
Assessment of Various Factors Impact on Cryptocurrency
Functioning using Economic and Mathematical Modeling
E. V. Chaykina
a
, E. A. Posnaya
b
and B. A. Bukach
c
Institute of Finance, Economics and Management, Sevastopol State University, Universitetskaya Street, Sevastopol, Russia
Keywords: Cryptocurrency, Gold, Silver, Platinum, US Dollar, Modeling, Exploratory Factors.
Abstract: This article has developed an economic and mathematical model that reflects the dependence of the
cryptocurrency rate on factors of an exploratory nature. At present, an interesting and promising area of
research is exploratory analysis, the economic meaning of which is to study the influence of sudden factors
on the final result. Against the backdrop of the development of modern technologies in the world, taking into
account the depreciation of the US dollar and the withdrawal of investors from the stock markets, the
cryptocurrency market is considered one of the most promising and most influenced by exploratory factors.
The cryptocurrency rate is based on economic expectation, and not on the availability of real assets. The
article discusses the main indicators that affect the cryptocurrency rate, using the example of Bitcoin. An
economic-mathematical model of the dependence of the price of bitcoin on a number of the most significant
indicators is built. The economic and mathematical model proposed in the study allows you to take into
account the degree of influence of exploratory factors on the formed cryptocurrency rate. The developed
model will allow the most accurate prediction of the cryptocurrency rate in modern financial and economic
conditions, since it takes into account exploratory factors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, the cryptocurrency market is actively
developing. At the beginning of 2017, due to the rapid
growth of the cryptocurrency market capitalization,
many saw it as signs of a financial pyramid, but
gradually the opinion began to change. “Financial
institutions introduced Bitcoin futures, large investors
began to come to the cryptocurrency market,
pessimistic forecasts began to be replaced by more
optimistic ones” (Kornilov et al., 2017).
The collapse of bitcoin in March 2020, according
to analysts at JPMorgan Chase, was a stress test for the
cryptocurrency market. “The industry managed to
cope with it in a matter of months. Now Bitcoin is
periodically subject to correction, but it has every
chance to become the main competitor for stock
markets. Many investors transfer their savings from
the stock market to the currency. According to Dan
Tapeiro, an investor and founder of Gold Bullion
International, “the dollar will weaken even more, and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4413-3414
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7716-9117
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0554-6980
digital assets will become its full-fledged
competitors”.
The iTrustCapital cryptocurrency trading platform
conducted its own research to find out which asset
people of different generations are willing to invest in
during pandemics and epidemics. “Respondents aged
33 to 44 are twice as likely as the others to call bitcoin
and cryptocurrencies the most protected asset in
general. They tend to invest in modern assets such as
cryptocurrencies, stocks and bonds, but they do not
exclude gold. It is worth noting that 44% of
respondents admitted that they consider gold to be the
most profitable investment tool, which is valuable at
any time and under any conditions”.
130
Chaykina, E., Posnaya, E. and Bukach, B.
Assessment of Various Factors Impact on Cryptocurrency Functioning using Economic and Mathematical Modeling.
DOI: 10.5220/0010665000003223
In Proceedings of the 1st International Scientific Forum on Sustainable Development of Socio-economic Systems (WFSDS 2021), pages 130-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-597-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 THEORETICAL, EMPIRICAL
AND METHODOLOGICAL
GROUNDS OF THE RESEARCH
Cryptocurrency is an encrypted unregulated digital
asset that is used as an analogue of currency in
exchange transactions. Cryptocurrency does not have
a physical form, it exists only in the electronic
network in the form of data. At the moment, there is
no single approach to determining the nature of
virtual currencies and their classification. According
to the opinion of a group of scientists,
cryptocurrencies can be classified according to their
functions and liquidity level (Jeskindarov et al.,
2018):
the first group: cryptocurrencies that are used as
a means of payment, means of accumulation
(savings), exchange, and as an investment tool
(Bitcoin, Bitcoin-cash, Ripple, etc.);
second group: cryptocurrencies tokens.
Cryptocurrencies of this group are used as a
means of payment, means of accumulation
(savings), exchange, and as an investment tool
(STRAT, Waves, etc.);
the third group: tokens and cryptocurrencies that
have not received distribution as a means of
payment, means of accumulation (savings) and
exchange, and are not used as an investment tool
(TRUMP-COIN etc.).
According to statistics of the Coinmarketcap
service, the list of cryptocurrencies is approaching
one and a half thousand, and according to the A.
Treschev calculations, the founder of the Russian
Association of Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain,
there are more than 900 of them.
