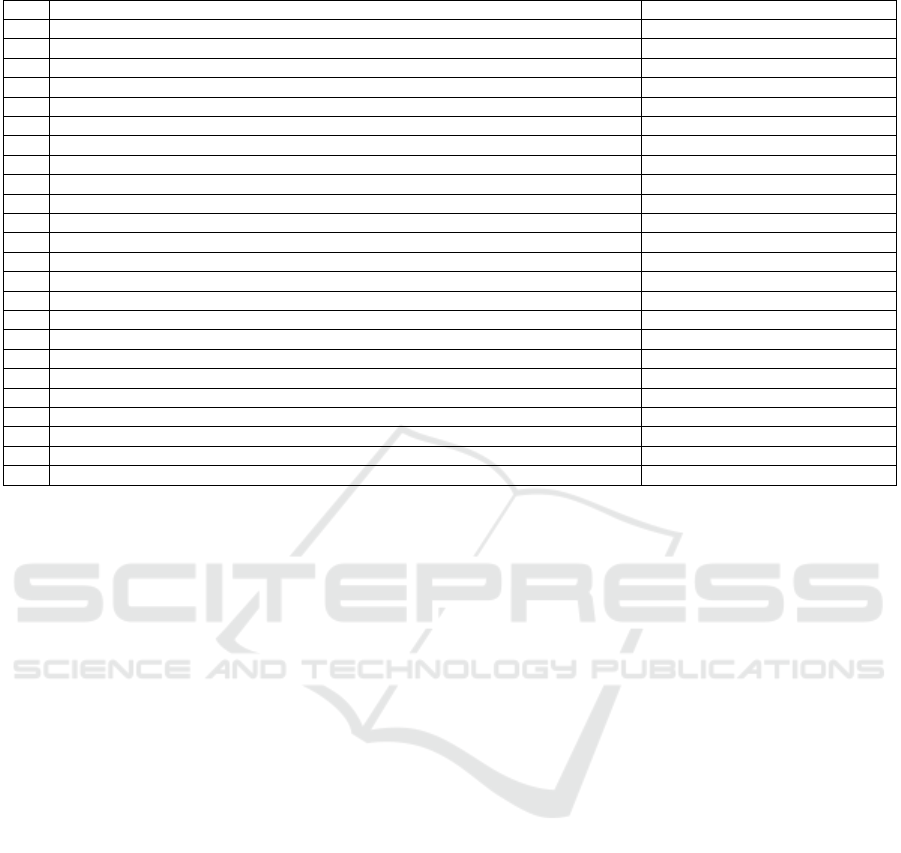
Table 2: Identified Categories of Influence Factors of DIE Usage of Employees.
No Category by objec
t
-related theory building Interviewees
1 Personal motivation M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
2 Relevance for daily business M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
3 Integration into the daily business M1, M2, P2, R1, A
4 Previous competencies M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
5 Workshops M1, M2, P1, R1, R2, A
6 Trainings according to needs M1, M2, P1, P2, R2, A
7 Software M1, M2, P2, R2, A
8 Guided projects M1, M2, P1, R1
9 Challenges M1, M2, P1, P2, R1
10 Equipmen
t
M1, M2, P1, R1, R2
11 Usage solicitation M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, A
12 Acceptance of the manage
r
M1, M2, P1, P2, R1,
13 Communication with other users M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
14 Reputation of the FabLab M1, M2, R1, R2, A
15 Presentation of project results M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
16 External presentation M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
17 Improvement recommendation system M1, P1, P2, A
18 Availability of contact persons M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
19 Time flexibility M1, M2, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
20 Requirements of use M2, P1, R1, R2, A
21 DIE Premises M2, R2
22 Personality of contact persons M1, M2, R1, A
23 Restructuring P1, R1
24 Permanent staff in the Fablab M1, P1, P2, R1, R2, A
4 FINDINGS
Through the iterative process of object-related theory
building (Glaser & Strauss, 1979), a total of 24
categories could be identified from the seven
interviews. Some of the categories can be assigned to
the dimensions previously derived through
theoretical considerations, which formed the basis of
the guiding questions of the interview, but some also
go beyond these. Thus, the method of guided
interviews in combination with the inductive category
building is confirmed as appropriate for such an
explorative study. In table 2, the 24 categories will be
presented, and an assignment of the interviewees will
be made.
The identified categories show the multifaceted
nature of the perspectives of the influencing factors.
Some, like "Personality of contact persons," can be
clearly assigned to a previously assumed dimension
(social aspects). Other categories such as "relevance
for daily business", on the other hand, cannot be
clearly assigned and go beyond existing theories in
terms of both content and level of detail. It can
therefore be deduced from the categories identified
that DIEs should not be viewed solely as
technologies, but rather represent significantly more
complex systems with more multi-faceted factors
influencing usage behavior. Single categories such as
"Permanent staff in the FabLab" appear to be a
company-specific category, since at the time of the
interviews the company had some employees from
the development department permanently located in
the FabLab. These company-specific categories,
which cannot provide generalizable factors, were not
considered further for the analysis.
In the next step, the interviewees' propositions
were extracted from the individual interview
protocols and assigned to the categories. Here, the
statements were successively brought to a uniform
level of abstraction with the help of qualitative
content analysis in the steps of paraphrasing,
generalization and reduction in order to identify the
final influencing factors (Mayring, 2002). In doing
so, the interrelationships as well as the impact
(positive or negative factor) had to be considered. In
the following, the 27 identified influencing factors
will be presented and explained. Individual factors
were inverted to present a uniformly positive
influence. Table 3 is already reasonably sorted for a
further generalization loop.
Some of the 27 identified impact factors derive
directly from the previously elaborated categories,
while others only revealed themselves through the
content analysis. In addition to the factors, the in-
depth analysis also made it possible to identify their
effects. For example, the equipment within the DIE
was identified as an influencing factor. However,
without in-depth analysis and description, it would
not be possible to assess how this factor affects usage
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
95
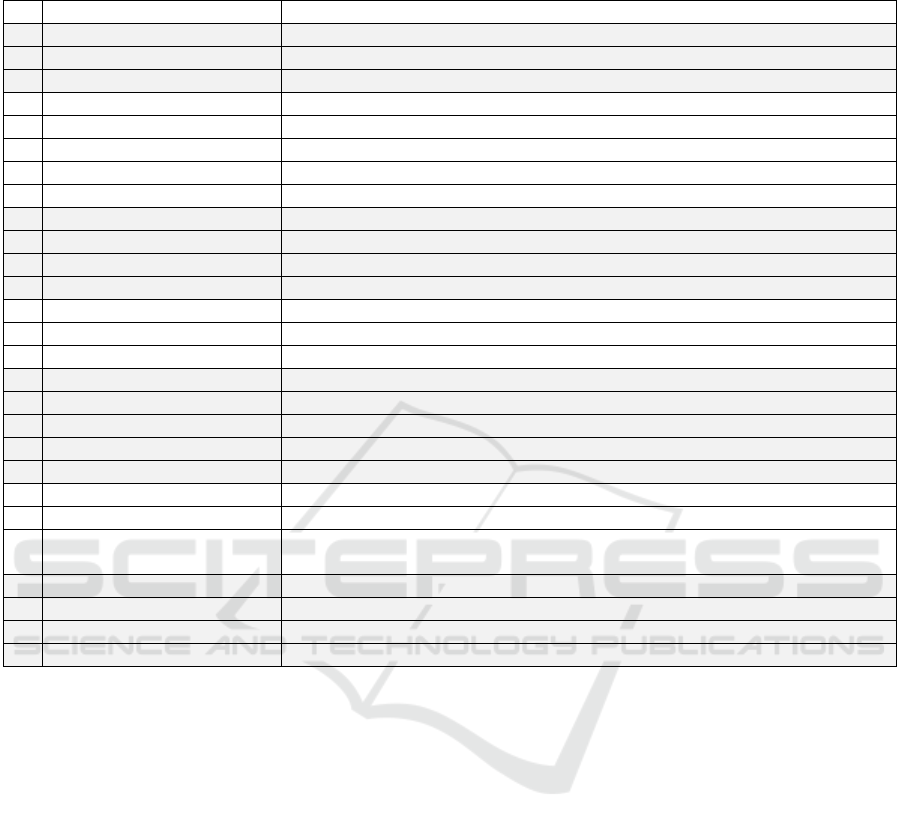
Table 3: Identified Influence Factors and Description.