The attractiveness of cryptocurrencies is due to
the following factors:
the release of cryptocurrency into circulation is
decentralized, there are no non-issuing nature of
crypto assets and state registration;
independence of emissions from political
preferences and economic views of the subjects
of the system. Cryptocurrency is not a debt
obligation of the issuer, it does not belong to
central banks, which distinguishes it from
electronic money and non-cash payments;
indisputable right of ownership (the presence of
an individual key, the operation with
cryptocurrency cannot be performed by the
counterparty without the private key of the
contract holder; the holder can choose to execute
the algorithm regardless of citizenship, place of
residence, nation, religion, gender);
An advanced technology of the register of blocks
of information of the blockchain, on the basis of
which the majority of cryptocurrencies are
created and transmitted. Blockchain technology
ensures the transparency of the cryptocurrency
circulation mechanism, all of whose elements are
controlled by a large number of independent
entities;
uninterrupted operation due to the low
probability of a simultaneous failure in the work
of all entities;
use of cryptocurrency as a means of payment;
current anonymity of payments (privacy of
personal data of the parties);
the transfer of a digital asset occurs without
intermediaries;
the cost of transfers is low or translation is free
of charge;
The transaction speed is higher compared to the
international interbank system SWIFT;
with respect to cryptocurrency, there is no
problem of limiting liquidity even when the
entire amount of cryptocurrency is developed,
since a unit of currency is divisible into smaller
parts. “The total volume of the currency is known
in advance, and the creation of each new block is
accompanied by the solution of more complex
mathematical problems, which leads to an
artificial limitation of the growth rate of the
currency supply” (Shaidullina, 2018).
cryptocurrencies are used by an unlimited
number of people to complete transactions for the
sale of goods, payment for work and services, as
well as for investment purposes;
cryptocurrencies are considered by market
entities as a source of revenue generation in
connection with their use, mining, participation