No Influence Factor Description
1 Self-Realization Employees can contribute their own ideas and implement them.
2 Fun Employees experience fun in using the DIE.
3 User Competencies Employees have basic skills in handling the equipment.
4 Communication Exchange among employees from different departments and areas of expertise is possible.
5 Promotion Employees are aware of the benefits of using the DIE.
6 Encouragement Employees are regularly encouraged to use the DIE.
7 Image The DIE has a consistent, professional, and positive image among its employees.
8 Outcome Presentation The results and added values are communicated consistently and positively.
9 Workshop There is a changing offer of workshops.
10 Training Individual training on skills acquisition is provided.
11 Projects Guided projects are offered.
12 Competitions Competitions with a business orientation are offered within the DIE.
13 Relevance The work in the DIE is related to the daily business of the employees.
14 Backup Supervisors support employees in using the DIE.
15 Hierarchies There are no hierarchies within the DIE.
16 Terms of use Employees can use the DIE independently of other players
17 Bureaucratic The bureaucratic hurdles for DIE access are low.
18 Access There are uniform regulations on the time of access of the DIE.
19 Structural Inclusion The DIE is part of the company innovation process (e.g. the improvement proposal system).
20 Concept There is a uniform and transparent concept of the DIE.
21 Contact person Personality The contact person within the DIE is helpful, independent, and friendly.
22 Contact Person Availability A contact person is available on a flexible basis.
23 Contact Person Competency
The contact person has all the necessary competencies to support the implementation of
ideas.
24 Equipment The available equipment enables the realization of products with a company connection.
25 Appearance The DIE has a welcoming and visible appearance.
26 Premises The premises are inviting and friendly in a central location.
27 Software The required software is intuitive and user-friendly.
behavior. For example, the equipment requirements
that have a positive effect on usage are described in
more detail in Table 3. All interviewees agreed on the
effects. No factor was evaluated in a contradictory
way. The large number of influencing factors
discussed once again highlights the complexity of the
cooperation system. It also becomes clear that a
digitized innovation environment cannot be
understood purely as a technology, since the
influence factors go far beyond those from familiar
models such as TAM3 (Venkatesh & Bala, 2008) or
IDT (Rogers, 1983). In order to develop a
manageable model despite the large number of
factors, thematically related influence factors were
combined into umbrella terms. Some factors are not
completely clear-cut and contain aspects of several
topics. In this case, the main focus of the factor was
taken as the reference. The factors can be summarized
into the following seven influence categories: user
(influence factor 1-3), presentation (4-8), offer (9-12),
perception (13-15), structure (16-20), contact person
(21-23), and environment (24-27). This results in the
model of factors influencing the use of DIEs by
employees shown in figure 1.
The user himself could be identified as a factor
and thus an influencing factor which can only be
influenced to a very limited extent. Thus, it is difficult
to make changes to the sense of fun, the already given
competencies or the striving for self-realization.
These factors can presumably be favored by other
factors such as an offer that is attractive to the specific
employee, but they cannot be addressed directly by
changing the form of cooperation.
The contact person was cited by all the interviews
as a further exceptional influencing factor. This is
special in the sense that in conventional DIEs in the
private or academic context such a person rarely
exists. In universities, there may well be some kind of
workshop manager, but he or she is assigned other
functions than those mentioned by the interviewees as
being conducive to user behavior. In the private
context, the dissolution of all hierarchies means that
this position does not usually exist at all.
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
96

Figure 1: Digitalized Innovation Environment Use Model.
From the interviews with the interviewees from
various departments, finally 27 influencing factors
were derived in seven influence topics. These are not
to be understood as stand-alone linear influences, but
also influence each other. These correlations are to be
investigated in further studies but were not the subject
of this first explorative study. Going further, these
factors initially form the basis for enabling the use of
the innovation and knowledge transfer capacities of
DIEs. Utilization alone will probably not necessarily
increase innovative and knowledge transfer capacity
and is likely to depend on other factors. However,
utilization is a fundamental barrier to entry, without
which the potentials known from the private and
academic context cannot be accessed. The indicated
connection between utilization and the actual
function as an innovation driver in figure 1 must be
investigated further in future research.