and raising capital through ICOs, operations on
the exchange.
Despite all its advantages, cryptocurrencies have
the following disadvantages:
cryptocurrency, as a subject of exchange,
settlement operations, a means of creating or
acquiring capital, as well as an object of
investment activity, is risky in nature, since it is
not provided with real assets and is highly
volatile, which creates a risk of losses
(Jeskindarov et al., 2018):
legal vulnerability of investors. The use of
cryptocurrency in many countries is not legally
regulated by legal documents or is prohibited,
due to the lack of the ability to centrally regulate
cryptocurrency and to prevent its use in the
process of combating money laundering and
terrorist financing;
Assessment of Various Factors Impact on Cryptocurrency Functioning using Economic and Mathematical Modeling
131
the danger of cyberattacks entails the possibility
of a risk of insecure cryptographic code, it is
almost impossible to deal with this risk, since the
existing financial infrastructure is built on key
principles of encryption;
the risk of losing access to the crypto asset due to
the loss of keys or because of their theft. This risk
can be reduced through the use of password
managers or specialized equipment.
Cryptocurrency does not act as a commitment to
anyone. It is not provided with anything, and its value
is based on the expectations of market players.
Cryptocurrency quotes are formed solely by the
balance of supply and demand, not initially tied to any
currency or other asset; however, there are factors that
affect its rate.
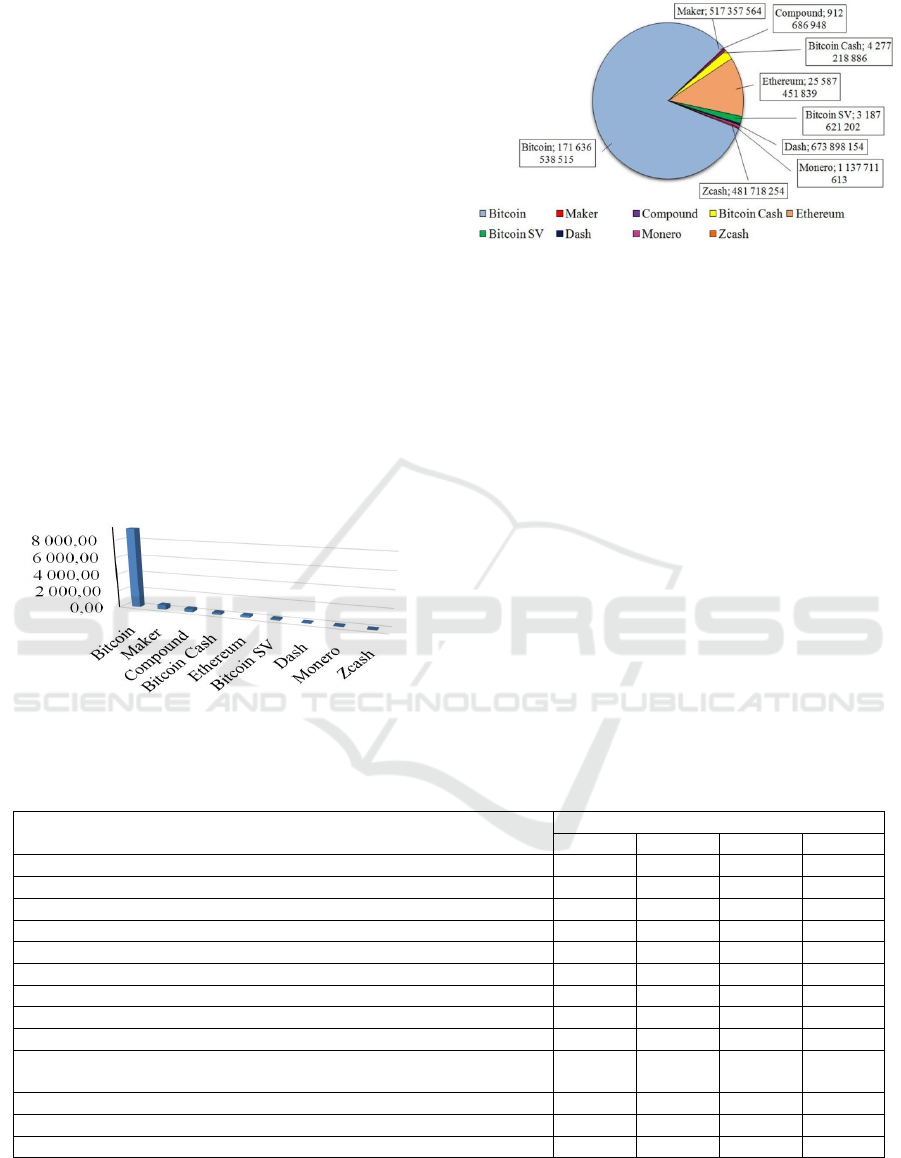
The most popular virtual and widespread currency
in the world is Bitcoin. Bitcoin's market capitalization
currently stands at about 172.6 billion US dollars.
Bitcoin, despite its high volatility, is considered one
of the most profitable investment tools in the
cryptocurrency market (Figures 1, 2).
Figure 1: Price of the TOP 10 cryptocurrencies as of
06/20/2020 (USD).
Figure 2: TOP 10 cryptocurrencies in terms of market
capitalization as of June 20, 2020 (USD).
An exploratory factor analysis is used to study
Bitcoin price formation that is, such an analysis
system, according to which it is not initially
determined which factors can most accurately
describe the relationships and interdependencies.
Explosiveness (from French explosion -