During the in-depth analysis of the interviews,
several qualitative and interpretative analysis steps
were necessary in order to identify the final
influencing factors (Mayring, 2018). In order to
exclude misinterpretations and to ensure the
robustness of the results, the study was measured
against the established quality criteria according to:
Truth Value, Applicability, Consistency, Neutrality
(Lincoln & Guba, 2007). Truth Value and
Applicability are given by the detailed description of
the research procedure as well as a detailed
description of the underlying context. Consistency
could be achieved by the close link to established
models and theories and their description.
Furthermore, neutrality is ensured by the research
design and the successive criterion-guided
interpretation. Thus, the most important criteria of
credibility of research approaches are met (Schou et
al., 2012). In addition, the results were validated
communicatively in a final iteration with the
interviewees in order to exclude misinterpretations.
No errors or inaccuracies were found during the
communicative validation.
In principle, the identified factors appear to
represent a realistic picture. Comparable factors to the
established acceptance models are found, but further
factors are also identified. Since a digitalized
innovation environment is not just a technology, but
a complex system, the additional factors are
conclusive. The complexity of the influencing factors
also reflects the different perspectives of the
interviewees. For example, it was to be expected that
an employee from the development department
would focus more on technological factors such as
"software” and "equipment", whereas employees
with less technical affinity would focus more on
factors relating to communication and presentation.
The logical validation also confirms the significance
of the identified factors.
5 DISCUSSION
The factors identified as influencing the usage
behavior of employees of a DIE show a very wide
range. It includes aspects of the Innovation Diffusion
Theory (IDT) (Rogers, 1983), Technology
Acceptance Model 3 (TAM3) (Venkatesh & Bala,
2008) and Customer Orientation (CO) (Handlbauer &
Renzl, 2009) identified as potentially relevant in the
preliminary work, but also goes beyond them. This
confirms the assumption that the introduction of a
DIE into a company cannot be understood purely as
innovation diffusion or as a new technology, but
rather represents a multi-layered challenge. The
proximity to the theories and models selected as a
basis confirms on the one hand the selection of the
scientific foundations, but on the other hand also
shows the complexity of the process of integrating a
DIE into a company. Individual aspects such as
"Relevance" (TAM3: "Job Relevance"), "Outcome
Presentation" (TAM3: "Result Demonstrability),
"Backup" (IDT: "Extent of Change Agents'
Promotion Efforts") or "Promotion" (IDT:
"Communication Channels") can already be found
similarly in the underlying theories and models. At
this point, the findings of the study emphasize the
multi-faceted nature of DIEs. They are a complex
system whose use is influenced by factors known
from technologies (TAM3), innovations (IDT) and
customers (CO).
At other points, the in-depth analysis has led to a
specification of the generic factors from the
established models and theories for the specific use
case of DIEs. For example, the factor "Ease of Use"
(TAM3) or "Complexity" (IDT) could be
differentiated in more detail for the context of DIEs
and individual subordinate dimensions could be
identified: e.g. "Terms of use", "Bureaucratic",
"Access" and "Software". This precision provides
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
97

important insights, especially for further research, but
can also be a first contribution to practice.
Finally, influencing factors could be identified,
which were not considered in previous models and
theories and thus consider the special system of DIEs.
Thus, a special focus was placed on the contact
person and their characteristics. This is interesting
because in privately and academically organized
DIEs there is no contact person in the sense that is
demanded in the corporate context. At this point,
there seems to be a stronger emphasis on results and
outcomes in companies and the try and error
mentality from the maker community is not yet
established (Bergner, 2017) These additionally
identified influencing factors contribute to the
understanding of DIEs and their underlying
structures. In addition, they represent a new
perspective from which to investigate the
phenomenon of DIEs in further research.