explosion) is a clinical violation. Readiness for a
sudden, sometimes inadequate, explosive nature,
manifestation of the effect.
We will build economic and mathematical models
of the impact on the price of Bitcoin of a number of
the most significant indicators indicated below (Table
1).
Table 1: Initial data.
Index
2014
I qr. II qr. III qr. IV qr.
X
1
–
Total Gold Offer
(
tn
)
1 104.1 1 104.1 1 104.1 1 104.1
X
2
–
Total
g
old demand
(
tn
)
1 093.9 1 093.9 1 093.9 1 093.9
X
3
–
Gold
p
rice
(
London PM fix
)
(
US$/tro
y
ounce
)
1 293.1 1 293.1 1 293.1 1 293.1
X
4
–
Silver (US$/troy ounce) 19.97 20.87 17.11 15.79
X
5
–
Platinum (US$/troy ounce) 1 418.0 1 480.0 1 300.0 1 206.0
X
6
–
Palladium (US$/troy ounce) 778.0 844.0 775.0 811.0
X
7
–
Brent Oil
(
dollars/barrel
)
107.70 112.40 94.80 57.54
X
8
–
Euro/dollar, €/$ 1.3771 1.3771 1.3771 1.3771
X
9
–
British
p
ound/dollar, £/$ 1.6663 1.6663 1.6663 1.6663
X
10
– S&P 500
1
872.34
1
872.34
1
872.34
1
872.34
X
11
–
U.S. Treasur
y
current liabilities
(
12 months
)
(
Treassur
y
Bills
)
, % 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13
X
12
–
US Federal Reserve Rate, % 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25
Y
–
Bitcoin, Bitcoin / $ 702.55 702.55 702.55 702.55
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
132
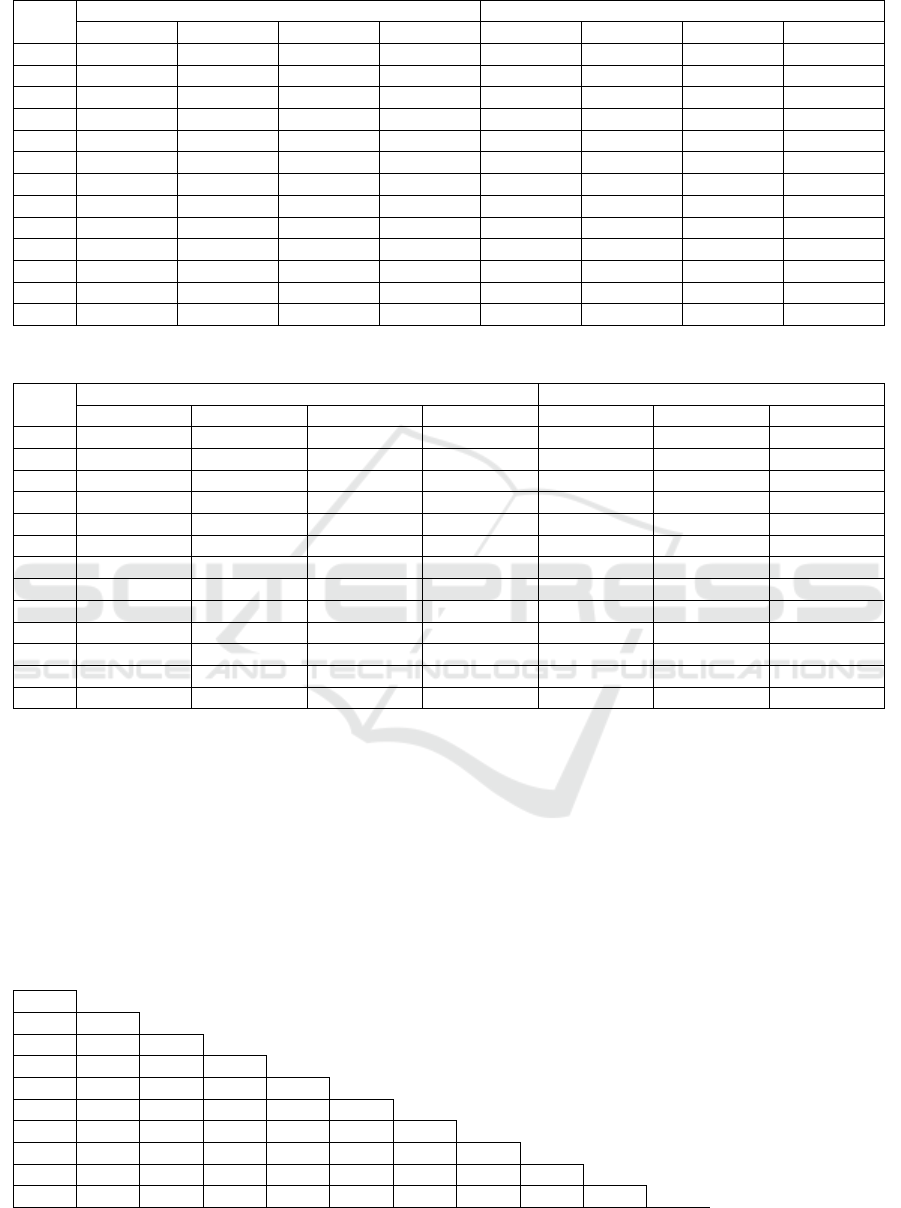
Table 1: Initial data (cont.).
Index
2015 2016
I
q
r. II
q
r. III
q
r. IV
q
r. I
q
r. II
q
r. III
q
r. IV
q
r.
X
1
1 086.2 1 044.1 1 128.8 1 092.1 1 182.8 1 167.2 1 174.3 1 086.1
X
2
1 110.1 958.3 1 162.7 1 112.2 1 284.0 1 055.1 1 027.7 972.0
X
3
1 218.5 1 192.4 1 124.3 1 106.5 1 182.6 1 259.6 1 334.8 1 221.6
X
4
16.60 15.70 14.65 13.82 15.38 18.36 19.35 16.24
X
5
1 129.0 1 078.0 908.0 868.0 976.0 999.0 1 034.0 898.0
X
6
729.0 677.0 661.0 555.0 569.0 589.0 722.0 670.0
X
7
55.10 62.05 47.92 36.56 39.61 50.73 49.41 56.75
X
8
1.0731 1.1138 1.1177 1.0861 1.1380 1.1105 1.1241 1.0516
X
9
1.4818 1.5709 1.5129 1.4739 1.4362 1.3311 1.2976 1.2338
X
10
2 067.89 2 063.11 1 920.03 2 043.94 2 059.74 2 098.86 2 168.27 2 238.83
X
11
0.26 0.28 0.33 0.65 0.59 0.45 0.59 0.85
X
12
0.25 0.25 0.25 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.75
Y 248.54 236.67 257.43 341.04 411.58 515.61 616.76 718.09
Table 1: Initial data (cont.).
Index
2017 2018
I
q
r. II
q
r. III
q
r. IV
q
r. I
q
r. II
q
r. III
q
r.