In terms of content, the factors range from those
that are easy to influence, such as appropriate
equipment and a welcoming atmosphere, to those that
are much more complex, such as the personality of
the contact person. Here, the various interviewees
also seem to set different priorities depending on their
individual backgrounds. Nevertheless, many factors
were addressed by several department
representatives. In general, there was agreement on
the respective impact of factors among all
interviewees. The different focus could come from
the different usage perspectives of the employees, but
this cannot be validly confirmed on the evidence base.
For example, it seems conclusive that an employee
from the development department is more interested
in the implementation of prototypes and is therefore
focused on the equipment, while an employee from
the marketing department, would rather use the DIE
to acquire competencies and is therefore more
interested in an interesting workshop offer.
It can also be deduced from the identified
influencing factors that employees have a certain
understanding of service from a DIE. A competent
and flexibly available contact person within the DIE
is a central aspect which is considered important by
all department representatives. In a way, this
contradicts the original concept of a DIE, which
benefits from its intrinsically motivated users and
their exchange with each other. In the private and
academic context, such permanently available contact
persons are not envisaged outside of specific event
formats. Rather, the approach relies on the formation
of a community in the DIE that develops its own
momentum and can therefore operate without an
internal structure and hierarchy. Here, the identified
influencing factors are an indication that employees
have a different interpretation of a DIE than private
or academic actors. In the analyzed company, this
may be due to the fact that in the year in which the
DIE was available, different strategies for integrating
it into daily business took place and, in particular,
there was no uniform concept at the beginning.
Basically, the multitude of different influence
topics also illustrates the complexity of the task of
integrating a DIE into an existing company and
supporting cooperation. It becomes clear, for
example, that a room with many digital technologies
without restrictions on use is not sufficient for actual
employee use. The influencing factors go far beyond
those known from other acceptance models and form
a much more complex web. For example,
organizational and social factors also play a decisive
role. In addition to these quite subjectively
perceivable factors, the user himself was also
identified as an influencing topic. Also factors were
mentioned, on which a company can take influence
only indirectly. For example, whether an employee
enjoys using digital technologies depends heavily on
his or her interests. Here, the company can create a
favorable atmosphere through other identified factors
but will not achieve this with every employee. Rather,
the identified influencing factors form a framework
on the basis of which an individual concept can be
developed for a specific company.
6 LIMITATIONS, OUTLOOK AND
CONTRIBUTION
The present study has a couple of limitations, which
are presented below and from which further research
needs are to be derived. Due to the very specific
condition of deriving the factors from employees'
experiences in actually using a DIE, the selection of
possible study participants is severely limited.
Although a broad spectrum of employees from
different departments could be recruited for
interviews, the results cannot be generalized without
restrictions. It must also be critically reflected that
only one company is considered as a case in the study.
This is due to the fact that such an integration of a
DIE into an existing company is a rare constellation
and the recruited company takes a pioneering role. It
is also important to point out the many interpretative
methodological steps, which, although they were
carried out with the greatest care and orientation to
quality criteria, cannot completely rule out bias.
Finally, it remains to be stated that some of the
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
98

identified influencing factors suggest that there is a
correlation between them, but this could not be
investigated in more detail in the process of this
research.
These correlations should be addressed in further
research to further expand our understanding. Also, a
quantitative evaluation of the influencing factors
would be a logical next step. Thus, further weighting
of the factors could be undertaken. Building on these
findings, it would then be possible to revise existing
models of cooperation and integration. The
phenomenon of DIEs has already proven to support
open innovation and digital innovation (Zakoth &
Mauroner, 2020). With the help of the new insights
gained it will be possible reach the long perspective
goal of unlocking these opportunities for companies
as well and thus address some key blind spots of
innovation and knowledge management research
(Nambisan et al., 2017).
Thus, the findings of this research make a
valuable contribution to the IS landscape on several
levels. On the one hand, it provides an empirical basis
for further research, and on the other hand, it offers
valuable insights for practice. DIEs, with their digital
technologies and communities, constitute a new
phenomenon in the IS discipline and have been little
studied to the current point. The first step is to create
a basis on which empirical research is possible. At
this point, the influencing factors guide a first
important step towards integrating such DIEs into
corporate contexts. The further research approaches
are manifold and can take different perspectives such
as DIE technologies, DIEs as competence incubators
or DIEs as communication platforms (Hellwig et al.).
Complementary to the scientific contribution,
significant added value can also be provided to
practice. The integration of DIEs in innovation
processes has already been identified as a promising
approach (Bergner, 2017), but has so far failed in
implementation. At this point, the factors influencing
user behavior offer initial insights into the design of
efficient integration or cooperation. Thus, the results
of this study form a valid basis for a variety of further
research approaches to better understand the
phenomenon of DIE and, at the same time, to gain an
important contribution to practice.
7 CONCLUSION
Digitized innovation environments as an umbrella
term for various facilities such as FabLabs,
Makerspaces and InnovationLabs are already known
from the private context and have already established
as competence incubators in the academic
environment with their digital technologies.
However, integration or cooperation with companies
has so far taken place only very partially and to a
limited extent. In order to be able to investigate the
potentials of this new phenomenon for companies as
well, the present work intended to identify factors
influencing the usage behavior of employees of a
company of DIEs. By conducting extensive
guideline-based expert interviews with seven
employees from different departments of a company,
it was possible to identify these through successive
analysis and interpretation. The interview guidelines
were based on established theoretical models such as
TAM3 (Venkatesh & Bala, 2008) and IDT (Rogers,
1983). A total of 27 influencing factors were
identified, which can be assigned to the seven topics:
user, presentation, offer, perception, structure,
contact person, and environment. These influencing
factors go beyond known factors from the underlying
models and show the complexity of the phenomenon
DIE. It also illustrates that DIEs should not be
understood as space with digital technology only, but
that many other aspects also influence this construct.
A critical reflection of the identified factors on usage
behavior suggests that a universal concept for
integrating a DIE into a company is a utopian notion
and that there must be specific employee-dependent
approaches.
The findings provide a basis for further
investigation of this still largely unknown
phenomenon. Thus, further investigation of usage
factors and their correlation with each other is a
purposeful next step. In addition to the contribution
to the scientific IS landscape, the findings offer added
value for practical applications, which is a key claim
of IS research (Nambisan et al., 2017). For example,
the factors can support companies in the development
of suitable concepts for the integration of DIEs, which
in turn provide the basis for further empirical
research. Thus, the present work contributes to both
science and practice and has great potential for
connecting research.
REFERENCES
Almirall, E., Lee, M., & Wareham, J. (2012). Mapping
living labs in the landscape of innovation
methodologies. Technology Innovation Management
Review, 2(9). http://timreview.ca/article/603
Aryan, V., Bertling, J., & Liedtke, C. (2020). Topology,
typology, and dynamics of commons ‐ based peer
production: On platforms, actors, and innovation in the
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
99

maker movement. Creativity and Innovation
Management. Advance online publication.
https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12392
Bergner, A. (2017). Make-Design-Innovate: Das Potential
des Maker-Movement für Innovation,
Kreativwirtschaft und Unternehmen. Coburg.
Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften Coburg.
Bharadwaj, A., El Sawy, O. A., Pavlou, P. A., &
Venkatraman, N. (2013). Digital business strategy:
Toward a next generation of insights. MIS Quarterly,
37(2), 471–482. https://doi.org/10.25300/MISQ/2013/
37:2.3
Boutillier, S., Capdevila, I., Dupont, L., & Morel, L. (2020).
Collaborative spaces promoting creativity and
innovation. Journal of Innovation Economics &
Management, n°31(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3917/
jie.031.0001
Capdevila, I. (2013). Typologies of localized spaces of
collaborative innovation. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Advance online publication.
https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2414402
Capdevila, I. (2014). How can living labs enhance the
participantss motivation in different types of innovation
activities? SSRN Electronic Journal. Advance online
publication. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2502795
Capdevila, I. (2017). A typology of localized spaces of
collaborative innovation. In M. van Ham, D. Reuschke,
R. Kleinhans, C. Mason, & S. Syrett (Eds.),
Entrepreneurial neighbourhoods (pp. 80–97). Edward
Elgar Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4337/97817853672
43.00013
Capdevila, I. (2018). Joining a collaborative space: Is it
really a better place to work? Journal of Business
Strategy, 86(6), 84. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBS-09-
2017-0140
Chesbrough, H. W. (2003). Open innovation: The new
imperative for creating and profiting from technology
[Repr.]. Harvard Business School Press.