X
1
1 037.2 1 092.1 1 185.7 1 138.0 1 107.1 1 079.0 1 161.6
X
2
1 107.5 1 031.9 988.8 1 073.6 998.3 992.8 1 013.0
X
3
1 219.5 1 256.6 1 277.9 1 275.4 1 329.3 1 306.0 1 213.2
X
4
18.06 16.47 16.86 16.74 16.52 16.03 14.31
X
5
940.0 922.0 920.0 917.0 936.0 851.0 815.0
X
6
798.0 841.0 935.0 1 033.0 970.0 953.0 1 094.0
X
7
53.62 48.94 56.53 66.87 69.35 79.12 82.98
X
8
1.0652 1.1426 1.1814 1.1998 1.2323 1.1685 1.1609
X
9
1.2550 1.3027 1.3397 1.3515 1.4018 1.3209 1.3039
X
10
2 362.72 2 423.41 2 519.36 2 673.61 2 640.87 2 718.37 2 913.89
X
11
1.03 1.24 1.31 1.76 2.09 2.33 2.59
X
12
1.00 1.25 1.25 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.25
Y 934.49 1864.46 3397.77 9398.57 10672.55 7829.15 6799.21
3 RESULTS
Quarterly values are considered for calculation:
indicators of supply and demand for gold, prices for
precious metals (gold, silver, platinum, palladium),
oil prices, exchange rates of major currencies, stock
indices, discount rate of the Fed, securities with a
guaranteed level of yield (short-term US Treasury
Obligations) for the period from 2014 to 2018
inclusive. The number of members of the time series
of indicators (20) is quite sufficient for reliable
statistical analysis. First, we compose a matrix of pair
correlations between the variables (Table 2). Since
this matrix is symmetric, its lower part is presented.
Table 2: Correlation matrix.
Index
X
1
1.00
X
2
0.20 1.00
X
3
0.09 -0.43 1.00
X
4
-0.06 -0.09 0.68 1.00
X
5
-0.16 0.17 0.28 0.68 1.00
X
6
0.06 -0.45 0.52 0.04 -0.12 1.00
X
7
-0.23 -0.19 0.52 0.53 0.67 0.47 1.00
X
8
0.06 0.02 0.50 0.55 0.73 0.38 0.84 1.00
X
9
-0.18 0.30 -0.10 0.24 0.83 -0.19 0.54 0.67 1.00
Assessment of Various Factors Impact on Cryptocurrency Functioning using Economic and Mathematical Modeling
133

Table 2: Correlation matrix (cont.).
Index
X
10
0.12 -0.48 0.32 -0.28 -0.65 0.80 0.00 -0.14 -0.67 1.00
X
11
0.11 -0.40 0.27 -0.35 -0.68 0.74 0.01 -0.11 -0.63 0.97 1.00
X
12
0.10 -0.42 0.32 -0.28 -0.64 0.77 0.06 -0.07 -0.63 0.98 0.99 1.00
Y 0.10 -0.36 0.44 -0.18 -0.43 0.80 0.19 0.17 -0.35 0.86 0.88 0.87 1.00
Y – the price of Bitcoin – is the resulting indicator,
and if we examine its functional dependence on other
indicators, then at the initial stage, the most obvious
is the idea of using linear regression.
y
= Xꞏb + e; (1)
where y is the vector (column matrix) of the bitcoin
exchange rate (Y) in the period from 2014 to 2018; X
- a matrix of supply values (X
1
) and demand (X
2
) of
gold, prices for banking metals and other indicators;
b - vector of regression coefficients; e - vector of
random deviations.
However, the classical linear regression model
does not fit in this case, since the regressors are
random variables and, at the same time, are
interdependent, as shown by the correlation matrix.
We will use the model of exploratory factor
analysis in order to circumvent this problem. She has
the form
X = FꞏA
T
+ U; (2)
where X is the matrix of values of indicators (the
same as in (1)); F - matrix of values of exploratory
factors; A - matrix of factor loads; ...
T
- sign of the
transpose of the matrix; U - matrix of random
deviations of the model of exploratory factor analysis.
We substitute expression (2) in (1), we obtain a
regression-factor model
Y = Fꞏc + u. (3)
Expression (3) is an equation of regression of a
dependent variable on independent exploratory
factors, in it
c = A
T
b
; (4)
u=Uꞏb + e. (5)
Expression (4) denotes the vector of regression
coefficients for factors, and in (5) the vector of
random deviations of the regression factor model.
It should be noted that in order to solve the issue
of joint consideration of indicators having different
units of measurement, they are all reduced to the so-
called standard form, i.e. centered and normalized:
z
t
= (
t
z
~
–
z
)/σ
z
;
(6)
where z
t
is the indicator in standard form;
t
z
~
- the
real value of the indicator;
z
- the average value of
the indicator; σ
z
- standard deviation of the indicator.
A variable in standard form has zero expectation
and unit variance. In this case, the values of
exploratory factors are also normalized and centered.
Moreover, the factors are interdependent and
orthogonal, i.e. satisfy the condition
F
T
F = I, (7
)
where I is the identity matrix.
After factor loads and factor values are found, to
obtain an estimate of the regression coefficients of
equation (3), you can use the usual least-squares
method:
c
ˆ
= (F
T
F)
-1
F
T
y;
(8
)
and taking into account (7), expression (8) takes the
form
c
ˆ
= F
T
y.
(9
)
Let us find an estimate of the regression
coefficients of model (1). To do this, we use
expression (4), on the basis of which we need to find
the vector of regression coefficients. If the matrix is
chosen so that
WꞏA
T
= I, (10
)
then
b
= Wꞏc. (11
)
Multiply (10) by A(A
T
A)
-1
the right, we get
Wꞏ(A
T
A) (A
T
A)
-1
= Aꞏ(A
T
A)
-1
,
then
W = Aꞏ(A
T
A)
-1
, (12
)
Substituting (12) in (11), we obtain an estimate of
the regression coefficients
b
= Aꞏ(A
T
A)
-1
ꞏc.
(13
)
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
134
In the course of calculations, 4 exploratory factors
for regressors were identified. The final results of the
calculations are summarized in Table 3.
We check the adequacy of the regression
equations according to the Fisher criterion, calculated
on the basis of the coefficient of determination
,
)1N(
)yy
ˆ
(
1R
2
N
1t
2
tt
2
where N is the number of observations;
t
y
ˆ
- the value
of the resulting indicator restored by the regression
equation; 𝑦
- the observed value of the resulting
indicator; 𝜎
- the variance of the index Y.
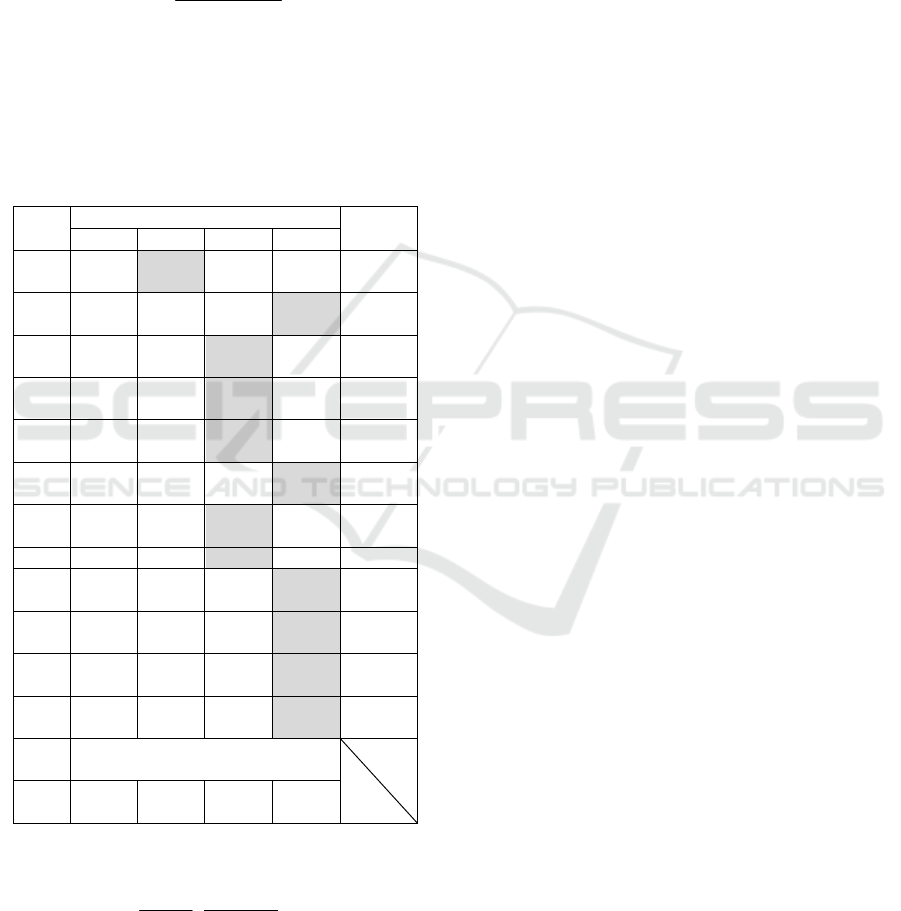
Table 3: Calculation results.
Index
Ex
p
lorator
y
factor loads
Regress.
coeff.
F1 F2 F3 F4
X
1
-
0.120
0.139
-
0.026
-
0.094
0.073
X
2
0.180
-
0.220
-
0.288
0.438
0.275
X
3
-
0.130
0.616 0.770
-
0.113
0.479
X
4
-
0.207
0.219 0.732 0.381
-0.448
X
5
0.119
-
0.280
0.699 0.627
-0.848
X
6
0.275 0.111 0.518
-
0.765
0.111
X
7
0.508
-
0.009
0.772 0.075
0.389
X
8
0.524 0.015 0.762 0.233 0.551
X
9
0.421
-
0.439
0.385 0.617
-0.296
X
10
0.102 0.336 0.032
-
0.935
0.676
X
11
0.261 0.420
-
0.069
-
0.865
1.345
X
12
0.251 0.415
-
0.007
-
0.871
1.252
Exploratory factor regression
coeff.