Cutcher-Gershenfeld, J., Gershenfeld, A., & Gershenfeld,
N. (2018). Digital fabrication and the future of work.
Perspectives on Work, Labor and Employment
Relations Association, 8–13.
Döring, N., & Bortz, J. (2016). Forschungsmethoden und
Evaluation in den Sozial- und Humanwissenschaften
(5. vollständig überarbeitete, aktualisierte und
erweiterte Auflage). Springer-Lehrbuch. Springer.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41089-5
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41089-5
Dougherty, D. (2012). The maker movement. Innovations:
Technology, Governance, Globalization, 7(3), 11–14.
https://doi.org/10.1162/INOV_a_00135
The fab charter. (2015, August 24).
http://fab.cba.mit.edu/about/charter/
Fitzgerald, M., Kruschwitz, N., Bonnet, D., & Welch, M.
(2014). Embracing digital technology: A new strategic
imperative. MIT Sloan Management Review(55), 1–12.
Gershenfeld, N. (2012). How to make almost anything: the
digital fabrication revolution. Foreign Affairs, 91(6),
43–57.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1979). Die entdeckung
gegenstandsbezogener theorie: Eine grundstrategie
qualitativer sozialforschung. In C. Hopf (Ed.), Klett-
Cotta-Sozialwissenschaften. Qualitative
Sozialforschung (1st ed., pp. 91–111). Klett-Cotta.
Glaser, B. G. (1978). Theoretical sensitivity. Advances in
the methodology of grounded theory. Soc. Pr.
Gregor (2006). The nature of theory in information systems.
MIS Quarterly, 30(3), 611. https://doi.org/10.2307/
25148742
Handlbauer, G., & Renzl, B. (2009). Kundenorientiertes
Wissensmanagement. In H. H. Hinterhuber (Ed.),
Kundenorientierte Unternehmensführung (pp. 147–
175). Springer Fachmedien. https://doi.org/10.1007/
978-3-8349-8051-9_7
Hartmann, F., Lahr, M., & Mietzner, D. (2016). Maker
movement as a path of digital transformation? current
understanding and how it May change the social and
economic environment. 2nd Annual International
Conference on Foresight, 29–30.
Hellwig, L., Pawlowski, J., & Schäfer, M. How digitalised
innovation environments impact companies' innovation
capability - a review and research agenda. In UK
academy for information systems conference
proceedings 2021 (Vol. 8, pp. 113–136).
https://aisel.aisnet.org/ukais2021/8
Hippel, E. v. (2007). The sources of innovation (1. publ. in
1988, [repr.]. Oxford Univ. Pr.
Iansiti, M., & Lakhani, K. R. (2014). Digital ubiquity: How
connections, sensors, and data are revolutionizing
business. Harvard Business Review, 92(11).
https://hbr.org/2014/11/digital-ubiquity-how-connectio
ns-sensors-and-data-are-revolutionizing-business
Kaiser, R. (2014). Qualitative Experteninterviews. Springer
Fachmedien Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-
3-658-02479-6
Kantar Millward Brown. (2020). Brandz - top 100 most
valuable global brands 2020. https://de.statista.com/
statistik/daten/studie/162524/umfrage/markenwert-
der-wertvollsten-unternehmen-weltweit/
Konopek, A., Hellwig, L., & Schäfer, M. (2018). A possible
ubiquitous way of learning within a fab lab - the
combination of blended learning and implementation-
oriented learning. Conference Proceeding: 10th
International Conference on Computer Supported
Education, 265–271. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006780
202650271
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2007). Naturalistic inquiry
[Nachdr.]. Sage.
Lo, A. (2014). Fab lab en entreprise : Proposition d’ancrage
théorique. In Xxiiie conférence de l’aims.