Y 1.097 1.844 -
0.048
-
3.638
The criterion itself has the form
,
k
1kN
R1
R
F
2
2
where k is the number of parameters of the regression
equation. In the regression equation of exploratory
factors, this is the number of factors (m), and in the
usual regression equation, this is the number of
variables (indicators) - n.
For the equation of regression of factors, the
calculated value of the criterion is F = 392.546; and
the critical value: qF (0.95; m; N – m – 1) = 3.112.
The calculated value of the criterion is more than
critical, therefore, the equation is adequate.
For the equation of regression of variables, the
calculated value of the criterion is F = 56.078; and the
critical value: qF (0.95; n; N – n – 1) = 4,000. The
calculated value of the criterion is more than critical,
therefore, the equation is adequate.To interpret the
factor solution in each row of the matrix of factor
loads, we select the largest absolute value (shaded
cells in Table 3).
The second factor accounted for one selected cell,
and this factor can be unambiguously interpreted as
the presence of gold on the market - the "gold factor".
The third factor is loading the prices of banking
metals, except for palladium, as well as the price of
oil and the euro-dollar pair the most. It can be
interpreted as a “price factor”.
The fourth factor has the largest load with a minus
sign on the S&P 500 index, as well as financial
obligations and the Fed discount rate, i.e. it
determines negative trends in the financial sector, so
it can be called a “crisis factor”. Note that the crisis
factor, in comparison with others, most determines
the decrease in the stock index (S&P 500), the
reduction in the rate of the Fed and securities with a
guaranteed level of profitability (short-term
obligations of the US Treasury) and increases the
demand for gold.
The first factor does not have allocated cells,
however, the loads are greater than 0.5 for the brand
oil price and the euro-dollar pair. These indicators
were under the dominant price factor. But the first
factor can be called European.
The Bitcoin exchange rate regression equation for
exploratory factors has the form
Y = 1.097 F
1
+1.844 F
2
–
0.048 F
3
–
3.638 F
4
+U. (14)
If we consider the coefficients of regression of
factors, it becomes obvious the dominant negative
impact of the "crisis factor" in the formation of the
Bitcoin exchange rate. The growth of the “crisis
factor” leads to a decrease in the price of Bitcoin,
while the formation of the above factor is
significantly affected by the following indicators: a
decrease in the stock index, the rate of short-term
liabilities of the US Treasury, the discount rate of the
Fed, as well as an increase in demand for gold.
Assessment of Various Factors Impact on Cryptocurrency Functioning using Economic and Mathematical Modeling
135

The second most important factor influencing
Bitcoin is the “golden” factor - the larger the gold
supply, the higher the Bitcoin exchange rate.
The factor determined by the price of oil and the
euro exchange rate is in third place. And the price
factor turned out to be in last place among the
exploratory factors, and its influence is negative and
insignificant.
Regression coefficients of variables allow you to
determine the sensitivity of the change in each
indicator to the cryptocurrency rate. So, an increase
in the supply of gold per unit leads to an increase in
the exchange rate of Bitcoin by 0.073 units.
In April 2020, Quantum Economics founder Mati
Greenspan noted that the entire financial industry
depends on the correlation of Bitcoin with the S&P
500 index.
Gold is also gradually increasing its correlation
with Bitcoin, while it remains an alternative financial
instrument and remains attractive to potential
investors. The influence of gold supply and demand
on the price of Bitcoin is increasing. The price of
Bitcoin with an increase in the supply (production) of
gold rises and with the emergence of factors that
reduce the demand for gold (the absence of global
financial turmoil), the price of cryptocurrency
decreases. The impact of the rising cost of other
precious metals, such as silver and platinum, is
negligible, but still reduces the cost of Bitcoin.
On the world market, the value of Bitcoin falls
during periods of political and economic instability
(along with US assets) and increases in times of
relative calm and prosperity. The price of Bitcoin has
a strong correlation with stocks and other American
traditional assets. With tight monetary policy in the
United States, Bitcoin will not be an attractive tool for
hedging the risks of global instability. The exchange
rate of Bitcoin with an increase in demand for
precious metals behaves similarly to the US currency.
Perhaps in the future, “Bitcoin will equal the US
dollar in terms of its payment properties and eclipse
gold as a means of savings” (interview with
Bloomberg CEO of Bitcoin exchange Kraken Jess
Powell).
The growth of investor interest in Bitcoin from
asset hedge funds, retail investors and day traders will
increase, but this will be associated with Bitcoin as an
alternative means of investment (in this quality,
Bitcoin competes with other financial assets in
different ways, yielding in terms of reliability, but
surpasses them in profitability), especially with the
improvement of technological characteristics of
cryptocurrencies.
The head of Kraken expects improved payment
functions of the first cryptocurrency thanks to second-
level solutions like the Lightning Network. They will
provide the same affordable and easy to understand
features, such as the popular payment systems PayPal
and Venmo, eliminating the need to transfer coins on
the blockchain. “Soon the technology underlying
Bitcoin will dissolve. It will become like an American
dollar: no one understands how it works, but everyone
uses it. ”
Cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, cannot be
considered as an alternative way of investing in
conditions of falling profitability of traditional
financial instruments. However, according to the
analytical center of the international audit and
consulting network FinExpertiza, which presented
the results of the study of the most profitable
investment investments, Bitcoin has become one of
the most profitable financial instruments for 2019.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the methods of correlation and regression
analysis, methods of exploratory factor analysis,
economic and mathematical models made it possible
to more deeply analyze and confirm the degree of
influence of indicators on changes in Bitcoin prices,
as well as to identify the most significant of these
indicators and use these results in the future to
forecast the rate of Bitcoin in the world market.
The financial analysis carried out in the study
using the exploratory principle made it possible to
formulate a factor analysis scheme, in which it was
not initially determined which system of factors made
it possible to describe the correlation matrix.
It should be noted that it is precisely when
constructing a model for assessing the level of
influence of explorer factors on the cryptocurrency
exchange rate that the introduction of an analysis
based on the exploratory principle is of particular
importance, since the cryptocurrency exchange rate,
the price of Bitcoin are indicators whose values are
most dependent not on constant, but on variables that
suddenly appear parameters.
REFERENCES
Cryptocurrency market capitalization will increase 30 times
thanks to $ 5 trillion investment in bitcoin,
https://mining-cryptocurrency.ru/kapitalizaciya-
kriptorynka-uvelichitsya-v-30-raz/
WFSDS 2021 - INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC FORUM ON SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC SYSTEMS
136

Eskindarov, M.A. Abramova, M.A., Maslennikov, V.V.,
Amosova, N.A., Barnavsky, A.V., Dubova, S.E.,
Zvonova, E.A., Krivoruchko, S.V., Lopatin, V.A.,
Pishchik, V.Ya., Rudakova, O.S., Ruchkina, G.F.,
Slavin, B.B., and Fedotova, M.A. (2018). Directions of
development of fintech in Russia: expert opinion of the
Financial University. World of the new economy, 2: 6-
23.
iTrustCapital Survey: Millennials Are More Likely to
Choose Bitcoin as the Best Investment During a
Coronavirus Pandemic,
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-
releases/itrustcapital-survey-millennials-are-more-
likely-to-choose-bitcoin-as-the-best-investment-
during-a-coronavirus-pandemic-301014915.html
Kornilov, D. A., Zajcev, D. A., and Kornilova, E. V. (2017).
Cryptocurrency market analytics. Dynamics and
forecasts, ITportal, 3(15).
Manuylenko, V.V., Mishchenko, A.A., Bigday, O.B.,
Sadovskay, T.A., and Lisitskay, T.S. (2017).
Evaluation Method for Efficiency of Financial and
Innovative Activities in Commercial Organizations
Based on Stochastic Modelling, Journal of Applied
Economic Sciences, 12, 4 (50): 1226 – 1246.
Manuylenko, V. V., Ryzin, D. A., Gryzunova, N. V.,
Bigday, O. B., and Mandrytsa, O. V. (2020). Toolset for
financial risk strategic assessment in corporations based
on stochastic modeling, Amozonia Investiga, 9(28): 451
– 464.
Melnikova, Y.V., Posnaya, E.A., Bukach, B.A.,
Shokhnekh, A.V., and Tarasenko, S.V. (2020).
Defining Key Determinants of the Strategic Economic
Security of the Agro-Industrial Complex in Terms of
Stabilizing Political Course, E3S Web of Conferences.
Posnaya, E.A., Kaznova, M.I., Shapiro, I.E., and
Vorobyova, I.G. (2018). Theory and Practice of Capital
Estimation Methods: An Application in Bank
Management, European Research Studies Journal,
21(2): 497-505.
Posnaya, E.A., Semenyuta, O.G., Dobrolezha, E.V., and
Smolander, M. (2019). Modern Features for Capital
Portfolio Monitoring, International Journal of
Economics and Business Administration, 7(1): 53-60.
Posnaya, E.A., Dobrolezha, E.V., Vorobyova, I.G., and
Chubarova, G.P. (2018). The economic capital model
in bank's capital assessment, Contemporary Studies in
Economic and Financial Analysis, 100: 111 – 119.
Posnaya, E.A., Tarasenko, S.V., Bukach, B.A., Shokhnekh,
and A.V. (2019). The Significance of Bank Financial
Security in Capital Management. Proceedings of the
"New Silk Road: Business Cooperation and Prospective
of Economic Development", Advances in Economics,
Business and Management Research, Atlantis Press,
131: 977-979.
Shaidullina, V.K. (2018). Cryptocurrency as a new
economic and legal phenomenon, University Bulletin,
2: 137-142.
Assessment of Various Factors Impact on Cryptocurrency Functioning using Economic and Mathematical Modeling
137