Mayring, P. (2002). Einführung in die qualitative
Sozialforschung: Eine Anleitung zu qualitativem
Denken (5., überarb. und neu ausgestattete Aufl.). Beltz
Studium : Erziehung und Bildung. Beltz.
Mayring, P. (2018). Gütekriterien qualitativer
Evaluationsforschung [Quality Standards for
Qualitative Evaluation Research]. Zeitschrift für
Evaluation, 17(1), 11-24,209. https://search.proquest.
com/scholarly-journals/gütekriterien-qualitativer-evalu
KMIS 2021 - 13th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
100

ationsforschung/docview/2037012190/se-2?accountid
=11774
Nambisan, S., Lyytinen, K., Majchrzak, A., & Song, M.
(2017). Digital innovation management: Reinventing
innovation management research in a digital world.
MIS Quarterly, 41(1), 223–238. https://doi.org/
10.25300/MISQ/2017/41:1.03
Piccinini, E., Gregory, R., & Kolbe, L. (2015). Changes in
the producer-consumer relationship – towards digital
transformation. In Wirtschaftsinformatik proceedings
2015 (pp. 1634–1648).
Rogers, E. M. (1983). Diffusion on innovations (3 ed.).
Free.
Ruberto, F. (2015a). Fablabs to transform the italian
industry: The case of the fablabs community.
University of Pavia. http://ssrn.com/abstract=2637830
Ruberto, F. (2015b). How the fablabs community can help
the italian industry.
Schou, L., Høstrup, H., Lyngsø, E. E., Larsen, S., &
Poulsen, I. (2012). Validation of a new assessment tool
for qualitative research articles. Journal of Advanced
Nursing, 68(9), 2086–2094. https://doi.org/
10.1111/j.1365-2648.2011.05898.x
Schumpeter, J. (1943). Capitalism, socialism and
democracy. Routledge.
Suire, R. (2016). Place, platform, and knowledge co-
production dynamics: Evidence from makers and
FabLab. http://ssrn.com/abstract=2830526
Tidd, J., & Bessant, J. (2016). Managing innovation:
Integrating technological, market and organizational
change (Fifth edition, reprinted.). Wiley.
Turnbull, D., Chugh, R., & Luck, J. (2021). The use of case
study design in learning management system research:
A label of convenience? International Journal of
Qualitative Methods, 20, 160940692110041.
https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069211004148
Urquhart, C. (Ed.). (2013). Grounded theory for qualitative
research: A practical guide. Sage. https://doi.org/
10.4135/9781526402196
Venkatesh, V., & Bala, H. (2008). Technology acceptance
model 3 and a research agenda on interventions.
Decision Sciences, 39(2), 273–315. https://doi.org/
10.1111/j.1540-5915.2008.00192.x
Vial, G. (2019). Understanding digital transformation: A
review and a research agenda. The Journal of Strategic
Information Systems, 28(2), 118–144. https://doi.org/
10.1016/j.jsis.2019.01.003
Webster, J., & Watson, R. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to
prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS
Quarterly, 26(2), xiii–xxiii. http://dl.acm.org/citation.
cfm?id=2017160.2017162
Westerman, G., Calméjane, C., Bonnet, D., Ferraris, P., &
McAfee, A. (2011). Digital Transformation: A Road-
Map for Billion-Dollar Organizations. Report. Paris &
Cambridge, MA. Capgemini Consulting & MIT Center
for Digital Business. https://www.capgemini.com/
resources/digital-transformation-a-roadmap-for-
billiondollar-organizations
Wolf, P., Troxler, P., Kocher, P. Y., Harboe, J., & Gaudenz,
U. (2014). Sharing is sparing: Open knowledge sharing
in fablabs. Journal of Peer Production. Issue 5 Shared
Machine Stops: Beyond Local Prototyping and
Manufacturing. https://surfsharekit.nl/publiek/hr/
5b7a9968-ab70-479d-9cf2-0ff6a2eb33a9
Zakoth, D., & Mauroner, O. (2020). Industry-specific
makerspaces: Opportunities for collaboration and open
innovation. Management International (24), 88–99.
Factors Influencing the Usage Behavior of Digitalized Innovation Environments in Companies: A Qualitative in-Depth Analysis
101
